Abstract
Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are at a higher mortality risk compared with the general population. Previous studies have described a relationship between mortality and patients with ESRD, but the data on standardized mortality ratio (SMR) corresponding to different causes of death in patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD) are limited. This study was designed as a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. Incident dialysis patients between January 2000 and December 2015 in Taiwan were included. Using data acquired from the Taiwan Death Registry, SMR values were calculated and compared with the overall survival. The results showed there were a total of 128,966 patients enrolled, including 117,376 incident HD patients and 11,590 incident PD patients. It was found that 75,297 patients (58.4%) died during the period of 2000–2017. The overall SMR was 5.21. The neoplasms SMR was 2.11; the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 13.53; the circulatory system SMR was 4.31; the respiratory system SMR was 2.59; the digestive system SMR was 6.1; and the genitourinary system SMR was 27.22. Therefore, more attention should be paid to these diseases in clinical care.
1. Introduction
According to the International Society of Nephrology 2019 Global Kidney Health Atlas cross-sectional survey, the global average number of newly diagnosed cases of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is 144 per million general population, and the incidence of ESRD varies greatly among different countries. Hemodialysis (HD) is the most common form of renal replacement therapy [1]. In most countries, ≥80% of chronic dialysis patients receive HD [2].
Patients with ESRD are at a higher mortality risk compared with the general population. Although previous studies have described a relationship between mortality and patients with ESRD, these studies had some limitations [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. First, some studies consisted of small sample sizes. Second, peritoneal hemodialysis (PD) patients usually had better baseline characteristics than HD patients; however, some studies did not separate these two groups. Third, many studies had short follow-up periods. Fourth, some studies also lacked general population data as the comparison group. Fifth, some studies only compared the overall mortality rate without including the specific cause of death. Most importantly, most of these studies investigated the risk of mortality. Only a few studies investigated the standardized mortality ratio (SMR) in a large representative cohort compared with the general population [37,38,39,40]. In addition, the study periods of the above studies were different from our study, and dialysis technologies have changed in recent years.
Therefore, the objectives of this study were to describe the causes of death and determine the all-cause SMR for a nationwide cohort of patients on dialysis.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study was designed as a population-based retrospective cohort study. HD patients and PD patients during a specific period (1 January 2000, to 31 December 2015) were included in the study. We then monitored the clinical outcomes (deaths) in these groups over time until the end of the study (31 December 2017).
2.2. Data Source
Taiwan National Health Insurance is a compulsory social health insurance plan that started in 1995. Approximately 99% of Taiwan’s 23 million people participate in the program. The National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) of Taiwan has been used by many parties for epidemiological research and research on prescription drug use. The accuracy of the disease diagnosis recorded in NHIRD has been verified, and the recorded data are of high quality [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51].
All NHIRD data sets can be externally linked to the Taiwan Death Registry (TDR). In Taiwan, the law requires that all deaths must be registered within 10 days. TDR is considered accurate and complete because registering a death in Taiwan is necessary for doctors to issue a death certificate [52].
2.3. Dialysis Cohort
All disease diagnosis codes are assigned according to the ninth and tenth editions of the International Classification of Diseases, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM or ICD-10-CM). First, patients with ESRD (who have catastrophic illness cards for ESRD, ICD-9-CM code 585 or ICD-10-CM code N18.6) who started receiving dialysis between 1 January 2000, and 31 December 2015, were included in the dialysis cohort. In Taiwan, if a patient is diagnosed with a disease classified as a catastrophic illness by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the patient can submit relevant disease information and apply for a catastrophic illness certificate [53]. Patients with catastrophic illness certificates do not need to pay deductibles for outpatient or inpatient treatment related to this disease during the validity period of the certificate. For example, a patient with a catastrophic illness certificate of ESRD does not need to pay the deductible for dialysis treatment. These dialysis patients were then divided into PD and HD patients according to their dialysis modality. Patients who had received both PD and HD were classified as HD group if the HD duration was longer than PD in the first six months, and vice versa for the PD group. Patients who received dialysis for less than six months were excluded. Follow-ups on all individuals continued until death, renal transplantation, a change of dialysis modality, or the end of the study (2017).
2.4. Definition of Study Outcomes
For each cohort participant, the TDR data link was contacted to determine any deaths of cohort members. The TDR has kept records of all death certificates in Taiwan since 1971. The TDR provides cause-specific mortality data, classified by the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9 and ICD-10) (Supplementary Table S1). The observation period of this study was from 2000 to 2017.
2.5. Reference Population
Mortality data of the entire country’s general population of Taiwan were used for reference. Data were also obtained from TDR data.
2.6. Validation
We validated our method of identifying ESRD (catastrophic illness card for ESRD, ICD-9-CM code 585 or ICD-10-CM code N18.6) by analyzing the medical records (charts) of 100 patients in E-DA Hospital, a teaching hospital with 1100 beds in Taiwan. We randomly selected 50 patients with ESRD major illness registration cards from the patient claims database from 2008 to 2010 and 2015 to 2016. The positive predictive value of ESRD was estimated. The results showed that the positive predictive value of ESRD was 100%.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
To examine whether differences in mortality between dialysis (PD and HD) and the general population were present, we calculated the overall SMR and determined the underlying causes of death in these patients. The expected number of deaths was calculated according to the average death incidence rate of the general population from 2000 to 2017, standardized for sex and age, and then multiplied by the person-years of the HD or PD cohort. SMR confidence intervals were calculated using Byar’s method [54].
2.8. Ethics Statement
The access to the research data has been reviewed and approved by the National Institutes of Health Review Board.
The study was approved by the ethics committee/Institutional Review Board of E-DA Hospital (IRB number: EMRP-108-061).
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
There were 128,966 patients enrolled in this study, including 117,376 incident HD patients and 11,590 incident PD patients. Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics and clinical comorbidities of the HD and PD cohorts.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of patients with end-stage renal disease by treatment status.
3.2. Follow-Up
During the follow-ups, 5516 patients (4.2%) were censored because of kidney transplantation, and 75,297 (58.4%) patients (38,699 men and 36,598 women) died. No causes of death were missing or unknown.
3.3. Observed Number of Deaths and SMR in All Dialysis Patients
The most common cause of death in all dialysis patients were diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 21,197) and circulatory system (n = 15,017) and endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders (n = 14,584). The SMR of dialysis patients compared with the general population in Taiwan’s NHIRD after standardizing for sex, age, and period was 5.21 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.17–5.25) (Table 2). The neoplasms SMR was 2.11 (95% CI: 2.07–2.16); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 13.53 (95% CI: 13.3–13.75); the circulatory system SMR was 4.31 (95% CI: 4.24–4.38); the respiratory system SMR was 2.59 (95% CI: 2.52–2.66); the digestive system SMR was 6.1 (95% CI: 5.93–6.27); and the genitourinary system SMR was 27.22 (95% CI: 26.86–27.59).

Table 2.
All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of all dialysis patients.
3.4. Observed Number of Deaths and SMR in Different Dialysis Modalities
Among the 11,590 PD patients, 3814 patients (32.9%, 1865 men and 1949 women) died. The most common causes of death in PD patients were diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 1455) and circulatory system (n = 993) and endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders (n = 872). The SMR of all PD patients was 7.30 (95% CI: 7.07–7.54) (Table 3). The neoplasms SMR was 2.62 (95% CI: 2.38–2.87); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 23.46 (95% CI: 21.93–25.07); the circulatory system SMR was 8.55 (95% CI: 8.02–9.10); the respiratory system SMR was 5.51 (95% CI: 4.91–6.17); the digestive system SMR was 14.32 (95% CI: 13.05–15.68); and the genitourinary system SMR was 59.48 (95% CI: 56.46–62.62).

Table 3.
All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of peritoneal dialysis (PD) and hemodialysis (HD).
Among the 117,376 HD patients, 71,483 patients (60.9%, 36,835 men and 34,651 women) died. The most common causes of death in HD patients were diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 19,742) and circulatory system (n = 14,024) and endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders (n = 13,712). The SMR of all HD patients was 5.13 (95% CI: 5.09–5.17). The neoplasms SMR was 2.09 (95% CI: 2.05–2.14); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 13.17 (95% CI: 12.95–13.39); the circulatory system SMR was 4.16 (95% CI: 4.09–4.23); the respiratory system SMR was 2.50 (95% CI: 2.43–2.57); the digestive system SMR was 5.76 (95% CI: 5.59–5.93); and the genitourinary system SMR was 26.18 (95% CI: 25.81–26.54).
3.5. Observed Number of Deaths and SMR in Different Gender of PD Patients
Among the 5604 male PD patients, 1865 (33.2%) patients died (Supplementary Table S2 and Figure 1). The most common causes of death in male PD patients were diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 653) and circulatory system (n = 565) and endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders (n = 419). The SMR of male PD patients was 6.30 (95% CI: 6.02–6.60) (Supplementary Table S2 and Figure 2). The neoplasms SMR was 2.44 (95% CI: 2.14–2.77); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 24.25 (95% CI: 21.98–26.68); the circulatory system SMR was 8.82 (95% CI: 8.11–9.58); the respiratory system SMR was 4.60 (95% CI: 3.91–5.38); the digestive system SMR was 11.44 (95% CI: 10.00–13.02); and the genitourinary system SMR was 61.53 (95% CI: 56.90–66.43).
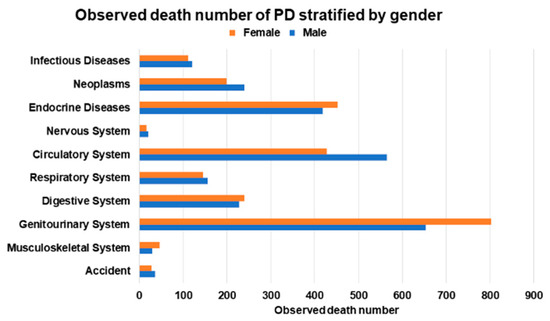
Figure 1.
Observed death number of peritoneal dialysis (PD) stratified by gender.
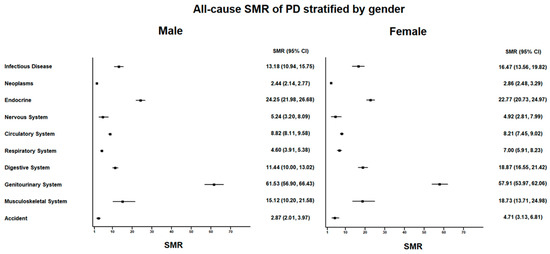
Figure 2.
All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients stratified by gender.
Among the 5986 female PD patients, 1949 patients (32.5%) died. The most common causes of death in female PD patients were diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 802); endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders (n = 453); and diseases of the circulatory system (n = 428). The SMR of female PD patients was 8.61 (95% CI: 8.23–9.00). The neoplasms SMR was 2.86 (95% CI: 2.48–3.29); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 22.77 (95% CI: 20.73–24.97); the circulatory system SMR was 8.21 (95% CI: 7.45–9.02); the respiratory system SMR was 7.00 (95% CI: 5.91–8.23); the digestive system SMR was 18.87 (95% CI: 16.55–21.42); and the genitourinary system SMR was 57.91 (95% CI: 53.97–62.06).
3.6. Observed Number of Deaths and SMR in Different Gender of HD Patients
Among the 60,186 male HD patients, 36,834 patients (61.2%) died (Supplementary Table S3 and Figure 3). The most common causes of death in male HD patients were diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 9383) and circulatory system (n = 7597) and endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders (n = 6560). The SMR of male HD patients was 4.75 (95% CI: 4.70–4.80) (Supplementary Table S3 and Figure 4). The neoplasms SMR was 1.97 (95% CI: 1.92–2.03); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 14.23 (95% CI: 13.89–14.58); the circulatory system SMR was 4.28 (95% CI: 4.19–4.38); the respiratory system SMR was 2.33 (95% CI: 2.24–2.42); the digestive system SMR was 5.34 (95% CI: 5.13–5.56); and the genitourinary system SMR was 28.57 (95% CI: 27.99–29.15).
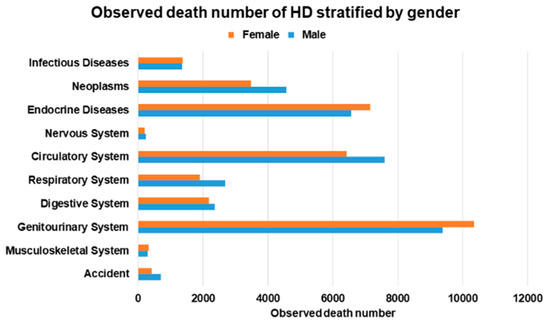
Figure 3.
Observed death number of hemodialysis (HD) stratified by gender.
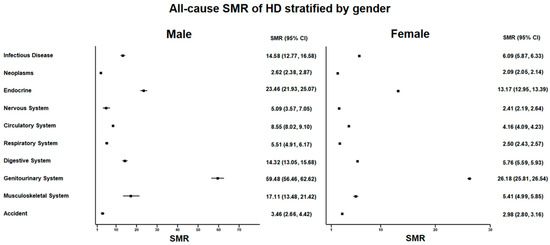
Figure 4.
All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of hemodialysis (HD) stratified by gender Figures.
Among the 57,190 female HD patients, 34,649 (60.5%) patients died. The most common cause of death in female HD patients were diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 10,359); endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders (n = 7152); and diseases of the circulatory system (n = 6427). The SMR of female HD patients was 5.61 (95% CI: 5.55–5.67). The neoplasms SMR was 2.27 (95% CI: 2.19–2.34); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 12.33 (95% CI: 12.05–12.62); the circulatory system SMR was 4.03 (95% CI: 3.93–4.13); the respiratory system SMR was 2.78 (95% CI: 2.66–2.91); the digestive system SMR was 6.28 (95% CI: 6.02–6.55); and the genitourinary system SMR was 24.33 (95% CI: 23.86–24.80).
3.7. PD and HD Patients Age Specific SMR
The SMR of PD patients aged 18–49 years was 12.93 (95% CI: 11.70–14.25), the SMR of PD patients aged 50–64 years was 9.76 (95% CI: 9.23–10.30), and the SMR of PD patients ≥ 65 years old was 5.91 (95% CI: 5.66–6.17) (Supplementary Table S4).
The SMR of HD patients aged 18–49 years was 14.18 (95% CI: 13.68–14.68), the SMR of HD patients aged 50–64 years was 10.50 (95% CI: 10.34–10.66), and the SMR of ≥ 65 years HD patients was 4.26 (95% CI: 4.22–4.29) (Supplementary Table S5).
4. Discussion
We studied a cohort of 128,966 incident dialysis patients, 58.4% of whom died during the follow-up period. The overall SMR (5.21; 95% CI: 5.17–5.25) in dialysis patients was substantially higher than that in the general population. In the cause-specific SMR, the neoplasms SMR was 2.11 (95% CI: 2.07–2.16); the endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity disorders SMR was 13.53 (95% CI: 13.31–13.75); the circulatory system SMR was 4.31 (95% CI: 4.24–4.38); the respiratory system SMR was 2.59 (95% CI: 2.52–2.66); the digestive system SMR was 6.1 (95% CI: 5.93–6.27); and the genitourinary system SMR was 27.22 (95% CI: 26.86–27.59). Except for genitourinary system diseases, the most common causes of death in dialysis patients were circulatory, endocrine/metabolic, and neoplasms diseases.
To the best of our knowledge, there are only a limited number of studies investigating the SMR in dialysis patients [37,38,39,40]. Villar et al. enrolled 3025 incident patients with ESRD between 1999 and 2003 and followed up on these patients until 2005. The overall SMR decreased during these 5 years from 7.4 to 5.2, and the SMR was higher 1.5-fold in women than in men [39]. Jager al. enrolled 123,407 incident patients with ESRD between 1994 and 2007; these patients underwent follow-up for a maximum of 3 years [37]. The SMR was 8.8 (95% CI: 8.6–9.0) in the cardiovascular system and 8.1 (95% CI: 7.9–8.3) in noncardiovascular systems compared with the general population. Wakasugi et al. enrolled 273,237 dialysis patients between 2008 and 2009 [40]. During the 2-year study period, the SMR for all-cause mortality was 4.6 (95% CI: 4.6–4.7) for the dialysis patients compared with the general population. Choi et al. enrolled 45,568 incident and 48,170 non-incident dialysis patients between 2009 and 2010 [38]. The overall SMR was 10.3 (95% CI: 10.0–10.6) in 2009 and 10.9 (95% CI: 10.7–11.2) in 2010.
Except for genitourinary system diseases, our results showed that cardiovascular disease is the principal cause of mortality in patients with ESRD. One reason is that patients with ESRD have high comorbidity rates, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, and these comorbidities are all cardiovascular disease risk factors. In addition to these traditional cardiovascular risk factors, there were non-traditional risk factors in dialysis patients, such as chronic volume overload, anemia, endothelial dysfunction, hyperparathyroidism, inflammation, malnutrition, and uremic toxin [55]. All these factors promote a high cardiovascular disease mortality rate in dialysis patients.
The reasons for a high neoplasms mortality rate are possible as follows: First, antioxidant capacity decreases in dialysis patients, which may lead to deoxyribonucleic acid damage because of the increase in reactive oxygen species [56]. Second, the increased production of cytokines during dialysis due to the bio-incompatibility of the dialysis membrane or dialysate has also been suggested to predispose to neoplasm [57]. Third, patients with ESRD are at risk for the accumulation of carcinogenic agents due to reduced renal elimination. Finally, the chronic inflammation status of dialysis patients may act together to accelerate neoplasm formation [58].
This study had some limitations. First, we did not have the personal information of enrolled cohorts, such as smoking history, family history, or laboratory parameters, which may be associated with specific causes of death. Second, misclassification of diseases may occur in an administrative database study. However, in our study, we included only patients with ESRD. The diagnoses of patients with ESRD are reliable because the catastrophic illness card for ESRD needs a formal review to confirm the diagnoses. Furthermore, long-term dialysis treatments are needed for patients with ESRD. Patients with ESRD can be exempted from copayment, and all these patients apply for catastrophic illness cards for ESRD. Most importantly, in our validation study, the results showed that the coding of PD and HD patients is credible. Third, misclassification of mortality causes may occur in TDR because most mortality causes depend on clinical diagnosis. Fourth, although obtained in a nationwide population-based cohort with clear SMR corresponding to different causes of death, our study findings do not add much to current knowledge, and the novelty may be limited.
In summary, this large nationwide population-based study showed that the overall SMR of dialysis patients was 5.21 compared with the general population. Except for genitourinary system diseases, the most common causes of death in dialysis patients were circulatory, endocrine/metabolic, and neoplasms diseases. Therefore, more attention should be paid to these diseases in clinical care.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijerph20032347/s1 Table S1: International Classification of Diseases Code; Table S2: All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of peritoneal dialysis (PD) stratified by gender; Table S3: All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of hemodialysis (HD) stratified by gender; Table S4: All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of peritoneal dialysis (PD) stratified by age; Table S5: All-cause standardized mortality ratio (SMR) of hemodialysis (HD) stratified by age.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, All authors; methodology, Y.-C.L.; software, S.-H.L.; validation, Y.-C.L.; formal analysis, S.-H.L.; investigation, Y.-C.L.; resources, Y.-C.L.; data curation, S.-H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.-C.L.; writing—review and editing, H.-H.W. and Y.-Y.C. and S.-H.L.; supervision, S.-H.L.; project administration, Y.-C.L.; funding acquisition, Y.-C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This was not an industry-supported study. This study was supported by EDAD2001, NCKUEDA11101, and EDAHP111023 from the Research Foundation of E-DA Hospital and National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Taiwan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the ethics committee/Institutional Review Board of E-DA Hospital (IRB number: EMRP-108-061).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent is waived by the ethics committee. The administrative data is held by governments; the data are used in compliance with local regulatory and legal frameworks that govern data use. The access to the research data has been reviewed and approved by the National Institutes of Health Review Board.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from National Health Insurance Research Database, but restrictions may apply to the availability of these data. However, processed datasets can be requested and made available from the authors with the permission of National Health Insurance Ad-ministration and Ministry of Health and Welfare.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Shih-Hann Tseng for critical discussion. This study is based in part on data from the National Health Insurance Research Database provided by the National Health Insurance Administration and Ministry of Health and Welfare and managed by National Health Research Institutes. The interpretation and conclusions contained herein do not represent those of National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, or National Health Research Institutes. We are grateful to Sheng-Hsiang Lin and Wan-Ni Chen for providing the statistical consulting services from the Biostatistics Consulting Center, Clinical Medicine Research Center, National Cheng Kung University Hospital. This research was also supported in part by the Higher Education Sprout Project, Ministry of Education to the Headquarters of University Advancement at National Cheng Kung University (NCKU).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Himmelfarb, J.; Vanholder, R.; Mehrotra, R.; Tonelli, M. The current and future landscape of dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Bhave, N.; Dietrich, X.; Ding, Z.; Eggers, P.W.; et al. US Renal Data System 2018 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73 (Suppl. S1), A7–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorca, R.; Cancarini, G.C.; Brunori, G.; Zubani, R.; Camerini, C.; Manili, L.; Movilli, E. Comparison of long-term survival between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Adv. Perit. Dial. 1996, 12, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.A.; Lamping, D.L.; Brown, E.A.; Constantinovici, N.; North Thames Dialysis Study (NTDS) Group. Clinical outcomes and quality of life in elderly patients on peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2002, 22, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Heaf, J.G.; Lokkegaard, H.; Madsen, M. Initial survival advantage of peritoneal dialysis relative to haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2002, 17, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termorshuizen, F.; Korevaar, J.C.; Dekker, F.W.; Van Manen, J.G.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: Comparison of adjusted mortality rates according to the duration of dialysis: Analysis of The Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis 2. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2851–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, K.C.; Lui, S.L.; Lo, W.K. Comparison of long-term survival (beyond 12 years) in patients on peritoneal dialysis and on hemodialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2003, 23 (Suppl. S2), S104–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, A.G.; Murthy, B.V.; Molony, D.A. Survival differences between peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis among “large” ESRD patients in the United States. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaar, B.G.; Coresh, J.; Plantinga, L.C.; Fink, N.E.; Klag, M.J.; Levey, A.S.; Levin, N.W.; Sadler, J.H.; Kliger, A.; Powe, N.R. Comparing the Risk for Death with Peritoneal Dialysis and hemodialysis in a national cohort of patients with chronic kidney disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircescu, G.; Garneata, L.; Florea, L.; Cepoi, V.; Capsa, D.; Covic, M.; Gherman-Caprioara, M.; Gluhovschi, G.; Golea, O.S.; Barbulescu, C.; et al. The success story of peritoneal dialysis in Romania: Analysis of differences in mortality by dialysis modality and influence of risk factors in a national cohort. Perit. Dial. Int. 2006, 26, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonesh, E.F.; Snyder, J.J.; Foley, R.N.; Collins, A.J. Mortality studies comparing peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: What do they tell us? Kidney Int. Suppl. 2006, 70, S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liem, Y.S.; Wong, J.B.; Hunink, M.G.; de Charro, F.T.; Winkelmayer, W.C. Comparison of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis survival in The Netherlands. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Cheng, K.F.; Wu, H.D. Survival analysis: Comparing peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis in Taiwan. Perit. Dial. Int. 2008, 28 (Suppl. S3), S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanabria, M.; Munoz, J.; Trillos, C.; Hernandez, G.; Latorre, C.; Diaz, C.S.; Murad, S.; Rodriguez, K.; Rivera, A.; Amador, A.; et al. Dialysis outcomes in Colombia (DOC) study: A comparison of patient survival on peritoneal dialysis vs hemodialysis in Colombia. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2008, 73, S165–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Taiwan Society of Nephrology. Incidence, prevalence and mortality trends of dialysis end-stage renal disease in Taiwan from 1990 to 2001: The impact of national health insurance. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2008, 23, 3977–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, S.P.; Marshall, M.R.; Johnson, D.W.; Polkinghorne, K.R. Relationship between dialysis modality and mortality. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinhandl, E.D.; Foley, R.N.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Arneson, T.J.; Snyder, J.J.; Collins, A.J. Propensity-matched mortality comparison of incident hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, R.; Chiu, Y.W.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Bargman, J.; Vonesh, E. Similar outcomes with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sens, F.; Schott-Pethelaz, A.M.; Labeeuw, M.; Colin, C.; Villar, E. Survival advantage of hemodialysis relative to peritoneal dialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease and congestive heart failure. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Luijtgaarden, M.W.; Noordzij, M.; Stel, V.S.; Ravani, P.; Jarraya, F.; Collart, F.; Schon, S.; Leivestad, T.; Puttinger, H.; Wanner, C.; et al. Effects of comorbid and demographic factors on dialysis modality choice and related patient survival in Europe. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.K.; Hsu, C.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Chen, P.C.; Huang, C.C.; Li, T.C.; Sung, F.C. A comparative assessment of survival between propensity score-matched patients with peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis in Taiwan. Medicine 2012, 91, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordzij, M.; Jager, K.J. Survival comparisons between haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 3385–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeates, K.; Zhu, N.; Vonesh, E.; Trpeski, L.; Blake, P.; Fenton, S. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are associated with similar outcomes for end-stage renal disease treatment in Canada. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukowsky, L.R.; Mehrotra, R.; Kheifets, L.; Arah, O.A.; Nissenson, A.R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Comparing mortality of peritoneal and hemodialysis patients in the first 2 years of dialysis therapy: A marginal structural model analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madziarska, K.; Weyde, W.; Penar, J.; Zukowska-Szczechowska, E.; Krajewska, M.; Golebiowski, T.; Klak, R.; Zmonarski, S.; Kozyra, C.; Klinger, M. Different mortality predictor pattern in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis diabetic patients in 4-year prospective observation. Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw. Online 2013, 67, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaf, J.G.; Wehberg, S. Relative survival of peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis patients: Effect of cohort and mode of dialysis initiation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircescu, G.; Stefan, G.; Garneata, L.; Mititiuc, I.; Siriopol, D.; Covic, A. Outcomes of dialytic modalities in a large incident registry cohort from Eastern Europe: The Romanian Renal Registry. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, S.; Kim, K.H.; Ryu, D.R.; Kim, H.; Joo, K.W.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.K. Dialysis Modality and Mortality in the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Khin, L.W.; Lau, T.; Chua, H.R.; Vathsala, A.; Lee, E.; Luo, N. Hemodialysis versus Peritoneal Dialysis: A Comparison of Survival Outcomes in South-East Asian Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; McLeggon, J.A.; Mehta, N.; Leung, S.; Barta, V.; McGinn, T.; Nesrallah, G. Mortality and Hospitalizations in Intensive Dialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2018, 5, 2054358117749531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, J.J.; Nelson, M.R.; Woods, R.L.; Lockery, J.E.; Wolfe, R.; Reid, C.M.; Kirpach, B.; Shah, R.C.; Ives, D.G.; Storey, E.; et al. Effect of Aspirin on All-Cause Mortality in the Healthy Elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.J.; Perl, J.; Tennankore, K.K. Survival comparisons of intensive vs. conventional hemodialysis: Pitfalls and lessons. Hemodial. Int. 2018, 22, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.J.; Zhou, H.; Shi, J.; Shaw, S.F.; Henry, S.L.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jacobsen, S.J. Disparities in early mortality among chronic kidney disease patients who transition to peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis with and without catheters. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, E.; Chan, C.T.; Perl, J. Dialysis modality and survival: Done to death. Semin. Dial. 2018, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.; Ravani, P.; Oliver, M.J.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.; Venturato, L.; Garg, A.X.; Quinn, R.R. Comparison of Patient Survival Between Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Among Patients Eligible for Both Modalities. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, N.R.; Son, S.K.; Kim, J.; Sul, A.R.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.T.; Lee, J.P.; Ryu, D.R. Comparative study of peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis on the clinical outcomes in Korea: A population-based approach. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, D.J.; Grootendorst, D.C.; Jager, K.J.; van Dijk, P.C.; Tomas, L.M.; Ansell, D.; Collart, F.; Finne, P.; Heaf, J.G.; De Meester, J.; et al. Cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality among patients starting dialysis. JAMA 2009, 302, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Pyo Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Tak Park, J.; Hoon Kim, K.; Sik Ahn, H.; Jae Hann, H.; Ryu, D.R. Excess mortality among patients on dialysis: Comparison with the general population in Korea. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2014, 33, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, E.; Remontet, L.; Labeeuw, M.; Ecochard, R. Effect of age, gender, and diabetes on excess death in end-stage renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakasugi, M.; Kazama, J.J.; Yamamoto, S.; Kawamura, K.; Narita, I. Cause-specific excess mortality among dialysis patients: Comparison with the general population in Japan. Apher. Dial. 2013, 17, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Lin, J.T.; Chen, T.T.; Wu, M.S.; Wu, C.Y. Long-term risk of recurrent peptic ulcer bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis: A 10-year nationwide cohort study. Hepatology 2012, 56, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Lin, J.T.; Ho, H.J.; Kao, Y.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Hsiao, N.W.; Wu, M.S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wu, C.Y. Antiviral treatment for hepatitis C virus infection is associated with improved renal and cardiovascular outcomes in diabetic patients. Hepatology 2013, 59, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Lai, M.S.; Syu, C.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Tseng, F.Y. Accuracy of diabetes diagnosis in health insurance claims data in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. Taiwan Yi Zhi 2005, 104, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Li, C.Y.; Lai, M.L. Validating the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke in a National Health Insurance claims database. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. Taiwan Yi Zhi 2015, 114, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; Kao, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lai, M.L. Validation of the National Health Insurance Research Database with ischemic stroke cases in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2011, 20, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Lin, J.W.; Wu, L.C.; Lai, M.S. Angiotensin receptor blockade and risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide case-control study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3001–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.H.; Lin, T.Y.; Huang, W.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Kao, C.H. Pneumoconiosis increases the risk of peripheral arterial disease: A nationwide population-based study. Medicine 2015, 94, e911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Hung, S.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Wang, H.K.; Lin, C.W.; Chang, M.Y.; Ho, L.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Wu, C.F.; Chen, H.C.; et al. Different Risk of Common Gastrointestinal Disease Between Groups Undergoing Hemodialysis or Peritoneal Dialysis or With Non-End Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Hung, S.Y.; Wang, H.K.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, S.W.; Chang, M.Y.; Ho, L.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Liou, H.H.; et al. Sleep apnea and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Sleep 2015, 38, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Hung, S.Y.; Wang, H.K.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, H.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Sung, J.M.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Lin, S.H. Is there different risk of cancer among end-stage renal disease patients undergoing hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis? Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Hung, S.Y.; Wang, H.K.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, H.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Wu, C.F.; Sung, J.M.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Lin, S.H. Male Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis Have a Higher Risk of Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.H.; Lee, M.C.; Chou, M.C. Accuracy of cause-of-death coding in Taiwan: Types of miscoding and effects on mortality statistics. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 29, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Insurance Research Database. Available online: http://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/Data_Subsets.html (accessed on 11 December 2016).
- Breslow, N.E.; Day, N.E. Statistical methods in cancer research. Volume II—The design and analysis of cohort studies. IARC Sci. Publ. 1987, 87, 590–591. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, E.; Mitsnefes, M.M. Cardiovascular disease in young adults with incident ESRD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Suemizu, H.; Nomoto, Y.; Sakai, H.; Katsuoka, Y.; Kawamura, N.; Moriuchi, T. Plasma glutathione peroxidase deficiency caused by renal dysfunction. Nephron 1996, 73, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Akizawa, T.; Kinugasa, E.; Koshikawa, S. Increased risk of malignancy and blood-membrane interactions in uraemic patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1994, 9 (Suppl. S2), 162–164. [Google Scholar]
- Vamvakas, S.; Bahner, U.; Heidland, A. Cancer in end-stage renal disease: Potential factors involved—Editorial. Am. J. Nephrol. 1998, 18, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).