Changes in Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism in Patients with Depression Undergoing ECT—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- summarize the findings of studies on changes in concentrations of Trp and kynurenines after ECT;
- (2)
- review important factors that could potentially affect the analyses of these metabolites in relation to therapeutic outcome;
- (3)
- consider the clinical role of measures of Trp and kynurenines;
- (4)
- propose how future studies should be designed to meet methodological issues and clarify the role of Trp metabolism in ECT.
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
2.1.1. Protocol
2.1.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.1.3. Information Sources
2.1.4. Study Selection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Synthesis and Presentation
2.3.1. Grouping
2.3.2. Effect Measures
2.3.3. Synthesis
2.3.4. Data Presentation Methods
3. Results
3.1. Databases, Search Structure and Study Selection
3.2. Included Studies
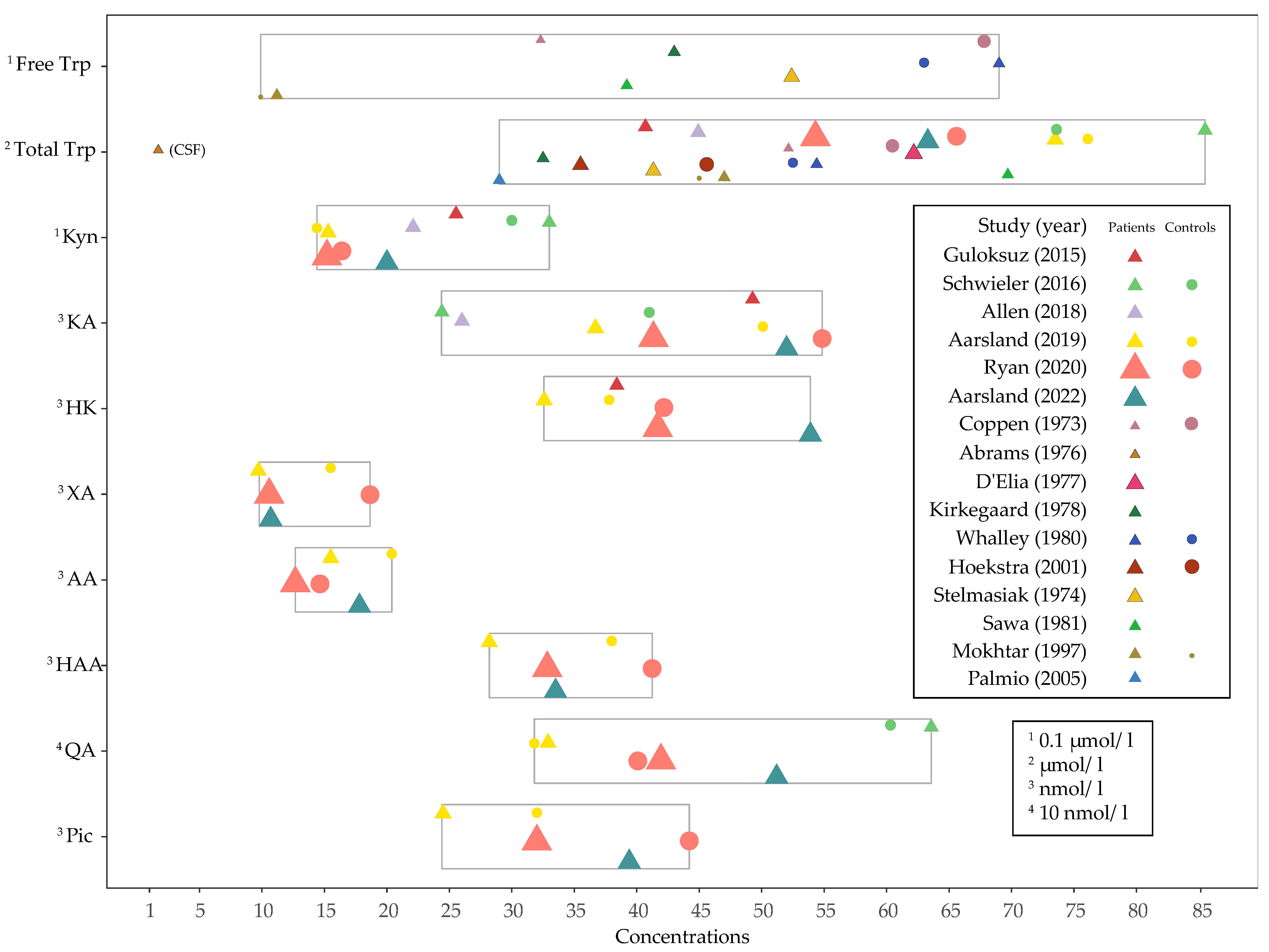
3.3. Baseline Concentrations and Changes in Levels of Tryptophan, Kynurenines and Ratios after ECT
3.4. Factors That Can Affect Analyses of Tryptophan and Kynurenines
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of ECT on Tryptophan, Kynurenines and Ratios
4.2. Effect Modifiers and Mediators
4.2.1. The Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism (Figure 1)
4.2.2. Factors That Can Affect Levels of Tryptophan and Kynurenines
4.2.3. Patient Characteristics
4.2.4. Intervention and Study Design
4.2.5. Summary of the Role of Factors That Can Influence Analyses of Tryptophan and Kynurenines in the Context of ECT
4.3. Challenges Regarding the Clinical Use of Tryptophan and Kynurenine Measures
4.3.1. Normal Ranges and Variability
4.3.2. Peripheral and Central Concentrations
4.3.3. Research Questions, Study Design and Methods of Analysis
4.4. Suggestions for Future Studies
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | anthranilic acid |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CAA | competing amino acid |
| ECT | electroconvulsive therapy |
| FAD | flavin adenine dinucleotide |
| HAA | 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid |
| HK | 3-hydroxykynurenine |
| ICC | intraclass correlation coefficient |
| IDO | indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| IFN | interferon; KA, kynurenic acid |
| KYNU | kynureninase |
| Kyn | kynurenine |
| KAT | kynurenine aminotransferase |
| KMO | kynurenine monooxygenase |
| KTR | kynurenine-tryptophan-ratio |
| NEFA | non-esterified fatty acid |
| NMDAr | N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| Pic | picolinic acid |
| PLP | pyridoxal 5‘-phosphate |
| QA | quinolinic acid |
| SSRI | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| TDO | tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| Trp | tryptophan |
| XA | xanthurenic acid |
References
- Arnone, D.; Saraykar, S.; Salem, H.; Teixeira, A.L.; Dantzer, R.; Selvaraj, S. Role of Kynurenine pathway and its metabolites in mood disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 92, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitz, J. The kynurenine pathway: A finger in every pie. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirthgen, E.; Hoeflich, A.; Rebl, A.; Gunther, J. Kynurenic Acid: The Janus-Faced Role of an Immunomodulatory Tryptophan Metabolite and Its Link to Pathological Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogyu, K.; Kubo, K.; Noda, Y.; Iwata, Y.; Tsugawa, S.; Omura, Y.; Wada, M.; Tarumi, R.; Plitman, E.; Moriguchi, S.; et al. Kynurenine pathway in depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 90, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reus, G.Z.; Jansen, K.; Titus, S.; Carvalho, A.F.; Gabbay, V.; Quevedo, J. Kynurenine pathway dysfunction in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: Evidences from animal and human studies. J. Psychiatr Res. 2015, 68, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Fujii, T.; Koga, N.; Hori, H.; Teraishi, T.; Hattori, K.; Noda, T.; Higuchi, T.; Motohashi, N.; Kunugi, H. Plasma L-tryptophan concentration in major depressive disorder: New data and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, e906–e915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massudi, H.; Grant, R.; Guillemin, G.J.; Braidy, N. NAD+ metabolism and oxidative stress: The golden nucleotide on a crown of thorns. Redox Rep. 2012, 17, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, J.R.; Arun, P.; Puthillathu, N.; Vengilote, R.; Ives, J.A.; Badawy, A.A.; Namboodiri, A.M. Quinolinate as a Marker for Kynurenine Metabolite Formation and the Unresolved Question of NAD(+) Synthesis During Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecsei, L.; Szalardy, L.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J. Kynurenines in the CNS: Recent advances and new questions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Toth, F.; Polyak, H.; Szabo, A.; Mandi, Y.; Vecsei, L. Immune Influencers in Action: Metabolites and Enzymes of the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Role of Kynurenine Pathway in Oxidative Stress during Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2021, 10, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervenka, I.; Agudelo, L.Z.; Ruas, J.L. Kynurenines: Tryptophan’s metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science 2017, 357, eaaf9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, K.; Harkin, A. Stress-related regulation of the kynurenine pathway: Relevance to neuropsychiatric and degenerative disorders. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; Nollen, E.A.A.; Rohrig, U.F.; Fallarino, F.; Opitz, C.A. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxenkrug, G. Serotonin-kynurenine hypothesis of depression: Historical overview and recent developments. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, A.T.; Eccleston, D. The effects of precursor loading in the cerebral metabolism of 5-hydroxyindoles. J. Neurochem. 1968, 15, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, D.A. Effects of a dietary excess of leucine on the metabolism of tryptophan in the rat: A mechanism for the pellagragenic action of leucine. Br. J. Nutr. 1983, 50, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Au, B.; Ollis, L.; Schmitz, N. The association between C-reactive protein, Interleukin-6 and depression among older adults in the community: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 102, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitharouli, M.C.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Glanville, K.P.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Hotopf, M.; Lewis, C.M.; Pariante, C.M. Elevated C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Depression, Independent of Genetic, Health, and Psychosocial Factors: Results From the UK Biobank. Am. J. Psychiatry 2021, 178, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Cengotitabengoa, M.; Carrascon, L.; O’Brien, J.T.; Diaz-Gutierrez, M.J.; Bermudez-Ampudia, C.; Sanada, K.; Arrasate, M.; Gonzalez-Pinto, A. Peripheral Inflammatory Parameters in Late-Life Depression: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapin, I.P. Kynurenines as probable participants of depression. Pharmakopsychiatr. Neuropsychopharmakol. 1973, 6, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, A.M.; Kim, Y.K. Cytokine-serotonin interaction through IDO: A neurodegeneration hypothesis of depression. Med. Hypotheses 2003, 61, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.P.; Muchowski, P.J.; Wu, H.Q. Kynurenines in the mammalian brain: When physiology meets pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Leonard, B.E.; Myint, A.M.; Kubera, M.; Verkerk, R. The new ‘5-HT’ hypothesis of depression: Cell-mediated immune activation induces indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, which leads to lower plasma tryptophan and an increased synthesis of detrimental tryptophan catabolites (TRYCATs), both of which contribute to the onset of depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 702–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, M.N.; Stone, T.W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982, 247, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenedo, R.; Pittaluga, A.; Cozzi, A.; Attucci, S.; Galli, A.; Raiteri, M.; Moroni, F. Presynaptic kynurenate-sensitive receptors inhibit glutamate release. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, G.J. Quinolinic acid, the inescapable neurotoxin. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated neuronal cell death induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, 3-hydroxykynurenine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, F.; Misiak, B.; Callovini, T.; Cavaleri, D.; Cioni, R.M.; Crocamo, C.; Savitz, J.B.; Carra, G. The kynurenine pathway in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis on the peripheral blood levels of tryptophan and related metabolites. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3419–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; McGuinness, A.J.; Rocks, T.; Ruusunen, A.; Cleminson, J.; Walker, A.J.; Gomes-da-Costa, S.; Lane, M.; Sanches, M.; Diaz, A.P.; et al. The kynurenine pathway in major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of 101 studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4158–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocki, T.; Wnuk, S.; Kloc, R.; Kocki, J.; Owe-Larsson, B.; Urbanska, E.M. New insight into the antidepressants action: Modulation of kynurenine pathway by increasing the kynurenic acid/3-hydroxykynurenine ratio. J. Neural. Transm. 2012, 119, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guloksuz, S.; Arts, B.; Walter, S.; Drukker, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Myint, A.M.; Schwarz, M.J.; Ponds, R.; van Os, J.; Kenis, G.; et al. The impact of electroconvulsive therapy on the tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieler, L.; Samuelsson, M.; Frye, M.A.; Bhat, M.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; Jungholm, O.; Johansson, A.G.; Landen, M.; Sellgren, C.M.; Erhardt, S. Electroconvulsive therapy suppresses the neurotoxic branch of the kynurenine pathway in treatment-resistant depressed patients. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, T.I.; Leskauskaite, I.; Midttun, O.; Ulvik, A.; Ueland, P.M.; Oltedal, L.; Erchinger, V.J.; Oedegaard, K.J.; Haavik, J.; Kessler, U. The effect of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) on serum tryptophan metabolites. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.P.; Naughton, M.; Dowling, J.; Walsh, A.; O’Shea, R.; Shorten, G.; Scott, L.; McLoughlin, D.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Clarke, G.; et al. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the neurobiology of treatment-resistant depression: Comparison of multiple ketamine infusions and electroconvulsive therapy. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 100, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.M.; Allers, K.A.; McLoughlin, D.M.; Harkin, A. Tryptophan metabolite concentrations in depressed patients before and after electroconvulsive therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 83, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofylaktopoulou, D.; Midttun, O.; Ulvik, A.; Ueland, P.M.; Tell, G.S.; Vollset, S.E.; Nygard, O.; Eussen, S.J. A community-based study on determinants of circulating markers of cellular immune activation and kynurenines: The Hordaland Health Study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A. Plasma free tryptophan revisited: What you need to know and do before measuring it. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; McKenzie, J.E.; Sowden, A.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Brennan, S.E.; Ellis, S.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Ryan, R.; Shepperd, S.; Thomas, J.; et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: Reporting guideline. BMJ 2020, 368, l6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, J.E.; Brennan, S.E. Chapter 12: Synthesizing and presenting findings using other methods. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2019. R Core Team (2019) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2019. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Barkai, A.I. Combined electroconvulsive and drug therapy. Compr. Ther. 1985, 11, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gerne, B. Treatment of depression. Sven. Farm. Tidskr. 1984, 88, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Heymans, C.; De Schaepdryver, A.F.; Delaunois, A.L.; Piette, Y. Pharmacology of Electroshock. Med. Mon. 1964, 18, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Heymans, C.; Deschaepdryver, A.F.; Delaunois, A.L.; Piette, Y. Drugs and Electroshock. Riforma Med. 1964, 78, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Broadhurst, A.D. L-tryptophan verses E.C.T. Lancet 1970, 1, 1392–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Cocheme, M.A. L-tryptophan versus E.C.T. Lancet 1970, 1, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.M. L-tryptophan in depression. Lancet 1970, 1, 1111. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, B.J.; Mowbray, R.M.; Davies, B. L-tryptophan in depression. Lancet 1970, 1, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, P.; Kirkegaard, C.; Bock, E.; Johannesen, M.; Rafaelsen, O.J. Hormones, electrolytes, and cerebrospinal fluid proteins in manic-melancholic patients. Neuropsychobiology 1978, 4, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, F.; Murry, E.; Weiner, R.D.; Carroll, B.J. Lack of relapse with tryptophan depletion following successful treatment with ECT. Am. J. Psychiatry 1997, 154, 1151–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy, F.; Weiner, R.D.; Cooper, T.B.; Carroll, B.J. Combined catecholamine and indoleamine depletion following response to ECT. Br. J. Psychiatry 2010, 196, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herrington, R.N.; Bruce, A.; Johnstone, E.C.; Lader, M.H. Comparative trial of L tryptophan and E.C.T. in severe depressive illness. Lancet 1974, 2, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranaster, L.; Hoyer, C.; Mindt, S.; Neumaier, M.; Muller, N.; Zill, P.; Schwarz, M.J.; Moll, N.; Lutz, B.; Bindila, L.; et al. The novel seizure quality index for the antidepressant outcome prediction in electroconvulsive therapy: Association with biomarkers in the cerebrospinal fluid. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 270, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, B.J.; Mowbray, R.M.; Davies, B. Sequential comparison of L-tryptophan with E.C.T. in severe depression. Lancet 1970, 1, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppen, A.; Brooksbank, B.W.; Eccleston, E.; Peet, M.; White, S.G. Tryptophan metabolism in depressive illness. Psychol. Med. 1974, 4, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppen, A.; Shaw, D.M.; Malleson, A.; Eccleston, E.; Gundy, G. Tryptamine metabolism in depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 1965, 111, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajossy, M.; Olajossy, B.; Potembska, E.; Skoczen, N.; Wnuk, S.; Urbanska, E. Differences in the dynamics of changes in the concentration of kynurenic acid in the blood serum of depressed patients treated with electroconvulsive therapy. Psychiatr 2018, 30, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, G.; Lehmann, J.; Raotma, H. Influence of tryptophan on memory functions in depressive patients treated with unilateral ECT. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1978, 57, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- D’Elia, G.; Lehmann, J.; Raotma, H. Bimodal distribution of serum tryptophan level. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1979, 60, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppen, A.; Eccleston, E.G.; Peet, M. Total and free tryptophan concentration in the plasma of depressive patients. Lancet 1973, 2, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, T.I.M.; Haavik, J.; Ulvik, A.; Ueland, P.M.; Dols, A.; Kessler, U. The effect of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) on serum kynurenine pathway metabolites in late-life depression. 2022. Manuscript submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, R.; Essman, W.B.; Taylor, M.A.; Fink, M. Concentration of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, homovanillic acid, and tryptophan in the cerebrospinal fluid of depressed patients before and after ECT. Biol. Psychiatry 1976, 11, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, G.; Lehmann, J.; Raotma, H. Evaluation of the combination of tryptophan and ECT in the treatment of depression. II. Biochemical analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1977, 56, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, R.; van den Broek, W.W.; Fekkes, D.; Bruijn, J.A.; Mulder, P.G.; Pepplinkhuizen, L. Effect of electroconvulsive therapy on biopterin and large neutral amino acids in severe, medication-resistant depression. Psychiatry Res. 2001, 103, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, C.; Moller, S.E.; Bjorum, N. Addition of L-tryptophan to electroconvulsive treatment in endogenous depression. A double-blind study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1978, 58, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, A.S.; Morgan, C.J.; Bradley, D.M.; Badawy, A.A.B. No early effects of electroconvulsive therapy on tryptophan metabolism and disposition in endogenous depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 42, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajossy, M.; Olajossy, B.; Wnuk, S.; Potembska, E.; Urbanska, E. Blood serum concentrations of kynurenic acid in patients diagnosed with recurrent depressive disorder, depression in bipolar disorder, and schizoaffective disorder treated with electroconvulsive therapy. Psychiatr. Pol. 2017, 51, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmio, J.; Huuhka, M.; Saransaari, P.; Oja, S.S.; Peltola, J.; Leinonen, E.; Suhonen, J.; Keranen, T. Changes in plasma amino acids after electroconvulsive therapy of depressed patients. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 137, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawa, Y. The effect of electroconvulsive therapy on plasma cyclic-AMP, non-esterified fatty acid, tryptophan and tyrosine in depression. Keio J. Med. 1981, 30, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stelmasiak, Z.; Curzon, G. Effect of electroconvulsive therapy on plasma unesterified fatty acid and free tryptophan concentrations in man. J. Neurochem. 1974, 22, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whalley, L.J.; Yates, C.M.; Christie, J.E. Effect of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) on plasma tryptophan. Psychol. Med. 1980, 10, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, G.; Lehmann, J.; Raotma, H. Evaluation of the combination of tryptophan and ECT in the treatment of depression. I. Clinical analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1977, 56, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.M.; Allers, K.A.; Harkin, A.; McLoughlin, D.M. Blood plasma B vitamins in depression and the therapeutic response to electroconvulsive therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 4, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichers, M.C.; Koek, G.H.; Robaeys, G.; Verkerk, R.; Scharpe, S.; Maes, M. IDO and interferon-alpha-induced depressive symptoms: A shift in hypothesis from tryptophan depletion to neurotoxicity. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Charych, E.; Lee, A.W.; Moller, T. Kynurenines in CNS disease: Regulation by inflammatory cytokines. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, M.; Manchia, M.; Oppo, R.; Scano, F.; Pillai, G.; Loche, A.P.; Salis, P.; Minnai, G.P. Clinical and biological predictors of response to electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): A review. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 669, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffioletti, E.; Carvalho Silva, R.; Bortolomasi, M.; Baune, B.T.; Gennarelli, M.; Minelli, A. Molecular Biomarkers of Electroconvulsive Therapy Effects and Clinical Response: Understanding the Present to Shape the Future. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yrondi, A.; Sporer, M.; Peran, P.; Schmitt, L.; Arbus, C.; Sauvaget, A. Electroconvulsive therapy, depression, the immune system and inflammation: A systematic review. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopra, E.; Mondelli, V.; Pariante, C.; Nikkheslat, N. Ketamine’s effect on inflammation and kynurenine pathway in depression: A systematic review. J. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 35, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadriu, B.; Farmer, C.A.; Yuan, P.; Park, L.T.; Deng, Z.D.; Moaddel, R.; Henter, I.D.; Shovestul, B.; Ballard, E.D.; Kraus, C.; et al. The kynurenine pathway and bipolar disorder: Intersection of the monoaminergic and glutamatergic systems and immune response. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaris, A.; Myint, A.M.; Savant, V.; Meresh, E.; Lim, E.; Guillemin, G.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Fareed, J.; Sinacore, J. Does escitalopram reduce neurotoxicity in major depression? J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 66–67, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bogdanov, M.B.; Boyle, S.H.; Matson, W.; Sharma, S.; Matson, S.; Churchill, E.; Fiehn, O.; Rush, J.A.; Krishnan, R.R.; et al. Pharmacometabolomics of response to sertraline and to placebo in major depressive disorder—Possible role for methoxyindole pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, G.M.; Forrest, C.M.; Christofides, J.; Bridel, M.A.; Mitchell, S.; Cowlard, R.; Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G. Kynurenine metabolites and inflammation markers in depressed patients treated with fluoxetine or counselling. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 36, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannestad, J.; DellaGioia, N.; Bloch, M. The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: A meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skorobogatov, K.; De Picker, L.; Verkerk, R.; Coppens, V.; Leboyer, M.; Muller, N.; Morrens, M. Brain Versus Blood: A Systematic Review on the Concordance Between Peripheral and Central Kynurenine Pathway Measures in Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, A.A. Tryptophan availability for kynurenine pathway metabolism across the life span: Control mechanisms and focus on aging, exercise, diet and nutritional supplements. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Imanishi, J.; Oku, T.; Kishida, T.; Hayaishi, O. Induction of pulmonary indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by interferon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofylaktopoulou, D.; Ulvik, A.; Midttun, O.; Ueland, P.M.; Vollset, S.E.; Nygard, O.; Hustad, S.; Tell, G.S.; Eussen, S.J. Vitamins B2 and B6 as determinants of kynurenines and related markers of interferon-gamma-mediated immune activation in the community-based Hordaland Health Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.; Guillemin, G. The Plasma [Kynurenine]/[Tryptophan] Ratio and Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase: Time for Appraisal. Int. J. Tryptophan. Res. 2019, 12, 1178646919868978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrocksnadel, K.; Wirleitner, B.; Winkler, C.; Fuchs, D. Monitoring tryptophan metabolism in chronic immune activation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 364, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, B.; Becker, K.; Fuchs, D.; Gostner, J.M. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and immune activation: Peripheral measurements in psychiatric and co-morbid conditions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deac, O.M.; Mills, J.L.; Gardiner, C.M.; Shane, B.; Quinn, L.; Midttun, O.; McCann, A.; Meyer, K.; Ueland, P.M.; Fan, R.; et al. Serum Immune System Biomarkers Neopterin and Interleukin-10 Are Strongly Related to Tryptophan Metabolism in Healthy Young Adults. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, D.; Moller, A.A.; Reibnegger, G.; Werner, E.R.; Werner-Felmayer, G.; Dierich, M.P.; Wachter, H. Increased endogenous interferon-gamma and neopterin correlate with increased degradation of tryptophan in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Immunol. Lett. 1991, 28, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midttun, O.; Ulvik, A.; Ringdal Pedersen, E.; Ebbing, M.; Bleie, O.; Schartum-Hansen, H.; Nilsen, R.M.; Nygard, O.; Ueland, P.M. Low plasma vitamin B-6 status affects metabolism through the kynurenine pathway in cardiovascular patients with systemic inflammation. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperner-Unterweger, B.; Neurauter, G.; Klieber, M.; Kurz, K.; Meraner, V.; Zeimet, A.; Fuchs, D. Enhanced tryptophan degradation in patients with ovarian carcinoma correlates with several serum soluble immune activation markers. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Allers, K.A.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Giltay, E.J.; Keller, S.; Schoevers, R.A.; Sussmuth, S.D.; Niessen, H.G.; Penninx, B. The association between plasma tryptophan catabolites and depression: The role of symptom profiles and inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 97, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, C.; Macedo, E.C.T.; Suchting, R.; de Dios, C.; Cuellar Leal, V.A.; Soares, J.C.; Dantzer, R.; Teixeira, A.L.; Selvaraj, S. Effect of immune activation on the kynurenine pathway and depression symptoms—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, J.; Ormstad, H.; Aass, H.C.; Malt, U.F.; Bendz, L.T.; Sandvik, L.; Brundin, L.; Andreassen, O.A. The plasma levels of various cytokines are increased during ongoing depression and are reduced to normal levels after recovery. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 45, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisie, V.; Filip, G.A.; Manea, M.C.; Manea, M.; Riga, S. The anti-inflammatory role of SSRI and SNRI in the treatment of depression: A review of human and rodent research studies. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojvodic, J.; Mihajlovic, G.; Vojvodic, P.; Radomirovic, D.; Vojvodic, A.; Vlaskovic-Jovicevic, T.; Peric-Hajzler, Z.; Matovic, D.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Sijan, G.; et al. The Impact of Immunological Factors on Depression Treatment—Relation Between Antidepressants and Immunomodulation Agents. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 3064–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgdrager, F.J.H.; Naude, P.J.W.; Kema, I.P.; Nollen, E.A.; Deyn, P.P. Tryptophan Metabolism in Inflammaging: From Biomarker to Therapeutic Target. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bie, J.; Guest, J.; Guillemin, G.J.; Grant, R. Central kynurenine pathway shift with age in women. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Fujigaki, S.; Heyes, M.P.; Shibata, K.; Takemura, M.; Fujii, H.; Wada, H.; Noma, A.; Seishima, M. Mechanism of increases in L-kynurenine and quinolinic acid in renal insufficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol 2000, 279, F565–F572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schefold, J.C.; Zeden, J.P.; Fotopoulou, C.; von Haehling, S.; Pschowski, R.; Hasper, D.; Volk, H.D.; Schuett, C.; Reinke, P. Increased indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity and elevated serum levels of tryptophan catabolites in patients with chronic kidney disease: A possible link between chronic inflammation and uraemic symptoms. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Velagapudi, C.; Redus, L.; Thameem, F.; Kasinath, B.; Hura, C.E.; Lorenzo, C.; Abboud, H.E.; O’Connor, J.C. Tryptophan Metabolism in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Secondary to Type 2 Diabetes: Relationship to Inflammatory Markers. Int. J. Tryptophan. Res. 2017, 10, 1178646917694600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Plasma kynurenic acid/tryptophan ratio: A sensitive and reliable biomarker for the assessment of renal function. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhee, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Joo, K.J.; Jung, S.S.; Lee, K.B. The clinical significance of serum and urinary neopterin levels in several renal diseases. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Kalaska, B.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenine Pathway in Chronic Kidney Disease: What’s Old, What’s New, and What’s Next? Int. J. Tryptophan. Res. 2020, 13, 1178646920954882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, D.; Tankiewicz, A.; Matys, T.; Buczko, W. Peripheral distribution of kynurenine metabolites and activity of kynurenine pathway enzymes in renal failure. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, S.; Vecchio, M.; Craig, J.C.; Tonelli, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Nicolucci, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Saglimbene, V.; Logroscino, G.; Fishbane, S.; et al. Prevalence of depression in chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, Q.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, C.; He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, F.F.; Qin, X. Bidirectional relations between depression symptoms and chronic kidney disease. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 311, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadvar, S.; Ferreira, D.M.S.; Cervenka, I.; Ruas, J.L. The weight of nutrients: Kynurenine metabolites in obesity and exercise. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Floc’h, N.; Otten, W.; Merlot, E. Tryptophan metabolism, from nutrition to potential therapeutic applications. Amino. Acids 2011, 41, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangge, H.; Summers, K.L.; Meinitzer, A.; Zelzer, S.; Almer, G.; Prassl, R.; Schnedl, W.J.; Reininghaus, E.; Paulmichl, K.; Weghuber, D.; et al. Obesity-related dysregulation of the tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism: Role of age and parameters of the metabolic syndrome. Obesity 2014, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favennec, M.; Hennart, B.; Caiazzo, R.; Leloire, A.; Yengo, L.; Verbanck, M.; Arredouani, A.; Marre, M.; Pigeyre, M.; Bessede, A.; et al. The kynurenine pathway is activated in human obesity and shifted toward kynurenine monooxygenase activation. Obesity 2015, 23, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.E.; Jain, A.; Matteini, A.; Beamer, B.A.; Wang, N.Y.; Leng, S.X.; Punjabi, N.M.; Walston, J.D.; Fedarko, N.S. Serum levels of the immune activation marker neopterin change with age and gender and are modified by race, BMI, and percentage of body fat. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolowczuk, I.; Hennart, B.; Leloire, A.; Bessede, A.; Soichot, M.; Taront, S.; Caiazzo, R.; Raverdy, V.; Pigeyre, M.; Consortium, A.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism activation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in adipose tissue of obese women: An attempt to maintain immune homeostasis and vascular tone. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 303, R135–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.R.; Schwieler, L.; Erhardt, S.; Boda, S.; Trepci, A.; Kampe, R.; Asratian, A.; Holm, L.; Yngve, A.; Dantzer, R.; et al. Peripheral and central kynurenine pathway abnormalities in major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 101, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deac, O.M.; Mills, J.L.; Shane, B.; Midttun, O.; Ueland, P.M.; Brosnan, J.T.; Brosnan, M.E.; Laird, E.; Gibney, E.R.; Fan, R.; et al. Tryptophan catabolism and vitamin B-6 status are affected by gender and lifestyle factors in healthy young adults. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvik, A.; Theofylaktopoulou, D.; Midttun, O.; Nygard, O.; Eussen, S.J.; Ueland, P.M. Substrate product ratios of enzymes in the kynurenine pathway measured in plasma as indicators of functional vitamin B-6 status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueland, P.M.; McCann, A.; Midttun, O.; Ulvik, A. Inflammation, vitamin B6 and related pathways. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017, 53, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulvik, A.; Ebbing, M.; Hustad, S.; Midttun, O.; Nygard, O.; Vollset, S.E.; Bonaa, K.H.; Nordrehaug, J.E.; Nilsen, D.W.; Schirmer, H.; et al. Long- and short-term effects of tobacco smoking on circulating concentrations of B vitamins. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertovaara, M.; Heliovaara, M.; Raitala, A.; Oja, S.S.; Knekt, P.; Hurme, M. The activity of the immunoregulatory enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is decreased in smokers. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 145, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, C.; Poplawski, T.; Chojnacki, J.; Fila, M.; Konrad, P.; Blasiak, J. Tryptophan Intake and Metabolism in Older Adults with Mood Disorders. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.K.; Wing, E.E.; Banks, W.A.; Dantzer, R. Leucine competes with kynurenine for blood-to-brain transport and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, T.; Gill, A.C.; Clohisey, S.M.; Barnett, M.W.; Pariante, C.M.; Harrison, N.A.; Consortium, M.R.C.I.; Hume, D.A.; Bullmore, E.T.; Freeman, T.C. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on the expression of tryptophan-metabolism genes by human macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, T.B.; Drevets, W.C.; Teague, T.K.; Wurfel, B.E.; Mueller, S.C.; Bodurka, J.; Dantzer, R.; Savitz, J. Kynurenic acid is reduced in females and oral contraceptive users: Implications for depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 67, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, R.; Sirtori, C., Jr.; Spano, P.F. Clinical relevance of drugs affecting tryptophan transport. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 1975, 15, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.N.; Dawkins, P.D.; Smith, M.J.; Hamilton, E.B. Mode of action of antirheumatic drugs. Br. Med. J. 1971, 2, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harrison, P.J.; Geddes, J.R.; Tunbridge, E.M. The Emerging Neurobiology of Bipolar Disorder. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlier, A.; Berkhof, J.G.; Rozing, M.; Bouckaert, F.; Sienaert, P.; Eikelenboom, P.; Veerhuis, R.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Berkhof, J.; Stek, M.L.; et al. Inflammation and remission in older patients with depression treated with electroconvulsive therapy; findings from the MODECT study(). J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 256, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattei, D.; Westrin, A.; Traskman-Bendz, L.; Brundin, L. Cytokine levels in the blood may distinguish suicide attempters from depressed patients. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundin, L.; Sellgren, C.M.; Lim, C.K.; Grit, J.; Palsson, E.; Landen, M.; Samuelsson, M.; Lundgren, K.; Brundin, P.; Fuchs, D.; et al. An enzyme in the kynurenine pathway that governs vulnerability to suicidal behavior by regulating excitotoxicity and neuroinflammation. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoud, A.; Mensi, R.; Douki, W.; Neffati, F.; Najjar, M.F.; Gobbi, G.; Valtorta, F.; Gaha, L.; Comai, S. Reduced peripheral availability of tryptophan and increased activation of the kynurenine pathway and cortisol correlate with major depression and suicide. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 20, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryleva, E.Y.; Brundin, L. Kynurenine pathway metabolites and suicidality. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurfel, B.E.; Drevets, W.C.; Bliss, S.A.; McMillin, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Ford, B.N.; Morris, H.M.; Teague, T.K.; Dantzer, R.; Savitz, J.B. Serum kynurenic acid is reduced in affective psychosis. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxenkrug, G.F. Increased Plasma Levels of Xanthurenic and Kynurenic Acids in Type 2 Diabetes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, S.; Schwieler, L.; Imbeault, S.; Engberg, G. The kynurenine pathway in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovainio, M.; Hurme, M.; Jokela, M.; Pulkki-Raback, L.; Kivimaki, M.; Hintsanen, M.; Hintsa, T.; Lehtimaki, T.; Viikari, J.; Raitakari, O.T.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation and depressive symptoms: Results from the Young Finns Study. Psychosom. Med. 2012, 74, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbay, V.; Ely, B.A.; Babb, J.; Liebes, L. The possible role of the kynurenine pathway in anhedonia in adolescents. J. Neural. Transm. 2012, 119, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbay, V.; Liebes, L.; Katz, Y.; Liu, S.; Mendoza, S.; Babb, J.S.; Klein, R.G.; Gonen, O. The kynurenine pathway in adolescent depression: Preliminary findings from a proton MR spectroscopy study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solvang, S.H.; Nordrehaug, J.E.; Tell, G.S.; Nygard, O.; McCann, A.; Ueland, P.M.; Midttun, O.; Meyer, K.; Vedeler, C.A.; Aarsland, D.; et al. The kynurenine pathway and cognitive performance in community-dwelling older adults. The Hordaland Health Study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 75, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hestad, K.A.; Engedal, K.; Whist, J.E.; Farup, P.G. The Relationships among Tryptophan, Kynurenine, Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase, Depression, and Neuropsychological Performance. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Rief, W. Diagnostic classifications in depression and somatization should include biomarkers, such as disorders in the tryptophan catabolite (TRYCAT) pathway. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 196, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stippl, A.; Kirkgoze, F.N.; Bajbouj, M.; Grimm, S. Differential Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluijms, E.M.; Kamperman, A.M.; Hoogendijk, W.J.; Birkenhager, T.K.; van den Broek, W.W. Influence of an adjuvant antidepressant on the efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2021, 55, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.; Evans, M. Inhibition of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity and elevation of brain tryptophan concentration by administration of antidepressants. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981, 30, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diermen, L.; van den Ameele, S.; Kamperman, A.M.; Sabbe, B.C.G.; Vermeulen, T.; Schrijvers, D.; Birkenhager, T.K. Prediction of electroconvulsive therapy response and remission in major depression: Meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2018, 212, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midttun, O.; Townsend, M.K.; Nygard, O.; Tworoger, S.S.; Brennan, P.; Johansson, M.; Ueland, P.M. Most blood biomarkers related to vitamin status, one-carbon metabolism, and the kynurenine pathway show adequate preanalytical stability and within-person reproducibility to allow assessment of exposure or nutritional status in healthy women and cardiovascular patients. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, E.; Welle, J.R.; Woolwine, B.J.; Goldsmith, D.R.; Baer, W.; Patel, T.; Felger, J.C.; Miller, A.H. Associations among peripheral and central kynurenine pathway metabolites and inflammation in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellgren, C.M.; Gracias, J.; Jungholm, O.; Perlis, R.H.; Engberg, G.; Schwieler, L.; Landen, M.; Erhardt, S. Peripheral and central levels of kynurenic acid in bipolar disorder subjects and healthy controls. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, K.R.; Lim, C.K.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Chatterjee, P.; Martins, R.N.; Brew, B.J.; Guillemin, G.J.; Lovejoy, D.B. Correlation between plasma and CSF concentrations of kynurenine pathway metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease and relationship to amyloid-beta and tau. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 80, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aarsland, T.I.M.; Instanes, J.T.; Posserud, M.-B.R.; Ulvik, A.; Kessler, U.; Haavik, J. Changes in Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism in Patients with Depression Undergoing ECT—A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111439
Aarsland TIM, Instanes JT, Posserud M-BR, Ulvik A, Kessler U, Haavik J. Changes in Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism in Patients with Depression Undergoing ECT—A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111439
Chicago/Turabian StyleAarsland, Tore Ivar Malmei, Johanne Telnes Instanes, Maj-Britt Rocio Posserud, Arve Ulvik, Ute Kessler, and Jan Haavik. 2022. "Changes in Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism in Patients with Depression Undergoing ECT—A Systematic Review" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111439
APA StyleAarsland, T. I. M., Instanes, J. T., Posserud, M.-B. R., Ulvik, A., Kessler, U., & Haavik, J. (2022). Changes in Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism in Patients with Depression Undergoing ECT—A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111439





