A Systematic Review of Advances in Plant-Based Phospholipid Liposomes in Breast Cancer Therapy: Characterization, Innovations, Clinical Applications, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
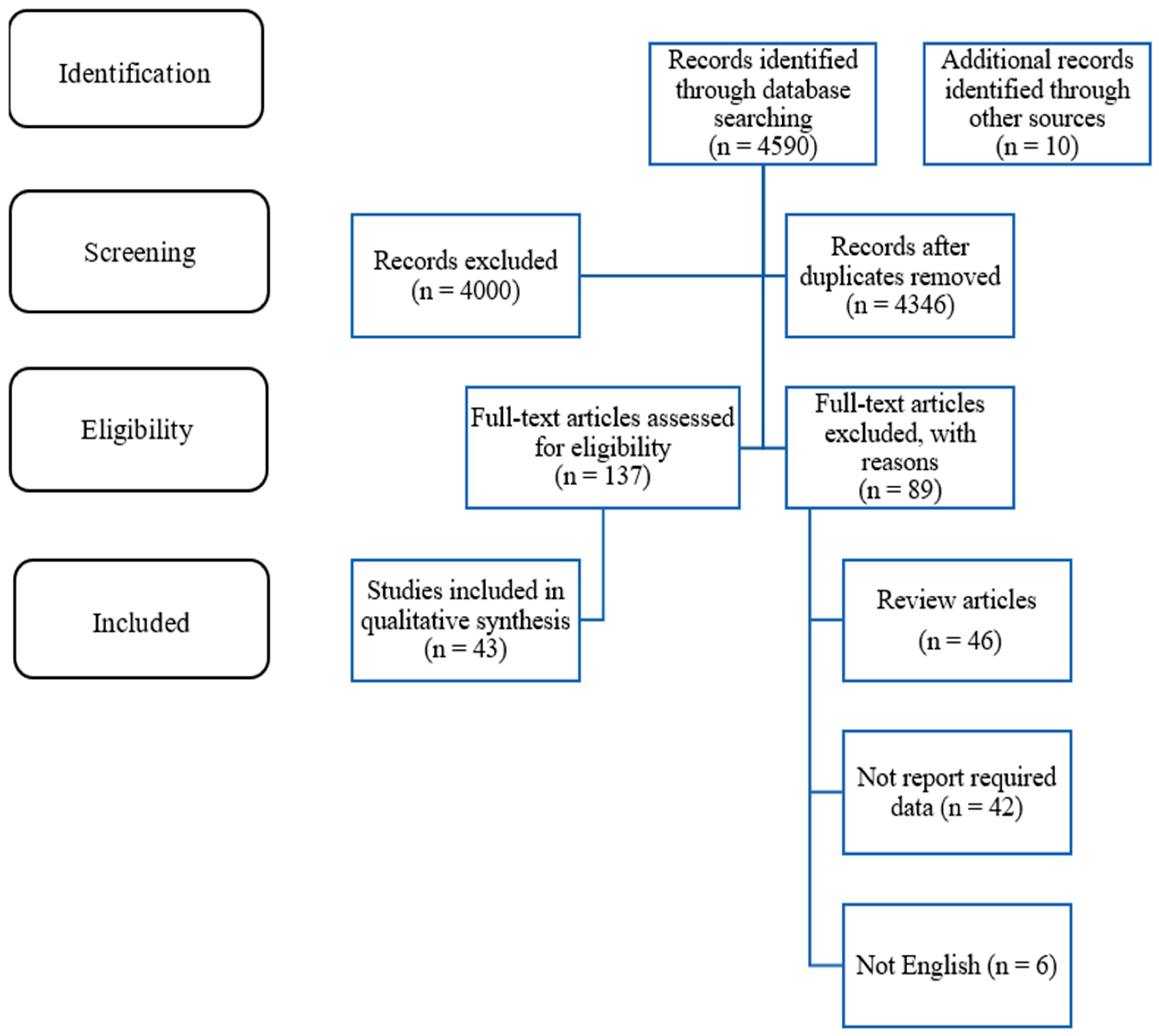
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy and Study Selection
3. Results
3.1. Data Extraction and Quality Assessed
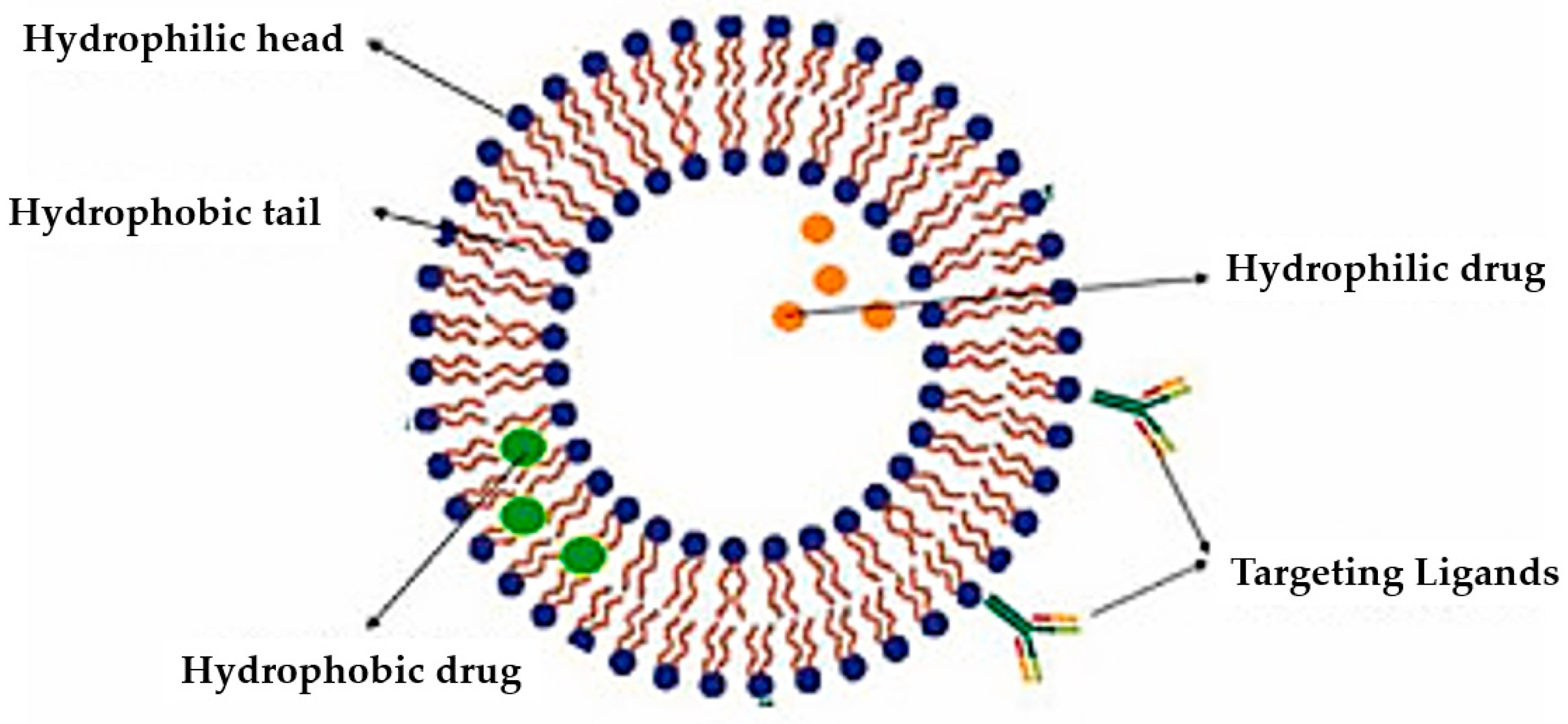
3.2. Liposome Functionalization
3.2.1. Imine-Crosslinked Strategy
3.2.2. Amide-Crosslinked Strategy
3.2.3. Disulfide-Crosslinking Strategy
3.2.4. Thiol–Maleimide-Crosslinking Strategy
3.2.5. Hydazone-Crosslinking Strategy
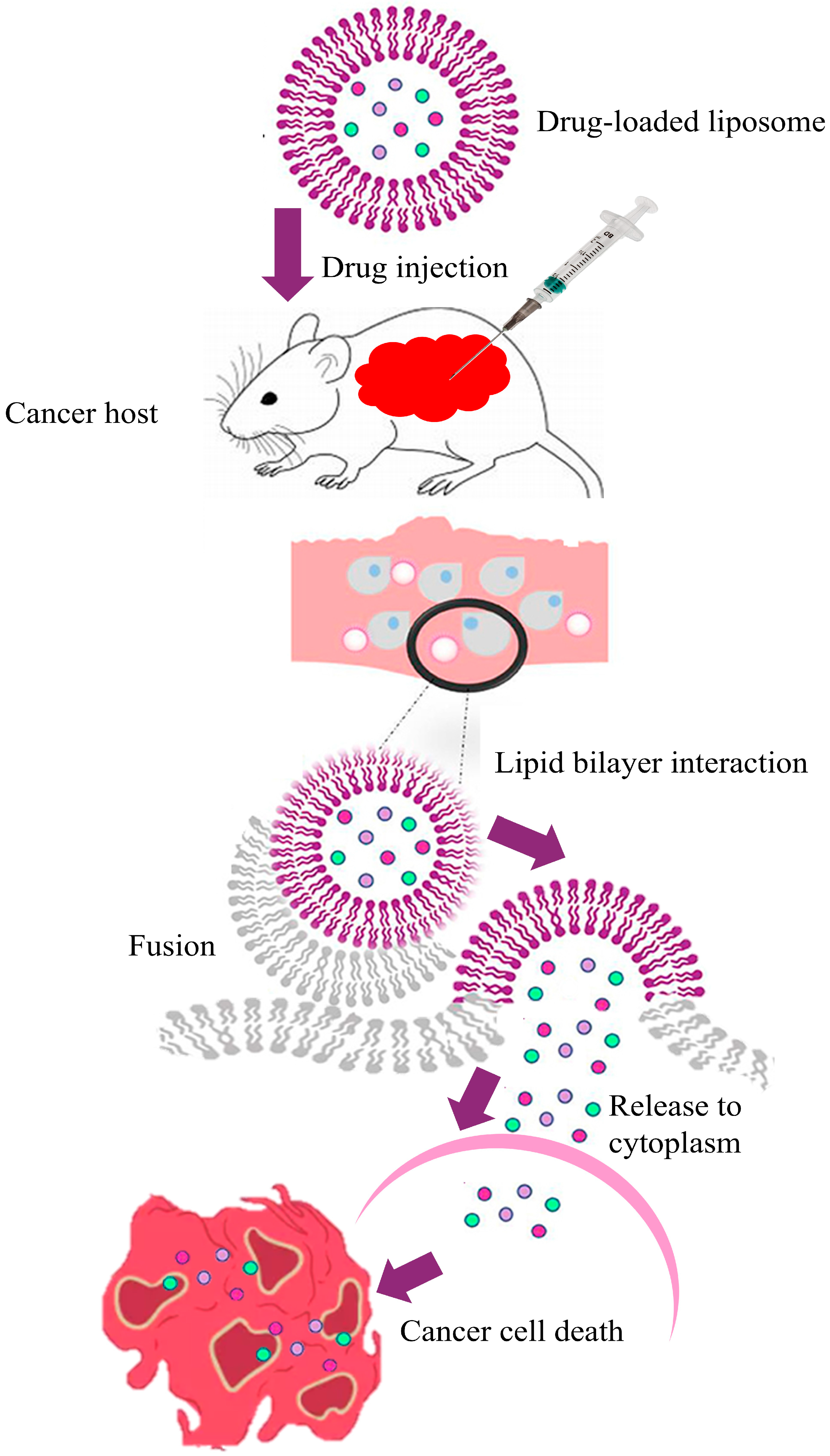
3.3. Targeted Nanoliposomes for Breast Cancer Treatment
3.3.1. Ligands in Targeted Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems
3.3.2. Synthetic Liposomal Drug Delivery Developments in Breast Cancer
3.3.3. Mechanisms in Breast Cancer
3.3.4. Cell Surface, Transmembrane, Internal Cell, and Enzyme Receptors in Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems for Breast Cancer
3.4. Plant-Based Phospholipids
4. Discussion
| Study | Study Type | Liposomal Composition | Chemotherapeutic Agent | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coutinho et al., 2023 [225] | Preclinical | Soy-derived phospholipids; genistein incorporated in phosphatidylcholine–cholesterol liposomes | Paclitaxel | Enhanced drug accumulation in tumor tissues; improved therapeutic outcomes compared to free paclitaxel. |
| Lo et al., 2024 [226] | Preclinical | Sunflower-derived phosphatidylcholine liposomes | Doxorubicin | Significant tumor regression and reduced systemic toxicity; demonstrated safety and efficacy of plant-based liposomes. |
| Chavda et al., 2023 [227] | Preclinical | Phosphatidylcholine (PC) with natural surfactants | Curcumin combined with chemotherapy | Enhanced anticancer effects of curcumin; improved response rates in breast cancer models. |
| Meng et al., 2016 [228] | Preclinical | Phosphatidylcholine–cholesterol liposomes co-encapsulating resveratrol (RSV) and paclitaxel (PTX) | RSV + PTX | Synergistic anticancer effects; enhanced efficacy versus single-drug formulations. |
| de Pace et al., 2013 [229] | In vitro | Soy lecithin–cholesterol liposomes coated with chitosan (CSLIPO-EGCG) | Green tea-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) | Enhanced apoptosis and proliferation inhibition in MCF7 cells; effective at ≤10 μM; chitosan coating improved stability and reduced immunogenicity. |
| Yousfan et al., 2024 [230] | Preclinical | Lipid droplet from date palm seed (DPLDs) | Paclitaxel | Enhancement of solubility, reduction in toxicity, and improved brain accumulation of paclitaxel via intranasal delivery. |
| Li et al., (2020) [231] | Preclinical | Corosolic acid liposomes (CALP) from Lagerstroemia speciosa, cholesterol-free | Doxorubicin | Higher cellular uptake, tumor penetration, and accumulation; significant tumor growth inhibition and extended survival in 4T1 murine model; high anti-inflammatory activity via STAT3 inhibition. |
| Tang et al., (2014) [222] | Preclinical | Platycodon (PD) derived from the Platycodon grandiflorum plant (balloon flower) | Doxorubicin | DOX/PD showed enhanced anti-proliferative effects on n human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Higher apoptosis-related protein expression (e.g., cleaved PARP). Reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential. Higher intracellular accumulation of DOX in MDA-MB-231 (a triple-negative breast cancer line). |
| Sabeti et al., (2014) [219] | Preclinical | Phosphatidylcholine liposomes containing 5% or 10% palm oil | Doxorubicin | Higher encapsulation efficiency; sustained release; lower IC50 in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. |
| Bedretdinov & Kostryukova, 2023 [218] | Preclinical | Palm oil phospholipids | Doxorubicin | Higher cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 cells, stable particle size, and zeta potential contributed to efficacy. |
| He et al., 2023 [232] | Preclinical | PLGA nanoparticles loaded with palmitic acid (from palm oil) | Doxorubicin | Reduced cell viability and migration in vitro; decreased tumor growth and metastasis in vivo; immunomodulatory effect via macrophage polarization. |
| Franco et al., 2019 [233] | Preclinical | Palm oil phospholipid liposomes | Paclitaxel + Doxorubicin | Higher tumor inhibition ratios in 4T1 breast cancer cell line. Improved cardiac toxicity profile. |
| Mahmoudi et al., 2021 [234] | Preclinical | Curcumin from plant Curcuma longa (turmeric) | Cisplatin | High entrapment efficiency Significant higher cytotoxicity (82.5%) and lowered breast cancer cell viability. Tenfold increase in apoptosis. |
| Sunoqrot et al., 2023 [217] | Preclinical | Polyquercetin (pQCT), a plant-derived polymer based on quercetin | Doxorubicin | Exhibited spherical morphology, high monodispersity, excellent drug loading capacity, and sustained drug release. Enhance induce apoptosis in breast cancer cell. |
| Chavoshi et al., 2023 [220] | Preclinical | Soybean lecithin–cholesterol liposomes loaded with crocin (from Crocus sativus) | Doxorubicin | Dose-dependent enhanced cytotoxicity in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Induced cell cycle arrest at Sub-G1 and G2/M phases. Downregulated anti-apoptotic genes (survivin, cyclin-B1, Bcl-xl). Upregulated pro-apoptotic genes (Bax, Bid). Better apoptotic and antiproliferative properties. |
| Pandey et al., 2025 [235] | Preclinical | Folic acid (FA) | 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) | Enhanced uptake, cytotoxicity, and migration inhibition in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Enhanced apoptosis. Superior tumor growth inhibition. Lower systemic toxicity, and improved overall safety profile compared to conventional 5-FU formulations. |
| Eloy et al., (2017) [236] | Preclinical | Anti-HER2 immunoliposomes | Paclitaxel + Rapamycin | Higher cytotoxicity in HER2-positive SKBR3 cells; reduced tumor volume to 25.27% of control. |
| Pogorzelska et al., 2023 [221] | Preclinical | Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli | Doxorubicin | Sulforaphane enhanced nuclear accumulation of DOX. Twofold inhibition of tumor growth observed in vivo. Potential to reduce DOX dose fourfold while maintaining efficacy due to synergistic interaction. Sulforaphane inhibited mitosis in cancer cells. Protected normal cells by displaying antagonistic cytotoxicity. Reduced cardiotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and hepatotoxicity in vivo. |
| Attia et al., 2025 [223] | Preclinical | Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) and ascorbic acid (AA) | Doxorubicin | Biphasic drug release. Effective cytotoxic activity against breast cancer cell lines. Reduced nephrotoxicity. |
| Vakilinezhad et al., 2019 [237] | Preclinical | PLGA nanoparticles co-loaded with curcumin (Curcuma longa) and methotrexate | Methotrexate | Enhanced cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells. Improved targeted delivery, controlled release, and reduced systemic toxicity. |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullah, F.O. Phospholipids. In Bioactive Compounds of Edible Oils and Fats; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, A.; Jaiswal, J.K. Structural and Signaling Role of Lipids in Plasma Membrane Repair. Curr. Top. Membr. 2019, 84, 67–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ali, O.; Szabó, A. Review of Eukaryote Cellular Membrane Lipid Composition, with Special Attention to the Fatty Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Farooq, S.; Hussain, A. Advances in Protein-and Lipid-Based Materials for Cosmetic Applications; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Froldi, G.; Ragazzi, E. Selected Plant-Derived Polyphenols as Potential Therapeutic Agents for Peripheral Artery Disease: Molecular Mechanisms, Efficacy and Safety. Molecules 2022, 27, 7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gali, L.; Pirozzi, A.; Donsì, F. Biopolymer-and Lipid-Based Carriers for the Delivery of Plant-Based Ingredients. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, A.; Mahmood, T.; Ahsan, F.; Kumar, A.; Bagga, P. Lipids: An Insight into the Neurodegenerative Disorders. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2018, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Otte, A.; Park, K. Evolution of Drug Delivery Systems: From 1950 to 2020 and Beyond. J. Control. Release 2022, 342, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Hossain, M.I.; Hossain, M.K.; Rubel, M.H.K.; Hossain, K.M.; Mahfuz, A.; Anik, M.I. Recent Progress in Nanostructured Smart Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy: A Review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 971–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahed, S.Z.; Salehi, R.; Davaran, S.; Sharifi, S. Liposome-Based Drug Co-Delivery Systems in Cancer Cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Nie, G. Biomembrane-Based Nanostructures for Cancer Targeting and Therapy: From Synthetic Liposomes to Natural Biomembranes and Membrane-Vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-H.; Ye, P.-J.; Zhou, Y.-C.; He, D.-X.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.-Y. Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles as Drug Carriers for Cancer Therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, S.; Martin, C.; Murphy, D.; Shokar, N.K. Breast Cancer Epidemiology, Prevention, and Screening. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 151, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gundarova, J. Anticancer-Effectiveness of Herbal Aldehyde Derivatives on Breast Cancer Cells; Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg im Breisgau: Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, 2024; Available online: https://books.google.jo/books/about/Anticancer_Effectiveness_of_Herbal_Aldeh.html?id=1Sz00AEACAAJ&redir_esc=y (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Rossi, C.; Cicalini, I.; Cufaro, M.C.; Consalvo, A.; Upadhyaya, P.; Sala, G.; Antonucci, I.; Del Boccio, P.; Stuppia, L.; De Laurenzi, V. Breast Cancer in the Era of Integrating “Omics” Approaches. Oncogenesis 2022, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxevanis, C.N.; Fortis, S.P.; Perez, S.A. The Balance between Breast Cancer and the Immune System: Challenges for Prognosis and Clinical Benefit from Immunotherapies. In Proceedings of the Seminars in Cancer Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 72, pp. 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Tumor Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Strategies for Cancer Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Hu, Y.; Pang, Z. Modulating the Tumor Microenvironment to Enhance Tumor Nanomedicine Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Yang, K.; He, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. Strategies to Enhance Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors by Harnessing the EPR Effects and Alternative Targeting Mechanisms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzari, M.T.; Shamay, Y.; Kiguchi, H.; Rosen, N.; Scaltriti, M.; Heller, D.A. Targeted Drug Delivery Strategies for Precision Medicines. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yang, Y.; Aziz, T.; Al-Asmari, F.; Sameeh, M.Y.; Lin, L. Exploring the Potential of Chlorogenic Acid/Chitosan Nanoparticle-Loaded Edible Films with Photodynamic Technology for Mongolian Cheese Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, K.; Rajora, A. Phytosomes: A Critical Tool for Delivery of Herbal Drugs for Cancer: Phytosomes: Advancing Herbal Medicine Delivery. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 24, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjsuren, B.; Chaurasiya, B.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Shi, D.; Evans, C.E.; Webster, T.J.; Shen, Y. Cetuximab-Coated Thermo-Sensitive Liposomes Loaded with Magnetic Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for Targeted EGFR-Expressing Breast Cancer Combined Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8201–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Carter, K.A.; Miranda, D.; Lovell, J.F. Chemophototherapy: An Emerging Treatment Option for Solid Tumors. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Gurav, P. PhytoNanotechnology: Enhancing Delivery of Plant Based Anti-Cancer Drugs. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 8, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajith, S.; Almomani, F.; Elhissi, A.; Husseini, G.A. Nanoparticle-Based Materials in Anticancer Drug Delivery: Current and Future Prospects. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Rahmani, A.H. Recent Strategies towards the Surface Modification of Liposomes: An Innovative Approach for Different Clinical Applications. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Yadav, K.; Shukla, R.P.; Gautam, S.; Marwaha, D.; Sharma, M.; Mishra, P.R. Surface Modification Strategies in Translocating Nano-Vesicles across Different Barriers and the Role of Bio-Vesicles in Improving Anticancer Therapy. J. Control. Release 2023, 363, 290–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.K.; Riaz, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Wong, K.H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Lu, A.; Yang, Z. Surface Functionalization and Targeting Strategies of Liposomes in Solid Tumor Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Bhaskar, R.; Han, S.S. Recent Advances in the Biomedical Applications of Functionalized Nanogels. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reszczyńska, E.; Hanaka, A. Lipids Composition in Plant Membranes. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 78, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, S.; Chaudhary, V.; Sharma, B.; Kumar, A.; Bhagi, A.K.; Singh, K.P. Sustainable Polysaccharide Hydrogels Based on Dynamic Schiff Base Linkages as Versatile Building Blocks for Fabricating Advanced Functional Materials. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y. Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked Ternary Carboxymethylcellulose/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyethyleneimine Film with Enhanced Mechanical Properties, Water Resistance, Antibacterial Activity, and UV-Shielding Ability without Any UV Absorbents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Hu, H.; Sun, Y.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. The Intracellular and Extracellular Microenvironment of Tumor Site: The Trigger of Stimuli-responsive Drug Delivery Systems. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2101437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Bassi, P. Drug Targeting to Cancer Cells through Stimuli-Responsive Imine Bonds: Fascinating Aspects of Site Specificity. In Polymer-Drug Conjugates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Wu, J. PH-Sensitive Nanogels for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Thompson, D.H. Stimuli-responsive Liposomes for Drug Delivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tageldin, A.; Omolo, C.A.; Nyandoro, V.O.; Elhassan, E.; Kassam, S.Z.F.; Peters, X.Q.; Govender, T. Engineering Dynamic Covalent Bond-Based Nanosystems for Delivery of Antimicrobials against Bacterial Infections. J. Control. Release 2024, 371, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.C.; Costa, P.J.; Velho, S.; Amaral, M.H. Functionalizing Nanoparticles with Cancer-Targeting Antibodies: A Comparison of Strategies. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 180–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Peng, Y.; Pu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, R.; Guo, L.; Wu, Y. Fructose and Biotin Co-Modified Liposomes for Dual-Targeting Breast Cancer. J. Liposome Res. 2022, 32, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichner, C.; Jelkmann, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated Polymers: Bioinspired Polymers Utilizing One of the Most Important Bridging Structures in Nature. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 151, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, P.F.; Travanut, A.; Conte, C.; Alexander, C. Reduction-responsive Polymers for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy—Is There Anything New to Discover? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y. Drug Release from Disulfide-Linked Prodrugs: Role of Thiol Agents. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Davis, E. Nanoplatforms for Targeted Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery: A Review of Platform Materials and Stimuli-Responsive Release and Targeting Mechanisms. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, B.; Nag, O.K.; Rogers, K.E.; Delehanty, J.B. Recent Progress in Bioconjugation Strategies for Liposome-Mediated Drug Delivery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirisala, A.; Uchida, S.; Tockary, T.A.; Yoshinaga, N.; Li, J.; Osawa, S.; Gorantla, L.; Fukushima, S.; Osada, K.; Kataoka, K. Precise Tuning of Disulphide Crosslinking in MRNA Polyplex Micelles for Optimising Extracellular and Intracellular Nuclease Tolerability. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Mitragotri, S. Challenges Associated with Penetration of Nanoparticles across Cell and Tissue Barriers: A Review of Current Status and Future Prospects. Nano Today 2014, 9, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, P.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. Targeted Nanotechnologies for Cancer Intervention: A Patent Review (2010–2016). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Tavakoli, S.; Parvathaneni, R.P.; Nawale, G.N.; Oommen, O.P.; Hilborn, J.; Varghese, O.P. Dynamic Covalent Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels and Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 6399–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Karimi, M.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B.; Torkashvand, M.; Alibolandi, M. Hybrid in Situ-Forming Injectable Hydrogels for Local Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 616, 121534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, P. Tumor Microenvironment-Based Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Controlled Release of Drugs in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, X. PH-Sensitive Biomaterials for Drug Delivery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, F.; Fanciullino, R.; Milano, G.; Ciccolini, J. Towards Rational Cancer Therapeutics: Optimizing Dosing, Delivery, Scheduling, and Combinations. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 108, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emon, J.H.; Rashid, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Hasan, M.N.; Patoary, M.K. Review on the Synthesis, Recyclability, Degradability, Self-Healability and Potential Applications of Reversible Imine Bond Containing Biobased Epoxy Thermosets. Reactions 2023, 4, 737–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, D.; Wan, Z.; Du, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ling, M.; Liang, C. Epoxy and Amide Crosslinked Polarity Enhanced Polysaccharides Binder for Silicon Anode in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 368, 137580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeValley, P.J.; Neelarapu, R.; Sutherland, B.P.; Dasgupta, S.; Kloxin, C.J.; Kloxin, A.M. Photolabile Linkers: Exploiting Labile Bond Chemistry to Control Mode and Rate of Hydrogel Degradation and Protein Release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4671–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobashy, M.M. Cross-Linking Method-Based Nanogels for Biomedical Applications. In Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 3289–3305. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, B.; Hijazi, H.H.; Wu, M.; Carp, S.A. Mechanical and Hemodynamic Responses of Breast Tissue under Mammographic-like Compression during Functional Dynamic Optical Imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 5425–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campea, M.A.; Lofts, A.; Xu, F.; Yeganeh, M.; Kostashuk, M.; Hoare, T. Disulfide-Cross-Linked Nanogel-Based Nanoassemblies for Chemotherapeutic Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 25324–25338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Y.; Noh, S.M.; Nam, J.H.; Oh, J.K. Dual Sulfide–Disulfide Crosslinked Networks with Rapid and Room Temperature Self-Healability. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrop, B.H.; Frayne, S.H.; Choudhary, U. Thiol–Maleimide “Click” Chemistry: Evaluating the Influence of Solvent, Initiator, and Thiol on the Reaction Mechanism, Kinetics, and Selectivity. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3415–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, K.; Fredy, J.W.; Renard, P.-Y.; Sabot, C. Covalent Modification of Biomolecules through Maleimide-Based Labeling Strategies. Bioconjug Chem. 2018, 29, 2497–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvinen, J. Hydrazone Crosslinked Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Soft Tissue Engineering; Tampere University of Technology: Tampere, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, B.M.; Wilcox, D.G.; Randolph, M.A.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrazone Covalent Adaptable Networks Modulate Extracellular Matrix Deposition for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, J.; Elkhoury, K.; Velot, É.; Bianchi, A.; Acherar, S.; Francius, G.; Tamayol, A.; Grandemange, S.; Arab-Tehrany, E. Functionalized Liposomes for Targeted Breast Cancer Drug Delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 24, 401–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Feng, J.; Liu, W.; Wen, C.; Wu, Y.; Liao, Q.; Zou, L.; Sui, X.; Xie, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. Opportunities and Challenges for Co-Delivery Nanomedicines Based on Combination of Phytochemicals with Chemotherapeutic Drugs in Cancer Treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Huang, Q. Liposomes for Tumor Targeted Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Xu, H. Research Progress in Strategies to Improve the Efficacy and Safety of Doxorubicin for Cancer Chemotherapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2021, 21, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kataoka, K. Chemo-Physical Strategies to Advance the in Vivo Functionality of Targeted Nanomedicine: The Next Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 538–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Malhotra, J.; Kulkarni, P.; Horne, D.; Salgia, R.; Singhal, S.S. Emerging Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cabral, H.; Mi, P. Nanocarriers Address Intracellular Barriers for Efficient Drug Delivery, Overcoming Drug Resistance, Subcellular Targeting and Controlled Release. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 207, 115239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miatmoko, A.; Christy, P.K.; Isnaini, A.; Hariawan, B.S.; Cahyani, D.M.; Ahmad, M.; Diyah, N.W.; Adrianto, M.F.; Deevi, R.K.; Hamid, I.S. Characterization and in Vitro Anticancer Study of PEGylated Liposome Dually Loaded with Ferulic Acid and Doxorubicin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, S.; Komal, K.; Sharma, R.; Kurmi, B.D. Small Molecule Therapeutics for Receptor-Mediated Targeting through Liposomes in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. Bioorganic Chem. 2025, 160, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, L.; Mishra, L.; Patel, P.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, G.D.; Kurmi, B. Das Emerging Targeted Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Drug Target. 2023, 31, 889–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.; Wani, M.Y. Overcoming Resistance: Chitosan-Modified Liposomes as Targeted Drug Carriers in the Fight against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria-a Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278 Pt 4, 135022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The Blood–Brain Barrier: Structure, Regulation, and Drug Delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Chin, P.X.; Phang, Y.L.; Cheah, J.Y.; Ooi, S.C.; Mak, K.-K.; Pichika, M.R.; Kesharwani, P.; Hussain, Z. Transferrin Receptors-Targeting Nanocarriers for Efficient Targeted Delivery and Transcytosis of Drugs into the Brain Tumors: A Review of Recent Advancements and Emerging Trends. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad-Jabali, S.; Mahdinloo, S.; Farshbaf, M.; Sarfraz, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Atyabi, F.; Valizadeh, H. Transferrin Receptor-Mediated Liposomal Drug Delivery: Recent Trends in Targeted Therapy of Cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawak, P.; Sawaftah, N.M.A.; Pitt, W.G.; Husseini, G.A. Transferrin-Targeted Liposomes in Glioblastoma Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Z. Targeting Brain Drug Delivery with Macromolecules through Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonju, J.J.; Dahal, A.; Singh, S.S.; Jois, S.D. Peptide-Functionalized Liposomes as Therapeutic and Diagnostic Tools for Cancer Treatment. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 624–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunachowicz, D.; Kłosowska, K.; Sobczak, N.; Kepinska, M. Applicability of Quantum Dots in Breast Cancer Diagnostic and Therapeutic Modalities—A State-of-the-Art Review. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, N.N.; Ulu, G.T.; Abdulhadi, N.A.; Gürdap, S.; İşoğlu, İ.A.; Baran, Y.; İşoğlu, S.D. HER2-Specific Peptide (LTVSPWY) and Antibody (Herceptin) Targeted Core Cross-Linked Micelles for Breast Cancer: A Comparative Study. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. Theranostics: Integrated Diagnostics and Therapy Using Nanomedicine. In Nanomedicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 505–530. ISBN 3031724674. [Google Scholar]
- Kunjiappan, S.; Pavadai, P.; Vellaichamy, S.; Ram Kumar Pandian, S.; Ravishankar, V.; Palanisamy, P.; Govindaraj, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Premanand, A.; Sankaranarayanan, M. Surface Receptor-mediated Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Cancer Treatment: A State-of-the-art Review. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 309–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, İ.; İbrahim, M. Liposome–Ligand Conjugates: A Review on the Current State of Art. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-M.; Cheng, T.-L.; Roffler, S.R. Polyethylene Glycol Immunogenicity: Theoretical, Clinical, and Practical Aspects of Anti-Polyethylene Glycol Antibodies. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14022–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Ke, W.; Dirisala, A.; Toh, K.; Tanaka, M.; Li, J. Stealth and Pseudo-Stealth Nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 198, 114895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, H.B.; Hunter, A.C.; Farhangrazi, Z.S.; Moghimi, S.M. A Brief History of Long Circulating Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Deng, H.; Lu, J.; Chen, W. Emerging Strategies against Accelerated Blood Clearance Phenomenon of Nanocarrier Drug Delivery Systems. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, J.I.; Lammers, T.; Ashford, M.B.; Puri, S.; Storm, G.; Barry, S.T. Challenges and Strategies in Anti-Cancer Nanomedicine Development: An Industry Perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 108, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, E.; Kayser, V. Monoclonal Antibody Therapy of Solid Tumors: Clinical Limitations and Novel Strategies to Enhance Treatment Efficacy. Biologics 2019, 13, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, V.; Agrahari, V. Facilitating the Translation of Nanomedicines to a Clinical Product: Challenges and Opportunities. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 974–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, M.M.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; Chinnappan, R.; Al-Kattan, K.; Zourob, M. Aptamers: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agents for Blood Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bravo, K.M.C.; Liu, J. Targeted Liposomal Drug Delivery: A Nanoscience and Biophysical Perspective. Nanoscale Horiz. 2021, 6, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, S.; Angkawinitwong, U. Overview of Antibody Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, R.; Song, J.G.; Patil, B.R.; Lee, S.H.; Noh, H.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, G.-L.; Seo, S.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Jeong, S.H. Functional Ligands for Improving Anticancer Drug Therapy: Current Status and Applications to Drug Delivery Systems. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewska, S.; Sadowska, A.; Stefaniuk, N.; Misztalewska-Turkowicz, I.; Wilczewska, A.Z.; Car, H.; Niemirowicz-Laskowska, K. Tumor-Homing Peptides as Crucial Component of Magnetic-Based Delivery Systems: Recent Developments and Pharmacoeconomical Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Saoji, S.D.; Dande, P. Cabozantinib-Phospholipid Complex for Enhanced Solubility, Bioavailability, and Reduced Toxicity in Liver Cancer. Ther. Deliv. 2025, 16, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, M.E.; Soylukan, C.; Kulabhusan, P.K.; Günaydın, B.N.; Yuce, M. Material and Design Toolkit for Drug Delivery: State of the Art, Trends, and Challenges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 55201–55231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, M.; Yuan, T.; Yang, W.; Tian, C.; Miao, Z.; Wang, T. Small Molecules in Targeted Cancer Therapy: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as Targeted Therapeutics: Current Potential and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati, M.; Roushani, M. Three-Dimensional Modeling of Streptomycin Binding Single-Stranded DNA for Aptamer-Based Biosensors, a Molecular Dynamics Simulation Approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 3430–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Liu, X.; Zu, Y. Oligonucleotide Aptamers for Pathogen Detection and Infectious Disease Control. Theranostics 2021, 11, 9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevendran, R.; Sarah, S.; Tang, T.-H.; Citartan, M. Strategies to Bioengineer Aptamer-Driven Nanovehicles as Exceptional Molecular Tools for Targeted Therapeutics: A Review. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.S.; Hussein, S.A.; Ali, A.H.; Korma, S.A.; Lipeng, Q.; Jinghua, C. Liposome: Composition, Characterisation, Preparation, and Recent Innovation in Clinical Applications. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 742–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Du, C.; Guo, N.; Teng, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Yu, P.; Galons, H. Composition Design and Medical Application of Liposomes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Liu, D.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Hu, K.; Gu, N.; Ji, M. Liposomally Formulated Phospholipid-Conjugated Novel near-Infrared Fluorescence Probe for Particle Size Effect on Cellular Uptake and Biodistribution in Vivo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 161, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.S.; Johnson, M.P.; Najahi-Missaoui, W. Targeted Liposomal Drug Delivery: Overview of the Current Applications and Challenges. Life 2024, 14, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeckova, K.; Eckschlager, T.; Sirc, J.; Hobzova, R.; Plch, J.; Hrabeta, J.; Michalek, J. Nanodrugs Used in Cancer Therapy. In Biomedical Papers of the Medical Faculty of Palacky University in Olomouc; Palacký University: Olomouc, Czechia, 2019; Volume 163. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, J.S.; Tan, L.K.S.; Lee, W.L.; Ming, L.C.; How, C.W.; Foo, J.B.; Kifli, N.; Goh, B.H.; Ong, Y.S. Do Lipid-Based Nanoparticles Hold Promise for Advancing the Clinical Translation of Anticancer Alkaloids? Cancers 2021, 13, 5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Redox-Sensitive Irinotecan Liposomes with Active Ultra-High Loading and Enhanced Intracellular Drug Release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahover, E.; Patil, Y.P.; Gabizon, A.A. Emerging Delivery Systems to Reduce Doxorubicin Cardiotoxicity and Improve Therapeutic Index: Focus on Liposomes. Anticancer Drugs 2015, 26, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwana, V.; Karanjia, J.; Haselhorst, T.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; Rudrawar, S. Liposomal Doxorubicin as Targeted Delivery Platform: Current Trends in Surface Functionalization. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, E.; Gomes, A.C.; Preto, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Design of Liposomal Formulations for Cell Targeting. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabeu, E.; Cagel, M.; Lagomarsino, E.; Moretton, M.; Chiappetta, D.A. Paclitaxel: What Has Been Done and the Challenges Remain Ahead. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 474–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Porter, M.; Konstantopoulos, A.; Zhang, P.; Cui, H. Preclinical Development of Drug Delivery Systems for Paclitaxel-Based Cancer Chemotherapy. J. Control. Release 2017, 267, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkewar, A.; Mahajan, N.; Kharwade, R.; Gangane, P. Liposomes in the Targeted Gene Therapy of Cancer: A Critical Review. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 350–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottle, A.G. Liposomal Encapsulation of the Anti-Leukemic Small Molecule UNC0642 for Increased Tolerability. Master’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, T.O.B.; Haj Ahmad, R.R.; Ibegbu, D.M.; Smith, J.R.; Elkordy, A.A. Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems and Anticancer Drugs. Molecules 2018, 23, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukne, A.; Nair, S.; Momin, M. Nanophytopharmaceuticals: Harnessing the Biopotential of Phytomolecules for Maximal Therapeutic Efficacy. In NanoAgroceuticals & NanoPhytoChemicals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 99–149. [Google Scholar]
- Aghdam, M.A.; Bagheri, R.; Mosafer, J.; Baradaran, B.; Hashemzaei, M.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; de la Guardia, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Recent Advances on Thermosensitive and PH-Sensitive Liposomes Employed in Controlled Release. J. Control. Release 2019, 315, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, G. Sphingosomes: Highlights of the Progressive Journey and Their Application Perspectives in Modern Drug Delivery. Int. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringhieri, P.; Pannunzio, A.; Boccarelli, A.; Morelli, G.; Coluccia, M.; Tesauro, D. Effect of Cisplatin Containing Liposomes Formulated by Unsaturated Chain-Containing Lipids on Gynecological Tumor Cells. J. Liposome Res. 2016, 26, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gou, J.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhao, L.; Jin, X.; Tang, X. Synergistic Antitumor Efficacy Mediated by Liposomal Co-Delivery of Polymeric Micelles of Vinorelbine and Cisplatin in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2357–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boztepe, T.; Castro, G.R.; León, I.E. Lipid, Polymeric, Inorganic-Based Drug Delivery Applications for Platinum-Based Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooja, D.; Kadari, A.; Kulhari, H.; Sistla, R. Lipid-Based Nanomedicines: Current Clinical Status and Future Perspectives. In Lipid Nanocarriers for Drug Targeting; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 509–528. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, D. A Sojourn on Liposomal Delivery System: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Assay. Drug Dev. Technol. 2023, 21, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodallec, A.; Brunel, J.-M.; Giacometti, S.; Maccario, H.; Correard, F.; Mas, E.; Orneto, C.; Savina, A.; Bouquet, F.; Lacarelle, B. Docetaxel–Trastuzumab Stealth Immunoliposome: Development and in Vitro Proof of Concept Studies in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3451–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Arrieta, M.R.; Uria-Canseco, E.; Perez-Casas, S. Simultaneous Encapsulation of Hydrophilic and Lipophilic Molecules in Liposomes of DSPC. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 687, 178462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perinelli, D.R.; Cespi, M.; Palmieri, G.F.; Aluigi, A.; Bonacucina, G. High-Resolution Ultrasound Spectroscopy for the Determination of Phospholipid Transitions in Liposomal Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callmann, C.E.; Kusmierz, C.D.; Dittmar, J.W.; Broger, L.; Mirkin, C.A. Impact of Liposomal Spherical Nucleic Acid Structure on Immunotherapeutic Function. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrorov, A.M. Hyalurosomes: A Newer Approach for Drug Delivery. In Systems of Nanovesicular Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- You, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G. Multifunctional Liposomes Co-Modified with Ginsenoside Compound K and Hyaluronic Acid for Tumor-Targeted Therapy. Polymers 2024, 16, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, I.; Zaroudi, M.; Zhang, Y.; Aisenbrey, E.; Hui, L. Fabrication of Active Targeting Lipid Nanoparticles: Challenges and Perspectives. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 16, 100299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.; Soares, T.; Lopes, C.M.; Oliveira, M.E.C.D.R.; Lúcio, M. Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Anticancer Drugs and Natural Compounds. In Functional Lipid Nanosystems in Cancer; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2021; pp. 231–272. [Google Scholar]
- La-Beck, N.M.; Liu, X.; Wood, L.M. Harnessing Liposome Interactions with the Immune System for the next Breakthrough in Cancer Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhai, N.J.; Ramteke, S. CNTs Mediated CD44 Targeting; a Paradigm Shift in Drug Delivery for Breast Cancer. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzy, L.; Nasr, M.; Metwally, A.A.; Awad, G.A.S. Cancer Nanotheranostics: A Review of the Role of Conjugated Ligands for Overexpressed Receptors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Arya, D.K.; Ramar, M.K.; Chidambaram, K.; Rajinikanth, P.S. Engineered Nanomaterials as an Effective Tool for HER2+ Breast Cancer Therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Li, J.; Tan, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Emerging Approaches of Cell-based Nanosystems to Target Cancer Metastasis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydd, J.; Jadia, R.; Velpurisiva, P.; Gad, A.; Paliwal, S.; Rai, P. Targeting Strategies for the Combination Treatment of Cancer Using Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianat-Moghadam, H.; Heidarifard, M.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Panahi, Y.; Hamishehkar, H.; Pouremamali, F.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Nouri, M. Cancer Stem Cells-Emanated Therapy Resistance: Implications for Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Release 2018, 288, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasan, N.; Baselga, J.; Hyman, D.M. A View on Drug Resistance in Cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J.M.; Peer, D. Progress and Challenges towards Targeted Delivery of Cancer Therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, Z.; Karim, S. Nanoparticles-Based Drug Delivery and Gene Therapy for Breast Cancer: Recent Advancements and Future Challenges. In Proceedings of the Seminars in Cancer Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 69, pp. 226–237. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Qiu, Y.; Su, X. Targeting CXCL12-CXCR4 Signaling Enhances Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy against Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 157, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cai, G.-X.; Han, B.-W.; Guo, Z.-W.; Wu, Y.-S.; Lyu, X.; Huang, L.-M.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Li, X.; Ye, G.-L. Association between the Nucleosome Footprint of Plasma DNA and Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response for Breast Cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toracchio, L.; Carrabotta, M.; Mancarella, C.; Morrione, A.; Scotlandi, K. EphA2 in Cancer: Molecular Complexity and Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehal, N.; Rohilla, A.; Sartaj, A.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Folic Acid Modified Precision Nanocarriers: Charting New Frontiers in Breast Cancer Management beyond Conventional Therapies. J. Drug Target. 2024, 32, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Song, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhou, H.; Wang, F.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, M. Annotation of CD8+ T-Cell Function via ICAM-1 Imaging Identifies FAK Inhibition as an Adjuvant to Augment the Antitumor Immunity of Radiotherapy. Theranostics 2024, 14, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, O.; Thevenard Devy, J.; Billottet, C.; Schneider, C.; Etique, N.; Dupuy, J.-W.; Raymond, A.-A.; Boulagnon Rombi, C.; Meunier, M.; Djermoune, E.-H. LRP-1 Matricellular Receptor Involvement in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Tumor Angiogenesis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongchot, S.; Aksonnam, K.; Thuwajit, P.; Yenchitsomanus, P.-T.; Thuwajit, C. Nucleolin-based Targeting Strategies in Cancer Treatment: Focus on Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 52, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Ren, J.; Orive, G.; Yu, G. P-Glycoprotein (P-Gp)-Driven Cancer Drug Resistance: Biological Profile, Non-Coding RNAs, Drugs and Nanomodulators. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 104161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.E.; Crawford, C.I.; Houson, H.A.; Omweri, J.M.; Pukkanasut, P.; Gallegos, C.A.; Whitt, J.D.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Lapi, S.E.; Sorace, A.G. Characterizing SSTR2 Expression and Modulation for Targeted Imaging and Therapy in Preclinical Models of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.S.; Osman, M.A. An Emerging Role for Sigma Receptor 1 in Personalized Treatment of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Guo, Z.; Yu, S.; Jiang, L.; Huang, M. Development of Inhibitors for UPAR: Blocking the Interaction of UPAR with Its Partners. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, G.; Alzhrani, R.; Alsaab, H.O.; Atef, M.; Sau, S.; Iyer, A.K.; Banna, H. El CD44 Targeted Nanomaterials for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.M.; Shastry, M.; Hamilton, E. Targeting HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: Advances and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Vatanmakanian, M.; Mahdiannasser, M.; Mashouri, L.; Alahari, N.V.; Monjezi, M.R.; Ilbeigi, S.; Alahari, S.K. Understanding the Role of Integrins in Breast Cancer Invasion, Metastasis, Angiogenesis, and Drug Resistance. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1043–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, H.S.A.; Varamini, P. New Drug Delivery Strategies Targeting the GnRH Receptor in Breast and Other Cancers. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, R251–R269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Guo, T.; Lin, M. Advances in MUC1-Mediated Breast Cancer Immunotherapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäenpää, N.; Tiainen, L.; Hämäläinen, M.; Luukkaala, T.; Tanner, M.; Lahdenperä, O.; Vihinen, P.; Karihtala, P.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L.; Moilanen, E. Neuropilin-1 and Placental Growth Factor as Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rej, R.K.; Thomas, J.E.; Acharyya, R.K.; Rae, J.M.; Wang, S. Targeting the Estrogen Receptor for the Treatment of Breast Cancer: Recent Advances and Challenges. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 8339–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyaratanakornkit, V.; McGowan, E.M.; Márquez-Garbán, D.C.; Burton, L.P.; Hamilton, N.; Pateetin, P.; Pietras, R.J. Progesterone Receptor Signaling in the Breast Tumor Microenvironment. Tumor Microenviron. Nov. Concepts 2021, 1329, 443–474. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, M.J. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Therapeutic Targets in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1108695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banudevi, S. Phospholipases A2 as a Therapeutic Target in Prostate Cancer. In Phospholipases in Physiology and Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 209–227. [Google Scholar]
- Drescher, S.; van Hoogevest, P. The Phospholipid Research Center: Current Research in Phospholipids and Their Use in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Ni, R.; Zhou, J.; Mao, S. Recent Advances in Controlled Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebati, S.K.; Marucci, G.; Santinelli, C.; Buccioni, M.; Amenta, F. Choline-Containing Phospholipids: Structure-Activity Relationships versus Therapeutic Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 4328–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.H.; Zou, X.; Abed, S.M.; Korma, S.A.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Natural Phospholipids: Occurrence, Biosynthesis, Separation, Identification, and Beneficial Health Aspects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, M.; Kaki, S.S.; Karuna, M.S.L.; Sarada, S.; Kumar, C.G.; Prasad, R.B.N. Synthesis and in Vitro Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Studies of Novel Structured Phosphatidylcholines with Phenolic Acids. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, E.; Onguka, O.; Claypool, S.M. Phosphatidylethanolamine Metabolism in Health and Disease. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 321, 29–88. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.; Witt, S.N. Ethanolamine and Phosphatidylethanolamine: Partners in Health and Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4829180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunsom, N.J.; Cockcroft, S. Phosphatidylinositol Synthesis at the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeh, K.; Summers, P.A.; Gould, I.R.; Woscholski, R.; Vilar, R. Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of a Tripodal Receptor for Phosphatidylinositol Phosphates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrouni, A.G.; Baskin, J.M. The Chemistry and Biology of Phosphatidylinositol 4-Phosphate at the Plasma Membrane. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2021, 40, 116190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, X.; Bi, Y. Phosphatidylserine: An Overview on Functionality, Processing Techniques, Patents, and Prospects. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Fan, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xue, C. Identification of a Novel Phospholipase D with High Transphosphatidylation Activity and Its Application in Synthesis of Phosphatidylserine and DHA-Phosphatidylserine. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 249, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Beisson, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Harwood, J. Lipids: From Chemical Structures, Biosynthesis, and Analyses to Industrial Applications. In Lipids in Plant and Algae Development; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 86, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zegarlinska, J.; Piaścik, M.; Sikorski, A.F.; Czogalla, A. Phosphatidic Acid–a Simple Phospholipid with Multiple Faces. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Jung, S.-W.; Kim, H.-K.; Nah, S.-Y. Plant Lysophosphatidic Acids: A Rich Source for Bioactive Lysophosphatidic Acids and Their Pharmacological Applications. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, G.; Wilson, I.D.; Plumb, R.S. Application of Hybrid Surface Technology for Improving Sensitivity and Peak Shape of Phosphorylated Lipids Such as Phosphatidic Acid and Phosphatidylserine. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1669, 462921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmmed, M.K.; Hachem, M.; Ahmmed, F.; Rashidinejad, A.; Oz, F.; Bekhit, A.A.; Carne, A.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. Marine Fish-Derived Lysophosphatidylcholine: Properties, Extraction, Quantification, and Brain Health Application. Molecules 2023, 28, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.-H.; Chan, M.-L.; Marathe, G.K.; Parveen, F.; Chen, C.-H.; Ke, L.-Y. An Updated Review of Lysophosphatidylcholine Metabolism in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, J.S.; Falabella, M.; Flannery, P.J.; Hanna, M.G.; Heales, S.J.R.; Pope, S.A.S.; Pitceathly, R.D.S. Advances in Methods to Analyse Cardiolipin and Their Clinical Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vítová, M.; Stránská, M.; Palyzová, A.; Řezanka, T. Detailed Structural Characterization of Cardiolipins from Various Biological Sources Using a Complex Analytical Strategy Comprising Fractionation, Hydrolysis and Chiral Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1648, 462185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Physico-Chemical Properties of Phospholipids and Lipid-Water Systems. In Liposome Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh, H.; Nik, M.E.; Mashreghi, M.; Saberi, Z.; Jaafari, M.R.; Teymouri, M. A Study on the Role of Cholesterol and Phosphatidylcholine in Various Features of Liposomal Doxorubicin: From Liposomal Preparation to Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Phosphatidylcholine-Rutin Complex as a Potential Nanocarrier for Food Applications. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Effects of Homogeneous and Ultrasonic Treatment on Casein/Phosphatidylcholine Complex-Emulsions: Stability and Bioactivity Insights. Ultrason. Sonochem 2023, 97, 106457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesiltas, B.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Sørensen, A.-D.M.; Akoh, C.C.; Jacobsen, C. Physical and Oxidative Stability of High Fat Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized with Sodium Caseinate and Phosphatidylcholine as Emulsifiers. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E. Historical Perspective: Phosphatidylserine and Phosphatidylethanolamine from the 1800s to the Present. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 923–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, E.E.; Jovanovic, O. The Role of Phosphatidylethanolamine Adducts in Modification of the Activity of Membrane Proteins under Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendecki, A.M.; Poyton, M.F.; Baxter, A.J.; Yang, T.; Cremer, P.S. Supported Lipid Bilayers with Phosphatidylethanolamine as the Major Component. Langmuir 2017, 33, 13423–13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges-Araújo, L.; Fernandes, F. Structure and Lateral Organization of Phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-Bisphosphate. Molecules 2020, 25, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Vogt, V.M.; Feigenson, G.W. Multivalent Cation-Bridged PI (4, 5) P2 Clusters Form at Very Low Concentrations. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2630–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozelli, J.C.; Jennings, W.; Black, S.; Hou, Y.H.; Lameire, D.; Chatha, P.; Kimura, T.; Berno, B.; Khondker, A.; Rheinstädter, M.C. Membrane Curvature Allosterically Regulates the Phosphatidylinositol Cycle, Controlling Its Rate and Acyl-Chain Composition of Its Lipid Intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 17780–17791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Niu, L. Aqueous–Solid System for Highly Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Transphosphatidylation Catalyzed by Phospholipase D to Produce Phosphatidylserine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7555–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehal, R.P.; Marbach, H.; Hubbard, A.T.M.; Sacranie, A.A.; Sebastiani, F.; Fragneto, G.; Harvey, R.D. The Influence of Mild Acidity on Lysyl-Phosphatidylglycerol Biosynthesis and Lipid Membrane Physico-Chemical Properties in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2017, 206, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugail, I.; Kayser, B.D.; Lhomme, M. Specific Roles of Phosphatidylglycerols in Hosts and Microbes. Biochimie 2017, 141, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretiakova, D.S.; Volynsky, P.E.; Kobanenko, M.K.; Alekseeva, A.S.; Le-Deygen, I.M.; Vodovozova, E.L.; Boldyrev, I.A. Phosphatidylglycerol in Lipid Bilayer. Molecular Recognition, Conformational Transitions, Hydrogen Bonding and Microviscosity. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 411, 125688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolik, S.; Albrieux, C.; Schneck, E.; Demé, B.; Jouhet, J. Sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol and Phosphatidylglycerol Bilayers Share Biophysical Properties and Are Good Mutual Substitutes in Photosynthetic Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 184037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.E.; Rieckmann, M.; Lucas, H.; Meister, A.; Loppnow, H.; Mäder, K. Phosphatidylserine (PS) and Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) Enriched Mixed Micelles (MM): A New Nano-Drug Delivery System with Anti-Inflammatory Potential? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Huo, Y.; Yang, N.; Wei, T. Phosphatidic Acid: From Biophysical Properties to Diverse Functions. FEBS J. 2024, 291, 1870–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putta, P.; Rankenberg, J.; Korver, R.A.; van Wijk, R.; Munnik, T.; Testerink, C.; Kooijman, E.E. Phosphatidic Acid Binding Proteins Display Differential Binding as a Function of Membrane Curvature Stress and Chemical Properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwolek, U.; Kulig, W.; Wydro, P.; Nowakowska, M.; Róg, T.; Kepczynski, M. Effect of Phosphatidic Acid on Biomembrane: Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 10042–10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Lin, J.; Yu, L.; Yan, M. Lysophosphatidylcholine: Potential Target for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabutzki, P.; Schiller, J.; Engel, K.M. Phospholipid-Derived Lysophospholipids in (Patho) Physiology. Atherosclerosis 2024, 398, 118569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemel, J.R.; Michaels, N.J.; Weishaupt, N.; Caprariello, A.V.; Keough, M.B.; Rogers, J.A.; Yukseloglu, A.; Lim, J.; Patel, V.V.; Rawji, K.S. Mechanisms of Lysophosphatidylcholine-induced Demyelination: A Primary Lipid Disrupting Myelinopathy. Glia 2018, 66, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.S.; Duarte, E.L.; Lamy, M.T.; Rozenfeld, J.H.K. DODAB Vesicles Containing Lysophosphatidylcholines: The Relevance of Acyl Chain Saturation on the Membrane Structure and Thermal Properties. Biophys. Chem. 2023, 300, 107075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathappa, M.; Alder, N.N. The Ionization Properties of Cardiolipin and Its Variants in Model Bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Villa, L.; Manrique-Moreno, M.; Leidy, C.; Jemioła-Rzemińska, M.; Ortíz, C.; Strzałka, K. Biophysical Evaluation of Cardiolipin Content as a Regulator of the Membrane Lytic Effect of Antimicrobial Peptides. Biophys. Chem. 2018, 238, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmer-Dixon, M.M. Elucidaton of the Pysical and Chemical Properties of Cytochrome C-Cardiolipin Interactions; University of Montana: Missoula, Montana, 2018; ISBN 0438159896. [Google Scholar]
- Panov, A.V.; Dikalov, S.I. Cardiolipin, Perhydroxyl Radicals, and Lipid Peroxidation in Mitochondrial Dysfunctions and Aging. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1323028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoqrot, S.; Abusulieh, S.; Abusara, O.H. Identifying Synergistic Combinations of Doxorubicin-Loaded Polyquercetin Nanoparticles and Natural Products: Implications for Breast Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 645, 123392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedretdinov, F.N.; Kostryukova, L.V. A Dual-Vector Phospholipid Nanosystem of Doxorubicin: Accumulation and Cytotoxic Effect in Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro. Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya 2023, 69, 409–419. [Google Scholar]
- Sabeti, B.; Noordin, M.I.; Mohd, S.; Hashim, R.; Dahlan, A.; Akbari Javar, H. Development and Characterization of Liposomal Doxorubicin Hydrochloride with Palm Oil. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 765426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavoshi, H.; Taheri, M.; Wan, M.L.Y.; Sabzichi, M. Crocin-Loaded Liposomes Sensitize MDA-MB 231 Breast Cancer Cells to Doxorubicin by Inducing Apoptosis. Process Biochem. 2023, 130, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelska, A.; Mazur, M.; Świtalska, M.; Wietrzyk, J.; Sigorski, D.; Fronczyk, K.; Wiktorska, K. Anticancer Effect and Safety of Doxorubicin and Nutraceutical Sulforaphane Liposomal Formulation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Animal Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-H.; Li, T.; Gao, H.-W.; Sun, W.; Chen, X.-P.; Wang, Y.-T.; Lu, J.-J. Platycodin D from Platycodonis Radix Enhances the Anti-Proliferative Effects of Doxorubicin on Breast Cancer MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Cells. Chin. Med. 2014, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.; Hill, D.; Chaw, C.S.; Elkordy, A.A. Novel Combinational Nanomedicines, Liposomes, to Tackle Breast Cancer. J. Microencapsul. 2025, 42, 368–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Das, T.K. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems: From Laboratory Research to Industrial Production—Instruments and Challenges. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.J.; Pinheiro, M.; Neves, A.R.; Pinto, M.M.M. Therapeutic Potential of Genistein: Preclinical Studies, Clinical Evidence, and Nanotechnology Application. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 2480–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.-J.; Wang, M.-H.; Ho, C.-T.; Pan, M.-H. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A New Revolutionization of Modern Healthy Diets and Biomedical Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 2853–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, V.P.; Nalla, L.V.; Balar, P.; Bezbaruah, R.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Singla, R.K.; Khadela, A.; Vora, L.; Uversky, V.N. Advanced Phytochemical-Based Nanocarrier Systems for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Guo, F.; Xu, H.; Liang, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.-D. Combination Therapy Using Co-Encapsulated Resveratrol and Paclitaxel in Liposomes for Drug Resistance Reversal in Breast Cancer Cells in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Pace, R.C.C.; Liu, X.; Sun, M.; Nie, S.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Q.; Gao, W.; Pan, X.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S. Anticancer Activities of (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Encapsulated Nanoliposomes in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Liposome Res. 2013, 23, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousfan, A.; Moursel, N.; Hanano, A. Encapsulation of Paclitaxel into Date Palm Lipid Droplets for Enhanced Brain Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 32057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Widjaya, A.S.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Long, Z.; Jiang, Y. Cell-Penetrating Corosolic Acid Liposome as a Functional Carrier for Delivering Chemotherapeutic Drugs. Acta Biomater. 2020, 106, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; de Araújo Júnior, R.F.; Cavalcante, R.S.; Yu, Z.; Schomann, T.; Gu, Z.; Eich, C.; Cruz, L.J. Effective Breast Cancer Therapy Based on Palmitic Acid-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 145, 213270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.S.; Roque, M.C.; de Barros, A.L.B.; de Oliveira Silva, J.; Cassali, G.D.; Oliveira, M.C. Investigation of the Antitumor Activity and Toxicity of Long-Circulating and Fusogenic Liposomes Co-Encapsulating Paclitaxel and Doxorubicin in a Murine Breast Cancer Animal Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, R.; Hassandokht, F.; Ardakani, M.T.; Karimi, B.; Roustazadeh, A.; Tarvirdipour, S.; Barmak, M.J.; Nikseresht, M.; Baneshi, M.; Mousavizadeh, A. Intercalation of Curcumin into Liposomal Chemotherapeutic Agent Augments Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 35, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Arya, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Kaushik, A.; Mishra, Y.K.; Rajinikanth, P.S. Dual Ligand Functionalized PH-Sensitive Liposomes for Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment: In Vitro and in Vivo Assessment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2025, 13, 2682–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloy, J.O.; Petrilli, R.; Chesca, D.L.; Saggioro, F.P.; Lee, R.J.; Marchetti, J.M. Anti-HER2 Immunoliposomes for Co-Delivery of Paclitaxel and Rapamycin for Breast Cancer Therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 115, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilinezhad, M.A.; Amini, A.; Dara, T.; Alipour, S. Methotrexate and Curcumin Co-Encapsulated PLGA Nanoparticles as a Potential Breast Cancer Therapeutic System: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Keywords/Search Terms |
|---|
| (“Breast Cancer” AND “Treatment” OR “Management” OR “Therapy”) AND (“Surgery” OR “Chemotherapy” OR “Radiation” OR “Targeted Therapy” OR “Hormonal Therapy” OR “Drug Delivery”)AND (“Plant-Based Phospholipids” OR “Plant-Derived Phospholipids” OR “Palm Oil” OR “Soy Lecithin” OR “Sunflower Lecithin) AND (“Liposomes” OR “Encapsulation”) AND (“Case Study” OR “Case Report” OR “Clinical Trial” OR “Patient Outcome”) |
| Functionalization Strategy | Chemistry Feature | Advantages | Mechanisms of Action | Limitations | Example Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imine-crosslinked | Glutaraldehyde-mediated linkage between aldehyde and primary amine | Simple, efficient, reversible bonding | Short-term release in mildly acidic tumor microenvironment (pH 5–6); enables nanoparticle or hydrogel surface functionalization via reversible imine bond formation | Hydrolysis-prone at physiological pH; potential cytotoxicity of glutaraldehyde | Tumor-targeted short-term drug release | [55] |
| Amide-crosslinked | Primary amine and carboxylic acid (often EDC/NHS-mediated) | Stable, robust in vivo covalent linkage | Durable bond for ligand (e.g., antibody/peptide) attachment; supports active targeting of tumor antigens | Requires available carboxylic group; coupling chemistry may require activation | Antibody–drug conjugates, peptide–nanoparticle conjugates | [56,57,58] |
| Disulfide-crosslinked | Thiol and pyridyldithiol exchange reaction | Redox-responsive release | Facilitates drug release inside tumor cells with high glutathione levels; offers intracellular specificity | Susceptible to premature cleavage in bloodstream due to reductants | Intracellular cancer drug delivery | [59,60,61] |
| Thiol–maleimide | Michael-type addition between thiol and maleimide | Specific, mild conditions | Enables site-specific conjugation of targeting ligands; supports efficient dual-ligand targeting | Potential thiol exchange or instability in vivo | Antibody–nanoparticle conjugation, dual-ligand targeting systems | [62,63] |
| Hydrazone-crosslinked | Aldehyde and hydrazine | pH-sensitive release in acidic tumor microenvironment | Hydrazone linker cleaves under mildly acidic conditions (pH 5–6), enabling controlled drug release | Hydrolysis at neutral pH can occur | Acidic tumor microenvironment-targeted drug release | [64,65] |
| Liposomal System | Name of Drugs | Composition | Size (nm) | Targeting Strategy | Advantages | Limitations | Approval Status | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doxil®/Caelyx® | Doxorubicin | PEGylated liposomes | ~100 | Passive (EPR effect via PEGylation) | Long circulation time, reduced cardiotoxicity | Hand–foot syndrome, stomatitis | Approved | [110] |
| Onivyde® | Irinotecan | Lipid bilayers encapsulating irinotecan | ~110 | Passive (EPR) | Improved stability, prolonged circulation | No active targeting | Approved | [111,112,113] |
| HER2-immunoliposome (investigational) | Doxorubicin | Cholesterol, DSPC, DSPE-PEG2000 with anti-HER2 antibody | 70–150 | Active (HER2) | Enhanced specificity for HER2+ tumors | Investigational, potential immunogenicity | Investigational | [114,115,116] |
| Lipusu® | Paclitaxel | Phosphatidylcholine, cholesterol | 100–200 | Passive (EPR) | Improved pharmacokinetics | High manufacturing costs | Approved (China) | [117,118] |
| Myocet® | Doxorubicin | Non-PEGylated liposomes (PC, cholesterol) | 150–200 | Passive (EPR) | Reduced cardiotoxicity vs. free DOX | Shorter circulation than PEGylated forms | Approved (EU, Canada) | [119,120,121] |
| Marqibo® | Vinorelbine | Sphingomyelin, Cholesterol | ~100 | Passive (EPR) | Improved stability, enhanced delivery to tumors | No active targeting, potential off-site accumulation | Approved (US) | [122,123,124] |
| Lipoplatin® | Cisplatin | Dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl glycerol (DPPG), soy phosphatidylcholine (SPC-3), cholesterol, polyethylene glycol (PEG) | 110–120 | Passive (EPR) | Reduced toxicity, prolonged circulation | Decreased recognition by the immune system. | Investigational/Limited markets | [125,126,127] |
| LEM-ETU (investigational) | Mitoxantrone | Egg phosphatidylcholine (EPC), cholesterol, polyethylene glycol (PEG) coating | 100–150 | Likely passive (no verified RNA targeting) | Enhanced tumor accumulation | Passive targeting and accumulation in off-targeted sites, hence leads to side effects in non-tumor tissues. | Investigational | [128,129] |
| Trastuzumab-immunoliposome | Doxorubicin | Phospholipids, cholesterol | 100–150 | Active (HER2) | High efficacy in HER2+ tumors | Not effective in HER2– tumors | Investigational | [27,130] |
| DMPC/DSPC Cholesterol liposomes | Doxorubicin | Dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC), distearoylphosphatidylcholine (DSPC), cholesterol | 100–150 | Passive (EPR) | Enhanced stability, reduced cardiotoxicity | Non-specific accumulation | Research | [131,132,133] |
| Hyaluronic acid-liposomes | Doxorubicin and paclitaxel | Phospholipids, cholesterol | 100–150 | Active (CD44) | Dual drug delivery, CD44 specificity | Limited to CD44+ tumors | Investigational | [134,135] |
| Hyaluronic acid-liposomes | Shikonin | Phospholipids, cholesterol and hyaluronic acid (HA) | 100–150 | Active (CD44) | Enhanced stability, CD44 specificity | Limited to CD44+ tumors | Investigational | [136,137] |
| Cell Surface Receptor | Role in Cancer | Targeting Strategy | Potential Benefits | Relevance to Breast Cancer | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4 (CXCR4) | Overexpressed in breast tumors; regulates migration, invasion, and metastatic spread via CXCL12 axis. | CXCR4 antagonists (e.g., AMD3100) in liposomal or nanoparticle formulations. | Reduces metastatic dissemination and enhances therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapeutics. | Highly expressed in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and linked to poor prognosis. | In TNBC xenografts, CXCR4 blockade reduced lung metastases and synergized with chemotherapy [148]. |
Cell Surface Nucleosomes | Involved in immune evasion by cancer cells. | Targeted liposomes to enhance immune response against tumors. | Promotes immune-mediated destruction of cancer cells. | Present on breast cancer cells, contributing to immune escape mechanisms. | Increased nucleosome levels correlate with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients [149]. |
Eph Receptors | Facilitates cell signaling and tumor progression. | Liposomes designed to disrupt Eph receptor signaling. | Reduces tumor growth; interferes with proliferative signaling. | EphA2 is particularly relevant; associated with aggressive breast cancer phenotypes. | EphA2-targeted therapies have shown reduced tumor growth in xenograft models [150]. |
Folate Receptor | Overexpressed in many cancers, including breast cancer. | Folate-targeted liposomes for improved drug delivery. | Enhances therapeutic agent concentration in tumors; minimizes off-target effects. | High expression in breast cancer cells; improves targeting for chemotherapeutics. | Folate-targeted liposomal formulations enhanced delivery and efficacy of doxorubicin in breast cancer models [151]. |
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) | Cell adhesion molecule involved in tumor–endothelial interactions and immune cell infiltration. | Antibody–drug conjugates, imaging probes, and RNA-based silencing. | May limit metastatic colonization and facilitate immune targeting. | ICAM-1 is expressed in several solid tumors; limited direct targeting data in breast cancer. | Breast cancer imaging studies demonstrate ICAM-1 overexpression; functional blockade studies sparse [152]. |
Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein-1 (LRP-1) | Endocytic receptor implicated in tumor cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. | siRNA-mediated knockdown, receptor-blocking peptides, and ligand-targeted nanocarriers. | Delays tumor growth and reduces angiogenic signaling. | Preferentially expressed in TNBC, correlating with invasive phenotype. | LRP-1 silencing in MDA-MB-231 xenografts caused ~60% tumor growth delay [153]. |
Nucleolin | Multifunctional protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and regulation of mRNA stability; overexpressed on cancer cell surfaces. | AS1411 aptamer-based nanocarriers and targeted drug delivery systems. | Enables selective drug delivery and tumor imaging. | Highly expressed in breast cancer cells; absent or low in normal tissues. | Nucleolin-targeted nanoparticles demonstrated selective cytotoxicity in breast cancer models [154] |
P-glycoprotein (P-gp)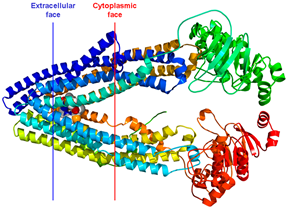 | ATP-dependent efflux transporter mediating multidrug resistance. | Co-delivery of P-gp inhibitors with chemotherapeutics using nanocarriers. | Restores chemosensitivity and increases intracellular drug accumulation. | Upregulated in resistant breast cancer cell lines. | P-gp inhibition via nanoparticle delivery increased doxorubicin retention and efficacy in resistant breast cancer cells [155]. |
Somatostatin Receptor | G-protein coupled receptor involved in hormone regulation and tumor growth suppression. | Radiolabeled peptides (e.g., 68Ga-DOTATATE) and SSTR2-inducing epigenetic modulators. | Improves imaging sensitivity and enables targeted radionuclide therapy. | Inducible in TNBC cells; baseline expression varies. | HDAC inhibitor pretreatment enhanced SSTR2 expression and imaging in TNBC models [156]. |
Sigma Receptor | Chaperone protein regulating calcium signaling, ER stress, and cell survival. | Small-molecule antagonists and targeted nanoparticles. | Induces apoptosis and reduces tumor proliferation. | Overexpressed in breast cancer tissue and cell lines. | Sigma-1 inhibition reduced breast tumor cell viability in vitro and tumor growth in vivo [157]. |
Transferrin Receptor (TfR) | Iron uptake receptor highly expressed in proliferating cells. | Tf-conjugated liposomes and nanoparticles for chemotherapeutic delivery. | Enhances drug accumulation in tumor cells and reduces systemic toxicity. | Upregulated in breast tumors; associated with aggressive phenotype. | TfR-targeted liposomal doxorubicin improved therapeutic index in preclinical breast cancer models [79]. |
Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (uPAR) | Regulates extracellular matrix degradation and cell migration. | Peptide-based ligands and antibody-drug conjugates targeting uPAR. | Suppresses invasion and metastasis. | Highly expressed in invasive breast carcinomas. | uPAR-targeted nanoparticles reduced metastatic burden in breast cancer xenografts [158]. |
| Transmembrane | |||||
Biotin Receptor | Overexpressed in many cancers. | Biotin-targeted liposomes improve drug delivery specificity. | Enhances specificity in drug delivery; minimizes off-target effects. | Increased expression in breast cancer enhances targeting capabilities. | Biotinylated liposomes have shown improved accumulation in breast cancer models [41]. |
Cluster of Differentiation 44 (CD44) | Involved in cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation. | CD44-targeted liposomes can reduce tumor growth and metastasis. | Inhibits tumor cell adhesion and migration; improves treatment efficacy. | CD44 is often overexpressed in breast cancer and is linked to aggressive behavior. | CD44-targeted therapies reduce tumor growth and improve survival rates in breast cancer models [159]. |
Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors 2 (HER2) | Receptor tyrosine kinase driving cell proliferation and survival. | Monoclonal antibodies (trastuzumab), antibody–drug conjugates, and HER2-targeted nanoparticles. | Improves survival and reduces recurrence in HER2+ breast cancer. | Overexpressed in ~20% of breast cancers; marker of aggressive disease. | HER2-targeted therapies have transformed prognosis in HER2+ breast cancer patients [160]. |
Integrin Receptors | Mediators of cell adhesion, migration, and angiogenesis. | RGD peptide-modified nanoparticles and integrin-blocking antibodies. | Reduces angiogenesis and metastatic spread. | Integrin αvβ3 and α6β4 overexpressed in aggressive breast cancer subtypes. | Integrin-targeted drug delivery enhanced anti-tumor efficacy in breast models [161]. |
Luteinizing Hormone-releasing Hormone Receptor (LHRHR) | Involved in hormone regulation; overexpressed in some cancers. | LHRHR-targeted liposomes deliver drugs to hormone-responsive tumors. | Enhances targeting for hormone-dependent therapies; improves outcomes. | LHRHR is expressed in some breast cancer types, enabling specific targeting. | LHRH analogs have been shown to inhibit breast cancer cell growth in preclinical studies [162]. |
Mucin 1 (MUC1) | Transmembrane glycoprotein involved in cell adhesion and signaling. | MUC1-specific antibodies, vaccines, and nanocarriers. | Enables selective targeting and immunomodulation. | Overexpressed in >90% of breast carcinomas. | MUC1-targeted liposomes improved drug delivery in breast cancer xenografts [163]. |
Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) | Involved in angiogenesis and tumor growth. | NRP1-targeted liposomes can inhibit blood vessel formation in tumors. | Reduces tumor growth and metastasis; disrupts angiogenic processes. | NRP1 is involved in the aggressive growth of breast tumors through angiogenesis. | NRP1 blockade has been shown to reduce tumor angiogenesis and growth in breast cancer studies [164]. |
| Internal Cell Receptor | |||||
Estrogen Receptors (ERs) | Mediate the effects of estrogen; involved in hormone-responsive breast cancer. | ER-targeted liposomes to deliver drugs specifically to estrogen-responsive tumors. | Enhances specificity of drug delivery; improves efficacy in ER-positive tumors. | ER is overexpressed in many breast cancers, making it a critical target for therapy. | ER-targeted therapies form backbone of hormone therapy in breast cancer [165]. |
Progesterone Receptors (PRs) | Mediate the effects of progesterone; involved in hormone-responsive breast cancer. | PR-targeted liposomes can improve drug delivery to progesterone-responsive tumors. | Increases drug concentration in PR-positive tumors; minimizes side effects. | PR expression is crucial in a subset of breast cancers, especially in ER-positive cases. | PR-targeted therapies enhance therapeutic efficacy in PR-positive breast cancer models [166]. |
| Enzyme | |||||
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) | Proteolytic enzymes promoting extracellular matrix degradation and metastasis. | MMP inhibitors and MMP-cleavable prodrugs. | Limits invasion and metastatic dissemination. | MMP-2 and MMP-9 overexpressed in invasive breast cancers. | MMP-activated drug conjugates reduced metastasis in preclinical models [167] |
Secretory Phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) | Involved in inflammation and tumor progression; associated with tumor microenvironment changes. | sPLA2-targeted liposomes can enhance drug delivery to tumors with high sPLA2 activity. | Increases drug accumulation in tumor sites; reduces side effects in healthy tissues. | High sPLA2 activity correlates with aggressive breast cancer phenotypes. | Targeting sPLA2 in liposomes has shown improved drug delivery and anti-tumor effects in breast cancer studies [168]. |
| Types | IUPAC Name | Sources | Synthesis | Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)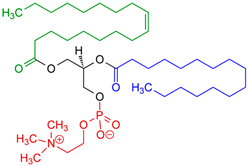 | 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Soybeans, sunflower seeds, mustard seeds, rapeseed, and palm oil. | Extraction from lecithin; lyso-PC generated enzymatically from PC when needed for derivatization (e.g., ethanolysis → 2-acyl-1-lyso-PC). | Commonly used in functional foods and pharmaceutical products, PC improves bioavailability and nutrient absorption. Palm oil-derived PC is especially valued for stability in emulsions and liposome formulations. | [171,172,173] |
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)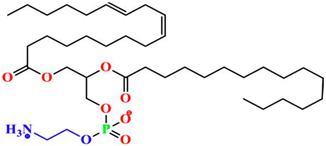 | 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Soybeans, sunflower seeds, mustard seeds, and palm oil. | Biological routes (cellular): CDP-ethanolamine (Kennedy) pathway and mitochondrial phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (PISD/PSD) are the two major PE sources; lyso-PE acylation and head-group exchange are minor. | PE is essential in cell membranes for flexibility and permeability. Palm oil-derived PE is particularly useful in creating stable liposomes for drug delivery systems due to its membrane-assisting properties. | [174,175] |
Phosphatidylinositol (PI)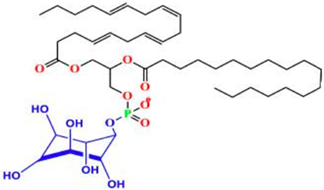 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate | Soybeans, peanuts, legumes, and palm oil. | De novo PI synthesis at the ER: PA → CDP-DG → PI (via CDS1/2 and PI synthase), followed by acyl-chain remodeling; PLD transphosphatidylation can access PI from PC. | Involved in cellular signaling and beneficial in cosmetics due to its hydrating properties. PI from palm oil is also valued in food and pharmaceutical formulations where additional stability is desired. | [176,177,178] |
Phosphatidylserine (PS)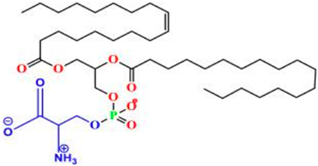 | 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine | Soybeans, sunflower seeds, and palm oil. | Dominant industrial method: PLD-mediated transphosphatidylation of PC with L-serine (aqueous/green solvent systems); avoids animal sources. | Known for supporting cognitive health, PS is popular in neuroprotective supplements. Palm oil-derived PS is used for its stability and bioavailability in cognitive support formulations. | [179,180] |
Phosphatidylglycerol (PG)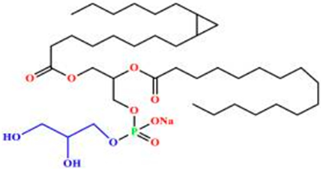 | 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-sn-glycerol | Soybeans, sunflower seeds, canola, chai seeds, flaxseeds, palm oil (not predominant). | Accessible via PLD-based transphosphatidylation from PC (rare phospholipids synthesis toolkit). | As emulsifier in dressings, sauces, and baked goods, helping to improve texture and stability. Also used as nutritional supplements for heart health and cholesterol management. In pharmaceuticals, it is used in liposomes to enhance the delivery of poorly soluble drugs. In cosmetics, PG provides hydration in moisturizers and stabilizes creams and lotions. It helps study lipid behavior and cell dynamics. | [169,181] |
Phosphatidic Acid (PA) | 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate | Soybeans, mustard seeds, oil-rich seeds, and palm oil. | Formed by PLD hydrolysis of PC/other phospholipids; also via glycerol-3-phosphate acylation → LPA → PA (ER pathway). | A precursor to other phospholipids and key for cellular signaling, PA from palm oil is used in cosmetics and supplements for muscle support and cellular energy enhancement. | [182,183,184] |
Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)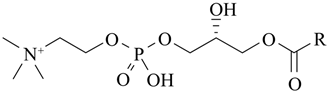 | 2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lyso-PC) | Sunflower seeds, rapeseed, soybeans, and palm oil. | Generated by hydrolysis/transesterification of PC (e.g., enzymatic ethanolysis to 2-acyl-1-lyso-PC) for further conjugation. | With strong emulsifying properties, LPC stabilizes emulsions in food products, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Palm oil-derived LPC is particularly beneficial for applications requiring stable and long-lasting emulsions. | [185,186] |
Cardiolipin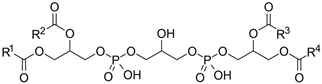 | 1,3-bis(sn-3′-phosphatidyl)-sn-glycerol | Wheat germ, soy lecithin, and palm oil (less commonly used). | Synthesized from PA within mitochondria; unique mitochondrial signature lipid (not typically plant-extracted for products). Its absence causes mitochondrial defects. | Important for mitochondrial health, cardiolipin is studied for energy metabolism and cellular health. Palm oil-derived cardiolipin is used in supplements focusing on mitochondrial function. | [187,188] |
| Types | Physical Properties | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Texture | Solubility | Melting Point | ||
| Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | Appears as a white or off-white powder or waxy solid. In its natural form within cell membranes, it appears as a component of lipid bilayers, contributing to membrane fluidity and structure. | Soft, waxy texture at room temperature. This texture aids in its ability to form smooth layers, which is critical for creating emulsions and liposomal structures. | Amphiphilic, meaning it has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. It is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, chloroform, and methanol but is generally insoluble in water unless dispersed as part of an emulsion or liposome. | Tm depends on acyl chains: DSPC ~55 °C, DPPC ~42 °C, DMPC ~22 °C, egg PC < 0 °C | [189,190,191,192,193] |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) | Typically appears as a white or off-white powder when isolated; in natural forms, it may vary from colorless to pale yellow. | Powder or crystalline texture in purified form; waxy in a lipid mixture. | Poorly soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, chloroform, and methanol. | Generally, between 60 and 80 °C, though it can vary based on the fatty acid chains attached. | [175,194,195,196] |
| Phosphatidylinositol (PI) | Appears as a white or off-white powder when purified. In its natural state within lipid mixtures, PI can have a yellowish to pale brown hue, depending on its extraction source and the presence of any minor impurities. | A powdery texture in its isolated form but can also appear waxy or sticky in more concentrated lipid mixtures. This texture can influence its ease of handling and formulation, particularly when incorporating it into liposomal or emulsion systems for research and pharmaceutical applications. | Poorly soluble in water due to its amphipathic structure, which means it has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. However, it is readily soluble in organic solvents like chloroform, ethanol, and methanol. This solubility characteristic makes PI ideal for extraction and purification through organic solvents and suitable for formulating lipid-based systems in non-aqueous environments. | Typically ranging from 55 to 75 °C, largely depending on the fatty acid composition. For example, PI molecules with more saturated fatty acid tails will have higher melting points, making them more stable at room temperature, whereas PI with unsaturated chains will have lower melting points and may be liquid at lower temperatures. This variability impacts its stability in formulations requiring specific thermal properties. | [197,198,199] |
| Phosphatidylserine (PS) | Appears as white to off-white, waxy solid or powder. | In its powder form, PS typically has a fine, dry texture. It may feel slightly greasy due to its lipid nature. | Sparingly soluble in water but is more soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, chloroform, and methanol. It forms micelles or liposomes in aqueous solutions, which helps in its incorporation in biological systems. | The melting point can vary depending on its source and purity but typically ranges from 180 °C to 220 °C. The specific structure, such as the types of fatty acid chains attached, influences its exact melting point. | [179,194,200] |
| Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) | Appears as white to off-white or a waxy solid when it is isolated. | Variations in terms of a powdered texture to a slightly waxy form, based on the purity and form. | Sparingly soluble in water but it is soluble in other solvents such as the organic solvents namely the chloroform and ethanol which are used as a medium to dissolve lipids. | The melting point range is between 60 °C and 80 °C, which depends on the presence of the fatty acid chains. | [201,202,203,204,205] |
| Phosphatidic Acid (PA) | Appears as a white to slightly off-white powder or as a crystalline solid. | In the form of a purified powder or waxy. | Sparingly soluble in water but it is soluble in other medium of organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, and chloroform. | The melting point range is between 55 °C and 65 °C, which varies with the presence of distinctive fatty acid chain lengths. | [182,206,207,208] |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) | Appears as white or light yellowish in the form of a powder or waxy substance. | In the form of a purified powder or lightly waxy. | Amphiphilic, meaning it has a better solubility in water in contrast to other phospholipids as it has single fatty acid tail, and it has solubility properties in ethanol and chloroform. | The melting point range is between 20 °C and 40 °C, which varies with the presence of distinctive fatty acid components. | [209,210,211,212] |
| Cardiolipin | Appears as white to off-white in the form of a powder or waxy solid. | In the form of waxy or crystalline, based on its isolation and purity characteristics. | Insolubility in water but soluble in other solvent mediums such as ethanol, chloroform, and methanol. | The melting point range is between 60 °C and 70 °C, which varies with the presence of fatty acid components. | [213,214,215,216] |
| Types | Chemical Properties | References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Regions | Acidic and Basic Properties | Oxidative Stability | Reaction to Heat | Interaction with Compounds | Hydration and Dehydration | ||
| Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | Choline head group linked to phosphate and glycerol backbone with two fatty acyl chains | Hydrophilic choline–phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | The phosphate group in PC is slightly acidic, but the choline moiety gives it an overall neutral or zwitterionic charge. This charge neutrality allows PC to interact with a wide range of molecules without strong electrostatic repulsion or attraction. | Stability against oxidation depends on the degree of unsaturation in its fatty acid chains. Unsaturated PCs are more susceptible to oxidation, potentially leading to rancidity. | Heat sensitive and can degrade at high temperatures, especially if it contains unsaturated fatty acids. Thermal degradation can affect its emulsifying and structural properties. | Interacts with proteins, carbohydrates, and other lipids, enhancing the stability and texture of emulsified products. It also interacts well with therapeutic compounds in liposomal formulations. | Can absorb water and form hydrated bilayers or vesicles. The bilayers can dehydrate and rehydrate without losing structural integrity, which is advantageous in liposome technology. | [189,190,191,192,193] |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) | Ethanolamine head group linked to phosphate and glycerol backbone with two fatty acyl chains | Polar ethanolamine–phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | Typically acts as a weak base due to the amine group in ethanolamine, which can be protonated, increasing its positive charge under acidic conditions. | Moderate oxidative stability: susceptible to oxidation if it contains unsaturated fatty acid chains, though less stable than phosphatidylcholine due to fewer methyl groups. | Moderate stability to heat; can degrade or oxidize at higher temperatures, particularly in the presence of unsaturated fatty acids. | Easily interacts with other phospholipids and membrane proteins due to its amphipathic nature; stabilizes lipid bilayers in cell membranes. | It can undergo hydration and dehydration cycles; it can absorb water due to the polar head group, which is key in liposome and bilayer formation. | [175,194,195,196] |
| Phosphatidylinositol (PI) | Inositol head group linked to phosphate and glycerol backbone with two fatty acyl chains | Polar inositol–phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | Generally neutral but exhibits weak acidity due to the phosphate group linked to the inositol ring. This phosphate group can donate hydrogen ions in slightly basic conditions, giving PI slight acidic properties that affect its charge and reactivity in the cellular environment. Additionally, the hydroxyl groups on the inositol ring provide additional polarity, enhancing its ability to form hydrogen bonds with surrounding molecules, especially within aqueous environments. | Moderate oxidative stability, with susceptibility to degradation if unsaturated fatty acids are present in its structure. The degree of unsaturation in the fatty acid chains significantly impacts its stability, as unsaturated chains are more prone to oxidation. This property is particularly relevant for PI’s application in liposome-based drug delivery, where oxidative stability can influence shelf-life and efficacy. | Stable under moderate heat but may begin to degrade at high temperatures, especially if the fatty acid tails contain unsaturated bonds. This thermal sensitivity makes PI suitable for some thermal processing methods, but caution is needed when exposed to prolonged or high heat to avoid lipid degradation, which could compromise its structural integrity in formulations. | Highly interactive with other molecules in cellular membranes and is essential in signaling due to its role as a precursor for phosphorylated derivatives, such as phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PIPs). These derivatives play significant roles in cell signaling pathways, particularly in response to external stimuli, and regulate various cellular functions like growth, metabolism, and survival. | It can attract water molecules, especially the PI’s inositol head group, which stabilizes within the cell membranes and undergoes interaction with signaling proteins. The impact of dehydration reduces the PI’s potential to interact with alternate molecules, hence impacting the stability of the membrane and leading towards the disruption of cell signaling pathways. | [197,198,199] |
| Phosphatidylserine (PS) | Serine head group linked to phosphate and glycerol backbone with two fatty acyl chains | Hydrophilic serine–phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | Acidic by nature with a negative net charge at the physiological pH due to the presence of phosphate and carboxylate groups. | Susceptible to oxidation if unsaturated, hence affects the membrane integrity. | Stability is maintained at moderate temperature, but degradation occurs at high temperatures, which results in the breaking up the fatty acid chains and impacting its structure. | The interaction is strongly with ions specifically calcium, which aids the cell membranes to stabilize. Interaction with membrane proteins which plays a part in cellular signaling. | It can undergo hydration which is crucial for the maintenance of its position in the cell membrane. The alterations in the membrane fluidity and stability is because of dehydration. | [179,194,200] |
| Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) | Glycerol–phosphate head group linked to glycerol backbone with two fatty acyl chains | Polar glycerol–phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | Slightly acidic due to the presence of the phosphate group with a negative charge at physiological pH. | Prone to oxidative degradation, specifically at the unsaturated fatty acid chains regions, which has a direct impact on the stability of the membrane. | Heat sensitivity, which leads towards the degradation of the fatty acid components at high temperatures, impacting the lipid bilayer initiations. | Interactions with ions, namely calcium and magnesium to form lipid bilayers that are stable combined with other phospholipids, essential for lung surfactant. | It can absorb water and results in swelling which is crucial for membrane formation. The reduction in the membrane fluidity and disruption of cellular functions is due to dehydration. | [201,202,203,204,205] |
| Phosphatidic Acid (PA) | Phosphate head group directly linked to glycerol backbone with two fatty acyl chains | Polar phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | Strongly acidic; anionic phospholipid by nature with a negative charge due to the presence of the phosphate group. | Susceptible to oxidation, particularly if unsaturated fatty acids. Oxidation has a direct impact on the cellular signaling processes. | Relative stability at moderate heat; however, this results in degradation at high temperatures, impacting the structural integrity and acts as a signaling molecule. | Interaction with positive charged ions and proteins, significant in signaling pathways implied in cell growth and development. | Hydration at a quick speed, which is essential for the membrane structure. Dehydration leads to alterations in cell membrane stability and signaling activity. | [182,206,207,208] |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) | Similar to PC but with one acyl chain | Hydrophilic choline–phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | Zwitterionic; presence of both acidic and basic regions. The phosphate is acidic, and the choline is basic, with a net neutral charge at physiological pH. | Sensitivity to oxidation, specifically at the site of the single fatty acid chain, resulting in membrane destabilization. | Less stability in high temperatures, resulting in the degradation of the fatty acid chain and the loss of functionality as an emulsifier. | Good interaction with proteins and other lipids and involved in repairing of the cell membrane and signal transduction processes. | Distinctly hydrophilic and can absorb water, resulting in the formation of micelles in the aqueous mediums. Dehydration leads to the reduction in solubility and biological activity. | [209,210,211,212] |
| Cardiolipin (CL) | Two phosphatidic acids linked by glycerol; four acyl chains | Polar ethanolamine–phosphate head; hydrophobic acyl tails | Acidic by nature with a net negative charge due to the presence of two phosphate groups essential for its interactions in mitochondrial membranes. | Prone to oxidation, particularly in the mitochondrial membrane, leading to loss of functionality and linked with cell apoptosis. | Relatively stable at moderate temperatures, but undergoes degradation at high temperatures, particularly in the fatty acid chains, which affects mitochondrial membrane stability. | Strongly interacted with proteins and other lipids in the mitochondrial membrane, which is vital for energy production and enzyme activity. | Reduced hydration ability; potentiality to absorb water, which is crucial for maintaining mitochondrial membrane structure. The impact of dehydration leads to the concession of the membrane stability and the functionality of the embedded proteins. | [213,214,215,216] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alawi, M.; Hashim, N.M.; Ahmad, N.; Mahmood, S.; Ge, Y. A Systematic Review of Advances in Plant-Based Phospholipid Liposomes in Breast Cancer Therapy: Characterization, Innovations, Clinical Applications, and Future Directions. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091288
Alawi M, Hashim NM, Ahmad N, Mahmood S, Ge Y. A Systematic Review of Advances in Plant-Based Phospholipid Liposomes in Breast Cancer Therapy: Characterization, Innovations, Clinical Applications, and Future Directions. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091288
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlawi, Marwa, Najihah Mohd Hashim, Noraini Ahmad, Syed Mahmood, and Yi Ge. 2025. "A Systematic Review of Advances in Plant-Based Phospholipid Liposomes in Breast Cancer Therapy: Characterization, Innovations, Clinical Applications, and Future Directions" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091288
APA StyleAlawi, M., Hashim, N. M., Ahmad, N., Mahmood, S., & Ge, Y. (2025). A Systematic Review of Advances in Plant-Based Phospholipid Liposomes in Breast Cancer Therapy: Characterization, Innovations, Clinical Applications, and Future Directions. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091288








