Abstract
International oil price forecasting is a complex and important issue in the research area of energy economy. In this paper, a new model based on web-based sentiment analysis is proposed. For the oil market, sentiment analysis is used to extract key information from web texts from the four perspectives of: compound, negative, neutral, and positive sentiment. These are constructed as feature and input into oil price forecasting models with oil price itself. Finally, we analyze the effect in various views and get some interesting discoveries. The results show that the root mean squared error can be reduced by about 0.2 and the error variance by 0.2, which means that the accuracy and stability are thereby improved. Furthermore, we find that different types of sentiments can all improve performance but by similar amounts. Last but not least, text with strong intensity can better support oil price forecasting than weaker text, for which the root mean squared error can be reduced by up to 0.5, and the number of the bad cases is reduced by 20%, indicating that text with strong intensity can correct the original oil price forecast. We believe that our research will play a strong supporting role in future research on using web information for oil price forecasting.
1. Introduction
As a strategic energy source, price fluctuations will have an important impact on economic growth, bond markets, and national security, so the prediction of oil prices has been receiving much attention [1,2]. However, oil prices are not only affected by the fundamental factors of supply and demand, but also by non-fundamental factors such as geopolitics, big country games and market speculation. Research has shown that oil price fluctuations are non-linear and chaotic [3,4], which bring significant challenges to those seeking to forecast oil prices.
Considering the availability of market data and the rapid development of intelligent algorithms, previous studies on oil price forecasting mainly focused on the field of quantitative analysis [5]. Among them, econometric theory is favored by researchers because of its relatively complete theoretical system and rigorous theoretical methods [6]. Hong et al. considered six factors that influence the forecast of crude oil prices (supply, demand, financial market, commodity market, speculation, and geopolitics), using LASSO regression to find that the prediction of eight forward steps can significantly reduce the mean square prediction error [7]; Zhao et al. proposed the concept of vector trend, using a variety of nonlinear functions to numerically fit oil prices, and estimating future trends from historical oil price trends. The results show that the percentage error caused by fitting different oil functions to the actual oil price does not exceed 4% [8]; Naser used dynamic model averaging (DMA) to test the 28-day monthly data set of WTI crude oil prices. The results showed that the DMA method could predict the spot price trend better than the futures price [9].
In addition, the rapid development of machine learning models has brought new development booms in the field of price forecasting. Gabralla et al. mainly used more abundant feature engineering, combined with SVM, Instance Base Learning, and the K* algorithm, to predict oil prices, and the results indicate that the error index of RMSE can be reduced by about 15% under the combination of various methods [10]. Wang et al. combined multi-layer perceptron, Elman neural network, and stochastic event effective functions for predicting fluctuation in crude oil prices, and the results show that the proposed hybrid model has an improvement of about 13% on the MAPE and RMSE indicators than the benchmark models such as BPNN and Elman [11]. Yu et al. proposed a new decomposition-set learning paradigm for integrated empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and extended the extreme learning machine (EELM) method to oil price prediction. The empirical results suggest that accuracy and effectiveness (time saving and robustness) were improved [12]. It can be found that researchers have made various attempts on models and features in the field of oil price forecasting, and made great breakthroughs. However, most studies rely heavily on the release of official macroeconomic statistics, which are collected, analyzed and aggregated by regulators, usually issued on a regular basis, and there are problems that are not sensitive to real-time economic issues [13].
With the rapid development of the Internet and big data technologies, the potential information embedded in unstructured big data provides a novel data source for price forecasting [14,15,16]. Recently, many web-based text mining studies have made significant contributions to market price forecasts. Fung et al. label ‘up’ and ‘down’ of stock-related news, and combined with the support vector machine model to generate the actual trading strategy. through real scenario simulation found that the method can really gain [17]; Liu et al. extracted the indicator system from the stock company’s Twitter to analyze its relationship with stock returns, and the results show that Twitter indicators and stock prices are better linked than traditional industrial indicators [18]; Fortuny et al. defined the number of abnormal network news before the release of the macroeconomic report as information density, and found that there is a close correlation between information density and stock price volatility [19]; Yao et al. used the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method to combine the Google search index to characterize oil market investor attention, and based on the Structural Vector Autoregression (SVAR) model, the results show investor attention has a significant negative impact on crude oil prices [20]; Wang et al. constructed an Internet concern index by analyzing the correlation between Google search trends and oil prices, and predicts oil prices by combining Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) methods, which improves the accuracy of forecasting [21].
Aside from the simple extraction of “quantity” in news, considering the emotional tendency of online texts will often lead to investor sentiment fluctuations, which will bring changes in the entire price market. Some studies focus on sentiment analysis and topic recognition of web texts, and mining deeper information to aid forecasting [22,23]. Nguyen used the Joint Theme-Emotion Model (JST) to give emotional comments on social media investors’ opinions to sentiment tags: Strong Buy, Buy, Hold, Strong Sell, Sell, and finally, to consider the prediction accuracy of 18 stocks in a year’s trading. The performance of the emotional factor model increased by 2.07% compared to the model using historical price alone [24]. Tetlock measured the interactions between the media and the stock market quantitatively using daily content from a popular Wall Street Journal column, and the result shows that media pessimism has predictive power for stock market prices [25]. Ho et al. extracted emotional information from on-line news and put it into the Fractionally Integrated Generalized Autoregressive Conditionally Heteroskedastic (FIGARCH) and Regime-Switching GARCH models to analyze the dynamic relationship between emotion and stock return rate, and the conclusion shows that news emotion can better reduce yield volatility [26]. Li et al. used Granger causality to analyze the relationship between news texts and investor sentiment information extracted from the text and oil prices, and used a support vector machine to predict the sentiment in oil prices, and analyzed the relationship between oil prices to forecast oil prices [27]. Yu et al. applied text mining to the prediction of oil prices, and a crude oil price sentiment prediction model based on fuzzy rough set text mining was proposed [28]. Wex et al. distributed news into topics such as OPEC, CRUDE OIL, JET, and NSEA, extracted quantitative indicators for different topics, and used linear regression to test their ability to predict WTI oil price returns. The results show that the effect is statistically significant [29]. Li et al. used the LDA topic model and the CNN neural network model to mine and extract news text sentiment features and online news topics. The results show that the topic-sense comprehensive predictive model performs better than the old benchmark model [30].
So far, there has been limited research on the application of sentiment analysis and topic recognition in online texts to oil price forecasting, and there are only some early attempts by some people [30]. The relevant analysis and research mainly focus on trend forecasting and not value forecasting. At the same time, only linear models are used: non-linear models should be taken into consideration and therefore, the application of web information in oil price forecasting deserves further study. Based on the above analysis, we propose a new hybrid oil price prediction model based on text mining. We introduce text sentiment obtained from web information through text mining into oil price forecasting and explore a better way to use network information. First, we explore the relationship between web information and oil prices, and test the performance improvement effect of introducing text sentiment into oil price forecasting. Then, we investigate the differences between types of text sentiment in their impact on oil price forecasting so that information can be used selectively. Finally, we reveal how big data information improves oil price forecasting performance, and provide a modelling basis and suggestions for the subsequent use of potentially valuable web information to improve oil price forecasting performance.
2. Materials and Methods
The model we proposed is mainly divided into two branches to process text and oil price data, respectively, and then merge them using a feature method, by using common oil price prediction model to achieve the result. On the one hand, for text processing, after collecting web text related to international oil prices, the web text is cleaned via a series of strategies, including abnormal vocabulary deletion, stop word deletion, root extraction, and vocabulary normalization. Then, text sentiment analysis is processed and the text sentiment can be obtained. On the other hand, for oil price processing, the oil price forecasting model is selected after pre-processing the oil price, and a better prediction model can be selected for subsequent prediction. After that, the oil price forecasting model is combined with oil price text information, and finally its performance is evaluated.
2.1. Web Text Pre-Processing
In the text pre-processing stage, the goal is to improve the quality of the text data, so that in the oil price web text analysis stage we can extract a clearer article tendency.
Firstly, we filter the abnormal text: the use of erroneous data will have an adverse effect on the model and this is also true of text analysis. During data crawling, some data will be unavailable due to expiration, insufficient permissions, and lost URLs. Some pages, according to our data exploration, may be invalid, whose contents with errors may be stored in the database, so we have to identify and filter “Error code: 500”, “Page not found” messages, and so on.
Secondly, we remove abnormal words: abnormal words are more common than abnormal new text, and are abundant in some normal news texts. They fail to provide an improved performance for the model and on the contrary, they will have a negative effect thereon. On the one hand, it comes from Web development languages, such as “HTML”; on the other, abnormal characters arise from web-pages themselves. The reasons for their occurrence are unclear but they often appear, such as “&ldqu” and the former type can be removed by certain development tools, but the latter cannot. To solve this problem, we remove 171 abnormal words according to the regulations governing abnormal characters for batch elimination.
Next, we remove stop words: these are words that have no tendency but influence tendency analysis when the subsequent tendency model is established. They are mainly reflected in lowering the actual tendency, so they need to be eliminated. Stopping words are mainly articles, some pronouns, and adverbs in the text [15,16,17].
Last but not least, any numbers need to be processed: although a number can reflect some numerical changes to a certain extent, it is generally believed that the number itself has no meaning, but it acts through the interpretation of the context, so the number also needs to be cleared [16].
2.2. Web Text Sentiment
We used a VADER method to analyze and predict the tendency of web text [31] VADER is a rule-based unsupervised method. It was primarily based on social web data when it was initially established. It has strong portability and has been applied in many fields owing to the standardization of rule-based mechanisms. At present, VADER has been adopted by a large number of research institutes and has strong reliability [32,33,34]. Its main advantages are: it is accurate and economical, which are the most basic requirements of an emotional analysis model; secondly, there is a perfect public dictionary, it is easy to explain, which makes the calculated text tendency more realistic; thirdly, based on rules, VADER is both self-contained and heuristic, with strong portability, and without supervision, it can avoid the huge cost of tagging data. In the financial markets, VADER is also applied to investor sentiment analysis. Through VADER, it is easy to forecast asset income trends and detect judge investors’ bullish sentiment towards a company or brand [35]. Research shows that VADER has strong reliability. Considering the similarity between oil markets and ordinary financial markets, and the portability of VADER itself, we chose the VADER method for text sentiment analysis. Then, the oil market text sentiment should be defined as Table 1 [31].

Table 1.
Parameter settings of VADER.
The text sentiment is required through use of the Algorithm 1, VADER as follows.
| Algorithm 1. VADER sentiment algorithms. | |
| Input: Text to be analysed, tendency rules, emotional dictionary. | |
| Output: , , , and | |
| Step 1. Calculate the emphasised weights in the sentence according to the tendency rule. | |
| Step 2. Calculate using the formula below for using Equation (1). | |
| (1) | |
| where indicates an article, indicates vocabulary, indicates vocabulary score, is a symbol function, emphasises weight, and dictionary information is used to measure vocabulary with emphasis in the article. For example, “very” and “extremely” can enlarge the value of . is a normalisation function, which is mapped onto to a real number on . | |
| Step 3. Calculate the sum scores including , , and by using Equation (2). | |
| (2) | |
| Step 4. Include the emphasis weight to get the modified sum score including , , and by using Equation (3). | |
| (3) | |
| Step 5. Calculate the total score, , using Equation (4). | |
| (4) | |
| Step 6. Calculate the final score based on the total score using Equation (5). | |
| (5) | |
To combine the text sentiment with the subsequent oil price forecasting, it is necessary to define the sentiments, which are shown in Table 2, from the time level to represent the overall sentiment of the web text per unit time.

Table 2.
Parameter settings of web text sentiment.
In order to calculate the lag order, capital form is used to represent the lag characteristic form, as shown in Equation (6).
2.3. Oil price Forecasting Model
At present, the research into forecasting has been advancing. In forecasting, linear models can provide stable results but there are cases where a linear-model cannot predict outcomes, while non-linear models can offer a higher precision but certain cases may diverge further than in the case when using a linear model. Considering their advantages and disadvantages, we chose ridge regression, LASSO (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator), SVR (support vector regression), BPNN (back propagation neural network), and RF (random forest) as the forecasting models to reveal the relationship between web information and oil price: the advantages and disadvantages of the model are displayed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of forecasting models.
Ridge analysis is a kind of regression method specially used to solve multiple collinearity problems. In essence, it is an improved least squares regression approach. With the help of L2 regularity, it is a more practical regression method at the cost of sacrificing some information and reducing accuracy. It is concluded that the parameter estimation method is biased, but it is still used in a large number of studies because its results have more practical implications and can have better effect on relatively long-term predictions [35,36,37].
LASSO is an improved Ridge model, which offers a stronger performance when solving multiple collinearity problems. Some studies even use LASSO for feature selection, because it can force the coefficients of some variables that are independent of the interpreted variables or related to the interpreted variables to be set to zero. In this way, the problem of multi-collinearity can be tackled, which can effectively avoid interference from redundant variables, searches faster, and offers better performance when solving multi-feature prediction problems [7,38,39].
SVR, a model based on the unique theory of the structural structure risk minimization principle, can resist over-fitting and simulate non-linear relations in an effective, stable way by means of kernel function form, thus solving non-linear regression and time series problems, however, SVR is sensitive to changes in input parameters due to its inherent structure [11,40,41]. BPNN is a classic neural network model, which is developed with multi-layered perceptron. Compared with multi-layer perceptron systems, BPNN has a more flexible network structure and activation function. It has a strong ability to transform and recognize features. It is the most popular predecessor of deep learning. BPNN’s flexibility and reduced dependence on data make it more important in the financial field where most problem datasets are not large [11,42,43].
RF is an integrated method based on decision tree analysis. It synthesizes the prediction results of each decision tree to achieve a final prediction and is mainly used for classification problems: however, due to the emergence of CART tree, continuous features can be reasonably discretized, which makes it possible to solve regression problems. At the same time, experiments indicate that it has strong fitting ability for highly non-linear problems; because it relies on rules to a certain extent, it has strong recognition ability for piecewise non-linear features, so it has become an important research method for dealing with many prediction problems [44,45].
Based on the above analysis, it can be found that the current oil price forecasting model system is relatively complete and can be used as a benchmark model for oil price forecasting. Next, we will consider incorporating the VADER sentiment factor mentioned in Section 2.2 into the prediction model to see if there is a significant increase in prediction accuracy. Specifically, oil prices and sentiment orientation factors are put into the oil price prediction model by constructing features. Generally, for any of the above prediction models f, the international oil price prediction problem is as follows.
where, is the predicted value of oil price, and is the feature required for prediction. For general time series, is usually historical information. Therefore, the prediction form can be expressed as follows for time series.
where, t is the arbitrary time point and i is the lag order. Unified, the lag order is defined by the following form.
So, we can rewrite Equation (8) as Equation (10)
Now web text sentiment is introduced into prediction model f to enrich the prediction information, and the following new form is obtained.
where, respectively correspond to the lag of 4 kinds of web text sentiment.
We change the lag order of input features respectively from 1 to 10 with in-sample data from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2017, evaluating prediction performance. In this way, prediction models can select optimal lag order of input features automatically.
3. Empirical Analysis
3.1. Data Sources
This paper uses Brent crude oil price data (USD/barrel) from 1 January 2013 to 31 August 2018 as empirical data. (EIA, Energy Information Administration), which covered 1447 observations. We select the data from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2017 as training and modelling data (a total of 1275 data points), and data from 1 January 2018 to 31 August 2018 as test data (a total of 172 data points) to explore the relationship between international oil prices and web text. It should be noted in advance that, unless otherwise specified, the following data results are derived from the results of the test data test.
Based on the above price data, we draw a time series diagram which describes how oil prices fluctuate over time, are shown in Figure 1.
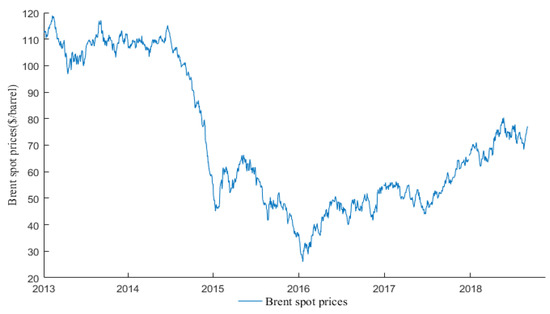
Figure 1.
Daily Brent crude oil prices.
As shown in Figure 1, the Brent oil prices have undergone significant fluctuations. Therefore, it is of great importance to forecast oil price fluctuations using an appropriate method. In order to reflect the fluctuation of crude oil price more clearly, we made a statistical analysis of Brent crude oil price data summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Summary of statistical tests for daily Brent crude oil prices.
As shown in Table 4, the average of Brent oil prices is 71.38, which means oil prices fluctuate around 70-value horizon. The highest oil price is 118.9, while the lowest is 26.01. There is a big gap between the maximum and minimum price and the standard deviation is 26.39, which means that oil prices fluctuate violently.
In terms of web text, we use Python, JavaScript, AJAX, and other technologies to acquire web text based on 20 oil price-related keywords such as “oil price” and “oil market”, from reliable on-line media such as Reuters (http://www.reuters.com/) and UPI (https://www.upi.com/). We have obtained 107,298 documents with a total of 38,075,959 words and after text pre-processing, data extraction, and data alignment, 47,808 documents remained available with 17,494,162 words, covering documents released from January 2013 to August 2018. The data capacity is 10 G. The relevant information is shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
The source of web text data.
3.2. Text Sentiment Analysis
After text pre-processing, it is necessary to analyze the text sentiment of all the 47,808 texts. After the text sentiment analysis mentioned in Section 2.2, the daily integration process which refers to the averaging of the sentiment intention values of all the articles in a day to ensure that daily public opinion is obtained for subsequent daily oil price forecasting, is performed, and finally all the daily tendencies are acquired, and the daily sentiment is illustrated in Figure 2.
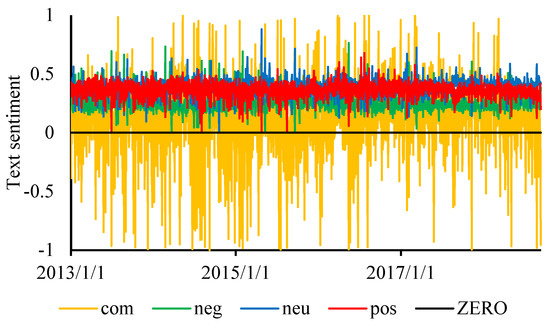
Figure 2.
Daily text sentiment. Notes: “com” indicates , “neg” indicates , “neu” represents , “pos” indicates , “ZERO” refers to zero line.
3.3. Choice of Oil Price Forecasting Model
There are many oil price prediction models which can mine different kinds of information from oil price from different perspectives. Before we begin to analyze the relationship, we choose a model that can better explain the relationship between oil price and text sentiment, evaluating this by forecasting performance. According to the introduction in Section 2.3, we select Ridge, Lasso, SVR, BPNN, and RF for testing. Since there are hyperparameters in each algorithm, manually adjustments are unavoidable. After more than 2000 attempts, the best results are selected for comparison and analysis. As for the text features, we choose which expresses the comprehensive sentiment of the article as the text sentiment feature.
As can be seen from Figure 3, these algorithms exhibit high accuracy, and have a high degree of fit between oil prices and offer good reliability. To compare the results of these algorithms, the error is measured by RMSE (root mean square error), MAPE (mean absolute percentage error), and the accuracy is thus assessed. The EV (error variance) is used to measure the stability of the predicted results [45,46]. The three statistical quantities are defined in Equations (12)–(14):
where is the number of samples, is real oil price, is the predicted oil price, is the difference between the real, and predicted, oil prices and is the mean of for all samples.
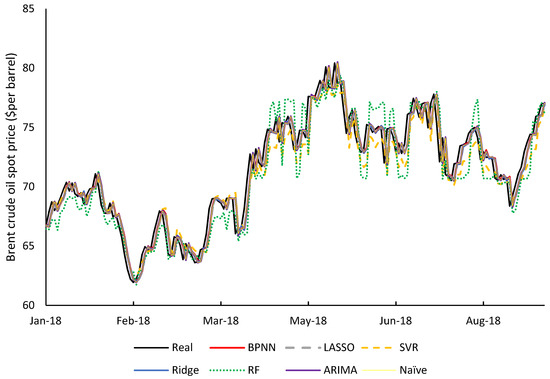
Figure 3.
Forecast oil prices.
Table 6 shows a comparison of the several algorithms on RMSE, MAPE, and EV. From the numerical value, it can be found that the error and error variance of SVR and RF are relatively large, and it does not offer a good prediction performance. The gap between BPNN, LASSO, and Ridge is not large, especially between BPNN, LASSO, and Ridge. BPNN has a certain advantage therein: its RMSE can be below 1.19, showing higher accuracy, while its lower EV indicates higher stability in prediction.

Table 6.
Forecasting error statistical characteristics.
In addition, from the relationship between the nature of the model and the predictive performance, it can be seen that the relationship between oil price and web text tendency information is quasi-linear: highly non-linear models, SVR and RF, do not offer good predictions, while the two modified linear models of LASSO and Ridge are better. BPNN is well-fitted with a flexible web form and price forecasts made therewith are excellent, therefore, the subsequent analysis of the relationship between web information and oil prices is performed using BPNN as a predictive model.
3.4. The Effect of Comprehensive Text Sentiment
This section analyses the comprehensive score of the text on the performance impact of oil price forecasts.
It is well known that news is time-sensitive, and people’s cognition of events is also time-sensitive. It takes time to digest a report to its effect on oil prices. After digestion, the information will not have an obvious long-term impact unless time is allowed for maturation, therefore, what needs to be considered here is to forecast the price of oil. It is better to use the news sentiment of the previous few days. In such a time series, it is necessary to know how many lag steps are optimal: here, the first step is delayed which indicates the sentiment to use text from yesterday, the second order represents the sentiment to use text from yesterday and the day before yesterday, and so on. Here, RMSE is selected as an indicator to measure accuracy, and different lags of web information tend to support the performance of oil price forecasting, while EV is used as an indicator to measure stability.
The first comparison is RMSE: according to Figure 4, when the text is not used, regardless of the lag order of the web information, the RMSE is 1.40. In contrast, once the web information tends to be used, the RMSE decreases significantly, with a drop of at least 0.2. In different orders, the prediction error also exhibits a certain difference. After the third order, it reaches the lowest level and can drop to 1.08. In the fourth order, the accuracy will decrease, and the RMSE will increase by 0.08 compared with the third order. The reason is that the information is overloaded, and information from four days ago will interfere with the oil price forecast.
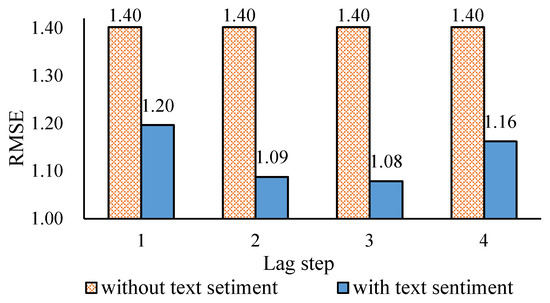
Figure 4.
Comparison of RMSE without, and with, text sentiment and different lag steps.
Then we compare the EV. According to Figure 5, when the text sentiment is not used, the EV is 1.64 regardless of the lag order of the web information sentiment, and the error variance decreases by about 0.2 after using the text sentiment, suggesting that, after using the text sentiment, the stability of the prediction is improved, indicating that the web text information plays a role in stabilizing the prediction results and correcting them. Furthermore, it can be found that the degree of lag is not particularly significant to the stability of oil price predictions.
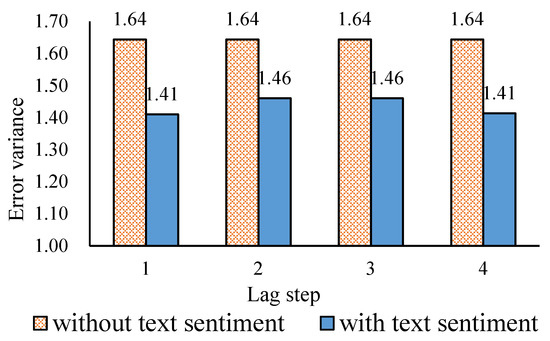
Figure 5.
Comparison of EV without, and with text, sentiment and different lag steps.
In summary, after using the web text sentiment, the accuracy and stability of oil price predictions can be further improved. The RMSE can be reduced by up to 0.4, and the EV can be decreased by 0.2. Using different lag-level text information, the accuracy will be different. The advantage is that the use of the text sentiment of the third-order lag to predict prices can maximize the accuracy of the prediction; however, adjusting different text sentiment lag steps cannot lead to further changes to the stability of an oil price prediction.
3.5. The Effect of Different Types of Text Sentiment
It can be seen from Section 3.4 that the comprehensive sentiment of the text has a relatively large positive effect on the performance of oil price prediction, and the accuracy and stability have been improved. Some studies have pointed out that negative information will have a greater impact on oil prices, and the extent of the specific improvement is unclear. This conclusion does not serve the oil price forecast very well, and thus we now conduct a more in-depth analysis.
As mentioned in Section 2.2, VADER can be used to extract the sentiment of the three angles of , , and in the text. We now put these three factors into the oil price prediction model using a BPNN, make the predictions, and assess the difference in performance of oil price forecasts by placing different propensity information into the forecasting model and the result is shown in Figure 6.
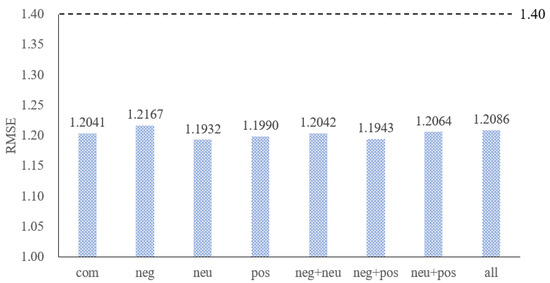
Figure 6.
Comparison of RMSE among different types of text sentiment. Notes: “com” means adding , “neg” means adding , “neu” means adding , “pos” means adding , “neg + neu” means adding and , “neg + pos” means adding and , “neu+pos” means adding and , “all” means all join, “1.40” is the predicted result when no sentiment is added.
First, we analyze the RMSE: as long as the text sentiment factor is added, no matter what its type, the accuracy of the prediction can be improved. Secondly, it can be found that, as long as the propensity information is added, no matter what its type, the difference in accuracy is not large, and it can even be considered as a random error. Moreover, regardless of the amount of information added, the addition of sentiment information, and the addition of multiple propensity information, the difference remained small.
Then, we analyze the EV according to Figure 7: as long as the text sentiment factor is added, no matter what its type, the stability of the prediction can be improved. Secondly, it can be found that as long as the propensity information is added, no matter what its type, there is little difference in stability, and it can even be considered to be a random error. Moreover, regardless of the amount of information added, the addition of sentiment information, and the addition of multiple propensity information, the difference remains small, therefore, it can be considered that, as long as text sentiment information is added, the accuracy and stability of the prediction can be improved, and there is no significant relationship with the type of sentiment. Adding more types of sentiment information does not further improve the prediction performance. Here, the sensitivity of oil prices to negative information is not fully reflected.
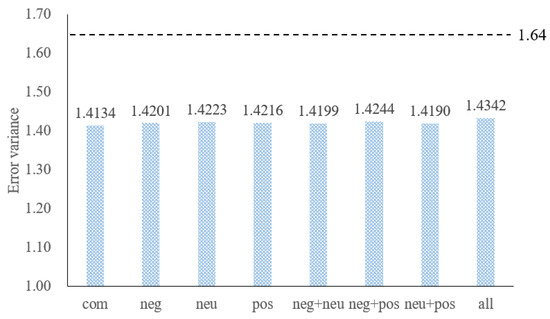
Figure 7.
Comparison of EV among different types of text sentiment. Notes: “com” means adding , “neg” means adding , “neu” means adding , “pos” means adding , “neg+neu” means adding and , “neg + pos” means adding and , “neu+pos” means adding and , “all” means all join, “1.64” denotes the predicted result when no sentiment is added.
3.6. The Effect of Text Sentiment with Different Strength
Generally speaking, only when there are more prominent events, will the text show an obvious sentiment. In terms of the oil price, it will only respond to major events, therefore, when the oil price is predicted through analysis of on-line text, a correction that is more conducive to oil price forecasts arises as explored in this section.
Figure 8 demonstrates the distribution of errors for samples with different propensities and different propensity strengths, and key statistical features are listed in Table 7. “Support” indicates the degree of support, and the number of days of the daily text sentiment value falling within the interval: only when the degree of support is high enough, is the statistical feature value sufficiently reliable. The mean error indicates the mean of the error within the corresponding interval, and the variance of error indicates the corresponding interval. The last four columns respectively represent the ratio of the data points under the error greater than the specific value for that level.
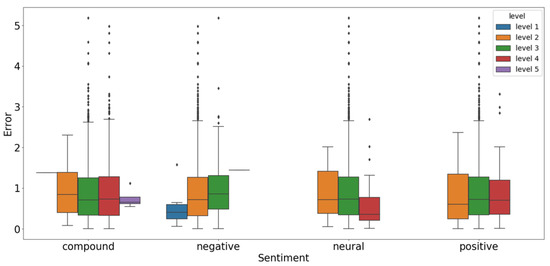
Figure 8.
The effect of different intensity sentiments on forecasting performance.

Table 7.
Error analysis of different intensity sentiments on forecasting performance.
For compound tendencies, Levels 1 to 5 in Figure 8 and Table 7 correspond to intervals [–1, –0.6), [–0.6, –0.2), [–0.2, 0.2), [0.2, 0.6), and [0.6, 1]. When , is at Level 3 or 4, more bad cases will appear, that is, there will be many extreme error points compared with the case at Levels 2 or 5. Similar outcomes can also be seen in Table 7. It can be seen that the proportion of the bad cases at Level 3 is the highest, the point with errors greater than 2 accounts for nearly 10% of all points at this level, and that with an error greater than 5 may still be found, accounting for 0.13% of all points, indicating that the degree of error is very high. Compared with Level 3, which has the same high level of support, it is much better than Level 4, and the number of bad cases predicted decreased somewhat. In terms of comprehensive performance, the degree of support at Levels 1 and 5 is not considered because it is too small. It can be seen that the average error at Level 3 is 0.91, and that at Levels 2 and 4 is less than 0.9, showing a decrease of about 0.1, which means that, when is in a larger or smaller position, is more conducive to oil price forecasting.
For the negative sentiment, Levels 1 to 5 in Figure 8 and Table 7 correspond to the intervals [0, 0.2), [0.2, 0.4), [0.4, 0.6), [0.6, 0.8), and [0.8, 1], respectively. When is at Levels 2 and 3, more bad cases will appear, that is, there will be many extreme error points. In contrast, at Level 1 they are fewer in number. The proportion of bad cases at Level 3 is the highest, the points at which the error is greater than 2 account for more than 10% of all points at this level, and that with an error greater than 5 may still be found, indicating extreme error. Compared with Level 3, which has higher support, this is much better: there are more data points at Level 2, but the proportion of bad cases is relatively small, indicating that the text tends to have the effect of correcting extreme errors. In terms of comprehensive performance, the degree of support at Levels 4 and 5 is too low to be considered. The average error at Level 3 is the highest, while those at Levels 2 and 1 are successively smaller. The average error at Level 1 is only 0.55, a decrease of about 50%, compared to the highest of 1.02, indicating that when is in a larger or smaller position, is more conducive to oil price forecasting.
For the sentiment of neutral, the Levels 1 to 5 in Figure 8 and Table 7 correspond to the intervals [0, 0.2), [0.2, 0.4), [0.4, 0.6), [0.6, 0.8), and [0.8, 1], respectively. When is at Level 3, more bad cases will appear, that is, there will be many extreme error points: in contrast, they are rarer at Levels 2 and 4. According to the situation of extreme error points and the ratio of the data points with an error above the value specific to each level, the proportion of bad cases at Level 3 is the highest, the points at which the error is greater than 2 account for nearly 9% of all points at this level, and that with an error greater than 5 may still be found, indicating extreme error. Levels 2 and 4, with their higher support, are much better than Level 3, and the proportion of bad cases that appear is relatively small, indicating that text sentiment does have the effect of correcting extreme errors. In terms of the comprehensive performance, the degree of support at Levels 1 and 5 is too small to be considered, and the average error at Level 3 is the highest, while the average error at Levels 2 and 4 is lower than that at Levels 3 and 4 where the average error drops to nearly 0.4, indicating that when is in a larger or smaller position, is more conducive to oil price prediction.
For positive sentiment, Levels 1 to 5 in Figure 8 and Table 7 correspond to the intervals [0, 0.2), [0.2, 0.4), [0.4, 0.6), [0.6, 0.8), and [0.8, 1], respectively. When is at Level 3, more bad cases will appear, that is, there will be many extreme error points. In contrast, they are much rarer at Levels 2 and 4. By deeper analysis from the ratio of the data points with extreme error, the proportion of bad cases at Level 3 is the highest, the points at which the error is greater than 2 account for nearly 10% of all points at this level, and that with an error greater than 5 may still be found, indicating that the error degree is very high. Levels 2 and 4, with their higher support, are much better than Level 3, and the proportion of bad cases that appear is relatively small, indicating that the text sentiments do have the effect on correcting extreme errors. As for the comprehensive performance, the degree of support at Levels 1 and 5 is lower, and the average error at Level 3 is the highest, while that at Levels 2 and 4 is lower than that at Level 3, indicating that when is in a larger or smaller position, is more conducive to oil price forecasting.
The above analysis shows the sentiment of the four types of propensity to support oil price predictions under different propensity strengths, all of which exhibit very similar properties. Under strong tendencies (stronger or weaker), it is more conducive to suppressing bad cases. There is also a more obvious improvement in accuracy. On the contrary, if the sentiment is not obvious, it may affect the prediction of the original oil price. The average error of the result obtained by using both strong and weak tendencies to predict oil prices can be about 0.5. From the proportion of bad cases, the sentiment to be strong is conducive to correcting the result, and the number of bad cases can be reduced by about 20%, therefore, when using the text sentiment to predict oil prices, the strength of the sentiment can be considered, and the text tends to be corrected at a position where the sentiment is more obvious, so as to maximize the accuracy and stability of the oil price prediction.
4. Conclusions
Since the oil market is very sensitive to non-market factors, most of which are difficult to be quantified and comprehensively considered, that is difficult to be analyzed and calculated, this forms a main bottleneck on oil price forecasting. The development of various technologies such as natural language processing technology, text mining methods, and big data technology provides market research with a way to obtain and extract information from the web. Therefore, introducing these concepts may be able to enhance the performance of oil price forecasting. Based on the oil market, we assess the current research status of the oil market using related methods, and develop a hybrid oil price forecasting model based on text mining. From the perspective of oil price forecasting, we explore the relationship between web text and oil price. We analyze the effect of introducing web text into oil price forecasting, the influence of texts of different propensity types on oil price forecasting, and the effect of text sentiment with different strengths on oil price forecasting performance. With these relationships, web text information can be better used in the research into oil price forecasting. Based on the above studies, the following conclusions may be drawn:
The relationship between oil price and web text sentiment is quasi-linear. The use of highly non-linear predictive models, such as SVR and RF, does not return a good performance. The better results obtained by LASSO and Ridge indicate that linear models still need to be addressed. Most importantly, flexible BPNN perform best due to their innate web flexibility.
After adding text sentiment into the oil price forecasting model, it can perform much better. The RMSE is decreased by about 0.2 and the EV can be reduced by 0.2, indicating a significant improvement in accuracy and stability.
The use of different types of text sentiment does not bring further changes to this improvement. From the perspective of RMSE and EV, the volatility is generally less than 0.1.
Text with stronger text sentiment performs better when correcting the oil price forecasting model. Text with stronger text sentiment can help to reduce RMSE by around 0.5 and decreases the number of bad cases by 20% compared with the use of text with weaker sentiment.
In summary, web text information confers significant benefits when carrying out oil price forecasting, but considering the relationship between web information and oil prices, it is necessary to be more cautious when making predictions. The corrective effect of web information appears only when the text sentiment is strong enough. Therefore, it is important to identify the strength of sentiment and use the text sentiment when it performs well. This provides important experience for better use of on-line text information for oil price forecasting in the future.
Author Contributions
L.-T.Z., G.-R.Z. and Z.-G.Z. performed the research; L.-T.Z., G.-R.Z., W.-J.W. and Z.-G.Z. co-wrote the paper. Conceptualization, L.-T.Z. and G.-R.Z.; Data curation, Z.-G.Z. and Wang W.-J.W.; Formal Analysis, L.-T.Z., G.-R.Z. and Z.-G.Z.; Methodology, L.-T.Z. and G.-R.Z.; Software, G.-R.Z. and L.-T.Z.; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 71871020, 71403014, 71521002 and the Sci-tech Innovation Foundation of CCTEG, grant number 2018-2-MS026.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers and seminar participants from the Department of Information and Computation Science, University of Science and Technology Beijing, for their helpful suggestions according to which we improved the original manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vo, D.H.; Vu, T.N.; McAleer, M. Modeling the Relationship between Crude Oil and Agricultural Commodity Prices. Energies 2019, 12, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tule, M.K.; Ndako, U.B.; Onipede, S.F. Oil price shocks and volatility spillovers in the Nigerian sovereign bond market. Rev. Financ. Econ 2017, 35, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panas, E.; Ninni, V. Are oil markets chaotic? A non-linear dynamic analysis. Energy Econ. 2004, 22, 549–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrangi, B.; Chatrath, A.; Dhanda, K.K.; Raffiee, K. Chaos in oil prices? Evidence from futures markets. Energy Econ. 2001, 23, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.T.; Liu, K.; Duan, X.L.; Li, M.F. Oil Price Risk Evaluation Using a Novel Hybrid Model Based on Time-varying Long Memory. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayalar, D.E.; Küçüközmen, C.C.; Selcuk-Kestel, A.S. The impact of crude oil prices on financial market indicators: Copula approach. Energy Econ. 2017, 61, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Ramchander, S.; Wang, T.; Yang, D. Influential Factors in Crude Oil Price Forecasting. Energy Econ. 2017, 68, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.Q.; Zeng, G.R. A novel method based on numerical fitting for oil price trend forecasting. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, H. Estimating and forecasting the real prices of crude oil: A data rich model using a dynamic model averaging (DMA) approach. Energy Econ. 2016, 56, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabralla, L.A.; Jammazi, R.; Abraham, A. Oil price prediction using ensemble machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ICCEEE), Khartoum, Sudan, 26–28 August 2013; pp. 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Du, R.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Tian, L. A novel hybrid method of forecasting crude oil prices using complex network science and artificial intelligence algorithms. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wei, D.; Ling, T. A novel decomposition ensemble model with extended extreme learning machine for crude oil price forecasting. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2016, 47, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; An, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y. Do all sectors respond to oil price shocks simultaneously? Appl. Energy 2018, 227, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Guo, J.F. Oil price volatility and oil-related events: An Internet concern study perspective. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Surdeanu, M.; MacCartney, B.; Jurafsky, D. On the Importance of Text Analysis for Stock Price Prediction. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; pp. 1170–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.S.; Ravi, V. A survey of the applications of text mining in financial domain. Knowl. Based Syst. 2016, 114, 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, G.P.C.; Yu, J.X.; Lam, W. News sensitive stock trend prediction. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Taipei, Taiwan, 6–8 May 2002; pp. 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Li, Q. A social-media-based approach to predicting stock comovement. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 3893–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqué de Fortuny, E.; De Smedt, T.; Martens, D.; Daelemans, W. Evaluating and understanding text-based stock price prediction models. Inf. Process. Manag. 2014, 50, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ma, C.Q. How does investor attention affect international crude oil prices? Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Athanasopoulos, G.; Hyndman, R.J.; Wang, S. Crude oil price forecasting based on internet concern using an extreme learning machine. Int. J. Forecast. 2018, 34, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassirtoussi, A.K.; Aghabozorgi, S.; Wah, T.Y.; Ngo, D.C.L. Text mining for market prediction: A systematic review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 7653–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cai, Y.; Lai, K.; Xie, H. A Topic-Based Sentiment Analysis Model to Predict Stock Market Price Movement Using Weibo Mood. In Web Intelligence; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Shirai, K.; Velcin, J. Sentiment analysis on social media for stock movement prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 9603–9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlock, P.C. Giving content to investor sentiment: The role of media in the stock market. J. Financ. 2007, 62, 1139–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z. How does news sentiment impact asset volatility? Evidence from long memory and regime-switching approaches. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2013, 26, 436–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Xu, H.; Tang, L.; Yu, L. Forecasting Oil Price Trends with Sentiment of Online News Articles. Asia Pac. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 91, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Lai, K.K. A Rough-Set-Refined Text Mining Approach for Crude Oil Market Tendency Forecasting. Int. J. Knowl. Syst. Sci. 2005, 2, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wex, F.; Widder, N.; Liebmann, M.; Neumann, D. Early warning of impending oil crises using the predictive power of online news stories. In Proceedings of the 46th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Wailea, Maui, HI, USA, 7–10 January 2013; pp. 1512–1521. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shang, W.; Wang, S. Text-based crude oil price forecasting: A deep learning approach. Int. J. Forecast. 2018, 35, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutto, C.J.; Gilbert, E. VADER: A Parsimonious Rule-Based Model for Sentiment Analysis of Social Media Text. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1–4 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Feng, S.; Gao, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C. Build Emotion Lexicon from Microblogs by Combining Effects of Seed Words and Emoticons in a Heterogeneous Graph. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM Conference on Hypertext & Social Media, Guzelyurt, Turkey, 1–4 September 2015; pp. 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Shi, F.; Wei, G.; Wang, D.; Ge, Y.; Wong, K.F. Personalized Sentiment Classification Based on Latent Individuality of Microblog Users. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 25–31 July 2015; pp. 2277–2283. [Google Scholar]
- Soleymani, M.; Garcia, D.; Jou, B.; Schuller, B.; Chang, S.F. A Survey of Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. Image Vision Comput. 2017, 65, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.; Yao, W.; Yu, L. A non-iterative decomposition-ensemble learning paradigm using RVFL network for crude oil price forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 70, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Haworth, J.; Shawe-Taylor, J.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J. Local online kernel ridge regression for forecasting of urban travel times. Transp. Res. Part C 2014, 46, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, W.; Ren, G.; Liu, J.; Hu, Q.; Yu, D. Ultra-short-term wind speed prediction based on multi-scale predictability analysis. Clust. Comput. 2016, 19, 741–755. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Jing, L.; Wahab, M.I.M.; Zhang, Y. Forecasting the aggregate oil price volatility in a data-rich environment. Econ. Model. 2018, 72, 320–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, N.; Feuerriegel, S.; Neumann, D. Putting Big Data analytics to work: Feature selection for forecasting electricity prices using the LASSO and random forests. J. Decis. Syst. 2015, 24, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xu, H.; Ling, T. LSSVR ensemble learning with uncertain parameters for crude oil price forecasting. Bibliometrics 2017, 56, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Yu, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, S. A New Method for Crude Oil Price Forecasting Based on Support Vector Machines. In International Conference on Computational Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Liu, W.; Jin, M. Stock price forecasting using a hybrid ARMA and BP neural network and Markov model. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Communication Technology, Chengdu, China, 9–11 November 2012; pp. 981–985. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, B.; Liu, W. Research on Prediction Methods of Residential Real Estate Price Based on Improved BPNN. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Grid and Electrical Automation (ICSGEA), Zhangjiajie, China, 11–12 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, A.; Gerding, E.; Mcgroarty, F. Automated trading with performance weighted random forests and seasonality. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 3651–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J. Forecasting energy market indices with recurrent neural networks: Case study of crude oil price fluctuations. Energy 2016, 102, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.T.; Zeng, G.R.; He, L.Y.; Meng, Y. Forecasting Short-Term Oil Price with a Generalised Pattern Matching Model Based on Empirical Genetic Algorithm. Comput. Econ. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).