Abstract
Inflammation and oxidative stress are closely related to cardiovascular complications and atherosclerosis, and have the potential to lead to an increase in death in patients receiving hemodialysis. Vitamin E has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the effects of vitamin E supplementation on endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress biomarkers in adult patients receiving hemodialysis. We searched the MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases and identified randomized controlled trials of adult patients receiving hemodialysis until 30 August 2021. A total of 11 trials with 491 randomized patients were included. The pooled data indicated that vitamin E supplementation significantly decreased intercellular adhesion molecule-1 [standardized mean difference (SMD): −1.35; 95% confidence interval (CI): −2.57, −0.13; p = 0.03, I2 = 89%], vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (SMD: −1.08; 95% CI: −2.05, −0.11; p = 0.03, I2 = 81%), C-reactive protein (SMD: −0.41; 95% CI: −0.75, −0.07; p = 0.02, I2 = 64%), and malondialdehyde (SMD: −0.76; 95% CI: −1.26, −0.25; p = 0.003, I2 = 77%) levels, but not interleukin-6 levels compared to those in the control group. Our results suggest that vitamin E supplementation may help alleviate oxidative stress and both vascular and systemic inflammation in patients receiving hemodialysis.
1. Introduction
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are strongly associated with the progression of chronic kidney disease and are common risk factors in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [1]. This may induce advanced cardiovascular complications and atherosclerosis through multiple pathogenic mechanisms [2,3]. Evaluation of this state through the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines [interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)], and acute-phase proteins [C-reactive protein (CRP)] may help predict the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic renal failure receiving hemodialysis [4,5].
The levels of biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis, such as intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), are increased in the serum of patients receiving hemodialysis [6]. Endothelial dysfunction increases vascular permeability and decreases nitric oxide bioavailability, leading to increased inflammation and thrombosis. Inflammation is also closely correlated with endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress, which may contribute to increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in these patients [3,7,8]. In relation to the connection between inflammation and oxidative stress, anti-oxidative therapy may be a promising strategy to ameliorate the risks of cardiovascular disease in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis [9]. Decreased kidney function is associated with an increased risk of thrombosis. Thrombosis is usually associated with venous thromboembolism, stroke, and coronary artery disease in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Anti-thrombotic therapy may have a beneficial effect on thrombotic diseases in patients with CKD.
Vitamin E is a lipid-soluble antioxidant composed of eight different forms, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols with high anti-inflammatory properties [10]. The pooled results of Asbaghi et al.’s study indicated the beneficial effect of vitamin E administration on the decrease in serum CRP concentration in adults [11]. In 2014, a meta-analysis indicated that vitamin E-coated dialyzer can help decrease inflammation and oxidative stress, reflected by reductions in serum CRP, IL-6, and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance levels in patients receiving hemodialysis [12]. Bergin et al. evaluated the pre- and post-treatment effects of vitamin E on malondialdehyde (MDA) levels [13]. They indicated that MDA levels are remarkably lower in patients receiving hemodialysis after receiving vitamin E supplementation. However, their pooled results did not show a comparison between the vitamin E treatment and control groups [13].
Recently, a randomized controlled clinical trial (RCT) demonstrated that vitamin E supplementation notably reduced biomarkers of vascular and systemic inflammation (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α) [14]. In addition, Pirhadi-Tavandashti et al. reported significant reductions in serum ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 levels when comparing vitamin E consumption and placebos in patients receiving hemodialysis. However, there were no remarkable changes in CRP and IL-6 levels [15].
To the best of our knowledge, no meta-analysis has assessed the effects of vitamin E supplementation on biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction, and there remains inconsistency between clinical trials investigating the benefits of vitamin E treatment on inflammation and oxidative stress. Thus, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs to evaluate the beneficial effects of vitamin E supplementation on biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress in patients receiving hemodialysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
We registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Review database (Registration No. CRD42021262773) and conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement [16].
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
The ‘Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study’ framework was used to select studies that were eligible for inclusion in this systematic review. (1) Participants: adult patients with ESRD receiving hemodialysis; (2) Intervention: vitamin E supplementation; (3) Comparison: control group receiving placebo or not receiving study-related intervention; (4) Outcome: the primary outcome measures were biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1), and the secondary outcomes included biomarkers of inflammation (CRP, IL-6) and oxidative stress (MDA); and (5) Study design: parallel groups and RCTs. All articles were published in English, without restrictions on the publication year. Studies were excluded if the outcome-of-interest was not assessed, or if they did not satisfy the eligibility criteria.
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
We conducted a comprehensive literature search of four databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library) and identified studies until 30 August 2021. The following text and medical subject heading terminologies were used to search for relevant articles: “vitamin E,” “tocopherol,” “tocotrienol,” and “hemodialysis”. For enhanced readability, the full search strategy is detailed in Appendix A. The duplicate results were cross-checked and excluded using Endnote X9 (Clarivates Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA). A secondary search was conducted using references from the relevant studies. Two investigators (T.T.U.N. and J.-h.Y.) performed and evaluated the search strategy.
2.4. Study Selection and Data Collection
According to the predetermined eligibility criteria, we used the PRISMA flow diagram to summarize the study collection processes. Two independent investigators reviewed the full-text articles after excluding unrelated titles and abstracts (T.T.U.N. and J.-h.Y.), and any disagreements were discussed and resolved to reach a consensus with the third author (W.K.). We used Microsoft Office Excel 2010 to extract the data and collect numerical data from the included studies. Two authors collected and examined the data. The divergent decisions were resolved by discussion and consensus with the third author (W.K.).
2.5. Data Items
The data from the included studies were independently collected according to the study source (authors, year of publication, and country), characteristics of the study and population (study design, sample size, proportion of men and women, mean age, mean body mass index, and hemodialysis duration), groups of trials (number of patients in each group, dosage, and duration of intervention), and outcomes. This process was conducted by two authors (T.T.U.N. and J.-h.Y.).
2.6. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
The Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials version 2 (RoB2) was used to assess the quality of the included RCTs [17]. This tool was structured into five domains with the risk-of-bias decisions including “Low risk of bias”, “high risk of bias”, or “some concerns”. Two authors (T.T. and J.-h.Y.) independently conducted the methodological quality assessments. The disagreements were discussed by the three authors to arrive at a conclusion (T.T.U.N., J.-h.Y. and W.K.).
2.7. Data Analysis
All extracted data are shown as means ± standard deviations (SDs). If the data of the outcome-of-interest were provided as means with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) or medians and interquartile ranges, we converted them to means and SDs according to the formula of the Cochrane Handbook, chapter 6.5.2, or Wan et al.’s report, respectively [18,19]. Statistical analyses were conducted using Review Manager (RevMan) (Computer program) (Version 5.4, The Cochrane Collaboration (https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/core-softwarecochrane-reviews/revman/revman-non-cochrane-reviews (accessed on 30 August 2021)), 2020). Standardized mean differences (SMDs) were used to evaluate the overall effect size of continuous data with different measurements or units. We extracted the means and SDs for changes between baseline and post-intervention. If these data were not provided, we estimated the means and SDs for changes following the recommendation of the Cochrane Handbook, chapter 6.5.2.8 [18].
The I square statistic (I2) was calculated to examine heterogeneity across studies; I2 ≤ 40% and p-value ≥ 0.1 were defined as low. In other cases, heterogeneity was considered moderate (40% < I2 ≤ 70%) or high (I2 > 70%) [20].
A random-effects model was used to estimate the pooled effect size for all the meta-analyses. Publication bias was assessed by Egger’s regression test (a formal statistical test of funnel plot asymmetry) using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis version 2.0 software [21]. Except for the heterogeneity test, p < 0.05 was considered significant for all statistical analyses in this study.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
The initial search results of the 4 electronic databases consisted of 1939 articles. After removing 792 duplicates, we screened the titles and abstracts and obtained 82 full-text articles for review. Of these, 71 articles that did not match the inclusion criteria were excluded, and 11 eligible studies were selected for the systematic review and meta-analysis. The PRISMA flowchart is shown in Figure 1.
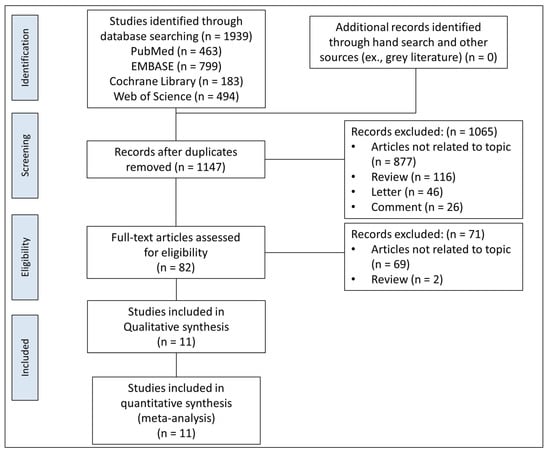
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram for selection of relevant trials.
3.2. Study Characteristics
The characteristics of the included studies are presented in Table 1. Eleven RCTs were published in English between 2006 and 2021, six of which were performed in Iran, with one each in the Czech Republic, Turkey, Spain, Philippines, and the USA. A total of 491 patients receiving hemodialysis were randomized into vitamin E (n = 246) or control (n = 245) groups, with the mean age ranging from 33 to 79 years. The duration of the intervention ranged from 2 to 20 weeks. The most commonly used dosage of vitamin E supplementation in the included trials was 400 IU daily. Among the included RCTs, 4 reported the effect of vitamin E supplementation on the levels of ICAM-1, 3 articles on VCAM-1, 9 articles on CRP, 5 articles on IL-6, and 6 articles on MDA, the data of which were pooled for meta-analysis. Other biomarkers such as E-selectin, P-selectin, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase, glutathione, and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) evaluated in several studies are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the included randomized controlled trials in the systematic review.
3.3. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
We summarized the quality assessment of the 11 RCTs included in Figure 2. Among them, four trials were judged as having a “low risk of bias” (36.4%), six trials as having “some concerns” (54.5%), and one trial as having a “high risk of bias” (9.1%). Notably, all trials were assessed as “low risk” in the domain of missing outcome data, and only the domain of the randomization process received a “high risk” assessment from one trial.
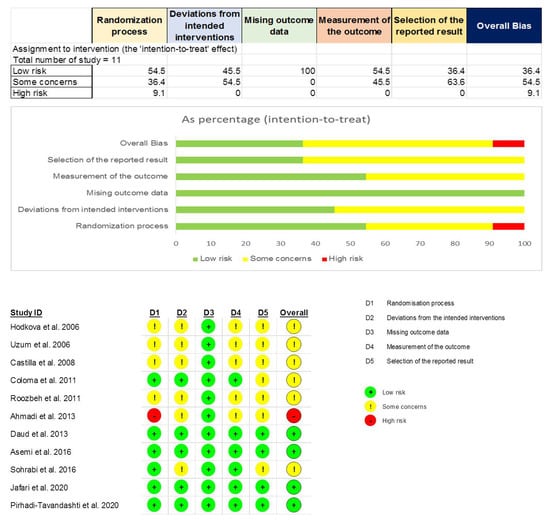
Figure 2.
Risk of bias assessment by Cochrane risk-of-bias tool version 2 for included RCTs.
3.4. Meta-Analysis
3.4.1. Effect of Vitamin E Supplementation on Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction
Four RCTs investigated ICAM-1 levels. The pooled results indicated a significant reduction in serum ICAM-1 levels after taking vitamin E (SMD = −1.35; 95% CI: −2.57, −0.13; p = 0.03, I2 = 89%). In a meta-analysis of three trials investigating VCAM-1, there was a remarkable decrease in serum VCAM-1 levels in the vitamin E group compared with that in the control group (SMD = −1.08; 95% CI: −2.05, −0.11; p = 0.03, I2 = 81%) (Figure 3). No publication bias was observed based on Egger’s test for ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 (p = 0.372 and p = 0.828, respectively).
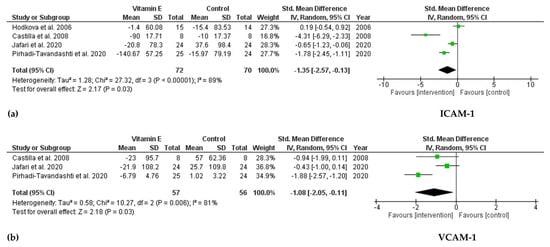
Figure 3.
Forest plot for effect of vitamin E supplementation on (a) ICAM-1 and (b) VCAM-1 in hemodialysis patients.
3.4.2. Effect of Vitamin E Supplementation on Biomarkers of Inflammation
As shown in Figure 4, a significant decrease in CRP levels was found in the vitamin E intervention group compared to that in the control group (SMD = −0.41; 95% CI: −0.75, −0.07; p = 0.02, I2 = 64%). However, there was no significant change after vitamin E supplementation in IL-6 levels (SMD = −0.16; 95% CI: −0.52, 0.21; p = 0.40, I2 = 53%). No publication bias was observed based on Egger’s test for CRP and IL-6 (p = 0.579 and p = 0.229, respectively).
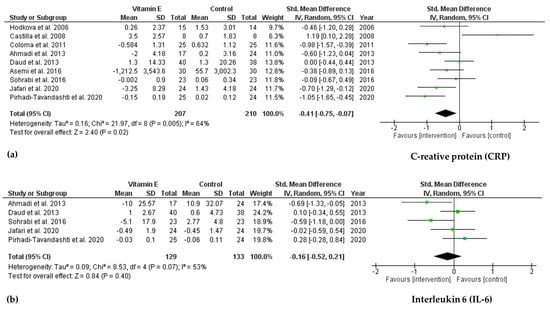
Figure 4.
Forest plot for effect of vitamin E supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation (a) Creative protein (CRP) and (b) Interleukin 6 (IL-6) in hemodialysis patients.
3.4.3. Effect of Vitamin E Supplementation on Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress
The meta-analysis of six RCTs revealed a significant difference in MDA levels following vitamin E supplementation when compared between the intervention and control groups (SMD = −0.76; 95% CI: −1.26, −0.25; p = 0.003, I2 = 77%) (Figure 5). Egger’s test for this meta-analysis suggested no publication bias (p = 0.059).
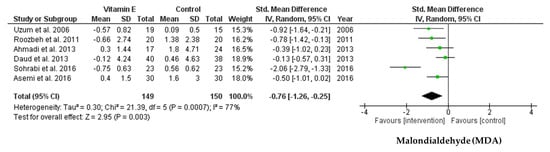
Figure 5.
Forest plot for effect of vitamin E supplementation on malondialdehyde (MDA) in hemodialysis patients.
4. Discussion
This review pooled the data of 11 RCTs in patients receiving hemodialysis to determine the beneficial effect of vitamin E supplementation on the reduction in biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress. Our study is the first meta-analysis to demonstrate the effect of this supplementation on significantly reducing biomarkers of vascular inflammation (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) in patients receiving hemodialysis. In addition, by evaluating CRP and MDA levels, we also showed remarkable evidence to assess the benefits of vitamin E in decreasing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress.
Hemodialysis may improve survival in patients with ESRD, but increased inflammation and oxidative stress are associated with several complications, such as atherosclerosis and malnutrition, and contribute to their acceleration in these patients [14,31,32]. Therefore, the use of adjuvant therapy in patients receiving hemodialysis to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress is a matter of concern. Vitamin E is a widely studied antioxidant. Many clinical trials have used vitamin E to coat dialysis membranes, the effectiveness of which on inflammation and oxidative stress has been demonstrated by the pooled results of previous meta-analyses [12,33,34,35]. In addition, several trials have investigated the effects of the oral administration of vitamin E in patients receiving hemodialysis. Based on the RCTs, we show the most valuable evidence of the benefits of vitamin E supplementation through a meta-analysis.
Adhesion molecules, including ICAM-1 and VCAM-1, which may indicate endothelial dysfunction, are increased under conditions of high inflammation and oxidative stress. Patients receiving hemodialysis are more likely to have higher atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevalence [14,15,36]. The serum concentrations of vascular inflammatory markers have been evaluated in patients with ERSD [37]. Their high levels are related to an increase in cardiovascular-induced mortality [38,39]. Our findings demonstrated a significant reduction in serum ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 levels in patients receiving hemodialysis and vitamin E supplementation compared with that in the group without intervention. The clearance of oxidative stress via the antioxidant capacity of vitamin E may reduce the gene expression of these molecules [15,40,41].
Elevated levels of acute-phase proteins or pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as CRP, IL-6 are evidence of systemic inflammation in patients receiving dialysis. An increase in this inflammatory factor during hemodialysis sessions is linked to high mortality [42]. In this review, we found a reduction in CRP levels after vitamin E supplementation. This is in line with the results of a previous meta-analysis by Asbaghi et al. of adults in general and patients receiving hemodialysis [11]. However, there was a slight methodological difference in their study compared to the present study. We aggregated the data to compare the effects between patients who received only vitamin E treatment and the control group, while they summarized data corresponding to both patients who received vitamin E and those who received vitamin E combined with another substance and compared them with the control group [11]. Similar to the previous study, we evaluated the change in IL-6 level. However, there was no evidence of a significant reduction in IL-6 levels in patients receiving vitamin E supplementation.
The imbalance between pro-oxidant and antioxidant systems in patients receiving hemodialysis leads to an increase in oxidative stress, which is associated with both pathophysiologic mechanism of ESRD and hemodialysis techniques [43]. MDA is the end-product of the reaction between reactive oxygen species and polyunsaturated fatty acids. This may interact with proteins and nucleic acids and is implicated in the pathogenesis of several disorders, including atherosclerosis [44]. Our meta-analysis indicated that vitamin E supplementation significantly reduces MDA levels in the intervention groups. Although a previous meta-analysis showed a decrease in MDA levels in the serum of patients receiving hemodialysis when comparing results between pre- and post-intervention, the comparison of effectiveness between vitamin E supplementation and control groups is unclear. To date, we pooled the results from RCTs to evaluate and demonstrate a significant difference in MDA levels between the vitamin E treatment and non-treatment groups.
Patients receiving hemodialysis are a population with many disorders related to inflammation, oxidative stress, and malnutrition. Inflammatory status can induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lead to increased consumption of antioxidants. On the other hand, oxidative stress can influence inflammation through the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and aggravate other syndromes, such as atherosclerosis and malnutrition. Vitamin E is one of many nutrients that is restricted or disrupted in metabolism, intake, and clearance in hemodialysis patients [45]. Moreover, gastrointestinal problems in this population may cause poor absorption, which leads to low plasma vitamin E levels in certain patients [46,47]. Vitamin E is a lipid-soluble antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties. It can act as an ROS scavenger and may control lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress. Therefore, vitamin E supplementation may improve vitamin E deficiency due to malnutrition and provide antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in patients receiving hemodialysis.
An increased risk of thromboembolism and stroke occurs when renal function is decreased. CKD patients, especially those on renal replacement therapy, exhibit an increased risk of thrombosis, including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. These complications may be due to the high incidence of atrial fibrillation, hypercoagulability or unknown factors in these patients. Supplementation with vitamin E may suppress thromboembolic events. The incidence of venous thromboembolism was decreased in women treated with vitamin E [48]. Vitamin E was associated with inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombin formation [49,50]. Therefore, vitamin E supplementation may have a beneficial effect on thrombotic events in patients with CKD.
Despite these remarkable results, our study has some limitations. In this systematic review, we included several studies that evaluated antioxidant defenses using antioxidant markers (GSH, SOD, and TAC), and inflammatory biomarkers such as TNFα and MCP-1. However, because of the small number of RCTs, we were unable to perform meta-analyses to assess the effect of vitamin E supplementation on these markers. Additionally, the number of RCTs and sample sizes included in the pooled analyses remain limited. Therefore, further studies with larger sample sizes are required.
The elevated plasma IL-6 level is commonly observed in CKD patients. Increased serum IL-6 level is largely caused by many variables such as the increased production resulting from oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, and the decreased renal clearance of IL-6 in CKD [51]. Vitamin E supplementation in diabetic patients suppresses the serum level of IL-6 by regulation of oxidation and inflammation [52]. However, the present meta-analysis study showed that there are no significant differences in serum IL-6 levels between the untreated and patients treated with vitamin E supplementation. This could be linked to several factors, including the study duration, the number of enrolled patients, dosage of vitamin E used, and the baseline levels of the inflammatory state. In addition, residual renal function may be an additional factor influencing the outcome [53]. We believe that further study is needed to measure the effect of vitamin E in CKD.
The heterogeneity across the included studies was moderate and high. The type, dosage, and duration of vitamin E supplementation differed among the studies. We were unable to provide evidence and recommend an appropriate dosage and duration for clinicians. Further studies should be conducted to compare the effectiveness of different types, doses, and durations of vitamin E supplementation. Although the percentage of studies with a high risk of bias was 9.1%, 54.5% of the included studies had “some concerns”. Based on the Cochrane risk-of-bias assessment, we have some recommendations to improve the quality of RCTs, such as using random methods for generating the allocation sequence and blinding of the outcome assessors and participants, following the pre-specified analysis plan before unblinding the data.
5. Conclusions
In the current meta-analysis, our results demonstrated that vitamin E supplementation significantly decreases the levels of biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1), systemic inflammation (CRP), and oxidative stress (MDA) compared to those in the control group. However, it does not influence IL-6 levels. Further RCTs of higher quality are needed to confirm these findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T.U.N. and W.K.; methodology, T.T.U.N. and W.K.; software, T.T.U.N. and W.K.; validation, T.T.U.N., J.-h.Y. and W.K.; formal analysis, T.T.U.N. and J.-h.Y.; data curation, T.T.U.N. and W.K.; writing—original draft preparation, T.T.U.N. and W.K.; writing—review and editing, T.T.U.N., J.-h.Y. and W.K.; supervision, W.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF−2019R1A2C1090358) and the Biomedical Research Institute, Jeonbuk National University Hospital (K.W.).
Data Availability Statement
All data are reported in this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Detailed search strategies for each database. MeSH terms, search terms, and combinations of the two were used for each database search.
Table A1.
Detailed search strategies for each database. MeSH terms, search terms, and combinations of the two were used for each database search.
| Database | Detailed Search Strategies | Records Founded |
|---|---|---|
| MEDLINE/PUBMED | (“vitamin e”[MeSH Terms] OR vitamin E[Text Word] OR “tocopherols”[MeSH Terms] OR tocopherol[Text Word] OR “tocotrienols”[MeSH Terms] OR tocotrienol[Text Word]) AND (“renal dialysis”[MeSH Terms] OR hemodialysis[Text Word]) | 463 |
| EMBASE | (“vitamin E” OR “tocopherol” OR “tocotrienol”) AND hemodialysis | 799 |
| Cochrane Library | (“vitamin E” OR “tocopherol” OR “tocotrienol”) AND hemodialysis | 183 |
| Web of Science | (“vitamin E” OR “tocopherol” OR “tocotrienol”) AND hemodialysis | 494 |
Ultimately, 1939 records were found, 463 from MEDLINE/PubMed, 799 from EMBASE, 183 from Cochrane Library, and 494 from the Web of Science. Studies were further selected according to the inclusion criteria listed in the Material and Methods (Figure 1).
References
- Bayés, B.; Pastor, M.C.; Bonal, J.; Juncà, J.; Hernandez, J.M.; Riutort, N.; Foraster, A.; Romero, R. Homocysteine, C-reactive protein, lipid peroxidation and mortality in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.A.; Ban, T.H.; Kang, C.-Y.; Hwang, S.D.; Choi, S.R.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kim, K.; Kwon, Y.E.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Trends in epidemiologic characteristics of end-stage renal disease from 2019 Korean Renal Data System (KORDS). Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Alvestrand, A. Inflammation in end-stage renal disease: Sources, consequences, and therapy. Semin. Dial. 2002, 15, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeun, J.Y.; Levine, R.A.; Mantadilok, V.; Kaysen, G.A. C-Reactive protein predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, D.V.; Barreto, F.C.; Liabeuf, S.; Temmar, M.; Lemke, H.D.; Tribouilloy, C.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A. Plasma interleukin-6 is independently associated with mortality in both hemodialysis and pre-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papayianni, A.; Alexopoulos, E.; Giamalis, P.; Gionanlis, L.; Belechri, A.M.; Koukoudis, P.; Memmos, D. Circulating levels of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and MCP-1 are increased in haemodialysis patients: Association with inflammation, dyslipidaemia, and vascular events. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenvinkel, P. Inflammatory and atherosclerotic interactions in the depleted uremic patient. Blood Purif. 2001, 19, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnak, M.J.; Levey, A.S. Cardiovascular disease and chronic renal disease: A new paradigm. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, S117–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Singh, P.; Khurana, S.; Ganguly, N.K.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Rana, D.S.; Taneja, V.; Bhargava, V. Implications of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: A review on current concepts and therapies. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Devaraj, S.; Jialal, I. Vitamin E, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2005, 25, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Sadeghian, M.; Nazarian, B.; Sarreshtedari, M.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Maleki, V.; Alizadeh, M.; Shokri, A.; Sadeghi, O. The effect of vitamin E supplementation on selected inflammatory biomarkers in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.K.; Xiao, L.; Xu, B.; Xu, X.X.; Liu, F.Y.; Sun, L. Effects of vitamin E-coated dialyzer on oxidative stress and inflammation status in hemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergin, P.; Leggett, A.; Cardwell, C.R.; Woodside, J.V.; Thakkinstian, A.; Maxwell, A.P.; McKay, G.J. The effects of vitamin E supplementation on malondialdehyde as a biomarker of oxidative stress in haemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, T.; Fallah, A.A.; Reyhanian, A.; Sarmast, E. Effects of pomegranate peel extract and vitamin E on the inflammatory status and endothelial function in hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7987–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhadi-Tavandashti, N.; Imani, H.; Ebrahimpour-Koujan, S.; Samavat, S.; Hakemi, M.S. The effect of vitamin E supplementation on biomarkers of endothelial function and inflammation among hemodialysis patients: A double-blinded randomized clinical trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 6.2 (updated February 2021); Cochrane Collaboration: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hodkova, M.; Dusilova-Sulkova, S.; Kalousova, M.; Soukupova, J.; Zima, T.; Mikova, D.; Malbohan, I.M.; Bartunkova, J. Influence of oral vitamin E therapy on micro-inflammation and cardiovascular disease markers in chronic hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2006, 28, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzum, A.; Toprak, O.; Gumustas, M.K.; Ciftci, S.; Sen, S. Effect of vitamin E therapy on oxidative stress and erythrocyte osmotic fragility in patients on peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis. J. Nephrol. 2006, 19, 739–745. [Google Scholar]
- Castilla, P.; Dávalos, A.; Teruel, J.L.; Cerrato, F.; Fernández-Lucas, M.; Merino, J.L.; Sánchez-Martín, C.C.; Ortuño, J.; Lasunción, M.A. Comparative effects of dietary supplementation with red grape juice and vitamin E on production of superoxide by circulating neutrophil NADPH oxidase in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coloma, R.S.; Jocson, V.R.A. Effects of vitamin E on a biomarker of inflammation and precursors of atherogenesis in chronic hemodialysis patients. Philipp. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 49, 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Roozbeh, J.; Shahriyari, B.; Akmali, M.; Vessal, G.; Pakfetrat, M.; Jalali, G.A.R.; Afshariani, R.; Hasheminasab, M.; Ghahramani, N. Comparative effects of silymarin and vitamin E supplementation on oxidative stress markers, and hemoglobin levels among patients on hemodialysis. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, A.; Mazooji, N.; Roozbeh, J.; Mazloom, Z.; Hasanzade, J. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid and vitamin E supplementation on oxidative stress, inflammation, and malnutrition in hemodialysis Patients. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 7, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Daud, Z.A.M.; Tubie, B.; Sheyman, M.; Osia, R.; Adams, J.; Tubie, S.; Khosla, P. Vitamin E tocotrienol supplementation improves lipid profiles in chronic hemodialysis patients. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2013, 9, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asemi, Z.; Soleimani, A.; Shakeri, H.; Mazroii, N.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effects of omega-3 fatty acid plus alpha-tocopherol supplementation on malnutrition–inflammation score, biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic hemodialysis patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, Z.; Eftekhari, M.H.; Eskandari, M.H.; Rezaianzadeh, A.; Sagheb, M.M. Intradialytic Oral Protein Supplementation and Nutritional and Inflammation Outcomes in Hemodialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Recent advances in understanding the malnutrition-inflammation-cachexia syndrome in chronic kidney disease patients: What is next? Semin. Dial. 2005, 18, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Vecchio, L.; Locatelli, F.; Carini, M. What we know about oxidative stress in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis--clinical effects, potential treatment, and prevention. Semin. Dial. 2011, 24, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ribera, L.; Corredor, Z.; Silva, I.; Díaz, J.M.; Ballarín, J.; Marcos, R.; Pastor, S.; Coll, E. Vitamin E-coated dialysis membranes reduce the levels of oxidative genetic damage in hemodialysis patients. Mutat. Res. 2017, 815, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmizis, D.; Papagianni, A.; Belechri, A.-M.; Memmos, D. Effects of vitamin E-coated membrane dialyser on markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in patients on chronic haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 26, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Arrigo, G.; Baggetta, R.; Tripepi, G.; Galli, F.; Bolignano, D. Effects of Vitamin E-Coated versus Conventional Membranes in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood Purif. 2017, 43, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Rasekhmagham, R.; Kord-Varkaneh, H.; Santos, H.O.; Yao, G. The effects of pomegranate supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stam, F.; van Guldener, C.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; ter Wee, P.M.; Donker, A.J.; Stehouwer, C.D. Impaired renal function is associated with markers of endothelial dysfunction and increased inflammatory activity. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blankenberg, S.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Bickel, C.; Peetz, D.; Hafner, G.; Tiret, L.; Meyer, J. Circulating cell adhesion molecules and death in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 2001, 104, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tedgui, A. The role of inflammation in atherothrombosis: Implications for clinical practice. Vasc. Med. 2005, 10, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Habas, K.; Shang, L. Alterations in intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in human endothelial cells. Tissue Cell 2018, 54, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuvaev, V.V.; Muzykantov, V.R. Targeted modulation of reactive oxygen species in the vascular endothelium. J. Control. Release 2011, 153, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korevaar, J.C.; van Manen, J.G.; Dekker, F.W.; de Waart, D.R.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T. Effect of an increase in C-reactive protein level during a hemodialysis session on mortality. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2916–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusu, C.C.; Racasan, S.; Kacso, I.M.; Moldovan, D.; Potra, A.; Patiu, I.M.; Vladutiu, D.; Caprioara, M.G. Malondialdehyde can predict survival in hemodialysis patients. Clujul. Med. 2016, 89, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, C.C.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Wu, C.C. Oxidative stress and nucleic acid oxidation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 2013, 301982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusu, A.E. Vitamin E in Hemodialysis Patients. In Vitamin E in Health and Disease; Morales-Gonzalez, J.A., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmadakis, G.; Da Costa Correia, E.; Carceles, O.; Somda, F.; Aguilera, D. Vitamins in dialysis: Who, when and how much? Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Buoncristiani, U.; Conte, C.; Aisa, C.; Floridi, A. Vitamin E in uremia and dialysis patients. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1031, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynn, R.J.; Ridker, P.M.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Zee, R.Y.; Buring, J.E. Effects of random allocation to vitamin E supplementation on the occurrence of venous thromboembolism: Report from the Women’s Health Study. Circulation 2007, 116, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freedman, J.E.; Farhat, J.H.; Loscalzo, J.; Keaney, J.F., Jr. alpha-tocopherol inhibits aggregation of human platelets by a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. Circulation 1996, 94, 2434–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, S.; McWilliam, N.A.; Baglin, T.P.; Byrne, C.D. Atherogenic lipoproteins support assembly of the prothrombinase complex and thrombin generation: Modulation by oxidation and vitamin E. Blood 1998, 91, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pecoits-Filho, R.; Bárány, P.; Lindholm, B.; Heimbürger, O.; Stenvinkel, P. Interleukin-6 is an independent predictor of mortality in patients starting dialysis treatment. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 1684–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upritchard, J.E.; Sutherland, W.H.; Mann, J.I. Effect of supplementation with tomato juice, vitamin E, and vitamin C on LDL oxidation and products of inflammatory activity in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pecoits-Filho, R.; Heimbürger, O.; Bárány, P.; Suliman, M.; Fehrman-Ekholm, I.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Associations between circulating inflammatory markers and residual renal function in CRF patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).