Technologies for Assessment of Motor Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
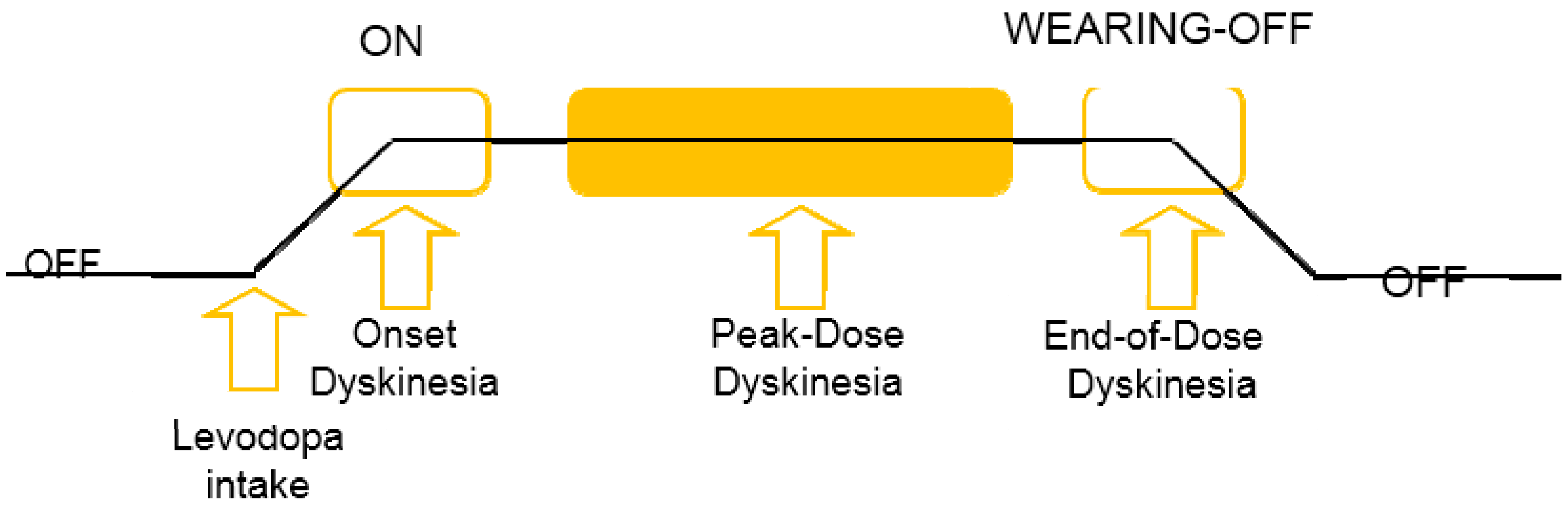
Assessment of Parkinson Disease-State of Art
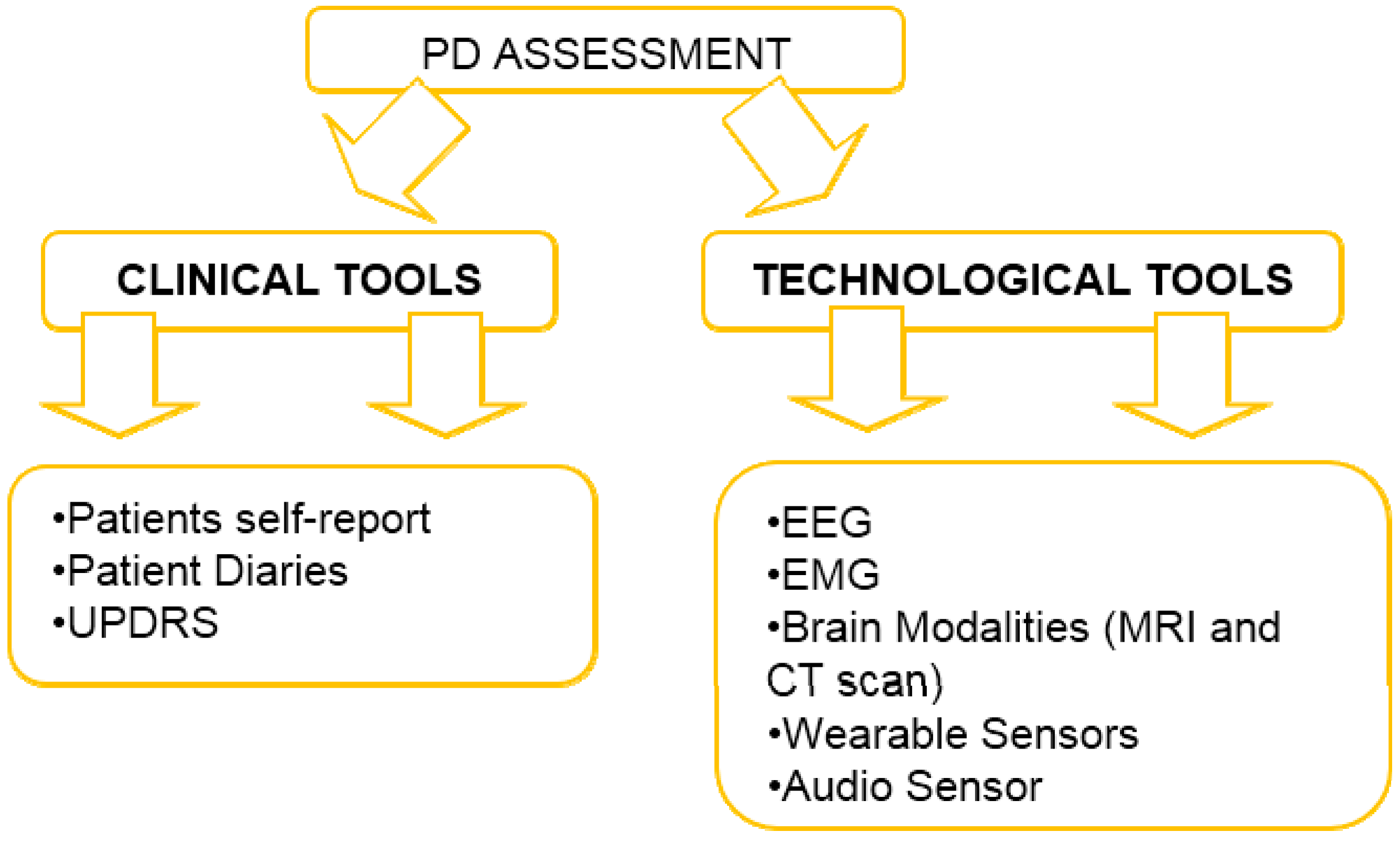
2. Related Research on PD advancement through Technological Tools
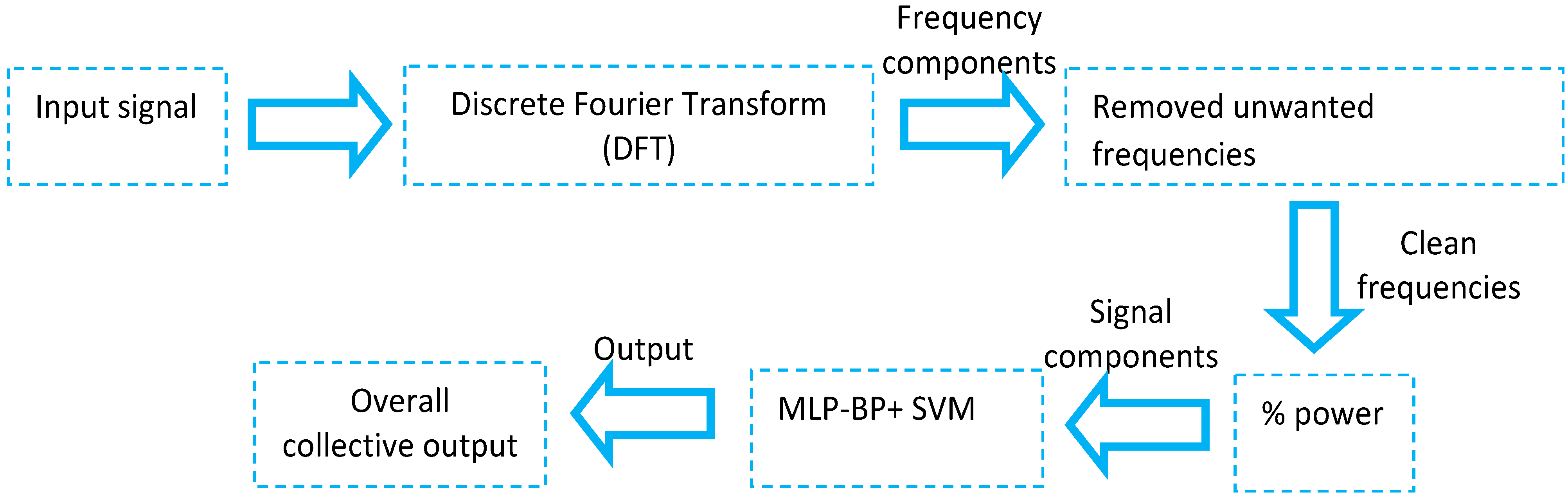
2.1. Monitoring on Progression of PD Using Electromyography (EMG)
| First Author and Year | Database | Techniques | Best Performance Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gennaro de Michele (2003) [32] | 16 male subjects (10 PWD and 6 healthy controls) | Wavelet correlation analysis with Global wavelet power (PCQ) parameters extracted from local wavelet power spectra | Accurately classify the PWP from healthy controls |
| Saara Rissanen (2007) [30] | 48 subjects (26 PWP and 22 healthy controls) | Histogram and crossing rate (CR) values applied as high dimensional feature vectors and the dimensionality was reduced using Korhunen-Loeve transform (KLT) | Precise discrimination for healthy controls: 86% and PWP: 72% |
| Saara Rissanen (2008) [34] | 33 healthy young controls 26 healthy old controls and 42 PWP | 1. Selected features (six from right side and six from left side variables): (1). Kurtosis variable (2). CR variable 3. Correlation dimension 4. Recurrence rate 5. Sample entropy 6. Coherence variable | Clustering analysis using k-means algorithms into 3 clusters: One cluster having 90% of the healthy controls while the two other clusters having 76% of PWP |
| A.I.Meigal (2008) [29] | −19 PWP (4 men and 15 women), −20 healthy old controls (7 men and 13 women) −20 young controls (10 men, 10 women) | Non-linear SEMG features (% Recurrence, % Determinism and SEMG distribution kurtosis, correlation dimension and sample) entropy) | Differentiate PWP from healthy controls |
| Bryan T.Cole (2010) [35] | 4 PWP and 2 healthy controls | 1. Linear classifier for detection when the subject is upright 2. DNN FoG detection given that the subject is upright | Sensitivity (82.9%) and Specificity (97.3%) |
| V.Ruonala (2013) [31] | 35 PWP and 17 patients with ET | Sample histograms during isometric contraction of biceps brachii muscle with varying loads and PCA for feature dimension reduction | Discriminate 13/17 (76%) patients with ET and 26/35 (74%) PWP |
2.2. Monitoring PD Using Electroencephalogram (EEG)
2.3. Monitoring PD Using Brain Imaging Modalities or 3D Motion Analysis
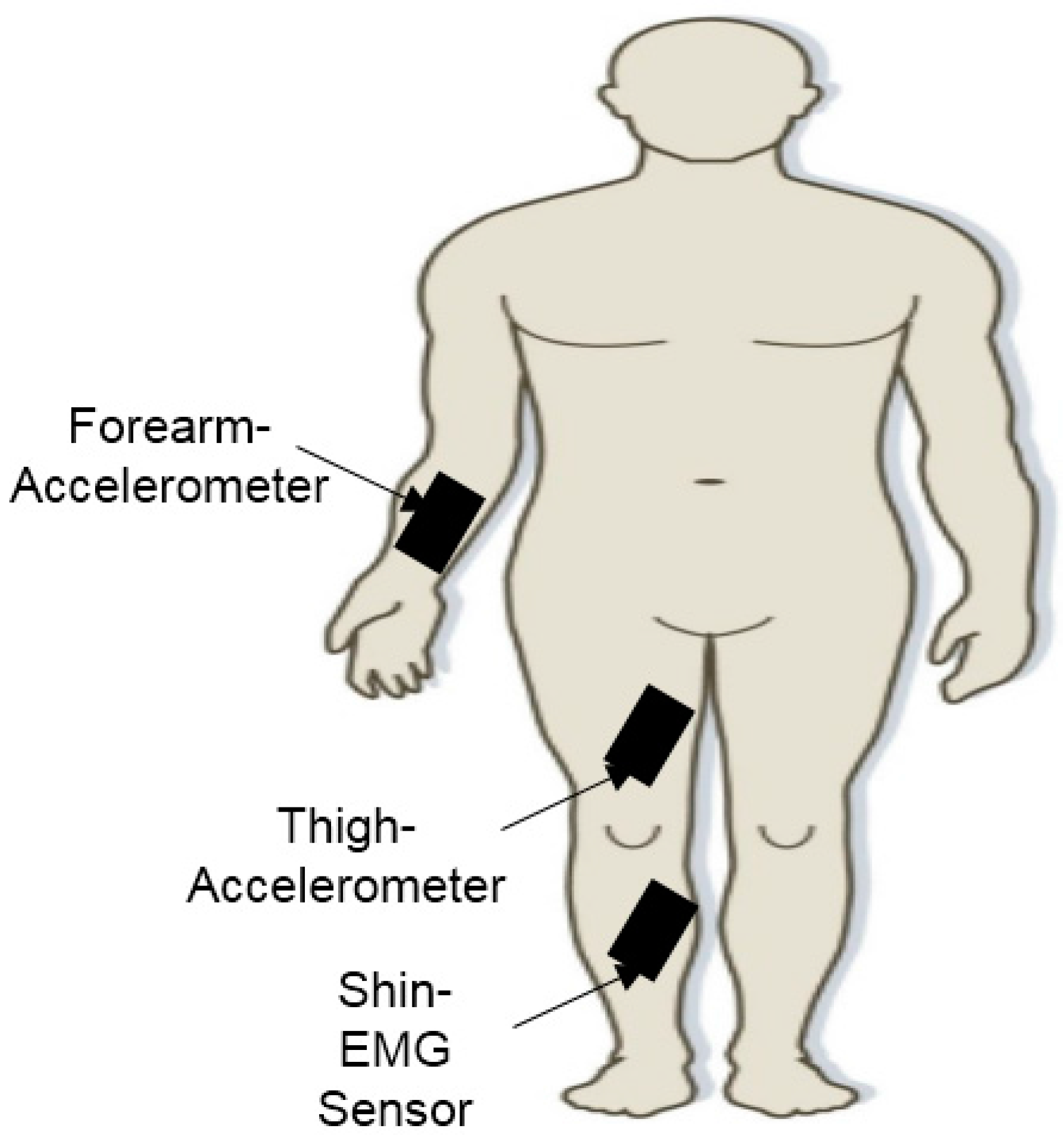
2.4. Monitoring PD Using Wearable Sensors
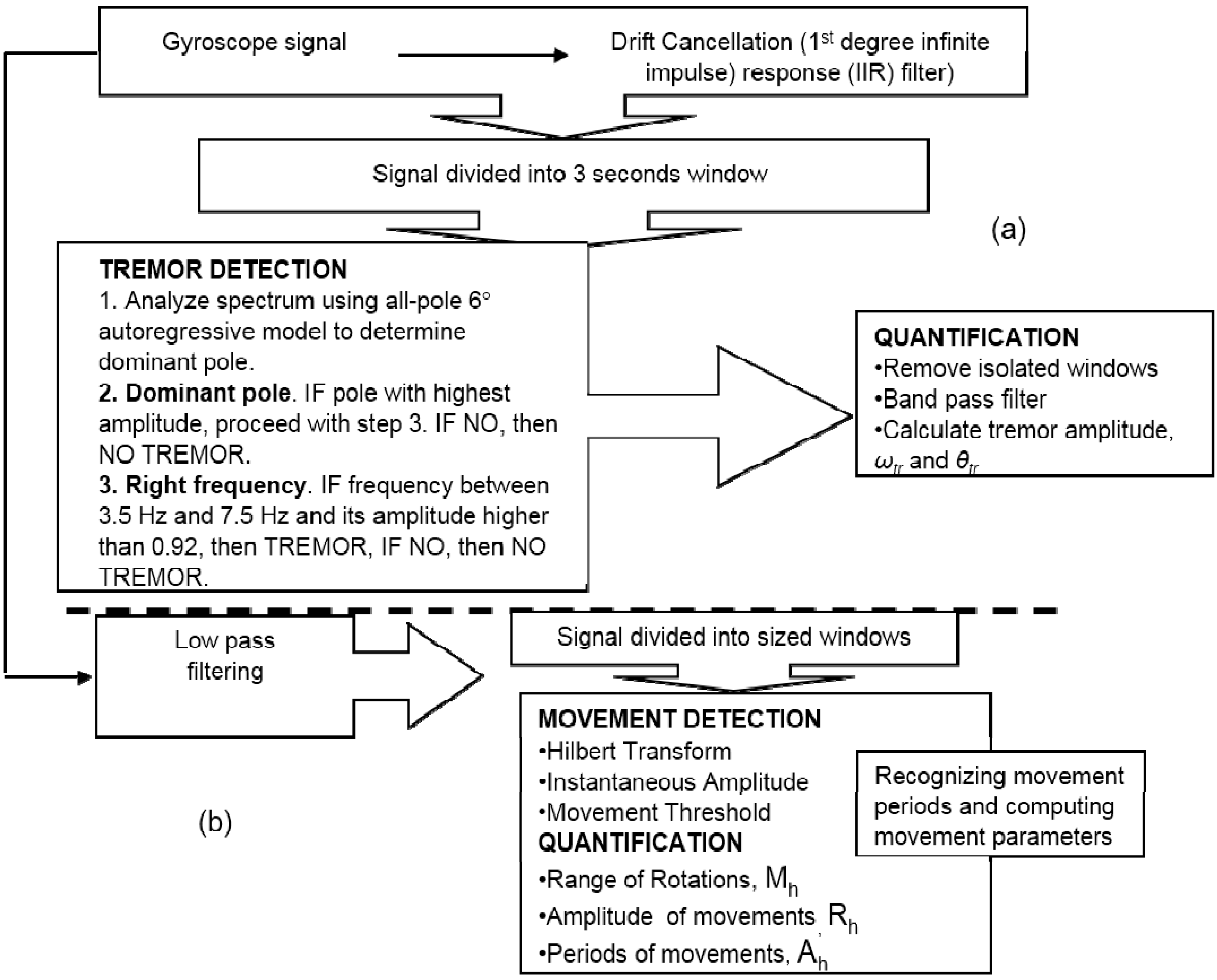
2.4.1. PD Symptoms Assessment-Tremor and Bradykinesia
2.4.2. PWP Physical Activities Monitoring
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| TD (s) | Period of transition: Time break between the two positive peaks before and after the transition time in the trunk tilt, θg-lp signal |
| Min(θg-lp) (°) | Minimum amplitude of negative peak of flexion and extension tilt of the trunk that in general much higher in the real posture transition patterns compared to the non-transitions patterns |
| Max(αtrunk-lp) (g × 10−3) | Signal αtrunk-lp was produced through the norm of the acceleration vector measured by the perpendicular accelerometers of the trunk sensor filtered using a low pass filter. The maximum, minimum and range, of this signal were generally higher in the posture transitions and lower in non-transitions. The relative time of the minimum and maximum peaks of this signal compared to the transition time was also different between SiSt and StSi transitions. |
| Min(αtrunk-lp) (g × 10−3) | |
| Range(αtrunk-lp) (g × 10−3) | |
| T[Max(αtrunk-lp)] (s) | |
| T[Min(αtrunk-lp)] (s) | |
| Range(θg-lp) (°) | Range of flexion and extension tilt of the trunk where the value of this parameter was lower for the non-transitions than for the real posture transitions. |
2.4.3. Levodopa Induced Dyskinesia (LID) Detection in PD
| Variables | Description |
|---|---|
| segment | Mean of segment velocity |
| <3 Hz segment | Mean of segment velocity for frequencies below 3 Hz |
| >3 Hz segment | Mean of segment velocity for frequencies above 3 Hz |
| <3 Hz segment/>3 Hz segment | Ratio between <3 Hz segment and >3 Hz segment |
| SD (V) segment | Segment velocity standard deviation |
| % Vθ segment | Percentage of time of segment’s movement |
| θ segment | Mean segment velocity of segment’s movement |
| P1–3 Hz segment | Power for frequencies in the range between 1 and 3 Hz |
| P<3 Hz segment | Power for frequencies in the range below 3 Hz |
| segment-segment | Mean value of the normalized cross-correlation between the segment velocities of different segments |
| Max (ρsegment-segment) | Maximum value of the normalized cross-correlation between the segment velocities of different segments |
| % sitting | Percentage of time during subject sitting posture |
| % upright | Percentage of time during subject upright posture |
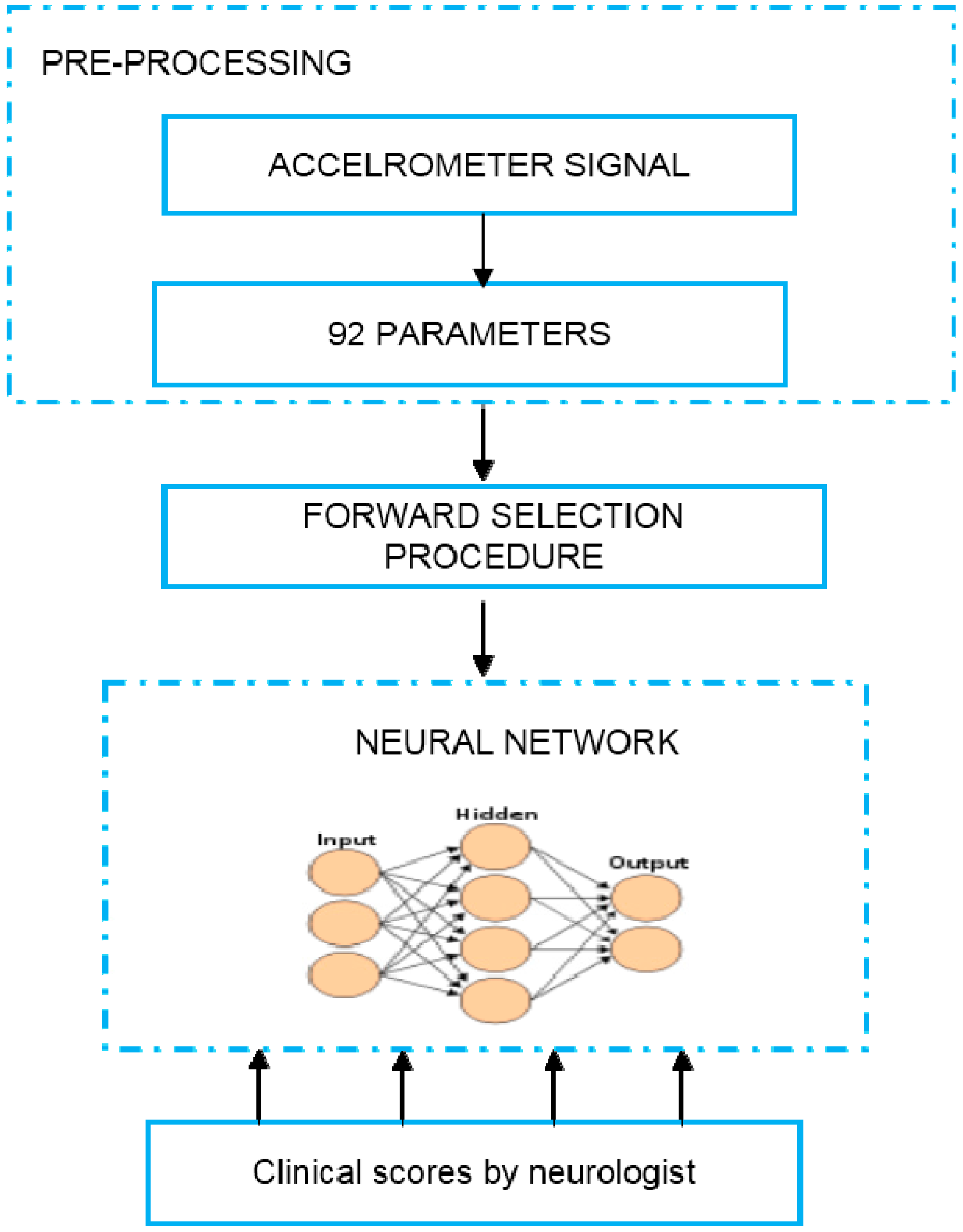
2.4.4. Estimation of PD Symptoms Severity-Tremor, Bradykinesia and Dyskinesia
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Length of the windows | Used for selecting data segments of the accelerometer data and deriving data featuresAchieving the average estimation errors below 5% Utilized length of windows ranging from 1 to 7 s with an increment of 1 s |
| SVM kernels | Three different types of kernels: polynomial, exponential and radial basis |
| Feature types | Five features types were compared: Data range, root mean square (rms) value, cross-correlation-based features, frequency based features and signal entropy |
2.4.5. PWP Home Monitoring System Using Web Based Application
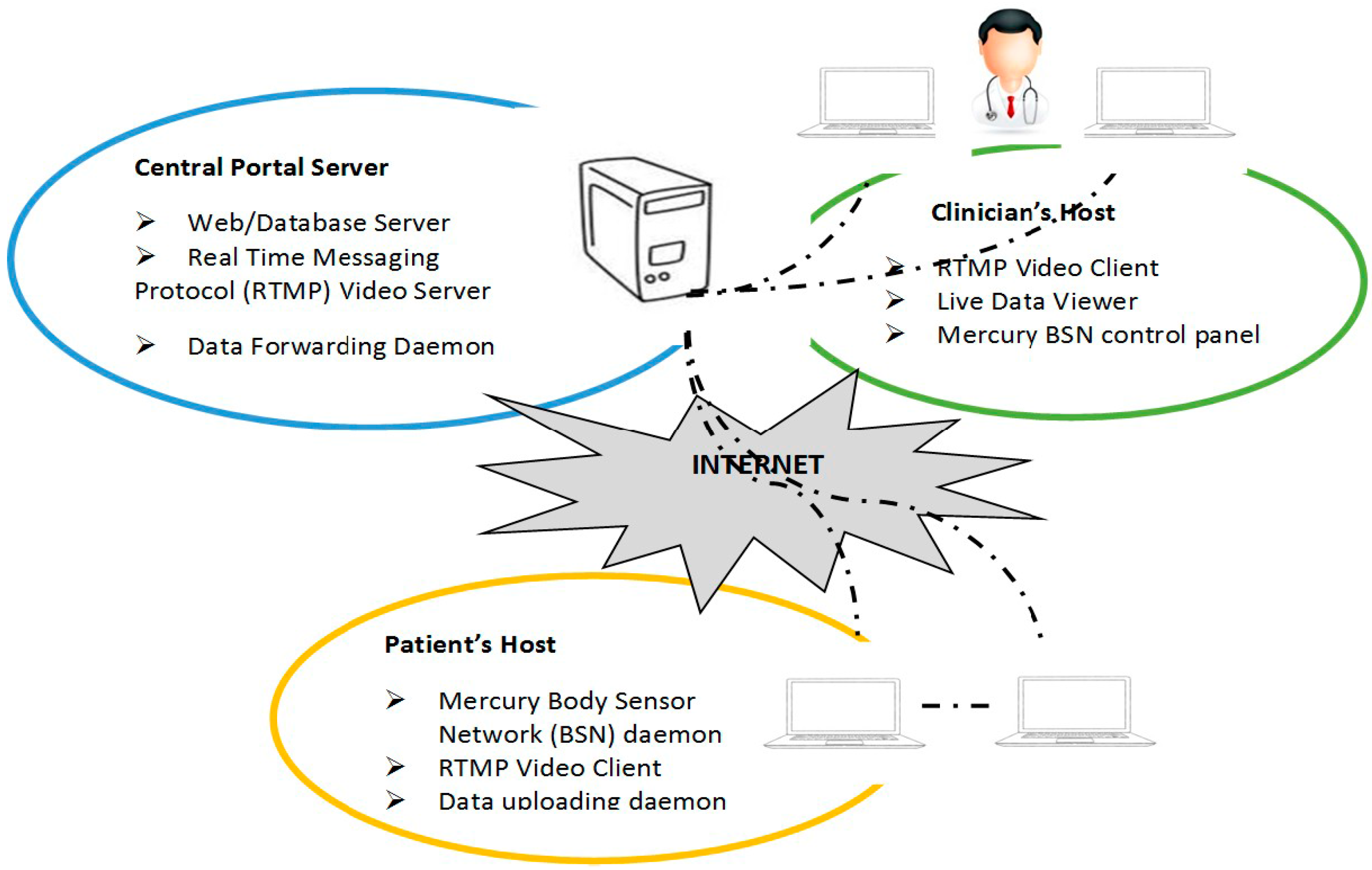
| Latency | Description |
|---|---|
| Command Latency |
|
| Data and Video Latency |
|
| Recovery latency |
|
| Data upload latency |
|
2.4.6. Assessment of Gait Impairment in PD
2.4.7. Detection of PD Motor Symptoms: Uncontrolled Home Environment

2.4.8. PD Hand Tremor Monitoring
2.4.9. Detection of Freezing of Gait (FoG) in PD
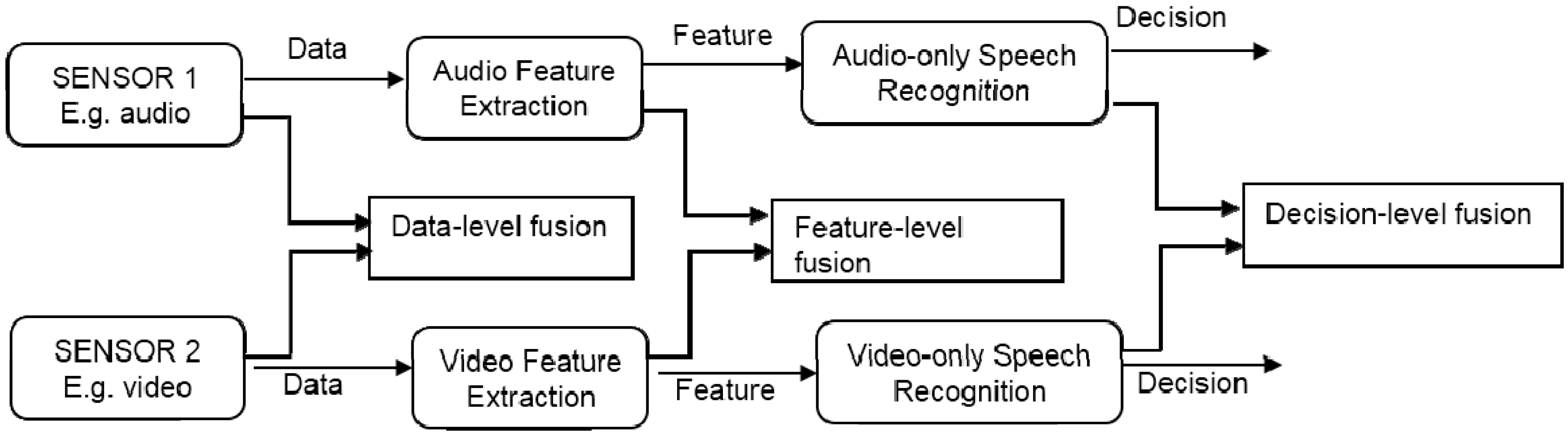
2.5. Monitoring PD Using Audio Sensors
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhury, T.; Consolvo, S.; Harrison, B.; Hightower, J.; LaMarca, A.; LeGrand, L.; Rahimi, A.; Rea, A.; Bordello, G.; Hemingway, B. The mobile sensing platform: An embedded activity recognition system. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2008, 7, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, P.; Pujol, O.; Radeva, P. Human activity recognition from accelerometer data using a wearable device. In Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.; Helal, S.; Cook, D. Human activity recognition and pattern discovery. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2010, 9, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.L.; Shahriman, A.B.; Za’aba, S.K.; Khairunizam, W.; Roohi, S.A.; Zuradzman, M.R. Upper Extremity Vein Graft Monitoring Device after Surgery Procedure: A Preliminary Study. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.L.; Shahriman, A.B.; Sazali, Y.; Zuradzman, M.R.; Khairunizam, W.; Ahmad, W.; Zunaidi, I.; Cheng, E.M.; Khadijah, S.; Nisha, S. In vitro evaluation of fingerʼs hemodynamics for vein graft surveillance using electrical bio-impedance method. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 8, 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, O.F. Ageing in Malaysia: National Policy and Future Direction; Faculty of Business and Accountancy, University of Malaya: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysian, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- De Lau, L.M.; Breteler, M.M. Epidemiology of parkinsonʼs disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, L.S. Goodman and Gilmanʼs the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Sherrill, D.; Hughes, R.; Hester, T.; Huggins, N.; Lie-Nemeth, T.; Standaert, D.; Bonato, P. Analysis of the Severity of Dyskinesia in Patients with Parkinsonʼs Disease via Wearable Sensors. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks, Cambridge, MA, USA, 3–5 April 2006.
- Parkinson Centre-Malaysian Parkinson Disease Association. Why is a Parkinson Centre Needed? Available online: http://www.mpda.org.my/helpparkinsonclub.php (accessed on 5 May 2015).
- Aarli, J.A.; Dua, T.; Janca, A.; Muscetta, A. Neurological Disorders: Public Health Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinsonʼs Disease: Hope through research. Available online: http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/parkinsons_disease/detail_parkinsons_disease.htm (accessed on 5 May 2015).
- Elbaz, A.; Bower, J.H.; Maraganore, D.M.; McDonnell, S.K.; Peterson, B.J.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Schaid, D.J.; Rocca, W.A. Risk tables for parkinsonism and parkinsonʼs disease. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2002, 55, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.; Marci, C.; Pentland, A. Wearable feedback systems for rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2005, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eeden, S.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Bernstein, A.L.; Fross, R.D.; Leimpeter, A.; Bloch, D.A.; Nelson, L.M. Incidence of parkinson’s disease: Variation by age, gender, and race/ethnicity. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 157, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, T.N. Levodopa therapy consequences of the nonphysiologic replacement of dopamine. Neurology 1998, 50, S17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.E.; Lozano, A.M. Parkinsonʼs disease. New Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso, J.A.; Olanow, C.W.; Nutt, J.G. Levodopa motor complications in parkinsonʼs disease. Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, S2–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oung, Q.W.; Hariharan, M.; Basah, S.; Yaacob, S.; Sarillee, M.; Lee, H.L. Use of technological tools for parkinsonʼs disease early detection: A review. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE), Penang, Malaysia, 28–30 November 2014; pp. 343–348.
- Jankovic, J. Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keijsers, N.L.; Horstink, M.W.; Gielen, S.C. Online monitoring of dyskinesia in patients with parkinsonʼs disease. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Maga. 2003, 22, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Lorincz, K.; Hughes, R.; Huggins, N.; Growdon, J.H.; Welsh, M.; Bonato, P. Analysis of feature space for monitoring persons with parkinsonʼs disease with application to a wireless wearable sensor system. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 6290–6293.
- Group, P.S. Evaluation of dyskinesias in a pilot, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of remacemide in advanced parkinson disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 1660. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor-Sanz, L.; Cancela, J.; Waldmeyer, M.T.A.; Pansera, M.; Pastorino, M. Mobile Systems as a Challenge for Neurological Diseases Management-the Case of Parkinsonʼs; InTech Open Access Publisher: Morn Hill, Winchester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Lorincz, K.; Hughes, R.; Huggins, N.; Growdon, J.; Standaert, D.; Dy, J.; Welsh, M.; Bonato, P. A body sensor network to monitor parkinsonian symptoms: Extracting features on the nodes. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Wearable Micro and Nanosystems for Personalised Health, Valencia, Spain, 21–23 May 2008; pp. 21–23.
- Goetz, C.G.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stebbins, G.T.; Stern, M.B.; Tilley, B.C.; Dodel, R.; Dubois, B. Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified parkinsonʼs disease rating scale (MDS-UPDRS): Process, format, and clinimetric testing plan. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R. Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified parkinsonʼs disease rating scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorini, L.; Felici, F.; Filligoi, G.; Traballesi, M.; Farina, D. Influence of high motor unit synchronization levels on non-linear and spectral variables of the surface EMG. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 143, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meigal, A.I.; Rissanen, S.; Tarvainen, M.; Karjalainen, P.; Iudina-Vassel, I.; Airaksinen, O.; Kankaanpää, M. Novel parameters of surface emg in patients with parkinson’s disease and healthy young and old controls. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, e206–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissanen, S.; Kankaanpää, M.; Tarvainen, M.P.; Nuutinen, J.; Tarkka, I.M.; Airaksinen, O.; Karjalainen, P.A. Analysis of surface EMG signal morphology in parkinsonʼs disease. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruonala, V.; Meigal, A.; Rissanen, S.; Airaksinen, O.; Kankaanpaa, M.; Karjalainen, P. EMG signal morphology in essential tremor and parkinsonʼs disease. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 5765–5768.
- De Michele, G.; Sello, S.; Carboncini, M.C.; Rossi, B.; Strambi, S.K. Cross-correlation time-frequency analysis for multiple emg signals in parkinson’s disease: A wavelet approach. Med. Eng. Phys. 2003, 25, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturman, M.M.; Vaillancourt, D.E.; Metman, L.V.; Bakay, R.A.; Corcos, D.M. Effects of subthalamic nucleus stimulation and medication on resting and postural tremor in parkinsonʼs disease. Brain 2004, 127, 2131–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissanen, S.M.; Kankaanpää, M.; Meigal, A.; Tarvainen, M.P.; Nuutinen, J.; Tarkka, I.M.; Airaksinen, O.; Karjalainen, P.A. Surface EMG and acceleration signals in parkinson’s disease: Feature extraction and cluster analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, B.T.; Roy, S.H.; Nawab, S.H. Detecting freezing-of-gait during unscripted and unconstrained activity. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 5649–5652.
- Handojoseno, A.A.; Shine, J.M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tran, Y.; Lewis, S.J.; Nguyen, H.T. The detection of freezing of gait in parkinsonʼs disease patients using eeg signals based on wavelet decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 69–72.
- Backer, J.H. The symptom experience of patients with parkinsonʼs disease. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2006, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutt, J.G.; Bloem, B.R.; Giladi, N.; Hallett, M.; Horak, F.B.; Nieuwboer, A. Freezing of gait: Moving forward on a mysterious clinical phenomenon. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrus, C.S.; Gopinath, R.A.; Guo, H. Introduction to Wavelets and Wavelet Transforms: A Primer; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bhosale, M.P.G.; Patil, S. Classification of EMG signals using wavelet transform and hybrid classifier for parkinson’s disease detection. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2012, 2, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Long, D.; Wang, J.; Xuan, M.; Gu, Q.; Xu, X.; Kong, D.; Zhang, M. Automatic classification of early parkinsonʼs disease with multi-modal mr imaging. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stawarz, M.; Polański, A.; Kwiek, S.; Boczarska-Jedynak, M.; Janik, L.; Przybyszewski, A.; Wojciechowski, K. A system for analysis of tremor in patients with parkinson’s disease based on motion capture technique. In Computer Vision and Graphics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 618–625. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, L.; Manolakos, E.S. Signal background estimation and baseline correction algorithms for accurate DNA sequencing. J. VLSI Signal Process. Syst. Signal Image Video Technol. 2003, 35, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarian, A.; Russmann, H.; Wider, C.; Burkhard, P.R.; Vingerhoets, F.J.; Aminian, K. Quantification of tremor and bradykinesia in parkinsonʼs disease using a novel ambulatory monitoring system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salarian, A.; Russmann, H.; Vingerhoets, F.J.; Burkhard, P.R.; Aminian, K. Ambulatory monitoring of physical activities in patients with parkinsonʼs disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 2296–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salarian, A.; Russmann, H.; Vingerhoets, F.; Burkhard, P.; Blanc, Y.; Dehollain, C.; Aminian, K. An ambulatory system to quantify bradykinesia and tremor in parkinsonʼs disease. In Proceedings of the 4th International IEEE EMBS Special Topic Conference on Information Technology Applications in Biomedicine, Birmingham, UK, 24–26 April 2003; pp. 35–38.
- Salarian, A.; Russmann, H.; Vingerhoets, F.J.; Dehollaini, C.; Blanc, Y.; Burkhard, P.R.; Aminian, K. Gait assessment in parkinsonʼs disease: Toward an ambulatory system for long-term monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keijsers, N.L.; Horstink, M.W.; Gielen, S.C. Ambulatory motor assessment in parkinsonʼs disease. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keijsers, N.L.; Horstink, M.W.; Gielen, S.C. Automatic assessment of levodopa-induced dyskinesias in daily life by neural networks. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keijsers, N.L.; Horstink, M.W.; Gielen, S.C. Movement parameters that distinguish between voluntary movements and levodopa-induced dyskinesia in parkinson’s disease. Human Mov. Sci. 2003, 22, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijsers, N.; Horstink, M.; van Hilten, J.; Hoff, J.; Gielen, C. Detection and assessment of the severity of levodopa-induced dyskinesia in patients with parkinson’s disease by neural networks. Mov. Disord. 2000, 15, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Lorincz, K.; Hughes, R.; Huggins, N.; Growdon, J.; Standaert, D.; Akay, M.; Dy, J.; Welsh, M.; Bonato, P. Monitoring motor fluctuations in patients with parkinsonʼs disease using wearable sensors. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Chen, B.R.; Buckley, T.; Rednic, R.; McClure, D.; Tarsy, D.; Shih, L.; Dy, J.; Welsh, M.; Bonato, P. Home monitoring of patients with parkinsonʼs disease via wearable technology and a web-based application. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 4411–4414.
- Chen, B.R.; Patel, S.; Buckley, T.; Rednic, R.; McClure, D.J.; Shih, L.; Tarsy, D.; Welsh, M.; Bonato, P. A web-based system for home monitoring of patients with parkinsonʼs disease using wearable sensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancela, J.; Pastorino, M.; Arredondo, M.; Pansera, M.; Pastor-Sanz, L.; Villagra, F.; Pastor, M.; Gonzalez, A. Gait assessment in parkinsonʼs disease patients through a network of wearable accelerometers in unsupervised environments. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 2233–2236.
- Das, S.; Amoedo, B.; de la Torre, F.; Hodgins, J. Detecting parkinsonsʼ symptoms in uncontrolled home environments: A multiple instance learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 3688–3691.
- Andrews, S.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Hofmann, T. Support vector machines for multiple-instance learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in neural information processing systems, Providence, RI, USA, 7 May 2002; pp. 561–568.
- Lathropb, T.G.D.R.H. Solving the multiple-instance problem with axis-parallel rectangles. J. Artif. Intell. 1997, 89, 31–71. [Google Scholar]
- Maron, O.; Lozano-Pérez, T. A framework for multiple-instance learning. In Proceedings of the 1997 Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 29 November–4 December 1997; pp. 570–576.
- Wang, J.; Zucker, J.D. Solving multiple-instance problem: A lazy learning approach. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Machine Learning, Standord, CA, USA, 29 June–2 July 2000; pp. 1119–1126.
- LeMoyne, R.; Mastroianni, T.; Grundfest, W. Wireless accelerometer configuration for monitoring parkinson’s disease hand tremor. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMoyne, R.; Coroian, C.; Mastroianni, T. Quantification of parkinsonʼs disease characteristics using wireless accelerometers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering, Tempe, AZ, USA, 9–11 April 2009; pp. 1–5.
- Lemoyne, R.; Coroian, C.; Mastroianni, T.; Grundfest, W. Accelerometers for quantification of gait and movement disorders: A perspective review. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2008, 8, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMoyne, R.; Mastroianni, T.; Cozza, M.; Coroian, C.; Grundfest, W. Implementation of an iphone for characterizing parkinson’s disease tremor through a wireless accelerometer application. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 4954–4958.
- Macht, M.; Kaussner, Y.; Möller, J.C.; Stiasny-Kolster, K.; Eggert, K.M.; Krüger, H.P.; Ellgring, H. Predictors of freezing in parkinsonʼs disease: A survey of 6620 patients. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bächlin, M.; Plotnik, M.; Roggen, D.; Giladi, N.; Hausdorff, J.; Tröster, G. A wearable system to assist walking of parkinson s disease patients. Methods Inf. Med. 2010, 49, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bächlin, M.; Plotnik, M.; Roggen, D.; Inbar, N.; Giladi, N.; Hausdorff, J.; Tröster, G. Parkinsons disease patients perspective on context aware wearable technology for auditive assistance. In Proceding of the 3rd International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, London, UK, 1–3 April 2009; pp. 1–8.
- Bächlin, M.; Plotnik, M.; Roggen, D.; Maidan, I.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Giladi, N.; Troster, G. Wearable assistant for parkinson’s disease patients with the freezing of gait symptom. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bächlin, M.; Roggen, D.; Tröster, G.; Plotnik, M.; Inbar, N.; Maidan, I.; Herman, T.; Brozgol, M.; Shaviv, E.; Giladi, N. Potentials of enhanced context awareness in wearable assistants for parkinsonʼs disease patients with the freezing of gait syndrome. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Linz, Austria, 4–7 September 2009; pp. 123–130.
- Bloem, B.R.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Visser, J.E.; Giladi, N. Falls and freezing of gait in parkinsonʼs disease: A review of two interconnected, episodic phenomena. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giladi, N.; Treves, T.; Simon, E.; Shabtai, H.; Orlov, Y.; Kandinov, B.; Paleacu, D.; Korczyn, A. Freezing of gait in patients with advanced parkinsonʼs disease. J. Neural Transm. 2001, 108, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazilu, S.; Calatroni, A.; Gazit, E.; Roggen, D.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Tröster, G. Feature learning for detection and prediction of freezing of gait in parkinson’s disease. In Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mazilu, S.; Hardegger, M.; Zhu, Z.; Roggen, D.; Troster, G.; Plotnik, M.; Hausdorff, J.M. Online detection of freezing of gait with smartphones and machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (PervasiveHealth), San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 May 2012; pp. 123–130.
- Moore, S.T.; MacDougall, H.G.; Ondo, W.G. Ambulatory monitoring of freezing of gait in parkinsonʼs disease. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 167, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabaleta, H.; Keller, T.; Fimbel, E. Gait analysis in frequency domain for freezing detection in patients with parkinson’s disease. Gerontechnology 2008, 7, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Zaarour, I.; Lefebvre, D.; Guerin, F.; Bejjani, P.; Ayache, M. About detection and diagnosis of freezing of gait. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), Tripoli, Libya, 11–13 September 2013; pp. 117–120.
- Titze, I.R.; Martin, D.W. Principles of voice production. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baken, R.J.; Orlikoff, R.F. Clinical Measurement of Speech and Voice; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, K.M.; Duffy, J.R. Parametric quantitative acoustic analysis of conversation produced by speakers with dysarthria and healthy speakers. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2006, 49, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartelius, L.; Svensson, P. Speech and swallowing symptoms associated with parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis: A survey. Folia Phoniatrica et Logopaedica 1994, 46, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.K.; Iansek, R.; Marigliani, C.; Bradshaw, J.L.; Gates, S. Speech impairment in a large sample of patients with parkinson’s disease. Behav. Neurol. 1999, 11, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, R.; Neoh, S.C.; Hariharan, M. A hybrid expert system for automatic detection of voice disorders. Int. J. Med. Eng. Inf. 2014, 6, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, M.; Polat, K.; Yaacob, S. A new feature constituting approach to detection of vocal fold pathology. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2014, 45, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; Fox, C.; Ramig, L.O. Objective automatic assessment of rehabilitative speech treatment in parkinsonʼs disease. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Spielman, J.; Ramig, L.O. Novel speech signal processing algorithms for high-accuracy classification of parkinson’s disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Hunter, E.J.; Spielman, J.; Ramig, L.O. Suitability of dysphonia measurements for telemonitoring of parkinson’s disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariharan, M.; Polat, K.; Sindhu, R. A new hybrid intelligent system for accurate detection of parkinsonʼs disease. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2014, 113, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanas, A. Accurate Telemonitoring of Parkinson’s Disease Symptom Severity Using Nonlinear Speech Signal Processing and Statistical Machine Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Roberts, S.J.; Costello, D.A.; Moroz, I.M. Exploiting nonlinear recurrence and fractal scaling properties for voice disorder detection. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2007, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanas, A. New nonlinear markers and insights into speech signal degradation for effective tracking of parkinson’s disease symptom severity. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Nonlinear Theory and its Applications, Krakow, Poland, 5–8 September 2010; pp. 457–460.
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Ramig, L.O. Nonlinear speech analysis algorithms mapped to a standard metric achieve clinically useful quantification of average parkinsonʼs disease symptom severity. J. Royal Soc. Interface 2011, 8, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Ramig, L.O. Enhanced classical dysphonia measures and sparse regression for telemonitoring of parkinsonʼs disease progression. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 594–597.
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Ramig, L.O. Accurate telemonitoring of parkinsonʼs disease progression by noninvasive speech tests. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åström, F.; Koker, R. A parallel neural network approach to prediction of parkinson’s disease. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 12470–12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbakhi, M.; Far, D.T.; Tahami, E. Speech analysis for diagnosis of parkinson’s disease using genetic algorithm and support vector machine. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukka, P. Feature selection using fuzzy entropy measures with similarity classifier. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 4600–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustempasic, I.; Can, M. Diagnosis of parkinson’s disease using fuzzy c-means clustering and pattern recognition. South East Eur. J. Soft Comput. 2013, 2, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjahmadi, A.; Askari, T. A decision support system for parkinsonʼs disease diagnosis using classification and regression tree. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2012, 4, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Das, R. A comparison of multiple classification methods for diagnosis of parkinson disease. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 1568–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, Z.A.; Ispawi, D.I.; Ibrahim, N.F.; Tahir, N.M. Classification of parkinsonʼs disease based on multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) neural network and anova as a feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 8th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications, Melaka, Malaysia, 23–25 March 2012; pp. 63–67.
- Chen, H.L.; Huang, C.C.; Yu, X.G.; Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.J. An efficient diagnosis system for detection of parkinson’s disease using fuzzy k-nearest neighbor approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, K. Classification of parkinsonʼs disease using feature weighting method on the basis of fuzzy c-means clustering. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2012, 43, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, D.A.; Chou, M.; Jiang, J.J.; Zhang, Y. Phonatory impairment in parkinsonʼs disease: Evidence from nonlinear dynamic analysis and perturbation analysis. J. Voice 2007, 21, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosa, E.; Wenning, G.; Poewe, W. The diagnosis of parkinsonʼs disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Pillay, V.; Choonara, Y.E. Advances in the treatment of parkinsonʼs disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S. EEG in the diagnosis, classification, and management of patients with epilepsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, ii2–ii7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.C. Electroencephalography: Basic principles, clinical applications, and related fields. Neurology 2006, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, E.; da Silva, F.L. Electroencephalography: Basic principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Criswell, E. Cramʼs Introduction to Surface Electromyography; Jones & Bartlett Publishers: Sudbury, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Robichaud, J.A.; Pfann, K.D.; Comella, C.L.; Corcos, D.M. Effect of medication on emg patterns in individuals with parkinsonʼs disease. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukhanina, E.; Karaban, I.; Berezetskaya, N. Diagnosis of Parkinsonʼs Disease by Electrophysiological Methods; InTech Open Access Publisher: Winchester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Electromyography (EMG): Monitors Peripheral, Lumbar, and Cranial Nerves. Available online: www.calderdevelopment.com/modalities/emg.html (accessed on 25 Janaury 2015).
- Neuroimaging: Advantages and Disadvatages of CT Scans. Available online: http://web.stanford.edu/group/hopes/cgi-bin/hopes_test/neuroimaging/#advantages-and-disadvantages-of-ct (accessed on 25 Janaury 2015).
- Gould, T.A. How MRI Works; HowStuffWorks Inc: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Khemphila, A.; Boonjing, V. Parkinsons disease classification using neural network and feature selection. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 64, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, P. Wearable sensors/systems and their impact on biomedical engineering. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, P. Wearable sensors and systems. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2010, 29, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, P. Advances in wearable technology for rehabilitation. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2009, 145, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Bonato, P. Advances in wearable technology and applications in physical medicine and rehabilitation. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2005, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, M.; Arredondo, M.; Cancela, J.; Guillen, S. Wearable sensor network for health monitoring: The case of parkinson disease. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviatt, S. Advances in robust multimodal interface design. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2003, 23, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.C.; Kay, M.G. Multisensor integration and fusion in intelligent systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 901–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, B.; Lalanne, D.; Oviatt, S. Multimodal interfaces: A survey of principles, models and frameworks. In Human Machine Interaction; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Oviatt, S. Multimodal interfaces. In The Human-Computer Interaction Handbook: Fundamentals, Evolving Technologies and Emerging Applications; L. Erlbaum Associates Inc: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 286–304. [Google Scholar]
- Oviatt, S.; Cohen, P. Perceptual user interfaces: Multimodal interfaces that process what comes naturally. Commun. ACM 2000, 43, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.C.; Chang, C.C. Multisensor fusion and integration: A review on approaches and its applications in mechatronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2012, 8, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.C.; Chang, C.C.; Lai, C.C. Multisensor fusion and integration: Theories, applications, and its perspectives. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3122–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.C.; Chou, Y.C.; Chen, O. Multisensor fusion and integration: Algorithms, applications, and future research directions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, 2007 (ICMA 2007), Harbin, China, 5–8 August 2007; pp. 1986–1991.
- Chew, N.; Goh, K.; Tan, C. Parkinson’s disease in university hospital, kuala lumpur. Neurol J. Southeast Asia 1998, 3, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oung, Q.W.; Muthusamy, H.; Lee, H.L.; Basah, S.N.; Yaacob, S.; Sarillee, M.; Lee, C.H. Technologies for Assessment of Motor Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. Sensors 2015, 15, 21710-21745. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150921710
Oung QW, Muthusamy H, Lee HL, Basah SN, Yaacob S, Sarillee M, Lee CH. Technologies for Assessment of Motor Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. Sensors. 2015; 15(9):21710-21745. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150921710
Chicago/Turabian StyleOung, Qi Wei, Hariharan Muthusamy, Hoi Leong Lee, Shafriza Nisha Basah, Sazali Yaacob, Mohamed Sarillee, and Chia Hau Lee. 2015. "Technologies for Assessment of Motor Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review" Sensors 15, no. 9: 21710-21745. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150921710
APA StyleOung, Q. W., Muthusamy, H., Lee, H. L., Basah, S. N., Yaacob, S., Sarillee, M., & Lee, C. H. (2015). Technologies for Assessment of Motor Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. Sensors, 15(9), 21710-21745. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150921710








