Abstract
Helium, as a strategic resource with broad applications in industry and science, has drawn increasing global attention due to its scarcity and non-renewable nature. Noble gas isotopes, especially those of helium, neon, and argon, provide unique geochemical tracers for understanding helium genesis, migration, and accumulation. This short review summarizes recent advances in the application of noble gas isotope techniques to helium resource research. It covers (1) the fundamental isotope systematics and transport mechanisms, (2) key analytical methods for gas extraction and measurement, and (3) typical case studies illustrating helium source identification and reservoir evaluation. In particular, we highlight three emerging trends: (i) field-adaptable analytical protocols for diverse geological samples, (ii) diffusion models incorporating nanoscale confinement effects, and (iii) isotopic ratio-based frameworks for guiding helium exploration strategies. These integrative approaches offer new insights into the “carrier–pathway–trap” paradigm in helium migration systems and support more effective helium resource assessment.
1. Introduction
Helium (He) is an indispensable strategic resource in the development of the defense and high-tech industries. It can be used as a propellant and as a pressurizing agent in liquid fuel systems for high-end equipment such as spacecraft and supersonic aircraft, ensuring the system’s normal operation. It can also serve as an essential cryogen in MRI diagnostics, enabling respiratory therapies for asthma patients. In addition, helium plays a critical role in the semiconductor manufacturing process and can considerably improve the performance and quality of semiconductor devices. The distribution of global helium resources is extremely uneven, however, and the stability and sustainability of its supply have attracted widespread attention from the international community. Currently, the total amount of helium resources in the world has reached about 51.9 billion cubic meters, mainly distributed in the United States, Qatar, Algeria, Russia, and Canada, which account for 39.7%, 19.5%, 15.8%, 13.1%, and 3.9% of the total resources, respectively. The helium resources in China are in short supply, accounting for only 2% of this total [1,2] (Figure 1).
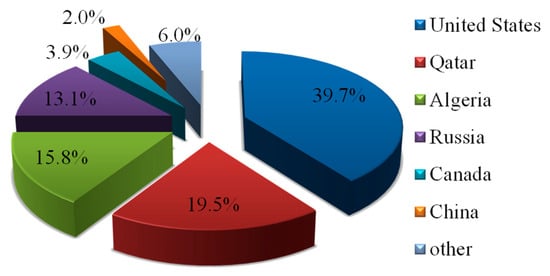
Figure 1.
Distribution of global helium resources (Data sources: USGS (2020) [1] and Danabalan et al. (2018) [2], reflecting reserves reported during 2015–2020).
Helium resource exploitation currently operates under a passive extraction paradigm, predominantly dependent on co-production with natural gas reservoirs, which reveals critical deficiencies in understanding helium-specific accumulation mechanisms [3]. The radiogenic production mechanisms governing helium generation fundamentally differentiate its migration and storage dynamics from conventional hydrocarbon systems [4,5], as helium accumulation requires spatiotemporal coupling of crust–mantle degassing [6], radiogenic production from basement lithologies [5], and structural entrapment via tectonically activated fault networks [4,7]. However, current research paradigms remain anchored in conventional petroleum geology frameworks, lacking a unified theoretical system to explain helium enrichment processes [3]. Three persistent technical limitations impede theoretical advancement: (1) inadequate capabilities in isotopic tracer acquisition for reconstructing helium migration pathways across geological media [4,5], (2) absence of robust parameterization frameworks for multiphase transport simulations integrating radiogenic production and tectonic dynamics [7,8,9], and (3) insufficient mechanistic characterization of helium–mineral interfacial interactions at micro-nanoscale reservoir conditions [10,11]. These constraints force reliance on empirical hydrocarbon analogies for resource prediction, significantly compromising global exploration efficiency [3]. To enable the crucial transition from opportunistic extraction to predictive exploration, future research must prioritize (a) advanced isotopic analysis techniques for high-resolution migration pathway reconstruction across diverse geological media including fluid inclusions, groundwater dissolved gases, and free gases [4,5]; (b) next-generation numerical models coupling radiogenic production rates with fault network evolution and retention efficiency across lithological boundaries [7,8,9]; and (c) nanoscale characterization methods (nanoSIMS) to quantify helium adsorption/desorption kinetics at mineral interfaces [10,11]. These technological advancements, when combined with systematic sampling of geological archives and interdisciplinary approaches integrating atmospheric transport models with subsurface fluid dynamics [12], will establish the mechanistic framework required for developing robust helium prospectivity models and optimizing future exploration strategies.
Helium generation, migration, and enrichment processes in geological bodies are closely related to underground fluids. Crust-derived helium is generated mainly by the decay of radioactive elements, such as uranium and thorium, and underground fluids serve as the migration media to transport the dissolved helium to different geological reservoirs. Helium follows Henry’s law during its migration, may exist in a water-soluble or gas-soluble state, and is controlled by environmental conditions such as the temperature, pressure, and chemical composition of the underground fluids. The detailed helium migration and accumulation process and dynamic mechanism under geological conditions, however, have not yet been constructed. Conventional carbon and hydrogen isotopes, affected by chemical and biological processes, cannot trace this process. Noble gases possess chemical inertness, their geochemical characteristics are associated only with physical processes, such as mixing, dissolution, phase partitioning, and diffusion, and they are not affected by complex biological activities, chemical action, and redox reactions. Therefore, noble gases are considered to be powerful geochemical tracers for tracing the migration and evolution of underground fluids (e.g., underground water, oil, and natural gas) [13,14,15]. Furthermore, the chemical composition and isotopic composition of noble gases in each of the Earth’s reservoirs (atmosphere, crust, and mantle) are significantly different, creating a significant constraint for the study of migration and storage processes of these underground fluids. It is feasible, however, to establish a series of mathematical models to conduct in-depth studies on the interactions between underground fluids and rocks, fluid migration mechanisms, and resource enrichment processes. Therefore, noble gas isotopes can reveal information about underground fluids that other geochemical tracers cannot provide [16,17], serving as an important technical means for investigating the migration, enrichment, and accumulation processes of helium resources.
In advancing beyond existing reviews, this study integrates three critical dimensions to better support helium exploration: (1) the establishment of a range of patent-protected analytical protocols for heterogeneous sample types; (2) incorporation of quantitative diffusion models that consider nanoscale confinement effects in geological media; and (3) the construction of decision-making frameworks that relate isotopic ratios to practical exploration targets. These efforts collectively help address the current gap in understanding the integrated “carrier–pathway–trap” system in helium migration and accumulation processes.
2. Noble Gas Isotope Tracing Theory
The generation and migration of noble gases in geological bodies are complex processes, involving multiple physical mechanisms [16]. In situ noble gases, such as 4He* produced by radioactive decay, can migrate from the location of generation through diffusion (driven by concentration gradients) or by advection related to fluid motion (caused by pressure gradients) [4,5,16]. Considering the time scale and concentration of parent elements, however, the generating rate of noble gases usually is not sufficient to form a continuous fluid that can move independently [18], and therefore, the fluid in the rock pores becomes the necessary “carrier” for the migration of noble gases [16]. These carriers can be produced from the chemical reactions in rocks, such as the hydrocarbons generated from origin rocks [7] or volatile components released from rock metamorphism [19]; they also can come from the external environment of the system, such as an aquifer [20] or magmatic fluid [15]. When fluid is moving in the rock pores, the in situ-generated noble gases migrate along with it. Additionally, during this process, noble gases interact with carrier fluids, including mixing, dissolution or evolution, and fractionation, leading to changes in the abundance and isotope ratios of noble gases [21,22]. These features record changes in the environmental conditions (e.g., properties, temperature, and pressure of the fluids), providing us with important information about fluid origins and migration and enrichment processes of noble gases [4,23]. The noble gases with inactive chemical properties are controlled mainly by physical processes during migration and strictly follow Henry’s law. By measuring Henry’s law constant under different temperature–pressure conditions [24,25,26,27], we can accurately describe the migration and enrichment behaviors of helium and other noble gases during the migration process [28,29,30].
During noble gas migration with underground fluids, the solubility of the noble gas is closely related to environmental conditions, such as temperature and fluid salinity (Figure 2a) [25,26]. The distributions of atmospheric He, Ne, and Ar in fresh water in the temperature range of 0 °C to 25 °C are shown in Figure 2b [24]. After entering the underground, air-saturated water maintains the abundance patterns of noble gases from atmospheric origins. An increase in fluid salinity does not considerably affect the relative solubility of each element in noble gases, but the absolute solubility of each component decreases along with increasing salinity [31]. As shown in Figure 2c, at any given temperature (within the given range of 0 °C to 25 °C), the concentration of dissolved Ar in water decreases significantly with increasing salinity, but the Ne/Ar ratio barely changes. Under geological conditions, if underground water interacts with other phases (such as oil or natural gas), the noble gases dissolved in the underground water will be redistributed among all of the phases [32]. The noble gases retained in the water display a new abundance pattern [33]. The abundance of each component is determined by the degree of interaction between the two phases in equilibrium with water as well as the water temperature and salinity during this period (Figure 2d). Through accurate isotopic analysis, the noble gases from different origins in the most crustal fluid samples can be analyzed to quantify their relative contributions, and restrictions can be imposed on their migration paths and processes.
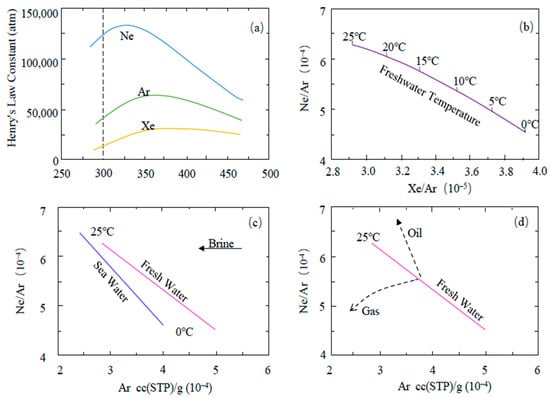
Figure 2.
(a) The relationship between Henry’s law constants of Ne, Ar, and Xe and temperature, (b) the trend of atmospheric Ne/Ar and Xe/Ar ratios dissolved in freshwater with water temperature, and (c) the relationship of the concentrations of Ne and Ar dissolved in seawater and freshwater with temperature and salinity. The increase in salinity will not considerably change the relative solubility of Ne and Ar but will reduce the concentration of noble gases from the atmosphere in the solution. (d) The interaction between groundwater and another phase will cause the noble gases to be redistributed between the two phases; the figure predicts the impact of oil–water and gas–water interaction on the concentrations of dissolved atmospheric Ne/Ar ratio and Ar concentration [24,25,26] (Henry’s law constant; temperature).
3. Techniques to Analyze the Noble Gases in Geological Samples
Large differences in noble gas composition and isotope concentrations exist among geological samples, with variations spanning up to nine orders of magnitude. For example, the concentrations of low-abundance isotopes such as 3He, Kr, and Xe can be at the parts-per-trillion level, making their simultaneous detection alongside more abundant isotopes like 4He and 40Ar a significant analytical challenge. To address this, noble gas mass spectrometers typically employ static vacuum magnetic systems equipped with both Faraday cups (for measuring abundant isotopes such as 4He, 20Ne, and 40Ar) and electron multipliers (for trace isotopes like 3He, Kr, and Xe), enabling full-spectrum analysis with high sensitivity [34,35,36,37].
However, accurate isotope measurement depends not only on instrumentation but also on the efficient extraction and purification of noble gases from complex geological matrices. Various pretreatment systems have been developed for gas, liquid, and solid samples (e.g., Chinese patents ZL201710377791.3; ZL201310634951.X; ZL201420014099.6; ZL201220689176.9), allowing precise isolation of noble gases for downstream analysis. For solid samples—such as quartz, olivine, carbonate, or sulfide minerals—three main extraction techniques are commonly employed: high-temperature heating and melting, laser ablation, and mechanical crushing. Each method has distinct advantages and limitations depending on sample type and analytical objective. The heating and melting method is widely used for single mineral grains (e.g., quartz, olivine, pyroxene), where samples are heated in a double-vacuum resistance furnace until melting occurs, releasing noble gases from both crystal lattices and inclusions. This method is effective for quantifying total gas content but may cause mixing of gases from different domains and thermal decomposition of sensitive minerals. Laser ablation allows precise micro-sampling by focusing high-energy beams on specific regions within solid samples, such as fluid inclusions or mineral zones. It offers high spatial resolution and minimal sample destruction, making it particularly suitable for distinguishing between early trapped atmospheric gases and late-stage radiogenic helium. However, it requires well-characterized mineral targets and is limited in total gas yield. The mechanical crushing method, commonly applied to carbonate rocks (e.g., calcite, dolomite) and sulfide minerals (e.g., pyrite), releases gas from fluid inclusions without subjecting the sample to high temperatures (Figure 3). This approach minimizes contamination from volatile compounds such as CO2 or H2S, preserving the integrity of inclusion-hosted noble gases. However, it is generally less effective for extracting lattice-bound gases and may yield lower amounts of total gas compared to melting.
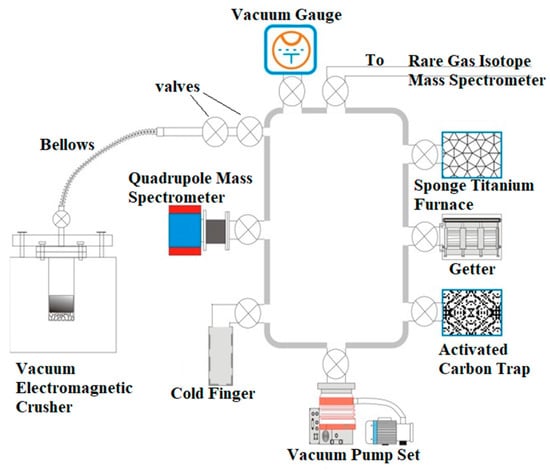
Figure 3.
The system to extract and purify noble gases from solid samples (vacuum gauge; titanium sponge furnace; quadrupole mass spectrometer; Zr–Al pump; vacuum electromagnetic breaker; cold finger; activated carbon trap; vacuum pump group).
Liquid samples, such as formation waters and crude oil, cannot be analyzed directly due to the presence of volatile and aqueous components. Instead, vacuum degassing techniques are used to extract dissolved gases, which are then purified using traps and getters to remove water vapor and organic impurities. Similar to established purification lines employed in laboratories such as the Noble Gas Laboratory in Montreal (GRAM) or the University of Michigan, an online high-vacuum degassing system (e.g., ZL202021311677.4) has been developed to enable efficient noble gas recovery from diverse subsurface fluids.
Gas samples—such as natural gas or hydrothermal gases—typically contain significant amounts of hydrocarbons (e.g., CH4, C2H6), CO2, and H2. These impurities must be removed through multi-stage purification before introduction to mass spectrometry. The efficiency of the purification line is a critical determinant of measurement accuracy.
In all cases, rigorous field sampling protocols are essential to preserve the integrity of noble gas data [20]. For instance, natural gas is collected using stainless steel cylinders equipped with airtight valves to minimize atmospheric contamination. Groundwater samples are extracted from deep wells using copper tubes sealed with stainless steel pinch-off clamps and are degassed immediately under vacuum [18]. Solid geological materials, such as granite and carbonate rocks, are obtained via in situ core drilling and promptly sealed in gas-tight containers to reduce helium loss [16]. These carefully designed procedures, combined with robust analytical techniques, enable accurate tracing of helium sources and migration pathways across diverse geological settings [9,21,28]. Nonetheless, practical challenges remain. Air contamination during sampling or handling and limited reproducibility in ultra-trace isotope measurements—particularly for 3He and Xe—can compromise data quality [18,31]. These limitations highlight the importance of standardized operating protocols, strict quality control, and inter-laboratory calibration to ensure the reliability and comparability of noble gas analyses [12,18,28,31].
4. The Application of Noble Gas Isotope in the Study of Helium Migration and Enrichment Processes
4.1. Gas Origin Indicated by Noble Gas Isotopes
Each noble gas component shows completely different physical properties. Their solubility in water shows a difference of one order of magnitude [14], and at 0 °C, the maximum difference among He, Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe in their diffusion rates is sevenfold [38]. Therefore, noble gases are sensitive to the physical processes during underground transport, and their concentrations and elemental ratios have been widely used as geochemical tracers for underground fluid migration [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. Natural gases normally contain noble gases from the atmosphere, crust, and mantle. These noble gases from different origins possess distinct isotopic compositions (Table 1). Additionally, the relative abundance of each isotope has been clearly defined, and any abnormal changes in their abundance distribution pattern can reflect the physical process of the underground fluids. Through calculation, the relative abundance of the components from each origin in natural gas can be analyzed, and the information on the physical processes of underground fluids can be identified and quantified, providing strong constraints for the study of the fluid origin and migration mechanisms.

Table 1.
Isotopic composition characteristics of noble gases from different sources [14].
For example, in the natural gases from the Pannonian Basin and Vienna Basin, the noble gas isotopes exhibited systematic geochemical characteristics [43]. The 4He/20Ne ratio was 290-32,700, far exceeding the atmospheric value of 0.288. This result suggests that the helium in natural gas is mainly a dual-component mixture of mantle-origin helium and radioactive-origin helium, and the helium contribution from atmospheric origins can be ignored. The helium isotopic ratio was 0.2–0.7 Ra. Through the calculation using the helium-mixing model of crustal radioactive origin (R/Ra = 0.02) and mantle origin (R/Ra = 8.0), it was evident that 2–8% helium was from mantle origin in the natural gas sample. The 21Ne/22Ne and 40Ar/36Ar ratios increased with increasing depth, the 21Ne/22Ne ratio increased to 0.0531 from 0.0290, and the 40Ar/36Ar ratio increased to 2460 from 295.5. Since 22Ne and 36Ar came primarily from the atmosphere [14], and the contributions of Ne and Ar from mantle origins in the sample were very small [43], the increases in the 21Ne/22Ne and 40Ar/36Ar ratios were caused primarily by the increases in the content of isotopes 21Ne and 40Ar. In the shallowest sample, the contributions of isotopic 21Ne and 40Ar were 0% and 6%, respectively, and in the deepest sample, the values were increased to 45% and 88%, respectively.
4.2. The Initial Helium Migration Process
The 3He in the crust is primarily produced by thermal neutrons captured by 6Li:6Li (n,α) 3H (β-)3He, and radiogenic 4He is primarily produced by α decay of 238U, 235U, and 232Th. They can migrate to within about 10–20 microns of the parent element and normally remain in the host mineral where the parent element is present. The concentration of 4He produced by radioactive isotopes of element R in rocks can be calculated using the following equation [16].
where Xr represents the relative abundance of isotope R; NA represents the Avogadro constant (6.023 × 1023); Ar represents the molar mass of R (g); λ represents the decay constant of R (yr−1); yieldr represents the number of α particles emitted in the decay chain; [R] represents the concentration of element R (ppm); and t represents the age (year). According to the average components of the lower, middle, and upper crusts, we calculated the yields of 3He and 4He, which are shown in Table 2.
4He atoms g−1yr−1 = Xr[R](NA/Ar) × 10−6(eλt − 1) × yieldr

Table 2.
Neutron production, lithium capture probability, and 3He and 4He yields in the homogeneous crust [16].
The yield of radiogenic helium was low, and helium atoms after generation primarily existed in the mineral lattice defects and inclusions or were adsorbed on the surface of minerals. The helium accumulation rate was controlled by porosity, local advection or diffusion, formation stress, and tectonic activity [48]. When the concentration gradually increased and the environmental temperature and pressure changed, helium migrated away from the place of origin. The initial migration of helium after generation was dominated by diffusion. The volume diffusion through minerals or along the grain boundaries was slow, and this process was affected by mineral type and temperature. Therefore, the temperature condition for the helium diffusion in each mineral was different. As shown in Table 3, minerals (e.g., apatite, zircon, and ilmenite) retained helium below their closure temperature.
Therefore, a large-scale diffusion of helium atoms needed a release mechanism. Shuster et al. [49] found that although the relative difference between 3He mass and 4He mass was significant, the diffusion rate was extremely similar; therefore, they speculated that helium isotope diffusion did not have the expected mass dependence [49]. In apatite, when the environmental temperature was between 100 °C and 300 °C, helium could obtain an energy of 32.9 ± 1.6 kcal/mol, and the frequency factor (D0) reached 50 cm2/s, thus causing the helium volume diffusion [50]. The release of helium in zircon was relatively complex, and its diffusion characteristics were affected by the grain size and annealing effect. Through potassium feldspar cooling history, the comparison of zircon helium age, and further diffusion experiments [51], however, we inferred that the minimum activation energy (EA) for 4He diffusion in zircon was about 44 kcal/mol. The diffusion of helium in ilmenite follows the linear Arrhenius relationship (D = D0exp (−EA/RT), where D is the diffusion coefficient; D0 is the maximum frequency factor at infinite temperature; EA is the activation energy of diffusion; T is temperature; and R is the gas constant), and the activation energy is about 45 kcal/mol [52,53]. Frick et al. [54,55] predicted the frequency factor D0 and activation energy EA of the Helium in ilmenite [54,55,56] using the 3He injection and release experiments and the Arrhenius equation, as shown in Table 4.

Table 3.
The closure temperatures of common minerals [40,57,58,59,60,61,62,63].
Table 3.
The closure temperatures of common minerals [40,57,58,59,60,61,62,63].
| Apatite | Hematite | Zircon | Garnet | Monazite | Ilmenite | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closure temperature (°C) | 55–100 | 90–250 | 180–200 | 590–630 | 182–299 | 150–200 |

Table 4.
The diffusion rate and activation energy obtained in the experiment of 3He released from ilmenite.
Table 4.
The diffusion rate and activation energy obtained in the experiment of 3He released from ilmenite.
| Temperature Range (°C) | 3He Flux (cm−2) | 4He Flux (cm−2) | Hydrogen Flux (cm−2) | Diffusion Factor D0 (cm2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 130–675 | 1 × 1013 | 1 × 1016 | - | 3 × 10−9 |
| 200–675 | 1 × 1013 | 1 × 1016 | 1 × 1017 | 9 × 10−9 |
| 675–750 | 1 × 1013 | 1 × 1016 | 1 × 1017 | 4 × 10−5 |
Furthermore, researchers observed a linear relationship of the He diffusion coefficient between temperature and pore size:
where ζmb is the correction factor for porous media geometry; δ represents the ratio of the gas molecule diameter, d, and the local average pore diameter, 2r; Df is the fractal dimension of the pore wall; M represents molecular mass; R represents the gas constant; and T represents temperature. Based on this relationship, researchers simulated the relationship between the diffusion coefficient and temperature, as shown in Figure 4a. Temperature had a significant impact on the helium diffusion in large pores (1000 nm). Under the same temperature, the diffusion coefficient of large pores (1000 nm) was one order of magnitude greater than that of small pores (10 nm). For small pores, the temperature impact on the diffusion coefficient was not obvious. The pore size of the space where helium occurs was also important in helium diffusion, as shown in Figure 4b. The diffusion coefficient dramatically increased with pore size in the range of small pores and stably increased in the range of large pores. Additionally, under the same pore size, the effect of temperature on the diffusion coefficient was more significant in the low-temperature range, and its effect decreased with increasing temperature. Furthermore, researchers found that the diffusion coefficient of the highest temperature was about five times greater than that of the lowest temperature [64].
Dk = (2/3) ζmbrδDf−2(8RT/πM)0.5
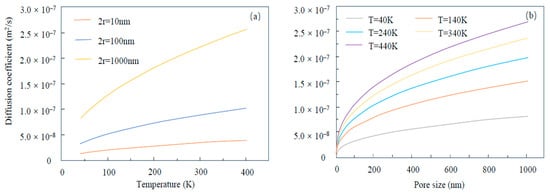
Figure 4.
The relationship of the diffusion coefficient of He with (a) temperature and (b) pore size.
4.3. The Secondary Helium Migration and Enrichment Processes
The migration and enrichment process of secondary helium is a complex geological process controlled by multiple stages and factors. Its complexity manifests in the dynamic coupling across spatial and temporal scales of various elements, including the decay rate of radioactive elements in source rocks; the connectivity and permeability of migration pathways (pores, fractures, faults); the effectiveness of trap structures and the sealing capacity of caprocks; as well as hydrodynamic conditions. (Figure 5). The crust-derived helium came primarily from the radioactive decay of U and Th, and its generation rate was stable and slow and did not exhibit a gas-producing peak. A long geological period was needed to accumulate a significant amount of helium, and therefore, helium was considered to be a “weak source gas”. Usually, media, such as underground water and natural gas, are needed to conduct helium migration and enrichment to form a commercially valuable helium-rich gas reservoir [23,65,66]. The helium accumulated on the surface and inside of the mineral needed sufficient temperature and pressure conditions to be released. For example, when the surface temperature was 10 °C and the geothermal gradient was 30 °C/km, the location of the minerals, such as zircon, apatite, and ilmenite, had to be deeper than 2 km to allow helium to obtain enough energy to diffuse out of these generating minerals. The depth of most helium-rich reservoirs was smaller than 2 km [6,9], however, and the helium content in shallow aquifer systems and oil and gas reservoirs was usually much higher than the value calculated by the steady-state helium flux equation
where D, l, and t are diffusion rate, crust depth, and time, respectively [40,67]. This finding indicates that it was difficult for He to form the high helium content in the shallow reservoir by volume diffusion. Therefore, the formation of a helium-rich gas reservoir needed not only a helium-release mechanism but also an effective migration and enrichment mechanism [65,68].
F/G = l − 8/π − 2 f (Dt/l2)
After being released from the source rock, helium alone cannot form a continuous fluid because of its low content, and it needs media to migrate, such as underground water, natural gas, and oil. The helium diffusing out of primary minerals can be dissolved in the gas phase (natural gas) and liquid phase (water, oil), or can be deposited in the solid phase (minerals with radioactive elements, surface adsorption, hydrates). In a system without advective fluid flow, transport occurs through overall diffusion, whereas overall diffusion is controlled by environmental temperature, pressure, and space fluid properties (Table 5).

Table 5.
Solubility coefficients of gas–water, heavy oil–gas (API 25), and light oil–gas (API 34) when atmospheric pressure is 1 bar and temperature is between 10 °C and 170 °C (in mol/m3)/(mol/m3) [26,31,69,70].
Table 5.
Solubility coefficients of gas–water, heavy oil–gas (API 25), and light oil–gas (API 34) when atmospheric pressure is 1 bar and temperature is between 10 °C and 170 °C (in mol/m3)/(mol/m3) [26,31,69,70].
| Solubility Water/Gas | Solubility Heavy Oil/Gas | Solubility Light Oil/Gas | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mol/m3)/(mol/m3) 1 bar | (mol/m3)/(mol/m3) 1 bar | (mol/m3)/(mol/m3) 1 bar | |||||||||||||
| T (°C) | He | Ne | Ar | Kr | Xe | He | Ne | Ar | Kr | Xe | He | Ne | Ar | Kr | Xe |
| 10 | 0.0089 | 0.0111 | 0.0407 | 0.0795 | 0.1515 | 0.0128 | 0.0111 | 0.154 | 0.477 | 1.491 | 0.0192 | 0.0236 | 0.163 | 0.504 | 2.256 |
| 50 | 0.0090 | 0.0096 | 0.0236 | 0.0388 | 0.0603 | 0.0211 | 0.0198 | 0.158 | 0.400 | 1.080 | 0.0269 | 0.0317 | 0.149 | 0.443 | 1.397 |
| 110 | 0.0125 | 0.0111 | 0.0199 | 0.0281 | 0.0394 | 0.0445 | 0.0474 | 0.165 | 0.308 | 0.666 | 0.0449 | 0.0494 | 0.130 | 0.365 | 0.681 |
| 170 | 0.0209 | 0.0163 | 0.0253 | 0.0326 | 0.0465 | 0.0939 | 0.1131 | 0.172 | 0.237 | 0.411 | 0.0749 | 0.0768 | 0.113 | 0.301 | 0.332 |
Note: Solubility can be expressed as Henry’s pressure or solubility coefficient. Henry pressure (expressed in bar) indicates that a gas (or its partial pressure) must reach a necessary pressure to achieve uniform concentration in water. For a given thermodynamic equilibrium, solubility represents the concentration ratio between the aqueous phase and the gas phase. In Table 5, solubility is expressed in mol/m3/mol/m3. According to the ideal gas law, the solubility coefficient does not change with absolute pressure, and in the case of nonideal solutions, a correction term must be added.
When fluids move in the pores, these fluids will remove or carry some of the noble gases away from the releasing site. These carrier fluids may be produced by chemical changes (e.g., formation and deterioration or volatilization of hydrocarbons) inside rock formations, and they also may come from the outside system (e.g., aquifer or magma). In the former situation, crust-derived gases provide information about the fluid origin; in the latter situation, the information about the systems they pass is provided [16]. Helium diffusing from primary minerals may exist in the gas phase (atmosphere, natural gas), liquid phase (water, oil), or solid phase (minerals with radioactive elements, surface adsorption, hydrates). The abundance patterns of noble gases in underground fluids of different origins are significantly different and are extremely sensitive to physical processes. During the underground migration and accumulation process of noble gases, fractionation occurs in two types of phase states: gas–liquid phase and liquid–liquid phase, and fractionation follows Henry’s law (Pg = Hx, where H is Henry’s law constant; x is the mole fraction solubility of the gas; and Pg is the partial pressure of the gas). According to the He, Ne, and Ar isotope abundances and ratios, the geochemical evolution and basin fluid dynamics of fluids with different phases during the migration and enrichment stage can be revealed, and the degree of the interaction of oil and gas samples with underground water and rocks during the migration process can be quantified. In particular, by calculating the gas-to-water volume ratio (Vg/Vw) and the volume of rock required for radioisotopes, the degree of localization and migration distance of oil and gas migration paths can be inferred [71].
Under the gas–liquid mixed phase situation, the volume of gas equilibrating with underground water and the volume of gas equilibrating with the gas phase can be calculated using the following equation:
where is the number of moles of component in the gas phase; is the total moles of component ; is the density of the liquid phase (g/cm3); is the volume of the liquid phase (cm3); is the temperature; is Henry’s law constant (molar concentration form); and are the gas-phase fugacity coefficient and liquid-phase activity coefficient, respectively; and is the volume of the gas phase (cm3).
Similarly, under the liquid–liquid (oil and water) mixing phase, measuring the noble gas concentration in the water of the oil phase can quantify the oil-to-water volume ratio in the system using the following equation:
where is the number of moles of component i in the oil phase; is the total moles of component ; and are the densities of water and oil, respectively (g/cm3); and are the volumes of water and oil, respectively (cm3); and and are Henry’s law constants (molar concentration form) of component in water (1 kg) and oil (1 kg), respectively.
Samples that have undergone long-distance migration typically exhibit low Vg/Vw ratios, indicating continuous mixing with external formation water during transport [65]. Elevated levels of radiogenic 40Ar* suggest extensive fluid–rock interaction and longer migration distances [16,24]. In the subsurface, noble gas transport occurs primarily through diffusion and advection. Diffusion dominates in low-permeability formations such as shale or crystalline basement [10,61], while advection is more prominent in faulted and fractured zones where fluids migrate rapidly under pressure gradients [9,28]. Fault systems connected to deep thermal or mantle sources often serve as vertical conduits for helium-rich fluids. Field studies from the Pannonian and Sichuan Basins reveal that noble gas signatures vary with proximity to major faults [6,36], reflecting dynamic flow conditions [37,43]. Transport is also affected by adsorption–desorption along mineral surfaces [11,64] and the presence of multiphase carriers (e.g., water, oil, gas) [7,30]. Previous research has demonstrated that noble gas isotopic variations in both unconventional source rocks and conventional reservoirs are closely linked to migration distance [21], providing a valuable geochemical tool for reconstructing helium transport and accumulation processes in sedimentary basins [24,29].
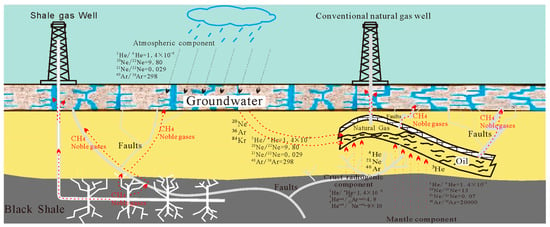
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of helium migration and enrichment process under geological conditions (Modified from Halford, 2018) [72,73,74].
5. Research and Development Trends
Helium stands as a strategic resource of global significance, yet the lack of mature reservoir formation theories continues to hinder its exploration and development. Recent advancements in noble gas isotopic analytical techniques have opened new avenues to address this challenge. Current methodologies now enable precise measurement of helium isotopes across diverse geological matrices—including solid, liquid, and gaseous samples—providing unprecedented insights into helium’s geochemical lifecycle encompassing generation mechanisms, migration dynamics, and enrichment patterns. To advance this critical field, future research must prioritize three interconnected objectives: First, the enhancement of analytical precision through technological innovation, particularly the optimization of mass spectrometer resolution and the development of advanced sample pretreatment systems to maximize detection efficiency; second, the establishment of robust standardization protocols, requiring both the development of standardized reference materials for noble gas isotopes and the implementation of intelligent data processing algorithms to ensure analytical reproducibility and cross-study comparability; third, the creation of interdisciplinary quantitative models that integrate structural evolution, rock–fluid interactions, and hydrodynamic parameters to simulate helium behavior under varying geological conditions. These computational frameworks must reconcile geochemical signatures with geophysical constraints to predict migration pathways, identify accumulation “sweet spots,” and ultimately formulate predictive models for helium reservoir distribution. The convergence of these technical and theoretical advancements promises to revolutionize helium exploration paradigms, transforming current empirical approaches into precision-driven resource assessment methodologies. By bridging the gap between isotopic geochemistry and reservoir engineering, this integrated approach will not only elucidate fundamental helium migration mechanisms but also establish predictive exploration criteria for identifying commercially viable deposits. Such progress carries profound implications for securing global helium supplies amid increasing industrial demand and geopolitical uncertainties surrounding this non-renewable strategic resource.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C. and L.L.; methodology, C.C.; validation, C.C., L.L. and Z.L.; investigation, C.C.; data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C.; writing—review and editing, C.C. and L.L.; project administration, C.C.; funding acquisition, C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42272185, and the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2021YFA0719003.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Peterson, J.B. Mineral Commodity Summaries-Helium; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020.
- Danabalan, D.; Gluyas, J.G.; Ballentine, C.J. Encyclopedia of Petroleum Geoscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.J.; Li, J.Y. A review of helium resources and development. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2025, 12, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballentine, C.J.; Burgess, R.; Marty, B. Tracing Fluid Origin, Transport and Interaction in the Crust. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 539–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, B.S.; Walsh, T.B.; Darrah, T.H. Using radiogenic noble gases to trace the conditions of crustal fluid migration. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 17, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.A.; Crosby, J.C.; Day, J.A.F.; Stuart, F.M.; DiNicola, L.; Riley, T.R. Systematic behaviour of 3He/4He in Earth’s continental mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 384, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, P.H.; Lawson, M.; Meurer, W.P.; Cheng, A.; Ballentine, C.J. Noble Gases in Deepwater Oils of the U.S. Gulf of Mexico. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2018, 19, 4218–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, S.A. Geology and Production of Helium and Associated Gases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Karolyte, R.; Warr, O.; Heerden, E.V.; Flude, S.; Lange, F.D.; Webb, S.; Ballentine, C.J.; Lollar, B.S. The role of porosity in H2/He production ratios in fracture fluids from the Witwatersrand Basin, South Africa. Chem. Geol. 2022, 595, 120788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Chen, J.F.; Liu, X.Q.; Xiao, H.; Li, M.J.; Peng, T. Adsorption behavior of helium in quartz slit by molecular simulation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Xue, Z.Y.; Yue, F.; Wen, J.J.; Li, M.J.; Xue, Y. Correction of gas adsorption capacity in quartz nanoslit and its application in recovering shale gas resources by CO2 injection: A molecular simulation. Energy 2022, 240, 122789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halford, D.T.; Karolytė, R.; Dellenbach, J.T.; Cathey, B.; Cathey, M.; Balentine, D.; Andreason, M.W.; Rice, G.K. Applications in utilizing soil gas geochemistry along with geological and geophysical data to construct helium exploration statistical models. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1434785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, D.; Ballentine, C.J. Models for distribution of terrestrial noble gases and evolution of the atmosphere. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 411–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozima, M.; Podosek, F.A. Noble Gas Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Burnard, P.; Zimmermann, L.; Sano, Y. The Noble Gases as Geochemical Tracers: History and Background. In The Noble Gases as Geochemical Tracers. Advances in Isotope Geochemistry; Burnard, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ballentine, C.J.; Burnard, P.G. Production, Release and Transport of Noble Gases in the Continental Crust. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 481–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, G.; Gilfillan, S. Application of Noble Gases to the Viability of CO2 Storage. In The Noble Gases as Geochemical Tracers. Advances in Isotope Geochemistry; Burnard, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.N. The isotopic composition of radiogenic helium and its use to study groundwater movement in confined aquifers. Chem. Geol. 1985, 49, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, D.R.; Fischer, T.P.; Marty, B. Noble Gases and Volatile Recycling at Subduction Zones. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 319–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipfer, R.; Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Peeters, F.; Stute, M. Noble Gases in Lakes and Ground Waters. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 615–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ballentine, C.; Kipfer, R.; Schoell, M.; Thibodeaux, S. Noble gas tracing of groundwater/coalbed methane interaction in the San Juan Basin, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 5413–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poreda, R.J.; Farley, K.A. Rare gases in Samoan xenoliths. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 113, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.F.; Dong, S.Y.; Fan, Y.H.; Dong, B.; Zheng, F.; Wang, Y.C.; Song, R.C. The origin and migration mechanism of natural gas in the Yacheng Gas Field, Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: Constraints from noble gas isotopes. Ore Energy Resour. Geol. 2025, 18, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballentine, C.J.; O’Nions, R.K. The use of natural He, Ne and Ar isotopes to study hydrocarbon-related fluid provenance, migration and mass balance in sedimentary basins. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1994, 78, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovetto, R.; Fernández-Prini, R.; Japas, M.L. Solubilities of inert gases and methane in H2O and in D2O in the temperature range of 300 to 600 K. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 76, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. Noble gas solubility in water at high temperature. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1985, 66, 397. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Prini, R.; Alvarez, J.L.; Harvey, A.H. Henry’s constants and vapor-liquid distribution constants for gaseous solutes in H2O and D2O at high temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2003, 32, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danabalan, D.; Gluyas, J.G.; Macpherson, C.G.; Abraham-James, T.H.; Bluett, J.J.; Barry, P.H.; Ballentine, C.J. The principles of helium exploration. Pet. Geosci. 2022, 28, petgeo2021-029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Nions, R.K.; Ballentine, C.J. Rare gas studies of basin scale fluid movement. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1993, 344, 141–156. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, H.; Khac, H.H.; Anne, B.; James, A.S.; Julien, C.; Magali, P.; Guillaume, G. Modeling Solubility Induced Elemental Fractionation of Noble Gases in Oils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 388, 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.P.; Kennedy, B.M. The solubility of noble gases in water and in NaCl brine. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 47, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.; Mazor, E. Natural gas association with water and oil as depicted by atmospheric noble gases: Case studies from the southeastern Mediterranean Coastal Plain. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1988, 87, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaikowski, A.; Spangler, R.R. Noble gas and methane partitioning from ground water: An aid to natural gas exploration and reservoir evaluation. Geology 1990, 18, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.H.; Zhang, M.J.; Li, L.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, Z.P.; Du, L.; Holland, G.; Zhou, Z. Tracing the sources and evolution processes of shale gas by coupling stable (C, H) and noble gas isotopic compositions Cases from Weiyuan and Changning in Sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 78, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Liu, W.; Guan, L.F.; Takahata, N.; Sano, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.C.; Chen, Z.; Cao, C.H.; Zhang, L.H.; et al. First Estimates of Hydrothermal Helium Fluxes in Continental Collision Settings: Insights from the Southeast Tibetan Plateau Margin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Guo, Z.F.; Xu, S.; Barry, P.H.; Sano, Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Halldórsson, S.A.; Chen, A.T.; Cheng, Z.H.; Liu, C.Q.; et al. Linking deeply-sourced volatile emissions to plateau growth dynamics in southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.H.; Zhang, M.J.; Tang, Q.Y.; Yang, Y.; Lv, Z.G.; Zhang, T.W.; Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Li, L.W. Noble gas isotopic variations and geological implication of Longmaxi shale gas in Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 89, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.H.; Zhao, F.H.; Han, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Greg, H.; Zhou, Z. Using noble gases to trace groundwater evolution and assess helium accumulation in Weihe Basin, central China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 251, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähne, B.; Heinz, G.; Dietrich, W. Measurement of the diffusion coefficients of sparingly soluble gases in water. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 1987, 92, 10767–10776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T.; Clarke, W.B. Helium accumulation in groundwater, I: An evaluation of sources and the continental flux of crustal 4He in the Great Artesian Basin, Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T. Terrestrial helium degassing fluxes and the atmospheric helium budget: Implications with respect to the degassing processes of continental crust. Chem. Geol. Isot. Geosci. Sect. 1989, 79, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, D.L.; Marty, B. Noble gases in crude oils from the Paris Basin, France: Implications for the origin of fluids and constraints on oil-water-gas interactions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 3389–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballentine, C.J.; O’Nions, R.K.; Oxburgh, E.R.; Horvath, F.; Deak, J. Rare gas constraints on hydrocarbon accumulation, crustal degassing and groundwater flow in the Pannonian Basin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1991, 105, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, J.; Stute, M.; Torgersen, T.; Moser, D.P.; Hall, J.A.; Lin, L.; Borcsik, M.; Bellamy, R.E.S.; Onstott, T.C. Dating ultra-deep mine waters with noble gases and 36Cl, Witwatersrand Basin, South Africa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4597–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.C.; Goblet, P.; Ledoux, E.; Violette, S.; Marsily, G.D. Noble gases as natural tracers of water circulation in the Paris Basin: 2. Calibration of a groundwater flow model using noble gas isotope data. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2467–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.C.; Jambon, A.; Marsily, G.D.; Schlosser, P. Noble gases as natural tracers of water circulation in the Paris Basin: 1. Measurements and discussion of their origin and mechanisms of vertical transport in the basin. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2443–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.C.; Patriarche, D.; Goblet, P. 2-D numerical simulations of groundwater flow, heat transfer and 4He transport-Implications for the He terrestrial budget and the mantle helium-heat imbalance. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 237, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T.; Ivey, G.N. Helium accumulation in groundwater. II: A model for the accumulation of the crustal 4He degassing flux. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, D.L.; Farley, K.A. 4He/3He thermochronometry. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 217, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, K.A. Helium diffusion from apatite: General behavior as illustrated by Durango fluorapatite. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 2903–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiners, P.W.; Farley, K.A.; Hickes, H.J. He diffusion and (U-Th)/He thermochronometry of zircon: Initial results from Fish Canyon Tuff and Gold Butte, Nevada. Tectonophysics 2002, 349, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiners, P.W.; Farley, K.A. Helium diffusion and (U-Th)/He thermochronometry of titanite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3845–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockli, D.A.; Farley, K.A. Empirical constraints on the titanite (U-Th)/He partial retention zone from the KTB drill hole. Chem. Geol. 2004, 207, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, U.; Becker, R.H.; Pepin, R.O. Solar wind record in the lunar regolith-Nitrogen and noble gases. In Proceedings of the 18th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 14–18 March 1988; pp. 87–120. [Google Scholar]
- Frick, U.; Pepin, R.O. Microanalysis of nitrogen isotope abundances: Association of nitrogen with noble gas carriers in Allende. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1981, 56, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nier, A.O.; Schlutter, D.J. Extraction of helium from individual IDPs and lunar grains by pulse heating. Meteoritics 1992, 27, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippolt, H.J.; Leitz, M.; Wernicke, R.S.; Hagedorn, B. (Uranium+thorium)/helium dating of apatite: Experience with samples from different geochemical environments. Chem. Geol. 1994, 112, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.A.; Farley, K.A.; Silver, L.T. Helium diffusion and low-temperature thermochronometry of apatite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bähr, R.; Lippolt, H.J.; Wernicke, R.S. Temperature-induced 4He degassing of specularite and botryoidal hematite: A 4He retentivity study. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 17695–17707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniak, D.J.; Watson, E.B.; Thomas, J.B. Diffusion of helium in zircon and apatite. Chem. Geol. 2009, 268, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunai, T.J.; Roselieb, K. Sorption and diffusion of helium in garnet: Implications for volatile tracing and dating. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 139, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, J.W.; Hodges, K.V.; Olszewski, W.J.; Jercinovic, M.J. He diffusion in monazite: Implications for (U-Th)/He thermochronometry. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2005, 6, Q12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, D.J.; O’Nions, R.K.; Hilton, D.R.; Oxburgh, E.R. The role of element distribution in production and release of radiogenic helium: The Carnmenellis Granite, southwest England. Chem. Geol. 1990, 88, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Wu, K.L.; Chen, Z.X.; Yu, X.R.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Hui, G.; Yang, M. Gas storage and transport in porous media: From shale gas to helium-3. Planet Space Sci. 2021, 204, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, F.H.; Han, W.; Chen, G.C. Henry’s law and accumulation of weak source for crust-derived helium: A case study of Weihe Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2017, 2, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danabalan, D. Helium: Exploration Methodology for a Strategic Resource. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mtilia, K.M.; Byrne, D.J.; Tyne, R.L.; Kazimoto, E.O.; Kimani, C.N.; Kasanzu, C.H.; Hillegonds, D.J.; Ballentine, C.J.; Barry, P.H. The origin of high helium concentrations in the gas fields of southwestern Tanzania. Chem. Geol. 2021, 585, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahata, N.; Sano, Y. Helium flux from a sedimentary basin. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2000, 52, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.H. Applications of Near-Critical Dilute-Solution Thermodynamics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 3080–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharaka, Y.K.; Specht, D.J. The solubility of noble gases in crude oil at 25–100 °C. Appl. Geochem. 1988, 3, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, D.J.; Barry, P.H.; Lawson, M.; Ballentine, C.J. The use of noble gas isotopes to constrain subsurface fluid flow and hydrocarbon migration in the East Texas Basin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 268, 186–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.H.; Li, L.W.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.H.; He, J. The Use of Noble Gas Isotopes in Detecting Methane Contamination of Groundwater in Shale Gas Development Areas: An Overview of Technology and Methods. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halford, D.T. Isotopic Analyses of Helium from Wells Located in the Four Corners Area, Southwestern, USA. Master’s Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Darrah, T.H.; Vengosh, A.; Jackson, R.B.; Warner, N.R.; Poreda, R.J. Noble gases identify the mechanisms of fugitive gas contamination in drinking-water wells overlying the Marcellus and Barnett Shales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14076–14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).