In the original publication [1], inadvertent errors were present in Figures 1A and 1C. Specifically, the control images in both Figures 1A and 1C, as well as the xe-60 image in Figure 1C, were duplicated unintentionally. These duplications resulted from an oversight during the final figure assembly. The correct Figure 1 is shown below.
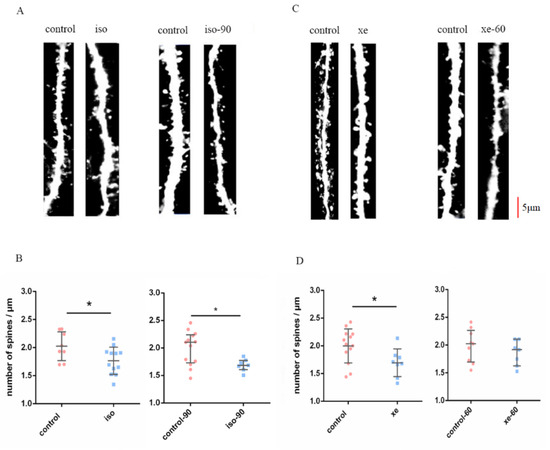
Figure 1.
(A,C) show representative dendrites from the control group and the isoflurane (Iso)/xenon (Xe) treated groups, at treatment and post wash out (60/90 min) of gas, respectively. Scale bar = 5 μm. Dendrites were analyzed from brain slices of GFP-M mice. (B,D) left graphs show both Iso and Xe reduced the DSD in the dentate gyrus of hippocampus (p = 0.0201 for iso, and p = 0.0244 for Xe, Mann–Whitney U test). (B,D) right graphs show that after 60 mins the reduction of DSD caused by Xe was reversed (p = 0.3441 Mann–Whitney U test), but not for Iso after 90 mins (p = 0.0297, Mann–Whitney U test). Error bars in all graphs indicate the means +/− SDs. Every data point in the scatter plots represents the mean spine density from 8–10 dendrites per one animal (n = 8–13). Dendrites that were 15 µm away from their respective cell’s soma were chosen for these analyses. Black horizontal bars below the * indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) between the groups.
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Shi, D.; Wong, J.K.Y.; Zhu, K.; Noakes, P.G.; Rammes, G. The Anaesthetics Isoflurane and Xenon Reverse the Synaptotoxic Effects of Aβ1–42 on Megf10-Dependent Astrocytic Synapse Elimination and Spine Density in Ex Vivo Hippocampal Brain Slices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).