Abstract
All-vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) are used as energy storage systems for intermittent renewable power sources. The performance of VRFBs depends on materials of key components and operating conditions, such as current density, electrolyte flow rate and electrolyte composition. Mass transfer overpotential is affected by the electrolyte flow rate and electrolyte composition, which is related to the limiting current density. In order to investigate the effect of operating conditions on mass transport overpotential, this study established a relationship between the limiting current density and operating conditions. First, electrolyte solutions with different states of charge were prepared and used for a single cell to obtain discharging polarization curves under various operating conditions. The experimental results were then analyzed and are discussed in this paper. Finally, this paper proposes a limiting current density as a function of operating conditions. The result helps predict the effect of operating condition on the cell performance in a mathematical model.
1. Introduction
Intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, prompt the requirement for energy storage systems. All-vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs), which store or release energy by a redox reaction between vanadium ions exhibiting different charge states in the electrolytes, are considered potential candidates for energy storage [1]. The reactions that occur during charging and discharging can be expressed as the following equations:
At the positive electrode:
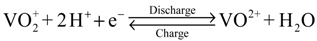

At the negative electrode:
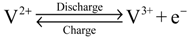
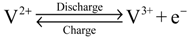
The efficiency of a VRFB system depends on electrode or separator materials and operating conditions. Many works have focused on the key materials, including electrolytes [2,3], electrodes [4,5] and separators [6,7]. Few studies investigated the effect of operating conditions as charging/discharging current, electrolyte flow rate and electrolyte concentration [8,9]. In a VRFB system, electrolytes are recirculated between the VRFB stack and electrolyte reservoirs. Accordingly, the concentration of electroactive vanadium ions varies during system operation. Cell performance decreases with reducing electrolyte concentration, which can be improved by increasing the electrolyte flow rate.
Watt-Smith et al. [8] examined the effect of electrolyte flow rate on cell efficiency and determined the optimal flow rate for electrolytes exhibiting different concentrations. Ma et al. [9] proposed an optimal flow rate strategy for a VRFB system to improve system efficiency. In addition to experimental studies, mathematical modeling plays a key role in improving performance and optimizing the operating conditions of VRFB systems.
A few models were developed for VRFB systems. Shah et al. [10] developed a dynamic model to examine the effects of electrolyte flow rate, concentration and electrode porosity on cell efficiency and used a constant to describe the reactant diffusion between the bulk and the electrode surface. You et al. [11] developed a two-dimensional model to investigate the effects of operating current density, electrode porosity and local mass transfer coefficient on cell performance. Ma et al. [12] developed a stationary, isothermal, three-dimensional model for the negative half-cell of a VRFB to evaluate the distributions of electrolyte velocity, vanadium concentration and overpotential. They concluded that the distribution of the electrolyte velocity significantly affects the distributions of overpotential and transfer current density. Yu et al. [13] developed a control-oriented model that included the mass transfer effect and vanadium crossover through the membrane to investigate the transient behavior of a VRFB. In their model, the limiting current density is related to the flow velocity, and the results showed that the concentration overpotential increased as the electrolyte flow rate decreased.
In the aforementioned studies [11,12,13], the limiting current density iL was mainly determined by considering the bulk concentration cb and mass transfer coefficient km:
where n represents the electrons involved in the redox reaction and F is the Faraday constant. The mass transfer coefficient is approximately related by an empirical equation [14]:
where v is the electrolyte flow velocity. However, the value of km for a VRFB has not been experimentally investigated nor reported. The effect of the operating conditions of a VRFB on the mass transfer coefficient is not well understood.
iL = nFkmcb
km = 1.6 × 10−4v0.4
In this study, the effective mass transfer coefficient in the porous graphite felt of VRFB electrodes was experimentally investigated. By using a unique experimental setup, in which electrolytes were not recirculated, the mass transfer coefficient at various vanadium concentrations in electrolytes was determined. At each vanadium concentration, the effect of the electrolyte flow rate on the coefficient was also included. Finally, based on the experimental results, a correlation equation for the mass transfer coefficient and operating conditions of a VRFB was suggested. The equation facilitates predicting the limiting current density and improving the accuracy of mathematical models.
2. Theoretical
2.1. Cell Voltage of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
The cell voltage model is a simplified control-oriented model similar to that in Shah’s study [15]. The operating cell voltage Ecell can be calculated by the reversible open circuit voltage (OCV) Erev subtracting activation overpotential Eact, ohmic overpotential Eohm and concentration overpotential Econ:
Ecell = Erev − Eact − Eohm − Econ
The reversible OCV is calculated by the Nernst equation based on the vanadium concentrations in the electrolytes:
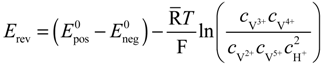 where
where 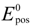 and
and 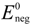 are standard reduction potentials for the reaction at the positive and negative electrodes, respectively;
are standard reduction potentials for the reaction at the positive and negative electrodes, respectively; 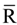 is the universal gas constant; T is the temperature; and ci is the molar concentration of species i. With measured OCV, the concentration ci can be calculated using Equation (6), and the state of charge (SOC) can be determined by:
is the universal gas constant; T is the temperature; and ci is the molar concentration of species i. With measured OCV, the concentration ci can be calculated using Equation (6), and the state of charge (SOC) can be determined by:
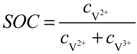
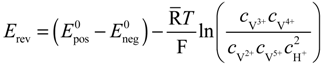
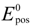 and
and 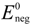 are standard reduction potentials for the reaction at the positive and negative electrodes, respectively;
are standard reduction potentials for the reaction at the positive and negative electrodes, respectively; 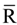 is the universal gas constant; T is the temperature; and ci is the molar concentration of species i. With measured OCV, the concentration ci can be calculated using Equation (6), and the state of charge (SOC) can be determined by:
is the universal gas constant; T is the temperature; and ci is the molar concentration of species i. With measured OCV, the concentration ci can be calculated using Equation (6), and the state of charge (SOC) can be determined by:
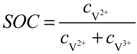
The activation overpotential is approximated by:
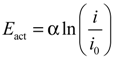
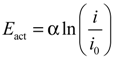
Equation (8) is known as the Tafel equation, which is equivalent to the Butler-Volmer equation. The parameters α and i0 in Equation (8) are determined by curve fitting based on measured polarization curves. Equation (8) is valid only for i > i0.
The ohmic overpotential is due to the internal resistance of the VRFB and is expressed as:
where Rcell is the cell resistance, including component resistance and contact resistance between components. The value of Rcell is measured using an impedance meter in this study.
Eohm = iAcellRcell
The concentration overpotential results from the change in the concentrations of V2+ and V5+ in the electrolytes and is expressed in a general form:
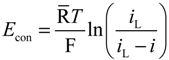 where iL is the limiting current density and is related to the electrolyte concentration by Equation (3). In Equation (3), the mass transfer coefficient of each vanadium species is assumed to be the same and varies according to the flow velocity v. The mass transfer coefficient can be approximated using an empirical equation:
where a and b are parameters to be determined based on experimental results.
where iL is the limiting current density and is related to the electrolyte concentration by Equation (3). In Equation (3), the mass transfer coefficient of each vanadium species is assumed to be the same and varies according to the flow velocity v. The mass transfer coefficient can be approximated using an empirical equation:
where a and b are parameters to be determined based on experimental results.
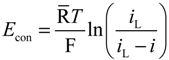
km = avb
2.2. Mean Flow Velocity
In a VRFB system, the electrolyte flow rates Q are controlled by recirculation pumps. The average normal electrolyte velocity vnor in the porous graphite felt is calculated using:
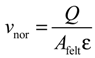 where Afelt is the cross-section area of the electrode and ɛ is the porosity of the graphite felt. Carman considered that the actual flow length is greater than the geometrical felt length; thus, the mean electrolyte velocity vmean inside the felt is modified as [16]:
where Afelt is the cross-section area of the electrode and ɛ is the porosity of the graphite felt. Carman considered that the actual flow length is greater than the geometrical felt length; thus, the mean electrolyte velocity vmean inside the felt is modified as [16]:
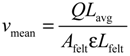 where Lavg is the average length of the fluid paths and Lfelt is the geometrical length of the felt. The ratio Lavg/Lfelt is known as the tortuosity of a porous medium. The tortuosity is not constant and depends on the porosity [17].
where Lavg is the average length of the fluid paths and Lfelt is the geometrical length of the felt. The ratio Lavg/Lfelt is known as the tortuosity of a porous medium. The tortuosity is not constant and depends on the porosity [17].
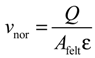
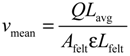
3. Experimental
3.1. Experimental Setup
Figure 1 shows a schematic of the experimental setup, which consists of a VRFB cell, an electrolyte supplying system and a measurement system.
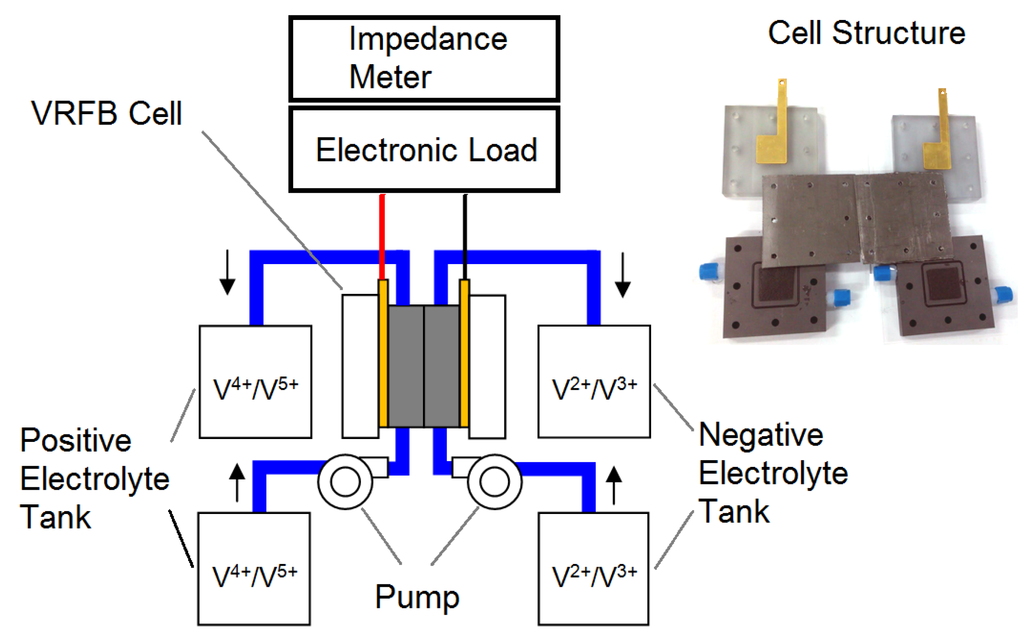
Figure 1.
Schematic of the experimental setup and a photo of the vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) cell in this study.
A VRFB single cell with an active area of 10.24 cm2 was designed and fabricated in this study. The separator was a proton exchange membrane (Nafion 117, DuPont, Wilmington, DE, USA). Both the anode and cathode flow field plates were composed of graphite and were machined for a space (3.2 × 3.2 × 0.5 cm3) for the electrodes. The electrodes (3.2 × 3.2 × 0.6 cm3) were composed of graphite felt (C0S1011, CeTech, Taichung, Taiwan). An O-ring was positioned between the separator and each graphite plate to prevent electrolyte leakage. The current collectors were composed of gold-plated copper plates. A flexible graphite foil was placed between the graphite plate and the current collector to reduce contact resistance. Two polyvinylchloride (PVC) end plates were used to compress the separator, electrodes, flow field plates and current collectors appropriately. The geometrical and physical parameters of the cell are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Geometrical and physical parameters of the VRFB cell.
| Quantity | Value | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Active area | 3.2 × 3.2 cm2 | - |
| Electrode thickness | 0.5 cm | After compression |
| Fiber density ρfiber | 1.75 g·cm−3 | Provided by manufacturer |
| Felt density ρfelt | 0.102 g·cm−3 | Provided by manufacturer |
| Porosity ɛ | 0.93 (after compression) | Calculated |
| Tortuosity Lavg/Lfelt | 1.09 | [17] |
| Cell resistance Rcell | 45 mΩ | Measured |
The electrolyte was prepared by dissolving 1.5 mol·dm−1 VOSO4 (97.2% purity) in a 2.0 mol·dm−1 H2SO4 solution. Initially, the positive electrolyte was 1000 mL, whereas the negative electrolyte was 500 mL. During the charging process, the V4+ in the electrolyte was converted to V5+ and V2+ for the positive and negative sides, respectively. Half of the positive electrolyte was then removed to equalize the electrolytes of both sides.
Both the positive and negative electrolytes were supplied to the cell via two diaphragm pumps (SMART Digital DDA7.5-16AR-PVC/V/C, Grundfos, Bjerringbro, Denmark) from reservoirs. In practical applications, both the positive and negative electrolytes are continuously recirculated to the reservoirs. Consequently, during the discharge process, the electroactive species diminishes. However, in this study, the outflow electrolytes were not recirculated to the original reservoirs to maintain a constant inflow concentration.
The VRFB was charged with a power supply (U8001A, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and discharged using an electronic load (PLZ664WA, Kikusui Electronics, Yokohama, Japan). An impedance meter (KFM2150, Kikusui Electronics) was connected with the electronic load to measure the AC impedance of the VRFB during operation. The cell voltage was monitored and recorded using a data acquisition card (NI 9219, National Instrument, Austin, TX, USA) for later analysis.
3.2. Experimental Procedure
The experiment involved two steps. In the first step, the SOC of the VRFB was estimated using Equations (6) and (7), based on the OCV of the VRFB, while the electrolytes were continuously recirculated through the cell. In the second step, the discharging polarization curves of the VRFB system were measured at selected stoichiometric ratios (SRs), ζ while the electrolytes were not recirculated. The supplied electrolyte flow rate was calculated according to electrolyte concentration and load current:
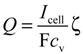 where cv is the electroactive vanadium concentration of the electrolyte, which was calculated by using Equation (6) with the measured OCV. The stable cell voltage was recorded when the load current was applied to the VRFB. The impedance measurement was performed by applying 10% of DC load current over the frequency range from 1 kHz to 20 kHz.
where cv is the electroactive vanadium concentration of the electrolyte, which was calculated by using Equation (6) with the measured OCV. The stable cell voltage was recorded when the load current was applied to the VRFB. The impedance measurement was performed by applying 10% of DC load current over the frequency range from 1 kHz to 20 kHz.
After a polarization curve of the VRFB with a known SOC was obtained, the VRFB was discharged at a constant current mode with recirculated electrolytes until the predetermined SOC of electrolytes was reached. Then, the measurement procedure was repeated as described above.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effect of Operating Conditions of Polarization Curves
A measured AC impedance plot of is shown in Figure 2. The cell resistance is approximated 45 mΩ according to the plot. The low-frequency intercept of the impedance semicircle provides the information about the activation kinetics of the electrochemical interface. It can be seen that the low-frequency resistance decreases with increasing cell current density. At a higher current density, the activation kinetics improves due to the higher electrolyte flow rate. When the current density increases from 400 mA·cm−2 to 500 mA·cm−2, the low-frequency resistance shows no considerable change. The improvement of activation kinetics by the increasing electrolyte flow rate is limited. Since all other impedance plots show the same cell resistance, they are not shown here.
Figure 3 shows the polarization curves and corrected curves of the VRFB system operating at different SRs and SOCs. The corrected curves were obtained by adding the activation overpotential and ohmic overpotential to the measured data. Thus, the corrected data also show the effect of mass transfer overpotential. An SOC of 99% represents the electrolytes at charge completion. All of the polarization curves were nearly linear outside the activation overpotential region. Because the electrolyte flow rate in this study was relatively higher than that in practical operations and the inlet electrolyte concentration was maintained constant during the discharging process, the dramatic voltage drop at a high current density is unclear. A significantly low performance curve was obtained at SOC = 20% and SR = 5, because of the relatively low electrolyte flow rate and electroactive vanadium concentration. At certain SOCs, the cell voltage was unstable when the VRFB was operated at a high current density. Thus, the limiting current density was determined by extending trend lines of corrected data to where the cell voltage was zero. Figure 3 indicates that the limiting current density increases as the SR and SOC increase, which can both be determined according to known operating conditions.
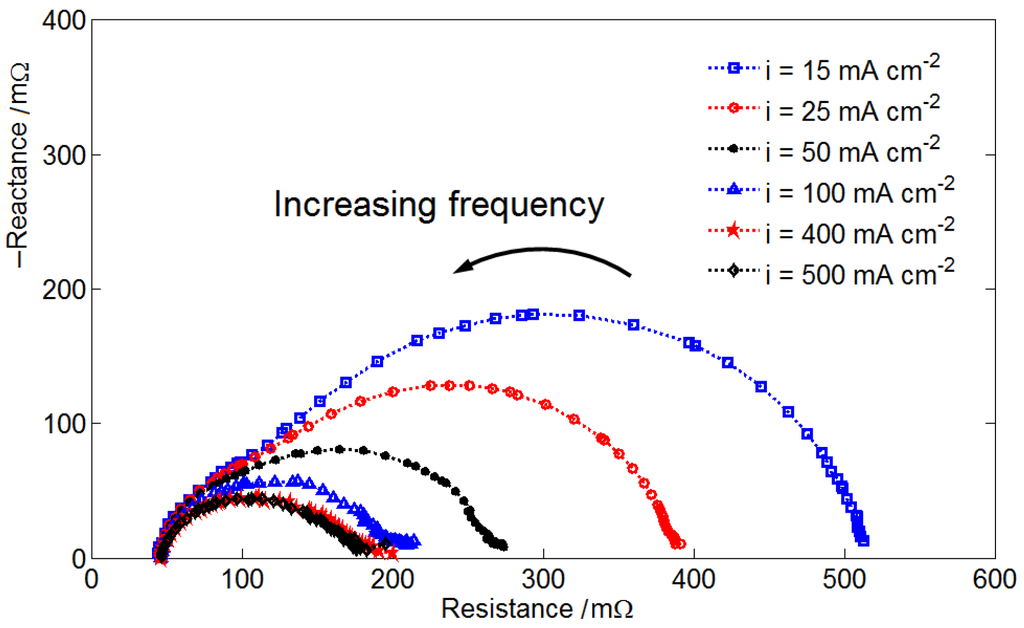
Figure 2.
AC impedance plot of the VRFB operating at a stoichiometric ratio (SR) = 20, state of charge (SOC) = 60% and under various cell current density values.
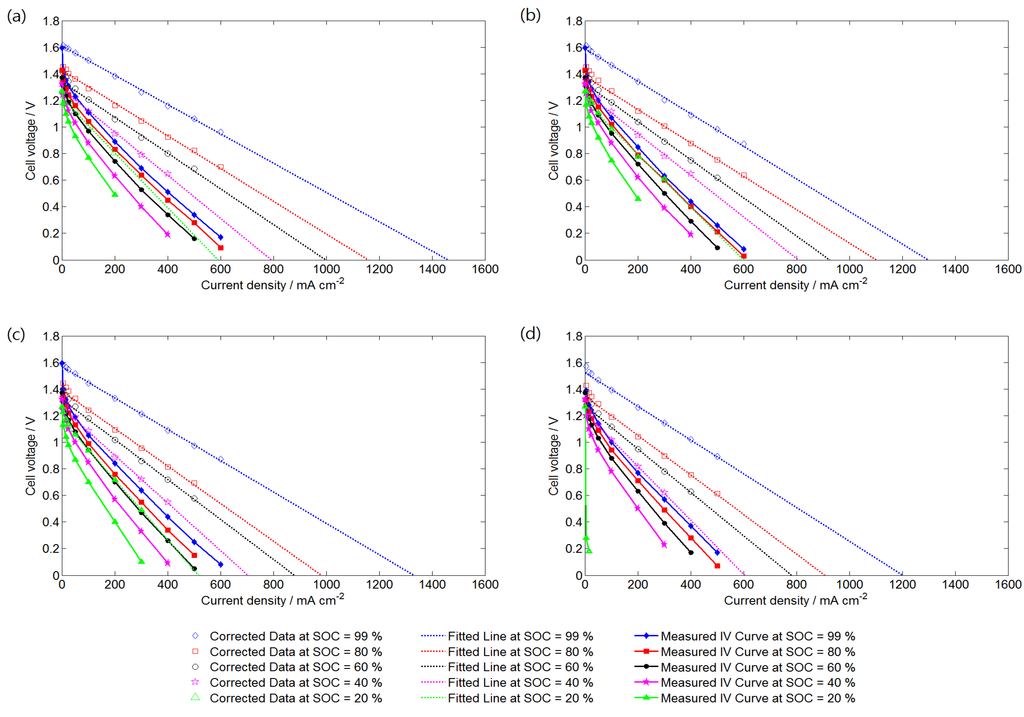
Figure 3.
Measured polarization curves and corrected curves of the VRFB cell operating at different SRs: (a) SR = 20; (b) SR = 15; (c) SR = 10; and (d) SR = 5.

Table 2.
Values of limiting current density and mass transfer coefficient obtained from Figure 3 and Equation (3).
| SR | 20 | 15 | 10 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC/% | Limiting current density/mA·cm−2 (mass transfer coefficient/m·s−1) | |||
| 99 | 1463 (1.02 × 10−4) | 1300 (0.91 × 10−4) | 1332 (0.93 × 10−4) | 1203 (0.84× 10−4) |
| 80 | 1161 (1.00 × 10−4) | 1102 (0.95 × 10−4) | 982 (0.85 × 10−4) | 908 (0.78 × 10−4) |
| 60 | 1000 (1.15 × 10−4) | 927 (1.07 × 10−4) | 880 (1.01 × 10−4) | 782 (0.90 × 10−4) |
| 40 | 793 (1.37 × 10−4) | 807 (1.39 × 10−4) | 705 (1.22 × 10−4) | 605 (1.05 × 10−4) |
| 20 | 591 (2.04 × 10−4) | 600 (2.07 × 10−4) | 517 (1.79 × 10−4) | N/A |
4.2. Determination of Mass Transfer Coefficient
Based on the known limiting current density and electroactive vanadium concentration of each polarization curve, the mass transfer coefficient km was calculated according to Equation (3). In addition, the mean flow velocity of an electrolyte was determined using Equation (13). Thus, the mass transfer coefficient was plotted versus the mean flow velocity for each curve, as shown in Figure 4.
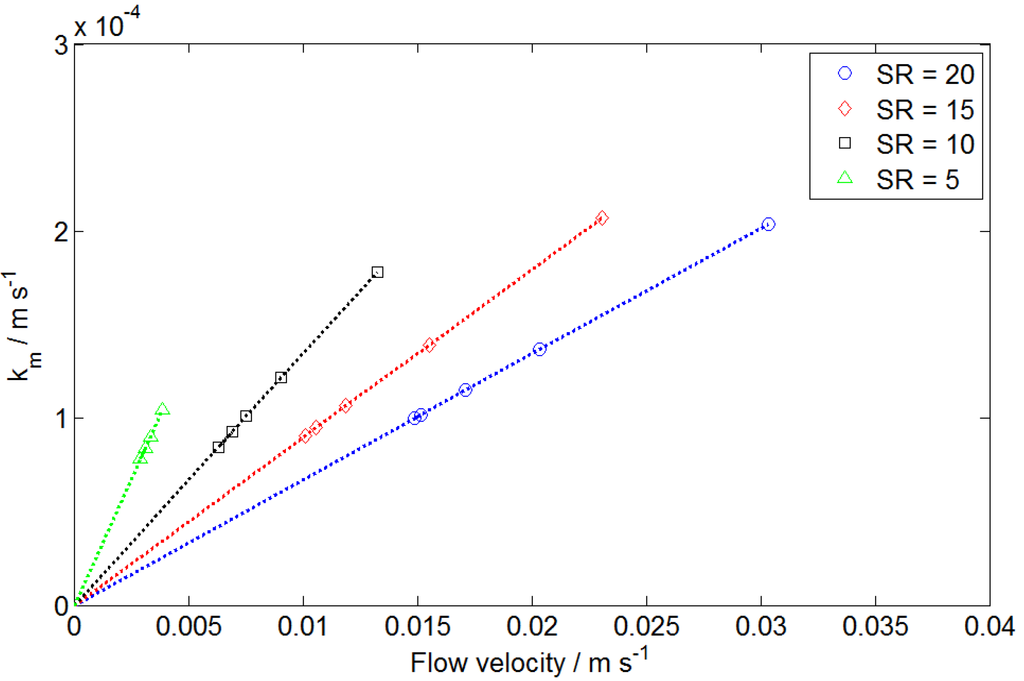
Figure 4.
Calculated mass transfer coefficient is plotted vs. mean flow velocity at different SRs.
For each SR value, the mass transfer coefficient was approximately linear with the mean flow velocity. The trend line at each SR extended to the origin, suggesting that the mass transfer coefficient is zero when the flow velocity is zero. The slope of the trend line was a function of SR and is plotted in Figure 5.
Accordingly, an empirical equation to describe the mass transfer coefficient can be expressed as:
km = (−8.983 × 10−6ζ3 + 4.492 × 10−4ζ2 − 7.86 × 10−3ζ + 5.314 × 10−2)v
The limiting current density was determined using Equations (3) and (15) based on the known operating current density and electrolyte flow rate. Currently, Equation (15) is valid for SR between 5 and 20. Equation (15) can also be programmed into the controller to predict cell performance under monitored operating conditions.
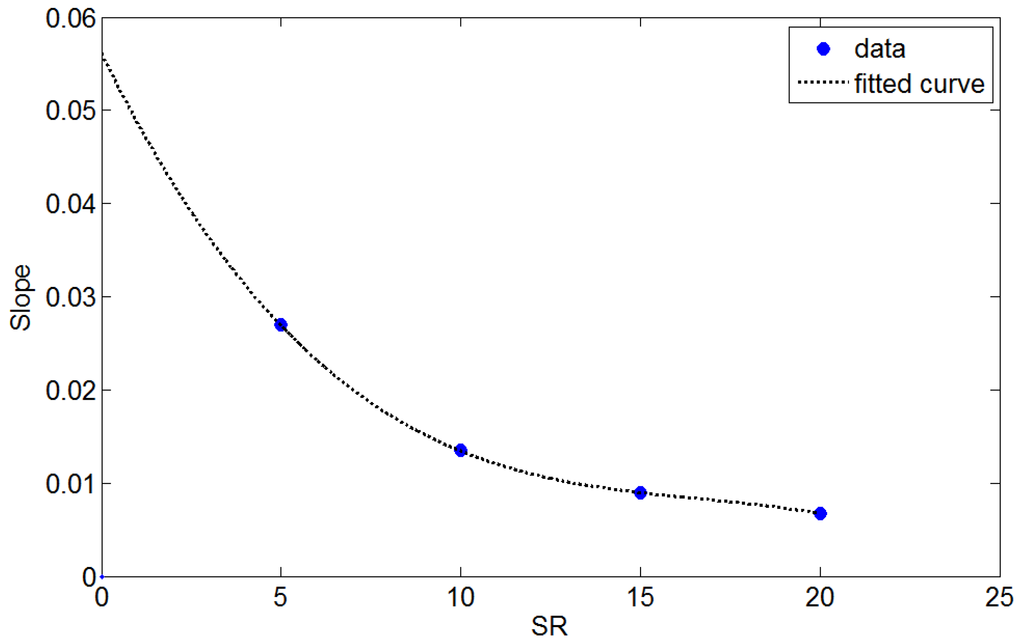
Figure 5.
The slopes of the trend lines in Figure 4 are plotted as a function of SR.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a uniquely designed experiment was conducted to determine the limiting current density of a VRFB. The electrolytes were not recirculated in this VRFB system in order to maintain a constant electrolyte concentration for measuring polarization curves. The experimental results show that the liming current density increases as the SOC and SR increase. In addition, the mass transfer coefficient can be expressed as a function of SR and flow velocity, which can both be determined under measurable operating conditions. The results of this study facilitate improving the accuracy of a mathematical model and predicting the cell performance of a VRFB system.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the Bureau of Energy, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taiwan, and the Institute of Nuclear Energy Research of Taiwan for the financial support for this study under Project Number 103-D0115.
Author Contributions
All authors read and approved the manuscript. Jen-Yu Chen conducted all the experiments. Chin-Lung Hsieh provided instruction and designed for experiments. Ning-Yih Hsu thoroughly reviewed literature and provided precious advice on the experimental procedure. Yi-Sin Chou analyzed experimental data and prepared plots and figures. Yong-Song Chen provided the main idea of this work and prepared the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fabjan, C.; Garche, J.; Harrer, B.; Jörissen, L.; Kolbeck, C.; Philippi, F.; Tomazic, G.; Wagner, F. The vanadium redox-battery: An efficient storage unit for photovoltaic systems. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 47, 825–831. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, B.; Song, S.; Chen, X. Effect of polyhydroxy-alcohol on the electrochemical behavior of the positive electrolyte for vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A843–A847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Kim, S.; Wang, W.; Vijayakumar, M.; Nie, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Xia, G.; Hu, J.; Graff, G.; et al. A stable vanadium redox-flow battery with high energy density for large-scale energy storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hung, C.-H.; Wang, S.-P.; Chiang, I.-L. Graphite felt with vapor grown carbon fibers as electrodes for vanadium redox flow batteries. Rare Met. 2011, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yue, L.; Li, W.S.; Li, G.L.; Shu, D.; Chen, H.Y. Graphite-carbon nanotube composite electrodes for all vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Ohya, H. Preparation of cation exchange membrane as a separator for the all-vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 120, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkar, T.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Modification of membranes using polyelectrolytes to improve water transfer properties in the vanadium redox battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 222, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt-Smith, M.J.; Ridley, P.; Wills, R.G.A.; Shah, A.A.; Walsh, F.C. The importance of key operational variables and electrolyte monitoring to the performance of an all vanadium redox flow battery. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 126–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, T. An optimal strategy of electrolyte flow rate for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 203, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Watt-Smith, M.J.; Walsh, F.C. A dynamic performance model for redox-flow batteries involving soluble species. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 8087–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. A simple model for the vanadium redox battery. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 6827–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Xing, F. A three-dimensional model for negative half cell of the vanadium redox flow battery. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 58, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, V.; Dongmei, C. Dynamic model of a vanadium redox flow battery for system performance control. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2013, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmal, D.; Erkel, J.; Duin, P.J. Mass transfer at carbon fiber electrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1986, 16, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Tangirala, R.; Singh, R.; Wills, R.G.A.; Walsh, F.C. A dynamic unit cell model for the all-vanadium flow battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A671–A677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Matyka, M.; Khalili, A.; Koza, Z. Tortuosity-porosity relation in porous media flow. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).