Abstract
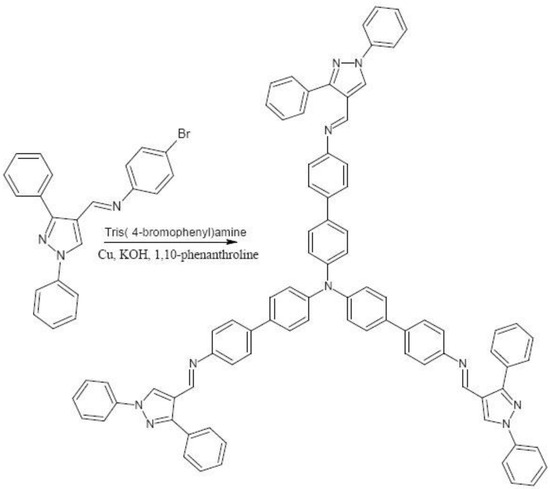
Tris{4-[(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]-41-aminobiphenyl}amine was synthesized from N-(4-bromophenyl)-N-[(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]amine and tris(4-bromophenyl)amine based on Ullmann coupling reaction. The synthesized compound was characterized by NMR, IR, MS and elemental analysis.
As part of a study towards the preparation of highly conjugated polyaromatcs incorporating a pyrazole motif with potential application in photovoltaic devices, the title compound tris{4-[(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]-41-aminobiphenyl}amine is prepared. The triarylamine moiety fulfills the requirement of easy and reversible oxidation and therefore constitutes the building block of many of the hole-transporting materials [1].
Electrolytic copper (100 mg, 1.6 mmol), KOH (10 mg, 0.178 mmol ) and 1,10-phenanthroline (1.0 mg, 0.006 mmol) were added to a stirred solution of N-(4-bromophenyl)-N-[(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]amine [2,3,4] (121 mg, 0.3 mmol) and tris(4-bromophenyl)amine (48 mg, 0.1 mmol) in anhydrous DMF. The resultant mixture was heated at 130 °C for 18 h and then filtered hot to remove the copper compounds and the base [5,6]. The solvent DMF was evaporated under vacuum and the dark brown solid was triturated with ethyl acetate, filtered and further purified by chromatography on silica gel, using ethyl acetate-hexane (1:4) as eluent. The product is most probably the E isomer, given the high degree of symmetry deduced from the 13C NMR data and the 1H NMR data which indicate there is only one product formed.
Yield: 65%
M.p.: 128 °C
IR (KBr) cm−1: 2998 (Ar C-Hstr), 1603 (C=Nstr), 1452 (Ar C=Cstr), 1337 (Ph-Nstr), 1023 (Ar C-Hdef).
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 10.23 (s, 3H, pyrazole 5-H), 8.72 (s, 3H, HC=N), 7.93–6.69 (m, 54H, Ar).
13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): 158.0, 140.5, 139.0, 136.0, 129.1, 128.3, 127.0, 123.0, 118.0, 112.5, 106.0, 103.7.
MS: m/z (ES), 1209 [(MH)+].
Elemental analysis calculated for C84H60N10 (1208.5): C, 83.42%; H, 5.00%; N, 11.58%. Found: C, 84.32%; H, 5.25%; N, 11.43%.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgement
We are thankful to NIIST, Thiruvanathapuram for recording NMR spectra.
References
- Thelakkat, M.; Schmitz, C.; Hohle, C.; Strohriegl, P.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Hofmann, U.; Schloter, S.; Haarer, D. Novel functional materials based on triarylamines-synthesis and application in electroluminescent devices and photorefractive systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, P.V.; Haridas, K.R. 1,3,5-Tris{[N-(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]-4-aminophenyl}benzene. Molbank 2009, 2009, M624. [Google Scholar]
- Mohite, S.K.; Magdum, C.S. Novel synthesis of functionally substituted N-{[3-(4-chlorophenyl)- 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]methylene}anilines and their pharmacological screening. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2006, 4, 980–988. [Google Scholar]
- Rathelot, P.; Azas, N.; El-Kashef, H.; Delmas, F.; Di Giorgio, C.; Timon-David, P.; Maldonado, J.; Vanelle, P. 1,3-Diphenylpyrazoles: Synthesis and antiparasitic activities of azomethine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 37, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbrand, H.B.; Hu, N.-X. Ligand-accelerated catalysis of the Ullmann condensation: Application to hole conducting triarylamines. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Liebeskind, L.S. Ambient temperature, Ullmann-like reductive coupling of aryl, heteroaryl, and alkenyl halides. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 2312–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).