Abstract
Balsaminaceae are world-famous ornamental flowers because of their high species diversity, rich variation, peculiar flower patterns, and long ornamental cycles. To study the species diversity, distribution patterns, and distribution hotspots of Balsaminaceae in China, we updated the list of Balsaminaceae by systematically searching the related literature. The distribution pattern and hotspots of Impatiens spp. were analyzed using the ArcGIS 10.8.2 software. Combining 19 meteorological factors and one elevation factor, the Maxent model was applied to analyze the dominant environmental factors that govern the distribution of Impatiens spp. As of February 2023, Balsaminaceae in China included 360 taxa in two genera, including one taxon in the genus of Hydrocera, 359 taxa in the genus Impatiens, 271 national endemic species, and 157 provincial endemic species. Impatiens spp. showed a diffusion pattern from the tropical and subtropical regions to the high-latitude and high-elevation regions concentrated in Southwest China, especially in the Hengduan Mountains in the broad sense, Southern Tibet, the Yunnan–Guizhou–Guangxi karst region, the Qinling–Daba Mountains, and the southeastern hills. The highest species richness was found in the 1200~1500 m elevation range, with 164 species of Impatiens spp. This high species richness was maintained at between 900 and 2700 m, the elevation range where Impatiens spp. are concentrated. When 100% of the species were screened out, 110 hotspots were found, including Southeast Yunnan, Northwest Yunnan, Southern Tibet, and Western Sichuan, where most of the hotspots were concentrated and overlapped with global biodiversity centers, but other hotspots were more scattered. Annual precipitation, the minimal temperature of the coldest month, the altitude and temperature annual range, and four environmental variables with a cumulative contribution of 93.7% were the dominant environmental factors affecting the distribution of Impatiens spp. in China. This study lays the foundation for subsequent studies of Balsaminaceae diversity and is conducive to the development and use of Impatiens spp. resources.
1. Introduction
The Balsaminaceae family contains the genera Hydrocera Blume ex Wight & Arn. and Impatiens L. The genus Hydrocera has only one species and is widely distributed in tropical Asia. The genus Impatiens has about 1000 species worldwide and is mainly distributed in the tropical and subtropical mountainous regions of Eurasia and tropical Africa [1,2]. There are five centers of diversity in the world: tropical Africa, Madagascar, the Eastern Himalayas, Southern India and Sri Lanka, Southwest China, and Southeast Asia in the broad sense [3]. China is one of the major distribution centers of Impatiens spp., with most species concentrated in Southwest China, for example, Yunnan, Sichuan, Tibet and Guizhou, with a large number of national and regional endemic species [4]. Yilin Chen was the first to conduct systematic research on the plant resources of the genus Impatiens in China, and in 2001, he compiled the Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinica, Balsaminaceae, which recorded more than 220 taxa of Impatiens spp. in China. In 2007 [5], he finishing compiling the Flora of China, which recorded 227 taxa of Impatiens spp. and 187 endemic species. In 2012, Shengxiang Yu published the first monograph of the family Balsaminaceae, which counted more than 270 taxa and more than 240 endemic species in China, and briefly described more than 130 taxa [6]. In 2016, Shengxiang Yu et al. proposed a new subgeneric classification system for the genus based on morphological and molecular phylogenetic evidence, dividing the genus into the subgen. Clavicarpa and the subgen. Impatiens [7].
Studies on the geographical distribution pattern of the genus Impatiens in China have mostly focused on the same provinces [8,9,10,11,12] and physical geographic areas [13,14,15,16]. Relevant experts [5] have explored the geographical distribution of this genus Impatiens in China based on the geographical information of specimens in the China Virtual Herbarium, finding that it is mainly produced in South China, with the highest concentration in the southwest and with an exceptional abundance in the Hengduan Mountains. Based on the number of specimens, geographical distribution patterns can reflect a species’ overall richness pattern to a certain extent, but species richness performance in some regions may show deviations due to the influence of plant expeditions and specimen collection efforts. Currently, information on the species diversity of Balsaminaceae in China has not been systematically sorted out, which is very unfavorable to the conservation, development, and utilization of this family. In the present study, the results of a large number of taxonomic revision articles are collated. Newly published new taxa are included, as well as those published by foreign scholars working in Southern Tibet, to obtain the most up-to-date species list of Balsaminaceae in China. This study explores the horizontal and vertical distribution patterns of the genus Impatiens and its hotspots based on the establishment of a species list and a geographic distribution database, aiming to provide a reference for Balsaminaceae spp. diversity research and resource development and use in China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
A list of Chinese Balsaminaceae was obtained based on the following sources: Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinica (Vol. 47) [4], Flora of China (Vol. 12) [5], and local flora books at all levels, supplemented by monographs on the genus Impatiens; family members included in the Species 2000 China node; and journal papers on new taxa and national records of the genus Impatiens in China published up to February 2023 [17,18,19,20,21].
The main sources of data for the geographical distribution database included the following: (1) botanical books, such as Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinica (Vol. 47), Flora of China (Vol. 12), and local botanical books and regional plant catalogs; (2) monographs on the genus Impatiens, such as Balsaminaceae of China, Wild Balsams of Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalaya—A Pictorial Handbook [22]; (3) academic papers, journal papers, and published doctoral and masters’ theses on new records of Impatiens spp. distribution; (4) collections of scientific expeditions to nature reserves at all levels in China; (5) other botanical monographs, such as Flowering Plants of Hengduan Mountain [23]. A total of 9043 points of distribution data were summarized. The main sources of species distribution data for analyzing relationships with environmental factors were the Chinese Virtual Herbarium (https://www.cvh.ac.cn/ (accessed on 1 September 2020)), the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (https://www.gbif.org/zh/ (accessed on 29 November 2020)), and a dataset on the diversity and geographical distributions of wild Impatiens in China. Nineteen common bioclimatic factors and elevation data were obtained from the World Climate Database (https://worldclim.org/ (accessed on 17 April 2021)).
2.2. Mapping of the Geographical Distribution
Based on the established geographical distribution database of Impatiens spp. in China [24], ArcGIS 10.2 software was used to map the genus’s geographical distribution. First, China’s administrative divisions were used as the base map, and provincial and county administrative division layers were retained. The statistics on species richness, Chinese endemic species richness, provincial endemic species richness, and the ratio of provincial endemic species to all species in the region were entered separately into Excel. The species richness was assigned to its corresponding area and graded using the nature break (Jenks) method to draw a horizontal distribution map. The map of China was divided into 100 × 100 km grids, the species distribution data were imported into the map, and the number of species present in the same grid was summed up to obtain the distribution pattern of species richness for Impatiens spp. in China [25].
2.3. Screening Algorithm
The Dobson [26] screening algorithm was used to identify the hotspots of Impatiens spp. in China. The counties obtained were Impatiens spp. hotspots in China. This collection included both regions with the highest species richness and regions with high endemism; thus, the regions with high abundance and endemism complemented each other to form the hotspots. If the number of species contained in two counties was the same, the counties with smaller areas were screened first; for the same number of species, the smaller the area, the higher the species richness in the region. The map layer for the distribution of 36 global biodiversity hotspots was obtained from the Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund (CEPF) (https://zh-cn.cepf.net/our-work/biodiversity-hotspots/hotspots (accessed on 26 August 2021)).
2.4. Model Establishment and Operation
The software used in this paper was Maxent v3.4.4. To avoid overfitting the model, 19 climate factors were initially screened, with a total of 10 being obtained for the model runs. Ten climatic factors and one elevation factor were screened, and the distribution data were added to Maxent. The relevant parameters were determined with reference to Roberto et al. [27]; 25% of the distribution points were set as testing data, and 75% of the distribution points were set as training data. The importance and contribution of environmental variables were assessed using the Jackknife method, and modeling was repeated 10 times. Most researchers determine the number of dominant factors based on the cumulative contribution rate and use them as dominant factors before the cumulative contribution rate exceeds a certain value. In this study, environmental factors with a cumulative contribution of more than 90% were used as dominant factors; factors with a contribution of more than 10% were considered the most important factors [28].
3. Results
3.1. Species Diversity of Balsaminaceae in China
As of February 2023, there are known to be two Balsaminaceae genera and 360 Balsaminaceae taxa in China. In the past 16 years, 81 new taxa have been added to the record, and five new national records have been created. Of these, only one taxon of the genus Hydrocera is distributed in Hainan Province. A total of 359 taxa (including 14 varieties and one subspecies) have been recorded for the genus Impatiens (Appendix A). Impatiens spp. has obvious regional species, and most of them are endemic to China, mainly concentrated in the southwest. The genus includes 271 endemic species in China, accounting for about 75.6% of the total species, with 157 endemic species at the provincial level, accounting for about 43.9% of the total species.
Three non-native balsams, Impatiens balsamina, I. glandulifera, and I. walleriana have been reported [21,29] as spontaneous plants in different parts of China (Figure 1). I. balsamina was the first genus of Impatiens to be naturalized in China and is widely distributed in the southeastern part of the country because of its extreme ecological adaptability. I. walleriana is naturalized only in Taiwan. As an invasive species, I. glandulifera is widely distributed all over the world, and in China, it is found in the northernmost city of Mohe, Heilongjiang Province.
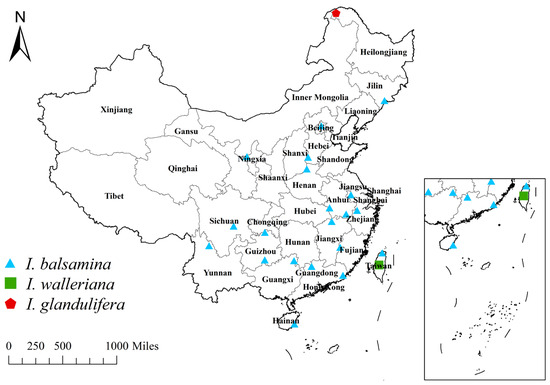
Figure 1.
Distribution of three non-native balsams in China.
The morphological variation in Impatiens spp. is complex, and the taxonomic problems are severe. Many plant taxonomists have differing views on the taxonomic status of some of these taxa. Based on published articles and books on taxonomic revision, the following decisions were made for taxa with controversial taxonomies: Impatiens chungtienensis and I. cristata are accepted as separate species, according to the related study by Akiyama S. et al. [30,31]. I. sunkoshiensis is accepted as a synonym of I. laxiflora [32], and I. taronensis as a synonym of I. prainii [33]. We cannot deny the identification of I. scabrida by Chinese taxonomists; thus, we still retain it in the list. I. walongensis is accepted as an independent species according to the related study by Gogoi et al. [34]. I. yui is accepted as a synonym of I. uncipetala [35]. I. atherosepala, I. crassiloba, I. ganpiuana, I. reptans, and I. rhombifolia are accepted as synonyms of I. procumbens based on a related study by Huang et al. [36]. Ruchisansakun et al. [37], in their study of the Balsaminaceae in Myanmar, treated I. aureliana as a synonym of I. violiflora, but in their recent book, Impatiens of Thailand, they concluded that more taxonomic evidence is still needed for the revision of these two species. Therefore, we accept that I. aureliana remains a separate species. In Impatiens of Thailand [38], the authors treated I. rubrostriata as a synonym of I. duclouxii, but according to field surveys, the stripes on the petals are an obvious taxonomic feature, as is a difference in flower color, so we retain I. rubrostriata as a separate species. Based on the field survey and related taxonomic studies by Ruchisansakun and Singh et al. [37,39], we accept I. monticola and I. mengtszeana as synonyms of I. pulchra. Based on the studies by Abrahamczyk et al. [40] on the plant longevity, flower morphology, and pollinators of I. namchabarwensis and I. arguta, we accept I. namchabarwensis as a separate species. I. wenshanensis and I. clavigeroides are treated as synonyms of I. damrongii, in accordance with Ruchisansakun and Souvannakhoummane et al. [38,41].
3.2. Geographic Distribution Patterns of Impatiens spp. in China at Different Scales
3.2.1. Provincial Scale
The species richness patterns of 34 provincial administrative regions in China were counted and divided into five levels. Level I contains 110–163 species, including Yunnan and Sichuan; Level II contains 55–79 species, including Tibet, Guizhou, and Guangxi; Level III contains 25–38 species, including Chongqing, Hunan, Hubei, and Jiangxi; Level IV contains 10–21 species, including Zhejiang, Guangdong, Fujian, and another 7 provinces; and Level V contains 1–3 species, including Liaoning, Taiwan, and another 17 provinces (Figure 2a). Impatiens spp. in China are mainly distributed in Southwest China, and are the most abundant in Yunnan Province (163 species), Sichuan Province (110 species), Tibet (79 species), Guizhou (60 species), and Guangxi (55 species). There are 300 species of Impatiens spp. in five provinces, accounting for 83.8% of the total number of Impatiens spp. in China, followed by Central and South China, which also have high species richness. The species richness in the northern provinces is generally low, and only one to four species of Impatiens spp. are distributed in most provinces (Table 1).
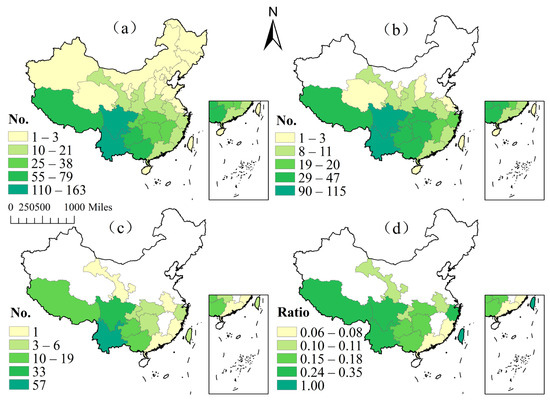
Figure 2.
Distribution pattern of Impatiens spp. at the provincial level. (a) Distribution map of species richness. (b) Abundance distribution map of Chinese endemic species. (c) Abundance distribution map of provincial endemic species. (d) Distribution map of provincial endemic species/all species in the province.

Table 1.
Species richness statistics for Impatiens spp. in China’s provincial administrative regions.
The distribution of endemic species in China is the highest in Yunnan (115 species) and Sichuan (90 species). Although the number of species in Tibet is second only to Yunnan and Sichuan, the number of endemic species in China is lower than in Guizhou, Guangxi, Hunan, Hubei, and Chongqing. There is no distribution of Chinese endemic species in Xinjiang, or in most areas of the northeast in North China (Figure 2b). Yunnan Province has the highest abundance of endemic species at the provincial level (57 species), followed by Sichuan Province (33 species), and Tibet, Guizhou, and Guangxi have more than 10 endemic species at the provincial level. Qinghai, Ningxia, Shaanxi, Henan, and Jiangsu have Chinese endemic species, but no provincial endemic species. Zhejiang has more endemic species (six species) than the surrounding provinces, with a higher endemic rate (Figure 2c). The largest ratio of provincial endemic species to all species in the province is Taiwan, followed by Yunnan, Sichuan, and Tibet, with high endemism rates (Figure 2d).
3.2.2. County Scale
A total of 714 county-level administrative units were found to have Impatiens spp. distributions. The counties with the highest species richness have as many as 51 species, namely, Gongshan County and Tengchong City, which are the richest county-level administrative units for Impatiens spp., while Gongshan County is smaller than Tengchong City. These are followed by Fugong County (42 species) and Lushui City (31 species), both in Yunnan Province. Other county-level administrative units with species richness exceeding 20 species include Emeishan City (27 species), Longyang District (27 species), Dali City (24 species), Nanchuan District (24 species), Shennongjia Forestry District (24 species), Yingjiang County (24 species), Longling County (26 species), and Wuxi County (21 species) (Figure 3a).
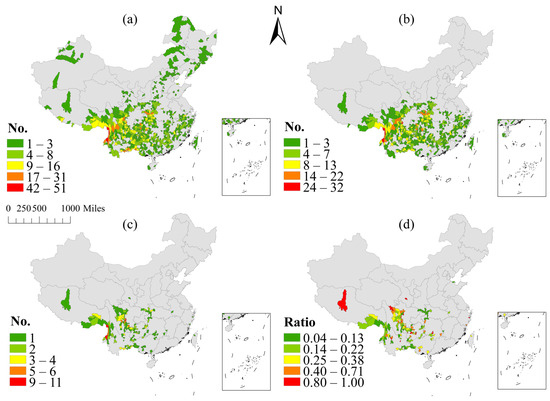
Figure 3.
Distribution patterns of Impatiens spp. at the county level. (a) Distribution map of species richness. (b) Abundance distribution map of Chinese endemic species. (c) Abundance distribution map of provincial endemic species. (d) Distribution map of provincial endemic species/all species in the county.
The county-level administrative region distribution of endemic species in China is mainly distributed in the vast area south of Qinling and the Huaihe River, where there are 525 county-level administrative regions with Chinese endemic species. The counties with the highest abundance of Chinese endemic species are Tengchong City (32 species), Gongshan County (30 species), and Fugong County (25 species) in the northwest of Yunnan Province. The countries with the second-highest abundance are Emeishan City, Sichuan (24 species); Nanchuan District, Chongqing (22 species); and Shennongjia Forest District, Hubei (21 species) (Figure 3b). At the county level, 139 county-level administrative regions were screened for provincial-level endemic species. Emeishan City has 11 provincial-level endemic species and is the county-level administrative unit with the highest number of endemic species, most of which are endemic to Emeishan. Next are Gongshan County (10 species), Tengchong City (9 species), Ebian County (6 species), Fugong County (6 species), Hongya County (6 species), and Lushui City (6 species), all of which are counties with highly abundant provincial-level endemic species (Figure 3c).
Based on the statistics for the proportion of endemic species, we found that the proportion of endemic species and the pattern of species richness are quite different, and the regions with a high proportion of endemic species presented discrete distributions. The counties with the highest proportion of endemic species reach 100%, including Chengjiang City, Dong’an County, Jinkouhe District, Longli County, Lushan County, Midu County, Nima County, Sanmen County, Seda County, Zhangxian County, Zhijin County, and Zhongshan District.
3.3. Vertical Distribution Pattern
The elevation distribution range of Impatiens spp. in China is 10~4200 m. The species with the lowest distribution is I. chinensis; those with the highest are I. delavayi, I. laxiflora, and I. margaritifera var. humilis. Based on the elevation distribution range of balsamina in China, we created 14 elevation gradients with an interval of 300 m to divide the species richness statistics. The elevation range with the highest species richness is 1200~1500 m, where there are 164 species of Impatiens spp., and the lowest richness is found in 3900~4200, with only 15 species. High abundance was maintained between 900 and 2700 m, with more than 139 species at each elevation, while the species richness decreases sharply above 3000 m (Figure 4).
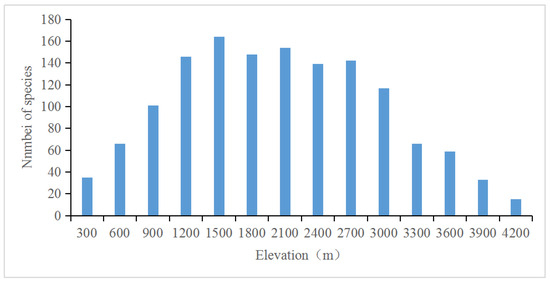
Figure 4.
Vertical distribution of Impatiens spp. in China.
3.4. Hotspots
When the screened species reached 75%, including 265 species of Impatiens spp., 54 hotspots were obtained. Thirteen counties overlapped with the Indo–Burma region among the global biodiversity hotspots, four counties overlapped with the Himalayas, and eighteen counties overlapped with the mountains of Southwest China. The rest of the hotspots were mainly distributed in the Daba Mountains, western Hubei, eastern Chongqing, and Guizhou Province (Figure 5a). When the number of species screened reached 100%, a total of 110 hotspots were obtained (Figure 5b), among which the hotspots with the highest concentrations overlapped with the southwest mountains, the Himalayas, and the Indo–Burma regions among the global biodiversity regions. The rest were scattered. The terrain of China is high in the west and low in the east, and is divided into three steps based on the average elevation. Impatiens spp. are mainly concentrated in the transition zone of the three steps, are highly dependent on the humid mountainous environment, and are rarely distributed in the plains and basins. The species distribution density is generally high in the Hengduan Mountains, Southern Tibet, Yunnan, Guizhou, the Guangxi karst region, the Qinling–Daba Mountains, and the southeast hills (Figure 6).
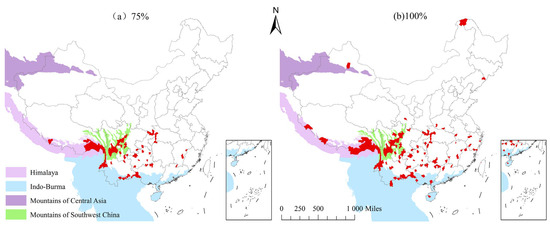
Figure 5.
The hotspots of Impatiens spp. in China, established based on the screening algorithm and its location with relation to global biodiversity hotspots. (a) The screened species reach 75%; (b) the screened species reach 100%.
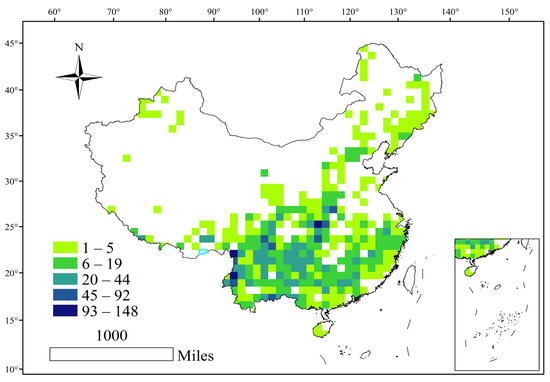
Figure 6.
Species richness distribution pattern of Impatiens spp. in China.
3.5. Relationship with Environmental Factors
The annual precipitation and the minimal temperature of the coldest month had a cumulative contribution rate of >10% and were the most important climatic factors in the distribution of Impatiens spp. The contribution rate of mean annual rainfall amounted to 65.7%, and the contribution rate of the minimum temperature of the coldest month amounted to 14.6%. The subsequent factors were altitude and annual temperature range. The cumulative contribution of these four environmental variables reached 93.7%, and they were dominant in affecting the distribution of Impatiens spp. in China.
The annual precipitation was the strongest environmental factor. Impatiens spp. are delicate plants with fleshy, juicy stems. Abundant water is the most important condition for their growth, meaning they often grow in shady and moist places at the bottom of valleys and streams, as well as in the undergrowth of forests. Some species, such as the Impatiens procumbens, can be fully submerged in water during the nutrient growth phase before flowering. The minimal temperature of the coldest month was the second-highest contributing climatic factor after annual precipitation, indicating that extreme cold weather severely affects the distribution of Impatiens spp. in China. The area south of Qinling Mountain–Huaihe River had a distribution of about 92% for Chinese Impatiens spp. Less than 30 Impatiens spp. were distributed north of this area, including some widely distributed and naturalized species, such as I. noli-tangere, I. stenosepala, I. glandulifera, etc. The contribution rate ranking of environmental factors affecting Impatiens spp. in China is as follows: moisture factor > heat factor > topography factor. The annual precipitation was 419.9~2004.4 mm and the minimal temperature of the coldest month was −15.6~22.7 ℃, both of which are suitable for the survival of Impatiens spp.
4. Discussion
Because the plants of Impatiens spp. are tender and juicy, specimens are not easy to dry or preserve. It is difficult to determine the original morphological characteristics of fragile flowers after they are flattened, and continuous variations in flower morphology, leaf morphology, and root morphology make it very difficult to classify their genera. With the completion of the compilation of Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinica, Flora of China, and local botanical books, China has more detailed data on the plant resources of Impatiens spp. However, as one of the major distribution centers of Impatiens in the world, field survey and plant taxonomy research in the country is not adequate. The species diversity catalog of Impatiens established in this paper is based on Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinica and Flora of China, both of which objectively include the published wild Impatiens spp. present in China. Molecular technology has become an important technical means of determining plant taxonomy. Some species are independent species at the molecular level, but they are difficult to morphologically distinguish from their relatives, which increases the difficulty of species identification in the field. It is important to establish a scientific list of wild Impatiens in China by integrating morphological and molecular evidence, conducting textual research and analysis on the origin of species patterns and collection history, and carrying out reasonable taxonomic treatments of suspected species. Research on the distribution of species should be based on accurate identification. The evolution and distribution of this genus can be more accurately determined only with further taxonomic studies and revisions of mispublished and misidentified species. This study lays the foundation for subsequent studies of Balsaminaceae diversity and is conducive to the development and use of Impatiens spp. resources. The distribution data obtained from extensive research can also more accurately show the distribution of Balsaminaceae in China.
Some scholars have investigated and studied the hotspot mountainous areas in China, such as Yiyan Cong [13,14], who conducted a detailed resource survey of the Hengduan Mountains and the Gaoligong Mountains and an in-depth study of the species composition, systematic characteristics, distribution, and origin of the genus Impatiens in this region. They found that the Impaiens spp. flora in the Hengduan Mountains region have an ancient evolutionary history, and their work has an important position in the global study of this species. With deepening botanical research, a large number of new taxa have been discovered [42], and the number of species in each region has increased greatly. However, affected by a variety of factors, such as anthropogenic interference and climate change, the habitats of Impatiens spp. are shrinking, and some species are facing endangerment [43], such as Impatiens hainanensis, which is a key wild plant under provincial protection, and relevant scholars have carried out many conservation studies on this species [44,45,46].
This study only quantified the dominant environmental factors affecting the distribution of Impatiens in China with respect to hydro-thermal factors and altitude, and the ways in which other environmental conditions, such as anthropogenic disturbances, vegetation types, and climate change, affect the distribution ranges of their species is still a worthy topic of research.
5. Conclusions
As of February 2023, 359 Impatiens taxa and Hydrocera triflora had been recorded in China. With deepening field investigations, the publication of new Impatiens taxa in China is growing at a stable rate. At the provincial level, Yunnan and Sichuan are not only the provinces with the highest Impatiens species richness in China, but are also the provinces with the highest proportion of endemic species. Yunnan and Sichuan overlap with the Indo–Burma region, global biodiversity hotspots, and the Hengduan Mountains of southwest China. These two provinces contain 63% of the Impatiens species in China. At the county level, the three administrative regions with the highest species richness are Gongshan County, Tengchong City, and Fugong County in Yunnan Province. The highest provincial-level endemic species richness is in Emeishan City in Sichuan Province, and most species are distributed on Emei Mountain. Given the special geographical location and natural conditions of Emei Mountain, its floristic elements have an ancient origin, which indicates the richness of its unique plant species population [47]. In screening Chinese hotspots, we found that most overlap with the global biodiversity hotspots, while the rest are scattered. When the screening species reached 100%, 110 hotspot counties were found. Some contained fewer species of the genus Impatiens, but some regional endemic species could not be found in other regions, and thus, they had a high complementary contribution and irreplaceability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.-X.B. and S.-W.L.; methodology, J.C. and T.-H.Y.; software, Q.W. and Y.C.; formal analysis, Y.C. and Q.-Q.Y.; data curation, Q.W. and M.-J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.C. and J.C.; writing—review and editing, X.-X.B. and S.-W.L.; visualization, Y.C. and Q.-Q.Y.; project administration, X.-X.B. and M.-J.L.; funding acquisition, X.-X.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects (grant No. Qiankehe Foundation-ZK (223) General 102); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32260782); and the Exploration and Research on Characteristic Flower Resources in Karst Area of Qianxinan Prefecture project (No.17 (2022)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
A dataset on the diversity and geographical distributions of wild Impatiens spp. in China can be downloaded at http://dataopen.info/home/datafile/index/id/246 (accessed on 20 May 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
List of Balsaminaceae in China.
Table A1.
List of Balsaminaceae in China.
| No. | Scientific Name | Synonym | China Specific | Altitudinal Limits (m) | Distribution in China |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrocera triflora (L.) Wight & Arn. | Impatiens triflora L. Tytonia triflora (L.) C.E.Wood Balsamina angustifolia Blume Hydrocera angustifolia (Blume) Blume ex Wight & Arn. Impatiens angustifolia Blume Impatiens baccifera Roxb. ex Wight & Arn. Impatiens natans Willd. Tytonia natans (Willd.) G.Don | 100 | Hainan | |
| 2 | Impatiens abbatis Hook.f. | √ | 1200~2100 | Yunnan | |
| 3 | Impatiens aconitoides Y.M.Shui & W.H.Chen | √ | 1800~2000 | Yunnan | |
| 4 | Impatiens alpicola Y.L.Chen & Y.Q.Lu | √ | 1050~2900 | Sichuan, Chongqing, Hubei, Yunnan | |
| 5 | Impatiens amabilis Hook.f. | √ | 1100~3100 | Sichuan | |
| 6 | Impatiens amplexicaulis Edgew. | Impatiens sulcata var. amplexicaulis (Edgew.) R.Kr.Singh & D.Borah | 2900~3900 | Tibet | |
| 7 | Impatiens angulata S.X.Yu, Y.L.Chen & H.N.Qin | 200~600 | Guangxi | ||
| 8 | Impatiens anhuiensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 1200 | Anhui | |
| 9 | Impatiens apalophylla Hook.f. | 200~2300 | Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan, Jiangxi | ||
| 10 | Impatiens apsotis Hook.f. | √ | 2000~3900 | Qinghai, Sichuan, Tibet, Shaanxi, Yunnan | |
| 11 | Impatiens aquatilis Hook.f. | Impatiens gagnepainii Hook. ex H.Lév. Impatiens tongchouanensis H.Lév. | √ | 200~3400 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan, Guangxi |
| 12 | Impatiens arctosepala Hook.f. | √ | 1800~2746 | Yunnan | |
| 13 | Impatiens arguta Hook.f. & Thomson | Impatiens arguta var. bulleyana Hook.f. Impatiens gagei Hook.f. Impatiens taliensis Lingelsh. & Borza | 900~3800 | Guizhou, Tibet, Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 14 | Impatiens armeniaca S.H.Huang | √ | 950~1500 | Yunnan | |
| 15 | Impatiens aureliana Hook.f. | 680~2800 | Yunnan | ||
| 16 | Impatiens austroyunnanensis S.H.Huang | 1850~2700 | Yunnan | ||
| 17 | Impatiens bachii H.Lév. | √ | 1900~2930 | Yunnan | |
| 18 | * Impatiens balsamina L. | Balsamina balsamina (L.) Huth Balsamina hortensis Desp. Impatiens balsamina var. vulgaris Wight & Arn. | 10~2000 | Beijing, Hebei, Jilin, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxj, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Ningxia, Taiwan | |
| 19 | Impatiens bahanensis Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 300~3000 | Yunnan, Tibet | |
| 20 | Impatiens baishaensis B.Ding & H.P.Deng | √ | 2100~2300 | Sichuan | |
| 21 | Impatiens balansae Hook.f. | 300~1400 | Yunnan | ||
| 22 | Impatiens baokangensis Q.L.Gan & X.W.Li | √ | 1430~1450 | Hubei | |
| 23 | Impatiens barbata H.F.Comber | √ | 2000~3000 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 24 | Impatiens begoniifolia S.Akiyama & H.Ohba | √ | 1000~1400 | Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 25 | Impatiens bellula Hook.f. | √ | 1000~2900 | Chongqing, Hubei | |
| 26 | Impatiens bicornuta Wall. | 2400~2800 | Tibet | ||
| 27 | Impatiens bijieensis X.X.Bai & L.Y.Ren | √ | 1915~2800 | Guizhou | |
| 28 | Impatiens biluoxueshanensis S.Akiyama & S.K.Wu | √ | 2540 | Yunnan | |
| 29 | Impatiens blepharosepala E.Pritz. | Impatiens silvestrii Pamp. | √ | 200~2280 | Guizhou, Anhui, Fujian, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Guangxi, Zhejiang, Sichuan, Yunnan, Henan, Jiangsu |
| 30 | Impatiens blinii H.Lév. | √ | 880~2800 | Yunnan, Hunan, Guangxi | |
| 31 | Impatiens bodinieri Hook.f. | √ | 700~2345 | Guizhou, Sichuan, Hubei, Guangxi, Yunnan | |
| 32 | Impatiens bomiensis Y.Y.Cong & Y.C.Peng | √ | 3035 | Tibet | |
| 33 | Impatiens brachycentra Kar. & Kir. | 800~2100 | Xinjiang | ||
| 34 | Impatiens bracteata Colebr. ex Wall. | Impatiens fimbriata Hook. | 2700 | Tibet | |
| 35 | Impatiens bracteolata Hook.f. | 1500~2200 | Tibet | ||
| 36 | Impatiens brevipes Hook.f. | √ | 1500~1800 | Sichuan, Chongqing | |
| 37 | Impatiens bullatisepala G.W.Hu, Y.Y.Cong & Q.F.Wang | √ | 1027 | Guizhou | |
| 38 | Impatiens cavaleriei X.X.Bai & R.X.Huang | √ | 1151 | Guizhou | |
| 39 | Impatiens ceratophora H.F.Comber | 1700~2950 | Yunnan | ||
| 40 | Impatiens chashanensis H.Y.Bi & S.X.Yu | √ | 2500 | Sichuan | |
| 41 | Impatiens chekiangensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 160~1000 | Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian | |
| 42 | Impatiens chekiangensis Y.L.Chen var. cangnanensis Y.L.Xu & X.F.Jin | √ | 180~260 | Zhejiang | |
| 43 | Impatiens chekiangensis Y.L.Chen var. multiflora Y.L.Xu & X.F.Jin | √ | 200~800 | Anhui, Zhejiang | |
| 44 | Impatiens chenmoui Zheng W.Wang, Xiao C.Li & Q.Wang ter | √ | 1639 | Yunnan | |
| 45 | Impatiens chimiliensis H. F. Comber | 2354~3700 | Tibet, Yunnan | ||
| 46 | Impatiens chinensis L. | Impatiens crassicornu Hook.f. Impatiens cosmia Hook.f. | 10~3100 | Anhui, Fujian, Guangdong, Hainan, Jiangxi, Yunnan, Zhejiang, Hong Kong, Guangxi, Hunan, Sichuan, Macao | |
| 47 | Impatiens chishuiensis Y.X.Xiong | √ | 398~950 | Guizhou | |
| 48 | Impatiens chiulungensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 2700~2900 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 49 | Impatiens chlorosepala Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 250~1610 | Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hunan, Jiangxi | |
| 50 | Impatiens chungtienensis Y.L.Chen | Impatiens badrinathii Pusalkar & D.K.Singh | 3200~3300 | Yunnan | |
| 51 | Impatiens citrina Hook.f. | 1000~1560 | Tibet | ||
| 52 | Impatiens clavicuspis Hook.f. ex W.W.Sm. | 700~3500 | Yunnan, Guangxi | ||
| 53 | Impatiens clavicuspis Hook.f. var. brevicuspis Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 2400~3450 | Yunnan | |
| 54 | Impatiens clavigera Hook.f. | 1000~1800 | Guangxi, Yunnan, Guangdong, Guizhou | ||
| 55 | Impatiens clavigera Hook.f. var. auriculata S.H.Huang | √ | 370~1200 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 56 | Impatiens commelinoides Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 300~1500 | Guizhou, Fujian, Guangdong, Hunan, Jiangxi, Zhejiang, Sichuan, Guangxi, Chongqing | |
| 57 | Impatiens compta Hook.f. | √ | 1400~2200 | Chongqing, Hubei | |
| 58 | Impatiens conaensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 2700~2800 | Tibet | |
| 59 | Impatiens conchibracteata Y.L.Chen & Y.Q.Lu | √ | 900~2800 | Sichuan | |
| 60 | Impatiens corchorifolia Franch. | √ | 1200~4000 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 61 | Impatiens cornucopia Franch. | √ | 1900~2700 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 62 | Impatiens cornutisepala S.X.Yu, Y.L.Chen & H.N.Qin | √ | 100~1300 | Guangxi | |
| 63 | Impatiens crassicaudex Hook.f. | √ | 3000~4100 | Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 64 | Impatiens crenulata Hook.f. | √ | 1900~2400 | Chongqing | |
| 65 | Impatiens cyanantha Hook.f. | √ | 850~2550 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Fujian, Chongqing, Sichuan, Hunan, Guangxi | |
| 66 | Impatiens cyathiflora Hook.f. | √ | 1000~2720 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guangxi, Jiangxi | |
| 67 | Impatiens cyclosepala Hook.f. | √ | 1555~2700 | Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 68 | Impatiens cymbifera Hook.f. | 2500~3500 | Tibet | ||
| 69 | Impatiens daguanensis S.H.Huang | √ | 1700~1750 | Yunnan | |
| 70 | Impatiens dalaiensis Gogoi & Borah | 2052 | Yunnan | ||
| 71 | Impatiens damingensis S.X.Yu, Chang Y.Xia & H.P.Deng | √ | 1120 | Guangxi | |
| 72 | Impatiens damrongii T.Shimizu | Impatiens wenshanensis S.H.Huang Impatiens clavigeroides S.Akiyama, H.Ohba & S.K.Wu | 1700~2200 | Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 73 | Impatiens dasyvexilla Q.L.Gan & X.W.Li | √ | 700~1477 | Hubei | |
| 74 | Impatiens davidii Franch. | √ | 300~2000 | Guizhou, Anhui, Fujian, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Sichuan | |
| 75 | Impatiens delavayi Franch. | √ | 600~4200 | Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 76 | Impatiens deqinensis S.H.Huang | √ | 3680 | Yunnan | |
| 77 | Impatiens desmantha Hook.f. | Impatiens valbrayana H.Lév. Impatiens gracilipes Hook.f. Impatiens recticalcarata S.Akiyama Impatiens recticalcarata f. alba S.Akiyama | 1550~4000 | Tibet, Yunnan, Chongqing, Sichuan | |
| 78 | Impatiens devolii T.C.Huang | √ | 2000~2100 | Taiwan | |
| 79 | Impatiens diaphana Hook.f. | √ | 1200~2100 | Chongqing | |
| 80 | Impatiens dicentra Franch. ex Hook.f. | √ | 200~2800 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Henan, Hubei, Shaanxi, Sichuan, Hunan, Chongqing, Jiangxi, Guangxi | |
| 81 | Impatiens dichroa Hook.f. | √ | 1200~2900 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 82 | Impatiens dichroocarpa H.Lév. | √ | 2700 | Yunnan | |
| 83 | Impatiens dimorphophylla Franch. | √ | 2410~3400 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 84 | Impatiens distracta Hook.f. | √ | 1400~2000 | Sichuan | |
| 85 | Impatiens divaricata Franch. | √ | 2000~3200 | Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 86 | Impatiens dolichoceras E.Pritz. | √ | 1200~2100 | Guizhou, Chongqing, Hubei | |
| 87 | Impatiens dorjeekhandui Chowlu, S.S.Dash & Gogoi | √ | 1719 | Tibet | |
| 88 | Impatiens drepanophora Hook.f. | 950~2960 | Tibet, Yunnan | ||
| 89 | Impatiens duclouxii Hook.f. | Impatiens jurpioides T.Shimizu Impatiens jurpia var. jurpioides (T.Shimizu) T.Shimizu | 400~2700 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan, Guangxi, Guangdong, Zhejiang | |
| 90 | Impatiens epilobioides Y.L.Chen | √ | 800~2500 | Guizhou, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan | |
| 91 | Impatiens ernstii Hook.f. | √ | 1000~2500 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 92 | Impatiens exiguiflora Hook.f. | √ | 800~1600 | Hubei | |
| 93 | Impatiens extensifolia Hook.f. | √ | 1090~1900 | Yunnan | |
| 94 | Impatiens faberi Hook.f. | √ | 1200~2323 | Sichuan | |
| 95 | Impatiens falcifera Hook.f. | 2007~3600 | Sichuan, Tibet | ||
| 96 | Impatiens fanjingshanica Y.L.Chen | √ | 680~1500 | Guizhou | |
| 97 | Impatiens fargesii Hook.f. | √ | 1300~1600 | Chongqing, Hubei, Guizhou | |
| 98 | Impatiens fenghwaiana Y.L.Chen | √ | 310~1248 | Jiangxi, Zhejiang, Hubei, Hunan | |
| 99 | Impatiens fissicornis Maxim. | √ | 440~2100 | Gansu, Hubei, Shaanxi, Sichuan | |
| 100 | Impatiens forrestii Hook.f. | 2600~3300 | Sichuan, Yunnan | ||
| 101 | Impatiens fragicolor C. Marquand & Airy Shaw | 2600~4000 | Tibet, Yunnan, Sichuan | ||
| 102 | Impatiens fugongensis K.M.Liu & Y.Y.Cong | 1450~2500 | Yunnan | ||
| 103 | Impatiens furcillata Hemsl. | 700~1100 | Hebei, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Tianjin | ||
| 104 | Impatiens gamblei Hook.f. | 2400~3600 | Tibet | ||
| 105 | Impatiens gammiei Hook.f. | 3000~3600 | Tibet | ||
| 106 | Impatiens gasterocheila Hook.f. | √ | 900 | Sichuan | |
| 107 | * Impatiens glandulifera Royle | 160 | Heilongjiang | ||
| 108 | Impatiens gongchengensis Z.C.Lu, B.Pan & Yan Liu | √ | 1100~1200 | Guangxi | |
| 109 | Impatiens gongshanensis Y.L.Chen | 1200~1500 | Yunnan, Sichuan | ||
| 110 | Impatiens guiqingensis S.X.Yu | √ | 2440 | Gansu | |
| 111 | Impatiens guizhouensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 700~1120 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan, Hubei, Hunan | |
| 112 | Impatiens hainanensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 1200~1300 | Hainan, Hunan | |
| 113 | Impatiens hancockii C.H.Wright | √ | 1000~1400 | Yunnan | |
| 114 | Impatiens harae H.Ohba & S.Akiyama | 1500~2800 | Tibet | ||
| 115 | Impatiens henanensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 1200~1500 | Henan, Shanxi, Jiangsu | |
| 116 | Impatiens hengduanensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 1266~1500 | Yunnan | |
| 117 | Impatiens henryi E.Pritz. | √ | 1000~2253 | Hubei, Jiangsu, Chongqing | |
| 118 | Impatiens holocentra Hand.-Mazz. | 1150~3105 | Yunnan, Sichuan | ||
| 119 | Impatiens hongkongensis Grey-Wilson | √ | 100~300 | Hong Kong, Guangdong | |
| 120 | Impatiens huangyanensis X.F.Jin & B.Y.Ding | √ | 200~700 | Fujian, Zhejiang | |
| 121 | Impatiens huangyanensis X.F.Jin & B.Y.Ding subsp. attenuata X.F.Jin & Z.H.Chen | √ | 150 | Zhejiang | |
| 122 | Impatiens hunanensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 450~800 | Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hunan, Jiangxi | |
| 123 | Impatiens imbecilla Hook.f. | √ | 1300~2300 | Sichuan | |
| 124 | Impatiens infirma Hook.f. | √ | 2700~3600 | Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 125 | Impatiens jinggangensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 500~1240 | Jiangxi, Hunan, Fujian, Guangdong | |
| 126 | Impatiens jinpingensis Y.M.Shui & G.F.Li | √ | 1650 | Yunnan | |
| 127 | Impatiens jiulongshanica Y.L.Xu & Y.L.Chen | √ | 878~1800 | Guizhou, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Hunan | |
| 128 | Impatiens jurpia Buch.-Ham. | 1100~2200 | Tibet | ||
| 129 | Impatiens kamtilongensis Toppin | 500~1248 | Yunnan, Guangxi | ||
| 130 | Impatiens kerriae Craib | 600~2100 | Yunnan | ||
| 131 | Impatiens labordei Hook.f. | √ | 1400 | Guizhou | |
| 132 | Impatiens lacinulifera Y.L.Chen | √ | 1400~1600 | Gansu, Sichuan, Shaanxi | |
| 133 | Impatiens lancisepala S.H.Huang | √ | 300~1720 | Yunnan | |
| 134 | Impatiens laojunshanensis S.H.Huang | √ | 1830 | Yunnan | |
| 135 | Impatiens lasiophyton Hook.f. | √ | 585~2700 | Guizhou, Guangxi, Yunnan, Jiangxi, Hunan | |
| 136 | Impatiens latebracteata Hook.f. | √ | 300~2200 | Sichuan, Shaanxi, Anhui | |
| 137 | Impatiens lateristachys Y.L.Chen & Y.Q.Lu | √ | 990~2500 | Sichuan | |
| 138 | Impatiens latiflora Hook.f. & Thomson | 400~1000 | Tibet | ||
| 139 | Impatiens latipetala S.H.Huang | √ | 1300 | Yunnan | |
| 140 | Impatiens laxiflora Edgew. | Impatiens sunkoshiensis S.Akiyama, H.Ohba & Wakab. Impatiens leggei Pusalkar & D.K.Singh | 2550~4200 | Tibet, Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 141 | Impatiens lecomtei Hook.f. | 1420~3000 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan | ||
| 142 | Impatiens lemeei H.Lév. | Impatiens hookeriana H.Lév. | √ | 1181~3000 | Yunnan, Sichuan |
| 143 | Impatiens lepida Hook.f. | √ | 1000~2500 | Guizhou, Yunnan | |
| 144 | Impatiens leptocaulon Hook.f. | √ | 188~3000 | Guizhou, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Jiangxi, Guangxi | |
| 145 | Impatiens leveillei Hook.f. | √ | 1200~1300 | Guizhou | |
| 146 | Impatiens liangshanensis Q.Luo | √ | 2100~3100 | Sichuan | |
| 147 | Impatiens liboensis K.M.Liu & R.P.Kuang | √ | 450~520 | Guizhou | |
| 148 | Impatiens lihengiana Y.Y.Cong & G.W.Hu | √ | 517 | Hunan | |
| 149 | Impatiens lilacina Hook.f. | √ | 1900 | Yunnan | |
| 150 | Impatiens linearisepala S.Akiyama, H.Ohba & S.K.Wu | √ | 400~2000 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 151 | Impatiens linghziensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 2500~2700 | Tibet | |
| 152 | Impatiens linocentra Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 800~1800 | Henan, Shaanxi, Hunan | |
| 153 | Impatiens liupanshuiensis X.X.Bai & T.H.Yuan | √ | 2730~2887 | Guizhou | |
| 154 | Impatiens lixianensis S.X.Yu | √ | 2680~3000 | Sichuan | |
| 155 | Impatiens lizipingensis Q.Luo | √ | 2506~2850 | Sichuan | |
| 156 | Impatiens lobulifera S.X.Yu, Y.L.Chen & H.N.Qin | √ | 700~1000 | Guangxi | |
| 157 | Impatiens longialata E.Pritz. | √ | 500~2500 | Guizhou, Hubei, Sichuan, Chongqing, Hunan, Yunnan | |
| 158 | Impatiens longiaristata S.Peng, G.W.Hu & Q.F.Wang | √ | 2680 | Sichuan | |
| 159 | Impatiens longicornuta Y.L.Chen | √ | Hunan | ||
| 160 | Impatiens longipes Hook.f. & Thomson | 1300~4100 | Tibet, Yunnan | ||
| 161 | Impatiens longirostris S.H.Huang | √ | 1850~2700 | Yunnan | |
| 162 | Impatiens longlinensis S.X.Yu | √ | 1780 | Guangxi | |
| 163 | Impatiens longshanensis Y.Y.Cong & Y.X.Song | √ | 1194~1336 | Hunan | |
| 164 | Impatiens longyangensis Y.Y.Cong, G.W.Hu & S.Peng | √ | 2391 | Yunnan | |
| 165 | Impatiens loulanensis Hook.f. | √ | 700~3750 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Guangdong, Sichuan | |
| 166 | Impatiens luchunensis S.Akiyama, H.Ohba & S.K.Wu | √ | 250~2500 | Yunnan | |
| 167 | Impatiens lucorum Hook.f. | √ | 800~2800 | Sichuan, Guizhou | |
| 168 | Impatiens lushiensis Y.L.Chen | Impatiens heterosepala S.Y.Wang | √ | 500~1200 | Henan, Anhui |
| 169 | Impatiens macrantha S.X.Yu & Ying Qin | √ | 300~574 | Guangxi | |
| 170 | Impatiens macrovexilla Y.L.Chen | √ | 100~1640 | Guangxi, Hunan | |
| 171 | Impatiens macrovexilla Y.L.Chen var. yaoshanensis S.X.Yu, Y.L.Chen & H.N.Qin | √ | 100~1640 | Guangxi, Hunan, Guizhou, Jiangxi | |
| 172 | Impatiens maculifera S.X.Yu & Chang Y.Xia | 1000~1200 | Yunnan | ||
| 173 | Impatiens maguanensis S.Akiyama, H.Ohba & S.K.Wu | √ | 1350~2500 | Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 174 | Impatiens mairei H.Lév. | √ | 2600~2700 | Yunnan | |
| 175 | Impatiens malipoensis S.H.Huang | √ | 700~1500 | Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 176 | Impatiens margaritifera Hook.f. | √ | 1500~3940 | Yunnan, Tibet, Sichuan | |
| 177 | Impatiens margaritifera Hook.f. var. humilis Y.L.Chen | 2700~4200 | Sichuan, Yunnan, Tibet, Hubei | ||
| 178 | Impatiens margaritifera Hook.f. var. purpurascens Y.L.Chen | √ | 2600 | Tibet | |
| 179 | Impatiens marianae Van Geert | 400 | Tibet | ||
| 180 | Impatiens martinii Hook.f. | √ | 700~2000 | Guizhou, Chongqing, Sichuan | |
| 181 | Impatiens medogensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 2800~3600 | Tibet | |
| 182 | Impatiens membranifolia Franch. ex Hook.f. | √ | 1100~1600 | Chongqing, Hubei | |
| 183 | Impatiens menghuochengensis Q.Luo | √ | 2751~2769 | Sichuan | |
| 184 | Impatiens meyana Hook.f. | √ | 1800~3000 | Yunnan | |
| 185 | Impatiens microcentra Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 2200~3500 | Yunnan | |
| 186 | Impatiens microstachys Hook.f. | √ | 2000~2500 | Sichuan | |
| 187 | Impatiens minimisepala Hook.f. | √ | 1900 | Yunnan | |
| 188 | Impatiens morsei Hook.f. | 220~1000 | Guangxi, Yunnan, Jiangxi | ||
| 189 | Impatiens muliensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 1450~3500 | Sichuan, Chongqing | |
| 190 | Impatiens multiramea S.H.Huang | √ | 1000~1300 | Yunnan | |
| 191 | Impatiens mussotii Hook.f. | √ | 1400~3000 | Sichuan | |
| 192 | Impatiens musyana Hook.f. | 800~1900 | Yunnan | ||
| 193 | Impatiens namchabarwensis R.J.Morgan, Y.M.Yuan & X.J.Ge | √ | 900~1000 | Tibet | |
| 194 | Impatiens nanlingensis A.Q.Dong & F.W.Xing | √ | 1000~1050 | Guizhou, Guangdong | |
| 195 | Impatiens napoensis Y.L.Chen | 800~1780 | Guizhou, Guangxi, Yunnan | ||
| 196 | Impatiens nasuta Hook.f. | √ | 1200~2500 | Chongqing, Hubei, Shaanxi | |
| 197 | Impatiens neglecta Y.L.Xu & Y.L.Chen | √ | 1000~1200 | Anhui, Zhejiang, Jiangxi | |
| 198 | Impatiens nobilis Hook.f. | √ | 1900 | Yunnan | |
| 199 | Impatiens noli-tangere L. | 300~2800 | Guizhou, Anhui, Beijing, Gansu, Hebei, Henan, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Shandong, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Zhejiang, Qinghai, Guangdong, Hubei, Hunan, Ningxia, Tianjin, Jiangxi, Sichuan, Chongqing, Guangxi | ||
| 200 | Impatiens notolopha Maxim. | √ | 1500~3600 | Guizhou, Gansu, Henan, Shaanxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Ningxia | |
| 201 | Impatiens nubigena W.W.Smith | √ | 2700~4050 | Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 202 | Impatiens nushanensis Zi Wang, P.P.Wu & S.X.Yu | √ | 3200~3300 | Yunnan | |
| 203 | Impatiens nyimana C.Marquand & Airy Shaw | √ | 2380~3600 | Tibet | |
| 204 | Impatiens obesa Hook.f. | Impatiens eramosa Tutcher | √ | 144~800 | Guangdong, Hunan, Jiangxi, Guangxi |
| 205 | Impatiens oblongipetala K.M.Liu & Y.Y.Cong | √ | 2700~2900 | Yunnan | |
| 206 | Impatiens occultans Hook.f. | 950~4050 | Tibet | ||
| 207 | Impatiens odontopetala Maxim. | √ | 1800 | Gansu, Sichuan | |
| 208 | Impatiens odontophylla Hook.f. | √ | 800~2400 | Hubei, Sichuan, Chongqing | |
| 209 | Impatiens oligoneura Hook.f. | √ | 2600~2900 | Sichuan | |
| 210 | Impatiens omeiana Hook.f. | √ | 900~1300 | Sichuan | |
| 211 | Impatiens oxyanthera Hook.f. | √ | 1036~2663 | Hubei, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan | |
| 212 | Impatiens pandurata Y.H.Tan & S.X.Yu | √ | 1200~1250 | Yunnan | |
| 213 | Impatiens paradoxa C.S.Chu & H.W.Yang | √ | 780~1800 | Henan, Hubei | |
| 214 | Impatiens paramjitiana Gogoi & Borah | 300~400 | Tibet | ||
| 215 | Impatiens parviflora DC. | 1200~1700 | Xinjiang | ||
| 216 | Impatiens parvisepala S.X.Yu & Y.T.Hou | 250~503 | Guangxi, Yunnan | ||
| 217 | Impatiens pasighatensis D.Borah, R.Kr.Singh & Taram | √ | 380~550 | Tibet | |
| 218 | Impatiens pathakiana Gogoi & Borah | 1591 | Tibet | ||
| 219 | Impatiens pianmaensis S.H.Huang | √ | 2080~3400 | Yunnan | |
| 220 | Impatiens pinetorum Hook.f. ex W.W.Smith | √ | 1900~2768 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 221 | Impatiens pingxiangensis H.Y.Bi & S.X.Yu | √ | 200~600 | Guangxi | |
| 222 | Impatiens piufanensis Hook.f. | √ | 200~2916 | Guizhou, Chongqing, Jiangxi, Hubei, Guangxi, Hunan, Yunnan | |
| 223 | Impatiens piufanensis Hook.f. var. villosa G.W.Hu, S.X.Ding & S.Peng | √ | 700~1000 | Hubei, Hunan | |
| 224 | Impatiens platyceras Maxim. | √ | 2000~3200 | Gansu, Hubei, Sichuan | |
| 225 | Impatiens platychlaena Hook.f. | √ | 700~2500 | Guizhou, Sichuan | |
| 226 | Impatiens platysepala Y.L.Chen | √ | 50~1000 | Jiangxi, Zhejiang, Fujian, Hunan | |
| 227 | Impatiens platysepala Y.L.Chen var. chloroxantha (Y.L.Chen) X.F.Jin & Y.L.Xu | √ | 484~700 | Zhejiang, Fujian | |
| 228 | Impatiens plicatisepala C.Y.Zou, Yan Liu & S.X.Yu | √ | 1071~1462 | Guangxi | |
| 229 | Impatiens poculifer Hook.f. | √ | 2800~3640 | Yunnan | |
| 230 | Impatiens polyceras Hook.f. ex W.W.Smith | √ | 2279~3500 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 231 | Impatiens polyneura K.M.Liu | √ | 400~420 | Hunan | |
| 232 | Impatiens porphyrea Toppin | 1700~1900 | Yunnan | ||
| 233 | Impatiens porrecta Wall. | 600~3048 | Yunnan, Tibet | ||
| 234 | Impatiens potaninii Maxim. | Impatiens potaninii Maxim. f. rubrobrunnea E. Pritz. | √ | 1200~2300 | Gansu, Shaanxi, Sichuan |
| 235 | Impatiens prainii Hook.f. | Impatiens taronensis Hand.-Mazz. Impatiens mallae S.Akiyama, H.Ohba & M.Suzuki | 1800~3600 | Tibet, Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 236 | Impatiens principis Hook.f. | √ | 800~2500 | Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 237 | Impatiens pritzelii Hook.f. | √ | 200~1800 | Guizhou, Hubei, Sichuan, Hunan, Chongqing | |
| 238 | Impatiens procumbens Franch. | Impatiens atherosepala Hook.f. Impatiens crassiloba Hook.f. Impatiens ganpiuana Hook.f. Impatiens reptans Hook.f. Impatiens rhombifolia Y. Q. Lu & Y.L.Chen | √ | 1500~2700 | Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hunan, |
| 239 | Impatiens pseudocitrina Hareesh, M.Sabu & Gogoi | √ | 1000 | Tibet | |
| 240 | Impatiens pseudokingii Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 2000~2600 | Yunnan | |
| 241 | Impatiens pseudolaevigata Gogoi, B.B.T.Tham & Lidén | √ | 1800 | Tibet | |
| 242 | Impatiens pseudolongipes Gogoi, Sherpa & Borah | √ | 2400 | Tibet | |
| 243 | Impatiens pterocaulis S.X.Yu & L.R.Zhang | √ | 1284 | Guangxi | |
| 244 | Impatiens pterosepala Hook.f. | √ | 450~1700 | Anhui, Guangxi, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Shaanxi, Sichuan, Jiangxi, Chongqing, Fujian, Guangdong | |
| 245 | Impatiens puberula DC. | 1500~3000 | Tibet, Yunnan | ||
| 246 | Impatiens pudica Hook.f. | √ | 1300~2200 | Sichuan | |
| 247 | Impatiens pulchra Hook.f. & Thomson | Impatiens mengtszeana Hook.f. Impatiens monticola Hook.f. | Guangxi, Guizhou, Sichuan, Yunnan, Hunan, Chongqing | ||
| 248 | Impatiens purpurea Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 2000~3300 | Yunnan, Tibet | |
| 249 | Impatiens purpureifolia S.H.Huang & Y.M.Shui | 1411~1533 | Yunnan | ||
| 250 | Impatiens pyrorhiza Lidén & Bharali | √ | 3400 | Tibet | |
| 251 | Impatiens qingchengshanica Y.M.Yuan, Y.Song & X.J.Ge | √ | 700~1400 | Sichuan | |
| 252 | Impatiens quadriloba K.M.Liu & Y.L.Xiang | √ | 1200~3520 | Sichuan | |
| 253 | Impatiens quintadecimacopii G.W.Hu & Q.F.Wang | √ | 1540 | Yunnan | |
| 254 | Impatiens racemosa DC. | Petalonema racemosum (DC.) Peter Impatiens micrantha D.Don Impatiens microsciadia Hook.f. Impatiens racemosa var. ecalcarata Hook.f. Impatiens trigonopteris Hook.f. ex Arisdason & Gogoi | 1100~3642 | Tibet, Yunnan, Guangxi, Sichuan | |
| 255 | Impatiens radiata Hook.f. | Impatiens centiflora H.Lév. | 1150~3970 | Guizhou, Tibet, Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 256 | Impatiens rapiformis Y.Y.Cong & Y.X.Song | √ | 1150~1300 | Yunnan | |
| 257 | Impatiens rectangula Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 1430~3700 | Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 258 | Impatiens rectirostrata Y.L.Chen & Y.Q.Lu | √ | 1800~1900 | Sichuan | |
| 259 | Impatiens recurvicornis Maxim. | √ | 500~1200 | Hubei, Sichuan, Chongqing | |
| 260 | Impatiens robusta Hook.f. | √ | 1500 | Sichuan | |
| 261 | Impatiens roingensis Hareesh, A.Joe & M.Sabu | √ | Tibet | ||
| 262 | Impatiens rostellata Franch. | √ | 980~2400 | Sichuan, Shaanxi, Yunnan, Gansu | |
| 263 | Impatiens rubrostriata Hook.f. | 1130~3500 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Guangxi, Sichuan | ||
| 264 | Impatiens rugata S.H.Huang & Y.M.Shui | √ | 300~560 | Yunnan | |
| 265 | Impatiens rugosipetala Gogoi & Borah | √ | 2600 | Tibet | |
| 266 | Impatiens ruiliensis S.Akiyama & H.Ohba | √ | 200~2000 | Yunnan, Tibet, Guangxi | |
| 267 | Impatiens rupestris K.M.Liu & X.Z.Cai | √ | 350 | Hunan | |
| 268 | Impatiens salwinensis S.H.Huang | √ | 3200~3400 | Yunnan | |
| 269 | Impatiens scabrida DC. | Balsamina cristata (Wall.) Ser. Impatiens calycina Wall. Impatiens cristata Wall. Impatiens hamiltoniana D.Don | 2300~3400 | Tibet | |
| 270 | Impatiens scitula Hook.f. | 3000~3600 | Tibet | ||
| 271 | Impatiens scullyi Hook.f. | 700~2400 | Tibet | ||
| 272 | Impatiens scutisepala Hook.f. | √ | 1800~3800 | Yunnan | |
| 273 | Impatiens serrata Benth. | Impatiens serrulata Hook.f. | 2900~3300 | Tibet | |
| 274 | Impatiens shangjiangensis Y.Y.Cong & J.Z.Gu | √ | 2600~2850 | Yunnan | |
| 275 | Impatiens shenglanii Q.L.Gan & X.W.Li | √ | 1100~1450 | Hubei | |
| 276 | Impatiens shennongensis Q.Wang & H.P.Deng | √ | 2300~3000 | Hubei | |
| 277 | Impatiens shimianensis G.C.Zhang & L.B.Zhang | √ | 2300 | Sichuan | |
| 278 | Impatiens shiyomiensis Hareesh & M.Sabu | √ | 1200 | Tibet | |
| 279 | Impatiens siangensis Gogoi | √ | 300~600 | Tibet | |
| 280 | Impatiens siculifera Hook.f. | 300~3400 | Guizhou, Tibet, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Taiwan | ||
| 281 | Impatiens siculifera Hook.f. var. mitis Lingelsh. & Borza | √ | 1445~3500 | Yunnan, Guizhou | |
| 282 | Impatiens siculifera Hook.f. var. porphyrea Hook.f. | 1431~3900 | Yunnan, Guangxi, Hunan, Guizhou | ||
| 283 | Impatiens sigmoidea Hook.f. | √ | 1200~1700 | Guizhou | |
| 284 | Impatiens sikaiensis Q.Luo & Ying Yuan | √ | 2468 | Sichuan | |
| 285 | Impatiens soulieana Hook.f. | 1400~3000 | Sichuan | ||
| 286 | Impatiens spathulata Y.X.Xiong | √ | 300~800 | Guizhou, Guangxi | |
| 287 | Impatiens spirifera Hook.f. & Thomson | 1400~2500 | Tibet | ||
| 288 | Impatiens stenantha Hook.f. | Impatiens asymmetrica Hook.f. | 900~3900 | Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 289 | Impatiens stenosepala E. Pritz. | √ | 500~2600 | Guizhou, Shanxi, Gansu, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Shaanxi, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan | |
| 290 | Impatiens stenosepala E. Pritz. var. parviflora E.Pritz. | √ | 1000~1100 | Chongqing | |
| 291 | Impatiens sterilis Y.Y.Cong & Y.X.Song | √ | 3296 | Yunnan | |
| 292 | Impatiens subecalcarata (Hand.-Mazz.) Y.L.Chen | Impatiens delavayi var. subecalcarata Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 1700~3800 | Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing |
| 293 | Impatiens suichangensis Y.L.Xu & Y.L.Chen | √ | 1100~1600 | Zhejiang | |
| 294 | Impatiens suijiangensis S.H.Huang | √ | 800 | Yunnan | |
| 295 | Impatiens sulcata Wall. | Impatiens gigantea Edgew. Impatiens sulcata var. minor Hook.f. | 2700~4000 | Sichuan, Tibet | |
| 296 | Impatiens sunii S.H.Huang | √ | 900 | Yunnan | |
| 297 | Impatiens sutchuenensis Franch. ex Hook.f. | √ | 1000~1900 | Hubei, Shaanxi, Sichuan, Chongqing, Gansu | |
| 298 | Impatiens taishunensis Y.L.Chen & Y.L.Xu | √ | 100~523 | Zhejiang, Hubei, Hunan | |
| 299 | Impatiens tatoensis Gogoi & W.Adamowski | √ | 1800 | Tibet | |
| 300 | Impatiens tayemonii Hayata | √ | 1700~3000 | Taiwan | |
| 301 | Impatiens tenerrima Y.L.Chen | √ | 2800 | Sichuan | |
| 302 | Impatiens tenuibracteata Y.L.Chen | √ | 2100~2400 | Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 303 | Impatiens textorii Miq. | Impatiens atrosanguinea (Nakai) B.U.Oh & W.P.Hong Impatiens hypophylla var. koreana (Nakai) Nakai Impatiens japonica Franch. & Sav. Impatiens kojeensis Y.N.Lee Impatiens koreana Nakai Impatiens textorii var. atrosanguinea Nakai Impatiens textorii var. koreana (Nakai) Nakai Impatiens textorii f. minuscula Hayashi Impatiens textorii var. pallescens Honda Impatiens textorii f. pallescens (Honda) H.Hara | 1000~1350 | Jilin, Liaoning, Shandong, Zhejiang, Anhui | |
| 304 | Impatiens thiochroa Hand.-Mazz. | √ | 1790~3770 | Yunnan | |
| 305 | Impatiens thomsonii Hook.f. | 3700 | Tibet | ||
| 306 | Impatiens tianlinensis S.X.Yu & L.J.Zhang | √ | 300~1260 | Guangxi, Guizhou | |
| 307 | Impatiens tienchuanensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 1100~1400 | Sichuan | |
| 308 | Impatiens tienmushanica Y.L.Chen | √ | 500~1000 | Zhejiang | |
| 309 | Impatiens tienmushanica Y.L.Chen var. longicalcarata Y.L.Xu & Y.L.Chen | √ | 900~1000 | Zhejiang | |
| 310 | Impatiens tirbinensis Hareesh & M.Sabu | √ | 787 | Tibet | |
| 311 | Impatiens tomentella Hook.f. | √ | 500~3300 | Yunnan, Guangxi, Sichuan | |
| 312 | Impatiens tongbiguanensis S.Akiyama & H.Ohba | √ | 1000~1400 | Yunnan | |
| 313 | Impatiens tortisepala Hook.f. | √ | 1500~2900 | Sichuan | |
| 314 | Impatiens torulosa Hook.f. | √ | 3000~3330 | Sichuan | |
| 315 | Impatiens toxophora Hook.f. | √ | 1700~2400 | Sichuan | |
| 316 | Impatiens trichopoda Hook.f. | √ | 1900~2000 | Chongqing | |
| 317 | Impatiens trichosepala Y.L.Chen | √ | 500~1600 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 318 | Impatiens tricornis Lindl. | Balsamina tricornis (Lindl.) Ser. Impatiens praetermissa Hook.f. Impatiens punctata Wall. ex Hook.f. & Thomson | 2000~3100 | Tibet | |
| 319 | Impatiens trigonosepala Hook.f. | √ | 1200~1300 | Sichuan, Chongqing | |
| 320 | Impatiens tripetala Roxb. ex DC. | 627~1400 | Tibet, Yunnan | ||
| 321 | Impatiens tropaeolifolia Griff. ex Hook.f. | 1400 | Tibet | ||
| 322 | Impatiens tsangshanensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 2000~3460 | Yunnan | |
| 323 | Impatiens tuberculata Hook.f. & Thomson | 2800~3800 | Tibet | ||
| 324 | Impatiens tubulosa F.B.Forbes & Hemsl. | √ | 200~1390 | Guizhou, Hunan, Fujian, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Yunnan | |
| 325 | Impatiens uliginosa Franch. | √ | 200~2800 | Guizhou, Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 326 | Impatiens uncipetala C.B.Clarke ex Hook.f. | Impatiens yui S.H.Huang | 1800~2900 | Tibet, Yunnan | |
| 327 | Impatiens undulata Y.L.Chen & Y.Q.Lu | √ | 1300~2258 | Sichuan, Chongqing | |
| 328 | Impatiens unguiculata K.M.Liu & Y.Y.Cong | √ | 950~1100 | Tibet | |
| 329 | Impatiens uniflora Hayata | √ | 1350~3000 | Taiwan | |
| 330 | Impatiens urticifolia Wall. | 2300~3600 | Tibet | ||
| 331 | Impatiens vaniotiana H.Lév. | √ | 2500~3200 | Yunnan | |
| 332 | Impatiens verrucifer Hook.f. | 800 | Yunnan | ||
| 333 | Impatiens vittata Franch. | √ | 1500~2900 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 334 | Impatiens waldheimiana Hook.f. | √ | 2200~2500 | Sichuan, Zhejiang | |
| 335 | * Impatiens walleriana Hook.f. | Impatiens bruantii Pynaert Impatiens episcopi H.J.Veitch Impatiens holstii Engl. & Warb. Impatiens lujae De Wild. Impatiens petersiana Gilg ex Grignan Impatiens sultani Hook.f. | Taiwan | ||
| 336 | Impatiens walongensis Hareesh, M.Sabu & Borah | Impatiens arguta var. walongensis (Hareesh, M.Sabu & Borah) R.Kr.Singh & D.Borah | Tibet | ||
| 337 | Impatiens wawuensis Bo Ding & S.X.Yu | √ | 2300~2400 | Sichuan | |
| 338 | Impatiens weihsiensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 2300~3600 | Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 339 | Impatiens wilsonii Hook.f. | √ | 450~1800 | Guizhou, Sichuan, Chongqing, Guangdong, Hunan | |
| 340 | Impatiens wuchengyihii S.Akiyama, H.Ohba & S.K.Wu | √ | 700~2128 | Yunnan, Guangxi | |
| 341 | Impatiens wutaishanensis R.L.Liao & Lei Cai | √ | 1311~1650 | Yunnan | |
| 342 | Impatiens wuyiensis J.S.Wang, Y.F.Lu & X.F.Jin | √ | 420 | Fujian | |
| 343 | Impatiens wuyuanensis Y.L.Chen | √ | 200~500 | Jiangxi, Hunan, Anhui | |
| 344 | Impatiens xanthina H.F.Comber | 1200~2800 | Tibet, Yunnan, Sichuan | ||
| 345 | Impatiens xanthina H.F.Comber var. pusilla Y.L.Chen | √ | 1200~2500 | Yunnan | |
| 346 | Impatiens xanthinoides G.W.Hu. | √ | 939 | Yunnan | |
| 347 | Impatiens xanthocephala W.W.Smith | √ | 2900~3200 | Sichuan, Yunnan | |
| 348 | Impatiens xishuangbannaensis S.H.Huang | √ | 1200~1350 | Yunnan | |
| 349 | Impatiens yangshanensi A.Q.Dong & F.W.Xing | √ | 740~810 | Guangdong | |
| 350 | Impatiens yaojiapingensis Y.Y.Cong, G.W.Hu & T.Hu | √ | 2464 | Yunnan | |
| 351 | Impatiens yaoshanensis K.M.Liu & Y.Y.Cong | √ | 2000~2600 | Yunnan, Sichuan | |
| 352 | Impatiens yilingiana X.F.Jin | √ | 900~1000 | Zhejiang | |
| 353 | Impatiens yingjiangensis S.Akiyama & H.Ohba | √ | 800~1400 | Yunnan | |
| 354 | Impatiens yongshanensis S.H.Huang | √ | 2450 | Yunnan | |
| 355 | Impatiens yunlingensis S.X.Yu, Chang Y.Xia & J.H.Yu | √ | 2500 | Yunnan | |
| 356 | Impatiens yunnanensis Franch. | √ | 1500~2500 | Yunnan | |
| 357 | Impatiens zhaojueensis Q.Luo | √ | 2416 | Sichuan | |
| 358 | Impatiens zhuxiensis Q.L.Gan & X.W.Li | √ | 700~1500 | Hubei | |
| 359 | Impatiens zironiana Gogoi, Hareesh & W.Adamowski | √ | 1560 | Tibet | |
| 360 | Impatiens zixishanensis S.H.Huang | √ | 200~2000 | Yunnan |
* Not native to China.
References
- Grey-Wilson, C. Impatiens of Africa; CRC Press: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 1–235. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Yuan, Y.M.; Küpfer, P. Chromosomal evolution in Balsaminaceae, with cytological observations on 45 species from Southeast Asia. Caryologia 2003, 56, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.M.; Song, Y.; Geuten, K.; Rahelivololona, E.; Wohlhauser, S.; Fischer, E.; Smets, E.; Küpfer, P. Phylogeny and biogeography of Balsaminaceae inferred from ITS sequences. Taxon 2004, 53, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinica; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 1–219. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Akiyama, S.; Ohba, H. Balsaminaceae. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2008; Volume 12, pp. 43–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.X. Balsaminaceae of China; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 1–214. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.X.; Janssens, S.B.; Zhu, X.Y.; Lidén, M.; Gao, T.G.; Wang, W. Phylogeny of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae): Integrating molecular and morphological evidence into a new classification. Cladistics 2016, 32, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Plant Resources and New Distribution Records of Impatiens in Sichuan Province. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2011, 29, 207–212+217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.L. Study on the Flora and Phylogeny of Impatiens L. in South Weast Sichuan. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, R.P. Study on the Flora in Guizhou/southern Sichuanand Phylogenetic problems of Impatiens L. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.R.; Xing, Z.; Chen, Y.; Bianba, D.J. Research on Diversity of the Plants of Genus Impatiens and Its Application in Tibet. North. Hortic. 2016, 40, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, M.J.; Yuan, T.H.; Ren, L.Y.; Bai, X.X. Species Diversity and Geographic Distribution of Wild Impatiens in Guizhou Province. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occident. Sin. 2021, 41, 863–871. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, Y.Y. Study on the Flora and Phylogeny of Impatiens L. in Hengduan Mountains. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, Y.Y. Study on the Flora of Impatiens L. in the Gaoligong Mountains Region, Yunnan. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.R.; Sang, L.Q.; Xing, Z. A Survey of the Impatiens Resource and It’s Application to Landscape Architecture in Shergyla Mountain in Tibet. For. By-Prod. Spec. Chin. 2014, 6, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, T.; Wu, H.; Huang, H.Q.; Huang, M.J. Investigation and Analysis on Germplasm Resources of Impatiens L. in the Southwest of Guizhou. Adv. Ornam. Hortic. Chin. 2017, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Peng, S.; Peng, Y.C.; Cai, X.Z.; Cong, Y.Y. Impatiens tripetala (Balsaminaceae), a newrecord species of Impatiens from China. Plant Sci. J. 2020, 38, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.F.; Peng, S.; Tian, J.; Hu, G.W.; Wang, Q.F. New species and a newly recorded species of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) from Yunnan, China. Plant Sci. J. 2020, 38, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Ren, L.Y.; Huang, R.X.; Li, M.J.; Bai, X.X. Impatiens liupanshuiensis (Balsaminaceae), a new species from Guizhou, China. PhytoKeys 2022, 192, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, T.H.; Huang, R.X.; Li, M.J.; Bai, X.X. Impatiens bijieensis (Balsaminaceae), a new species from karst plateau in Guizhou, China. PhytoKeys 2022, 192, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Zhang, W.D.; Liu, Q.; Xu, W.B.; Nong, Y.; Gao, F.; Hao, L.D.; Yu, S.X. Impatiens glandulifera (Balsaminaceae), A Newly Naturalized Alien Species in China. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2023, 31, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, R.; Sherpa, N.; Rai, S. Wild Balsams of Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalaya a pictorial handbook. West Bengal: Botanical survey of India. In Directorate of Cinchona and Other Medicinal Plants; Naipunya Publication: Darjeeling, India, 2021; pp. 1–295. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Sun, H. Flowering Plants of Hengduan Mountains; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2021; pp. 484–502. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.H.; Li, M.J.; Ren, L.Y.; Huang, R.X.; Chen, Y.; Bai, X.X. A dataset on the diversity and geographical distributions of wild Impatiens in China. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Du, H.D.; Jin, X.H.; Ma, K.P. Species diversity and geographic distribution of wild Orchidaceae in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 179–188+1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, A.P.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Roberts, W.M.; Wilcove, D.S. Geographic Distribution of Endangered Species in the United States. Science 1997, 275, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.; Zamora, R.; Molina, J.R.; Vasquez, A.; Herrera, M.Á. Predictive modeling of microhabitats for endemic birds in South Chilean temperate forests using Maximum entropy (Maxent). Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.A. Quantitative Study on the Prediction of Potential Distribution Area and Temporal and Spatial Changes of Habitats of Thuja, an Endangered Plant. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.H.; Aleck Yang, T.Y.; Teng, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Yang, K.C.; Hsieh, C.F. Insights of the Latest Naturalized Flora of Taiwan: Change in the Past Eight Years. Taiwana 2020, 55, 139–159. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, S.; Ohba, H. Studies of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) of Nepal (1) Impatiens amplexicaulis Edgew. and I. chungtienensis Y. L. Chen. Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Ser. B Bot. 2015, 41, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, S.; Ohba, H. Studies of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) of Nepal 3. Impatiens scabrida and Allied Species. Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Ser. B 2016, 42, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, S. Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) of Nepal (2): Taxonomy of the Species of Sections Racemosae and Sulcatae. Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Ser. B 2021, 47, 193–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, S. Impatiens prainii (Balsaminaceae), a New Record for the Flora of Nepal and the Flora of Myanmar. J. Jpn. Bot. 2017, 92, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Gogoi, R.; Adamowski, W.; Sherpa, N.; Sharma, A.; Borah, S. Misinterpretations and plagiarism in a publication about Himalayan Impatiens: Polemics with the paper of Singh R.K. et al. 2021. Biodiv. Res. Conserv. 2021, 63, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, R.; Adamowski, W.; Sherpa, N.; Chhetri, G. On the taxonomic identity and lectotypification of Impatiens uncipetala C.B.Clarke ex Hook.f. Phytotaxa 2016, 273, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.X.; Yuan, T.H.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.J.; Bai, X.X. Five new synonyms for Impatiens procumbens (Balsaminaceae) in China. PhytoKeys 2023, 222, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchisansakun, S.; Suksathan, P.; van der Niet, T.; Smets, E.F.; Saw-Lwin; Janssens, S.B. Balsaminaceae of Myanmar. Blumea 2018, 63, 199–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksathan, P.; Ruchisansakun, S. Impatiens of Thailand; Natural History Publications: Borneo, Thailand, 2022; pp. 1–396. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Borah, D.; Taram, M. Typifications, new combinations and new synonyms in Indian Impatiens (Balsaminaceae). Biodiv. Res. Conserv. 2021, 61, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamczyk, S.; Steudel, B. Impatiens namchabarwensis is distinct from I. arguta. Nord. J. Bot. 2023, 2023, e03900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souvannakhoummane, K.; Newman, M.F.; Lanorsavanh, S.; Suksathan, P. Impatiens rostrata (Balsaminaceae), a new species from Khammouane province, Laos, and nine new records. Edinb. J. Bot. 2021, 78, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.X.; He, B.Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.J.; Bai, X.X. Impatiens cavaleriei (Balsaminaceae), a new species from the MiaolingMountains in Guizhou Province. Taiwania 2023, 68, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Yang, H.; Luo, Q. Four newly recorded species of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) from Sichuan Province, China. Guihaia 2019, 39, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.F.; Wu, H.Z.; Song, X.Q.; Zhou, Z.D. Species Diversity and the Relationship with Habitat Community Characteristics of Impatiens hainanensis, Endemic to Hainan Island. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2014, 35, 355–361. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y.; Lei, J.R.; Song, X.Q.; Zhou, Z.D. Modeling the potential suitable habitat of Impatiens hainanensis, a limestone-endemic plant. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2018, 42, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.F. Conservation Ecology of Impatiens hainanensis (Balsaminaceae), Endemic Species in Hainan Island. Ph.D. Thesis, Hainan University, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yang, M. The Biodiversity Monitoring and Sustainable Tourism Development of Mount Emei. Sichuan Environ. 2012, 31, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).