Torsional Stiffness Effects on the Dynamic Stability of a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Blade
Abstract
:1. Introduction
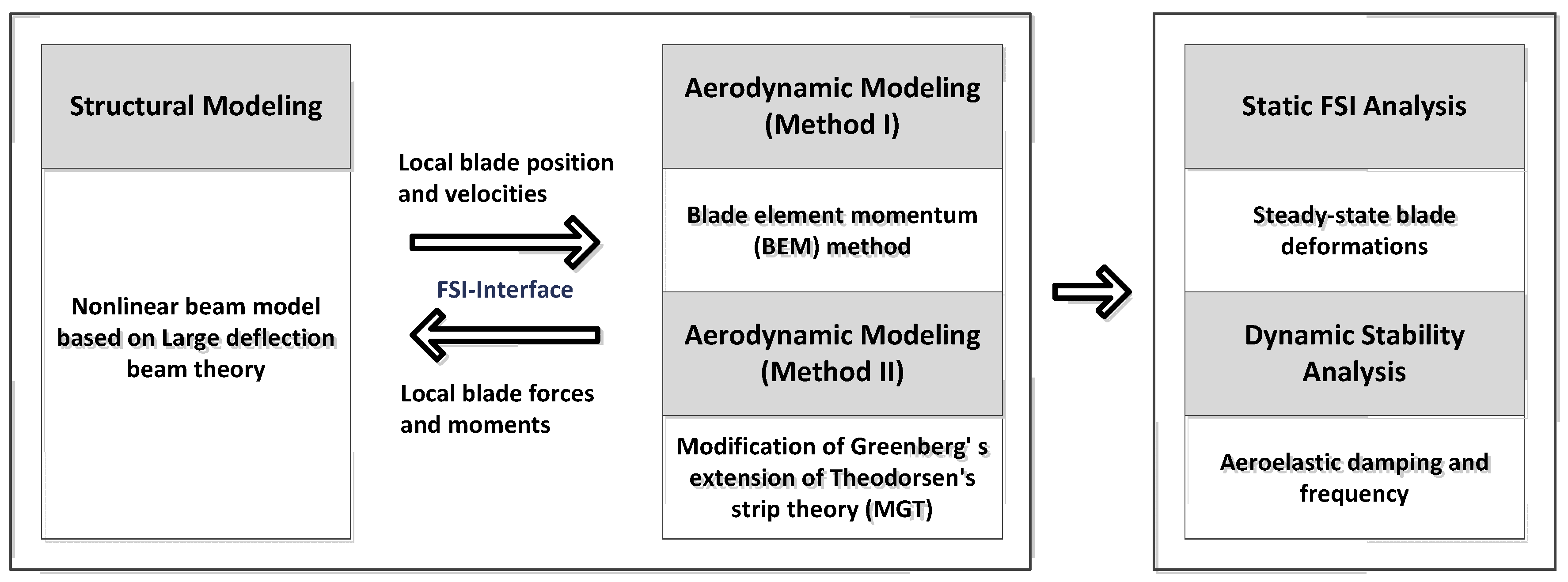
2. Analysis
2.1. Rotor Structural Model
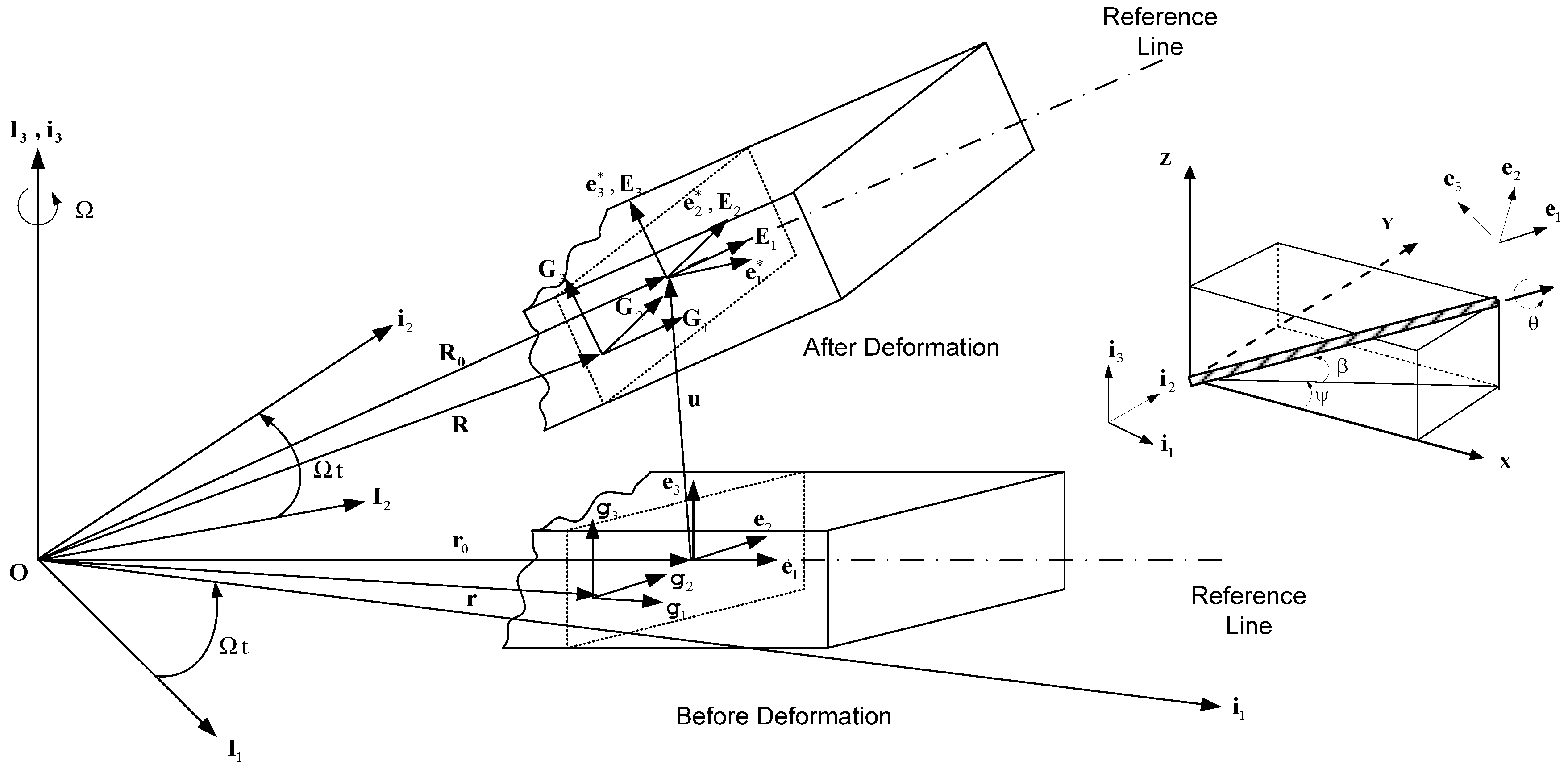
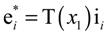
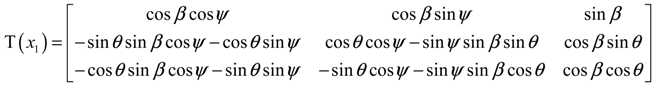
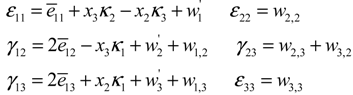
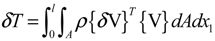
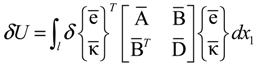
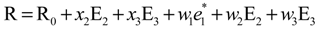
2.2. Rotor Aerodynamic Model
2.2.1. Modification of Greenberg’s Extension of Theodorsen’s Strip Theory
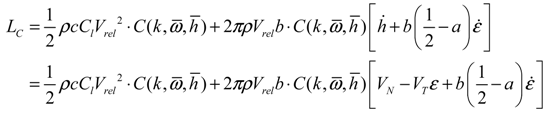
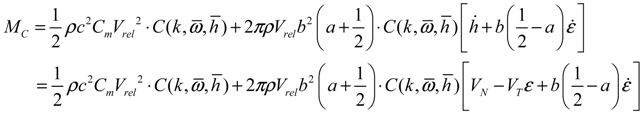
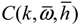 is the Theodorsen’s lift deficiency function [28,29], which is defined as:
is the Theodorsen’s lift deficiency function [28,29], which is defined as:
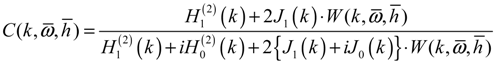
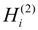 (i = 0, 1) is the Hankel function of second kind of order i, and the term of Ji (i = 0, 1) is the real part of the complex Bessel function of order i, and the k is reduced frequency. To obtain a solution to non-constant free-stream for the unsteady motions as well as the airfoil at constant angle of attack, it is assumed that the wake is sinusoidal.
(i = 0, 1) is the Hankel function of second kind of order i, and the term of Ji (i = 0, 1) is the real part of the complex Bessel function of order i, and the k is reduced frequency. To obtain a solution to non-constant free-stream for the unsteady motions as well as the airfoil at constant angle of attack, it is assumed that the wake is sinusoidal.
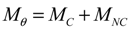
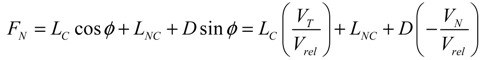
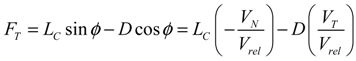
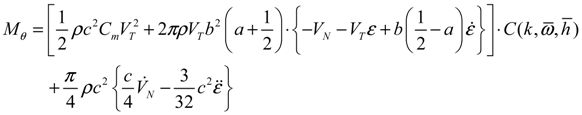
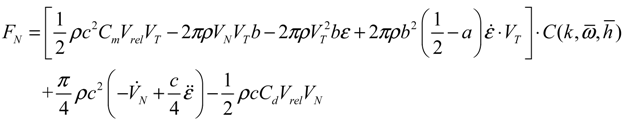
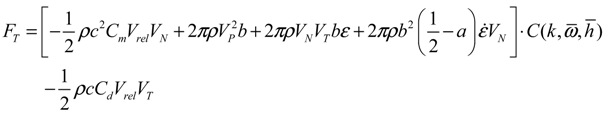
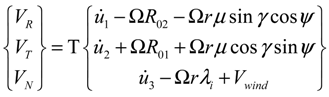
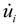 (i = 1, 2, 3) is the component of elastic velocity vectors of the blade and R0i (i = 1, 2, 3) is the component of position vector; and R0i is an arbitrary point of the cross-section in the deformed blade configuration. The term r is the blade radius; Ω, the constant angular velocity; γ, the yaw angle; Ψ, the azimuth angle of the blade and Vwind, the mean wind speed. The term μ denotes the nondimensional term given by μ = Vwind/ΩR. The term λi is The inflow ratio λi denotes the inflow ratio, which is defined as a non-dimensionalized operational speed [31], and can be defined as follows:
(i = 1, 2, 3) is the component of elastic velocity vectors of the blade and R0i (i = 1, 2, 3) is the component of position vector; and R0i is an arbitrary point of the cross-section in the deformed blade configuration. The term r is the blade radius; Ω, the constant angular velocity; γ, the yaw angle; Ψ, the azimuth angle of the blade and Vwind, the mean wind speed. The term μ denotes the nondimensional term given by μ = Vwind/ΩR. The term λi is The inflow ratio λi denotes the inflow ratio, which is defined as a non-dimensionalized operational speed [31], and can be defined as follows:
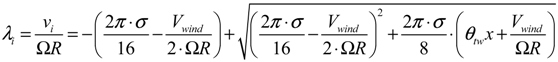
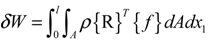
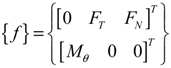
2.2.2. Blade Element Momentum Method
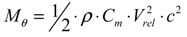
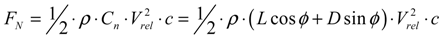
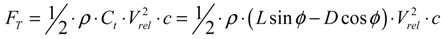
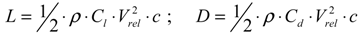
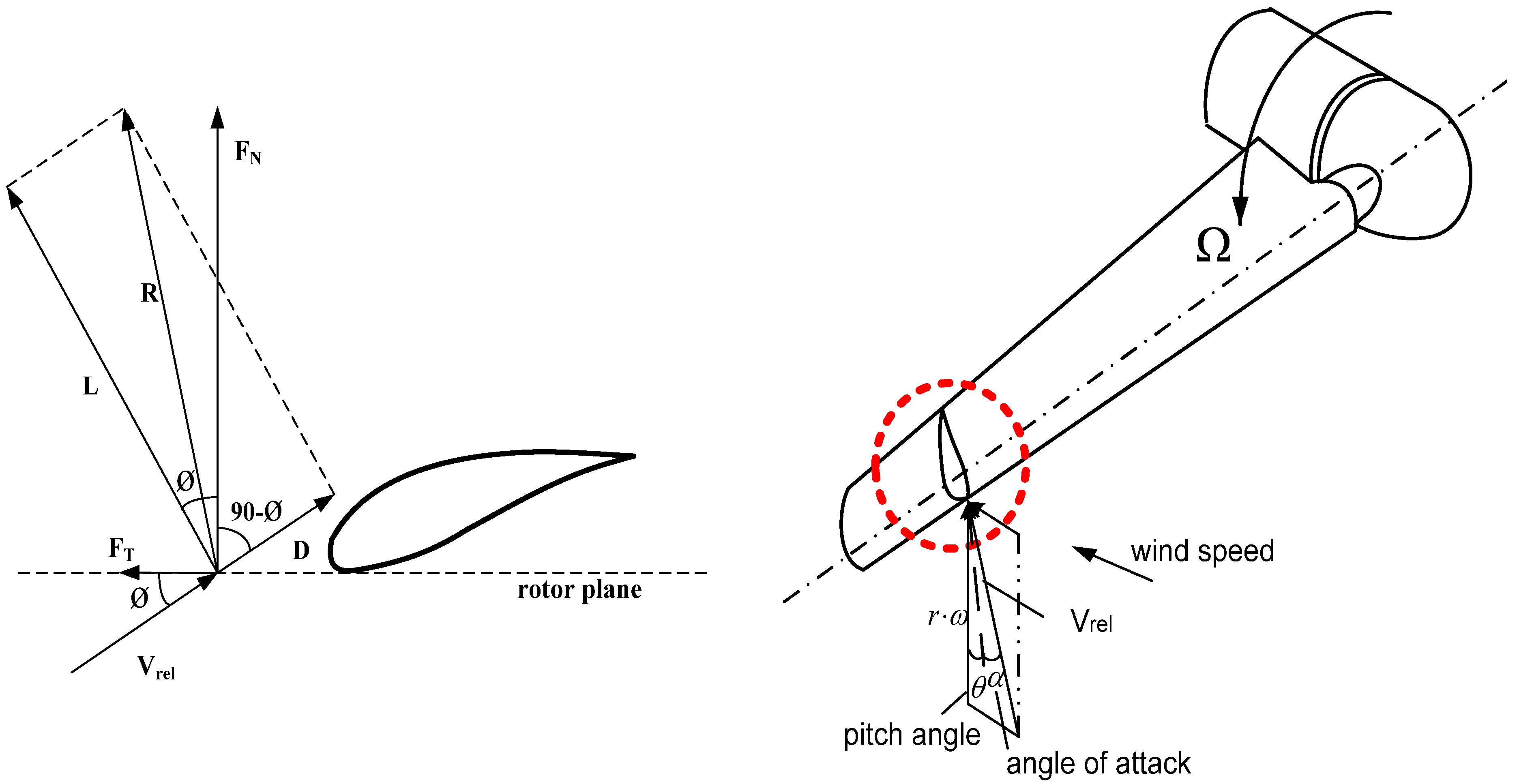
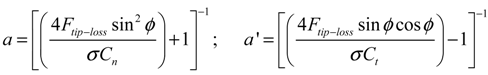
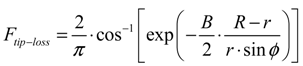
2.3. Rotor Aeroelastic Model
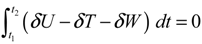
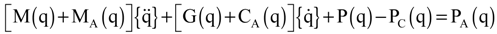
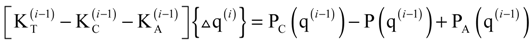
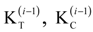 , and
, and 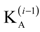 are the tangential stiffness, centrifugal stiffness and tangential aerodynamic matrices, respectively. The term q is the generalized nodal displacement vector, and the equilibrium deflections can be predicted through the Newton-Raphson iterative method. Assuming that the flutter motion is a small perturbation
are the tangential stiffness, centrifugal stiffness and tangential aerodynamic matrices, respectively. The term q is the generalized nodal displacement vector, and the equilibrium deflections can be predicted through the Newton-Raphson iterative method. Assuming that the flutter motion is a small perturbation 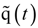 about the equilibrium position q0, or q(t) = q0 +
about the equilibrium position q0, or q(t) = q0 + 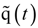 , then the linearization of the nonlinear finite element equations of motion can be expressed as follows:
, then the linearization of the nonlinear finite element equations of motion can be expressed as follows:
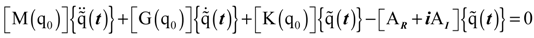
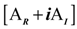 is the coupling term relevant to aerodynamic states. It is well known that modal representation is convenient for reducing a matrix size and for identifying the flutter mode. The preceding linearized flutter equations are transformed into the modal space using the expression of
is the coupling term relevant to aerodynamic states. It is well known that modal representation is convenient for reducing a matrix size and for identifying the flutter mode. The preceding linearized flutter equations are transformed into the modal space using the expression of 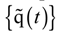 = [ø]{y(t)}, where [ø] is the modal matrix of the first m coupled rotating modes, and {y(t)} is the vector of m generalized coordinates in the modal space. Equation (27) can be rewritten by substituting
= [ø]{y(t)}, where [ø] is the modal matrix of the first m coupled rotating modes, and {y(t)} is the vector of m generalized coordinates in the modal space. Equation (27) can be rewritten by substituting 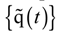 = [ø]{y(t)} and pre-multiplied [ø]T. Therefore, the rearranged equation is expressed as follows:
= [ø]{y(t)} and pre-multiplied [ø]T. Therefore, the rearranged equation is expressed as follows:
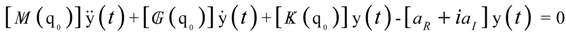
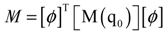
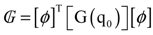
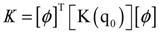
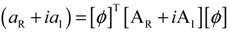
3. Results and Discussion
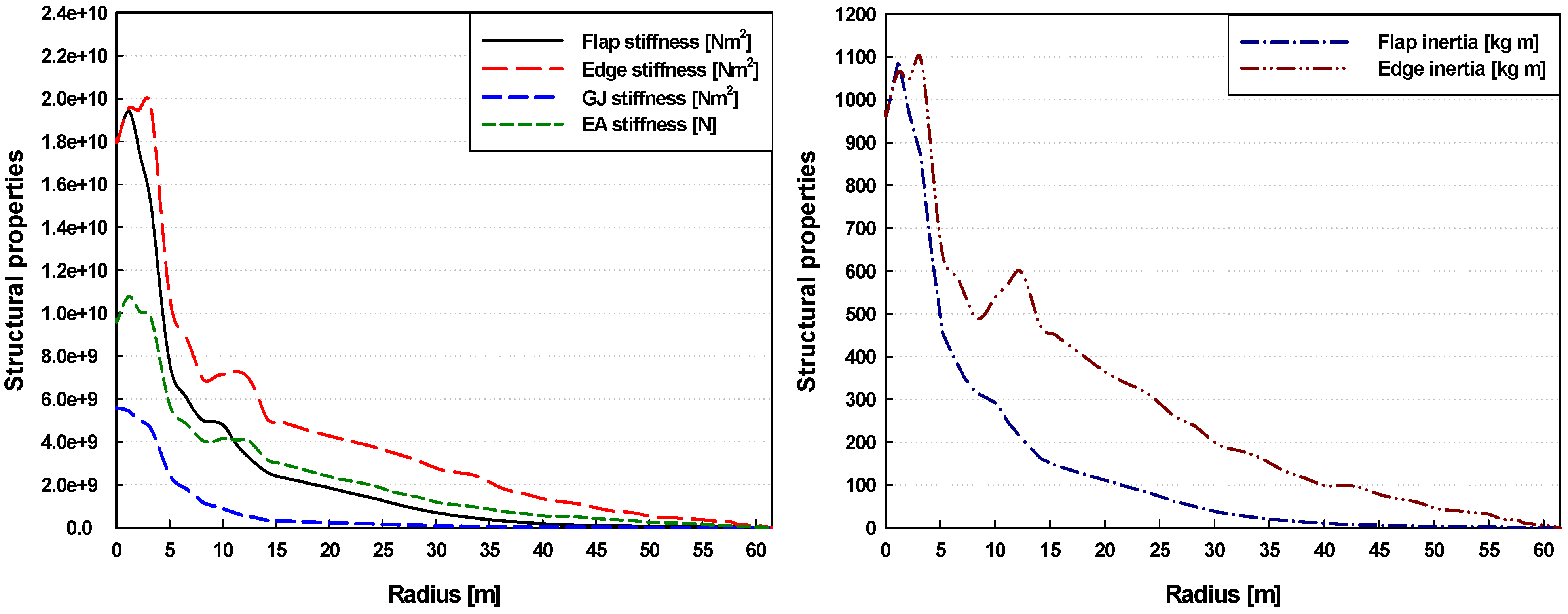
3.1. Validation for Aerodynamic Predictions and Steady-State Blade Deflections
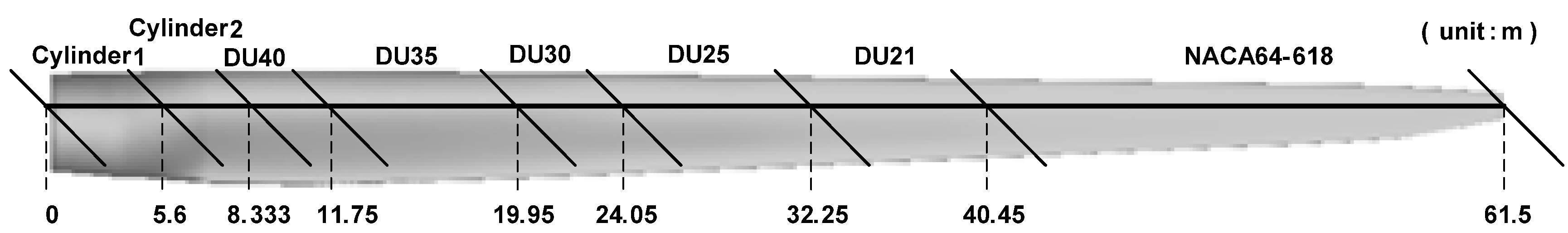
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rating | 5 mega-watt |
| Rotor orientation | Upwind, 3 blades |
| Rotor, Hub diameter | 126 m, 3 m |
| Cut-in, Rated, Cut-out wind speed | 3 m/s, 11.4 m/s, 25 m/s |
| Cut-in, Rated, Cut-out rotor speed | 0.722 rad/s, 1.267 rad/s, 1.267 rad/s |
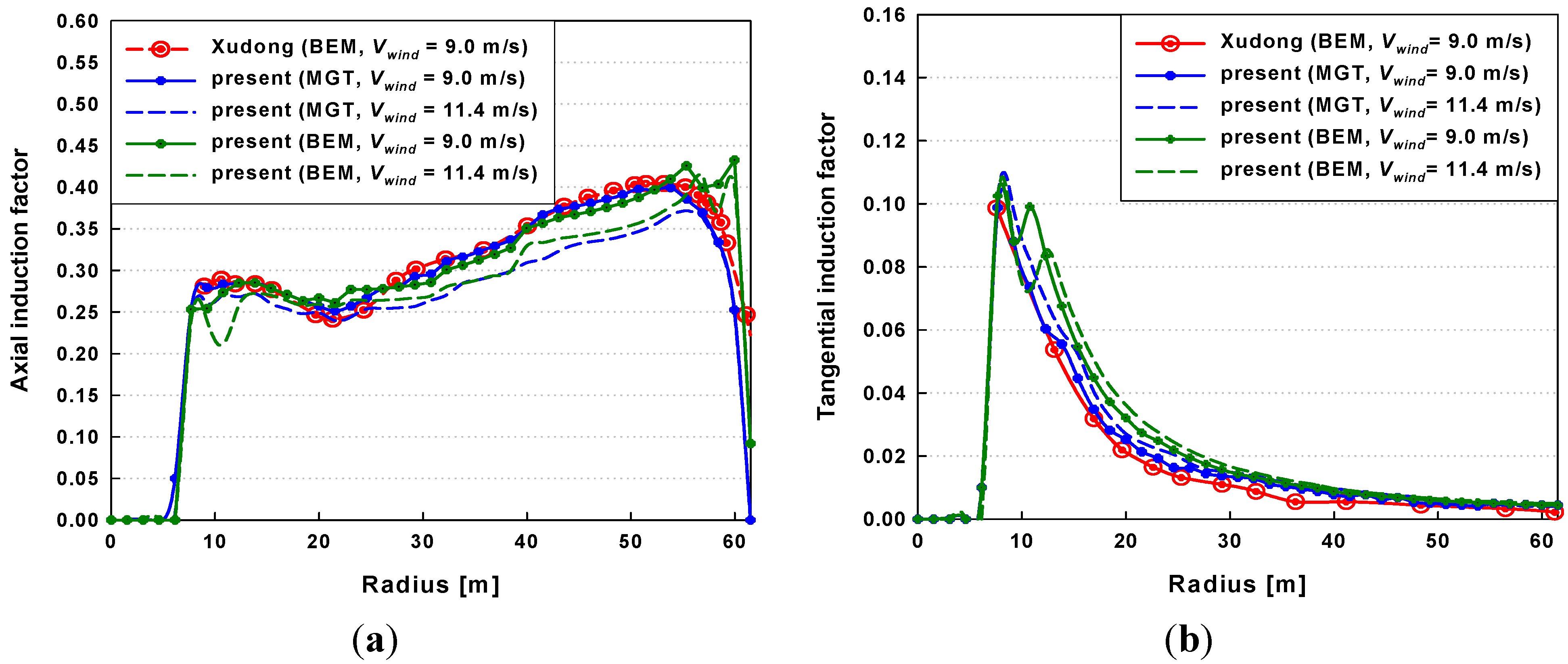
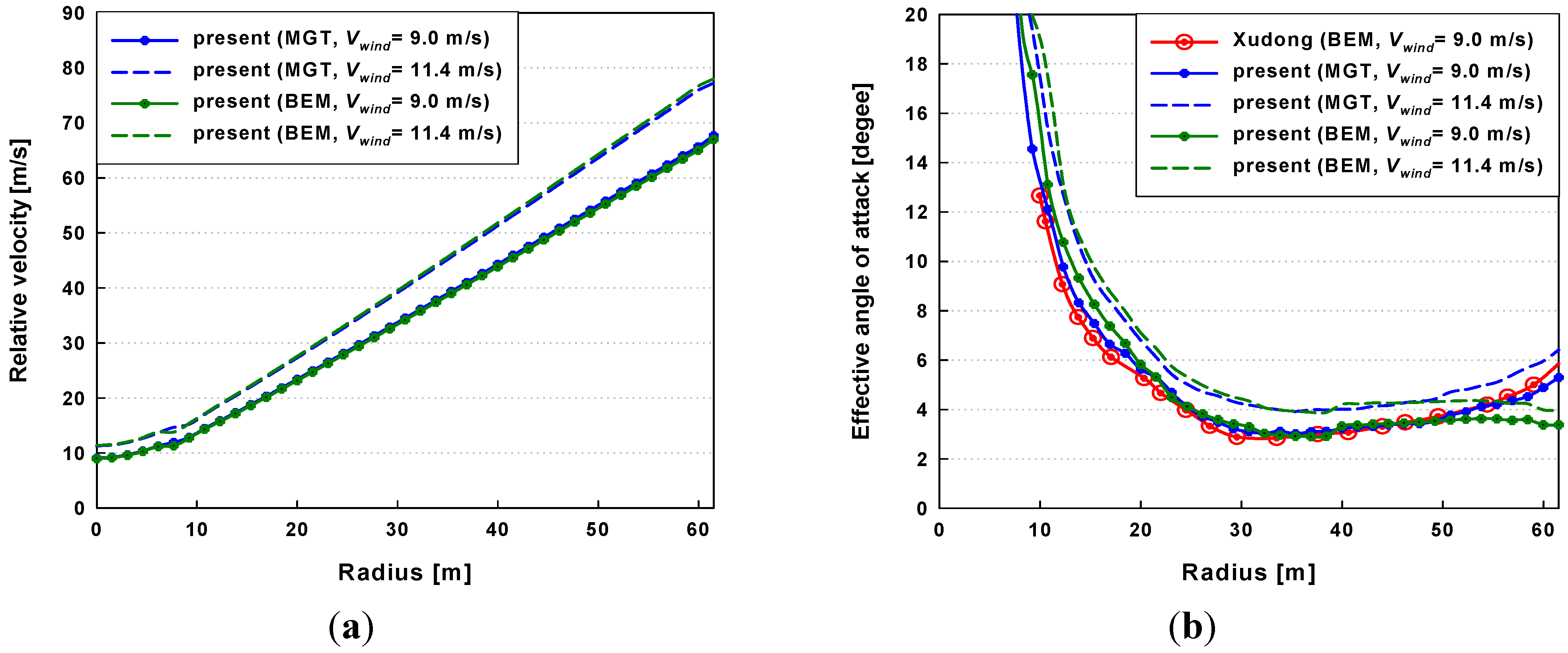
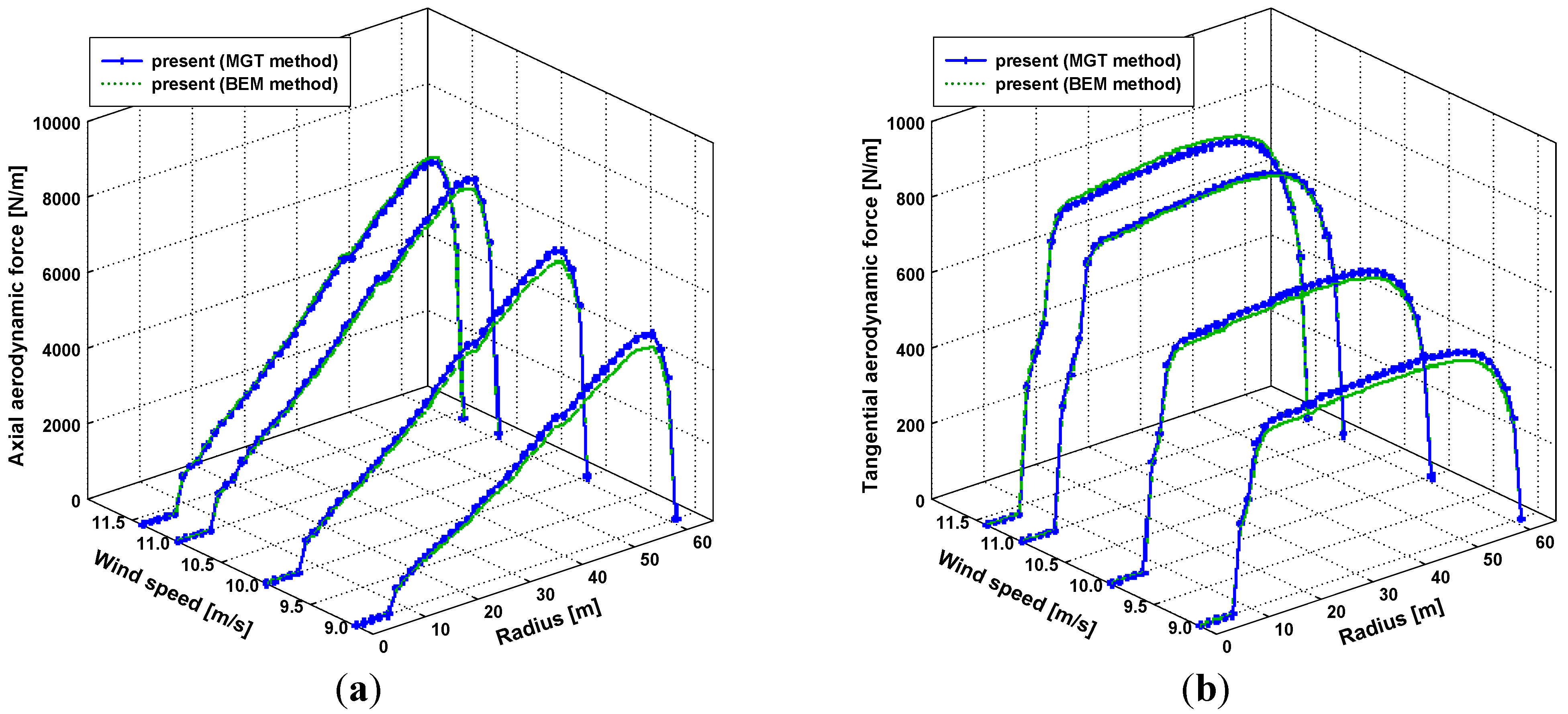
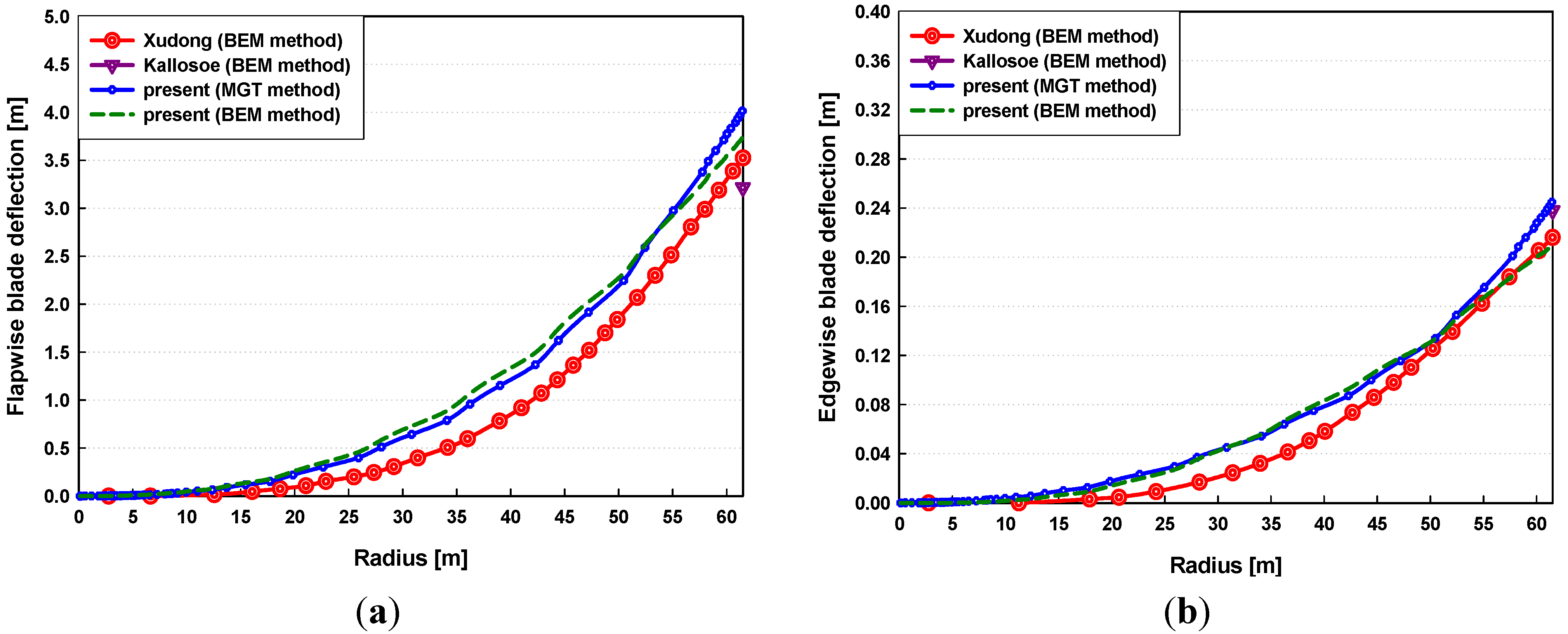
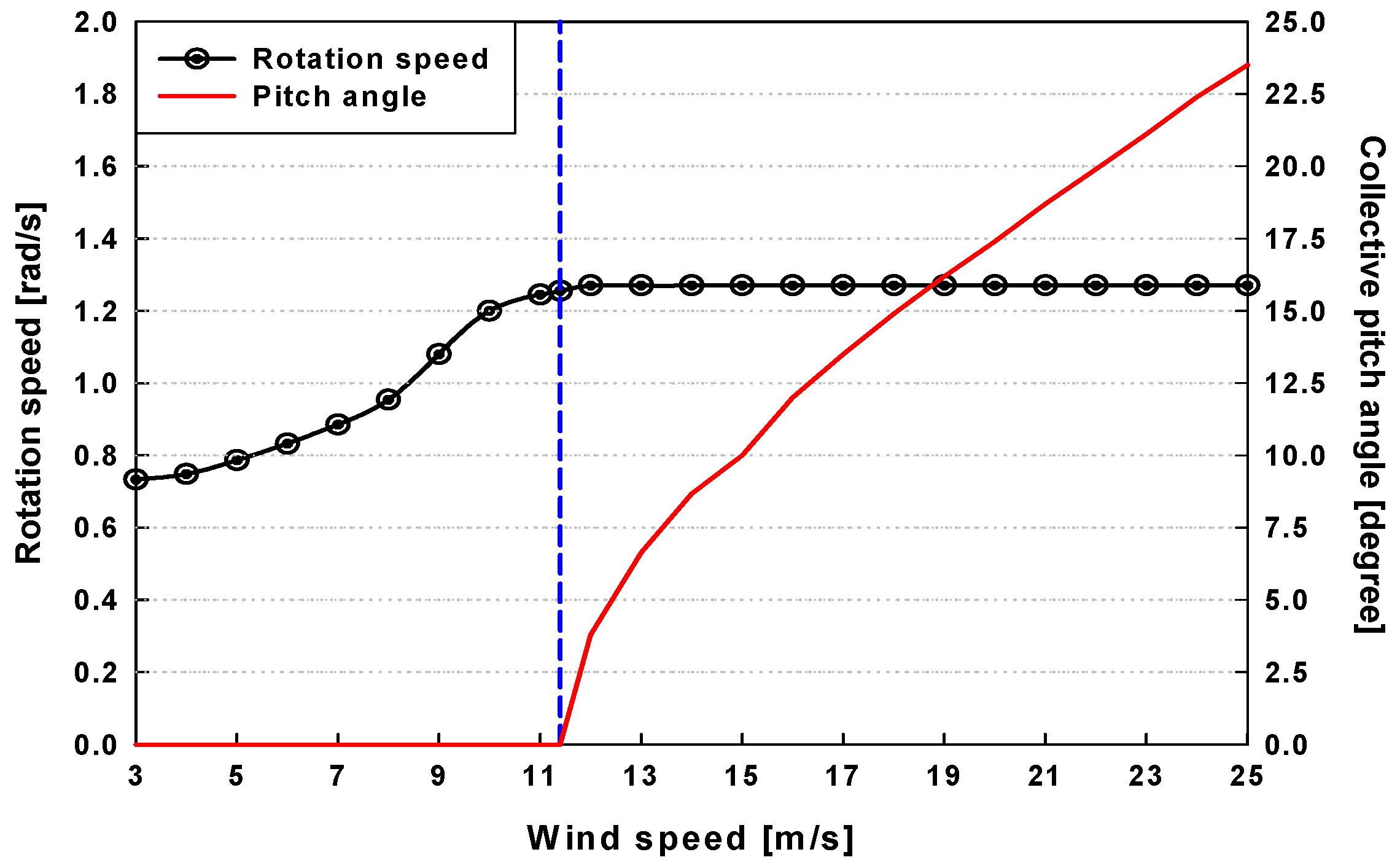
3.2. Dynamic Stability Analysis under Normal Operating Conditions
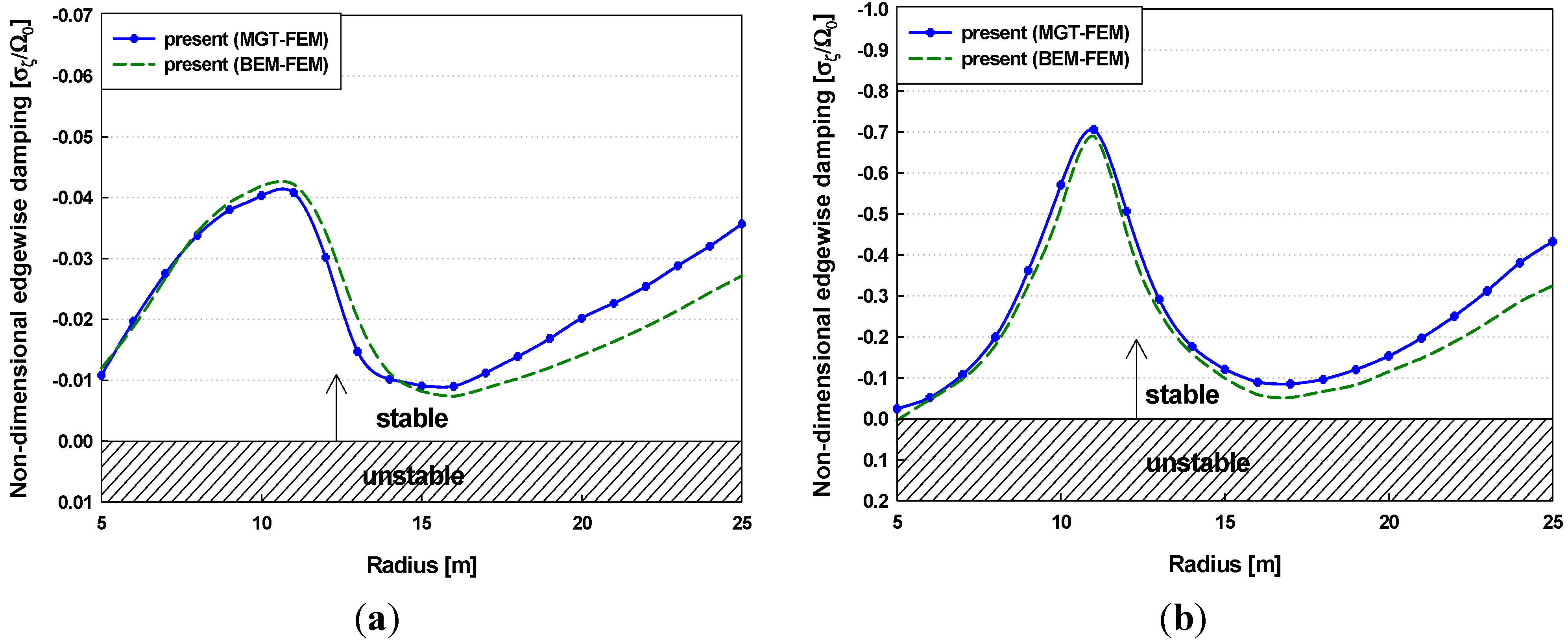
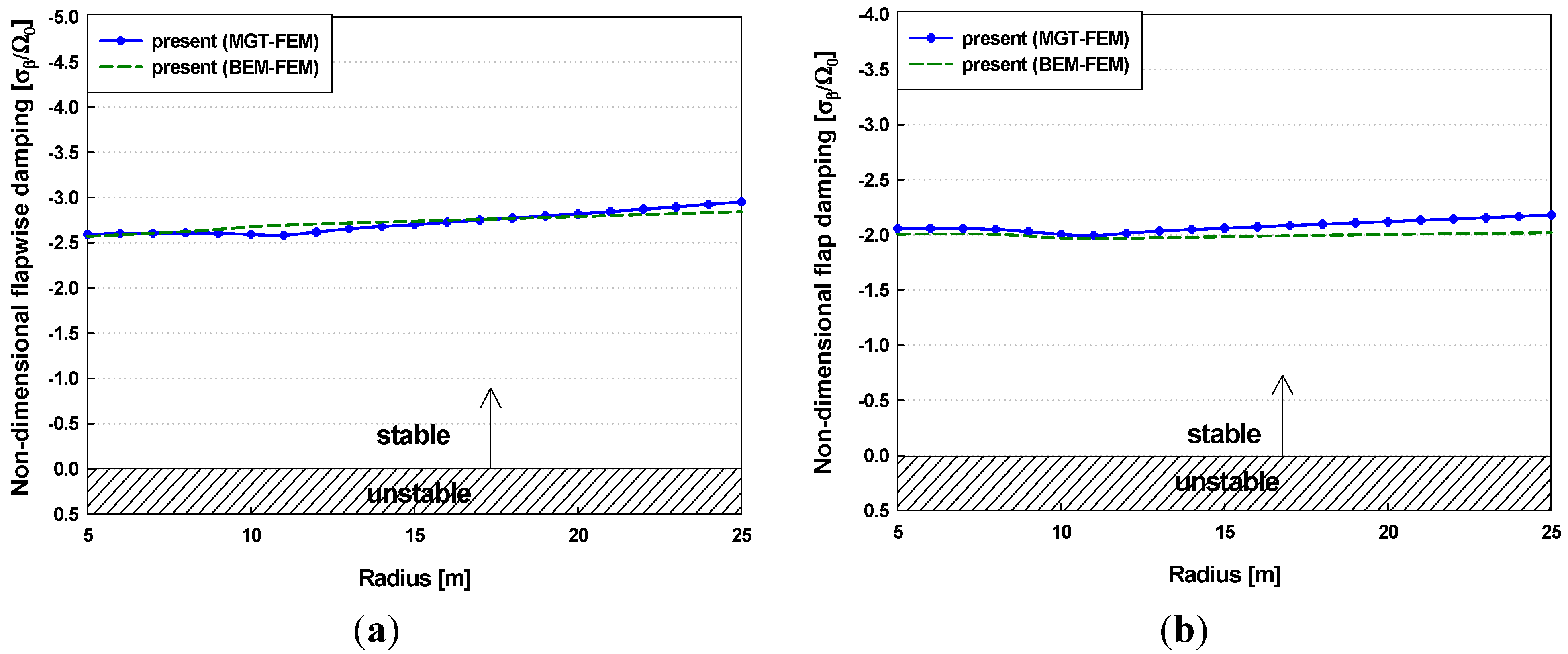
3.3. Effects of Torsional Stiffness Reductions on Dynamic Stability
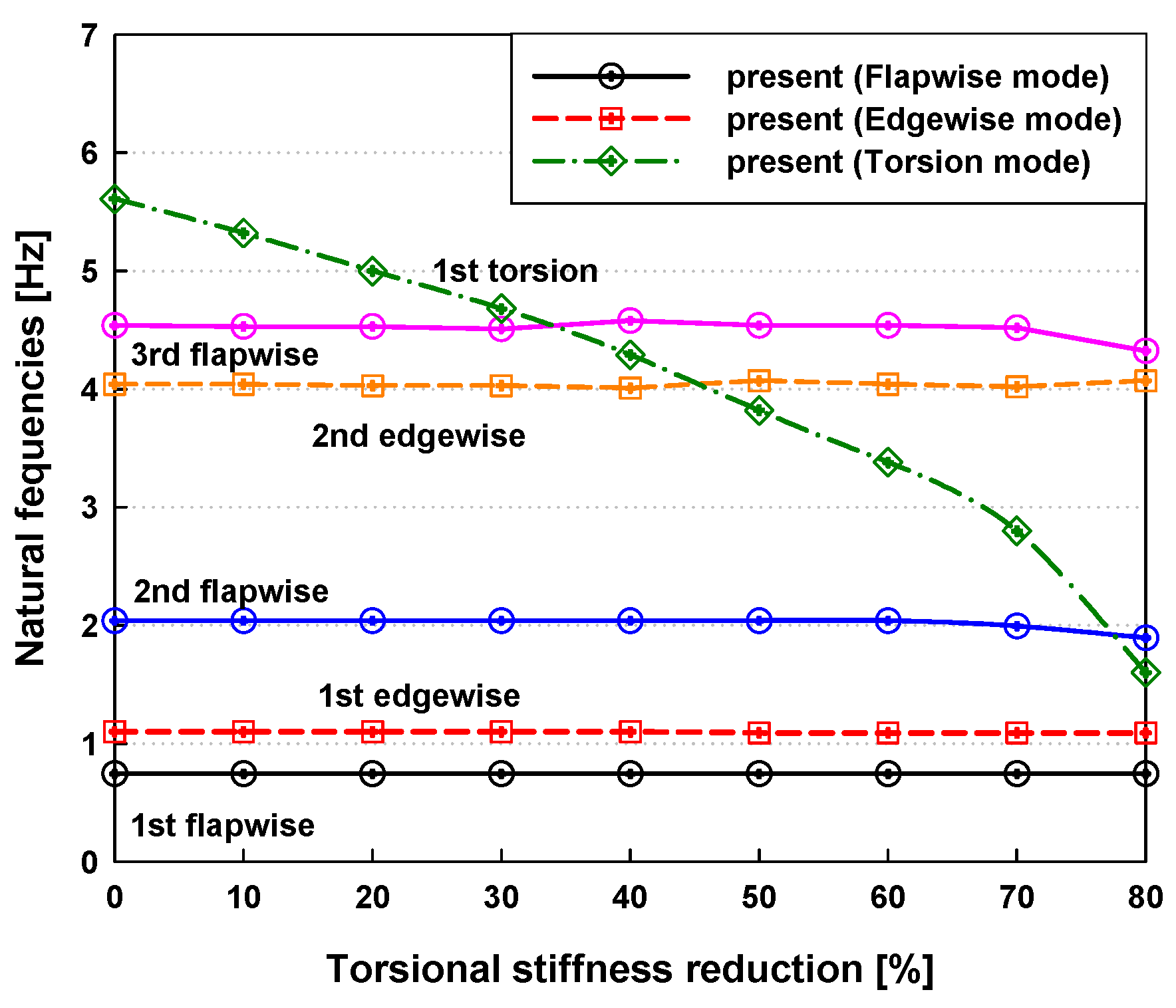
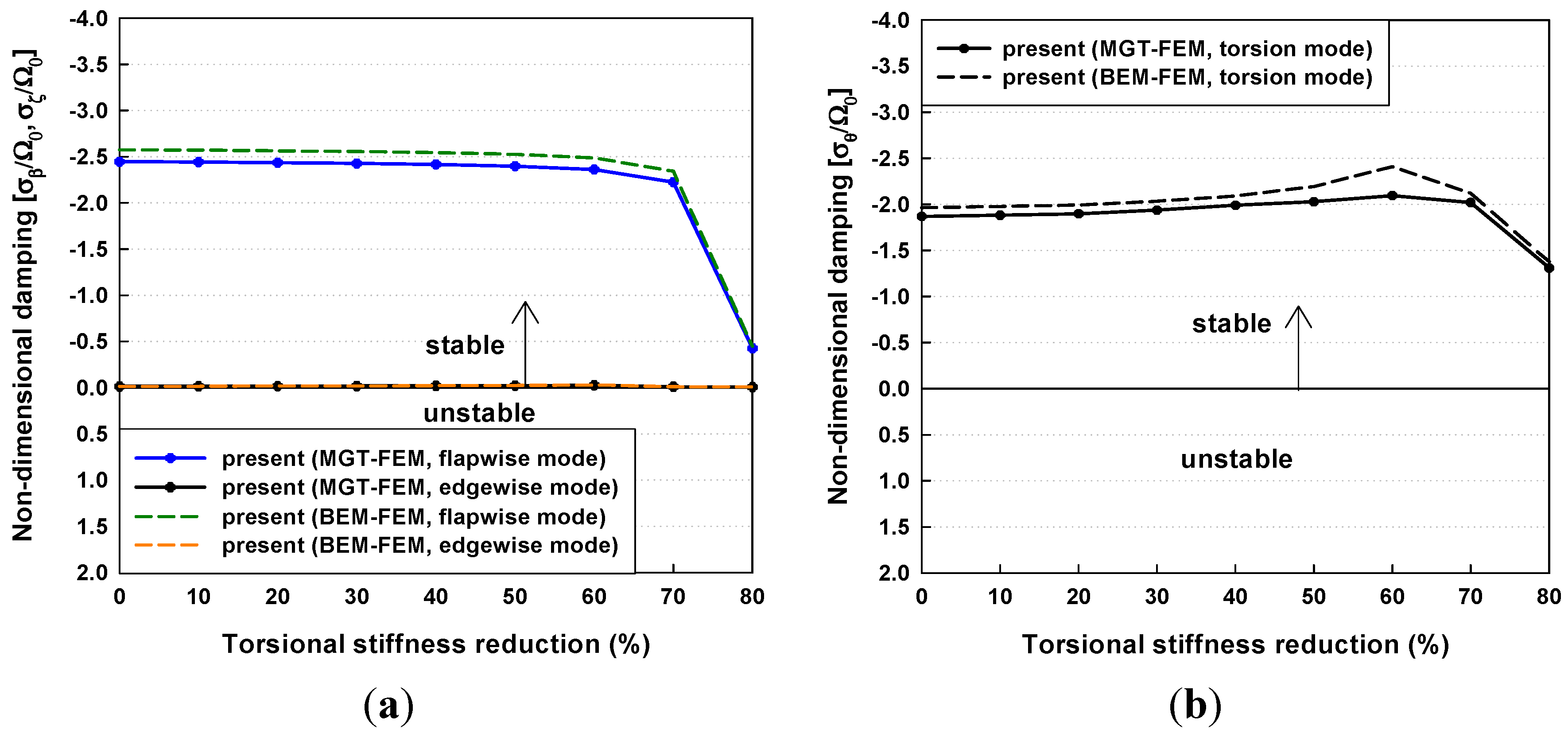
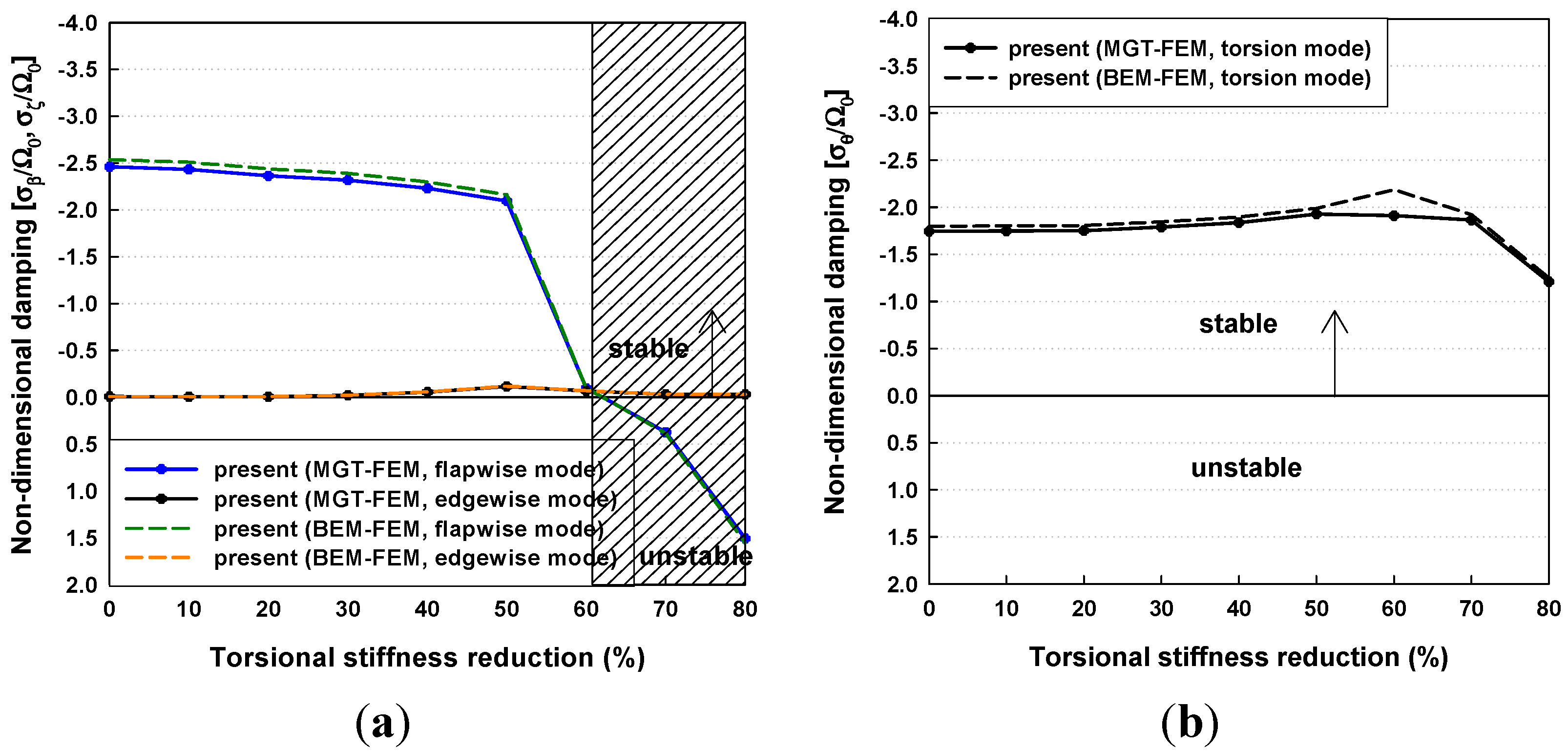
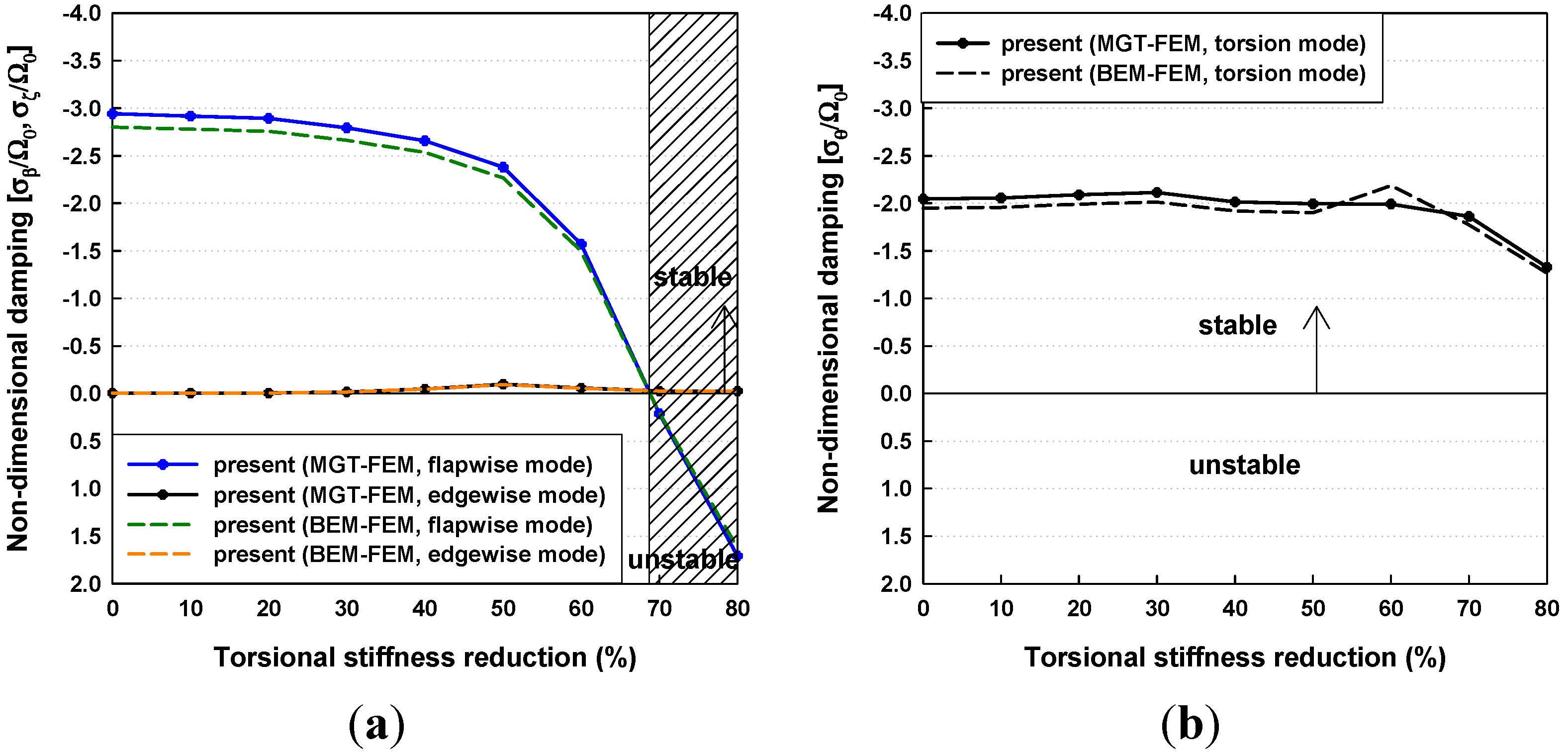
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Riziotis, V.A.; Voutsinas, S.G.; Politis, E.S.; Chaviaropoulos, P.K. Aeroelastic stability of wind turbines: The problems, the methods and the issues. Wind Energy 2004, 7, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, Y.C. An Introduction to the Theory of Aeroelasticity; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bisplinghoff, R.L.; Ashley, H.; Halfman, R.L. Aeroelasticity; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Lobitz, D.W. Aeroelastic stability predictions for a MW-sized blade. Wind Energy 2004, 7, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobitz, D.W. Parameter sensitivities affecting the flutter speed of a MW-sized blade. J. Solar Energy Eng. Trans. ASME 2005, 127, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.T.; Madsen, H.A. Prediction of Dynamic Loads and Induced Vibration in Stall; Technical Report Risø-R-1045; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, K.; Petersen, J.T.; Nim, E.; Øye, S.; Petersen, B. A method for determination of damping for edgewise blade vibrations. Wind Energy 2001, 3, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, F.; Petersen, J.T.; Madsen, H.A. Dynamic stall and aerodynamic damping. ASME J. Sol. Energy Eng. 1999, 121, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaviaropoulos, P.K. Flap/lead-lag aeroelastic stability of wind turbine blades. Wind Energy 2001, 4, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björck, A.; Dahlberg, J.; Östman, A.; Ganander, H. Computations of Aerodynamic Damping for Blade Vibrations in Stall. In Proceedings of the 1997 European Wind Energy Conference, Dublin Castle, Ireland, 6–9 October 1997.
- Holierhoek, J.G. Investigation into the Possibility of Flap-Lag-Stall Flutter. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2007.
- Acree, C.W., Jr.; Peyran, R.J.; Johnson, W. Rotor Design for Whirl Flutter: An Examination of Options for Improving Tiltrotor Aeroelastic Margins. In Proceedings of American Helicopter Society 55th Annual Forum, Montreal, Canada, 25–27 May 1999.
- Nixon, M.W. Parametric studies for tiltrotor aeroelastic stability in high speed flight. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 1993, 38, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, G.S.; Chopra, I. Aeromechanical instability of rotorcraft with advanced geometry blades. J. Math. Comp. Model. 1994, 19, 159–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, G.S.; Wright, A.D.; Butterfield, C.P. Stability Analysis of A Variable-Speed Wind Turbines. In Proceedings of the 1997 ASME Wind Energy Symposium, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 January 1997.
- Bir, G.; Jonkman, J. Aeroelastic instabilities of large offshore and onshore wind turbines. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. Development of A Time-Accurate Viscous Lagrangian Vortex Wake Model for Wind Turbine Applications. PhD Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, D.H. Nonlinear Equations for the Dynamics of Pre-Twisted Beams Undergoing Small Strains and Large Rotations; Technical Report TP-240; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bauchau, O.A.; Hong, C.H. Finite element approach to rotor blade modeling. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 1987, 32, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauchau, O.A.; Hong, C.H. Nonlinear composite beam theory. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 1988, 55, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B. Assembly of moderate-rotation finite elements used in helicopter rotor dynamics. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 1987, 32, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xudong, W.; Shen, W.Z.; Zhu, W.J.; Sørensen, J.N. Shape optimization of wind turbine blades. Wind Energy 2009, 12, 781–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallesøe, B.S.; Hansen, M.H. Effects of Large Bending Deflections on Blade Flutter Limits; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stemple, A.D.; Lee, S.W. Large Deflection Static and Dynamic Finite Element Analyses of Composite Beams with Arbitrary Cross Sectional Warping. In Proceedings of 30th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ACS Structures. Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Mobil, AL, USA, 3–5 April 1989; pp. 1788–1798.
- Cho, M.H.; Lee, I. Aeroelastic stability of hingeless rotor blade in hover using large deflection theory. Am. Inst. Aeronaut. Austronaut. J. 1994, 32, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Det Norske Veritas (DNV) and Risø National Laboratory. In Guidelines for Design of Wind Turbines; DNV/Risø in Technical Co-Operation: Roskilde, Denmark, 2001.
- NWTC Design Codes (PreComp by Gunjit Bir). Available online: http://wind.nrel.gov/designcodes/preprocessors/precomp/ (accessed on 22 January 2011).
- Greenberg, J.M. Airfoil in Sinusoidal Motion in a Pulsating Stream; TN-1326; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA): Washington, DC, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Loewy, R.G. A two-dimensional approach to the unsteady aerodynamics of rotary wings. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 1957, 24, 82–98. [Google Scholar]
- Leishman, J.G. Principles of Helicopter Aerodynamics; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vity, V.; Coppotelli, G.; de Pompeis, F.; Marzocca, P. Development of An Aerodynamic and Aeroelastic Tool for Wind Turbine Design. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structure Dynamics, and Material Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2007.
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Computer-aided engineering tools. Available online: http://wind.nrel.gov/designcodes/preprocessors/airfoilprep/ (accessed on 13 January 2013).
- Yamane, T.; Friedmann, P.P. Aeroelastic tailoring analysis for preliminary design of advanced turbo propellers with composite blades. Comp. Fluids 1993, 21, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, J.; Butterfield, S.; Musial, W.; Scott, G. Definition of 5-MW Reference Wind Turbine for Offshore System Development; Technical Report NREL/TP-500–38060; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Denver, CO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kallosøe, B.S. Effect of steady deflections on the aeroelastic stability of a turbine blade. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, T.; Markou, H.; Hansen, H.; Thomsen, K.; Rasmussen, F. Aeroelastic Stability Analysis and Passive Instability Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2006 European Wind Energy Conference and Exhibition, Athens, Greece, 27 February–2 March 2006.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, M.-S.; Lee, I.; Yoo, S.-J.; Park, K.-C. Torsional Stiffness Effects on the Dynamic Stability of a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Blade. Energies 2013, 6, 2242-2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042242
Jeong M-S, Lee I, Yoo S-J, Park K-C. Torsional Stiffness Effects on the Dynamic Stability of a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Blade. Energies. 2013; 6(4):2242-2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042242
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Min-Soo, In Lee, Seung-Jae Yoo, and Kwang-Choon Park. 2013. "Torsional Stiffness Effects on the Dynamic Stability of a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Blade" Energies 6, no. 4: 2242-2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042242
APA StyleJeong, M.-S., Lee, I., Yoo, S.-J., & Park, K.-C. (2013). Torsional Stiffness Effects on the Dynamic Stability of a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Blade. Energies, 6(4), 2242-2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042242




