Abstract
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy R3, a rare genetic disorder affecting the limb proximal muscles, is caused by mutations in the α-sarcoglycan gene (Sgca) and aggravated by an immune-mediated damage, finely modulated by the extracellular (e)ATP/purinoceptors axis. Currently, no specific drugs are available. The aim of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic effectiveness of a selective P2X7 purinoreceptor antagonist, A438079. Sgca knockout mice were treated with A438079 every two days at 3 mg/Kg for 24 weeks. The P2X7 antagonist improved clinical parameters by ameliorating mice motor function and decreasing serum creatine kinase levels. Histological analysis of muscle morphology indicated a significant reduction of the percentage of central nuclei, of fiber size variability and of the extent of local fibrosis and inflammation. A cytometric characterization of the muscle inflammatory infiltrates showed that A438079 significantly decreased innate immune cells and upregulated the immunosuppressive regulatory T cell subpopulation. In α-sarcoglycan null mice, the selective P2X7 antagonist A438079 has been shown to be effective to counteract the progression of the dystrophic phenotype and to reduce the inflammatory response. P2X7 antagonism via selective inhibitors could be included in the immunosuppressant strategies aimed to dampen the basal immune-mediated damage and to favor a better engraftment of gene-cell therapies.
1. Introduction
Limb girdle muscular dystrophy R3 (LGMD R3), an autosomal recessive primary myopathy characterized by progressive involvement of the pelvic and shoulder girdles, is caused by mutations in the α-sarcoglycan gene (SGCA) [1,2]. SGCA encodes a transmembrane protein, α-sarcoglycan (α-SG), which, together with other 3 SG members (β, γ and δ), interacts with dystrophin, forming the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) [3]. The DGC is crucially responsible for connecting the muscle fiber cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix, preventing damage to the muscle fiber sarcolemma through shearing forces [4]. As other muscular dystrophies [5], LGMD R3 muscle histology is characterized by myofiber necrosis and regeneration, reactive fibrosis and adipose tissue substitution, reduced long-term regenerative capacity and inflammatory infiltrates [6,7,8]. In physiological conditions, skeletal muscle is considered a privileged immunological site characterized by few immune cells, poorly able to generate localized immune responses. In contrast, the dystrophic muscle presents a high level of inflammation associated with the activation of an innate and adaptive immune response [9,10]. In LGMD R3, the DGC disruption causes fragile muscle fibers and unstable sarcolemma, which, in turn, leads to muscle necrosis and to the release of damage-associated molecular pattern molecules (DAMPs), such as ATP, thus initiating a well-orchestrated immune reaction. Specifically, in α-SG-deficient muscle cells, the effect of ATP release can be further amplified since the ecto-ATPase activity of sarcoglycan, responsible for extracellular ATP (eATP) hydrolysis, is lost [11,12]. Once in the extracellular space, eATP binds and activates ionotropic (P2X) or metabotropic (P2Y) receptors [13]. Among P2X receptors, P2X7 has attracted vivid interest since it plays a relevant role in the induction of immune cell responses via inflammasome activation [14], and the consequent release of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) by mononuclear and polymorphonuclear phagocytes [14,15,16,17]. P2X7 is also over-expressed in dystrophic muscle cells [18,19,20,21], where it contributes to exacerbate myofiber injury by increasing sarcolemma permeability [22] and participates in the amplification of the inflammatory process by releasing IL-1β [20]. From these observations, P2X7 is an attractive therapeutic target, not only for reducing inflammation but also for decreasing myofiber damage and supporting the regenerative potential of dystrophic myoblasts [23]. In this respect, genetic ablation and pharmacological inhibition of the eATP-P2X7 axis by the broad-spectrum antagonist oxidized ATP (oATP) alleviated dystrophic phenotypes in mouse models of dystrophinopathy and sarcoglycanopathy [18,24,25]. In this study, we performed a long-term treatment in Sgca null mice with A438079, a potent and selective P2X7 antagonist. Functional, biochemical, cytofluorimetric and histological analysis are shown, providing evidence that A438079 improved muscle force and morphology by dampening the extent of muscle fibrosis and local inflammation.
2. Results
2.1. P2X7 Targeting by A438079 Improves Functional, Biochemical and Morphological Parameters in Sgca Mice
In order to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of a selective P2X7-targeting compound in an experimental model of α-sarcoglycanopathy, we treated four-week-old male Sgca knockout mice (also termed Sgca-null) mice with A438079, a specific antagonist of P2X7 [26]. The drug was administered to Sgca-null (here from referred as Sgca) mice by i.p. injections at the dose of 3 mg/kg every other day for 24 weeks (Figure 1a). Sgca mice injected with PBS (Sgca CTR) and Wild-Type (WT) mice served as controls.
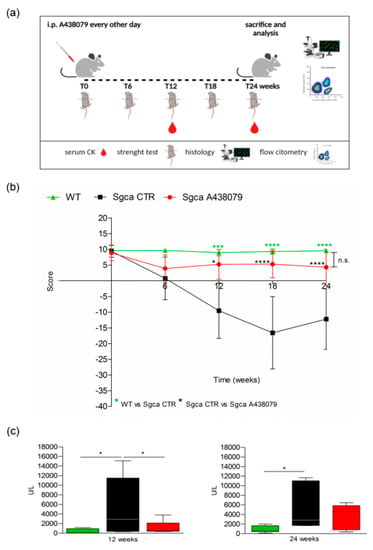
Figure 1.
A438079 improves functional, biochemical and histological parameters in Sgca mice. (a): Experimental design: Four-week-old male Sgca mice were treated with PBS vehicle (Sgca CTR, n = 12) and A438079 (Sgca A438079 n = 8) that was administered intraperitoneally at the dose of 3 mg/Kg every other day for 24 weeks. Age-matched male C57BL/6 Wild Type (WT n = 12) mice were used as negative control; (b): four-limb hanging test was performed before treatment and at the end of 6, 12, 18 and 24 weeks of treatment. Each value represents the mean ± SD of animals evaluated. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Green asterisks indicate statistical significance between WT and Sgca CTR (***, p < 0.001, ****, p < 0.0001). Black asterisks indicate statistical significance between Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 (*, p < 0.05; ****, p < 0.0001). No statistical significance (n.s.) was identified between WT and Sgca A438079 mice; (c): serum creatine kinase (CK) levels were evaluated at the end of the twelfth and the twenty-fourth week of treatment. Blood samples were obtained by retro orbital withdraw from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of animals evaluated. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*, p < 0.05).
The animals were weighted and followed once a week for signs of toxicity until the sacrifice. As shown in Supplementary Figure S1, the weight gain curve of Sgca mice treated with A438079 (Sgca A438079) was not significantly different from that of Sgca CTR mice. In addition, no signs of toxicity, including ruffled fur, vomiting, hyperactivity or loss of ambulation and breathing depression, were observed (data not shown). At the beginning (0 time) and after 6, 12, 18 and 24 weeks of treatment, animals were evaluated for muscle strength by the four-limb hanging test. Figure 1b shows that Sgca CTR mice progressively lost muscle strength up to 18 weeks (Sgca CTR vs. WT at 12 week p < 0.001, at 18 week p < 0.0001). At 24 weeks, they still showed significantly lower strength when compared to WT mice (p < 0.0001). The apparent slight recovery between 18 and 24 weeks was not significant. On the contrary, Sgca A438079 initially showed reduced functional performance, similarly to Sgca CTR mice, but after 6 weeks of treatment, muscle strength began to recover, almost reaching the performance of WT animals up to 24 weeks. The difference between Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice at 12, 18 and 24 weeks was highly significant (p < 0.05 at 12, p < 0.0001 at 18 and 24 weeks). Accordingly, muscle strength in WT and Sgca A438079 mice was not significantly different at any time point. The efficacy of A438079 was confirmed by the analysis of serum levels of CK, a marker of muscle degeneration. As shown in Figure 1c, CK serum levels of Sgca CTR mice measured >10 times more than the WT levels (mean value of WT mice: 406 UI/l, n = 9; mean value of Sgca CTR mice: 5537 UI/l, n = 12, p < 0.05). Interestingly, A438079 treatment significantly reduced (by 76%) serum CK in Sgca mice after 12 weeks of treatment (mean value in Sgca A438079 mice: 1338 UI/l, n = 8 vs. Sgca CTR mice p < 0.05). After 24 weeks of treatment serum CK levels of Sgca CTR mice were 6.3 times higher than the WT levels and A438079 led to a serum CK decrease in the treated mice, although it did not reach statistical significance, likely due to increased variability of the measurements (mean value of WT mice: 829 UI/l, n = 12; mean value of Sgca CTR mice: 5235 UI/l, n = 10, p < 0.05).
To investigate whether the improved functional performance of Sgca A438079 mice correlated with decreased inflammation and muscle degeneration, we performed histological analysis by H&E staining of quadriceps from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice.
Quadriceps from Sgca CTR mice presented areas of necrotic cells surrounded by reactive macrophage infiltration (Figure 2a) which were reduced upon A438079 treatment (Figure 2a). According to the histological analysis (Figure 2b), the percentage of centrally nucleated myofibers dramatically increased in quadriceps of Sgca mice in comparison to WT animals (p < 0.001) and was reduced by 12% in A438079-treated animals (p < 0.001) (Figure 2c). As expected, the fiber size variability, calculated as coefficient variance Z of minimal Feret’s diameter, was wider in Sgca CTR compared to WT mice (p < 0.001) but was significantly down-modulated by A438079 treatment (p < 0.05) (Figure 2d).
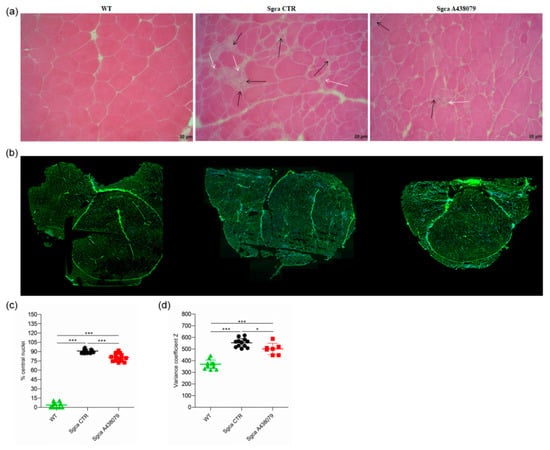
Figure 2.
A438079 ameliorates the muscle morphology of Sgca mice. (a): frozen quadriceps tissue sections from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice were collected at the end of the twenty-fourth week of treatment and stained with standard H&E technique. A representative image is shown. Black arrows indicate inflammatory infiltrates, white arrows indicate degenerating muscle fibers. Final magnification, 20×; (b): frozen quadriceps tissue sections from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice were collected at the end of the twenty-fourth week of treatment and stained with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and DAPI. The whole quadricep section has been re-constructed; (c): percentage of central nuclei was quantified in four consecutive fields for each muscle section stained with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and DAPI and normalized for the fiber number of each field (WT n= 4; Sgca CTR n = 4; Sgca A438079 n = 4); (d): muscle fiber diameter variability from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice was calculated in the whole area as variance coefficient Z of minimal Feret’s diameter (WT n= 12; Sgca CTR n = 12; Sgca A438079 n = 7). In panels (c,d), data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001).
2.2. A438079 Reduces Muscular Fibrosis and Inflammation in Sgca Mice
Fibrosis as characterized by replacement of muscle tissue with collagen deposits is the histopathological hallmark of end-stage muscular dystrophies, including alfa-sarcoglycanopathy [27]. In order to establish whether A438079 might impact collagen deposits, we performed a Masson trichrome staining on quadriceps of WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice and evaluated the fraction area of fibrotic reactions. As shown in Figure 3a, Sgca CTR quadriceps accumulated abundant extracellular matrix deposits which were increased in comparison to WT mice (mean value of WT mice: 1.47, n = 7; mean value of Sgca CTR mice: 2.92, n = 11, p < 0.05). A438079 treatment led to a 37% reduction of extracellular matrix deposition fraction area as compared to Sgca CTR mice (mean of Sgca A438079 mice: 1.85, n = 7, p < 0.05). No significant difference was observed between WT and Sgca A438079 animals.
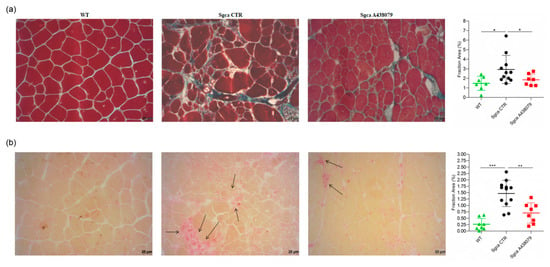
Figure 3.
A438079 reduces muscle fibrosis and inflammatory infiltrates in Sgca mice. (a): frozen sections of quadriceps from WT (n = 7), Sgca CTR (n = 11) and Sgca A438079 (n = 7) were collected after 24 weeks and stained with a standard Masson trichrome stain protocol. A representative image is shown. Final magnification, 20×. In the right part of the panel (a) a graph of the fraction areas of fibrotic green positive signal/fraction area (%) of total section area of muscles evaluated is shown. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one-tailed ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*, p < 0.05); (b): frozen sections of quadriceps from WT (n = 8), Sgca CTR (n = 12) and Sgca A438079 (n = 8) were collected after 24 weeks and stained with an acid phosphatase technique. A representative image is shown. Black arrow indicates inflammatory infiltrates. Final magnification, 20×. In the right part of panel (b), a graph of the fraction areas of inflammatory red positive signal/fraction area (%) of total section area of muscles evaluated is shown. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
To evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of A438079, quadricep sections of WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice were stained with acid phosphatase, which provides a red positive signal in activated macrophages and degenerative myofibers. As shown in Figure 3b, the acid phosphatase-positive area fraction of quadriceps from Sgca CTR mice was increased in comparison to that of WT mice (mean value of WT mice: 0.26, n = 8; mean value of Sgca CTR mice: 1.47, n = 12, p < 0.001). Interestingly, A438079 led to 52% reduction of inflammatory area fraction of Sgca mice (mean of Sgca A438079 mice: 0.70, n = 8, p < 0.01). In contrast, no significant difference was observed between WT and Sgca A438079 animals.
2.3. A438079 Reduces Innate Inflammatory Cells and Increases T Regulatory Lymphocytes in Limb Muscles of Sgca Mice
In order to better characterize the phenotype of inflammatory muscle infiltrates, we performed a cytometric analysis of a pool of limb muscles, including gastrocnemius, quadriceps and anterior tibialis, isolated from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice. As shown in Figure 4a, limb muscles of Sgca CTR mice were characterized by the presence of CD45+ hematopoietic immune cells which, in contrast, were not detected in WT mice (WT vs. Sgca CTR, p < 0.01).
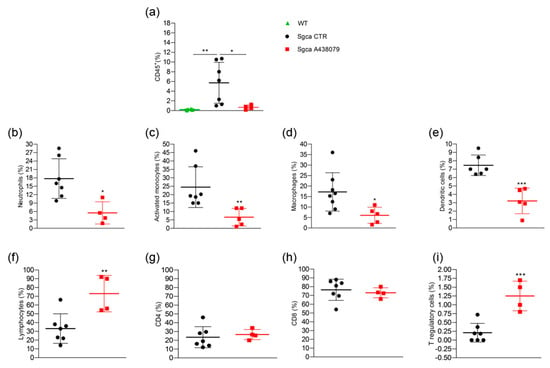
Figure 4.
A438079 reduces innate inflammatory cells and increases T regulatory lymphocytes in muscles of Sgca mice. Flow cytometric analysis of immune cells isolated from a pool of gastrocnemius, quadriceps, anterior tibialis excised from WT (n = 6), Sgca CTR (n = 7) and Sgca A438079 (n = 5) mice and stained with specific anti-surface markers mAbs are shown; (a): percentage of CD45+ cells gated on alive cells; (b): percentage of Ly6G+/CD11b+neutrophils gated on CD45+ alive cells; (c): percentage of Ly6G−/Ly6C+/CD11b+ activated monocytes gated on CD45+ alive cells; (d): percentage of Ly6G−/F480+/CD11b+ macrophages gated on CD45+ alive cells; (e): percentage of Ly6G−/F480−/CD11c+ dendritic cells gated on CD45+ alive cells; (f): percentage of CD3+ T cells gated on CD45+ alive cells; (g): percentage of CD3+/CD4+ T cells gated on CD45+/CD3+ alive cells. (h): percentage of CD3+/CD8+ T cells gated on CD45+/CD3+ alive cells; (i): percentage of CD3+/CD4+CD25+/Foxp3+ T cells gated on CD3+ alive cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test Panel (a) and unpaired t-test Panels (b–i). Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
A438079 treatment significantly reduced the percentage of CD45+ cells infiltrating the limb muscles of Sgca mice (Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.05). The further characterization of CD45+ cells was only performed for Sgca animals since the amount of CD45+ cells was negligible in the muscle of WT mice. Sgca A438079 mice presented a significant reduction of muscle infiltrating innate inflammatory cells, including Ly6G+/CD11b+ neutrophils (Figure 4b, Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.05), Ly6G−/CD11b+/Ly6C+ activated monocytes (Figure 4c, Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.01), Ly6G−/CD11b+/F480+ macrophages (Figure 4d, Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.05) and Ly6G−/CD11c+/F480−dendritic cells (DC) (Figure 4e, Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.001) in comparison to Sgca CTR animals. In contrast, the percentage of CD3+/CD4+/CD25+/Foxp3+ T regulatory (Treg) was significantly increased in the muscles of A438079 Sgca mice in comparison to Sgca CTR mice (Figure 4i, Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.001).
Furthermore, the analysis of the peripheral blood (PB) immune cell populations of WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice showed that the dystrophic animals presented significantly higher percentages of DC compared to WT animals (Figure 5c, WT vs. Sgca CTR, p < 0.001 for DC). Treatment with A438079 significantly reduced the percentage of DC, CD8+ lymphocytes and T reg cells (Figure 5c,f,g, Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.05 for DC; p < 0.001 for CD8+ lymphocytes and p < 0.001 for Treg).
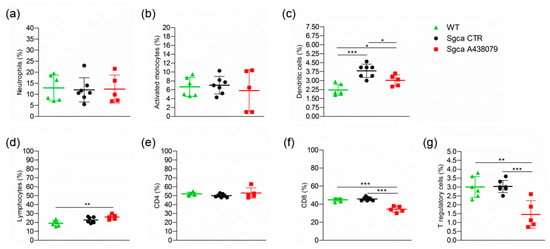
Figure 5.
A438079 reduces peripheral cytotoxic and T regulatory cells in Sgca mice. Flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood immune cells isolated from WT (n = 6), Sgca CTR (n = 7) and Sgca A438079 (n = 5) mice and stained with specific anti-surface markers mAbs are shown; (a): percentage of Ly6G+/CD11b+neutrophils gated on CD45+ alive cells; (b): percentage of Ly6G−/Ly6C+/CD11b+ activated monocytes gated on CD45+ alive cells; (c): percentage of Ly6G−/F480−/CD11c+ dendritic cells gated on CD45+ alive cells; (d): percentage of CD3+ T cells gated on CD45+ alive cells; (e): percentage of CD3+/CD4+ T cells gated on CD45+/CD3+ alive cells; (f): percentage of CD3+/CD8+ T cells gated on CD45+/CD3+ alive cells; (g): Percentage of CD3+ /CD4+/CD25+/Foxp3+ T cells gated on CD3+ alive cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
No significant changes were observed in the spleen of WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice, with the only exception of CD3+ T lymphocytes, which were slightly increased in Sgca A43879 mice vs. Sgca CTR (Supplementary Figure S2e, Sgca CTR vs. Sgca A438079, p < 0.01).
3. Discussion
In the present study, we provide evidence that the pharmacological inhibition of P2X7 by the selective antagonist A438079 attenuated the dystrophic phenotype of Sgca mice by reducing fibrosis and inflammation and improved muscle performance. P2X7 is an ATP receptor belonging to the ionotropic purinergic P2X subfamily, which is expressed on virtually all cell types of the immune system and regulates the innate and adaptive immune responses [28]. Alongside its expression on immune cells, P2X7 expression and function are upregulated in the dystrophic muscle [18,21,25,29,30,31]. In this context, we and other groups demonstrated that the genetic ablation of P2RX7 and its pharmacological inhibition by oATP, an irreversible, broad-spectrum P2X7 antagonist [17], produced significant improvements in key functional and molecular disease parameters in mdx and Sgca mice [18,24,25,30]. However, oATP can also interact with other P2X receptors, including P2X4 [32,33,34], and appears to exert anti-inflammatory effects, modulating the immune response independently of P2X7 blockage [33,35,36]. Therefore, experiments using oATP cannot unambiguously establish a role in inflammatory diseases for a specific member of the P2X family. Neurotoxicity has been described for oATP, likely due to the low specificity of the drug [37]. In order to overcome the above-described limitations, and to define the therapeutic effect of P2X7 targeting approaches in α-sarcoglycan-deficient muscular dystrophy, we specifically inhibited P2X7 using the A438079 molecule, one of the most potent and selective antagonists that competitively blocks P2X7 receptor in vitro activation and produces anti-nociceptive effects in in vivo settings [38,39,40]. In addition to nociception, A438079 has already been successfully used in in vivo models of hyperalgesia [41], epilepsy [42,43], Parkinson’s disease [44], salivary gland exocrinopathy [45], and Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1A disease [46]. Our results clearly show that, by targeting P2X7, A438079 ameliorated functional and morphological parameters in Sgca mice. In particular, A438079 improved muscle morphology by reducing the percentage of centralized nuclei and the coefficient variance Z of minimal Feret’s diameter (Figure 2c,d), which are typical signs of dystrophic damage [47]. Furthermore, according to previous studies [24], a relevant therapeutic effect exerted by A438079 was the reduction of muscle fibrosis (Figure 3a). P2X7 has been described to play a nodal role in triggering fibrosis through activation of multiple intracellular pathways that converge in inducing the collagen biosynthetic machinery in various organs [48]. As such, P2X7 blockade may interfere with the main pro-fibrotic pathways, thus possibly representing a target for the pharmacological modulation of fibrotic processes. The most evident beneficial effect of A438079 in Sgca animals was a significant modulation of muscle inflammation, a key feature of muscular dystrophies participating in the disease progression but also mediating muscle repair. The dichotomous role of inflammation has been extensively studied in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), in which CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, macrophages, eosinophils and natural killer T cells infiltrated both human and mouse dystrophic muscle [9,49]. In particular, proinflammatory monocytes CD11b+/Ly6G−/Ly6c+ have been reported to be the first innate immune cells to be mobilized from the bone marrow into the circulation and recruited to the site of tissue injury [50], such as dystrophic muscles, where they differentiated into inflammatory macrophages [51,52]. Different studies demonstrated that neutrophils actively participated in the exacerbation of muscular dystrophy and their specific depletion reduced muscular necrosis and inflammation in mdx mice [53,54,55]. Moreover, neutrophil-derived elastase impaired myoblast proliferation, survival and differentiation [56]. In line with this notion, we found that A438079 caused a significant reduction of innate immune cells, including neutrophils, activated monocytes and dendritic cells infiltrating the limb muscles of Sgca mice. The downregulation of innate immune response by P2X7 blockade was also observed in dystrophic mice (mdx and Sgca) treated with other P2X7 antagonists, i.e., oATP or zidovudine (AZT) [18,25,57]. However, the mechanism underlying the latter effect is still unclear. P2X7 antagonists could directly inhibit P2RX7 expressed by inflammatory innate immune cells infiltrating the dystrophic muscle. Alternatively, these agents might reduce inflammatory cell migration into the injured tissue. In favor of the first hypothesis, innate immune cells are known to express functional P2X7, which in turn triggers inflammasome activation [17,28,58,59,60]. The second hypothesis is sustained by data showing P2X7-dependent release of chemotactic factors by macrophages. These factors, including CXCL2/macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), were involved in the recruitment of neutrophils into the injured tissue [61]. The immune phenotype of limb muscle from Sgca mice treated with A438079 also showed that the pharmacological treatment significantly increased Foxp3+ Treg without affecting CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. These findings are consistent with previous studies in which P2X7 blockade by oATP or P2X7 genetic ablation in dystrophic mice resulted in a significant increase of Foxp3+ Treg [18,24,25]. Treg have been described to play a dual beneficial role in dystrophic muscles. On one side, they suppress type 1 inflammation by secreting IL-10; on the other side, Treg may also have direct effects on muscle growth and regeneration through secretion of amphiregulin, an epidermal growth factor family member whose receptors are expressed on muscle satellite cells that are critical for muscle regeneration [62,63]. Interestingly, our results showed that A438079 exerted not only a local but also a systemic anti-inflammatory effect by reducing circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in Sgca mice. Currently, physical therapy and prevention of secondary cardiac, pulmonary or orthopedic complications are the only possible care interventions. Although a chronic inflammatory response is documented in muscle specimens from LGMD R3 patients, no trials assessing the effects of immunosuppressive therapies have been proposed in alpha-sarcoglycan deficiency. However, two unrelated LGMD R3 patients treated with steroids showed clinical improvement [64,65,66]. In light of these considerations, strategies aimed at reducing muscle inflammation, increasing the amount of Treg infiltrating an injured muscle and exerting a systemic anti-inflammatory effect, i.e., antagonists of P2X7, might represent a therapeutic approach for LGMD R3. Immunomodulatory regimens become even more relevant as new gene therapies or gene editing approaches are being developed for alpha-sarcoglycanopathy [67,68,69], with gene therapy being in Phase I/II clinical trials for LGMD R3 patients (NCT01976091; NCT00494195). Since the success of gene therapy in the muscle tissue has to challenge the pre-existing status of chronic tissue inflammation typically identified in this diseases [67,68,69,70,71], our data suggest that P2X7 antagonism might represent a good strategy to dampen chronic inflammation, possibly leading to a better delivery of gene therapy. To date P2X7 selective antagonists have already been tested in Phase I/II clinical trials for the treatment of Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, basal cell carcinoma with an overall good tolerability and variable efficacy [72] and a new trial is currently ongoing assessing the effects of JNJ-54175446, a potent, brain-penetrant, selective P2X7 antagonist [73] in patients with major depressive disorder (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04116606).
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vivo Experiments
C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) and Sgca knockout mice (also termed Sgca-null) were bred in the Animal Facility at Policlinico San Martino, Genova. All mice were housed under standard specific pathogen–free conditions and allowed access to food and water ad libitum. All experimental protocols were approved by the Policlinico San Martino Animal Welfare Body and by the Italian Ministry of Health (Authorization n° 215–2018-PR). Sgca mice were previously described [74]. The study design defined a minimum goal of a n = 8 animals per genotype and experimental group. According amounts of the drug A438079 was acquired from Tocris Bioscience Bristol, UK. Four week old Sgca male mice were randomly divided into two groups: one treated by i.p. injections with A438079 at 3 mg/Kg every other day in the morning between 10–12 for 24 weeks (Sgca A438079) and one treated with the same volume of phosphatase-buffered saline (PBS, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) every other day for 24 weeks (Sgca Control: Sgca CTR). In consideration of the high variability of the histological markers in mouse models of muscular dystrophies [18,25], and in order to increase the statistical power of the study a n of 12 WT mice and a n of 12 Sgca CTR were included. The dose of 3 mg/kg of A438079 proved to be well tolerated by wild-type rats [46]. A438079 was reconstituted at a final concentration of 1 mg/mL in PBS and stored at −20 °C; the reconstituted drug was thawed and immediately used at a final concentration of 3 mg/Kg. All animals were euthanized at the end of treatment by carbon dioxide inhalation and muscles were collected for histological and cytofluorimetric analysis. A group of age-matched WT C57Bl/6 male mice was used as internal control. All animals were weighed and followed for any sign of toxicity, including ruffled fur, vomiting, hyperactivity or loss of deambulation and breathing depression once a week. Blood samples from Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice were obtained from the saphenous vein (90 µL) before treatment and 12 and 24 weeks after treatment. The samples were centrifuged at 3600× g for 30 min and immediately after centrifugation the serum was isolated and stored at −80 °C. Serum creatine kinase (CK) levels were measured using a clinical-standard automatic chemistry analyzer (BS-380 Mindray, Milan, Italy).
4.2. Four-Limb Hanging Test
Before treatment and at the end of the sixth, twelfth, eighteenth and twenty-fourth week of treatment, the muscle strength of WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079- mice was scored through the four-limb hanging test. Mice were subjected to a 180-s lasting hanging test, during which a falling score was recorded. The animals had to hang for three trials, and the average maximum hanging time of the three trials was measured (standard operating procedure, https://treat-nmd.org/research-overview/preclinical-research/experimental-protocols-for-dmd-animal-models, last accessed on September 2021.
4.3. Histological Studies, Imaging and Analysis
Quadriceps isolated from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice were cut on cryostat, and 7-μm-thick sections were stained with standard hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (reagents from Sigma Aldrich), acid phosphatase (reagents from Sigma Aldrich) to detect inflammatory reactions and Masson trichrome (reagents from Sigma Aldrich) to evaluate muscle fibrosis. Representative pictures were taken at 20× magnification. To quantify the extension of the inflammatory response and fibrotic area, images of stained sections were acquired using a Nikon Ti Eclipse microscope equipped with a 20× objective. Whole sections were imaged with an automated tile scan acquisition (usually over a 45 mm2-surface) by using the perfect focus system (PFS) to control the focal plane. Quantification of acid phosphatase and trichrome staining was performed using semi-automated measurement tools in NIS-Elements AR software version 4.20 and expressed in terms of fraction area (the ratio between total section area and the area of the stained objects that were detected by HSI thresholding mode). All the histological analyses were performed blind to experimental group identity. The Masson Trichrome and acid phosphatase staining were completely negative in WT mice; therefore, the n was reduced to 7 animals.The histological sections of Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 treated mice displaying freezing artifacts were not analyzed and are excluded from the results.
4.4. Immunofluorescence
The wheat germ agglutinin (WGA)/DAPI (WGA Alexa Fluor™ 488 Conjugate Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA; DAPI, Fluoromount-G® Southern Biotech, Birmingham, USA) staining was performed on quadricep 5-μm-thick sections, in order to calculate the Minimum Feret’s Diameter and the percentage of centralized nuclei. Briefly, unfixed quadriceps sections were incubated with a blocking solution containing 0.2% TritonX-100 (Sigma Aldrich), 2% bovine serum albumin (Sigma Aldrich), 5% fetal bovine serum (GIBCO, Thermo Fisher Scientific), 2% goat serum (GIBCO) in PBS for 1 h at room temperature (RT) and then with WGA Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated diluted 1:200 in Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) (GIBCO) for 2 h at RT. Finally, sections were mounted with Fluoromount G. Images were acquired by Axioplan Imager M2 miscroscope software AxioVs40 version 4.8.2.0 (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) and manually overlapped using Adobe Photoshop CS6 to generate whole cross-section. Image analysis was performed using Fiji, ImageJ 1.52i (NIH, Bethesda, MA, USA). A plugin (Muscle Morphometry) developed as described in [24] was used to quantify the muscle fiber diameter (minimal Feret’s diameter) and the percentage of centralized nuclei, as described in TREAT-NMD-recommended protocol (https://treat-nmd.org/research-overview/preclinical-research/experimental-protocols-for-dmd-animal-models, last accessed on 10 September 2021). All the analyses were performed blind to experimental group identity.
4.5. Flow Cytometry
Hematopoietic cells were collected from different districts, namely PB, spleen and limb muscles. Cells collected from PB were first incubated with 2 μL/sample of TruStainFcXTM anti-mouse CD16/32 for 5 min in order to block Fc receptor and then with cocktails of antibodies specific for CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD11b, CD11c, CD25, F4/80, Ly-6C, Ly-6G and Foxp3 for 30 min. The intracellular staining of transcription factor Foxp3 was performed using the Foxp3/Transcription factor staining buffer set (Thermo Fisher) as described by the manufacturer. After antibody incubation, samples were lysed (Becton Dickinson Pharm Lyse TM, San Josè, CA, USA), washed and resuspended in 300 ul of PBS. All the antibodies were purchased from Biolegend (San Diego, CA, USA). Gastrocnemius, quadriceps and anterior tibialis excised from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice were resuspended in RPMI 1640 base medium (Euro Clone, Milan, Italy), mechanically and enzimatically digested using Skeletal Muscle Dissociation Kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Bologna, Italy) and filtered through 100- and 70-μm mesh filters (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA) (Supplementary Method). After filtration, cells were purified using gradient centrifugation by Percoll solution (GE Healthcare Bio-sciences, Uppsala, Sweden) and stained with Live/DeadTM Fixable Yellow Dead Cell Stain Kit (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and the antibodies listed above. The spleen from WT, Sgca CTR and Sgca A438079 mice was mechanically digested, filtered through 100- and 70-μm mesh filters, counted and stained as described for PB and muscle. All acquisitions were performed with a three laser LSR Fortessa X20 (Becton Dickinson) and obtained FSC files were analysed with Kaluza Software (version 2.1, Beckman Coulter). The immune profile of the peripheral blood, spleen and muscles was performed in the same animals (WT n = 6, Sgca CTR n = 7 and Sgca A438079 n = 5).
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical parameters, including the exact value of n and statistical significance, are reported in the figures and their associated legends. Results were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test or unpaired t-test, where indicated, using GraphPad Prism 3.0 software (GraphPad Software, El Camino Real, San Diego, CA, USA). Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, ****, p < 0.0001).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, A438079 ameliorated the dystrophic phenotype of Sgca mice by reducing muscle fibrosis and inflammation and by improving functional muscle performance. In the current scenario of clinical trials including gene therapy, selective P2X7 antagonists could represent candidates for a combinatory therapy to endorse the efficacy of disease-specific gene therapy by dampening the basal muscular inflammation.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph15010089/s1. Figure S1: Weight of Sgca mice treated (not) with A438079; Figure S2: A438079 modulation of splenic immune cells of Sgca mice and Supplementary Methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.B., L.R., E.G.; methodology, S.B. (Serena Baratto), E.P., S.P., F.A., G.D.Z., A.B., P.S.; software C.P., P.S.; validation, S.B. (Serena Baratto), E.P., S.P., F.A., G.D.Z., A.B., P.S., C.P.; formal analysis, L.R., E.G., S.B. (Santina Bruzzone); investigation, S.B. (Serena Baratto), E.P., C.P., L.R.; resources, C.B., L.R.; data curation, S.B. (Serena Baratto), E.P., S.B. (Santina Bruzzone), C.P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.R.; writing—review and editing, E.P., S.B. (Serena Baratto), L.R., C.B., E.G., S.B. (Santina Bruzzone), C.P., C.M.; visualization, L.R., S.B. (Serena Baratto), E.P., S.B. (Santina Bruzzone), C.P.; supervision, L.R., E.G., C.B., C.M.; project administration, E.G., C.B.; funding acquisition, L.R., C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by by Telethon-Italy grant GGP17192 (to C.B.), by the Italian Ministry of Health RF 2016–02364503 (to C.B.), and by Fondazione Compagnia di San Paolo grant ROL 32561 (to L.R.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study was conducted according to the Ethical Guidelines for the Use of Animals in Research (3Rs) and approved by the Policlinico San Martino Animal Welfare Body, Genova, Italy and by the Italian Ministry of Health (Authorization n° 215–2018-PR).
Informed Consent Statement
Not available.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the main text and Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank C.B. and C.M. They are members of the European Reference Network for Neuromuscular Disorders.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Alonso-Pérez, J.; González-Quereda, L.; Bello, L.; Guglieri, M.; Straub, V.; Gallano, P.; Semplicini, C.; Pegoraro, E.; Zangaro, V.; Nascimento, A.; et al. New genotype-phenotype correlations in a large European cohort of patients with sarcoglycanopathy. Brain A J. Neurol. 2020, 143, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vainzof, M.; Souza, L.S.; Gurgel-Giannetti, J.; Zatz, M. Sarcoglycanopathies: An update. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2021, 31, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandona, D.; Betto, R. Sarcoglycanopathies: Molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic prospects. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrof, B.J.; Shrager, J.B.; Stedman, H.H.; Kelly, A.M.; Sweeney, H.L. Dystrophin protects the sarcolemma from stresses developed during muscle contraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3710–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tidball, J.G.; Welc, S.S.; Wehling-Henricks, M. Immunobiology of Inherited Muscular Dystrophies. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1313–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner, J.; Lochmüller, H. Sarcoglycanopathies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2011, 101, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Bönnemann, C.G.; Muntoni, F. Muscular dystrophies. Lancet 2019, 394, 2025–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanin, M.; Angelini, C. Regeneration in sarcoglycanopathies: Expression studies of sarcoglycans and other muscle proteins. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 165, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.S.; Puig, M.; Nagaraju, K.; Hoffman, E.P.; Villalta, S.A.; Rao, V.A.; Wakefield, L.M.; Woodcock, J. Immune-mediated pathology in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 299rv294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panicucci, C.; Baratto, S.; Raffaghello, L.; Tonin, P.; D’Amico, A.; Tasca, G.; Traverso, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Minetti, C.; Previtali, S.C.; et al. Muscle inflammatory pattern in alpha- and gamma-sarcoglycanopathies. Clin. Neuropathol. 2021, 40, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betto, R.; Senter, L.; Ceoldo, S.; Tarricone, E.; Biral, D.; Salviati, G. Ecto-ATPase activity of alpha-sarcoglycan (adhalin). J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7907–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandona, D.; Gastaldello, S.; Martinello, T.; Betto, R. Characterization of the ATP-hydrolysing activity of alpha-sarcoglycan. Biochem. J. 2004, 381, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Adinolfi, E. Extracellular purines, purinergic receptors and tumor growth. Oncogene 2017, 36, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Sarti, A.C.; Grassi, F. Modulation of innate and adaptive immunity by P2X ion channels. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 52, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Planillo, R.; Kuffa, P.; Martinez-Colon, G.; Smith, B.L.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Nunez, G. K(+) efflux is the common trigger of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by bacterial toxins and particulate matter. Immunity 2013, 38, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKenzie, A.; Wilson, H.L.; Kiss-Toth, E.; Dower, S.K.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Rapid secretion of interleukin-1beta by microvesicle shedding. Immunity 2001, 15, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, M.; Katsnelson, M.A.; Dubyak, G.R.; Pearlman, E. Neutrophil P2X7 receptors mediate NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent IL-1beta secretion in response to ATP. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazzerro, E.; Baldassari, S.; Assereto, S.; Fruscione, F.; Pistorio, A.; Panicucci, C.; Volpi, S.; Perruzza, L.; Fiorillo, C.; Minetti, C.; et al. Enhancement of Muscle T Regulatory Cells and Improvement of Muscular Dystrophic Process in mdx Mice by Blockade of Extracellular ATP/P2X Axis. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 3349–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeung, D.; Zablocki, K.; Lien, C.F.; Jiang, T.; Arkle, S.; Brutkowski, W.; Brown, J.; Lochmuller, H.; Simon, J.; Barnard, E.A.; et al. Increased susceptibility to ATP via alteration of P2X receptor function in dystrophic mdx mouse muscle cells. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, R.; Cohen, T.V.; Ampong, B.; Francia, D.; Henriques-Pons, A.; Hoffman, E.P.; Nagaraju, K. Inflammasome up-regulation and activation in dysferlin-deficient skeletal muscle. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2891–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.N.; Brutkowski, W.; Lien, C.F.; Arkle, S.; Lochmuller, H.; Zablocki, K.; Gorecki, D.C. P2X7 purinoceptor alterations in dystrophic mdx mouse muscles: Relationship to pathology and potential target for treatment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, L.A.; Puebla, C.; Cisterna, B.A.; Escamilla, R.; Vargas, A.A.; Frank, M.; Martinez-Montero, P.; Prior, C.; Molano, J.; Esteban-Rodriguez, I.; et al. Fast skeletal myofibers of mdx mouse, model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, express connexin hemichannels that lead to apoptosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2583–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorecki, D.C. P2X7 purinoceptor as a therapeutic target in muscular dystrophies. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinadinos, A.; Young, C.N.; Al-Khalidi, R.; Teti, A.; Kalinski, P.; Mohamad, S.; Floriot, L.; Henry, T.; Tozzi, G.; Jiang, T.; et al. P2RX7 purinoceptor: A therapeutic target for ameliorating the symptoms of duchenne muscular dystrophy. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzerro, E.; Baratto, S.; Assereto, S.; Baldassari, S.; Panicucci, C.; Raffaghello, L.; Scudieri, P.; De Battista, D.; Fiorillo, C.; Volpi, S.; et al. The Danger Signal Extracellular ATP Is Involved in the Immunomediated Damage of alpha-Sarcoglycan–Deficient Muscular Dystrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.W.; Gregg, R.J.; Kort, M.E.; Perez-Medrano, A.; Voight, E.A.; Wang, Y.; Grayson, G.; Namovic, M.T.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Niforatos, W.; et al. Structure-activity relationship studies on a series of novel, substituted 1-benzyl-5-phenyltetrazole P2X7 antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozsgai, E.R.; Griffin, D.A.; Heller, K.N.; Mendell, J.R.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R. β-Sarcoglycan gene transfer decreases fibrosis and restores force in LGMD2E mice. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Dal Ben, D.; Sarti, A.C.; Giuliani, A.L.; Falzoni, S. The P2X7 Receptor in Infection and Inflammation. Immunity 2017, 47, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, C.N.; Sinadinos, A.; Lefebvre, A.; Chan, P.; Arkle, S.; Vaudry, D.; Gorecki, D.C. A novel mechanism of autophagic cell death in dystrophic muscle regulated by P2RX7 receptor large-pore formation and HSP90. Autophagy 2015, 11, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.N.J.; Chira, N.; Rog, J.; Al-Khalidi, R.; Benard, M.; Galas, L.; Chan, P.; Vaudry, D.; Zablocki, K.; Gorecki, D.C. Sustained activation of P2X7 induces MMP-2-evoked cleavage and functional purinoceptor inhibition. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 10, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panicucci, C.; Raffaghello, L.; Bruzzone, S.; Baratto, S.; Principi, E.; Minetti, C.; Gazzerro, E.; Bruno, C. eATP/P2X7R Axis: An Orchestrated Pathway Triggering Inflammasome Activation in Muscle Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, L.E.B.; de Andrade Mello, P.; da Silva, C.G.; Coutinho-Silva, R. The P2X7 Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: Angel or Demon? Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Virgilio, F. Novel data point to a broader mechanism of action of oxidized ATP: The P2X7 receptor is not the only target. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 140, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Marchi, E.; Orioli, E.; Dal Ben, D.; Adinolfi, E. P2X7 Receptor as a Therapeutic Target. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2016, 104, 39–79. [Google Scholar]
- Beigi, R.D.; Kertesy, S.B.; Aquilina, G.; Dubyak, G.R. Oxidized ATP (oATP) attenuates proinflammatory signaling via P2 receptor-independent mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 140, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Figliuolo, V.R.; Chaves, S.P.; Santoro, G.F.; Coutinho, C.M.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Rossi-Bergmann, B.; Coutinho-Silva, R. Periodate-oxidized ATP modulates macrophage functions during infection with Leishmania amazonensis. Cytom. A 2014, 85, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craighead, M.W.; Middlehurst, K.M.; LeFeuvre, R.; Kimber, I.; Rothwell, N.J. Oxidised adenosine 5′-triphosphate, a P2X(7) antagonist, is toxic to rat cerebellar granule neurones in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 311, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Namovic, M.T.; Han, P.; Jarvis, M.F. Mammalian P2X7 receptor pharmacology: Comparison of recombinant mouse, rat and human P2X7 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honore, P.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.; Namovic, M.T.; Hsieh, G.; Zhu, C.Z.; Mikusa, J.P.; Hernandez, G.; Zhong, C.; Gauvin, D.M.; Chandran, P.; et al. A-740003 [N-(1-{[(cyanoimino)(5-quinolinylamino)methyl]amino}-2,2-dimethylpropyl)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetamide], a novel and selective P2X7 receptor antagonist, dose-dependently reduces neuropathic pain in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGaraughty, S.; Chu, K.L.; Namovic, M.T.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Harris, R.R.; Zhang, X.F.; Shieh, C.C.; Wismer, C.T.; Zhu, C.Z.; Gauvin, D.M.; et al. P2X7-related modulation of pathological nociception in rats. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.M.; Oliveira, M.C.; Parada, C.A.; Tambeli, C.H. Peripheral mechanisms underlying the essential role of P2X7 receptors in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 644, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Pacheco, A.; Mesuret, G.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Tanaka, K.; Mooney, C.; Conroy, R.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Henshall, D.C.; Engel, T. Increased neocortical expression of the P2X7 receptor after status epilepticus and anticonvulsant effect of P2X7 receptor antagonist A-438079. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesuret, G.; Engel, T.; Hessel, E.V.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Jimenez-Pacheco, A.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Henshall, D.C. P2X7 receptor inhibition interrupts the progression of seizures in immature rats and reduces hippocampal damage. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellino, D.; Suárez-Boomgaard, D.; Sánchez-Reina, M.D.; Aguirre, J.A.; Yoshitake, T.; Yoshitake, S.; Hagman, B.; Kehr, J.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K.; et al. On the role of P2X(7) receptors in dopamine nerve cell degeneration in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Studies with the P2X(7) receptor antagonist A-438079. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalafalla, M.G.; Woods, L.T.; Camden, J.M.; Khan, A.A.; Limesand, K.H.; Petris, M.J.; Erb, L.; Weisman, G.A. P2X7 receptor antagonism prevents IL-1β release from salivary epithelial cells and reduces inflammation in a mouse model of autoimmune exocrinopathy. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16626–16637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sociali, G.; Visigalli, D.; Prukop, T.; Cervellini, I.; Mannino, E.; Venturi, C.; Bruzzone, S.; Sereda, M.W.; Schenone, A. Tolerability and efficacy study of P2X7 inhibition in experimental Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A (CMT1A) neuropathy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 95, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folker, E.S.; Baylies, M.K. Nuclear positioning in muscle development and disease. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gentile, D.; Natale, M.; Lazzerini, P.E.; Capecchi, P.L.; Laghi-Pasini, F. The role of P2X7 receptors in tissue fibrosis: A brief review. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 11, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villalta, S.A.; Rosenberg, A.S.; Bluestone, J.A. The immune system in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Friend or foe. Rare Dis. 2015, 3, e1010966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingersoll, M.A.; Platt, A.M.; Potteaux, S.; Randolph, G.J. Monocyte trafficking in acute and chronic inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mojumdar, K.; Liang, F.; Giordano, C.; Lemaire, C.; Danialou, G.; Okazaki, T.; Bourdon, J.; Rafei, M.; Galipeau, J.; Divangahi, M.; et al. Inflammatory monocytes promote progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and can be therapeutically targeted via CCR2. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1476–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, S.A.; Nguyen, H.X.; Deng, B.; Gotoh, T.; Tidball, J.G. Shifts in macrophage phenotypes and macrophage competition for arginine metabolism affect the severity of muscle pathology in muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kranig, S.A.; Tschada, R.; Braun, M.; Patry, C.; Poschl, J.; Frommhold, D.; Hudalla, H. Dystrophin deficiency promotes leukocyte recruitment in mdx mice. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 86, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgetts, S.; Radley, H.; Davies, M.; Grounds, M.D. Reduced necrosis of dystrophic muscle by depletion of host neutrophils, or blocking TNFalpha function with Etanercept in mdx mice. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2006, 16, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulangekar, A.; Sztal, T.E. Inflammation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy-Exploring the Role of Neutrophils in Muscle Damage and Regeneration. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecco, N.; Clarke, C.J.; Jones, F.K.; Simpson, D.M.; Mason, D.; Beynon, R.J.; Pisconti, A. Elastase levels and activity are increased in dystrophic muscle and impair myoblast cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Khalidi, R.; Panicucci, C.; Cox, P.; Chira, N.; Róg, J.; Young, C.N.J.; McGeehan, R.E.; Ambati, K.; Ambati, J.; Zabłocki, K.; et al. Zidovudine ameliorates pathology in the mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy via P2RX7 purinoceptor antagonism. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrin, P. Targeting interleukin-1 signaling in chronic inflammation: Focus on P2X(7) receptor and Pannexin-1. Drug News Perspect. 2008, 21, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegrin, P.; Barroso-Gutierrez, C.; Surprenant, A. P2X7 receptor differentially couples to distinct release pathways for IL-1beta in mouse macrophage. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7147–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzirani, C.; Ferrari, D.; Chiozzi, P.; Adinolfi, E.; Sandonà, D.; Savaglio, E.; Di Virgilio, F. Stimulation of P2 receptors causes release of IL-1beta-loaded microvesicles from human dendritic cells. Blood 2007, 109, 3856–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, H.; Kawamura, T.; Kanda, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Abo, T. Extracellular ATP-stimulated macrophages produce macrophage inflammatory protein-2 which is important for neutrophil migration. Immunology 2012, 136, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, S.A.; Rosenthal, W.; Martinez, L.; Kaur, A.; Sparwasser, T.; Tidball, J.G.; Margeta, M.; Spencer, M.J.; Bluestone, J.A. Regulatory T cells suppress muscle inflammation and injury in muscular dystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 258ra142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzyn, D.; Kuswanto, W.; Kolodin, D.; Shadrach, J.L.; Cerletti, M.; Jang, Y.; Sefik, E.; Tan, T.G.; Wagers, A.J.; Benoist, C.; et al. A special population of regulatory T cells potentiates muscle repair. Cell 2013, 155, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quattrocelli, M.; Zelikovich, A.S.; Salamone, I.M.; Fischer, J.A.; McNally, E.M. Mechanisms and Clinical Applications of Glucocorticoid Steroids in Muscular Dystrophy. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2021, 8, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, A.M.; Pestronk, A.; Mehta, S.; Al-Lozi, M. Primary alpha-sarcoglycan deficiency responsive to immunosuppression over three years. Muscle Nerve 1998, 21, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, C.; Fanin, M.; Menegazzo, E.; Freda, M.P.; Duggan, D.J.; Hoffman, E.P. Homozygous alpha-sarcoglycan mutation in two siblings: One asymptomatic and one steroid-responsive mild limb-girdle muscular dystrophy patient. Muscle Nerve 1998, 21, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.A.; Pozsgai, E.R.; Heller, K.N.; Potter, R.A.; Peterson, E.L.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R. Preclinical Systemic Delivery of Adeno-Associated α-Sarcoglycan Gene Transfer for Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2021, 32, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, S.; Farruggio, A.P.; Srifa, W.; Day, J.W.; Calos, M.P. Precise Correction of Disease Mutations in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Derived From Patients With Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2016, 24, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozsgai, E.; Griffin, D.; Potter, R.; Sahenk, Z.; Lehman, K.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Mendell, J.R. Unmet needs and evolving treatment for limb girdle muscular dystrophies. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2021, 11, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.L.; Moran, E. The Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies: Is Treatment on the Horizon? Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escobar, H.; Krause, A.; Keiper, S.; Kieshauer, J.; Müthel, S.; de Paredes, M.G.; Metzler, E.; Kühn, R.; Heyd, F.; Spuler, S. Base editing repairs an SGCA mutation in human primary muscle stem cells. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokoples, B.G.; Paradis, P.; Schiffrin, E.L. P2X7 Receptors: An Untapped Target for the Management of Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recourt, K.; van der Aart, J.; Jacobs, G.; de Kam, M.; Drevets, W.; van Nueten, L.; Kanhai, K.; Siebenga, P.; Zuiker, R.; Ravenstijn, P.; et al. Characterisation of the pharmacodynamic effects of the P2X7 receptor antagonist JNJ-54175446 using an oral dexamphetamine challenge model in healthy males in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple ascending dose trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos, F.; Straub, V.; Moore, S.A.; Venzke, D.P.; Hrstka, R.F.; Crosbie, R.H.; Durbeej, M.; Lebakken, C.S.; Ettinger, A.J.; van der Meulen, J.; et al. Progressive muscular dystrophy in alpha-sarcoglycan-deficient mice. J. Cell. Biol. 1998, 142, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).