Abstract
There are two pygoscelid penguins, the Gentoo (Pygoscelis papua Forster, 1781) and Adélie (P. adeliae Hombron and Jacquinot, 1841) penguins, breeding sympatrically on Ardley Island, Fildes Peninsula region, South Shetlands, Antarctica. Whether the two closely related penguin species with similar dietary habits possess compositional similarity in gut microbiota remains unknown. DNA barcoding of feces is an emerging approach for gut microbiota analysis of protected animals. In the present study, the 16S rRNA gene from penguin feces was sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq platform to investigate the gut microbiota of the two pygoscelid penguin species. The fecal community of Gentoo penguins has higher diversity indices and OTU (operational taxonomic unit) richness compared to Adélie penguins. Besides unclassified bacteria, sequences fell into 22 major lineages of the domain Bacteria: Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Armatimonadetes, Bacteroidetes, Chlamydiae, Chloroflexi, Cloacimonetes, Cyanobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus, Fibrobacteres, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Ignavibacteriae, Planctomycetes, Proteobacteria, Tenericutes, Verrucomicrobia, and candidate divisions BRC1, SR1, WPS-2, and Saccharibacteria. Among these, Firmicutes (37.7%), Proteobacteria (23.1%, mainly Gamma- and Betaproteobacteria), Fusobacteria (14.3%), Bacteroidetes (7.9%), and Actinobacteria (6.6%) were dominant in the fecal microbiota of the two penguin species. At the same time, significantly higher abundances of Actinobacteria and Cyanobacteria were detected in Gentoo penguins than in Adélie penguins (p < 0.05). Overall, there was a clear difference in the composition of gut microbiota between the Adélie and Gentoo penguins. The results suggested that both the phylogeny of penguin species and the diet could be responsible for the differences in the gut microbiota of the two pygoscelid penguins breeding in the same area.
1. Introduction
As important marine mesopredators and sensitive indicators of Antarctic ecosystem changes, penguins have become a major focus of long-term biological research in the Antarctic [1]. The Fildes Peninsula region located west of the Antarctic Peninsula, including the Fildes Peninsula and neighboring Ardley Island, is part of King George Island in the South Shetland Islands. This region is also part of the largest ice-free area in the maritime Antarctic region and is characterized by its comparatively high biodiversity due to higher mean temperature and precipitation compared to the continental region [2,3]. Ardley Island is well known for its high diversity of nesting seabirds and extensive plant cover. There are three congeneric penguin species, the Adélie (Pygoscelis adeliae Hombron and Jacquinot, 1841), Chinstrap (P. antarctica Forster, 1781), and Gentoo (P. papua Forster, 1781) penguins breeding sympatrically on the island. However, an increase in the numbers of Gentoo penguins and a decrease in the Adélie and Chinstrap penguin populations were observed on Ardley Island between 1970 and 2010 [3]. At present, breeding Chinstrap penguins are rarely found on the island.
The gut microbiota influences the health and physiology of vertebrate hosts [4,5]. For example, the presence of butyrate-producing microbes (e.g., Fusobacteria and Clostridia) in the gastrointestinal tract of the Little penguin (Eudyptula minor Forster, 1781) and King penguin (Aptenodytes patagonicus Miller, 1778) influences host adiposity levels prior to molting [4]. At the same time, previous studies have reported that there are large differences in bacterial community composition among the congeneric Chinstrap, Adélie and Gentoo penguins, even though their diets are relatively similar [6,7]. However, information on the gut microbiota of congeneric pygoscelid penguins breeding in the same area remains limited. Pygoscelid penguins breeding on Ardley Island provide an ideal opportunity to compare the gut microbiota between closely related penguin species with similar dietary habits. We investigated whether there exist clear differences in gut microbiota composition between the Adélie and Gentoo penguins breeding sympatrically on Ardley Island.
Over the years, advances in molecular techniques have enabled fecal DNA analysis with a non-invasive sampling strategy to be used for research on the gut microbiota of endangered but rarely encountered animal species, especially when the fieldwork takes place in wild and uninhabited areas [8]. Researchers have applied DNA-based fecal methods to investigate the gut microbiota of penguins in Antarctica, including Adélie, Chinstrap, Gentoo, and King penguins [4,6,7,9,10,11]. The aim of this research was to investigate the bacterial communities in the feces of the closely related Adélie and Gentoo penguins breeding on Ardley Island to characterize the gut microbiota of the two pygoscelid species. Our main hypothesis was that there should be a difference in gut microbiota composition between Adélie and Gentoo penguins even with similar dietary habits because being different species they could have slightly different physiology and immune systems that affect their microbiome. Fecal DNA analyses were thus conducted in this study by sequencing the 16S rRNA gene.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Fecal samples were collected on land from adult Gentoo (P. papua; n = 32) and Adélie (P. adeliae; n = 8) penguins breeding on the northeastern side of Ardley Island (62°12′36″–62°12′58″ S, 58°54′56″–58°55′48″ W; Figure 1), South Shetland Islands, Antarctica in January 2019. All fieldwork was carried out under a permit issued by the Chinese Arctic and Antarctic Administration and was strictly in accordance with the relevant articles and clauses of the Antarctic Treaty and the Protocol in Madrid and its Annexes. Fecal samples were preserved by freezing at −80 °C until use in DNA extraction.
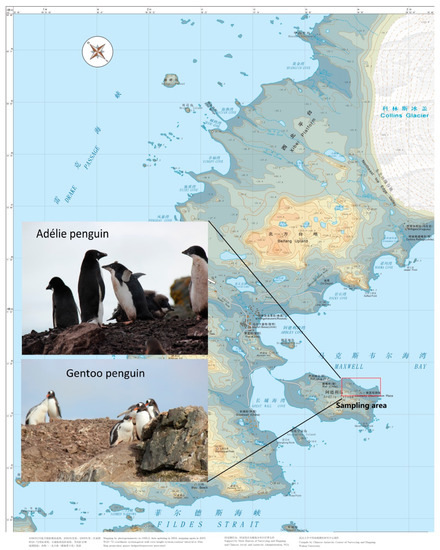
Figure 1.
Map of the sampling area on the northeastern side of Ardley Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, where sampling was performed in January 2019. Photos were taken by Yin-Xin Zeng.
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
DNA was extracted from 200 mg of feces using an E.Z.N.A Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit (OMEGA, Norcross, GA, USA) following the manufacturer’s standard protocol. Extracted DNA was visualized in 1.0% agarose gels stained with 4S Red plus Nucleic Acid Stain (Sangon, Shanghai, China) to check the integrity of the DNA. The DNA concentration was determined using a Qubit 3.0 fluorometer (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Extracted DNA concentrations were between 0.84 and 120 ng μL−1.
The V4–V5 region of bacterial 16S rRNA genes was amplified using the universal primers 515F-Y (5′-GTGYCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA) and 926R (5′-CCGYCAATTYMTTTRAGTTT) [12] with a T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) as described previously [13].
The PCR products were assessed via electrophoresis in 2% (w/v) agarose gels stained with 4S Red Plus Nucleic Acid Stain and visualized under UV light, and then purified with MagicPure Size Selection DNA Beads (Transgen, Beijing, China). The recovered DNA concentration was accurately determined using a Qubit 3.0 fluorometer prior to analysis using a MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) at a read length of 2 × 300 bp for sequencing at Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The DNA content of each sample was 10 ng when mixed equally. Raw sequence data are available from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under accession number SRP288016.
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
The sequence data were processed to trim the reads with Qphred scores below 20 using Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology (QIIME; [14]). Adapters were removed using Cutadapt v1.18. Trimmed paired-end reads were merged with a maximum mismatch rate of 1 mismatch in 10 bases using Pear v0.9.8. Then, reads were demultiplexed based on barcode sequences using an in-house Perl script and assigned to their respective fecal samples. The quality filtering was performed using Prinseq v0.20.4 to remove barcode sequences, primer sequences, homopolymers longer than 8 bp, and sequences less than 200 bp showing an ambiguous base “N” or with average base quality scores less than 20. Chimeric sequences were detected and removed from the dataset using the USEARCH tool with the UCHIME algorithm [15]. Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) were clustered with a 97% similarity cutoff using USEARCH v11.0.667. The 16S rRNA gene sequences were classified against the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) dataset with a confidence level cutoff of 80% [16]. Sequences flagged as chloroplasts and archaea were excluded from bacterial community analysis.
Alpha diversity analysis to determine species diversity and richness was performed via calculation of the ACE, Chao, Shannon, Simpson, Fisher’s alpha, and Coverage indices as well as through rarefaction analysis. The analyses were conducted using Mothur v1.43.0 after removing singleton OTUs (OTUs containing only one read) to assess how well the recovered communities represented the total community. Beta diversity applied Bray-Curtis distances using the R package phyloseq v1.30.0 and Principal Coordinates Analyses (PCoA) using the R package vegan 2.5–6 to visually evaluate the overall difference and similarity of bacterial communities between the two pygoscelid penguin species. Hierarchical clustering for fecal samples was performed using the hclust function in R, and the resulting Newick-formatted tree was constructed using the R package ape v5.3. A permutational multivariate analysis of variance (Permanova) was used to test for group differences. Differential abundance analysis of fecal microbiota between Adélie and Gentoo penguin groups was performed via Welch’s t-test in Stamp v2.1.3 using a compositional analysis approach with standard transformation, and p-values were corrected through Storey’s false discovery rate (FDR) control. An FDR q < 0.1 was considered statistically significant. LDA (linear discriminant analysis) effect size (LEfSe) analysis was utilized to identify bacterial taxa with significantly different abundance between the two penguin groups based on LEfSe software v1.1.0. The threshold for the logarithmic LDA score was 3.0. For all analyses, p values of 0.05 or less were considered to be statistically significant. The microbe–microbe correlation was calculated with SparCC v1.0.0 based on the relative abundance of bacterial OTUs. The correlation and p-value matrices were imported to R and visualized with the package corrplot v0.84. Only correlations >0.6 that were statistically significant were included in the correlation analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis
The 16S rRNA gene sequence was used to compare the bacterial community composition of Adélie penguin feces with that of Gentoo penguins. A total of 2,009,520 (on average 50,238 ± 12,606.22) clean reads were obtained from 40 fecal samples of the two pygoscelid penguin species. The average read length was 376 bp. After removing the sequences affiliated with archaea and chloroplasts, the total number of clean reads decreased to 1,911,933 (on average 47,798.33 ± 11,422.9; Table 1). Good’s coverage estimate in each sample was >99%. These results were consistent with rarefaction curve analyses (Figure S1), which indicated that overall sequencing depth was sufficient to saturate the recovery of bacterial diversity in fecal samples.

Table 1.
Comparison of phylotype coverage, richness, and diversity indices of the 16S rRNA gene library obtained from sequencing analysis of penguin feces.
The reads in the 40 fecal samples could be classified into 1038 OTUs (Figure 2A). There were 541 OTUs shared between the two penguin species, accounting for 98.7% and 52.4% of the total OTUs in Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively. Seven and 490 OTUs were unique to Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively. Overall, the number of OTUs for 16S rRNA gene libraries was higher in Gentoo penguins than in Adélie penguins with a statistically significant difference (p = 0.0006; Figure 2B). This result was consistent with Chao 1 indices indicating that Gentoo penguins had higher species richness than Adélie penguins. The Shannon and Fisher’s alpha diversity indices of 16S rRNA gene libraries were also higher in Gentoo penguins than in Adélie penguins (Table 1) but showed no statistically significant difference (p > 0.05). The results indicated that the overall diversity of gut microbiota was higher in Gentoo penguins than in Adélie penguins.
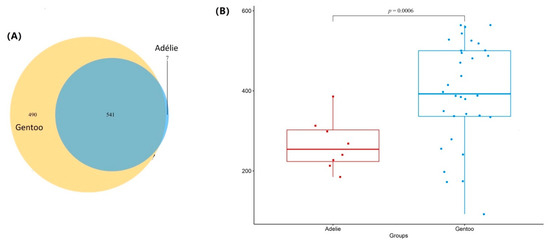
Figure 2.
Lower phylogenetic diversity in the Adélie group relative to the Gentoo group. (A) Venn diagram showing shared and unique OTUs at 97% sequence identity of the 16S rRNA gene in the two pygoscelid penguin groups. (B) Student’s t-test of OTUs showing that the Adélie group was characterized by lower OTU abundance relative to the Gentoo group.
3.2. Bacterial Community Composition in Fecal Micobiota
Besides taxonomically unaffiliated bacteria, 22 bacterial phyla, Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Armatimonadetes, Bacteroidetes, BRC1, WPS-2, Candidatus Saccharibacteria, Chlamydiae, Chloroflexi, Cloacimonetes, Cyanobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus, Fibrobacteres, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Ignavibacteriae, Planctomycetes, Proteobacteria, SR1, Tenericutes and Verrucomicrobia were detected. Bacterial taxa exhibiting a relative abundance greater than 1% of the total sequences at various taxonomic levels were designated as dominant. Firmicutes (37.7% of the total reads), Proteobacteria (23.1%, mainly Gamma- and Betaproteobacteria), Fusobacteria (14.3%), Bacteroidetes (7.9%), and Actinobacteria (6.6%) were dominant in fecal micobiota of the two penguin species (Figure 3A). Compared to being rare (0.2%) in Adélie penguins, sequences affiliated with Cyanobacteria were dominant (6.8%) in Gentoo penguins, revealing a difference in bacterial community composition between the Adélie and Gentoo penguins (Figure 3B).
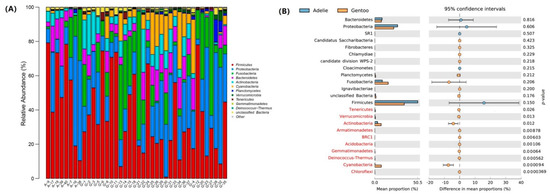
Figure 3.
Bacterial community composition in pygoscelid penguin feces. (A) Distribution of bacterial taxa at the phylum level in penguin feces. “Other” indicates the sum of phyla that represented less than 1% of the total bacterial sequences in the feces. (B) Difference in bacterial abundance in fecal microbiota at the phylum level between Adélie and Gentoo groups. Mean proportions are shown in stacks for Adélie (blue) and Gentoo (orange) groups. Phyla in red indicate statistically significant differences (p ≤ 0.05).
Overall, Bacilli (represented by an unclassified Carnobacteriaceae group and an unclassified Bacillaceae 2 group), Clostridia (represented by an unclassified Clostridiales group and an unclassified Clostridiales Incertae Sedis XI), and Erysipelotrichia (represented by the genus Erysipelothrix) within the phylum Firmicutes, Gammaproteobacteria (represented by the genus Psychrobacter) within the Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidia (represented by an unclassified Porphyromonadaceae group) within the Bacteroidetes were more abundant in Adélie penguins (81.2% of the total reads) than in Gentoo penguins (48.3%) at the class level (Figure S2). In contrast, Alpha- (represented by the family Rhodobacteraceae) and Betaproteobacteria (represented by the genus Rhodoferax and an unclassified Comamonadaceae group) within the Proteobacteria, Fusobacteriia (represented by genera Cetobacterium and Fusobacterium) within the Fusobacteria, Flavobacteriia (represented by the family Flavobacteriaceae) and Sphingobacteriia (represented by an unclassified Chitinophagaceae group) within the Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria (represented by unclassified Intrasporangiaceae, Micrococcineae and Propionibacteriaceae groups) and Cyanobacteria were more abundant in Gentoo penguins (44.8%) than in Adélie penguins (15.6%).
At the genus level, sequences affiliated with the genus Peptostreptococcus and an unclassified Lachnospiraceae group within the class Clostridia as well as an unclassified Xanthomonadaceae group within the Gammaproteobacteria were also much more abundant in Gentoo penguins (10.5% in total) than in Adélie penguins (0.5%). As for sequences affiliated with the genera Clostridium XI, Clostridium sensu stricto and Tissierella within the Clostridiales, and Pasteurella within the Gammaproteobacteria, these were abundant in both pygoscelid penguin groups, together accounting for 22.5% and 19.4% in Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively.
3.3. Differences in Gut Microbiota between Adélie and Gentoo Penguin Groups
PCoA based on Bray-Curtis distances was used to evaluate compositional differences among bacterial communities. Overall, the bacterial composition was significantly different between the Adélie and Gentoo penguin groups, as confirmed by the Permanova test (p = 0.001) (Figure 4A), indicating a significant difference in gut microbiota composition between Adélie and Gentoo penguins. At the same time, similar bacterial community compositions were also observed between some Adélie and Gentoo penguin fecal samples. For example, Adélie penguin fecal sample A-9 showed similar gut microbiota to Gentoo penguin sample G-11 (Figure 4B).
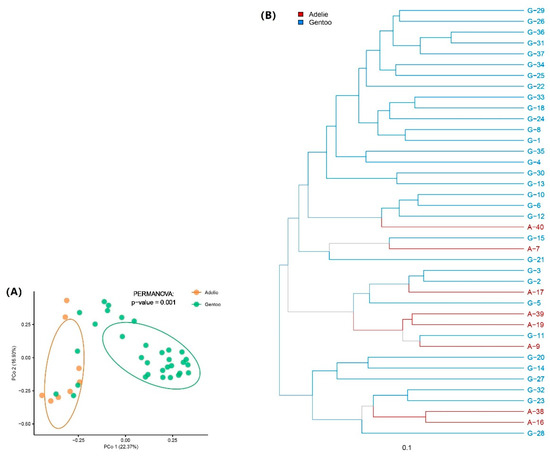
Figure 4.
Difference and similarity of bacterial communities between the two pygoscelid penguin groups. (A) Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of bacterial community composition in feces at the OTU level according to Bray-Curtis distance. (B) Hierarchical clustering of bacterial community composition in feces at the OTU level according to Bray-Curtis distance.
Differential abundance analysis of fecal microbiota between Adélie and Gentoo penguin groups revealed that among the dominant bacterial phyla, Actinobacteria exhibited a statistically significant difference in relative abundance (Figure 3B). In addition, as described above, the relative abundance of Cyanobacteria in the Gentoo group was also significantly different from that of the Adélie group. Among the dominant bacterial groups at the genus level, an unclassified Cyanobacteria group and the genus Peptostreptococcus within the Firmicutes were much more abundant in the Gentoo group (p < 0.01). These results were consistent with the LEfSe analysis (Figure S2).
4. Discussion
Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria are the most consistently observed bacterial phyla across the animal gut microbiota [5]. The composition of the Adélie penguin fecal microbiota in the present study displayed high proportions of Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria, similar to the gut microbiota of Adélie penguins breeding on the Victoria Land coast of the Ross Sea [9] and the Western Shore of Admiralty Bay at King George Island [11]. However, different from those studies, Fusobacteria was found to be abundant in both Adélie and Gentoo penguins in this study. A rich community of Fusobacteria has frequently been observed in the guts of carnivorous and omnivorous avian species [5]. Pygoscelid penguins primarily feed on krill (Euphasia superba Dana, 1852) and fish. Besides Fusobacteria, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria dominated in Gentoo penguins, in accordance with previous reports [7,10]. At the same time, in contrast to those studies [7,10], high abundances of Cyanobacteria (6.8%) and Planctomycetes (1.2%) were observed in Gentoo penguins in this study. It should be noted that fecal samples in this study were collected at different times due to the difficulties associated with Antarctic fieldwork, suggesting that the temporal variability of the gut microbiota composition and how it varies with diet should be explored in the future.
4.1. Firmicutes and Fusobacteria
Members of the Firmicutes are associated with host adiposity by enhancing energy extraction and through modulation of genes regulating fat storage [17,18,19]. In this study, Firmicutes was the most abundant phylum in both Adélie and Gentoo penguins. In addition, Fusobacteria was the third most abundant phylum in Adélie and Gentoo penguins. The microbiota of both Adélie and Gentoo penguins was dominated by the classes Clostridia (41.9% and 32.8% of total reads, respectively) and Fusobacteriia (9.8% and 16.8%, respectively), which are potential butyrate producers [20,21]. Butyrate in poultry has been shown to not only boost the immune system and protect against colonization by pathogenic bacteria but also can influence host adiposity [22]. The fecal samples in this study were collected in the austral summer (January), the time for rearing of young when the penguins on Ardley Island begin to molt. Therefore, the high abundance of Clostridia and Fusobacteriia suggests that the penguins build up large reserves of fat prior to molting.
Bacteria belonging to the family Peptostreptococcaceae within the Clostridia were dominant in the penguin feces, accounting for 9.4% and 17.3% of the total 16S rRNA gene sequences in Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively. In addition, the family Erysipelotrichaceae (represented by the genus Erysipelothrix) within the Erysipelotrichia comprised 1.6% and 0.4% of the total 16S rRNA gene sequences in Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively. All members of the families Peptostreptococcaceae and Erysipelotrichaceae are anaerobes with fermentative type metabolism [23,24], suggesting that these bacteria are presumably of penguin intestinal origin [11]. The family Lachnospiraceae was rare in the Adélie group (0.1%) but abundant in the Gentoo group (3.2%) (p < 0.02). Relative abundance of this family in the fecal microbiota of Gentoo and Chinstrap penguins increased significantly from the feeding to molting stage, suggesting that the growth of Lachnospiraceae could be positively affected by the limitation of food supply [7]. It should be mentioned here that the analysis of compositional data by traditional methods used in this study can appear to give satisfactory results. However, these results may be misleading and unpredictable [25]. Further study should be performed to compare the results based on standard transformation and ratio transformation.
The genus Clostridium XI within the family Peptostreptococcaceae was abundant in both pygoscelid penguin groups (9.0% and 10.1% in Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively). It has been suggested that a high intake of carbohydrates, fat, and protein is associated with increasing amounts of Clostridium XI bacteria in the feces of humans and mice [26,27]. The genus Clostridium (i.e., Clostridium sensu stricto) represented 6.7% and 5.4% in Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively. Dewar et al. [4] documented that the Clostridia (represented by the genus Clostridium) was dominant in the gastrointestinal tract of King penguins and could be associated with host adiposity level. In addition, members of the genus Clostridium have been identified as having the ability to degrade chitin [28], a main component of Antarctic krill. Clostridium-related sequences are frequently detected in the stomach microbiota of Adélie and Chinstrap penguins on Signy Island [29], where penguins feed almost exclusively on Antarctic krill. There was a positive correlation between the genera Clostridium XI and Clostridium across study samples (SparCC R > 0.75, p < 0.01; Figure S3). The genus Peptostreptococcus within the same family was much more abundant (7.5%) in Gentoo penguins than in Adélie penguins (0.3%) (p < 0.01). This genus was also abundant in the fecal microbiota of Gentoo penguins during the feeding stage in Barton Peninsula on King George Island [7]. Sequences belonging to this genus have been detected in the stomach microbiota of Chinstrap penguins but were absent in Adélie penguins [29]. Members of the Peptostreptococcus can increase colon dysplasia [30] or have protective effects on colitis [31] in animals. Cellulose and amylose degrading and amino acid fermenting bacteria such as Clostridium and Peptostreptococcus are indicator taxa of the fast-growing rainbow trout [32]. Compared to Adélie penguins, Gentoo penguins have a larger percentage of fish in their diet [33]. Whether the higher abundance of Peptostreptococcus in Gentoo than in Adélie penguins indicates a difference in diet composition between the two pygoscelid penguins requires further research. In contrast to the positive correlation between the genera Clostridium XI and Peptostreptococcus in the Gentoo group (SparCC R = 0.61, p < 0.01), a negative correlation between the two genera (SparCC R = −0.74, p = 0.03) was observed in the Adélie group, suggesting different physiological functions of these bacteria in the gut environment between the two pygoscelid penguins.
Although being a minor part of the fecal microbiota of the two pygoscelid penguins, more Desulfonispora within the family Peptococcaceae 1 were detected in Adélie penguins (0.82%) than in Gentoo penguins (0.06%) (p = 0.03). Being strictly anaerobic, Desulfonispora specializes in taurine fermentation and synthesizes thiosulfate from sulfite [34]. In the Adélie group, the Desulfonispora showed negative correlations with genera Fusobacterium (class Fusobacteriia), Sutterella (class Betaproteobacteria), and Psychrobacter (class Gammaproteobacteria) (SparCC R < −0.80, p ≤ 0.02) but exhibited positive correlations with Firmicutes members (e.g., genera Erysipelothrix and Sporosarcina) and an unclassified Propionibacteriaceae within the Actinobacteria (SparCC R > 0.72, p ≤ 0.05).
Erysipelothrix spp. have a worldwide distribution and can infect a variety of hosts including mammals, fish, birds, reptiles, and insects [35]. In contrast to this study showing abundant Erysipelothrix (1.6%) in the fecal microbiota of Adélie penguins, Erysipelothrix-related sequences were absent in the stomach microbiota of Adélie penguins but were detected in Chinstrap penguins [29]. The genus Erysipelothrix has also been detected in the fecal microbiota of Adélie penguins on the Victoria Land coast [9]. Boerner et al. [36] reported a case of Erysipelothrix septicemia in the Little penguin. Whether the presence of the genus Erysipelothrix will affect the health of the two pygoscelid penguins should be considered in future studies. It has been suggested that butyrate supplementation in penguins leads to a significant increase in host defense peptide gene expression, enhancing antibacterial properties of monocytes against pathogenic bacteria, and boosting host immunity [4,22]. The genus Erysipelothrix showed positive correlations with an unclassified Clostridiales Incertae Sedis XI group and some Bacilli members (e.g., Sporosarcina, Carnobacteriaceae, and Bacillaceae 2) in the two penguin species (SparCC R > 0.71, p ≤ 0.05). Whether there is a connection between the high abundance of potentially butyrate-producing microbes (e.g., Clostridia) and the possible pathogens (e.g., Erysipelothrix) requires further study.
The class Fusobacteriia was dominated by the genera Fusobacterium and Cetobacterium within the family Fusobacteriaceae. Fusobacterium comprised 6.7% and 10.5%, while Cetobacterium accounted for 3.0% and 6.3% in Adélie and Gentoo penguins, respectively. Abundant Fusobacterium and Cetobacterium were also found in the fecal microbiota of Gentoo and Chinstrap penguins in Barton Peninsula on King George Island [7] and in the stomach microbiota of Adélie and Chinstrap penguins on Signy Island [29]. Members of the genus Fusobacterium are involved in prey tissue decomposition [37] and bacteriocin production [38] in the guts of birds and poultry. Fusobacterium-related sequences were found to be more abundant in Chinstrap penguin chicks than in adults [6], suggesting that an abundant population of Fusobacterium appears to be beneficial or at the very least harmless to the host bird. In both Adélie and Gentoo penguins, a positive correlation was observed between the Fusobacterium and the possible pathogen Pasteurella (SparCC R > 0.77, p < 0.01). In addition, Fusobacterium showed a positive correlation with Mycoplasma (SparCC R = 0.79, p < 0.01) in Gentoo penguins and Psychrobacter (SparCC R = 0.70, p = 0.05) in Adélie penguins, while it exhibited negative correlations with members of the Clostridiales (SparCC R < −0.74, p ≤ 0.01) and an unclassified Porphyromonadaceae group (SparCC R = −0.83, p < 0.01) in Adélie penguins. The genus Cetobacterium has been identified as a component of the microbiota in freshwater fish [39] and is associated with the production of vitamin B12 in fish [40]. Michel et al. [41] reported that except for the vampire finch, Cetobacterium was either absent or extremely rare in Darwin’s finches. The high abundance of the genus Cetobacterium in the two pygoscelid penguins may be associated with the fish in the diet. However, the physiological functions of Fusobacterium and Cetobacterium in the penguin gut remain unexplored.
4.2. Proteobacteria
Proteobacteria was the second most abundant phylum in Adélie and Gentoo penguins. Gammaproteobacteria (14.6%) were the most abundant Proteobacteria in penguin feces, followed by Betaproteobacteria (5.8%). Beta- and Gammaproteobacteria are the most abundant Proteobacteria in adults of Chinstrap penguin [6], a congeneric species with Adélie and Gentoo penguins.
AhHigher abundance of Gammaproteobacteria was observed in Adélie penguins (27.1%) than in Gentoo penguins (14.3%). Belonging to the Moraxellaceae family within Gammaproteobacteria, Psychrobacter spp. were much more abundant in Adélie penguins (23.1%) than in Gentoo penguins (9.3%). A high abundance of Psychrobacter has also been observed in the King penguin microbiota [4]. Being uric acid and triglycerides degraders, Psychrobacter strains have been found to be an integral part of penguin excrement [11,42]. Species of the genus Psychrobacter have been isolated from poultry and birds [43]. The type strain Psychrobacter pygoscelis I-STPP5bT was isolated from the trachea of one Gentoo penguin chick individual [44]. Psychrobacter-related sequences are reported to exist in the stomach microbiota of Adélie and Chinstrap penguins, though they are not frequently encountered in the two penguin species [29]. This genus has been shown to have probiotic properties boosting the immune system and weight gain of Groupers [45]. Psychrobacter showed a negative correlation with the possible pathogen Erysipelothrix in Adélie penguins (SparCC R = −0.90, p = 0.01), but had positive correlations with the genera Fusobacterium within the Fusobacteriia and Tissierella within the Clostridia (SparCC R > 0.70, p ≤ 0.05). However, this genus exhibited a positive correlation with Pseudomonas (SparCC R = 0.76, p < 0.01) and had negative correlations with the Bacteroidetes members (e.g., genus Ferruginibacter; SparCC R < −0.70, p < 0.01) in Gentoo penguins. Whether the genus Psychrobacter plays similar roles in the gut environment of different penguin species requires further analysis.
It should be mentioned that abundant Pasteurella-related sequences were observed in this study, accounting for 1.6% in both penguin species. Pasteurella bacteria are part of the natural oral, respiratory, genital, and gastrointestinal microbiota of various wild and domestic animals (https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Pasteurella, accessed on 20 September 2021). Some Pasteurella species are causative agents of disease, as they are often detected in sick birds [46]. Attention should be given to the presence of abundant Pasteurella in penguins. As mentioned above, Pasteurella showed a positive correlation with Fusobacterium in both Adélie and Gentoo penguins. Pasteurellaceae decreased significantly from the feeding to molting stages in the fecal microbiota of both Gentoo and Chinstrap penguins [7], suggesting a relationship between this bacterial group and the food supply for penguins.
In contrast to Gammaproteobacteria, more abundant Betaproteobacteria were detected in Gentoo penguins (6.9%) than in Adélie penguins (1.6%) (p < 0.01). Including the genus Rhodoferax, the family Comamonadaceae accounted for 5.0% and 1.2% in Gentoo and Adélie penguins, respectively. In contrast to this study, Dewar et al. [10] reported that Comamonadaceae was not a dominant family in Gentoo or King penguins, although it was abundant in Little penguins. Carotenoid biosynthesis genes have been reported in the purple nonsulfur bacterium Rhodoferax antarcticus ANT.BRT [47]. As one of the carotenoid-synthesizing bacteria families, Comamonadaceae are found in higher abundance in Atlantic salmon individuals with darker flesh color [48]. In addition, dominant members belonging to Comamonadaceae were also detected in the intestinal bacterial community of white shrimp [49]. Krill represents the main food for both Adélie and Gentoo penguins, who also feed on fish [11,33,50]. All fecal samples collected in this study were colored red, indicating that the feces contained carotenoid-stained chitin from undigested krill shells [11]. However, whether the abundant Comamonadaceae found in this study are of penguin gut origin or food origin remains uncertain.
4.3. Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria
Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria were the last two dominant phyla in both Adélie and Gentoo penguins. Abundant Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria have been observed in fecal microbiota of Adélie penguins in the Ross Sea area [9], Gentoo penguins on Bird Island, and Possession Island [10], and Chinstrap penguins on Deception Island [6]. Krill possess a chitinous exoskeleton, and they represent the main food item for the three pygoscelid penguins [6]. The krill diet promotes dominance by chitin degraders in penguin gut microbiota. Chitin is degraded mainly by Bacteroidetes in aquatic environments and by Actinobacteria in soil environments [51]. In addition, the high abundance of Bacteroidetes in penguin gut microbiota can be attributed to their capacity to detoxify fluoride from krill. Increased Bacteroidetes has been observed in the intestinal microflora of mice after fluoride treatment [52]. Banks et al. [9] suggest that the high abundance of Actinobacteria in penguin feces may be associated with the Antarctic soils, where Actinobacteria is usually one of the dominant phyla [53,54,55]. In fact, Actinobacteria is one of four major phyla, including Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidetes, in the shared core microbiota of wild bird species [56]. However, in the stomach microbiota of Adélie and Chinstrap penguins, neither Bacteroidetes nor Actinobacteria were the dominant phyla [29]. Therefore, abundant Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria in the fecal microbiota of penguins should be attributed to their intestinal origin.
An unclassified Porphyromonadaceae group within the Bacteroidetes was found to be much more abundant in Adélie penguins (6.7%) than in Gentoo penguins (0.6%). In Adélie penguins, this bacterial group showed positive correlations with genera Erysipelothrix and Rhodoferax (SparCC R > 0.71, p ≤ 0.04) but negative correlations with Pasteurella, Psychrobacter, and Fusobacterium (SparCC R < −0.73, p ≤ 0.03). In Gentoo penguins, this bacterial group showed positive correlations with Firmicutes members (e.g., Clostridium XII and Erysipelothrix) and an unclassified Propionibacteriaceae group within Actinobacteria (SparCC R > 0.73, p < 0.01). The family Porphyromonadaceae is dominant in the fecal microbiota of different penguins including Adélie, Gentoo, King, Macaroni, and Little penguins [10,11], and has also been observed in low abundance in the stomach microbiota of Adélie and Chinstrap penguins [29]. Being strict non-spore-forming anaerobes [57], Porphyromonadaceae are often described as fecal bacteria [58] and can play important roles in the decomposition of penguin guano [11].
An unclassified Propionibacteriaceae group within the Actinobacteria was abundant in both Adélie (1.1%) and Gentoo (1.2%) penguins. In addition to the genus Sporosarcina, this bacterial group showed positive correlations with members of the Firmicutes in the two penguin groups (SparCC R > 0.70, p ≤ 0.04). However, in contrast to the negative correlation with the genus Singulisphaera within the Planctomycetes (SparCC R = −0.72, p < 0.01) in the Gentoo group, this bacterial group showed a negative correlation with the genus Psychrobacter (SparCC R = −0.82, p = 0.01) in the Adélie group. Abundant Propionibacteriaceae sequences have been observed in the fecal microbiota of Gentoo, Little, and Macaroni penguins, but were absent in King penguins [10]. This family has also been detected in Adélie penguin feces [9]. However, Propionibacteriaceae-related sequences were not detected in the stomach microbiota of Adélie penguins, although the bacteria were found in low abundance in Chinstrap penguins [29]. Members of the Propionibacteriaceae such as Propionibacterium freudenreichii and P. acidipropionici are well known for their probiotic properties in the food industry [59]. The presence of Propionibacteriaceae seems to be beneficial to the host penguins. Sequences affiliated with an unclassified Intrasporangiaceae group and an unclassified Micrococcineae group were also abundant in Adélie (combined 1.1%) and Gentoo (3.4%) penguins (p < 0.03). In Gentoo penguins, a positive correlation was observed between the two actinobacterial groups (SparCC R = 0.75, p < 0.01). In Adélie penguins, the unclassified Micrococcineae group showed a positive correlation with the genus Clostridium XII (SparCC R = 0.86, p = 0.01) but had a negative correlation with the genus Tissierella (SparCC R = −0.82, p = 0.01). Grzesiak et al. [11] reported that Intrasporangiaceae represented 1.08% on average in Adélie penguin guano samples. The majority of the family Intrasporangiaceae have been isolated from activated sludge or soils from different geographic regions, including agricultural fields, permafrost soil, and marine sediments [60]. Some of the strains are associated with insects [61]. Micrococcineae members have also been isolated from insect guts and are considered beneficial gut inhabitants involved in the maintenance of a healthy microbiota [62]. However, the physiological functions of the two families in the penguin gut remain unclear.
4.4. Cyanobacteria and Planctomycetes
The Gentoo group (6.8%) harbored many more Cyanobacteria-related sequences than the Adélie group (0.2%) (Figure 3B). Most of the Cyanobacteria were unclassified. In contrast to the positive correlation with the genus Clostridium XII (SparCC R > 0.75, p = 0.02) in the Adélie group, a dominant but unclassified Cyanobacteria group showed positive correlations with the genera Polaromonas within the Betaproteobacteria, Dokdonella within the Gammaproteobacteria, and Ferruginibacter and Pedobacter within the Sphingobacteriia (SparCC R > 0.71, p < 0.01) in the Gentoo group. Cyanobacteria have been detected as a minor component of fecal bacterial microbiota in Chinstrap penguins [6]. They have also been observed in the stomach microbiota of Adélie penguins, but not in Chinstrap penguins [29]. Cyanobacteria detected in the feces could be regarded as originating from the diet. Small phytoplankton, including dinoflagellates, small diatoms, and cyanobacteria, are the dominant primary producers in the Antarctic Polar Front region [63]. Krill feed on phytoplankton (e.g., diatoms) during the day and switch to carnivory (e.g., copepods) at night [64,65]. Copepods are also the dominant primary consumers of phytoplankton in Antarctic waters, and as such are an important alternative food for mesopelagic fish, especially myctophids [66]. Cyanobacteria may supplement the diet of copepods [67], though they have often been described to be nutritionally inadequate for zooplankton feeding. Myctophids are a major food source for many higher marine predators, including penguins, seals, petrels, squid, and large predatory fish in Antarctic waters [66]. Whether the difference in abundance of Cyanobacteria reflects a difference in diet component, especially fish, between the Adélie and Gentoo groups requires further study.
Similar to Cyanobacteria, a higher abundance of Planctomycetes represented by the genus Rhodopirellula was observed in the Gentoo group (1.2%) than in the Adélie group (0.4%). Members of the genus Rhodopirellula are widespread and have been described in many marine environments [68]. Planctomycetes have been detected in low abundance in the fecal bacterial microbiota of Chinstrap penguins [6]. Dewar et al. [10] reported that this phylum dominated in fecal bacterial microbiota of the Little penguin but was not abundant in Gentoo, King, or Macaroni penguins. Planctomycetes sequences also have been found in the stomach microbiota of Adélie penguins [29]. It should be mentioned that adding vitamin B12 to isolation media can produce favorable results for the isolation of Planctomycetes [68]. As described above, the genus Cetobacterium, which is associated with the production of vitamin B12 in fish [40], was dominant in the fecal microbiota of both Adélie and Gentoo penguins. In addition, providing N-acetylglucosamine as the only carbon and nitrogen source [69] is also useful for the isolation of Planctomycetes. Chitin, a polymer of N-acetylglucosamine units with β-1,4-glycosidic linkages, is the second most abundant organic compound in nature and is present in fungi and in animals including copepods and krill [70]. Therefore, whether there is a connection between Planctomycetes and the penguin diet deserves further study.
5. Conclusions
Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria were found to dominate the gut microbiota of both Adélie and Gentoo penguins breeding on Antarctic Ardley Island. However, there was an overall difference in fecal bacterial community composition between the two penguin species, suggesting that the gut microbiota of the two pygoscelid penguins with similar dietary habits has a close connection to the penguin species. The Gentoo penguins harbored a higher abundance of Actinobacteria and Cyanobacteria relative to Adélie penguins. In addition, at the class level, more Sphingobacteriia and Betaproteobacteria were observed in the Gentoo group than in the Adélie group; at the family level, more Lachnospiraceae was also detected in the Gentoo group. The genus Peptostreptococcus was significantly abundant in the Gentoo group, while an unclassified Clostridiales group was significantly abundant in the Adélie group. This result is in accordance with previous studies, suggesting that the fecal bacteria of penguins are inherited on evolutionary time scales at the host species level [6,7,9]. At the same time, the differences in the relative abundance of specific bacteria (e.g., Cyanobacteria) between the two pygoscelid penguins could be in part due to differences in diet composition. The results of this study suggest that both the phylogeny of penguin species and diet could be responsible for the differences in the gut microbiota of two closely related penguins with similar dietary habits. Further research is required to fully understand the physiological functions of the same bacterial species colonizing the guts of different penguin species.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d13100500/s1, Figure S1: Rarefaction curves for 16S rRNA gene from penguin fecal samples, Figure S2: Cladogram indicated the phylogenetic distribution of fecal microbiota associated with Adélie and Gentoo penguin groups., Figure S3: SparCC correlations between gut microbe-microbe at the genus level detected in Adélie (A) and Gentoo (B) penguin groups.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments, Y.-X.Z.; performed the experiments, Y.-X.Z. and W.H.; analyzed the data, Y.-X.Z. and H.-R.L.; contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools, Y.-X.Z. and W.L.; wrote the paper, Y.-X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFC1406903) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 91851201).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. No penguins were handled or approached closely as the study material was fecal samples collected outside breeding colonies. All fieldwork was carried out under a permit issued by the Chinese Arctic and Antarctic Administration (No. 2018/003, 4 December 2018) and was strictly in accordance with the relevant articles and clauses of the Antarctic Treaty and the Protocol in Madrid and its Annexes.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequence data are available from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under accession number SRP288016.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the assistance of Rong-Rong Wu of Polar Research Institute of China and Li Zheng of First Institute of Oceanography for collecting penguin fecal samples. Each moist fecal sample was collected by a sterile spoon and then placed into a sterile Whirl-Pak bag (Nasco, Fort Atkinson, WI, USA). We also are grateful to three anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lynch, H.J.; Naveen, R.; Trathan, P.N.; Fagan, W.F. Spatially integrated assessment reveals widespread changes in penguin populations on the Antarctic Peninsula. Ecology 2012, 93, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Convey, P. Antarctic ecosystems. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Levin, S.A., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, H.U.; Braun, C.; Janowski, S.; Nordt, A.; Nordt, A.; Stelter, M. The Current Environmental Situation and Proposals for the Management of the Fildes Peninsula Region. Available online: http://www.uba.de/uba-info-medien-e/4424.html (accessed on 15 February 2013).
- Dewar, M.L.; Arnould, J.P.Y.; Krause, L.; Trathan, P.; Dann, P.; Smith, S.C. Influence of fasting during moult on the faecal microbiota of penguins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waite, D.W.; Taylor, M.W. Exploring the avian gut microbiota: Current trends and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.; Balagué, V.; Valera, F.; Martínez, A.; Benzal, J.; Motas, M.; Diaz, J.I.; Mira, A.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Age-related differences in the gastrointestinal microbiota of chinstrap penguins (Pygoscelis antarctica). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Cho, H.; Kim, M.; Tripathi, B.M.; Jung, J.W.; Chung, H.; Kim, J.H. Faecal microbiota changes associated with the moult fast in chinstrap and gentoo penguins. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, S.; Kidawa, D.; Stempniewicz, L.; Łoś, M.; Łoś, J.M. Environmental DNA as a valuable and unique source of information about ecological networks in Arctic terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Rev. 2017, 25, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.C.; Cary, S.C.; Hogg, I.D. The phylogeography of Adelie penguin faecal flora. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, M.L.; Arnould, J.P.; Dann, P.; Trathan, P.; Groscolas, R.; Smith, S. Interspecific variations in the gastrointestinal microbiota in penguins. MicrobiologyOpen 2013, 2, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesiak, J.; Kaczyńska, A.; Gawor, J.; Żuchniewicz, K.; Aleksandrzak-Piekarczyk, T.; Gromadka, R.; Zdanowski, M.K. A smelly business: Microbiology of Adélie penguin guano (Point Thomas rookery, Antarctica). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every base matters: Assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, D.; Wu, Z. Phosphorus removal performance and biological dephosphorization process in treating reclaimed water by Integrated Vertical-flow Constructed Wetlands (IVCWs). Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.M.; et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D141–D145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. A role for the gut microbiota in energy harvesting? Gut 2010, 59, 1589–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potrykus, J.; White, R.L.; Bearne, S.L. Proteomic investigation of amino acid catabolism in the indigenous gut anaerobe Fusobacterium varium. Proteomics 2008, 8, 2691–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; Imaoka, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Momose, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yamasaki, S.; Saito, T.; Ohba, Y.; et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.K.; Rama Rao, S.V.; Raju, M.V.L.N.; Sunder, G.S. Effect of butyric acid in performance, gastrointestinal tract health and carcass characteristics in broiler chickens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodkin, A. The family Peptostreptococcaceae. In The Prokaryotes—Other Major Lineages of Bacteria and the Archaea, 4th ed.; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeier, D.; Riese, C.; Geissinger, O.; Radek, R.; Brune, A. Breznakia blatticola gen. nov. sp. nov. and Breznakia pachnodae sp. nov., two fermenting bacteria isolated from insect guts, and emended description of the family Erysipelotrichaceae. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 39, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloor, G.B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J. Microbiome datasets are compositional: And this is not optional. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Loo, T.M.; Atarashi, K.; Kanda, H.; Sato, S.; Oyadomari, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Oshima, K.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M.; et al. Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer through senescence secretome. Nature 2013, 499, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Adachi, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Shimozato, A.; Ebi, M.; Ogasawara, N.; Funaki, Y.; Goto, C.; Sasaki, M.; Kasugai, K. Association of intestinal microbiota with metabolic markers and dietary habits patients with type 2 diabetes. Digestion 2016, 94, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.C.; Chang, C.C.; Mau, W.J.; Yen, L.S. Evaluation of N-acetylchitooligosaccharides as the main carbon sources for the growth of intestinal bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 209, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yew, W.C.; Pearce, D.A.; Dunn, M.J.; Samah, A.A.; Convey, P. Bacterial community composition in Adélie (Pygoscelis adeliae) and Chinstrap (Pygoscelis antarctica) Penguin stomach contents from Signy Island, South Orkney Islands. Polar Biol. 2017, 40, 2517–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, H.; Chu, E.S.H.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, J.; Nakatsu, G.; Ng, S.C.; Chan, A.W.H.; Chan, F.K.L.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Yu, J. Peptostreptococcus anaerobius induces intracellular cholesterol biosynthesis in colon cells to induce proliferation and causes dysplasia in mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1419–1433.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S.; Sokal, A.; Filip, R. What was first, obesity or inflammatory bowel disease? What does the gut microbiota have to do with it? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, P.; Arivett, B.; Cleveland, B.M.; Walker, D.M.; Salem, M. Analysis of the fecal microbiota of fast- and slow-growing rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D. The Penguins: Spheniscidae; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 1–295. [Google Scholar]
- Denger, K.; Stackebrandt, E.; Cook, A.M. Desulfonispora thiosulfatigenes gen. nov., sp. nov., a taurine-fermenting, thiosulfate-producing anaerobic bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Opriessnig, T.; Forde, T.; Shimoji, Y. Erysipelothrix spp.: Past, present, and future directions in vaccine research. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerner, L.; Nevis, K.R.; Hinckley, L.S.; Weber, E.S.; Frasca, S., Jr. Erysipelothrix septicemia in a little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2004, 16, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggenbuck, M.; Bærholm Schnell, I.; Blom, N.; Bælum, J.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Sørensen, S.J.; Gilbert, M.T.; Graves, G.R.; Hansen, L.H. The microbiome of New World vultures. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portrait, V.; Cottenceau, G.; Pons, A.M. A Fusobacterium mortiferum strain produces a bacteriocin-like substance(s) inhibiting Salmonella enteritidis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, C.; Coronado, J.; Silva, A.; Romero, J. Cetobacterium is a major component of the microbiome of giant Amazonian fish (Arapaima gigas) in Ecuador. Animals 2018, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, H.; Miyajima, C.; Deguchi, Y. The vitamin B12-producing ability of the intestinal microflora of freshwater fish. Aquaculture 1991, 92, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A.J.; Ward, L.M.; Goffredi, S.K.; Dawson, K.S.; Baldassarre, D.T.; Brenner, A.; Gotanda, K.M.; McCormack, J.E.; Mullin, S.W.; O’Neill, A.; et al. The gut of the finch: Uniqueness of the gut microbiome of the Galápagos vampire finch. Microbiome 2018, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, M.L.; Arnould, J.P.; Allnutt, T.R.; Crowley, T.; Krause, L.; Reynolds, J.; Dann, P.; Smith, S.C. Microbiota of little penguins and short-tailed shearwaters during development. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kämpfer, P.; Jerzak, L.; Wilharm, G.; Golke, J.; Busse, H.J.; Glaeser, S.P. Psychrobacter ciconiae sp. nov., isolated from white storks (Ciconia ciconia). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, P.; Glaeser, S.P.; Irgang, R.; Fernández-Negrete, G.; Poblete-Morales, M.; Fuentes-Messina, D.; Cortez-San Martín, M.; Avendaño-Herrera, R. Psychrobacter pygoscelis sp. nov. isolated from the penguin Pygoscelis papua. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Yang, H.L.; Ma, R.L.; Zhang, C.X.; Lin, W.Y. Effect of dietary administration of Psychrobacter sp. on the growth, feed utilization, digestive enzymes and immune responses of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, e733–e740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, R.H.; Neubauer, C.; Christensen, H.; Korczak, B.; Bojesen, A.M.; Hess, M.; Bisgaard, M. Characterization of Pasteurellaceae-like bacteria isolated from clinically affected psittacine birds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.M.; Riester, C.J.; Skinner, B.M.; Newell, A.W.; Swingley, W.D.; Madigan, M.T.; Jung, D.O.; Asao, M.; Chen, M.; Loughlin, P.C.; et al. Genome sequence of Rhodoferax antarcticus ANT.BRT.; A psychrophilic purple nonsulfur bacterium from an Antarctic microbial mat. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.D.H.; Amoroso, G.; Ventura, T.; Minich, J.J.; Elizur, A. Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L., 1758) gut microbiota profile correlates with flesh pigmentation: Cause or Effect? Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Shao, Z. Changes in the intestinal bacterial community during the growth of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, S.A.; Barnes, D.A.; Dunn, M.J. Predicting which species succeed in climate-forced polar seas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Bertilsson, S. Bacterial chitin degradation-mechanisms and ecophysiological strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Miao, C.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.Q.; Zhou, B.H. Fluoride-induced rectal barrier damage and microflora disorder in mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 7596–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yergeau, E.; Newsham, K.K.; Pearce, D.A.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Patterns of bacterial diversity across a range of Antarctic terrestrial habitats. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2670–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.F.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, F.; Wang, E.T.; He, J.F.; Ding, H.; Zhang, B.T.; Liu, J.; Ran, X.B.; Zang, J.Y. Diversity and structure of soil bacterial communities in the Fildes Region (maritime Antarctica) as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.N.; Park, D.; Seong, H.J.; Kim, D.; Sul, W.J. Antarctic tundra soil metagenome as useful natural resources of cold-active lignocelluolytic enzymes. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, K.; Sandercock, B.K.; Jumpponen, A.; Zeglin, L.H. The avian gut microbiota: Community, physiology and function in wild birds. J. Avian Biol. 2018, 49, e01788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, M. The family porphyromonadaceae. In The Prokaryotes—Other Major Lineages of Bacteria and the Archaea, 4th ed.; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 811–824. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.J.; Bootsma, M.J.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; McLellan, S.L. A microbial signature approach to identify fecal pollution in the waters off an urbanized coast of Lake Michigan. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabah, H.; Rosa do Carmo, F.L.; Jan, G. Dairy Propionibacteria: Versatile probiotics. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, P.; Groth, I. Intrasporangiaceae. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Rainey, F., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, M., Chun, J., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Dedysh, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhuang, X.; Cao, P.; Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Xiang, W. Community composition, antifungal activity and chemical analyses of ant-derived Actinobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.I.; Shah, A.H.; Aurongzeb, M.; Kori, J.; Azim, M.K.; Ansari, M.J.; Bin, L. Characterization of gut bacterial flora of Apis mellifera from north-west Pakistan. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Salas, M.F.; Eriksen, R.; Davidson, A.T.; Wright, S.W. Protistan communities in the Australian sector of the Sub-Antarctic Zone during SAZ-Sense. Deep-Sea Res. II 2011, 58, 2135–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passmore, A.J.; Jarman, S.N.; Swadling, K.M.; Kawaguchi, S.; McMinn, A.; Nicol, S. DNA as a dietary biomarker in Antarctic Krill, Euphausia superba. Mar Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, W.; Yoshida, T.; Virtue, P.; Kawaguchi, S.; Swadling, K.M.; Nicol, S.; Nichols, P.D. Effect of a carnivorous diet on the lipids, fatty acids and condition of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba. Antarct. Sci. 2007, 19, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.A.; Hill, S.L.; Tarling, G.A.; Murphy, E.J. Myctophid fish (family Myctophidae) are central consumers in the food web of the Scotia Sea (Southern Ocean). Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Jónasdóttir, S.H. Nutritional quality of two cyanobacteria: How rich is ‘poor’ food? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 151, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J. Bringing Planctomycetes into pure culture. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesner, H. The development of media suitable for the microorganisms morphologically resembling Planctomyces spp., Pirellula spp., and other Planctomycetales from various aquatic habitats using dilute media. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 17, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lee, A.M.; Bassler, B.L.; Roseman, S. Chitin utilization by marine bacteria. A physiological function for bacterial adhesion to immobilized carbohydrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 24260–24267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).