Molecular Dysfunction and Phenotypic Derangement in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of Diabetes in Patients with Heart Failure
3. Impact of Diabetes on Heart Failure Occurrence
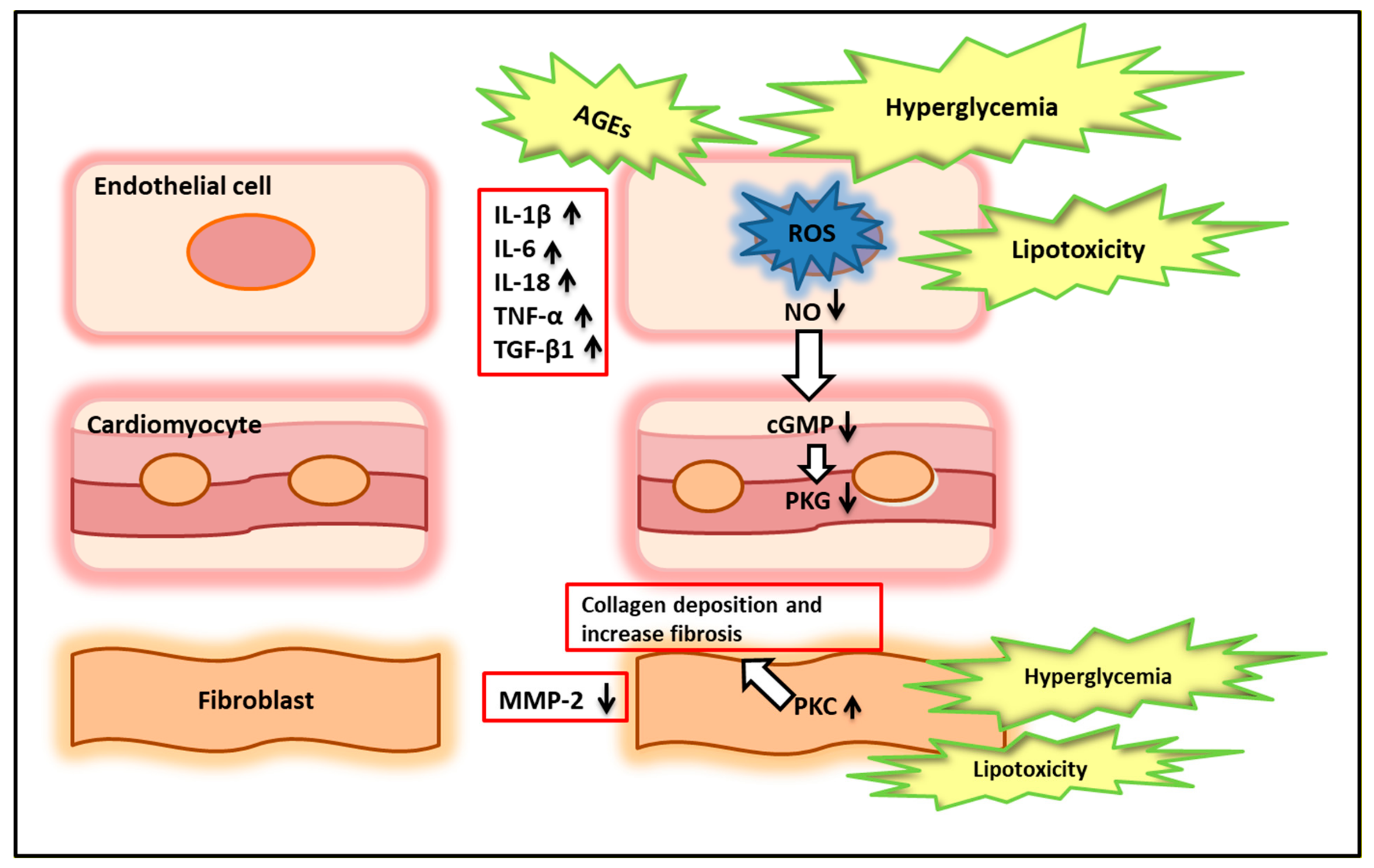
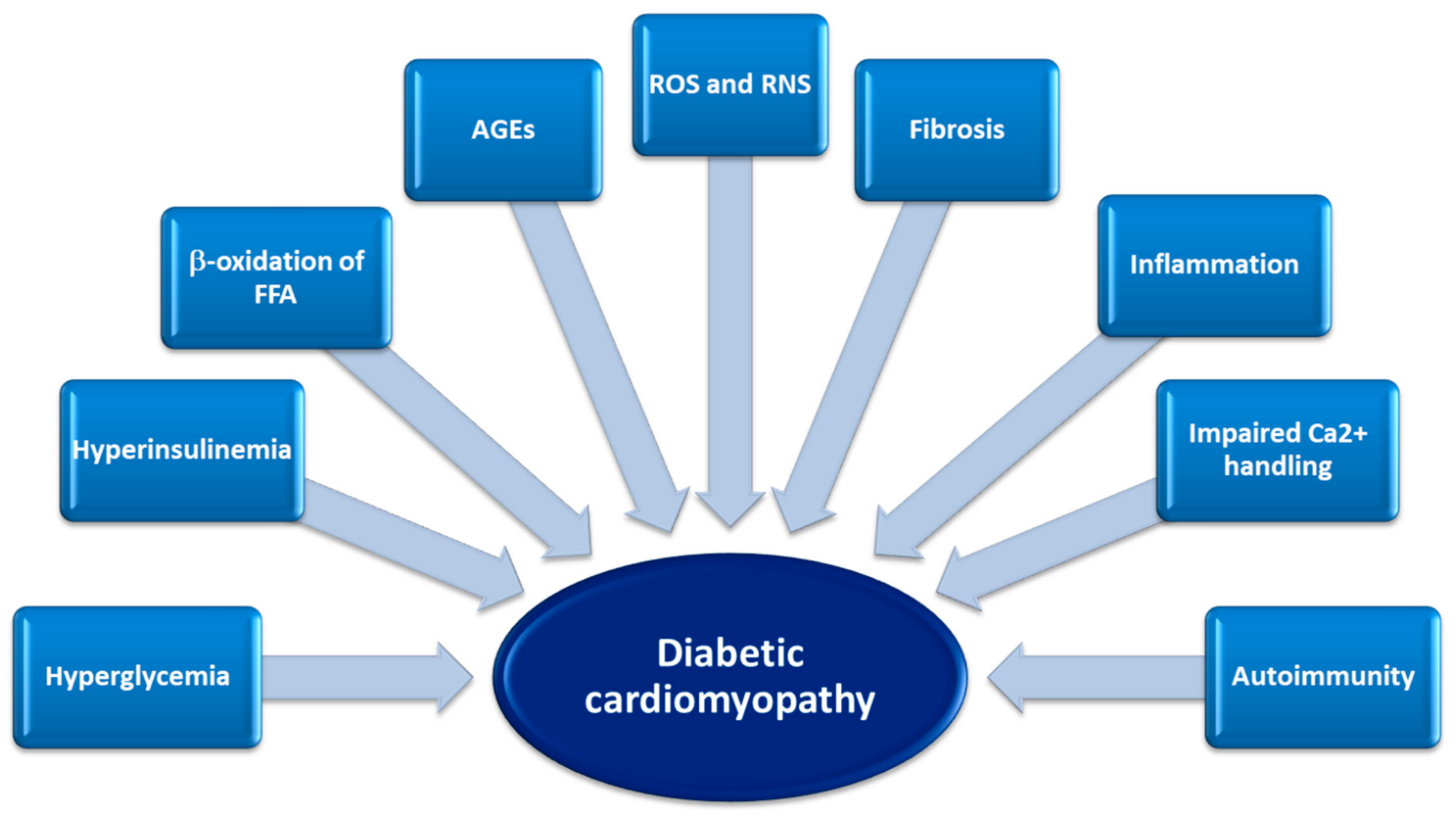
4. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: from Molecular to Structural Dysfunction
5. MicroRNA Signals in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
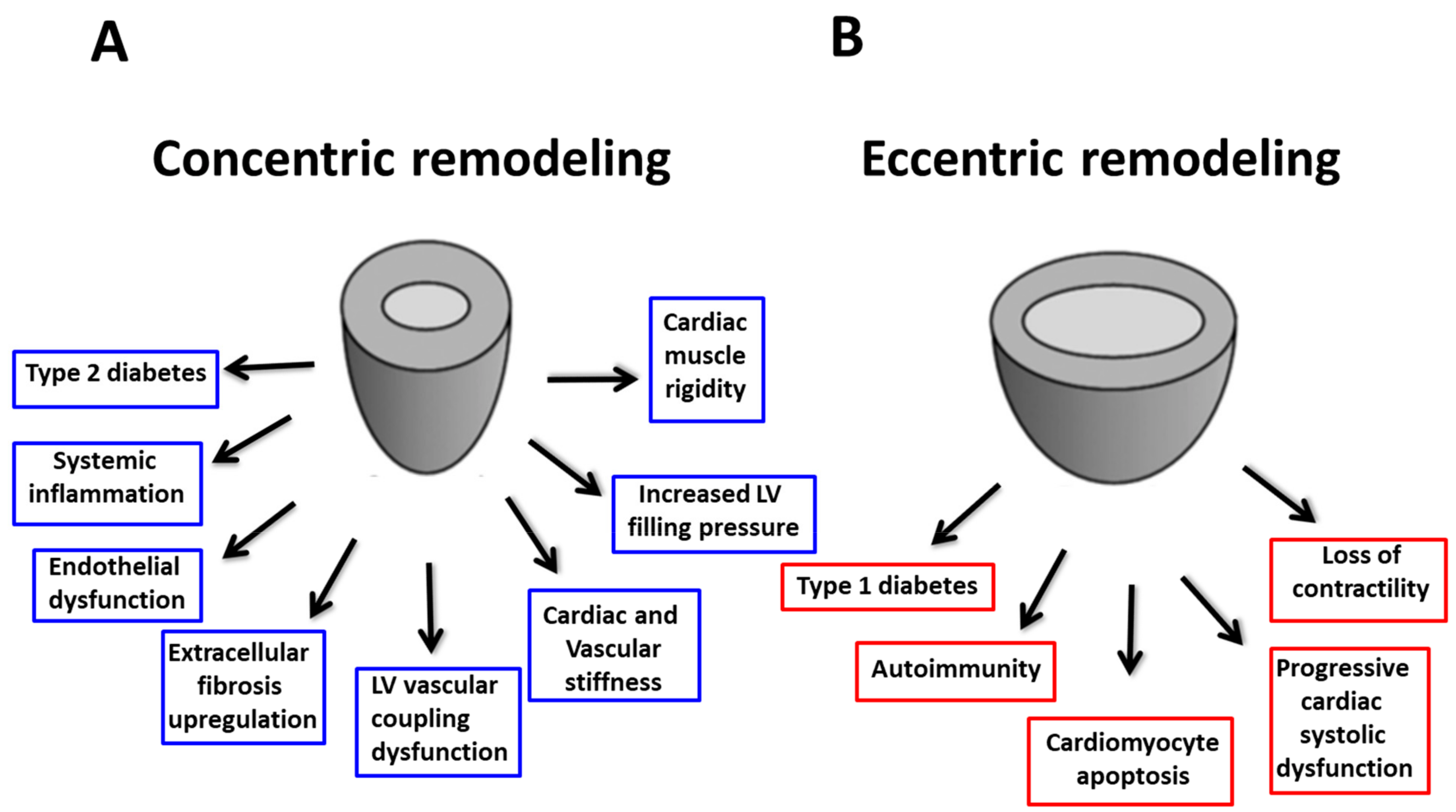
6. Different Phenotypes in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seferovic, P.M.; Paulus, W.J. Clinical diabetic cardiomyopathy: A two-faced disease with restrictive and dilated phenotypes. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J.; Goldfine, A.B. Cardiovascular safety and diabetes drug development. Lancet 2011, 377, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, G.A.; Gullion, C.M.; Koro, C.E.; Ephross, S.A.; Brown, J.B. The incidence of congestive heart failure in type 2 diabetes: An update. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, D.H.; Singh, J.S.; Levin, D.; Donnelly, L.A.; Choy, A.M.; George, J.; Struthers, A.D.; Doney, A.S.; Lang, C.C. Mean HbA1c and mortality in diabetic individuals with heart failure: A population cohort study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Dauriz, M.; Laroche, C.; Temporelli, P.L.; Hassanein, M.; Seferovic, P.M.; Drozdz, J.; Ferrari, R.; Anker, S.; Coats, A.; et al. ESC-HFA HF Long-Term Registry investigators. In-hospital and 1-year mortality associated with diabetes in patients with acute heart failure: Results from the ESC-HFA Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsen, B.; Lund, S.S.; Gluud, C.; Vaag, A.; Almdal, T.; Hemmingsen, C.; Wetterslev, J. Intensive glycaemic control for patients with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, C.; Karter, A.J.; Go, A.S.; Ferrara, A.; Liu, J.Y.; Sidney, S.; Selby, J.V. Glycemic control and heart failure among adult patients with diabetes. Circulation 2001, 103, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dei Cas, A.; Khan, S.S.; Butler, J.; Mentz, R.J.; Bonow, R.O.; Avogaro, A.; Tschoepe, D.; Doehner, W.; Greene, S.J.; Senni, M.; et al. Impact of diabetes on epidemiology, treatment, and outcomes of patients with heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.R.; Petrie, M.C.; Varyani, F.; Ostergren, J.; Michelson, E.L.; Young, J.B.; Solomon, S.D.; Granger, C.B.; Swedberg, K.; Yusuf, S.; et al. CHARM Investigators. Impact of diabetes on outcomes in patients with low and preserved ejection fraction heart failure: An analysis of the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) programme. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferović, P.M.; Petrie, M.C.; Filippatos, G.S.; Anker, S.D.; Rosano, G.; Bauersachs, J.; Paulus, W.J.; Komajda, M.; Cosentino, F.; de Boer, R.A.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: A position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 853–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender, M.A.; Steg, P.G.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Eagle, K.; Ohman, E.M.; Goto, S.; Bhatt, D.L. Impact of Diabetes mellitus on hospitalization for Heart failure, cardiovascular events, and death: Outcomes at 4 years from the reduction of Atherothrombosis for continued health (REACH) registry. Circulation 2015, 132, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, L.; Paolisso, G.; Cacciatore, F.O.; Ferrara, N.; Ferrara, P.; Canonico, S.; Rengo, F. Congestive heart failure predicts the development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the elderly. The Osservatorio Geriatrico Regione Campania Group. Diabetes Metab. 1997, 23, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.B.; Yap, J.; Tay, W.T.; Teng, T.K.; MacDonald, M.; Anand, I.S.; Sharma, A.; O’Connor, C.M.; Kraus, W.E.; Mentz, R.J.; et al. HF-ACTION and ASIAN-HF Investigators Multi-ethnic comparisons of diabetes in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Insights from the HF-ACTION trial and the ASIAN-HF registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosmi, F.; Shen, L.; Magnoli, M.; Abraham, W.T.; Anand, I.S.; Cleland, J.G.; Cohn, J.N.; Cosmi, D.; De Berardis, G.; Dickstein, K.; et al. Treatment with insulin is associated with worse outcome in patients with chronic heart failure and diabetes. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Mogensen, U.M.; Jhund, P.S.; Petrie, M.C.; Preiss, D.; Win, S.; Komajda, M. Clinical and echocardiographic characteristics and cardiovascular outcomes according to diabetes status in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: A report from the I-Preserve trial (Irbesartan in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction). Circulation 2017, 135, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McHugh, K.; DeVore, A.D.; Wu, J.; Matsouaka, R.A.; Fonarow, G.C.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Yancy, C.W.; Green, J.B.; Altman, N.; Hernandez, A.F. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Diabetes: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauriz, M.; Targher, G.; Temporelli, P.L.; Lucci, D.; Gonzini, L.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Marchioli, R.; Tognoni, G.; Latini, R.; Cosmi, F.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Diabetes and Prediabetes on Survival Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Post-Hoc Analysis of the GISSI-HF (Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nella Insufficienza Cardiaca-Heart Failure). Trial J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Mentz, R.J.; Kwasny, M.J.; Fought, A.J.; Huffman, M.; Subacius, H.; Nodari, S.; Konstam, M.; Swedberg, K.; Maggioni, A.P.; et al. Association between diabetes mellitus and post-discharge outcomes in patients hospitalized with heart failure: Findings from the EVEREST trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 15, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Preiss, D.; Jhund, P.S.; Squire, I.; Cardoso, J.S.; Merkely, B.; Martinez, F.; Starling, R.C.; Desai, A.S.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; et al. Risk Related to Pre-Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes Mellitus in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: Insights from Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure Trial. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e002560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauriz, M.; Mantovani, A.; Bonapace, S.; Verlato, G.; Zoppini, G.; Bonora, E.; Targher, G. Prognostic Impact of Diabetes on Long-term Survival Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure: A Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.; Gerstein, H.C.; Holman, R.R.; Pfeffer, M.A. Heart failure: A cardiovascular outcome in diabetes that can no longer be ignored. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, W.B.; Hjortland, M.; Castelli, W.P. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: The Framingham study. Am. J. Cardiol. 1974, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.H.; Donal, E.; Oger, E.; Hage, C.; Persson, H.; Haugen-Löfman, I.; Ennezat, P.V.; Sportouch-Dukhan, C.; Drouet, E.; Daubert, J.C.; et al. KaRen Investigators. Association between cardiovascular vs. non-cardiovascular co-morbidities and outcomes in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Anker, S.D.; Januzzi, J.L.; McGuire, D.K.; Sattar, N.; Woerle, H.J.; Butler, J. Heart Failure Epidemiology in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus without Coronary Heart Disease. J. Card. Fail. 2019, 25, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, G.A.; Hiller, T.A.; Erbey, J.R.; Brown, J.B. Congestive heart failure in type 2 diabetes: Prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Diabetes Care 2001, 2489, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Burdmann, E.A.; Chen, C.Y.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Eckardt, K.U.; Feyzi, J.M.; Ivanovich, P.; Kewalramani, R.; Levey, A.S.; et al. TREAT InvestigatorsA trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, A.G.; Hundley, W.G.; Massing, M.W.; Bonds, D.E.; Burke, G.L.; Goff, D.C. Heart failure prevalence, incidence, and mortality in the elderly with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Nishikage, T.; Lang, R.M.; Otsuji, Y. Subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in asymptomatic diabetic patients assessed by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: Correlation with diabetic duration. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2009, 10, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, M.M.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Mahoney, D.W.; Bailey, K.R.; Rodeheffer, R.J. Burden of systolic and diastolic ventricular dysfunction in the community: Appreciating the scope of the heart failure epidemic. JAMA 2003, 289, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trial Investigators, O.; Gerstein, H.C.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.R.; Díaz, R.; Jung, H.; Maggioni, A.P.; Pogue, J.; Probstfield, J.; Ramachandran, A.; et al. Basal insulin and cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, S.A.; Patel, B.; Khattar, R.S.; Malik, R.A. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Clin. Sci. 2004, 107, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; DeMarco, V.G.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Ussher, J.R.; Folmes, C.D.; Jaswal, J.S.; Stanley, W.C. Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 207–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, F.; Hishikawa, K.; Katusic, Z.S.; Luscher, T.F. High glucose increases nitric oxide synthase expression and superoxide anion generation in human aortic endothelial cells. Circulation 1997, 96, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Eto, M.; De Paolis, P.; van der Loo, B.; Bachschmid, M.; Ullrich, V.; Kouroedov, A.; Delli Gatti, C.; Joch, H.; Volpe, M.; et al. High glucose causes upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and alters prostanoid profile in human endothelial cells: Role of protein kinase C and reactive oxygen species. Circulation 2003, 107, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münzel, T.; Daiber, A.; Ullrich, V.; Mülsch, A. Vascular Consequences of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling for the Activity and Expression of the Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase and the cGMP-Dependent Protein Kinase. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heerebeek, L.; Hamdani, N.; Falcao-Pires, I.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; Begieneman, M.P.; Bronzwaer, J.G.; van der Velden, J.; Stienen, G.J.; Laarman, G.J.; Somsen, A.; et al. Low myocardial protein kinase G activity in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 2012, 126, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenouda, S.M.; Widlansky, M.E.; Chen, K.; Xu, G.; Holbrook, M.; Tabit, C.E.; Hamburg, N.M.; Frame, A.A.; Caiano, T.L.; Kluge, M.A.; et al. Altered mitochondrial dynamics contributes to endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2011, 124, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, K.J.; Isshiki, K.; Suzuma, K.; Yokota, T.; Zvagelsky, D.; Schoen, F.J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Pechous, P.A.; Vlahos, C.J.; Wakasaki, H.; et al. Expression of connective tissue growth factor is increased in injured myocardium associated with protein kinase C beta2 activation and diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhalla, N.S.; Pierce, G.N.; Innes, I.R.; Beamish, R.E. Pathogenesis of cardiac dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Can. J. Cardiol. 1985, 1, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.A.; Jang, H.J.; Martinez-Lemus, L.A.; Sowers, J.R. Activation of mTOR/p70S6 kinase by ANG II inhibits insulin-stimulated endothelial nitric oxide synthase and vasodilation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E201–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.A.; Montagnani, M.; Koh, K.K.; Quon, M.J. Reciprocal relationships between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: Molecular and pathophysiological mechanisms. Circulation 2006, 113, 1888–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, B.; Cam, M.C.; McNeill, J.H. Metabolic disturbances in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 180, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E. Molecular and cellular basis of the aetiology and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy: A short review. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 261, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Kypson, A.P.; Rodriguez, E.; Anderson, C.A.; Lehr, E.J.; Neufer, P.D. Substrate-specific derangements in mitochondrial metabolism and redox balance in the atrium of the type 2 diabetic human heart. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Rodriguez, E.; Anderson, C.A.; Thayne, K.; Chitwood, W.R.; Kypson, A.P. Increased propensity for cell death in diabetic human heart is mediated by mitochondrial-dependent pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H118–H124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, A.; Beckman, J.A.; Schmidt, A.M.; Creager, M.A. Advanced glycation end products: Sparking the development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation 2006, 114, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, G.R.; Candy, G.; Woodiwiss, A.J. Aminoguanidine prevents the decreased myocardial compliance produced by streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in rats. Circulation 1996, 93, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragno, M.; Mastrocola, R.; Medana, C.; Catalano, M.G.; Vercellinatto, I.; Danni, O.; Boccuzzi, G. Oxidative stress-dependent impairment of cardiac specific transcription factors in experimental diabetes. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 5967–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, E.; Pecoraro, M.; Rusciano, M.R.; Ciccarelli, M.; Popolo, A. Cross-Talk between Neurohormonal Pathways and the Immune System in Heart Failure: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, S.; Falcao-Pires, I.; Balligand, J.L.; Bauersachs, J.; Brutsaert, D.; Ciccarelli, M.; Dawson, D.; de Windt, L.J.; Giacca, M.; Hamdani, N.; et al. The innate immune system in chronic cardiomyopathy: A European Society of Cardiology (ESC) scientific statement from the Working Group on Myocardial Function of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Auria, F.; Polito, M.V.; Vitulano, G.; Ciccarelli, M.; De Rosa, R.; Gigantino, A.; Piscione, F.; Galasso, G. Predictors of left ventricular reverse remodeling in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 19, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöpe, C.; Walther, T.; Escher, F.; Spillmann, F.; Du, J.; Altmann, C.; Noutsias, M. Transgenic activation of the kallikrein-kinin system inhibits intramyocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 2057–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermann, D.; Rutschow, S.; Van Linthout, S.; Linderer, A.; Bücker-Gärtner, C.; Sobirey, M.; Tschöpe, C. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase attenuates left ventricular dysfunction by mediating pro-inflammatory cardiac cytokine levels in a mouse model of diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermann, D.; Van Linthout, S.; Dhayat, S.; Dhayat, N.; Escher, F.; Bücker-Gärtner, C.; Tschöpe, C. Cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of interleukin converting enzyme inhibition in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Bátkai, S.; Kechrid, M.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Lee, W.S.; Horváth, B.; Haskó, G. Cannabinoid 1 receptor promotes cardiac dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 2012, 61, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Satoh, H.; Favelyukis, S.; Babendure, J.L.; Imamura, T.; Sbodio, J.I.; Zalevsky, J.; Dahiyat, B.I.; Chi, N.W.; Olefsky, J.M. JNK and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediate free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35361–35371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alvaro, C.; Teruel, T.; Hernandez, R.; Lorenzo, M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha produces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by activation of inhibitor kappaB kinase in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17070–17078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Commane, M.; Jiang, Z.; Stark, G.R. IL-1-induced NFkappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation diverge at IL-1 receptorassociated kinase (IRAK). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4461–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, M.C.; Kong, Y.Y.; Hwang, I.K.; Won, M.H.; Rho, J.; Kwon, Y.G. TNF-related activation-induced cytokine enhances leukocyte adhesiveness: Induction of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 via TNF receptor-associated factor and protein kinase C-dependent NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, J.; Farhangkhoee, H.; Xu, B.Y.; Chen, S.; George, B.; Chakrabarti, S. PARP mediates structural alterations in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 45, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Linthout, S.; Seeland, U.; Riad, A.; Eckhardt, O.; Hohl, M.; Dhayat, N.; Schultheiss, H.P. Reduced MMP-2 activity contributes to cardiac fibrosis in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2008, 103, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Yang, X.; Ceylan-Isik, A.F.; Du, M.; Sreejayan, N.; Ren, J. Cardiac contractile dysfunction in Lep/Lep obesity is accompanied by NADPH oxidase activation, oxidative modification of sarco (endo) plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and myosin heavy chain isozyme switch. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauconnier, J.; Lanner, J.T.; Zhang, S.J.; Tavi, P.; Bruton, J.D.; Katz, A.; Westerblad, H. Insulin and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate trigger abnormal cytosolic Ca2+ transients and reveal mitochondrial Ca2+ handling defects in cardiomyocytes of ob/ob mice. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2375–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottumukkala, R.V.; Lv, H.; Cornivelli, L.; Wagers, A.J.; Kwong, R.Y.; Bronson, R.; Stewart, G.C.; Schulze, P.C.; Chutkow, W.; Wolpert, H.A.; et al. Myocardial infarction triggers chronic cardiac autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 138ra80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvin, E.; Lazo, M.; Chen, Y.; Shen, L.; Rubin, J.; McEnvoy, J.W.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Sharrett, A.R.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Coresh, J. Diabetes mellitus, prediabetes and incidence of subclinical myocardial damage. Circulation 2014, 130, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, N.; Katare, R. Molecular mechanism of diabetic cardiomyopathy and modulation of microRNA function by synthetic oligonucleotides. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.J.; Gupta, S.K.; O’Connell, E.; Thum, S.; Glezeva, N.; Fendrich, J.; Gallagher, J.; Ledwidge, M.; Grote-Levi, L.; McDonald, K.; et al. MicroRNA signatures differentiate preserved from reduced ejection fraction heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.; Keller, A.; Frese, K.S.; Leidinger, P.; Sedaghat-Hamedani, F.; Kayvanpour, E.; Kloos, W.; Backe, C.; Thanaraj, A.; Brefort, T.; et al. Multivariate miRNA signatures as biomarkers for non-ischaemic systolic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2812–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, S.; Paneni, F.; Lüscher, T.F.; Cosentino, F. MicroRNA profiling unveils hyperglycaemic memory in the diabetic heart. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Dong, W.; Qiu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zou, Y.; Song, L.; et al. MicroRNA-221 inhibits autophagy and promotes heart failure by modulating the p27/CDK2/mTOR axis. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Fiedler, J.; Erikci, E.; Kardasinski, M.; Batkai, S.; Dangwal, S.; Kumarswamy, R.; Bang, C.; Holzmann, A.; et al. The miRNA-212/132 family regulates both cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, R.A.; Iekushi, K.; Lechner, S.; Seeger, T.; Fischer, A.; Heydt, S.; Kaluza, D.; Treguer, K.; Carmona, G.; Bonauer, A.; et al. MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature 2013, 495, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakikes, I.; Chaanine, A.H.; Kang, S.; Mukete, B.N.; Jeong, D.; Zhang, S.; Hajjar, R.J.; Lebeche, D. Therapeutic cardiac-targeted delivery of miR-1 reverses pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and attenuates pathological remodeling. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundbaek, K. Diabetic angiopathy: A specific vascular disease. Lancet 1954, 266, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubler, S.; Dlugash, J.; Yuceoglu, Y.Z.; Kumral, T.; Branwood, A.W.; Grishman, A. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1972, 30, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisch, B.; Alter, P.; Pankuweit, S. Diabetic cardiomyopathy-fact or fiction? Herz 2011, 36, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, W.J.; Dal Canto, E. Distinct Myocardial Targets for Diabetes Therapy in Heart Failure with Preserved or Reduced Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzuoli, A.; Ceccarelli, E.; Ruocco, G.; Nuti, R. Clinical impact of oral antidiabetic medications in heart failure patients. Heart Fail. Rev. 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E.; Drazner, M.H.; Johnson, M.R. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, e147–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed incollaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3035–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermeier, F.; Riquelme, J.A.; Pavez, M.; Garrido, V.; Díaz, A.; Verdejo, H.E.; Castro, P.F.; García, L.; Lavandero, S. New Molecular Insights of Insulin in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, G.; Evangelista, I.; Franci, B.; Lucani, B.; Martini, S.; Nuti, R.; Palazzuoli, A. Combination of ST2 and B-type natriuretic peptide in diabetic patients with acute heart failure: Relation with ventricular stiffness and outcome. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 20, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| miRs | Expression Pattern | Pathophysiological Role | Expression Sight |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 [69,75] | Downregulated | Hypertrophy and oxidative stress | Cardiac and skeletal muscle |
| miR-1/206 [71] | Upregulated | Cardiomyocytes apoptosis | Cardiac muscle |
| miR-34a [71,74] | Upregulated | Cardiomyocytes apoptosis | Cardiac muscle |
| miR-133a [69] | Downregulated | Hypertrophy and oxidative stress | Cardiac and skeletal muscle |
| miR-195 [71] | Upregulated | Cardiomyocytes apoptosis | Cardiac muscle |
| miR-212 [71,73] | Upregulated | Hypertrophy and autophagic response | Cardiac and skeletal muscle |
| miR-221 [71,72] | Upregulated | Hypertrophy and autophagic response | Cardiac and skeletal muscle |
| miR-320 [71] | Upregulated | Cardiomyocytes apoptosis | Cardiac muscle |
| miR-373 [69] | Downregulated | Hypertrophy and oxidative stress | Cardiac muscle, endothelium |
| miR-378 [71] | Downregulated | Hypertrophy and oxidative stress | Cardiac muscle, endothelium |
| Upregulated | Cardiomyocytes apoptosis | Cardiac muscle | |
| miR-451 [69] | Upregulated | Cardiomyocytes hypertrophy | Cardiac muscle |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evangelista, I.; Nuti, R.; Picchioni, T.; Dotta, F.; Palazzuoli, A. Molecular Dysfunction and Phenotypic Derangement in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133264
Evangelista I, Nuti R, Picchioni T, Dotta F, Palazzuoli A. Molecular Dysfunction and Phenotypic Derangement in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(13):3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133264
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvangelista, Isabella, Ranuccio Nuti, Tommaso Picchioni, Francesco Dotta, and Alberto Palazzuoli. 2019. "Molecular Dysfunction and Phenotypic Derangement in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 13: 3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133264
APA StyleEvangelista, I., Nuti, R., Picchioni, T., Dotta, F., & Palazzuoli, A. (2019). Molecular Dysfunction and Phenotypic Derangement in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(13), 3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133264






