Abstract
The aim of this work was to obtain dense Cu2S superionic thermoelectric materials, homogeneous in terms of phase and chemical composition, using a very fast and cheap induction-melting technique. The chemical composition was investigated via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) combined with an energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) method, and the phase composition was established by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The thermoelectric figure of merit ZT was determined on the basis of thermoelectric transport properties, i.e., Seebeck coefficient, electrical and thermal conductivity in the temperature range of 300–923 K. The obtained values of the ZT parameter are comparable with those obtained using the induction hot pressing (IHP) technique and about 30–45% higher in the temperature range of 773–923 K in comparison with Cu2S samples densified with the spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique.
1. Introduction
Cu2S is an environmentally friendly and low-cost superionic thermoelectric material that has been intensively studied in recent years as a potential material for thermoelectric generator applications [1,2,3,4]. The energy conversion efficiency of such thermoelectric generators depends on the temperature difference between the junctions of the thermoelectric materials and the properties of materials expressed by the value of the thermoelectric figure of merit, ZT = α2σλ−1T [5,6], (α—Seebeck coefficient, σ—electrical conductivity, λ—thermal conductivity). The remarkable thermoelectric properties of Cu2S, both undoped and doped with e.g., Se [2], in particular for the high-temperature cubic phase α-Cu2S (T > 708 K) [7] are closely related to the migration of copper ions. Explanation of this phenomenon is provided by the phonon-liquid electron-crystal PLEC [8] concept, which is an extension of the phonon-glass electron-crystal PGEC concept [9] to ionic conductors. The migration of ions in the Cu2S crystal structure, on the one hand, has a positive effect on the thermoelectric properties, i.e., a decrease in thermal conductivity and an increase in the electrical conductivity of the material, but on the other hand causes a lack of stability of Cu2S under electric current. This may result in a deficiency of copper atoms in the Cu2S structure, which affects the transport properties of the material [10].
The most efficient and widely used sintering technique for thermoelectric materials is spark plasma sintering (SPS) [11] using a pulsed DC current. However, for materials with high ion mobility, which include superionic compounds, this technique does not seem to be suitable due to possible ion migration, resulting in a change in chemical composition of such materials [12]. In our previous work [13], we have shown that using the induction hot pressing (IHP) technique, it is possible to significantly improve the thermoelectric figure of merit ZT by up to 40% compared to Cu2S obtained via the SPS technique [14,15]. This improvement seems to be related to the way the samples are heated during sintering, i.e., without any current flowing through the sintered material [16]. However, both SPS and IHP techniques require the use of expensive equipment, which often limits their potentially wide range of applications. To address the latter problem, this work proposes a very fast and at the same time inexpensive method of Cu2S densification, which is based on the application of the induction melting (IM) technique.
The principles of operation of SPS, IHP and IM methods is shown in Figure 1. The SPS and IHP methods use temperature and pressure to compact material. The powder material is placed in a graphite matrix, which, together with the powder, is heated by impulse current (SPS) or eddy current (IHP). Additionally, a pressure-generating force is applied to the punches of the die compressing the powder. The matrix is placed in a vacuum chamber, allowing anaerobic conditions, but this requires long flushing and pump-down times. These devices are quite large and expensive. Despite the fact that sintering takes quite a short time in both methods, much shorter than in the hot-pressing method, the time needed for preparation and cooling is several dozen minutes. The induction-melting method for densification uses both melting and crystallization. For this reason, induction melting is, in practice, applicable for congruent melting compounds. As in the IHP method, eddy currents are the source of heat, but they are generated in a small graphite crucible and directly in the melted powder. The advantage of these eddy currents is the mixing of the liquid melt, limiting the separation of the components. The powder is placed in a quartz ampoule with gas inlets, allowing it to be vacuum-filled or filled with an inert gas. Measurement and adjustment of the charge temperature are made contactless using a pyrometer, placed above the outlet of the ampoule, with a closed visor. This allows for better temperature control than in the case of SPS and IHP, where the temperature is measured with a thermocouple or with a pyrometer in a graphite die. The low heat capacity of such a system allows very fast heating and cooling rates of several thousand degrees per minute, so the process time can be very short. As a result, the growth of the grains can be limited and, in some cases, the high-temperature phase can be frozen if desired.
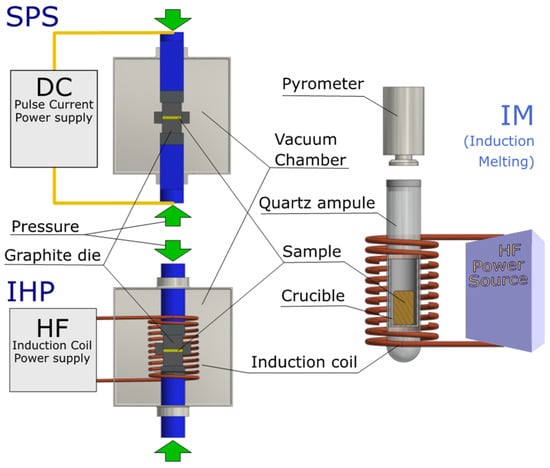
Figure 1.
Schematic diagrams of SPS, IHP and IM techniques.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, Cu2S samples, obtained from powders synthesized under three different conditions and then inductively melted, were obtained and studied. In the following part of the work, the designations IM1, IM2, and IM3 are used for the samples. In the first step, Cu (Alfa Aesar, Thermo Fisher (Kandel) GmbH, Kandel, Germany, 99.9%) and S (Alfa Aesar, Thermo Fisher (Kandel) GmbH, Kandel, Germany, 99.999%) powders were weighed in a glovebox in stoichiometric amounts and then encapsulated in a quartz ampule under vacuum. The synthesis was carried out via one- or two-step annealing. Sample IM1 was annealed at T = 673 K for t = 3 h and sample IM2 at T = 673 K for t = 24 h. In the first stage, sample IM3 was annealed at T1 = 673 K for t1 = 24 h and, after grinding the obtained ingot and resealing in a quartz ampoule, it was annealed at T2 = 1173 K for t2 = 18 h. The ingots obtained after synthesis were then ground in an agate mortar and remelted (T = 1423 K, v = 2500 K·min−1, t = 1 min) using the IM technique. The density of the obtained samples, measured by the hydrostatic Archimedes method was high and amounted to approx. 98% of the theoretical density (98.3 ± 0.2% for IM3, 97.9 ± 0.2% for IM2 and 97.4 ± 0.2% for IM1).
Both powders after synthesis and sinters were examined for phase composition by X-ray diffraction (X-ray Diffractometer Panalytical Empyrean, Malvern, Worcestershire, United Kingdom), CuKα, λ = 1.5418 Å, 2Θ angle range from 10° to 137°) at room temperature and, due to the high number of reflections at room temperature and the resulting difficulty in identification of all phases present in the system, additionally at 493 K. The chemical composition and microstructure of the specimens after melting were determined using a scanning electron microscopy SEM technique (FEI Nova NanoSEM 200 FEI Europe Company Scanning Electron Microscope, FEI COMPANY, Hillsboro, OR, United States) equipped with an EDAX detector.. Electrical conductivity and the Seebeck coefficient were studied in the temperature range of 300–923 K, using a homemade apparatus. Electrical conductivity was studied using a four-probe method with variable DC polarization. Seebeck coefficient measurements were carried out using a small (ΔT < 3 K), forced-temperature gradient across the specimen. Thermal diffusivity and heat capacity (Cp) were measured using a laser flash method LFA (Laser Flash Apparatus (LFA) 427, Netzsch, Selb, Germany) in the temperature range of 300–920 K (Figures S1 and S2 in the Supplementary Materials, respectively). Thermal conductivity was calculated from the relationship: λ = α·Cp·ϱ, where ϱ represents the density.
3. Results
3.1. Structural and Microstructural Analysis
Figure 2a shows the XRD patterns obtained at room temperature for the Cu2S specimens. All obtained samples consist mainly of the monoclinic Cu2S phase. As can be seen, extending the synthesis time and increasing the temperature allows obtaining a better-crystallized form of the material. The precipitations of other phases, including copper, are not visible on the recorded diffraction patterns, which may be due to a large number of reflections in the monoclinic Cu2S phase. Larger differences between the samples are revealed in the XRD measurements at the temperature of 493 K, i.e., above the phase transition temperature of the Cu2S monoclinic to hexagonal phase [7,17] (Figure 2b). There is a clear difference in phase composition between the samples obtained at 673 K and the sample also annealed at 1173 K, which comprises the pure hexagonal copper sulfide phase. The samples obtained by annealing at 673 K contain two Cu2S phases—cubic and hexagonal. Additionally, the presence of copper can be observed, the amount of which clearly decreases with increasing synthesis time. After induction melting of the synthesized Cu2S, the XRD studies presented in Figure 2c show that, at room temperature, the resulting materials still consist mainly of a monoclinic phase. For samples IM1 and IM2, the observed XRD patterns reveal a much better crystallinity of the obtained material relative to the post-synthesis state, equal to that of sample IM3.
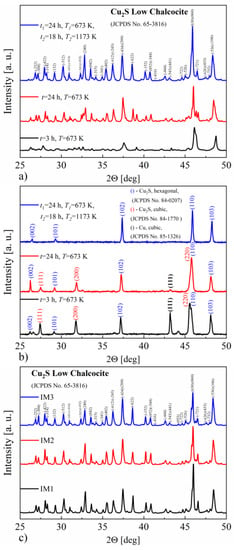
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction patterns for Cu2S samples synthesized under various conditions, measured at (a) RT and (b) 493 K, and (c) additionally measured at RT for the samples after induction-melting densification.
Figure 3 shows the cross-sections of the samples, which confirm their high degree of densification, with no visible pores or voids. For a sample annealed for 3 h at 673 K, the fracture resembles a glassy material, while a sample annealed at 1173 K shows the features of a polycrystalline material. The EDS analysis (Figure 4) confirms the results of the XRD measurements. The ratio of Cu to S is close to 2:1 and is fairly homogeneous over the whole analyzed area. Similarly to XRD measurements, Cu precipitates are observed in samples synthesized exclusively at 673 K. These observations show that the induction melting process is so fast that the kinetics of the processes occurring in the melt are too slow to homogenize the melted and crystallized material. This indicates the necessity of using well-reacted and homogenized Cu2S as a starting material in this type of densification method, which, as we have shown, can be achieved by allowing a sufficiently long 24-hour synthesis stage at 1173 K.
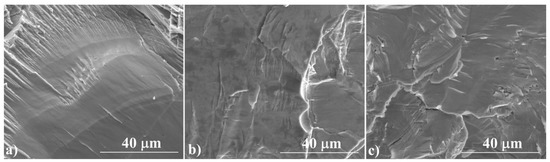
Figure 3.
SEM photographs of the surface of cross-section fractures in the Cu2S samples (a) IM1, (b) IM2, (c) IM3, at a magnification of 3000×.
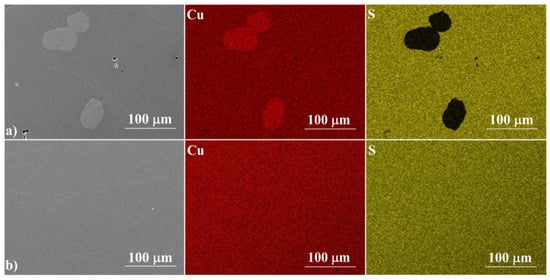
Figure 4.
SEM photographs of a selected surface, with respective maps of element distribution for (a) IM2 and for (b) IM3.
3.2. Thermoelectric Transport Properties
The electrical conductivity measurements are shown in Figure 5a. For all the samples, temperature dependence follows a fairly typical form, with a clearly visible decrease in conductivity for the hexagonal phase. In general, the conductivity of the melted samples is higher than that reported in the literature, which is particularly visible in the temperature range specific to the cubic phase. It can be seen that the longer the synthesis time and the smaller the number of foreign phases, the lower the Cu2S conductivity. In view of the results obtained, this increase in conductivity can be explained by the presence of Cu precipitates, which should be accompanied by the nonstoichiometry of the material. For the sample after induction-remelting that has the highest purity and homogeneity, the conductivity values are very close to our previous results for the material compacted by the IHP method. The results of the Seebeck coefficient measurements (Figure 5b) also agree well with the literature data. In the entire temperature range, the Seebeck coefficient takes positive values, and a step-change in its value can be observed near the phase transition temperatures [18]. For the sample annealed at 1173 K, the Seebeck coefficient values are slightly higher, especially near the temperature of transformation of the hexagonal to cubic phases. As in the case of electrical conductivity, the results obtained for this sample agree very well with the results of our previous studies [13]. The thermal conductivity (Figure 5c) varies little with temperature and does not deviate from the literature data. The total thermal conductivity is slightly higher for samples synthesized exclusively at 673 K, which is related to their higher electrical conductivity.
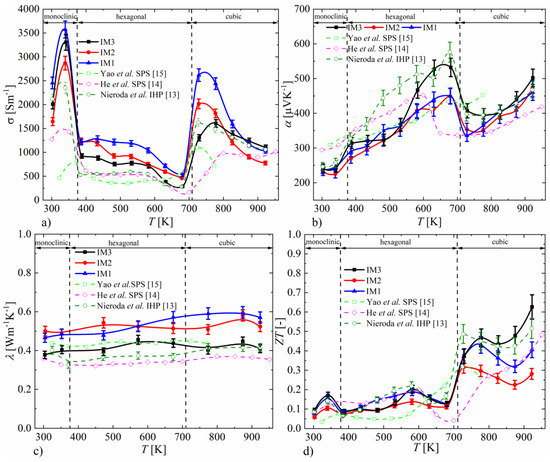
Figure 5.
Temperature dependence of electrical conductivity (a), Seebeck coefficient (b), thermal conductivity (c), and ZT parameter (d) for Cu2S samples (absolute errors equal to 5% for α, σ, λ and 10% for ZT).
The thermoelectric figure of merit, ZT (Figure 5d), similarly to electrical conductivity and the Seebeck coefficient, noticeably changes during phase transitions between individual Cu2S structures. For the monoclinic and hexagonal phases, the ZT values vary between 0.05 and 0.2. A several-times-higher ZT of Cu2S is observed after transformation to the cubic phase. The temperature dependence of ZT for the cubic phase is non-monotonic. As the temperature increases, the ZT decreases, reaching a minimum at a temperature dependent on the method of synthesis, after which it increases. In the case of samples IM1 and IM2, this minimum is at a temperature around 870 K, and the maximum ZT value is reached at a temperature below this minimum except in the cubic phase. For sample IM3, the ZT minimum for the cubic phase is at around 820 K; the maximum ZT value is observed at 920 K and reaches around 0.6, which is the highest value for all samples obtained in this work. The improved thermoelectric properties of sample IM3 with respect to samples IM1 and IM2 are mainly due to the lower thermal conductivity and the smaller decrease in electrical conductivity with increasing temperature. These more favorable properties are related to the greater homogeneity of the material synthesized at 1173 K, expressed by the absence of copper precipitates and the more favorable, more stoichiometric composition of Cu2S. The temperature dependence of ZT, determined for the materials obtained by induction melting, is similar to the results presented in the literature [13,14,15]. The most comparable properties can be observed for the sample obtained by IHP sintering in our previous studies [13], which has a very similar temperature dependence and values of ZT as for the IM3 sample. However, the thermoelectric properties are better than those of SPS-densified samples synthesized both by direct high-temperature synthesis and by mechanical alloying, which may be due to their degradation during the SPS process resulting from the current flow through the material.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have shown in the current work that by using induction remelting, it is possible to obtain dense and homogeneous Cu2S. The IM (induction melting) method offers very short compaction times, and the remelting time is so brief that the mixing and segregation processes have virtually no time to take place. Therefore, it is preferable to use materials of high purity and phase homogeneity as starting materials for densification. The obtained samples have a higher value of electrical and thermal conductivity than materials densified using the SPS and IHP methods. This results in significantly higher ZT values than for materials compacted by the SPS method, and slightly higher than those for materials compacted by the IHP method. The inferior properties of SPS-sintered materials may be due to the degradation of the material subjected to direct current flow, which does not occur in the case of IHP sintering and IM densification. Since the IM method proposed in this work is much faster than the SPS and IHP methods and, simultaneously, does not require such expensive equipment, it can find a wide application in obtaining other bulk materials, not only thermoelectrics, that melt congruently.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ma14237311/s1, Figure S1: Temperature dependence of thermal diffusivity for Cu2S samples, Figure S2: Temperature dependence of specific heat for Cu2S samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.N.; methodology, P.N. and K.Z.; formal analysis, P.N.; investigation, P.N., P.R. and K.Z.; data curation, P.N.; writing—original draft preparation, P.N., J.L. and A.K.; writing—review and editing, P.N., J.L. and A.K.; visualization, P.N. and J.L.; project administration, P.N. and A.K.; funding acquisition, P.N. and A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This scientific work has been financed as a research project, No. (UMO-2016/23/D/ST8/00022) and (UMO-2016/21/B/ST8/00409), from the resources assigned for science by the National Science Center (NCN) in the years 2017–2021. The research project is partly supported by the program “Excellence initiative–research university” for the AGH University of Science and Technology.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, W.-D.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z.-G.; Zou, J. Promising and eco-friendly Cu2X-based thermoelectric materials: Progress and applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Qiu, P.; Shi, X.; Chen, L. Recent Advances in Liquid-Like Thermoelectric Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1903867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.-H.; Zhao, L.-D.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.-P.; Li, J.-F.; He, J. Low-cost, abundant binary sulfides as promising thermoelectric materials. J. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Shi, X.; Chen, L. Cu-based thermoelectric materials. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 3, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.J.; Toberer, E.S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, C. Materials Aspect of Thermoelectricity; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, D.J.; Laughlin, D.E. The Bi-Cu (Bismuth-Copper) System. Bull. Alloy Phase. Diagr. 1983, 4, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Uher, C.; Day, T.; Snyder, J. Copper ion liquid-like thermoelectrics. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, D.M. CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics; CRC Press LLC: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dennler, G.; Chmielowski, R.; Jacob, S.; Capet, F.; Roussel, P.; Zastrow, S.; Nielsch, K.; Opahle, I.; Madsen, G. Are Binary Copper Sulfides/Selenides Really New and Promising Thermoelectric Materials? Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, J.P.; Hamm, C.M.; Birkel, C.S. Microwave heating and spark plasma sintering as non-conventional synthesis methods to access thermoelectric and magnetic materials. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 041314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.J.; LaLonde, A.; Ikeda, T. Rapid Hot Pressing Using an Inductive Heater. U.S. Patent No. US 2012/0098162 A1, 26 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nieroda, P.; Leszczyński, J.; Mikuła, A.; Mars, K.; Kruszewski, M.J.; Koleżyński, A. Thermoelectric properties of Cu2S obtained by high temperature synthesis and sintered by IHP method. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 25460–25466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Day, T.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Chen, L.; Snyder, J.G. High Thermoelectric Performance in Non-Toxic Earth-Abundant Copper Sulfide. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3974–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, B.-P.; Pei, J.; Liu, Y.-C.; Li, J.-F. Thermoelectric performance enhancement of Cu2S by Se doping leading to a simultaneous power factor increase and thermal conductivity reduction. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7845–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaLonde, A.D.; Ikeda, T.; Snyder, G.J. Rapid consolidation of powdered materials by induction hot pressing. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 025104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Sturm, C.; Kleinke, H. Chalcogenides as thermoelectric materials. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 270, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X. Mobile copper ions as heat carriers in polymorphous copper sulfide superionic conductors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 133902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).