Abstract
Understanding how species richness changes along elevational gradients has attracted increasing attention from many researchers. The relationships between species richness and elevations were characterized by monotonic decreases or mid-elevational peaks. The western Sichuan Plateau is an important species diversity hotspot. However, there is little information available about the ant species diversity and distribution patterns of this region. In this study, we hypothesize that ant diversity will show a monotonic decrease from mid-elevation with increasing elevation. Here, the ant species diversity and distribution patterns of this region were investigated by plot surveys. A total of 22,645 ants were collected from eight elevational transects in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau, which were identified as belonging to 40 species, 18 genera, and 4 subfamilies. We found a unimodal relationship between elevation and ant species richness, with the highest ant species richness occurring at mid-elevations. The similarity coefficient of ant communities in each elevational transect was at a moderate level of dissimilarity, indicating that the elevation difference and habitat heterogeneity had a great impact on ant communities in the central and northern areas of the western Sichuan Plateau.
1. Introduction
Ants (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) nearly occur in all terrestrial ecosystems and have important ecological functions [1,2]. Some ants can improve the soil environment and soil fertility [3,4,5,6]; they also play an important role in dispersing seed [7,8] and biological control [9,10,11]. However, some ant species are pests of forests, agriculture, and households [12]. Ant diversity is usually regarded as an indicator of biodiversity and forest health [13,14].
Biodiversity conservation is an important aim of forest management [15,16,17]. An assessment of forest biodiversity is fundamental to ensuring the sustainability of ecosystem functions [18]. Bioindicators could be used to monitor ecosystem health. Ants are one of the most important representative insects for assessing biodiversity because they are sensitive and respond rapidly to environmental changes [14,19]. Therefore, understanding ant diversity and distribution patterns is helpful for evaluating changes in ecosystems and developing conservation priorities and policies [20,21].
The relationship between elevation and species richness has been used as a model [22] for investigating the response of biodiversity to environmental changes within a small geographic scale [23], which makes it easy to test hypotheses about patterns that may occur at a larger scale [24]. In recent years, understanding how ant species richness changes along elevational gradients has attracted increasing attention from global researchers [25]. In general, along elevational gradients, ant species richness exhibits a heterogeneous pattern. Two main patterns of biodiversity along elevational gradients have been identified: (1) a monotonous decrease with elevation [25,26]; and (2) a unimodal pattern with maximum diversity at middle elevation [27]. Although there have been many studies describing elevational ant diversity patterns [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38], a unanimous conclusion about patterns remains elusive. Therefore, further investigation is required in different regions, especially in previously unstudied areas. Furthermore, in view of the unparalleled importance of mountain ecosystems, exploring the ant distribution patterns and factors that generate and maintain biodiversity should provide valuable insights for conservation biologists.
China has 12 subfamilies, 117 genera, and 1026 species of ants [28]. In view of the unique geographical, climatic, and ecological diversity, many ant species are yet to be discovered, and their diversity and distribution patterns are still to be studied in the country. The western Sichuan Plateau is located between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Sichuan Basin, which is an important geographical transitional zone connecting the inland region and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [39]. This region is rich in vegetation types and has high forest cover. As a result, the western Sichuan Plateau is an ideal area for studying species diversity [40,41]. Although much is known about the faunal diversity of plants [42,43], there is little information about ant diversity and distribution patterns in this region.
The present study focuses on the ant diversity along elevational gradients in the western Sichuan Plateau and characterizes the ant distribution pattern by testing the following hypothesis: a unimodal pattern with maximum diversity at middle elevation. Our study will improve our knowledge of how ants in China are distributed along elevational gradients. Furthermore, our findings will reveal useful and relevant information for biodiversity monitoring and conservation planning.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sample Collection
The western Sichuan Plateau belongs to the plateau climate. Most areas have long winters, no summer, spring, or autumn connections, little precipitation, and concentration. The temperature difference between day and night is large, the sunshine is strong, and the sunshine is abundant. There is a complete climate distribution zone in the south of the western Sichuan Plateau from south to north, which is the south subtropical zone, the middle subtropical zone, the north subtropical zone, and the warm temperate zone, and the change in dry and wet seasons in the temperate zone is extremely obvious. Due to the complex geographical environment and obvious elevational height difference in this area, there are still abundant natural vegetation types [29].
In this study, a total of 8 elevational transects were set up in order of geographical location: northwest slope of Wogong Township (NWWGT), Dege County; northeast slope of Wogong Township (NEWGT), Dege County; southeast slope of Manigange Town (SEMGT), Dege County; northwest slope of Manigange Town (NWMGT), Dege County; northwest slope of Shangluokema Town (NWSLT), Luhuo County; southeast slope of Shangluokema Town (SESLT), Luhuo County; northwest slope of Miyaluo Town (NWMYT), Lixian County; and southeast slope of Miyaluo Town (SEMYT), Lixian County. In each elevational transect, one sample plot was set for every 250 m elevation, and the size of the sample plot is 50 m × 50 m, so there are 42 sample plots in total (Figure 1). Due to the complexity of terrain and the limitations of vegetation conditions, there will be some deviation when selecting specific sample plots, and the error range is usually controlled within 50 m. The survey situation of the study sample plot is shown in Table S1.
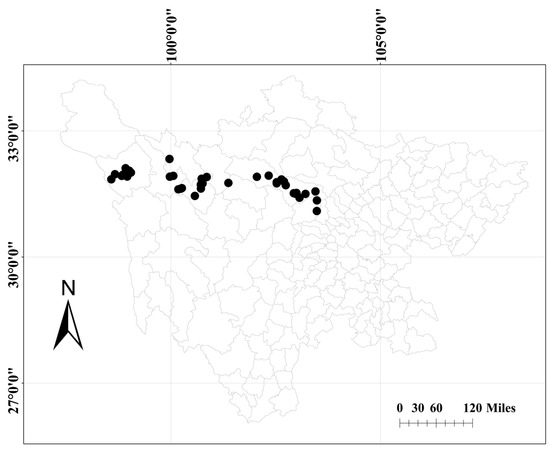
Figure 1.
The location of the study site in Sichuan Province, China. The black dots represent the collected sites in the western Sichuan Plateau.
2.2. Survey Method
Ants were investigated and collected by sample plot investigation and search methods [44]. For the selected sample plots, 5 quadrants with a size of 1 m × 1 m were selected by the diagonal sampling method, and the ground-active ants were collected and counted in the quadratic plots first. At each plot, three different sampling techniques (soil scoring, stick beating, and hand picking) were used to collect ants. The soil layer with a depth of 20 cm was excavated with a small hand pick. These soil cores were sifted using a hand sieve pan to collect ants. To sample ants on trees, bushes, etc., the stick beating method was used. Finally, ants were collected by hand picking (one person working for one hour) [45]. After finishing the above investigations, the information about the sample plot location, geographical location, elevation, vegetation type, investigated time, and collector was recorded, and then photos of the sample plot were taken. The collected ant specimens were stored in a 2 mL cryopreservation tube filled with absolute ethanol and brought back to the laboratory for classification and identification.
2.3. Ant Species Identification
According to the principle of the same nest, the same species, and the same morphology, the ant samples were classified, and the individuals in the same nest or the same species were numbered. In each specimen, less than 9 ant individuals were made into triangular paper dry specimens, and more than 9 ant individuals were put back into a cryopreservation tube filled with absolute ethanol for impregnation and preservation. According to the works and documents on ant taxonomy [44,46], the ant specimens were identified using the morphological taxonomy method. Finally, the ant specimen was carefully checked by an ant taxonomist, Professor Xu Zhenghui. Ant species were finally identified. Samples and voucher specimens were deposited in the Southwest Forestry University Herbarium.
2.4. Diversity Index
To compare the composition, species richness, and diversity of ant communities in different altitudinal gradients in elevational transects, EstimateS 9.1.0 software [47] was used to process the data [48]. The ant species diversity was measured by three main indexes: species richness, Shannon–Wiener diversity index, and Jaccard similarity coefficient [44,45]. At the same time, the iNEXT package in R [49] was used to draw the species sparsity and prediction curve based on the number of individuals [50]. The relationship between ant species richness and elevation was analyzed using logistic regression. The statistical analysis was performed using R v.4.0.0 [51].
To verify the adequacy of sampling in biodiversity and community surveys, species accumulation curves were used. The solid line of the cumulative curve represents the actual number of species and individuals, while the dotted line represents the estimated value of species and individuals. It is generally believed that when the dotted line tends to be flat, it indicates that the sampling is sufficient. The dashed lines of the eight elevational transects all show a strong rise and then tend to become flat, indicating that the sampling is sufficient for diversity analysis (Figure 2).
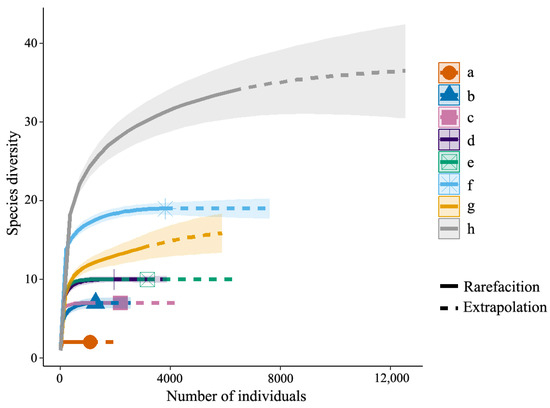
Figure 2.
Accumulation curves for the observed and estimated number of ant species in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau, China. a-h, respectively, represent eight elevational transects, which are the northwest slope of Wogong Township, Dege County; the northeast slope of Wogong Township, Dege County; the northwest slope of Manigange Town, Dege County; the southeast slope of Manigange Town, Dege County; the northwest slope of Shangluokema Town, Luhuo County; the southeast slope of Shangluokema Town, Luhuo County; the northwest slope of Miyaluo Town, Lixian County; and the southeast slope of Miyaluo Town, Lixian County.
2.5. Community Structure Analysis
According to the percentage of individual species in the community, it can be divided into five grades: (1) ≥10% is the dominant species, which is indicated by A; (2) 5.0~9.9% are common species, represented by B; (3) 1.0~4.9% are less common species, which are expressed by C; (4) 0.1~0.9% are rare species, which are expressed by D; (5) <0.1% is a very rare species represented by E [36].
3. Results
A total of 22,645 ant individuals were recorded and identified in 40 species from 18 genera representing four subfamilies (Table 1, Figure 3) in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau. Among them, two are dominant species, Formica sentschuensis Ruzsky and Myrmica kozlovi Ruzsky, accounting for 5% of the total species. Ectomomyrmex javanus Mayrita; Myrmica ritae Emery; Lordomyrma bhutanensis (Baroni Urbani); Temnothorax reticulatus (Chang and He); and Camponotus sp. are the rarest species (Table 1). The elevational pattern of ant species diversity distribution was unimodal, increasing from seven species at 1000 m to thirteen species at 2000 m and then decreasing to one species at 4500 m (Figure 4, Table S2). The most diverse elevational transect was the southeast slope of Miyaluo Town in Lixian County, followed by the southeast slope of Shangrokoma Town in Luhuo County. There were no species in the 3750 m alpine meadow and the 4530 m alpine meadow on the northwest slope of Wogong Township, Dege County (Table S3, Figure 4).

Table 1.
Ant community composition in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau.
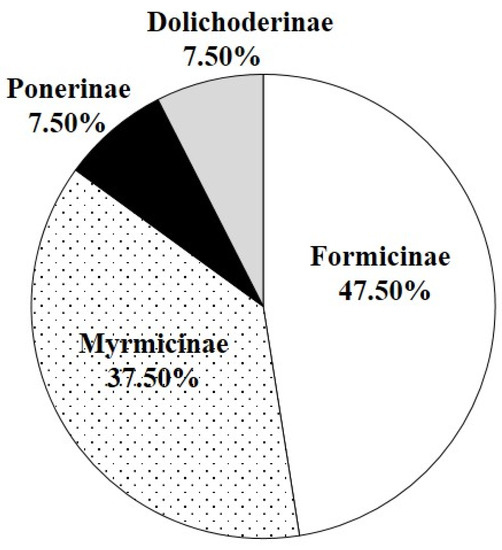
Figure 3.
Species-richness pattern of subfamilies in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau, China. The members of subfamilies are given as percentages of a total of 40 species occurrences.
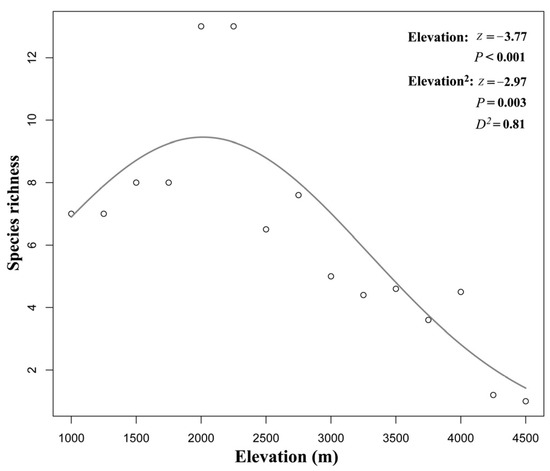
Figure 4.
The relationships between ant species richness and elevation for every 250 m elevation from 1000 m to 4500 m across 42 sampling plots in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau, China. The empty circles represent the means after the same elevation was averaged. The graph was visualized according to ant species richness. The fitted lines display the predicted probabilities of ant species as fit by logistic regression models.
The southeast slope of Miyaluo Town in Lixian County was the elevation belt with the highest diversity (8.62), while the northwest slope of Wogong Town in Dege County had the lowest diversity index of ant communities in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau (1.17) (Table S3).
The similarity between ant communities in the west and southeast slope of Miyaluo Town in Lixian County and the northwest slope of Wogong Township in Dege County is the lowest at a very dissimilar level (0.08). The similarity of ant communities between the northwest slope of Shangluokoma Town in Luhuo County and the southeast slope of Manigango Town in Dege County is the highest (1.00) (Figure S1, Table S4).
4. Discussion
A total of 22,645 ants were collected in 8 elevational transects in the north and central parts of the western Sichuan Plateau, which were identified as belonging to 4 subfamilies, 18 genera, and 40 species. The species richness in this area was lower than that in neighboring areas, such as eastern Daliangshan, Sichuan Province (135 species, 43 genera, 6 subfamilies) [52], central Daliangshan (44 genera, 115 species, 6 subfamilies) [53], western Daliangshan (37 genera, 95 species, 8 subfamilies) [54], Wang Lang Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province, and its neighboring areas (5 subfamilies, 37 genera, 77 species) [37].
The results of previous studies showed that ant species richness decreased as the elevation increased [25,38,55,56,57]. However, in the eight elevational transects of the central and northern Sichuan Plateau, this trend is not consistent. Our data would have supported the prediction that ant species richness decreases with increasing elevation if we had only sampled above 2000 m. However, we would have found the opposite trend if we had only sampled below 2000 m. This highlights the importance of quantifying geographical gradients and supports the idea that the mixed findings of previous studies might be attributable to their limited sampling scale [55,56,57]. There are in fact many studies on species, including studies on ants, that found unimodal relationships have been predicted based on several hypotheses [30,31,58,59,60], and such mid-elevation peaks are probably the rule rather than the exception. Such unimodal diversity and distribution patterns make it possible that abiotic variables that are associated with elevation, such as temperature, precipitation, ultraviolet radiation, and the soil’s physical and chemical properties, may influence ant species diversity [27,61,62,63]. We hope that the intriguing patterns revealed here might stimulate future studies to collect detailed abiotic data (including data on soil, light, and climate) and biotic data (including measurements of predators by both vertebrate animals and invertebrate insects) to shed light on the relative importance of different factors in shaping large-scale patterns in ant diversity and distribution patterns.
The similarity coefficients of ant communities in the eight elevational transects in the north and central parts of the western Sichuan plateau showed a moderate dissimilarity level; that is, different ant communities inhabited different elevational transects, and each elevational transect had different community characteristics. Among them, the northwest slope of Shangluokoma Town in Luhuo County and the southeast slope of Manigange Town in Dege County have similar elevation gradients, so they reach a very similar level. The difference between the west and southeast slopes of Miyaluo Town in Li County and the northwest slope of Wogong Township in Dege County is due to the great difference in elevation between elevational transects caused by the change in elevation ladder. In terms of habitats, most of the habitats in the north and central parts of the western Sichuan Plateau are coniferous forest, broad-leaved forest, mixed forest of coniferous and broad-leaved forest, and shrubs. The vegetation types are complex and diverse, and the typical geological environment and rich ecosystem types should make the overall species richness higher.
5. Conclusions
Our findings confirm the elevational pattern of ant diversity and distribution is unimodal, with mid-elevations having the highest ant diversity relative to lower and higher elevations in the central and northern parts of the western Sichuan Plateau. While the ant communities of some of the studied transects are very similar to each other, others are extremely dissimilar. A difference in ant diversity between different slopes was not found. The vegetation types are diverse in this region, and the typical geological environment and rich ecosystem types should make the overall species richness higher. Our study highlights the importance of quantifying geographical gradients and supports the idea that the mixed findings of previous studies may be attributable to their limited sampling scale.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15080935/s1, Figure S1: Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of ant community similarity from different elevational transects in the central and northern part of western Sichuan Plateau, China. Table S1: Sample plot situation of the ant community survey at the central and northern part of western Sichuan Plateau; Table S2: The mean of ant species richness were from every 250m increase in elevation across 42 sampled plots; Table S3: Main indices of ant communities in the central and northern part of western Sichuan Plateau; Table S4: Similarity coefficients among ant communities form elevational transects in the central and northern part of western Sichuan Plateau. The index was sorted by sampling order.
Author Contributions
X.-M.Z. and Z.-H.X. conceived the ideas for the study; Z.-Y.L., X.-M.Z., T.L., X.-D.Y. and J.-H.D. collected the data; Z.-Y.L. analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 32060122, 31760633, Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department Applied Basic Research Joint Special Funds of Agriculture, grant number 202101BD070001-057.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are presented in the manuscript and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the editors and reviewers for carefully reading this manuscript, and for all suggestions and comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Andersen, A.N. The use of ant communities to evaluate change in Australian terrestrial ecosystems: A review and a recipe. Proc. Ecol. Soc. Aust. 1990, 16, 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Guénard, B. An overview of the species and ecological diversity of ants. In eLS; JohnWiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Folgarait, P.J. Ant biodiversity and its relationship to ecosystem functioning: A review. Biodivers. Conserv. 1998, 7, 1221–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouz, J.; Jilková, V. The effect of ants on soil properties and processes (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol. News 2008, 11, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kovář, P.; Vojtíšek, P.; Zentsová, I. Ants as ecosystem engineers in natural restoration of human made habitats. J. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 6, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bolton, B. An Online Catalog of the Ants of the World [EB/OL]. 2021. Available online: http://www.antcat.org/ (accessed on 24 June 2023).
- Warren, R.J.; Giladi, I. Ant-mediated seed dispersal: A few ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) benefit many plants. Myrmecol. News 2014, 20, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Anjos, D.V.; Andersen, A.N.; Carvalho, R.L.; Sousa, R.M.; Del-Claro, K. Switching roles from antagonist to mutualist: A harvester ant as a key seed disperser of a myrmecochorous plant. Ecol. Entomol. 2020, 45, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.T. The Fauna of British India Including Ceylon and Burma. In Ants and Cuckoo Wasps; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1903; Volume 2, 237p. [Google Scholar]
- Offenberg, J.; Cuc, N.T.T.; Wiwatwitaya, D. The effectiveness of weaver ant (Oecophylla Smaragdina) biocontrol in Southeast Asian citrus and mango. Asian Myrmecol. 2013, 5, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wetterer, J.K. Geographic distribution of the weaver ant Oecophylla smaragdina. Asian Myrmecol. 2017, 9, e009004. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database; Invasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, S.S.; Wagner, M.R. Using ground foraging ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) functional groups as bioindicators of forest health in northern Arizona ponderosa pine forests. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, J.D.; Orabi, G.; Bisevac, L. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) pass the bioindicator scorecard. Myrmecol. News 2007, 10, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Margules, C.R.; Botkin, D.B. Indicators of biodiversity for ecologically sustainable forest management. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmayer, D.; Franklin, J.; Fischer, J. General management principles and a checklist of strategies to guide forest biodiversity conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 131, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junninen, K.; Penttilä, R.; Martikainen, P. Fallen retention aspen trees on clear-cuts can be important habitats for red-listed polypores: A case study in Finland. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.; Humphrey, J. A review of potential biodiversity indicators for application in British forests. Forestry 1999, 72, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, L.E. Ants as indicators of diversity. In Standard Methods for Measuring and Monitoring Biodiversity; Agosti, D., Majer, J.D., Alonso, L.E., Schultz, T.R., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, E.C.; Fisher, B.L. The role of ants in conservation monitoring: If, when, and how. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 132, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Guo, X.; Duan, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Xu, Z.H. Diversity of ants on the ground in different habitats in Yuanmou Arid-. Hot Valley, Yunnan. J. Fujian Coll. For. 2007, 27, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist, M.K.; Sanders, N.J.; Wardle, D.A. Community and Ecosystem Responses to Elevational Gradients: Processes, Mechanisms, and Insights for Global Change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2013, 44, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, T.R.; Robertson, M.P.; van Rensburg, B.J.; Parr, C.L. Elevation-diversity patterns through space and time: Ant communities of the Maloti-Drakensberg Mountains of southern Africa. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 2256–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, N.J.; Lessard, J.P.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Dunn, R.R. Temperature, but not productivity or geometry, predicts elevational diversity gradients in ants across spatial grains. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunene, C.; Foord, S.H.; Scharff, N.; Pape, T.; Malumbres-Olarte, J.; Munyai, T.C. Ant diversity declines with increasing elevation along the Udzungwa Mountains, Tanzania. Diversity 2022, 14, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhl, C.A.; Mohamed, V.; Linsenmair, K.E. Altitudinal distribution of leaf litter ants along a transect in primary forests on Mount Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia. J. Trop. Ecol. 1999, 15, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyai, T.C.; Foord, S.H. Ants on a mountain: Spatial, environmental and habitat associations along an altitudinal transect in a centre of endemism. J. Insect Conserv. 2012, 16, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Jiang, M.; Yang, G.L. Ant Illustrated Handbook of Gaoligong Mountain; Chinese Forestry Science Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 1–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, Z.M. A study on the ant fauna of Sichuan Province (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2002, 3, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Romdal, T.S.; Grytnes, J.A. An indirect area effect on elevational species patterns. Ecography 2007, 30, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grytnes, J.A.; Beaman, J.H.; Romdal, T.S.; Rahbek, C. The mid-domain effect matters: Simulation analyses of range-size distribution data from Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.N.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, C.L.; Liu, X.; Li, Q. Ant communities from East Slope of Mount Demola to Zayu Valley in Southeastern Tibet. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2012, 10, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Li, A.N. Ant species diversity of Mount Everest Section of the Himalaya Mountains. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2016, 36, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Z.H.; Yu, N.N.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhou, X.Y. Ant species diversity of Mount Galongla and Medog Valley in Southeastern Tibet. For. Res. 2017, 30, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Q.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, X.M.; He, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Ant species diversity of Southeastern Yunnan. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 41, 533–544. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Li, L.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Shi, S.H.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Z.F. Ant species diversity in northeastern Yunnan. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 3697–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.L.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhu, H.Q.; Yuan, D.Y.; Qi, B.; Ran, M.J. Altitudinal gradient of ant species diversity of Wanglang Nature Reserve and adjacent area in Sichuan Province. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 48, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilgado, J.D.; Rusterholz, H.P.; Braschler, B.; Zimmermann, S.; Chittaro, Y.; Baur, B. Six groups of ground-dwelling arthropods show different diversity responses along elevational gradients in the Swiss Alps. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.D.; Wang, F.J. A Study on the geological and landform tourism resources of the Western Sichuan Plateau. J. Leshan Teach. Coll. 2009, 24, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.J. Vertical distribution of insect species diversity in Planteau Forest of West Sichuan. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A & F University, Xianyang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.P.; Peng, Y.; Tian, H. A study of Eco-Climate Zoning for Ophiocordyceps sinensis in Westeern Sichuan Plateau. J. Southwest Univ. 2019, 41, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, P.H.; Peng, J.S.; Wang, C.S.; Hu, Z.Y.; Wang, J.X. The forest bio-diversity and its ecological function in the plateau area of Western Sichan. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 2003, 30, 436–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Yang, X.; Hao, L.N. Phenology of vegetation and its response to climate change in the Western Sichuan Plateau. J. Chang. River Sci. Res. Inst. 2023, 40, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H. A Study on the Biodiversity of Formicidae Ants of Xishuangbanna Nature Reserve; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H.; Li, J.G.; Fu, L.; Long, Q.Z. A study on the ant communities on West Slope at different elevation of the Gaoligongshan Mountain Nature Reserve in Yunnan, China. Zool. Res. 2001, 22, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.E.; Zhang, B.Y. Economic Entomology of China. In Hymenoptera: Formicidae (I); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1995; Volume 47. [Google Scholar]
- Colwell, R.K. EstimateS: Statistical Estimation of Species Richness and Shared Species from Samples. Version 9—User’s Guide and Application. 2019. Available online: http://purl.oclc.org/estimates (accessed on 27 May 2019).
- Li, Q. Species accumulation curves and its application. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2011, 48, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Ma, K.H.; Chao, A. Inext: An R package for rarefaction and extrapolation of species diveristy (Hill numbers). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, H.; Sharma, Y.P.; Bharti, M.; Pfeiffer, M. Ant species richness, endemicity and functional group, along an elevational gradient in the Himalayas. Asian Myrmecol. 2013, 5, 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: http://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Han, X.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, B.; Zhai, J. Ant Species Diversity of Eastern Daliangshan, Sichuan Province. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2021, 39, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Guo, N.Y.; Liu, X. Ant Species Diversity of Middle Daliangshan in Sichuan, China. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 40, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.C.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Huang, Z.; Xiong, Z.P. Ant Species diversity in the western of Daliangshan in Sichuan Province. J. Southwest For. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2020, 40, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotelli, N.J.; Ellison, A.M. Biogeography ant a regional scale: Determinants of ant species density in New England bogs and forests. Ecology 2002, 83, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspari, M.; Ward, P.S.; Yuan, M. Energy gradients and the geographic distribution of local ant diversity. Oecologia 2004, 140, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.W.; Chen, S.B.; Bi, M.J.; Chen, W.D.; Zhou, K.X. Relationships between geographic patterns of ant species richness and environmental factors in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7732–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sanders, N.J. Elevational gradients in ant species richness: Area, geometry, and Rapoport’s rule. Ecography 2002, 25, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.K.; Rahbek, C.; Gotelli, N.J. The mid-domain effect and species richness patterns: What have we learned so far? Am. Nat. 2004, 163, E1–E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.K.; Hemp, A.; Appelhans, T.; Behler, C.; Classen, A.; Detsch, F.; Ensslin, A.; Ferger, S.W.; Frederiksen, S.B.; Gebert, F.; et al. Predictors of elevational biodiversity gradients change from single taxa to the multi-taxa community level. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botes, A.; McGeoch, M.A.; Robertson, H.G.; Van Niekerk, A.; Davids, H.P.; Chownm, S.L. Ants, altitude and change in the northern Cape Floristic Region. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botes, A.; McGeoch, M.A.; Chown, S.L. Ground-dwelling beetle assemblages in the northern Cape Floristic Region: Patterns, correlates and implications. Austral. Ecol. 2007, 32, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcos, D.; Cerretti, P.; Mei, M.; Taglianti, A.V.; Paniccia, D.; Santoiemma, G.; De Biase, A.; Marini, L. Predator and parasitoid insects along elevational gradients: Role of temperature and habitat diversity. Oecologia 2018, 188, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).