A reference is missing in our paper [1]. Figure 2 was adapted from Reference [2] with permission. The figure is listed and described as below:
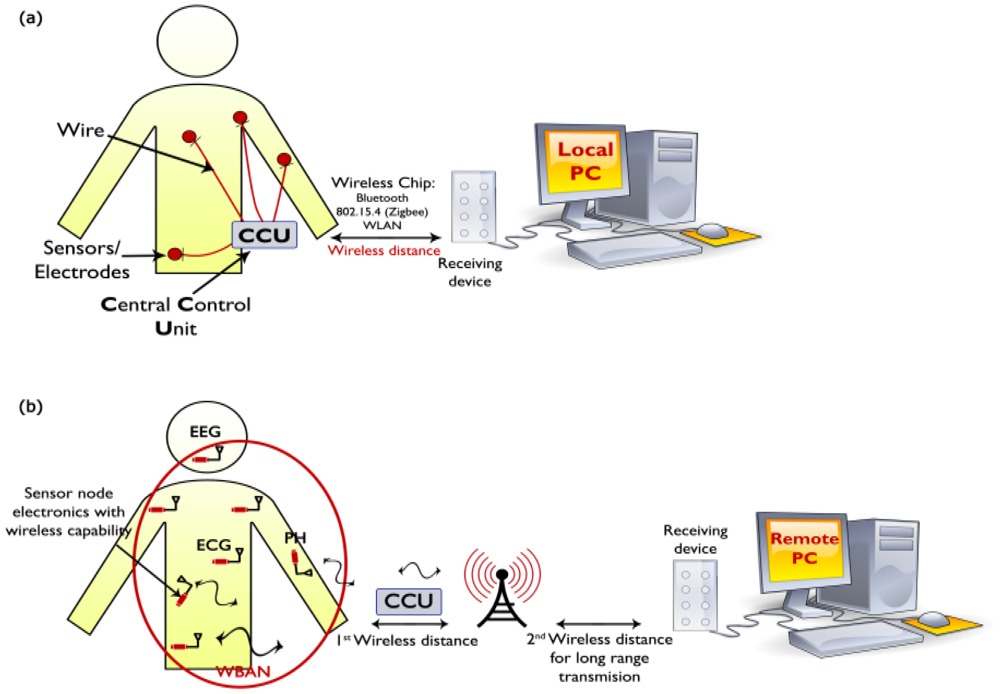
Figure 2.
A WSN system: (a) wired system and (b) wireless system. Adapted with permission from [2].
WBANs application in the medical field are composed of wearable and implantable sensors that can detect information from the human body and send it to a central unit as shown in Figure 2. These sensors have some characteristics such as small, low-power detection and have the capability to detect medical signals data from the control unit. There is a difficulty in the monitoring devices that are not completely wearable where the wires are used to connect many sensors. Yuce [2] explored a vision to the future of medical sensor networks should be miniaturized and also wearable sensors that can communicate with the receiving device wirelessly.
References
- Darwish, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Wearable and Implantable Wireless Sensor Network Solutions for Healthcare Monitoring. Sensors 2011, 11, 5561–5595. [Google Scholar]
- Yuce, M.R. Implementation of Wireless Body Area Networks for Healthcare Systems. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 2010, 162, 116–129. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).