Abstract
Access to finance by small-to-medium-enterprises (SMEs) remains an enigma that still warrants further research. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the funding gap and necessitated the need for entrepreneurs to seek alternative financing due to tight credit rationing by the traditional finance institutions. There is a marked increase in demand for alternative online finance known as crowdfunding amid social distancing and lockdowns occasioned by the COVID-19 pandemic. The main objective of this study was to examine the trends in the financing of African SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic with a particular focus on crowdfunding. The postpositivist research philosophy and deductive strategy was adopted in this study with the view to test an existing theory and hypothesis. Secondary data sourced from TheCrowdDataCentre were utilised for the study. Eight hundred and fifty-nine African crowdfunding campaigns were employed as the unit of analysis. The study employed econometric techniques to test the research objectives of this study. The probit model was employed in the analysis. The results of the study revealed that backers, the COVID-19 and social network variables were positively and significantly related to campaign success. On the other hand, duration was found to be negatively and significantly related to crowdfunding success. The study contributes to the growing literature on the impact of COVID-19 on crowdfunding performance, as well as the literature on alternative sources of finance.
1. Introduction
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic adversely affected financial and economic growth globally. Furthermore, this has severely affected the ability of the entrepreneurs and government to respond to the country’s economic needs, such as job creation and economic growth (Zribi 2022). The traditional financial institutions as such were not able to mobilise sufficient credit lines, resulting in credit rationing. As a result, entrepreneurs and SMEs were starved of credit to finance their projects or their working capital requirements. The challenge of accessing finance from traditional financial sources by SMEs remains pervasive. Worldwide SMEs provide an estimated 60% of employment yet they are unable to access finance (Sahay et al. 2020). The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift by entrepreneurs in the quest for funding from traditional finance sources to alternative online finances known as crowdfunding, amid the social distancing and lockdowns occasioned by the pandemic. During the COVID-19 pandemic, crowdfunding platforms became the main source of finance, influenced by applied physical distancing policies (Santos and Dias 2021). The crowdfunding platform is described as an attractive finance source that is accessible and easy to use, particularly during the pandemic era (Igra et al. 2021).
Arguably, access to finance and financial inclusion of SMEs could help overcome the problem of inequality by enhancing economic growth and employment. Crowdfunding is a method of raising finance or money from a large number of people who each contribute small amounts (Shneor 2020). However, in Africa, crowdfunding is still at the infancy level due to limited technological infrastructure and internet usage (Chao et al. 2020). Regardless of the low adoption of crowdfunding in Africa, crowdfunding has potential to provide access to finance to entrepreneurs (Wachira 2021).
Crowdfunding provides financial resources to SMEs and entrepreneurs after launching a project idea via the internet or an online crowdfunding platform without any involvement from financial institutions and financial intermediaries (Kim and Viswanathan 2019). The social media or network and advancement in technology increases the popularity of crowdfunding as it provides easy, instant, and unlimited accessibility to funds, since it does not require collateral (Fernandez-Blanco et al. 2020). Economic growth can be realised if it is supported by technological development and innovation (Block et al. 2018). In addition to that, regulation remains important for crowdfunding platforms to overcome the problem associated with risk of fraud concerning crowdfunding campaign projects (Wenzlaff 2020). Consequently, crowdfunding remains an alternative source of finance that alleviates limited access to finance for entrepreneurs.
The limited access to finance by SMEs in Africa is the major impediment to overcoming poverty and unemployment. African governments have been trying all other means to alleviate the limited credit problem; however, the problem remains persistent still to date. Crowdfunding is a viable alternative access to finance that has the potential to overcome the problem of limited finance in the African continent (Berndt 2016). The significance of SMEs in fostering development of the economies, growth, and job creation worldwide is well documented (see, for instance, among others: Mpofu and Sibindi 2022; Moyo and Sibindi 2020; Adjakou 2021; Berndt 2016). Further, Adjakou (2021) contend that insufficient capital supply from traditional sources of finance limits the growth and development of SMEs. Crowdfunding could potentially contribute to overcoming the limited access to finance for SMEs.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated the access to finance conundrum, as traditional financial institutions instituted tighter lending requirements. Since the start of the COVID-19 health crisis, the global economy has contracted, and access to finance by SMEs was expected to decrease from the year 2019. Furthermore, many countries experienced an alarming increase in COVID-19 cases during the second and third waves that might curtail economic growth further. Therefore, the current crisis is widening the gap for credit and accelerating the shift towards alternative financing sources in general and crowdfunding in particular. Crowdfunding helps to overcome the imbalances between the demand for access to finance and the supply by focusing on all neglected SMEs and entrepreneurs. Furthermore, crowdfunding promotes originality and innovation, thereby improving sustainable development (Ryu and Ko 2020). Crowdfunding is an effective alternative source of finance to purge this gap in funding. This new form of finance provides accessible and cost-effective funding that enhances the economic growth and job creation in developing, emerging, and developed nations (FSD Africa 2017).
Research on crowdfunding during the COVID-19 pandemic has attracted several researchers, such as Farhoud et al. (2021), Zribi (2022), Santos and Dias (2021), Cumming and Reardon (2022), among others. However, their studies were limited to developed countries and collected data from one specific crowdfunding platform—in particular, the reward-based. Therefore, the findings of this study help to purge the research gap on the dynamics of crowdfunding in Africa. There is a dearth of literature, especially in the context of Africa. Suffice it to highlight that African countries are different from the developed countries due to differences in: culture, legal requirements, social interaction, technology advancement, and the political and business environment. Moreover, crowdfunding in Africa is at a nascent stage and conceptual; hence, the current study is aimed at filling the gap in the literature. Unsurprisingly, the most difficult issue facing SMEs is limited access to finance for their SMEs and working capital requirements (Sahay et al. 2020).
Against this backdrop, the present inquiry sought to contribute towards the access to finance and financial inclusion debacle in the context of African countries. The objectives underpinning the study were the following:
- To establish whether African SMMEs were accessing finance from crowdfunding sources during the COVID-19 pandemic
- To determine the success rate of African crowdfunding campaigns during the COVID-19 pandemic
- To establish the enablers of crowdfunding success during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- To determine the leading crowdfunding campaign categories during COVID-19 in Africa.
The rest of the article is organised as follows: Section 2 analyses the global trends in crowdfunding finance. Section 3 describes the mechanics of crowdfunding and characterises the role players. Section 4 identifies the enablers of crowdfunding. Section 5 decribes the theoretical framework and hypotheses development. Section 6 describes the research methodology applied in the study. Section 7 identifies the most successful crowdfunding models in Africa during the COVID-19 pandemic. Section 8 concludes the study.
2. Global Trends in Crowdfunding Financing
Globally crowdfunding represents financial technology (FinTech), which addresses capital needs for entrepreneurs through effective digital solutions (Haddad and Hornuf 2019). There are an estimated 3000 crowdfunding platforms around the world from the years 2015 to 2017 (T. Ziegler et al. 2020). The volume of crowdfunding in the year 2019 reached USD 14 billion and was estimated to reach 28.8 billion by the year 2025. However, in the African continent, crowdfunding is still in the infancy stage, which delays the access to finance and financial inclusion (Drake 2016). The limited technological innovation in the African continent is delaying the growth and the development of crowdfunding. In 2015, crowdfunding platforms raised approximately USD34.4 billion which is about a 200% increase compared to the previous year (World Bank 2015). Crowdfunding usage and its popularity are influenced by the usage of the internet and social media. The low internet and social media usage in parts of African countries contribute to the lower popularity of crowdfunding.
Crowdfunding has become a viable alternative source of finance for SMEs. Typically, SMEs require funding for their business existence (working capital requirements), start-ups, and growth and source this from financial institutions such as banks. Due to the opaqueness of SMEs, banks and other financial institutions charge exorbitant interest rates in exchange for credit granted to SMEs. As such, crowdfunding emerges as an alternative source of capital for SMEs who cannot pay such high interest rates. Crowdfunding can alleviate the limitation of access to finance worldwide (Calic and Mosakowki 2016).
It is projected that the economic growth of African continent will decrease 3.4% due to uncertainties from the COVID-19 pandemic (Namatovu and Larsen 2021, p. 104). The gross domestic product (GDP) decreased from USD 145.5 billion to USD 189.7 billion. Due to the lockdown and subsequent social and physical distancing policies brought on by the COVID-19 epidemic, internet crowdfunding sites have emerged as the primary means of fund raising for non-profits (Santos and Dias 2021). Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, crowdfunding platforms proved to be a useful way to raise funds. Authors provided evidence of the determinants related to the success rate of the campaigns shared by these platforms, namely, the image or text of the posts (Y. Zhang et al. 2020). According to the African Bank Development Group (2022), the African continent experienced high levels of poverty among its population, with an estimated number of 453.4 million people living in abject poverty. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic, this number has increased by an additional 28 to 29 million people. South Africa is currently leading crowdfunding activities in the African continent with Thunda fundraising with an estimated USD 3.8 million from 1420 reward-based projects.
Table 1 presents the statistics on annual crowdfunding revenue per region from the year 2020. The annual crowdfunding annual revenue activity per region was mostly concentrated in North America with an estimated USD 17.2 billion, followed by Asia with USD 10.54 billion, and European continents with USD 6.84 billion. In the year 2020, the growth of crowdfunding has increased as Asia exceeded Europe in the size of the crowdfunding market, reaching USD 10.54 billion, as illustrated above. It is not surprising that North America dominates the crowdfunding, which was positively influenced by its origin. This crowdfunding market was carried in the US in the year 1885 to fund the crowdfunding project of the statue of Liberty (Kallio and Vuola 2020). Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 health crisis, the crisis accelerated the popularity and the need to use crowdfunding globally. Therefore, crowdfunding has the potential to respond to the need of finance needed globally in the African continent. The crowdfunding platforms such as M-Changa and Back-a-buddy showed designed digital solutions.

Table 1.
Annual Crowdfunding Activity Per Region.
The African continent maintains the lowest crowdfunding with an estimated USD 25.16 million, compared to Oceanic crowdfunding with USD 68.8 million and South American crowdfunding USD 85.74 million. There is currently limited research on crowdfunding, and it has lower penetration in the market; most relevant studies are limited to conceptual research. Despite its lower penetration in the African continent, crowdfunding is considered an innovative opportunity that enhances access to finance for SMEs and entrepreneurs (Chao et al. 2020). Overall, the health and strength of SMEs and entrepreneurs in Africa are often viewed as a policy priority in most countries across the continent. Accordingly, African governments may address crowdfunding regulation as an enabler of domestic innovation and entrepreneurship to develop this sector. However, several regulatory initiatives to support financial innovation need to be adopted by government agencies to limited regulation in the African continent in some countries, such as South Africa, Uganda, Rwanda, and Mozambique (A. Ziegler et al. 2018).
3. Mechanics of Crowdfunding: Models, Transactions and the Role Players
3.1. Crowdfunding Models
There are four main types of crowdfunding models that have developed over the years. These are the: donation-based, reward-based, lending-based, and equity-based crowdfunding models. These are depicted in Table 2. We describe each of these in turn.

Table 2.
Crowdfunding models.
- Donation-based crowdfunding
Donation-based crowdfunding does not provide compensation to the backers or supporters in the form of rewards in exchange for money contributed. Donation-based crowdfunding provides an opportunity for potential donors to contribute to the crowdfunding campaign without any expectation of returns for their contribution. Such donors do not worry about the risk of the return for their contribution made. Donation-based crowdfunding is also described as accepting donations of funds over the internet without expecting anything in return (Salido-Andres et al. 2021).
- b.
- Reward-based crowdfunding
In reward-based crowdfunding, the supporters or backers are compensated with a reward, which is a nonmonetary return. Reward-based crowdfunding is seen as the most general crowdfunding type around the globe (Shneor and Munim 2019). This type of crowdfunding allows investors or backers to contribute financial resources to the crowdfunding campaign in exchange for a reward. Therefore, the reward may be in monetary or non-monetary forms. The below Table 2 presents crowdfunding models.
- c.
- Lending-based crowdfunding
Lending-based crowdfunding provides a financial resource in the form of a loan where the recipient of the funds has to repay the finance in interest. The lending-based crowdfunding is basically about granting a loan to financially needy SMEs with the exchange of interest charged on the initial amount granted. It implies that backers or investors lend money to several SMEs or financial seekers, thus, spreading their risk (Ibsen-Jensen et al. 2015). Lending-based crowdfunding is an investment crowdfunding model through which a crowd or investors provide loans to SMEs to support their project ideas in exchange for regular returns, awaiting repayment of the initial capital investment (Boulahbel 2021).
- d.
- Equity-based crowdfunding
Equity-based crowdfunding is another form to access finance through the use of shares in the project or business. Equity-based crowdfunding offers SMEs an opportunity to access finance and secure online investments on crowdfunding platforms (Estrin et al. 2018). Equity-based crowdfunding is another access to finance for SMEs where the investors expect returns in exchange for risk. The below figure summarises the crowdfunding models.
3.2. Crowdfunding Transactions and the Role Players
The crowdfunding platform presents transparency by disclosing the project creator and fund seeker in the process of raising finance. The project creator may provide limited information to the supporters or backers of the project’s idea, which creates the problem of information asymmetry. However, all types have in common that compared to more conventional investments, financial means are derived from a range of backers. The crowdfunding transaction and role players are depicted in Figure 1.
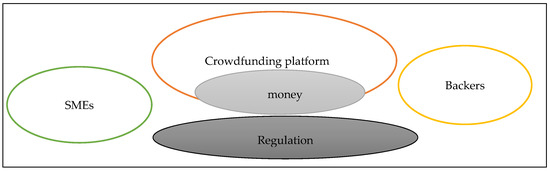
Figure 1.
Crowdfunding Model. Source: Adapted from Shneor (2020).
The crowdfunding platform appears to help to increase the awareness about an alternative access to finance for entrepreneurs. To date, insufficient information is available on the influence of crowdfunding during the COVID-19 pandemic and its strategies to overcome the limited access to finance (Farhoud et al. 2021). It appears that entrepreneurs are struggling to survive during the uncertainties of the health crisis (World Economic Forum 2020). Therefore, the reactionary health crisis has led an increase in the number of charitable crowdfunding campaigns (Farhoud et al. 2021). Figure 1 illustrates the crowdfunding model.
- (i)
- Entrepreneurs
The intention is to access finance from crowdfunding sources to finance projects and for working capital requirements. The process of raising finance from crowdfunding needs to attract members of the public who wish to contribute to a project that needs funds (Belleflamme et al. 2015). It commonly takes place via an online internet platform where the supporters contribute a small amount of money through the internet. The awareness of the crowdfunding project reaches the members of the public through the use of social media such as Twitter, Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram, and so on. According to Zhou et al. (2018) the term founder refers to a person who develops a project idea on a crowdfunding platform seeking to access finance from supporters or members of the public and investors who wish to provide support in the form of a monetary contribution. From the different academic sources, it is used as an entrepreneur, creator, owner, founder, SMEs, and entrepreneurs.
- (ii)
- Crowdfunding platforms
The crowdfunding platform is the internet and online social network that invites all members of the public and investors to contribute financial resources. The crowdfunding platform allows technology to take part in the process of raising funds for the fund seeker, whereas the website provider plays, a critical role and provides transparency.
- (iii)
- Backers
The backers are defined as supporters who contribute funds to a crowdfunding platform for an entrepreneur seeking finance. Commonly the backers contribute money through the online internet platform to the needy entrepreneurs seeking finance. These backers are informed by the social media involvement and the word-of-mouth network about the projects’ needs. Some backers expect a return in exchange for money invested in a project campaign. The supporters or backers of the crowdfunding campaign projects are not limited to individual investors, can be a large number of investors contributing to the campaign. The awareness of the crowdfunding campaign to the backers is being influenced by the spread of information in the form of social media, word of mouth.
- (iv)
- Regulations
The regulations consist of a set of rules under which crowdfunding models are in compliance with. The strength of the crowdfunding platform relies on the regulations and policies to overcome the problems concerning the risk of fraud (Chao et al. 2020). The crowdfunding project campaign is being supported when it is reliable and trustworthy (X. Zhang et al. 2022). Consequently, African governments need to address crowdfunding regulations to improve innovation and enhance crowdfunding participation and awareness.
4. Crowdfunding Enablers: Information Communication Technologies (ICT) Adoption
Arguably ICT adoption is the biggest enabler of crowdfunding in the world. From this vantage point, we analyse the key metrics in ICT adoption with a particular focus on internet and Facebook penetration from a global and African continent standpoint. The trends in internet and Facebook penetration are presented in Table 3 From the metrics documented in Table 3, it is apparent that Africa is lagging behind in internet penetration, as well as Facebook penetration. Internet penetration in Africa stands at 43% compared to the rest of the world, which is at 69%. A similar trend is observed with Facebook penetration in Africa being approximately 50% that of the rest of the world. Thus, Facebook penetration recorded in Africa is at 19% compared to 38%, which is recorded for the rest of the world.

Table 3.
Trends in internet and Facebook users as of December 2020.
Globally, the use of internet, as well as social media, plays an important role in facilitating crowdfunding. Notwithstanding, the utilisation of internet and social media in Africa is limited, as can be adduced from the above information. Consequently, the rest of the world dominates Africa in the crowdfunding arena.
5. Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses Development
Information asymmetry may be considered in crowdfunding as a problematic concern between the two parties, namely, backers and entrepreneurs or fund seekers. It is, therefore, important to overcome the problem of information asymmetry. The theory of information asymmetry originates from Akerlof (1978) and Rothschild and Stiglitz (1978), and it disrupts the credit market. To overcome the negative effects of asymmetric information, the more informed party can create an action to signal the less informed party about the quality of their product. This signalling process was first identified in the seminal works of Ross (1977) and Spence (1978), essays on labour market signals that highlighted the asymmetric information in the labour market and that without some form of signals, employers are unable to separate high-skilled workers from low-skilled ones. Hence, it is adaptable to crowdfunding where the backers have limited access to information concerning crowdfunding campaign projects.
Signals from the project creators or entrepreneurs could be identified based on the number of backers, presence on social media, duration, and the state of the COVID-19 pandemic as they pertain to the project’s successful performance. A large number of backers signal the crowdfunding’s successful performance based on the amount contributed to the project campaign. The presence on social network attracts backers by creating awareness of the crowdfunding project, thus, signalling success. A longer crowdfunding campaign project may not attract backers due to its untrustworthiness, thus, signalling and unsuccessful campaign. Finally, the COVID-19 pandemic has potential to disrupt the success of the crowdfunding campaign, hence, signalling an unsuccessful performance. However, in some instances, the COVID-19 pandemic may increase the participation of digital access to finance due to the social distancing created. This increase in information asymmetry puts distant funders at a disadvantage compared to nearby funders. Quality signals are more valuable and informative to the informationally disadvantaged backers. The importance of the digital crowdfunding platform is to decrease the transaction cost and provide effective transactions (Ben Arfi and Hikkerova 2021). Entrepreneurs or project creators attempt to mitigate information problems either directly by making the description of their activities and new projects known to the public or indirectly by selecting measures that can be positively interpreted by potential investors (Miglo 2022).
COVID-19 is the first deadly pandemic to ever attack the world. This outbreak started in China in late 2019, spread swiftly (in less than three months), and affected more than 200 nations, leading to a significant number of infections and fatalities. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many crowdfunding projects were affected by this disruption worldwide. As a result, the COVID-19 pandemic has negatively increased the market crashes and economic effect (Sansa 2020; Baker et al. 2020).
H1:
The COVID-19 pandemic is negatively influencing crowdfunding campaign success.
The large backing of experienced investors who are able to identify the potential of a project that is worth investing in is associated with lower cost compared to a small number of investors (Fourkan 2021). The large number of backers influences investor’s confidence and crowdfunding success. Crowdfunding campaigns are more likely to be successful in fundraising if they manage to attract both a large number of investors and a large amount of funds (Lukkarinen 2020).
H2:
The number of backers is positively related to the success of a crowdfunding campaign.
Social distancing could have increased the use of social media platforms, and this aspect could positively influence the success of the campaign (Zribi 2022). Network involvement is the information that informs the backers about the project’s need to obtain funding. The social media links backers to the campaign creator (X. Zhang et al. 2022; Tang et al. 2022). The literature shows that network involvement has positively influenced the crowdfunding success. Social media platforms such as Facebook build their digital platform based on network interactions that include data analytics used for digital marketing purposes and to better target consumers.
H3:
The network involvement in the crowdfunding project is positively associated with the crowdfunding campaign success.
Duration is the period of time in which the project can receive financial support from backers (Liang et al. 2020). Based on the other academic research such as (Zhou et al. 2018; Nyberg and Åberg 2017), the longer duration led to an increase or decrease in crowdfunding success. The study by Lagazio and Querci (2018) shows that the probability of success can reach 43% when the number of Facebook shares is between 1000 and 10,000.
H4:
The duration of the campaign decreases the crowdfunding campaign success.
6. Research Methodology
The research methodology adopted in this study was quantitative. The study utilised secondary data that were extracted from TheCrowdDataCentre database. Mainly, the study applied descriptive statistics to examine trends in crowdfunding in Africa. A regression analysis was also conducted to establish the relationships described in the aforementioned. The study period was the COVID-19 period, which ran from 1 March 2020 to 29 December 2020, and pre-COVID-19 data collected from 1 January 2019 to 30 December 2019. The convenience sampling frame was adopted for the study. The sample analysed consisted of 859 projects. These included 749 campaigns launched before the COVID-19 pandemic and 110 campaigns launched during the COVID-19 pandemic. The variables are defined in Table 4.

Table 4.
Variable Description and Measurement.
Hence, the following models were specified to test the relationship between crowdfunding campaign success and its regressors:
7. Crowdfunding in Africa: Which Models Are the Most Popular
There were 56 successful crowdfunding campaigns over a total of 749 projects in Africa before the COVID-19 health crisis (refer to Table 5). However, the number of projects that were not successful remains relatively high. There were many crowdfunding campaign projects launched before the COVID-19 health crisis. In addition to that, descriptive results revealed that despite the high number of crowdfunding campaigns, the projects launched were unsuccessful. Therefore, it can be concluded that the failure rate of crowdfunding campaigns launched before the COVID-19 pandemic remained high in the African continent.

Table 5.
Trends in Crowdfunding Campaigns.
It is evident that a higher number of backers increases the probability of crowdfunding campaign success during the COVID-19 pandemic (refer to Figure 2). The crowdfunding projects with insufficient numbers of backers decreased the success rate of a crowdfunding campaign in Africa. There, campaigns with a high number of backers (4499 supporters) reported high success rates. A large number of crowdfunding campaigns during the COVID-19 pandemic failed to reach targeted amount, hence, there was a low success rate of 13%. In addition to that, the higher number of backers contributing to the crowdfunding platform increases the probability of success rate as compared to the lower number of backers. Hence, the results are in line with the findings by Mollick (2014) and Wachira (2021).
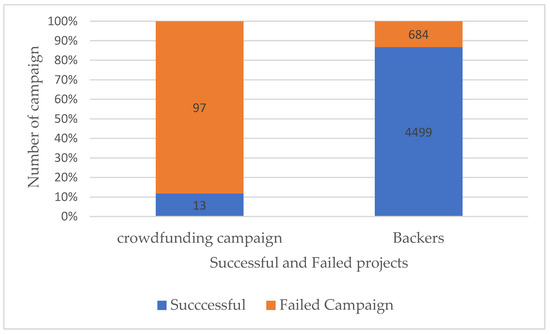
Figure 2.
Crowdfunding Campaign and Backers. Source: Authors’ own compilation.
Figure 3 shows that 23 crowdfunding categories were used in the African continent during the sample period. The x axis shows categories in the bar graph; blue, orange, and grey show the number of project campaigns per category, the number of successful projects, and the number of failed campaign projects, respectively. The y axis shows the number of crowdfunding campaigns projects considered. Consequently, animals, photography, travel, gaming, design, publishing, fashion, music, film, art, and technology reached success of 100%, 100%, 50%, 50%, 29%, 25%, 17%, 15%, 13% and 8%. respectively. The most popular crowdfunding categories were animal, photography, travel, and gaming. Consequently, animal and photograph categories were identified as the leading crowdfunding projects during the year 2020 in the African continent.
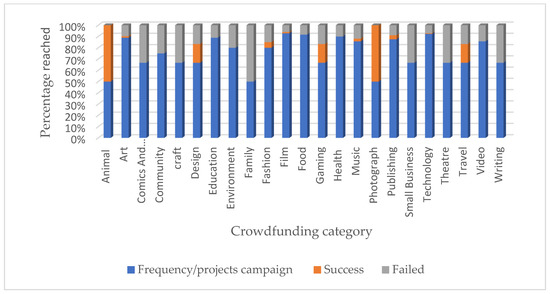
Figure 3.
Percentage of goal reached per crowdfunding category.
Figure 4 documents the amount raised compared to the targeted amount reached. Thus, USD 115,605 was the highest amount raised. Based on the money pledged and category, it shows that an estimated USD 2057, USD 69, 5509 and USD 54 were raised by the leading popular crowdfunding categories, which include animals, photography, gaming and design.
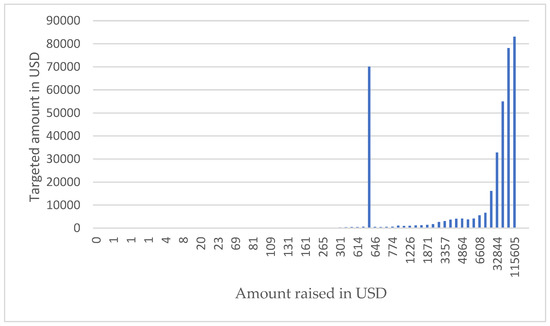
Figure 4.
Total amount raised. Source: Authors’ own compilation.
The duration of the campaigns is presented in Figure 5. Typically, the time frame for projects to raise money ranges from 30 to 90 days. The more successful projects have a duration that ranges from 26 to 31 days with the crowdfunding campaign reaching over 100% of its target. From 60 days upward, the success rate drops, compared to 29 to 36 days, which showed success rates of over 119% to 385%. It is advisable for project creators to aim for a campaign that lasts between 26 to 36 days to ensure success.
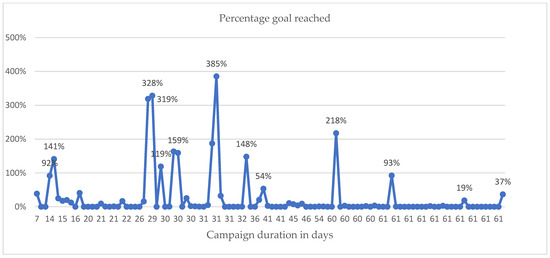
Figure 5.
Duration of Crowdfunding Campaign. Source: Authors’ own compilation.
The Table 6 below presents descriptive and correlation matrix. The findings of descriptive statistical analysis shown in Table 6 consists of means, standard deviation, and correlated relationships between the independent variables. The correlation coefficients are all between 0.023 and 0.44. As a result, the model is free from multicollinearity problems as the correlation is below 0.80. McDonald and Moffit (1980) stated that the VIF threshold should be less than 10 to ensure that the overall model does not suffer from multicollinearity. The VIF ranges from 1.00 to 1.02, which is within the threshold. Consequently, there is no problem of multicollinearity.

Table 6.
Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Matrix.
The regression results are presented in Table 7. The probit regression results are reported in model 1. These showed a pseudo-R-square of 57%, which represents the goodness fit and ordinary least square presented in Table 7 model 2 showed an R-square of 22%. The regression coefficients β indicate the direction of impact between the access to finance criterion (dependent variable) and each signal (independent variable), and p values show the level of significance.

Table 7.
Regression analysis results.
The model 1 results reported the probit regression analysis results. This showed that backers, the COVID-19 pandemic, and social networks were positively and significantly associated with crowdfunding success (β = 0.032, 0.030, and 0.268 respectively; p < 0.01, p < 0.05, and p < 0.10). The findings are consistent with the findings by Bu et al. (2020), Bansal et al. (2019), Liu et al. (2021), and Fourkan (2021). However, duration was found to negatively and significantly influence crowdfunding success (β = −0.012; p < 0.1). The findings are consistent with the results by Butticè and Noonan (2020) and Zhou et al. (2018). On the contrary, Tan and Reddy (2021) found a positive association between duration and crowdfunding success. The results implied that many numbers of backers involved in the crowdfunding campaign project enhances the possibility of success. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many fund seekers or entrepreneurs relied on digital access to finance due to social distancing imposed by the government. Hence, the COVID-19 pandemic increases the probability of crowdfunding success. The presence of social network attracts backers to contribute to the crowdfunding campaign project, which ultimately increases the success. Finally, the longer duration creates many doubts in potential backers or investors to contribute to the crowdfunding campaign projects, resulting in the failure of the campaign.
The ordinary least square (ODL) model in model 2 revealed that the duration and COVID-19 pandemic are negatively and significantly associated with crowdfunding success (β= −0.002 and −0.03, respectively; p < 0.01). The results are supported by Zribi (2022) and Butticè and Noonan (2020). However, backers and social network were found to positively and significantly influence crowdfunding campaign success (β = 0.001; p < 0.1, and β = 0.0576; p < 0.05 respectively). The findings corroborate the results by X. Zhang et al. (2022) and Tian et al. (2018). It makes sense that duration extended the possibility for the backers to contribute due to a signal of lack of confidence in the crowdfunding campaign project. Because of the disruption imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic, backers seem to access insufficient information concerning the crowdfunding campaign project, hence, decreasing the success performance. The social network is an important communication strategy amid the social distancing imposed by COVID-19; hence, it attracts backers to contribute to the crowdfunding campaign project that ultimately increases the success. Finally, a larger number of backers positively influences the crowdfunding success performance.
According to N’Guessan et al. (2017), many crowdfunding projects in the African continent benefit from internationally based crowdfunding platforms because most African based platforms are relatively small and not well established. A large number of international crowdfunding platforms are more successful in financing projects based in the African continent compared to the African crowdfunding platform. Furthermore, N’Guessan et al. (2017) contend that the constraints concerning the crowdfunding platform in Africa are influenced by the limited internet, social media, and online payment access, since they are underdeveloped. African-based crowdfunding platforms are mostly focused on raising funds for entrepreneurs and SMEs seeking capital for their start-up (Sommer 2021). The Table 8 below present the international crowdfunding platforms operating in African continent. The analysis in Table 7 revealed that donation-based crowdfunding is the leading type of crowdfunding platform used in the African continent.

Table 8.
International crowdfunding platforms operating in the African Continent.
The main findings revealed that SMEs or entrepreneurs during the reactionary time of COVID-19 were not able to access finance adequately from crowdfunding funding sources. The results revealed that the crowdfunding success rate remains relatively low, 13% during the COVID-19 pandemic in Africa. In addition to that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of crowdfunding campaigns decreased from 749 project campaigns to 110 crowdfunding. The unsuccessful rate was 97% during this uncertain time, which is in line with the findings by Y. Zhang et al. (2020). Crowdfunding categories that reached the targeted amount during the reactionary time of health crisis involve animals, photography, design, and games, respectively. Despite the success categories, the larger number of unsuccessful crowdfunding campaign projects remains relatively high. Hence, the higher number of backers is identified as an enabler of crowdfunding success performance, whereas a longer duration or number of days decreases the success rate. The donation-based crowdfunding model is leading in Africa, illustrated in Table 8. Finally, descriptive statistics revealed that crowdfunding campaign projects launched before the COVID-19 pandemic showed a low success rate. Conversely, crowdfunding campaign project launched during the COVID-19 pandemic showed a high success rate.
8. Conclusions
The aim of the study was to examine the trends in the financing of African SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic with a particular focus on crowdfunding. The study found that although crowdfunding is still at an infancy stage, it is increasingly providing a significant amount of financing for African SMEs. This has not been done before, so the findings of this study provide a way to add to the existing literature on the COVID-19 pandemic concerning crowdfunding. The research findings have a valuable practical implication for crowdfunding platforms, project creators, and social media by determining factors that enhance crowdfunding performance that guide the SMEs in Africa after and during the COVID-19 pandemic and the economy at large. The study identified factors that influence crowdfunding success p can be and can act as an interesting guide to help African entrepreneurs, platform managers and the wider economy during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, the theoretical contribution of this article is to combine the literature on digital platforms and transformational entrepreneurship by focusing on the complications of the COVID-19 crisis. The social media, backers, and duration were identified as the enablers of crowdfunding in Africa.
The presence of the COVID-19 pandemic has increased the usage of social media platforms due to social distance imposed by government. On the other hand, the COVID-19 pandemic decreased the crowdfunding success due to lower participation in crowdfunding. The study found that the most leading crowdfunding categories for SMEs in the African continent were animals and photography during the health crisis of COVID-19. Additionally, the study provides the information that reward- and donation-based crowdfunding platforms offer a more efficient mechanism to deliver access to finance for SMEs and the community in general, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. The limited regulatory framework on crowdfunding exists in the whole continent of Africa, which limits the growth of crowdfunding volumes (Afrikstart 2016).
The study suggests that crowdfunding platforms could potentially be used as alternative access to finance for SMEs and to limit the widening gap of funding occasioned by the COVID-19 pandemic. Arguably, crowdfunding possibly provides a solution to the problem of the lack of access to finance for SMEs in the African continent. However, the development and growth of crowdfunding in Africa is constrained by the lack of an appropriate regulatory framework, limited internet and digital payment penetration, and the lack of awareness and trust by the supporters, amongst a plethora of issues. The entrepreneurs in the African continent need to adapt to recent innovations and digital access to finance for survival. Second, the study contributes to policy makers to formalise and enhance awareness of crowdfunding, which will ultimately decrease the higher demands for funds from banks. Finally, it contributes to the growing literature on crowdfunding for entrepreneurs in the Africa.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, L.P.M. and A.B.S.; methodology, L.P.M.; software, L.P.M.; validation, L.P.M. and A.B.S.; formal analysis, L.P.M.; investigation, L.P.M.; resources, L.P.M.; data curation, L.P.M.; writing—original draft preparation, L.P.M.; writing—review and editing, A.B.S.; visualisation, L.P.M. and A.B.S.; supervision, A.B.S.; project administration, L.P.M.; funding acquisition, L.P.M. and A.B.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by University of South Africa.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Attendees at the Global Development Finance Conference for their valuable inputs on this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adjakou, Oloutchègoun Josias Lawrence. 2021. Crowdfunding: Genesis and Comprehensive Review of Its State in Africa. Open Journal of Business and Management 9: 557–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- African Bank Development Group. 2022. African Development Fund Approves $4.3 million Grant to Somalia for Statistics Development. Available online: https://www.afdb.org/en/news-and-events/press-releases/african-development-fund-approves-43-million-grant-somalia-statistics-development-49219 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Afrikstart. 2016. Crowdfunding in Africa. Available online: http://afrikstart.com/report/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Afrikstart-Crowdfunding-In-Africa-Report.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Akerlof, George A. 1978. The market for “lemons”: Quality uncertainty and the market mechanism. In Uncertainty in Economics. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press, pp. 235–51. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, Scott R., Robert A. Farrokhnia, Steffen Meyer, Michaela Pagel, and Constantine Yannelis. 2020. How does household spending respond to an epidemic? Consumption during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic. The Review of Asset Pricing Studies 10: 834–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, Sanchita, Isha Garg, and Gagan Deep Sharma. 2019. Social entrepreneurship as a path for social change and driver of sustainable development: A systematic review and research agenda. Sustainability 11: 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleflamme, Paul, Nessrine Omrani, and Martin Peitz. 2015. The economics of crowdfunding platforms. Information Economics and Policy 33: 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Arfi, Wissal, and Lubica Hikkerova. 2021. Corporate entrepreneurship, product innovation, and knowledge conversion: The role of digital platforms. Small Business Economics 56: 1191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, Adele. 2016. Crowdfunding in the African context: A new way to fund ventures. In Entrepreneurship and SME Management across Africa. Singapore: Springer, pp. 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Block, Jörn, Lars Hornuf, and Alexandra Moritz. 2018. Which updates during an equity crowdfunding campaign increase crowd participation? Small Business Economics 50: 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulahbel, Zoubir. 2021. Crowdfunding as an alternative form of islamic financing for startups and small enterprises. South East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business, Economics and Law 24: 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, Di, Tobin Hanspal, Yin Liao, and Yong Liu. 2020. Risk taking during a global crisis: Evidence from Wuhan. Covid Economics 5: 106–46. [Google Scholar]
- Butticè, Vincenzo, and Douglas Noonan. 2020. Active backers, product commercialisation and product quality after a crowdfunding campaign: A comparison between first-time and repeated entrepreneurs. International Small Business Journal 38: 111–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calic, Goran, and Elaine Mosakowski. 2016. Kicking off social entrepreneurship: How a sustainability orientation influences crowdfunding success. Journal of Management Studies 53: 738–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Emmanuel James, Priscilla Serwaah, Prince Baah-Peprah, and Rotem Shneor. 2020. Crowdfunding in Africa: Opportunities and challenges. Advances in Crowdfunding 14: 319–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cumming, Douglas, and Robert S. Reardon. 2022. COVID-19 and entrepreneurial processes in US equity crowdfunding. Journal of Small Business Management 10: 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, David. 2016. 2000 global crowdfunding sites to choose from by 2016: Top five growth indicators. Huffington Post. October 23. Available online: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/david-drake/2000-global-crowdfunding-_b_8365266.html (accessed on 23 March 2016).
- Estrin, Saul, Daniel Gozman, and Susanna Khavul. 2018. The evolution and adoption of equity crowdfunding: Entrepreneur and investor entry into a new market. Small Business Economics 51: 425–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoud, Mohamed, Sheeza Shah, Pekka Stenholm, Ewald Kibler, Maija Renko, and Siri Terjesen. 2021. Social enterprise crowdfunding in an acute crisis. Journal of Business Venturing Insights 15: e00211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Blanco, Aladino, Joaquin Villanueva-Balsera, Vicente Rodriguez-Montequin, and Henar Moran-Palacios. 2020. Key factors for project crowdfunding success: An empirical study. Sustainability 12: 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourkan, Md. 2021. Crowdfunding: Antecedents of Number of Backers and Success of a Project. Fourkan, M.(2021). CROWDFUNDING: ANTECEDENTS OF NUMBER OF BACKERS AND SUCCESS OF A PROJECT. International Journal of Small Business and Entrepreneurship Research 9: 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- FSD Africa. 2017. Crowdfunding in East Africa: Regulation and Policy for Market Development. Cambridge: Cambridge Center for Alternative Finance. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, Christian, and Lars Hornuf. 2019. The emergence of the global fintech market: Economic and technological determinants. Small Business Economics 53: 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibsen-Jensen, Jakob, Kaisa Johanna Matschoss, Juha Petteri Repo, and Anita Tregner-Mlinaric. 2015. Crowdfunding in sustainable innovation: Insights from and for Denmark. Available online: http://www.casi2020.eu/library/#d7307 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Igra, Mark, Nora Kenworthy, Cadence Luchsinger, and Jin-Kyu Jung. 2021. Crowdfunding as a response to COVID-19: Increasing inequities at a time of crisis. Social Science & Medicine 282: 114105. [Google Scholar]
- Kallio, Aki, and Lasse Vuola. 2020. History of crowdfunding in the context of ever-changing modern financial markets. In Advances in Crowdfunding. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 209–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Keongtae, and Siva Viswanathan. 2019. The Experts in the Crowd: The Role of Expereinced Investors in a Crowdfunding Market. MIS Quarterly 43: 347–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagazio, Corrado, and Francesca Querci. 2018. Exploring the multi-sided nature of crowdfunding campaign success. Journal of Business Research 90: 318–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Xiaobei, Xiaojuan Hu, and Jiang Jiang. 2020. Research on the effects of information description on crowdfunding success within a sustainable economy—The perspective of information communication. Sustainability 12: 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Yang, Yuan Chen, and Zhi-Ping Fan. 2021. Do social network crowds help fundraising campaigns? Effects of social influence on crowdfunding performance. Journal of Business Research 122: 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkarinen, Anna. 2020. Equity crowdfunding: Principles and investor behaviour. In Advances in Crowdfunding. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 93–118. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, J. F., and R. A. Moffit. 1980. The uses of Tobit analysis. The review of econometrics and statistics. Kristjanson, P., Okike, I., Tarawali S., Singh, BB and 1000: 195–210. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2307/1924766 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Miglo, Anton. 2022. Theories of crowdfunding and token issues: A review. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 15: 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollick, Ethan. 2014. The dynamics of crowdfunding: An exploratory study. Journal of Business Venturing 29: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, Busani, and Athenia Bongani Sibindi. 2020. Does Bank Competition Affect Credit Access in Sub-Saharan Africa? Evi-dence from World Bank Informal Firms Surveys. Journal of African Business 23: 180–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpofu, Olipha, and Athenia B. Sibindi. 2022. Informal Finance: A Boon or Bane for African SMEs? Journal of Risk and Financial Management 15: 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Guessan, M., Ines Alegre, and Miguel Canela. 2017. Crowdfunding in Africa: An Empirical Study of Kiva Platform Users in Sub-Saharan Africa. WP-1172-E, 05/2017. Madrid: Business School University of NavaraIESE. [Google Scholar]
- Namatovu, Rebecca, and Marcus M. Larsen. 2021. Responding to COVID-19: Insights from African firms. Africa Journal of Management 7: 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, Anna, and Malin Åberg. 2017. Crowdfunding Social Entrepreneurship, the Influential Factors in Crowdfunding Success for Social Entrepreneurs. Master’s thesis, Gothenburg University, Gothenburg, Sweden. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, Stephen A. 1977. The determination of financial structure: The incentive-signalling approach. The Bell Journal of Economics 8: 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, Michael, and Joseph Stiglitz. 1978. Equilibrium in competitive insurance markets: An essay on the economics of imperfect information. In Uncertainty in Economics. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press, pp. 257–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, Hyun-Sun, and Kwang Sun Ko. 2020. Sustainable development of Fintech: Focused on uncertainty and perceived quality issues. Sustainability 12: 7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, Ms Ratna, Mr Ulric Eriksson von Allmen, Ms Amina Lahreche, Purva Khera, Ms Sumiko Ogawa, Majid Bazarbash, and Ms Kimberly Beaton. 2020. The Promise of Fintech: Financial Inclusion in the Post COVID-19 Era. Washington, DC: International Monetary Fund. [Google Scholar]
- Salido-Andres, Noelia, Marta Rey-Garcia, Luis Ignacio Alvarez-Gonzalez, and Rodolfo Vazquez-Casielles. 2021. Mapping the field of donation-based crowdfunding for charitable causes: Systematic review and conceptual framework. VOLUNTAS: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations 32: 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansa, Nuhu A. 2020. The impact of the COVID-19 on the financial markets: Evidence from China and USA. Electronic Research Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities 2: 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, Márcia, and Rui Manuel Teixeira Santos Dias. 2021. Financial Return of Crowdfunding Platforms: Are Funding Trends and Success Rates Changing in the Covid-19 Era? Volume 13, pp. 57–64. Available online: https://repositorio.iscte-iul.pt/handle/10071/25232 (accessed on 5 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Shneor, Rotem. 2020. Crowdfunding models, strategies, and choices between them. In Advances in Crowdfunding. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Shneor, Rotem, and Ziaul Haque Munim. 2019. Reward crowdfunding contribution as planned behaviour: An extended framework. Journal of Business Research 103: 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, Christoph. 2021. Addressing the Challenges of Digital Lending for Credit Markets and the Financial System in Low-and Middle-Income Countries. Briefing Paper No. 23/2021. Bonn: German Development Institute. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, Michael. 1978. Job market signaling. In Uncertainty in Economics. Oxford: Oxford University Press, Cambridge, MA: Academic Press, pp. 281–306. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Yee Heng, and Srinivas K. Reddy. 2021. Crowdfunding digital platforms: Backer networks and their impact on project outcomes. Social Networks 64: 158–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Linghui, Richard Baker, and Liping An. 2022. The success of crowdfunding projects: Technology, globalization, and geographic distance. Economics of Innovation and New Technology 31: 553–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Zhiyuan, Lei Guan, and Meilin Shi. 2018. The key factors of successful internet crowdfunding projects-an empirical study based on different platforms. Paper presented at 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM), Hangzhou, China, July 21–22; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wachira, Virginia Kirigo. 2021. Crowdfunding in Kenya: Factors for Successful Campaign. Public Finance Quarterly 3: 413–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzlaff, Karsten. 2020. Civic crowdfunding: Four perspectives on the definition of civic crowdfunding. In Advances in Crowdfunding. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 441–72. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. 2015. Crowdfunding in Emerging Markets: Lessons from East African Startups. Washington, DC: The World Bank Group. [Google Scholar]
- World Economic Forum. 2020. The Future of Jobs Report 2020. Retrieved from Geneva. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/reports/the-future-of-jobs (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Zhang, Xi, Xiaopei Liu, Xianhai Wang, Hongke Zhao, and Wei Zhang. 2022. Exploring the Effects of Social Capital on Crowdfunding Performance: A holistic analysis from the empirical and predictive views. Computers in Human Behavior 126: 107011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Yali, Chrissie Diane Tan, Jun Sun, and Zhaojun Yang. 2020. Why do people patronize donation-based crowdfunding platforms? An activity perspective of critical success factors. Computers in Human Behavior 112: 106470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Mi Jamie, Baozhou Lu, Weiguo Patrick Fan, and G. Alan Wang. 2018. Project description and crowdfunding success: An exploratory study. Information Systems Frontiers 20: 259–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, Anna B., Gérard Manière, and Yael Grosjean. 2018. JhI-21 plays a role in Drosophila insulin-like peptide release from larval IPCs via leucine transport. Scientific Reports 8: 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, Tania, Rotem Shneor, and Bryan Zheng Zhang. 2020. The global status of the crowdfunding industry. In Advances in Crowdfunding. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zribi, Sirine. 2022. Effects of social influence on crowdfunding performance: Implications of the covid-19 pandemic. Humanities and Social Sciences Communication 9: 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).