Abstract
The aim of this study is to provide a brief summary of the epidemiological data on obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) diagnosis and therapy in different regions of Poland from 2010 to 2019. We performed a retrospective study in the sleep center of the Department of Sleep Medicine and Metabolic Disorders, Medical University of Lodz, Poland. We requested data from the National Health Service concerning the number of new diagnoses of OSAS, the polysomnographies (PSGs) that were performed, and reimbursements of positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy in each region of Poland in the period 2010–2019. The constant increase in the number of polysomnographies performed and PAP reimbursements suggests the need to create a national network between regional sleep centers to provide proper care for patients with OSAS, and PAP therapy.
1. Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete breathing cessation during sleep due to pharyngeal airway closure [1]. Common symptoms of OSAS include excessive daytime sleepiness, loud snoring, recurrent arousals during sleep, as well as morning headaches [2]. The prevalence of OSAS in the adult population is estimated to be 3–7% [3]; however, some recent studies suggest that OSAS is considerably more frequent and affects up to approximately 84% of men and 61% of women [4,5]. Pływaczewski et al. estimated the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in Poland at 7.5% on the basis of a group of 676 patients from Warsaw [6]. To our knowledge, information about general epidemiological data on OSAS diagnosis in Poland is limited. We wish to highlight that this is the first OSAS epidemiological study performed in Poland.
To the major risk factors for OSAS we can include obesity, hypertension, male sex, and age. Moreover, OSAS leads to the development of many severe health consequences, such as cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, as well as endocrine and metabolic disorders [2,7,8,9,10,11]. Furthermore, OSAS is related to impairment in work performance and a higher risk of occupational and industrial accidents [12,13]. The number of possible consequences of OSAS shows the importance of both proper diagnosis and adequate treatment.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) defined four types of sleep study devices used for diagnostic testing for sleep disorders [14,15,16]. A Type I study, which is considered as the “gold standard” in OSAS diagnosis, entails polysomnography (PSG). This is an attended, full laboratory examination, which uses at least 7 monitoring channels: electroencephalography, electrocardiography, electromyography, electrooculography, airflow, oxygen saturation, and respiratory effort. However, there are several limitations of PSG, such as low accessibility, high cost, and requirement of highly trained technologists for data collection and interpretation. A Type II study constitutes an unattended, full polysomnography (with at least 7 channels); therefore, it does not require access to a sleep laboratory. A Type III study entails modified, portable apnea testing, which measures at least four parameters: oxygen saturation, two respiratory variables (respiratory movement and airflow), and a cardiac variable (heart rate or electrocardiogram). A Type IV study measures only one or two parameters, usually oxygen saturation or airflow. The OSAS diagnosis is based on the apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) during nocturnal polysomnography. The AHI is defined as the number of apneas and hypopneas per hour of sleep and represents the OSAS severity: mild (AHI of 5–15 events/h), moderate (AHI of 15–30 events/h), and severe (AHI > 30 events/h) [17,18,19].
The AASM propose several options for OSAS treatment in adult patients: positive airway pressure (PAP) treatment options; oxygen therapy; oral appliance therapy; surgical treatment options; hypoglossal nerve stimulators; nasal resistive valves; and pharmacological therapies. Due to the significant body of evidence supporting its impact on clinical outcomes, PAP is considered as a first-line therapy for the management of OSAS [14]. The main limitation to the efficacy of PAP therapy is the willingness of patients to accept PAP therapy up front and, in those who do, remaining adherent to therapy over time. According to the current authors’ knowledge, there are no national data regarding compliance of PAP therapy in the Polish population.
Initially, we performed a retrospective study in the sleep center of the Department of Sleep Medicine and Metabolic Disorders, Medical University of Lodz, Poland. However, we realized that there is neither national nor regional data about the general epidemiology of OSAS in Poland. Therefore, we requested data from the National Health Service to further study this field. We hope that a deeper understanding of this issue will indicate some specific needs and clarify problems associated with diagnostic incidence and treatment of OSAS in Poland, providing material for further discussion and improvement of sleep-related healthcare by the development of dedicated systemic solutions.
The aim of this study is to provide a brief summary of the epidemiological data on the incidence of OSAS diagnosis and prescribed therapy in different regions of Poland from 2010 to 2019.
2. Materials and Methods
We requested raw epidemiological data from the National Health Service to answer the following questions:
- How many new diagnoses of OSAS have been made during 2010–2019 in each region of Poland?
- How many PSGs have been performed during 2010–2019 in each region of Poland?
- How many reimbursements of PAP therapy have occurred during 2010–2019 in each region of Poland?
The National Health Service in Poland gathers statistical data exclusively on Type I devices; other types of devices (Type II–IV) were excluded from the study. A PSG performed as a nocturnal PAP titration was excluded from the study as well.
The data regarding number of habitants in each region of Poland were obtained from the Central Statistical Office for 2019 and we assumed no significant changes among number of habitants in each of the regions during the previous 10 years. Frequencies in the separate regions were compared using multi-way tables and chi2 tests.
3. Results
All variables of interest are listed in Table 1 and Figure 1. The total number of new diagnoses of OSAS, polysomnographies, and reimbursements were calculated per 100,000 habitants in each of the regions of Poland. The prevalence of OSAS diagnosis per 100,000 habitants is highest in the regions Kujawsko-Pomorskie (N = 1328), Świętokrzyskie (N = 1028), and Mazowieckie (N = 918). A PSG was performed the most frequently in the regions Świętokrzyskie (N = 910), Lubuskie (N = 803), and Opolskie (N = 803). PAP therapy was the most common in the regions Kujawsko-Pomorskie (N = 265), Świętokrzyskie (N = 257), and Lubuskie (N = 244).

Table 1.
Number of patients with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), the number of polysomnographies, and the number of reimbursements of positive airway pressure (PAP) treatment in all regions of Poland from 2010 to 2019. The bold in number is summary of all data provided.
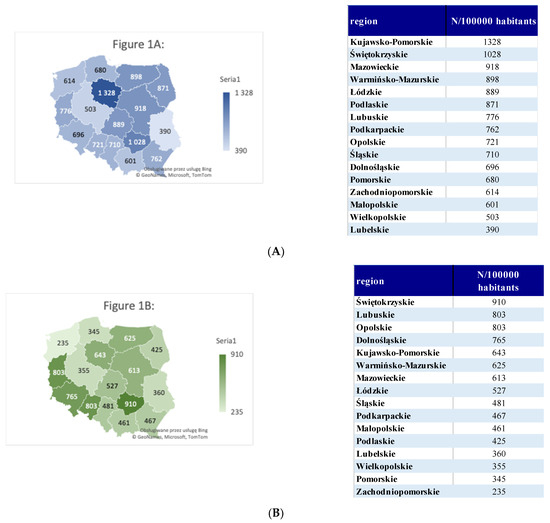
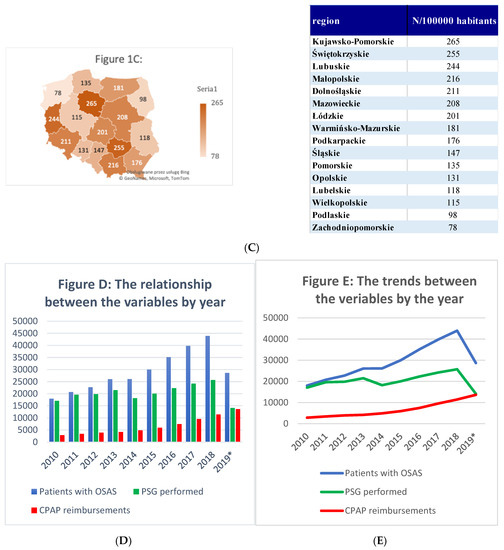
Figure 1.
Number of patients with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), the number of polysomnographies, and the number of reimbursements of positive airway pressure (PAP) treatment in regions of Poland from 2010 to 2019. (A) Number of patients with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome during 2010–2019 in all regions of Poland. (B) Number of polysomnographies during 2010–2019 in all regions of Poland. (C) Number of reimbursements by the National Health Service for the positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy for obstructive sleep apnea. (D,E) The relationship and the trends between the number of patients with an OSAS diagnosis, the PSG performed, and PAP reimbursements for the years 2010–2019. * 2019 from January to June.
We observed statistically significant differences among regions according to the number of new diagnoses of OSAS (chi2 = 22,052, p < 0.001), polysomnographies (chi2 = 19,242, p < 0.001), and reimbursements (chi2 = 5631, p < 0.001).
The diagnosis of OSAS assumes an AHI of >5 events/h. The data do not indicate the severity of the disease.
4. Discussion
Our data provide a general overlook of the epidemiology of diagnosis and PAP therapy of OSAS in Poland from 2010 to 2019. Our data suggest that, depending on the region, OSAS diagnoses range from 390 to 1328/100,000 habitants (p < 0.001). As expected, the regions differ significantly according to the number of new diagnoses of OSAS, polysomnographies, and PAP reimbursements. The economic, social, and demographic differences will be investigated in additional studies. To the author’s knowledge, this is the first study that summarizes the epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea in Poland and provides a general overlook of the epidemiological data.
The data highlight that, in each region of Poland, the number of performed PSGs increases continuously with every year, as presented in Figure 1D,E. This trend is followed by an increase in the number of newly diagnosed OSAS cases. The number of reimbursements of PAP therapy is lower than the number of performed PSGs and diagnoses of OSAS. However, this trend was not observed for the Kujawsko-Pomorskie, Lubuskie, Łódzkie, Małopolskie, Mazowieckie, and Śląskie regions, where the increase in the number of PAP reimbursements is accompanied by a decrease in the number of polysomnographies performed. One of the reasons that can be discussed in this context is an increasing number of polygraphies (PGs), which are often performed instead of an PSG. Indeed, PG is one of the most available tools to screen for OSAS, but is limited by the lack of professional training for physicians to perform and score the PG results, which may lead to diagnostic pitfalls.
Another important issue is that, in Poland, there are just a few sleep centers specialized in sleep-related disorders other than sleep-related breathing disorders, which may lead to limited comprehensiveness of the diagnostic process.
There are no data on compliance with PAP usage at home. Non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIV) is an important player in this field. Implementation of the “National program to reduce mortality from chronic respiratory diseases by creating NIV units in the years 2016–2019” (acronym: POL-VENT) provided numerous departments of general pulmonology with PSG and PG equipment. This fact may explain a continuous increase in the number of PSGs performed, as well as the number of new patients with an OSAS diagnosis. The constant increases in the number of polysomnographies performed and PAP reimbursements suggest the need to create a national network between regional sleep centers to provide proper care for patients with OSAS, and PAP therapy. It should be discussed whether there are conditions to propose a new medical specialization in sleep medicine, as what the AASM or European Sleep Research Society (ESRS) provides, that would emphasize the need for providing diagnoses and therapy to conditions other than sleep-related breathing disorders. Undoubtedly, obtaining an international, European-level certification would be beneficial for increasing the knowledge and standards of sleep medicine in Poland. Such an opportunity is offered by the ESRS in the form of an examination in sleep medicine, the passing of which results in the title of somnologist—an expert in sleep medicine. Currently, the database of this society shows that there is only one certified somnologist in Poland. It also seems reasonable to focus on creating national guidelines on sleep medicine, especially on sleep diagnostic procedures, to regulate, among others, the usage of PG.
Our study has some limitations. First of all, the data provided in this summary are based on data available from the National Health Service and do not refer to particular sleep centers. There also are no data on diagnostic types other than PSG, distinguished by the AASM to make a diagnosis of OSAS. Moreover, the data do not cover the private sector, which is a potentially significant player in this field. Furthermore, as we previously mentioned, the data do not provide detail on the severity of the disease.
5. Conclusions
To summarize, the data in this study underestimate the epidemiology of OSAS in Poland but illustrate the overall landscape of this issue and open the debate in this field.
Author Contributions
The contribution of the first two authors is equivalent and accounts for 80% of the contribution to this research; W.K. conceived the idea of the study; W.K. and A.K. wrote the manuscript; W.K., A.K., A.M. and U.K. were involved in data collection and creation of the database; P.B. and A.B. were involved in reviewing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Medical University of Lodz, Poland (protocol code RNN/393/19/KE 12 September 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository that does not issue DOIs Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found in the National Health Service in Poland.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Spicuzza, L.; Caruso, D.; Di Maria, G. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and its management. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2015, 6, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spałka, J.; Kędzia, K.; Kuczyński, W.; Kudrycka, A.; Małolepsza, A.; Białasiewicz, P.; Mokros, Ł. Morning Headache as an Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Symptom among Sleep Clinic Patients—A Cross-Section Analysis. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjabi, N.M. The epidemiology of adult obstructive sleep apnea. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzer, R.; Marti-Soler, H.; Haba-Rubio, J. Prevalence of sleep apnoea syndrome in the middle to old age general population. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, e5–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K.A.; Lindberg, E. Obstructive sleep apnea is a common disorder in the population—A review on the epidemiology of sleep apnea. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pływaczewski, R.; Bednarek, M.; Jonczak, L.; Zielinski, J. Sleep-disordered breathing in a middle-aged and older Polish urban population. J. Sleep Res. 2008, 17, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokros, Ł.; Kuczyński, W.; Gabryelska, A.; Franczak, Ł.; Spałka, J.; Białasiewicz, P. High Negative Predictive Value of Normal Body Mass Index for Obstructive Sleep Apnea in the Lateral Sleeping Position. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyński, W.; Gabryelska, A.; Mokros, Ł.; Białasiewicz, P. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and hypothyroidism—merely concurrence or causal association? Pneumonol. Alergol. Polska 2016, 84, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, R.D.; Antic, N.A.; Heeley, E.; Luo, Y.; Ou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Mediano, O.; Chen, R.; Drager, L.F.; Liu, Z.; et al. CPAP for Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, F.J.; Young, T.B.; Lind, B.K.; Shahar, E.; Samet, J.M.; Redline, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Newman, A.B.; Lebowitz, M.D.; Pickering, T.G.; et al. Association of Sleep-Disordered Breathing, Sleep Apnea, and Hypertension in a Large Community-Based Study. JAMA 2000, 283, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaggi, H.K.; Concato, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Lichtman, J.H.; Brass, L.M.; Mohsenin, V. Obstructive Sleep Apnea as a Risk Factor for Stroke and Death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accattoli, M.P.; Muzi, G.; dell’Omo, M.; Mazzoli, M.; Genovese, V.; Palumbo, G.; Abbritti, G. Infortuni e performances sul lavoro in lavoratori affetti da sindrome delle apnee ostruttive nel sonno (OSAS) [Occupational accidents, work performance and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS)]. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2008, 30, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tregear, S.; Reston, J.; Schoelles, K.; Phillips, B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Risk of Motor Vehicle Crash: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundel, V.; Shah, N. Impact of Portable Sleep Testing. Sleep Med. Clin. 2017, 12, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collop, N.; Anderson, W.M.; Boehlecke, B.; Claman, D.; Goldberg, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Hudgel, D.; Sateia, M.; Schwab, R. Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Unattended Portable Monitors in the Diagnosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adult Patients. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2007, 3, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kales, A.; Rechtschaffen, A. A Manual of Standardized Terminology, Techniques and Scoring System for Sleep Stages of Human Subjects; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for Scoring Respiratory Events in Sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEG arousals: Scoring rules and examples: A preliminary report from the Sleep Disorders Atlas Task Force of the American Sleep Disorders Association. Sleep 1992, 15, 173–184. [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).