Abstract
Two new isosarcophine derivatives, cherbonolides M (1) and N (2), were further isolated from a Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri. The planar structure and relative configuration of both compounds were established by the detailed analysis of the IR, MS, and 1D and 2D NMR data. Further, the absolute configuration of both compounds was determined by the comparison of CD spectra with that of isosarcophine (3). Notably, cherbonolide N (2) possesses the unique cembranoidal scaffold of tetrahydrooxepane with the 12,17-ether linkage fusing with a γ-lactone. In addition, the assay for cytotoxicity of both new compounds revealed that they showed to be noncytotoxic toward the proliferation of A549, DLD-1, and HuCCT-1 cell lines. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory activities of both metabolites were carried out by measuring the N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLF/CB)-induced generation of superoxide anion and elastase release in the primary human neutrophils. Cherbonolide N (2) was found to reduce the generation of superoxide anion (20.6 ± 6.8%) and the elastase release (30.1 ± 3.3%) in the fMLF/CB-induced human neutrophils at a concentration of 30 μM.
1. Introduction
The chemical constituents for soft corals of the genera Sarcophyton have been well studied. According to the statistics, more than 500 marine natural products have been isolated from this genus during the past two decades. Among these metabolites, over 300 diterpenoids with the 14 membered cembranoidal skeleton were discovered [1]. Therefore, the Sarcophyton genus has been frequently considered to be an important source of the 14 membered ring diterpenoidal skeleton [2,3,4]. These secondary metabolites help the organisms to defend themselves against the predators and adapt to the environment stress [5]. Furthermore, some of the isolates have been demonstrated to possess various biological activities, such as cytotoxic [6,7,8,9,10,11,12], anti-inflammatory [6,7,13,14,15,16,17,18], neuroprotective [19], antibacterial [19], and antiviral activities [12,20]. The diversified structures and various biological applications of marine natural products thus prompt us to further explore the secondary metabolites from organisms of the Sarcophyton genus.
Sarcophine, the dihydrofuran-containing cembranoidal diterpene, is one of the major metabolites in the soft corals of Sarcophyton genera [21]. Bernstein et al. discovered this metabolite from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum in 1974 [22]. Subsequently, the absolute configuration of sarcophine was determined by Kashman et al. in 1977 [23]. Furthermore, Frincke et al. indicated that sarcophine was converted from the other 14 membered diterpene, sarcophytoxide, by auto-oxidation in 1980 [24]. Isosarcophine, an isomer of sarcophine, was proven to be converted from isosarcophytoxide via auto-oxidation and isolated from the soft coral Sinularia mayi by Kusumi et al. in 1990 [25]. It was found that isosarcophine showed significant cytotoxicities toward some cancer cell lines [25,26].
Our previous investigation of soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri had contributed to the isolation of 13 new cembranoids derived from the isosarcophine [13,14]. In the present study, the continuous chemical investigation of S. cherbonnieri resulted in the discovery of two new isosarcophine derivatives, cherbonolides M (1) and N (2) as shown in Figure 1. The planar structures and relative configurations of both compounds were elucidated by analyzing the infrared (IR), MS, and 1D and 2D NMR data. Furthermore, to determine the absolute configurations, the circular dichroism (CD) spectra of both new compounds were measured and compared with those of isosarcophine (3). Moreover, in order to discover bioactive natural products for the development of drug leads, the cytotoxicity against human lung adenocarcinoma (A549), human colorectal adenocarcinoma (DLD-1), and human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (HuCCT-1) was examined. In addition, the anti-inflammatory activity of both isolates was investigated by measuring the N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLF/CB)-induced generation of superoxide anion and elastase release in the primary human neutrophils.
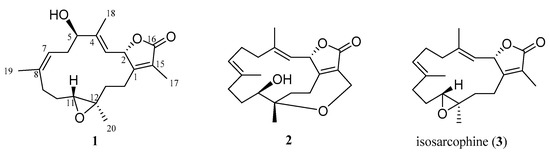
Figure 1.
Marine natural products 1–3 isolated from the soft coral S. cherbonnieri.
2. Results and Discussion
The chemical structures of metabolites 1 and 2 were elucidated by analyzing the MS, IR, CD, and 1D and 2D NMR data (Supplementary Materials Figures S1–S32). Additionally, the 13C and 1H chemical shifts of 1 and 2 are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
13C and 1H NMR spectroscopic data of 1 and 2.
Compound 1, cherbonolide M, was isolated as a colorless oil. The molecular formula of 1 was C20H28O4 deduced from the pseudomolecular ion peak at m/z 355.1882 (calculated 355.1880, C20H28O4Na) in the high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS). Its IR spectrum showed the absorptions at 3445 and 1749 cm–1, indicating the presence of hydroxy and ester groups. The 13C and distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer (DEPT) spectra displayed 20 carbon signals, including four methyls, five methylenes, five methines, and six quaternary carbons. 1H and 13C NMR spectra showed the signals of an α-methyl-α, β-unsaturated-γ-lactone (δH 5.64, d, J = 10.4 Hz; 1.78, s; δC 174.6, C; 162.4, C; 123.5, C; 78.4, CH; 8.6, CH3), two trisubstituted double bonds (δH 4.98, d, J = 10.4 Hz; δC 123.4, CH; 147.5, C; δH 4.98, d, J = 10.8 Hz; δC 122.5, CH; 134.9, C), an oxygen-bearing methine (δH 4.21, dd, J = 10.8, 5.2 Hz; δC 77.5, CH), and an epoxy groups (δH 2.45, d, J = 10.8 Hz; δC 62.0, CH and 61.1, C).
The planar structure of 1 was established according to the analysis of 2D NMR spectra as shown in Figure 2. The correlation spectroscopy (COSY) spectrum showed four partial moieties from the correlations of H-2 to H-3, H-5 via H2-6 to H-7, H2-9 via H2-10 to H-11, and H2-13 to H2-14. These partial structures were assembled by heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) correlations from H3-17 to C-1, C-15, C-16; H3-18 to C-3, C-4, C-5; H3-19 to C-7, C-8, C-9; H3-20 to C-11, C-12, C-13; and H2-14 to C-1 and C-2. Furthermore, the NMR spectroscopic data of 1 were compared with those of the previous metabolite cherbonolide H [13] for structural elucidation. It was shown that compound 1 should possess a hydroxy group at C-5 and a 7,8-trisubstituted double bond from this NMR data comparison. According to the above evidence, the gross structure of 1 was elucidated.
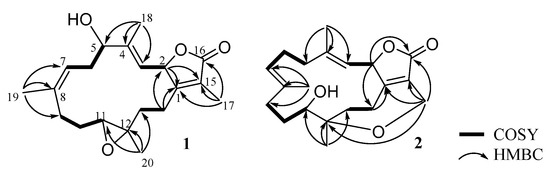
Figure 2.
COSY and selective HMBC correlations of 1 and 2.
The relative configuration of 1 was established by analyzing the nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) spectrum, as shown in Figure 3. Assuming the β-orientation of H-2 (δH 5.64, d, J = 10.4 Hz), it was found the NOE correlations of H-2 with H-13β (δH 1.04, t, J = 11.2 Hz), H-13β with H-11 (δH 2.45, d, J = 10.8 Hz), and H-11 with H3-19 revealed the β-orientation of H-11. By contrast, H-2 did not exhibit NOE interaction with H-3, revealing the downward orientation of H-3. The NOE correlation of H-3 (δH 4.98, d, J = 10.4 Hz) with H-5 (δH 4.21, dd, J = 10.8, 5.2 Hz), H-5 with H-7 (δH 4.98, d, J = 10.8 Hz), H-7 with H-9α (δH 2.08, m), and H-9α with H3-20 (δH 1.28, s), suggesting the α-orientation of H-5 and H3-20. Further, the E geometry of C-3/C-4 and C-7/C-8 was determined from the upfield shifted methyl groups of C-18 (δC 10.3) and C-19 (δC 14.9). The 3J values between H-2 and H-3 (10.4 Hz), H-5 and H-6β (10.8 Hz), and H-6β and H-7 (10.8 Hz) were found to be consistent with the relative configuration shown in Figure 3. In order to compare the NMR data with those of 2 and other isosarcophine-derived metabolites measured in C6D6 of our previous studies [13,14], the 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 1 were also measured, and the results (Table 1) can further confirm the structure of 1 was elucidated. The absolute configuration of 1 was determined by comparison the CD spectrum of 1 with that of isosarcophine (3), as shown in Figure 4. The CD spectrum of 1 showed the positive Cotton effect at 227.0 nm (Δε = +34.8) for the π–π* transition, while the negative Cotton effect at 245.5 nm (Δε = −15.6) for the n–π* transition. This evidence demonstrated the fact of 2S-configuration [27,28]. Due to the biogenesis of 1 from isosarcophine, the absolute configuration of 1 was defined as 2S,5R,11R,12R,3E,7E.
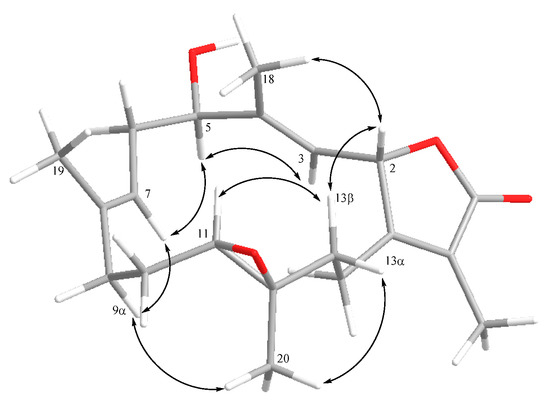
Figure 3.
Selective NOE correlations of 1.
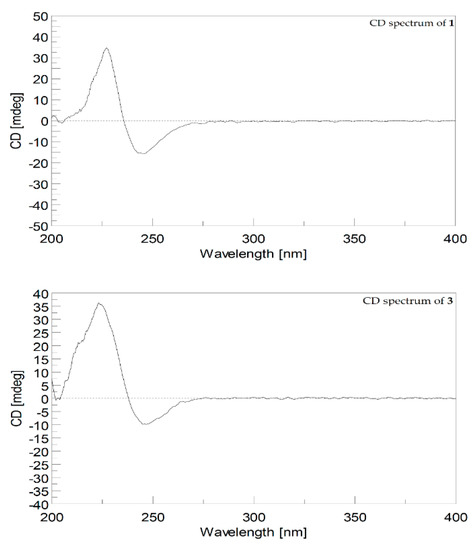
Figure 4.
CD spectrum (1.2 × 10–4 M, MeOH) of 1 and CD spectrum (1.6 × 10–4 M, MeOH) of 3.
Cherbonolide N (2) was afforded as a colorless oil. Its HRESIMS data showed the sodiated ion peak at m/z 355.1880 [M + Na]+ (calculated 355.1879, C20H28O4Na), indicating the molecular formula of C20H28O4 and seven degrees of unsaturation. The IR spectrum showed the absorption peaks at 3481 and 1741 cm−1, suggesting the presence of the hydroxy group and ester group. In the 13C spectrum, 2 showed 20 carbon signals, assigning to three methyls, seven methylenes, four methines, and six quaternary carbons with the DEPT spectrum assistance. 1H and 13C NMR spectra revealed the signals of a carbonyl group (δC 172.3, C), a tetrasubstituted double bond (δC 166.1, C; 128.1, C), two trisubstituted double bonds (δH 4.50, d, J = 8.4 Hz; δC 120.7, CH; 139.2, C; δH 4.76, d, J = 10.4 Hz; δC 127.2, CH; 133.8, C), an oxygen-bearing quaternary carbon (δC 79.4, C), two oxygen-bearing methines (δH 4.93, d, J = 8.4 Hz; δC 79.2, CH; δH 3.21, dd, J = 10.4, 6.4 Hz; δC 70.7, CH), and an oxygen-bearing methylene (δH 4.46, d, J = 14.8 Hz; 4.31, dd, J = 14.8, 1.6 Hz; δC 55.9, CH2).
The planar structure of 2 was also elucidated by the 2D NMR spectra. The COSY spectrum showed that compound 2 possesses four partial structures from H-2 to H-3, H2-5 via H2-6 to H-7, H2-9 via H2-10 to H-11, and H2-13 to H2-14. All of the partial structures were linked by HMBC correlations from H2-17 to C-1, C-15, C-16; H3-18 to C-3, C-4, C-5; H3-19 to C-7, C-8, C-9; H3-20 to C-11, C-12, C-13; and H2-13 and H2-14 to C-1. Further, the HMBC correlation from both H-2 (δH 4.93, d, J = 8.4 Hz) and H2-17 (δH 4.46, d, J = 14.8 Hz; 4.31, dd, J = 14.8, 1.6 Hz) to C-16 (δC 172.3) indicated the presence of an α-methylene-α, β-unsaturated-γ-lactone ring. Accordingly, 2 should possess an additional degree of unsaturation which could be an additional ring. The HMBC correlation from H2-17 to C-12 (δC 79.4) demonstrated the presence of an ether linkage between C-12 and C-17. Based on the above evidence, the structure of 2 was established.
Detailed analysis of the NOESY spectrum was applied for the elucidation of the relative configuration of 2 (Figure 5). It was found the NOE correlations between H-2 and H-14β (δH 1.66, m), H-14β and H-13β (δH 1.97, m), and also H-13β and H3-20 (δH 1.02, s), suggesting the β-orientation of H3-20. On the other hand, the NOE correlations between H-3 (δH 4.50, d, J = 8.4 Hz) and H-14α (δH 2.19, m), H-14α and H-11 (δH 3.21, dd, J = 10.4, 6.4 Hz), and H-11 and H-3 were observed, indicating the α-orientation of H-11 and the downward orientation of H-3. Furthermore, the upshift resonances of C-18 (δC 18.5) and C-19 (δC 15.2) demonstrated the E geometry of C-3/C-4 and C-7/C-8. The 3J values of H-2 and H-3 (8.4 Hz) and H-10 and H-11 (10.4 Hz) were also consistent with the relative configuration as shown in Figure 5. Based on the above evidence, the relative configuration of 2 was defined as 2S*,11R*,12S*,3E,7E.
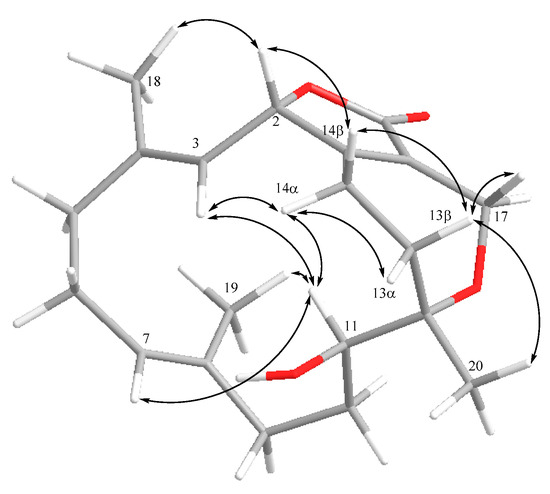
Figure 5.
Selective NOE correlations of 2.
In the present study, we isolated two cembranoids, cherbonolide M and N (1 and 2), from the soft coral S. cherbonnieri. Structurally, both isolates belong to the isosarcophine derivatives. By consideration of the chemical types of reported cembranoids, this is the first time to discover the cembranoidal scaffold possessing the unique tetrahydrooxepane with 12,17-ether linkage fusing with a γ-lactone. The plausible biosynthetic pathway was postulated, as shown in Scheme 1. Moreover, the CD spectrum of 2 (Figure 6) also revealed the positive effect at 225.0 nm (Δε = +25) and the negative effect at 255.4 nm (Δε = −2.0) as that of isosarcophine (3). Similar to compound 1, metabolite 2 should also be biotransformed from isosarcophine and thus possessesed a (2S,11R,12S,3E,7E) absolute configuration.
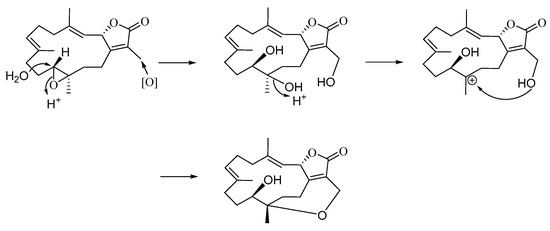
Scheme 1.
Proposed biosynthetic pathway of cherbonolide N (2).
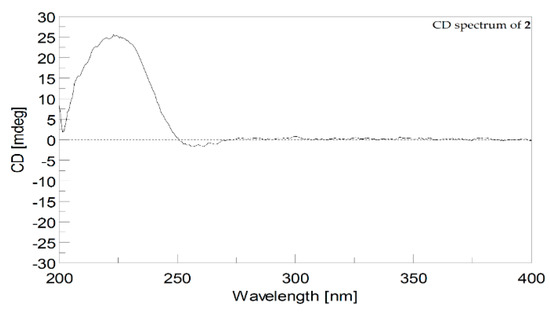
Figure 6.
CD spectra (1.2 × 10–4 M, MeOH) of 2.
In 1990, Kusumi et al. afforded isosarcophine from the Okinawan soft coral, Sinularia mayi, and demonstrated its moderate cytotoxicity against human colorectal carcinoma (HCT-116) cell line with the IC50 value of 64 μg/mL [25]. Subsequently, in 1992, Wu et al. also isolated the same metabolite from a Formosan soft coral, Sarcophyton trocheliophorum, which was also found to exhibit significant cytotoxicities toward human lung epithelial cells (A549), human colon carcinoma cells (HT-29), human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells (KB), mouse lymphoid neoplasm cells (P388), and promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60) with the ED50 values of 13.3, 16.9, 24.5, 0.7, and 6.7 μg/mL, respectively [26]. Many isosarcophine derivatives have been discovered from different marine soft corals and reported to display various biological activities [13,14,27].
For the discovery of bioactivities of new metabolites 1 and 2, both compounds were examined according to the cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities. In the evaluation of cytotoxicity, both isolates were shown to be inactive against the proliferation of A549, DLD-1, and HuCCT-1 cell lines at the concentration of 30 μM. On the other hand, in anti-inflammatory assays at 30 μM, metabolite 2 showed inhibition of superoxide anion generation (20.6 ± 6.8%) and the elastase release (30.1 ± 3.3%), while 1 only displayed 12.9 ± 5.7% and 16.7 ± 5.9% inhibition of superoxide anion generation and elastase release, respectively, in the fMLF/CB-induced human neutrophils.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Specific optical rotations of both compounds 1 and 2 were measured on a JASCO P-1020 polarimeter (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan), and their IR spectra were recorded on an FT/IR-4100 infrared spectrophotometer (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The low-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LR-ESI-MS) and HR-ESI-MS experiments were carried out on a Bruker APEX II (Bruker, Bremen, Germany) mass spectrometer. The CD spectra of 1–3 were recorded by Jasco J-815 spectropolarimeter (JASCO, Tokyo, Japan) in MeOH. NMR spectra of 1 were acquired on a Varian Unity Inova 500 FT-NMR (Varian Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) at 500 MHz for 1H and 125 MHz for 13C in C6D6 at room temperature (25 °C). Further, NMR spectra of 1 and 2 were acquired on a Varian 400 MR FT-NMR (Varian Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) instrument at 400 MHz for 1H and 100 MHz for 13C in acetone-d6 and C6D6 at the same condition. Low-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LRESIMS) and HRESIMS data were recorded on a Bruker APEX II (Bruker, Bremen, Germany) mass spectrometer. Normal-phase column chromatography was undertaken using silica gel (Merck, 230–400 mesh). Pre-coated silica gel plates (Merck, Kieselgel 60 F-254, 0.2 mm, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) were used for analytical thin-layer chromatography (TLC). High-performance liquid chromatography was carried out for further purification of isolates, using a Hitachi L-2455 HPLC apparatus (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) with a Supelco C18 column (250 × 21.2 mm, 5 μm; Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA).
3.2. Animal Material
The collection and identification of the soft coral S. cherbonnieri were carried out as described previously [13,14].
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The soft coral S. cherbonnieri (wet weight: 1.2 kg) was freeze-dried to remove the water. The dried sample was sliced into small pieces for EtOAc extraction. The combined EtOAc extract was concentrated under reduced pressure to afford an oily residue (10.2 g), which was chromatographed by a normal phase column with the gradient elution of acetone in n-hexane (0–100%) and methanol in acetone (0–100%) to separate 19 fractions. Fraction 13, eluting with n-hexane-acetone (1:1), was further purified over Sephadex LH-20 column using acetone to afford five subfractions (A–E). Subfraction 13-D was further purified by reversed-phase HPLC with the elution of acetonitrile-H2O (1.6:1, 5.0 mL/min) to afford 1 (7.1 mg, tR 61.9 min). Subfraction 13-E was also purified by reversed-phase HPLC with the elution of acetonitrile-H2O (1.7:1, 5.0 mL/min) to afford 2 (3.6 mg, tR 54.5 min).
- Cherbonolide M (1): colorless amorphous oil, +29.0 (c 1.00, CHCl3), IR (KBr) νmax 3445, 2927, 2862, 1749, 1679, 1455, 1387, 1093, 1006, 755 cm−1; CD (1.2 × 10–4 M, MeOH) λmax Δε 245.5 (−15.6), and 227.0 (+34.8) nm; for 13C and 1H data see Table 1; electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESIMS) m/z 355; HRESIMS m/z 355.1882 [M + Na]+ (calculated for C20H28O4Na: 355.1880).
- Cherbonolide N (2): colorless amorphous oil, +15.0 (c 1.00, CHCl3), IR (KBr) νmax 3481, 2930, 1741, 1678, 1437, 1383, 1102, 1061, 986, 754 cm−1; CD (1.2 × 10−4 M, MeOH) λmax Δε 255.4 (−2.0), and 225.0 (+25.0) nm; for 13C and 1H data see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 355; HRESIMS m/z 355.1880 [M + H]+ (calculated for C20H28O4Na: 355.1879).
3.4. Cytotoxicity Testing
To measure the cytotoxicities of 1 and 2, three different concentrations of both compounds were added to A549, DLD-1, and HuCCT-1 cell lines for 72 h. The results were detected using the Alamar Blue assay [29,30].
3.5. Anti-Inflammatory Assay
The generation of the superoxide anion and elastase release in the fMLF/CB-induced primary human neutrophils was screened according to the previous description [13].
4. Conclusions
Two new isosarcophine derivatives, cherbonolides M (1) and N (2), were isolated from the continuous investigation of the soft coral S. cherbonnieri. Structurally, metabolite 2 is the first cembranoid possessing the unique cembranoidal scaffold of tetrahydrooxepane with the 12,17-ether linkage fusing with a γ-lactone. A plausible biosynthetic pathway was postulated for compound 2. In the anti-inflammatory assay, compound 2 was found to show moderate activity in inhibiting the generation of superoxide anion and elastase release in the fMLF/CB-induced human neutrophils. Based on the above statements and our previous discoveries [13,14], the soft coral S. cherbonnieri was demonstrated to be an attractive source of bioactive diterpenoids. Further, it has been proven that the soft coral S. glacum existed in more than seven genetically distinct clades and led to the high structural diversification of natural products of this species [31]. Currently, over 300 cembranoids have been discovered from the Sarcophyton genera [1], which might also come from the same reason. According to our investigation and related studies of other research groups [13,14,32,33,34,35,36,37,38], the soft corals of genus Sarcophyton could be considered ideal organisms for discovering natural products with diversified structures and biological activities.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md19050260/s1, Figure S1: ESIMS spectrum of 1; Figure S2: HRESIMS spectrum of 1; Figure S3: IR spectrum of 1; Figure S4: CD spectrum (1.2 × 10−4 M, MeOH) of 1; Figure S5: 1H NMR spectrum of 1 in acetone-d6 at 400 MHz; Figure S6: 1H NMR spectrum (from 0.9 to 2.9 ppm) of 1 in acetone-d6 at 400 MHz; Figure S7: 13C NMR spectrum of 1 in acetone-d6 at 100 MHz; Figure S8: DEPT spectrum of 1 in acetone-d6; Figure S9: HSQC spectrum of 1 in acetone-d6; Figure S10: COSY spectrum of 1 in acetone-d6; Figure S11: HMBC spectrum of 1 in acetone-d6; Figure S12: NOESY spectrum of 1 in acetone-d6; Figure S13: 1H NMR spectrum of 1 in C6D6 at 500 MHz; Figure S14: 1H NMR spectrum (from 0.6 to 2.5 ppm) of 1 in C6D6 at 500 MHz; Figure S15: 13C NMR spectrum of 1 in C6D6 at 125 MHz; Figure S16: DEPT spectrum of 1 in C6D6; Figure S17: HSQC spectrum of 1 in C6D6; Figure S18: COSY spectrum of 1 in C6D6; Figure S19: HMBC spectrum of 1 in C6D6; Figure S20: NOESY spectrum of 1 in C6D6; Figure S21: ESIMS spectrum of 2; Figure S22: HRESIMS spectrum of 2; Figure S23: IR spectrum of 2; Figure S24: CD spectrum (1.2 × 10−4 M, MeOH) of 2; Figure S25: 1H NMR spectrum of 2 in C6D6 at 400 MHz; Figure S26: 1H NMR spectrum (from 0.8 to 3.2 ppm) of 2 in C6D6 at 400 MHz; Figure S27: 13C NMR spectrum of 2 in C6D6 at 100 MHz; Figure S28: DEPT spectrum of 2; Figure S29: HSQC spectrum of 2; Figure S30: COSY spectrum of 2; Figure S31: HMBC spectrum of 2; Figure S32: NOESY spectrum of 2. Figure S33: CD spectrum (1.6 × 10−4 M, MeOH) of isosarcophine (3).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-H.S.; investigation, C.-C.P., C.-Y.H., T.-L.H. and J.-H.S.; writing—original draft, C.-C.P., T.-Y.H. and C.-Y.H.; writing—review and editing, T.-Y.H. and J.-H.S.; bioactivity screening, C.-Y.H. and T.-L.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded mainly by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST; 104-2113-M-110-006, 104-2320-B-110-001-MY2, and 107-2320-B-110-001-MY3).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Elkhawas, Y.A.; Elissawy, A.M.; Elnaggar, M.S.; Mostafa, N.M.; Al-Sayed, E.; Bishr, M.M.; Singab, A.N.B.; Salama, O.M. Chemical diversity in species belonging to soft coral genus Sacrophyton and its impact on biological activity: A review. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 175–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.G.; Miguel, M.G.; Mnif, W. A brief review on new naturally occurring cembranoid diterpene derivatives from the soft corals of the genera Sarcophyton, Sinularia, and Lobophytum since 2016. Molecules 2019, 24, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratake, S.; Tomura, T.; Saitoh, S.; Yokokura, R.; Kawanishi, Y.; Shinjo, R.; Reimer, J.D.; Tanaka, J.; Maekawa, H. Soft coral Sarcophyton (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Octocorallia) species diversity and chemotypes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.C.; Sung, P.J.; Duh, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Sheu, J.H.; Yang, N.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of nature products isolated from soft corals of Taiwan between 2008 and 2012. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4083–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, S.R.; Weng, J.R.; Tu, T.H.; Cheng, Y.B.; Wu, S.H.; Sheu, J.H. New hydroquinone monoterpenoid and ccembranoid-related metabolites from the soft coral Sarcophyton tenuispiculatum. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Chao, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Dai, C.F.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Wu, S.H.; Sheu, J.H. New biscembranoids sardigitolides A-D and known cembranoid-related compounds from Sarcophyton digitatum: Isolation, structure elucidation, and bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.E.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Elshamy, A.I.; Hamed, A.R.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Ohta, S.; Umeyama, A.; Paré, P.W.; Efferth, T. Sarcoehrenbergilides D–F: Cytotoxic cembrene diterpenoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27183–27189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.B.; Babu, D.C.; Bharadwaj, T.V.; Srikanth, D.; Vardhan, K.S.; Raju, T.V.; Bunce, R.A.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Isolation, structural assignment and synthesis of (SE)-2-methyloctyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl) propenoate from the marine soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Eltahawy, N.A.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Radwan, M.M.; ElSohly, M.A.; Hassanean, H.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Cytotoxic cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral, Sarcophyton auritum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3984–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhateeb, A.; El-Beih, A.A.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; Alhammady, M.A.; Ohta, S.; Paré, P.W.; Hegazy, M.E.F. New terpenes from the Egyptian soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.K.; Hsieh, M.K.; Duh, C.Y. New diterpenoids from soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4318–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Ahmed, A.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory cembranoids from a Formosa soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Ahmed, A.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. New cembranoids and a biscembranoid peroxide from the soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Lin, C.C.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Isolation and structure elucidation of cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton stellatum. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zou, Y.H.; Ge, M.X.; Lou, L.L.; Xu, Y.S.; Ahmed, A.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Tang, G.H.; Yin, S. Biscembranoids and cembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Sung, P.J.; Su, J.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive cembranoids, sarcocrassocolides P–R, from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.Y.; Su, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badria, F.A.; Guirguis, A.N.; Perovic, S.; Steffen, R.; Müller, W.E.; Schröder, H.C. Sarcophytolide: A new neuroprotective compound from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Toxicology 1998, 131, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.F.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Yao, L.G.; Li, J.; Lan, L.F.; Guo, Y.W. Structural, stereochemical, and bioactive studies of cembranoids from Chinese soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Fekry, M.I.; Al-Hammady, M.A.; Khalil, M.N.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Meyer, A.; Porzel, A.; Westphal, H.; Wessjohann, L.A. Cytotoxic effects of Sarcophyton sp. soft coral–is there a correlation to their NMR fingerprints? Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.; Shmeuli, U.; Zadock, E.; Kashman, Y.; Néeman, I. Sarcophine, a new epoxy cembranolide from marine origin. Tetrahedron 1974, 30, 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y. Marine Natural Products Chemistry; Faulkner, D.J., Fenical, W.H., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Frincke, J.M.; McIntyre, D.E.; Faulkner, D.J. Deoxosarcophine from a soft coral, Sarcophyton sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, T.; Yamada, K.; Ishitsuka, M.O.; Fujita, Y.; Kakisawa, H. New cembranoids from the Okinawan soft coral Sinularia mayi. Chem. Lett. 1990, 19, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Hsieh, P.W.; Duh, C.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Soong, K.; Fang, L.S. Studies on the Formosan soft corals I-cytotoxic cembrane diterpenes from Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 1992, 39, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Ye, F.; Zhu, Z.D.; Huang, H.; Mao, S.C.; Guo, Y.W. Cembrane-type diterpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton mililatensis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawronski, J.K.; van Oeveren, A.; van der Deen, H.; Leung, C.W.; Feringa, B.L. Simple circular dichroic method for the determination of absolute configuration of 5-substituted 2(5H)-furanones. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 1513–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, G.R.; Caton, M.C.; Nova, M.P.; Parandoosh, Z. Assessment of the Alamar Blue assay for cellular growth andviability in vitro. Immunol. Methods 1997, 204, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, K.N.; Botts, R.T.; Davis, T.S.; Okada, B.K.; Maloney, E.M.; Leber, C.A.; Alvarado, O.; Brayton, C.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Chari, J.V.; et al. Cryptic species account for the seemingly idiosyncratic secondary metabolism of Sarcophyton glaucum specimens collected in Palau. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elias, N.; Farag, M.A.; Chen, L.; Saeed, A.; Hegazy, M.E.F.; Moustafa, M.S.; El-Wahed, A.A.; Al-Mousawi, S.M.; Musharraf, S.G.; et al. Marine natural products: A source of novel anticancer drugs. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, V.T.; Dat, T.T.H.; Vinh, L.B.; Cuong, L.C.V.; Oanh, P.T.T.; Ha, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Anh, H.L.T.; Yang, S.Y. Coral and coral-associated microorganisms: A prolific source of potential bioactive natural products. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.H.; Li, W.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Ahmed, A.F.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Lu, M.C.; Liaw, C.C.; Sheu, J.H. Isoprenoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chen, B.W.; Hwang, T.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Tortuosenes A and B, new diterpenoid metabolites from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton tortuosum. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Ahmed, A.F.; Su, J.H.; Chao, C.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Crassocolides A–F, cembranoids with a trans-fused lactone from the soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, M.; Gu, Y.C.; Liang, L.F.; Tang, W.; Guo, Y.W. Rare cembranoids from Chinese soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi: Structural and stereochemical studies. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 5091–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.F.; Bie, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W.H. Sarcophytolides G–L, new biscembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2013, 96, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).