Abstract
The natural populations of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and silage quality of pineapple residue silage were investigated in this study. A total of 34 LAB strains originally isolated from pineapple residue silage were characterized and identified by phenotypic and genotypic methods. These LAB strains were Gram-positive and catalase-negative bacteria, which were divided into four groups: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (52.9%), Levilactobacillus brevis (14.7%), Lacticaseibacillus paracasei (17.6%) and Leuconostoc citreum (14.7%). Lactiplantibacillus plantarum was the dominant species. Homofermentative strains accounted for 70.5%. After 30 days of ensiling, the pineapple residue silage could be well preserved with low pH value (3.65) and high content of lactic acid (75.57 g/kg of DM). In this study, LAB populations of pineapple residue silage fermentation were investigated, which indicated that pineapple residue silage was a potential good animal feed source. In addition, this result will be valuable for screening-appropriate inoculants aimed at improving the quality.
1. Introduction
Pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) residues mainly refer to the skin and residual pulp of pineapple after being made into juice, jam, canned fruit, preserved fruit or wine, and usually contain abundant minerals and fiber, accounting for about 50% to 60% of the total amount of fresh fruit [1]. However, most of them are deposed onto fields or used as compost, which is a waste of resources and their spoilage causes unpleasant odors and attracts insects, rodents, and other vermin. In recent years, these residues have received great attention, with the aim to develop value-added alternatives.
Pineapple residues can partly or completely replace the roughage portion in the diet and partly replace the cereals in the diet of livestock [2]. One of the challenges in utilizing these residues is their stabilization during storage, because they have a high level of moisture (80–95%) making them difficult to store, as they can easily perish. Currently, dry storage of fresh pineapple residue is the primary method to prevent decomposition. However, dry storage has several inherent disadvantages including costs associated with drying and climate and regional limitations [3].
Ensiling is a common method to preserve moist forages for livestock. It depends upon the production of sufficient organic acid to inhibit the activity of undesirable microorganisms under anaerobic conditions [4,5,6,7,8]. During the fermentation process, lactic acid bacteria (LAB) utilize water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) to produce lactic acid, the primary acid responsible for decreasing the pH in silage. It is well known that LAB play a major role in the natural ensiling process, so it is necessary to investigate the diversity of LAB in silage. Pang et al. [8,9] found that most of the characterized LAB in forage silages belonged to the genus Weissella. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is little research regarding the LAB composition associated with pineapple residue silage. Yang et al. found that strains of LAB isolated from fruit residues such as banana leaf and stem, pineapple peel and papaya peel belonged to the genera Lactiplantibacillus, Lactococcus, Weissella and Leuconostoc [2]. Other studies on pineapple residue silage had showed that pineapple residue silage had the best nutritional value after 4 weeks (28 d) of fermentation [10]. Gowda, et al. reported that the fungal count on the 15th day of ensiling was minimal (<3–4 colony forming units) and contained 6–7% lactic acid (DM basis) [1]. Acaína et al. found that using pineapple residue silage instead of elephant grass to feed lambs would not affect the growth of lambs [11].
Therefore, the objective of the present study was to screen, isolate and identify the LAB in pineapple residue silage. Isolates were identified at the molecular level using 16S rRNA sequence analysis and recA gene amplification product. In order to evaluate the relationship between natural populations of LAB and silage quality, the fermentation characteristics and chemical composition of silage samples were also studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of LAB from Pineapple Residue Silage
The pineapple residue (Ananas comosus L.) was sampled in a fruit-processing factory in Henan Province, China in May 2017. Silages were prepared using a small-scale system, and approximately 200 g pineapple residue was chopped into pieces of about 20 mm length and packed into plastic bags (N-9, Asahi Kasei Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), each group had 15 replicates. The bags were sealed with a Sharp Vacuum Seal/Package (SQ-202, Sharp Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), and the plastic bags were stored at room temperature.
Five bags for each the silage samples were collected at the 3rd, 7th and 30th day of ensiling process. Samples (10 g) were then blended with 90 mL sterilized water, and serially diluted from 10−1 to 10−5 in sterilized water. The number of LAB were measured by plate count on lactobacilli de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) [12] agar incubated at 30 °C for 48 h under anaerobic conditions (DG 250/min MACS; Don Whitley Science; London, England). Each LAB colony was isolated and purified twice by streaking on MRS agar plates. Pure cultures were grown on MRS agar at 30 °C for 24 h, and then the purified strains were stored at −80 °C in nutrient broth (Difco). Coliform bacteria were counted on blue light broth agar (Nissui-Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), incubated at 30 °C for 48 h. Molds and yeasts were counted on potato dextrose agar (Nissui), incubated at 30 °C for 24 h, and yeasts were distinguished from molds and other bacteria by colony appearance and the observation of cell morphology. Coliform bacteria and aerobic bacteria were counted on nutrient agar (Nissui), incubated at 30 °C for 24 h under aerobic conditions. Colonies were counted as viable numbers of microorganisms in colony-forming unit CFU/g of fresh matter (FM).
2.2. Morphological, Physiological and Biochemical Tests of LAB
Morphology and Gram-staining response was examined after 24 h of incubation on MRS agar. Catalase activity and gas production from glucose were determined via the Cai’s methods [5]. Growth at different temperature was observed in MRS broth after incubation at 5 and 10 °C for 14 d, and at 45 and 50 °C for 7 d. Growth at pH 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 5.0 and 8.0 was observed in MRS broth after incubation at 30 °C for 7 d. Salt tolerance of LAB was tested in MRS broth containing 3.0 and 6.5% NaCl at 30 °C for 48 h. Carbohydrate assimilation and fermentation of 49 compounds with 1 control were identified on API 50 CH strips (bioMerieux, Tokyo, Japan). API 50 CH is used in conjunction with API 50 CHL Medium (OT-50410) for the identification of LAB and related genera. The bacterial characteristics of 4 groups of strains were based on the carbohydrate fermentation map of the API 50 CHL database [13]. Lactococcus lactis strains were examined for their ability to produce c-aminobutyric acid and bile salt tolerance, as reported by Kim et al. [14] and Nomura et al. [15].
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and RecA Gene Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification
The strains grown at 30 °C for 24 h in MRS agar were used for 16S rRNA gene sequence. The coding region of 16S rRNA gene sequence was amplified by PCR thermal cycle. The sequences of the PCR products were determined directly with a sequencing kit using the prokaryotic 16S rRNA universal primers 27 F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′). Sequence similarity searches were performed using the DNA Database of Japan (DDBJ) and the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). The sequence information was then imported into the Clustal X 1.81 software program (Hitachi Software Engineering Co., Tokyo, Japan) for assembly and alignment. The 16S rRNA sequences of strains were compared with the sequences from type LAB strains held in the DDBJ. Nucleotide substitution rates (Kunc values) were calculated and phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method. Bacillus subtilis NCDO 1769T was used as an outgroup organism. The topologies of trees were evaluated using bootstrap analysis of the sequence data with Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis (MEGA) 7 software, based on 1000 random resampling. These sequences were aligned with the typical published sequences from DDBJ, GenBank and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL).
The recA multiplex-PCR assay was performed to distinguish the closely related species and subspecies of the Lactobacillus plantarum group [16].
2.4. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
The nucleotide sequences for the 16S rRNA gene described in this report were deposited with GenBank under accession number. AB969778, AB969779, AB969780 and AB969781 for the representative strains P15, P12, P22 and P24, respectively.
2.5. Chemical Composition and Fermentation Characteristics Analysis of Pineapple Residue Silage
After 30 days of ensiling, the silages were opened for the analysis of chemical composition and fermentation characteristics. The samples were dried in a forced-air drying oven at 65 °C for 48 h and ground to pass a 1 mm screen with a Wiley mill (ZM200, Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany). Dry matter (DM), crude protein (CP), ether extract (EE) and ash were analyzed according to AOAC Methods 934.01, 976.05, 920.39 and 942.05, respectively [17,18]. Wet silage (10 g) was homogenized with 90 mL sterilized distilled water. Then, the pH was measured with a glass electrode pH meter (pH 213; HANNA; Italy). The ammonia-N was determined by steam distillation of the filtrates [19]. The concentration of organic acid including lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (column: Shodex RS Pak KC-811; Showa Denko K.K., Kawasaki, Japan; detector: DAD, 210 nm, SPD-20A; Shimadzu Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan; eluent: 3 mmol L−1 HClO4, 10 mL min−1; temperature: 50 °C) [4].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All the data obtained in the present study were analyzed using One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) to determine the fermentation quality of pineapple residues andpineapple residue silage, and Tukey’s honestly significant difference test was conducted for post hoc analysis via IBM SPSS 24.0 software (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Statistically significant difference was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. The Microbial Composition, Chemical Component and Fermentation Characteristics of Pineapple Residue
The microbial composition, chemical components and fermentation characteristics of pineapple residue is shown in Table 1. In the fresh material, 103 CFU/g of FM LAB, 106 CFU/g of FM coliform bacteria, 107 CFU/g of FM yeasts and 103 CFU/g of FM molds were detected; the contents of organic matter (OM), CP and EE were 95.95%, 5.91% and 1.32% on DM basis, respectively; the lactic and acetic acids in fresh pineapple residue were 3.78 and 1.22 g/kg of DM, respectively.

Table 1.
The microbial composition, chemical component and quality of pineapple residue raw material and silage.
After 30 days of ensiling, LAB increased to 107 CFU/g of FM while yeasts decreased to 104 CFU/g of FM; coliform bacteria and molds were not detected. Compared to the fresh matter, pH value, DM and OM were lower (p < 0.05), and lactic and acetic acids were higher on the 30th day of ensiling.
3.2. The Morphological and Physiological Properties of Representative Strains Isolated from Pineapple Residue Silage
The morphological and physiological properties of representative strains isolated from pineapple residue silage are shown in Table 2. The 34 LAB strains were divided into 4 groups (A–D) according to growth temperature, salt tolerance, growth pH and carbohydrate fermentation method, and the number of strains in each group was group A (6 strains), group B (18 strains), group C (5 strains) and group D (5 strains). This analysis resulted in the delineation of four groups of isolates, each of which displayed a distinct carbohydrate fermentation pattern. All the isolates were Gram-positive and catalase-negative bacteria, which are unable to grow between 5 and 50 °C and able to grow between pH 4.0 to 8.0. The Groups A, B and C strains included rods that did not produce gas from glucose and could grow at pH 3.5 except for group C. The cocci-shaped strains in Group D were heterofermentative and unable to grow at pH 3.5. Strains A, B, C and D can grow in 3.0% NaCl. For the 6.5% NaCl, A and B can survive, while C and D cannot. Results of API 50 CH fermentation patterns showed that strains in group A and group C can use L-Arabinose, α-Methy1-D-glucoside, Melibiose, D-Raffinose, D-Turanose, Ribose, N-acety1 glucosamine, Salicine, Galactose and Trehalose, but cannot use Mannitol, Amygdaline, Esculine, Arbutine, Lactose, D-Tagatose and Gluconate, but in group C use Ribose, N-acety1 glucosamine, Salicine, Arbutine and Lactose, showing weak positivity; strains in group B can use Ribose, N-acety1 glucosamine, Salicine, Galactose, Trehalose, Mannitol, Amygdaline, Esculine, Arbutine and Lactose, but cannot use L-Arabinose, α-Methy1-D-glucoside, Melibiose, D-Raffinose, D-Turanose and D-Tagatose; strains in group D can use L-Arabinose, Ribose, Amygdaline and D-Tagatose.

Table 2.
The characteristics of isolated strains from pineapple residue silage.
3.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
Phylogenetic trees were shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. According to the phylogenetic analysis, the strain P12 from Group A was categorized in the Lacticaseibacillus paracasei cluster in a 100% bootstrap cluster. A representative strain in Group B, namely P15, clearly belonged to the genus Lactiplantibacillus (L.), because it was clustered in the L. plantarum branch, which included L. pentosus, L. plantarum, L. argentoratensis, L. paraplantarum and L. fabifermentans, on the phylogenetic tree (Figure 1). The strain P22 from Group C was closely related to the Levilactobacillus brevis with a bootstrap value of 100%. The strain P24 from Group D was categorized in the Leuconostoc (Ln.) cluster because it was grouped with Ln. citreum on the phylogenetic tree, and this grouping was supported with a bootstrap value of 98% (Figure 2).
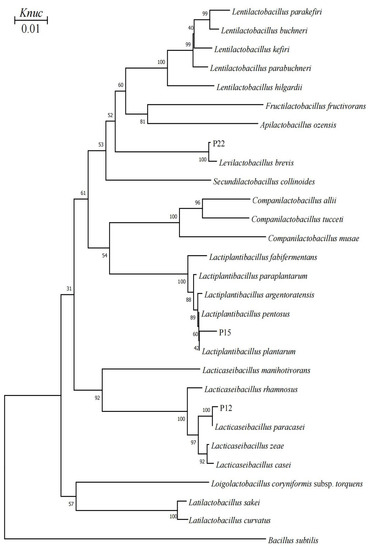
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree showing the relative positions of rod-shaped LAB strains isolated from pineapple residue silage by the neighbor-joining method of complete 16S rRNA sequences. Bootstrap values for 1000 replicates are shown at the nodes of the tree. Bacillus subtilis is used as an outgroup organism. The bar indicates 1% sequence divergence. Knuc = nucleotide substitution rate.
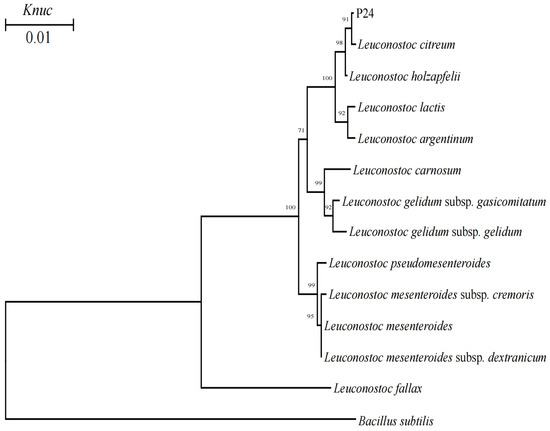
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree showing the relative positions of cocci-shaped LAB strains isolated from pineapple residue silage by the neighbor-joining method of complete 16S rRNA sequences. Bootstrap values for 1000 replicates are shown at the nodes of the tree. Bacillus subtilis is used as an outgroup organism. The bar indicates 1% sequence divergence. Knuc = nucleotide substitution rate.
3.4. Amplification Products Obtained from the recA Gene Multiplex Assay
The amplification products obtained from the recA gene are shown in Figure 3. Based on Bergey’s manual of Systematic Bacteriology, the amplification products shown in lanes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 are from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei JCM 16167T (negative control), L. paraplantarum JCM 12533T, L. pentosus JCM 1558T, L. plantarum JCM 1149T and L. argentoratensis JCM 16169T, respectively, and Lane 6 shows the PCR amplification product from strain P15. P15 and JCM 1149T had the same amplification product. Therefore, P15 was clearly identified as L. plantarum.
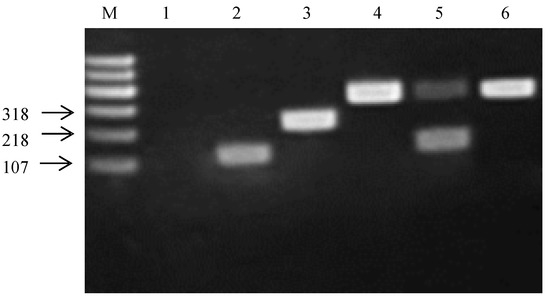
Figure 3.
Amplification products obtained from the recA multiplex assay. Lane M contained a 600 bp PLUS DNA ladder (Tiangen Biotech Co, Ltd., Beijing, China). Lanes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 contain PCR amplication products from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei JCM 16167T (negative control), L. paraplantarum JCM 12533T, L. pentosus JCM 1558T, L. plantarum JCM 1149T and L. argentoratensis JCM 16169T, respectively; Lane 6, PCR amplification product from P15.
4. Discussion
It is well established that LAB play a major role and can out-compete undesirable microorganisms, such as coliform bacteria in natural silage fermentation. Many studies have been conducted to investigate the natural population of LAB in forage and grass-based silages, and they have found that the quantity and species of LAB become a significant factor in predicting the adequacy of silage fermentation and the necessity to apply bacterial inoculants to silage materials [20]. Cai found that the number of LAB was generally low (less than 103) in forages and vegetables [5]. It has been reported that the residues of banana, pineapple and papaya presented relatively high numbers—103 to 105 (cfu/g of FM)—of LAB, and found that the main microbial groups on fruit residue were Lacticaseibacillus plantarum and Lacticaseibacillus casei, which played an important role in silage fermentation [2]. In this investigation, 40 strains isolated from pineapple residue silage were screened, of which 34 were considered as LAB determined by culture on MRS agar, Gram stain appearance, catalase test and lactic acid production from glucose. All the presumptive LAB were further characterized by sugar fermentation assays using API50 CH strips. This led to four groups of isolates, each displaying an obvious carbohydrate fermentation pattern. The various groups presumably represented three genera: Lactiplantibacillus, Levilactobacillus and Leuconostoc, which were the dominant counts of the LAB population in pineapple residue silage.
Sequencing of 16S rRNA has been successfully applied for the identification of bacteria at the species level [21]. The representative strains of groups A (P12), C (P22) and D (P24) were identified as Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, Levilactobacillus brevis and Ln. citreum. L. plantarum cluster members had similar 16S rRNA gene sequences with a difference of only 2 bp [21]. Because of the fundamental role of the recA gene, its gene product is considered to be a phylogenetic marker for distantly related species [22]. PCR analysis of recA gene products showed that the four strains were significantly different to group B strains. Strain P15 was a group B strain and had the same product (318 bp) as L. plantarum subsp. plantarum. Therefore, strain P15 can be identified as L. plantarum subsp. plantarum.
Following biochemical and phylogenetic analysis, the isolates of pineapple residue silage fell within well-recognized groups of LAB, and it was found that most of the characterized LAB belonged to Lactiplantibacillus and Leuconostoc. The species diversity was observed because four species were also identified: Lacticaseibacillus paracasei (17.6% of the total number of LAB isolates in this study), L. plantarum (52.9%), Levilactobacillus brevis (14.7%) and Leuconostoc citreum (14.7%). Furthermore, homofermentative species accounted for 70.6% of the total LAB community. Lactiplantibacillus and Leuconostoc were also found living in plant material and dairy products and several reports have declared that they dominate the microbial population in forage crops and grass silages, which is consistent with the results of our investigation, as well as those of other authors [23,24,25,26]. The most prevalent species in pineapple residue silage, L. plantarum, is reported to be the most dominant in the fermentation of forage crops and grass silages. As shown in Table 2, strains in group B (L. plantarum) had a relatively low pH (3.50) tolerance. For this reason, these strains could grow well in an anaerobic environment and produce more lactic acid even in pH values below 4.0, which was in accordance with the low pH value (3.65) of pineapple residue after 30 days of ensiling in present study. The heterofermentative Leuconostoc did not improve the fermentation characteristics and may cause organic matter loss [4]. In addition, the low frequencies (14.7%) of Leuconostoc found in the pineapple residue silage indicated that it did not play a key role in the ensiling process compared with L. plantarum. However, silage microbial screening is an effective way to obtain live lactic acid bacteria in silage based on MRS medium culture method [27,28]. Many microorganisms can survive on the surface of silage material, but cannot be cultured on selective medium, so there may be cognitive bias. With the development and application of high-throughput sequencing technology, it is possible to better understand the composition and dynamics of the microbial community during fermentation [29]. Therefore, the concept of using metagenomics or real-time high-throughput sequencing methods to explore the application effect of specific strains in this study on pineapple residue silage and its impact on the overall microbial community of pineapple residue silage fermentation is worthy of further study.
At 30 d of ensiling, the pineapple residue silage can be well preserved with a high content of lactic acid (75.57 g/kg of DM) and low pH value (3.65). That is probably due to the homofermentative LAB which were dominant in the pineapple residue silage and had a strong survival ability under relatively low pH conditions (Table 2). As we know, homofermentative LAB, such as Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, can produce almost exclusively lactic acid from fermentative sugars and reduce pH value quickly [30,31]. The reduction of molds, coliform bacteria and yeasts in the ensiling process was mainly related to the acidic and anaerobic environment conditions not suitable for their growth [32]. They still survived at the level of 104 CFU/g of FM when the pH value of the pineapple residue silage was 3.65. Pieper et al. [33] reported that fermentative activity of microorganism depended on the water available in the substrate and increasing moisture content could enable fermentation activity of microorganism. The water content of pineapple residues silage was much higher than that of usual silage (55–70%), which indicated the possibility of a high level of water activity. This might be the main reason why the yeasts were not strongly inhibited even under the conditions of higher lactic acid concentration and lower pH value [34,35]. During the ensiling fermentation process, yeast converts six-carbon sugar into ethanol, which is then oxidized to acetic acid. The high moisture content (beyond 85%) might contribute to the growth of yeasts even with low pH in our study. Therefore, the increase in acetic acid content also means the possibility of frequent yeast metabolism. In addition, the reduction of DM and OM contents compared to raw matter was probably due to yeasts fermenting soluble carbohydrate in the ensiling process. Concentrations of butyric acid from all the samples were not detected, which was indicative of well-preserved silages.
5. Conclusions
The pineapple residue can be well preserved with a low pH value and a high content of lactic acid in the ensiling process. In addition, the identification results revealed the LAB composition inhabiting pineapple residues and enabling the future design of appropriate inoculants aimed at improving the fermentation quality of silage.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and K.N.; methodology K.N.; software, Y.L., Z.D. and Y.X.; validation, Y.L., Z.D., Y.X. and N.W.; formal analysis, Y.L., N.W. and X.W.; investigation, Y.L., X.W. and X.Z.; data curation, Y.L., N.W. and X.W.; writing-original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing-review and editing, F.Y.; visualization, F.Y. and K.N.; supervision, F.Y. and K.N.; project administration, F.Y. and K.N.; funding acquisition, F.Y. and K.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1300302).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the first author. The data are not publicly available due to restrictions by the research group.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Mingyan Duan for help improving this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gowda, N.; Vallesha, N.C.; Awachat, V.B.; Anandan, S.; Pal, D.T.; Prasad, C.S. Study on evaluation of silage from pineapple (Ananas comosus) fruit residue as livestock feed. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2015, 47, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Tan, H.; Cai, Y. Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their effect on silage fermentation of fruit residues. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5325–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Yates, M.; Aung, H.; Cheng, Y.S.; Yu, C.; Guo, H.; Zhang, R.; Vandergheynst, J.; Jenkins, B.M. Influence of moisture content on microbial activity and silage quality during ensilage of food processing residues. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 34, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.M.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an Inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y. Identification and characterization of Enterococcus species isolated from forage crops and their influence on silage fermentation. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.W.; Zhao, T.; Li, J.P.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Z.Z.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y.G.; Yu, C.L.; Gao, X.H.; Wang, X.L. Identification of lactic acid bacteria and fermentation characteristics of mixed ensilages of corn stover and cabbage waste. Pratacultural Sci. 2015, 9, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Xu, C. Phylogenetic diversity of lactic acid bacteria associated with soybean curd residue silage as determined by 16S ribosomal DNA analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics & Computational Intelligence, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 15–17 August 2017; pp. 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Qin, G.; Tan, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Natural populations of lactic acid bacteria associated with silage fermentation as determined by phenotype, 16S ribosomal RNA and recA gene analysis. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qin, G.; Tan, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from corn stovers. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ge, Y.; Lan, R.; Fan, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Yin, F. Effect of fermentation time on the quality of pineapple residue silage. Pratacultural Sci. 2019, 6, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Acaína, K.S.E.; Kaliandra, S.A.; Luis, R.S.O.; Darley, O.C.; Daiany, I.G. Carcass yield, cuts and body components in lambs fed a pineapple by-product silage diet. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 12, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Man, J.; Rogosa, M.; Sharpe, M.E. A Medium for the Cultivation of Lactobacilli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1960, 23, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, N.A.; Berkeley, R.C.W. Identification of Bacillus Strains Using the API System. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1984, 130, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Ren, J.; Dunn, N.W. Differentiation of Lactococcus lactis subspecies lactis and subspecies cremoris strains by their adaptive response to stresses. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 171, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Kimoto, H.; Someya, Y.; Suzuki, I. Novel characteristic for distinguishing Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis from subsp. cremoris. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torriani, S.; Felis, G.E.; Dellaglio, F. Differentiation of Lactobacillus plantarum, L. pentosus, and L. paraplantarum by recA Gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3450–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.O.A.C. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemist: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarisalo, E.; Skyttä, E.; Haikara, A.; Jalava, T.; Jaakkola, S. Screening and selection of lactic acid bacteria strains suitable for ensiling grass. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Tan, Z.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, J.Y. Phenotypic and phylogenetic analysis of lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage crops and grasses in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohno, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Tajima, K.; Uegaki, R. Strain-dependent effects of inoculation of Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum on fermentation quality of paddy rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp. japonica) silage. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 337, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Tan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Qin, G.; Huo, Y.; Cai, Y. Identification and characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria isolated from Tibetan Qula cheese. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennahar, S.; Cai, Y.; Fujita, Y. Phylogenetic Diversity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Associated with Paddy Rice Silage as Determined by 16S Ribosomal DNA Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Haruta, S.; Wang, P.; Ishii, M.; Igarashi, Y.; Cui, Z. Diversity of a stable enrichment culture which is useful for silage inoculant and its succession in alfalfa silage. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 57, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tanganurat, W.; Quinquis, B.; Leelawatcharamas, V.; Bolotin, A. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Thai fermented fruits and vegetables. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 49, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, M.; Yu, Z. Lactic acid bacteria strains for enhancing the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of Leymus chinensis silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, F. Evaluation of lactic acid bacteria isolated from alfalfa for silage fermentation. Grassl. Sci. 2018, 64, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcallister, T.A.; Dunière, L.; Drouin, P.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Munns, K.; Zaheer, R. Silage review: Using molecular approaches to define the microbial ecology of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4060–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, F.S.; Elferink, S.; Wikselaar, P. Fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of grass silage inoculated with Lactobacillus buchneri, with or without homofermentative lactic acid bacteria. Grass Forage 2010, 57, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Muck, R.E.; Broderick, G.A.; Weimer, P.J. Lactobacillus plantarum effects on silage fermentation and in vitro microbial yield. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2013, 179, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, S.; Sun, Q. The effects of wilting and storage temperatures on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of stylo silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, R.; Hackl, W.; Korn, U.; Zeyner, A.; Souffrant, W.B.; Pieper, B. Effect of ensiling triticale, barley and wheat grains at different moisture content and addition of Lactobacillus plantarum (DSMZ 8866 and 8862) on fermentation characteristics and nutrient digestibility in pigs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2011, 164, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, H.D.; Dagher, S.F.; Bruno-Bárcena, J.M. Production and Conservation of Starter Cultures: From “Backslopping” to Controlled Fermentations. In How Fermented Foods Feed a Healthy Gut Microbiota; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peleg, M. A New Look at Models of the Combined Effect of Temperature, pH, Water Activity, or Other Factors on Microbial Growth Rate. Food Eng. Rev. 2021, 14, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).