The authors want to change Figure 1 of the paper published in IJMS [1]. In Figure 1, 5-position of OH was at 6-position. Therefore, Figure 1 is revised as follows. The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience caused to the readers by this change.
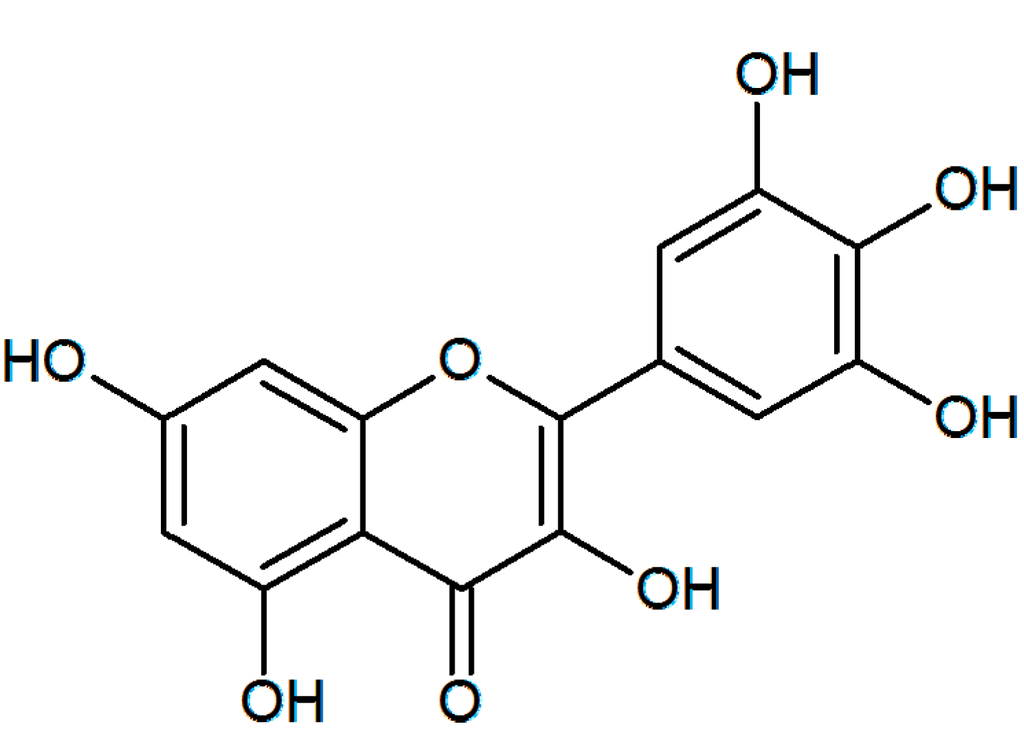
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of myricetin (3,3',4',5,5',7-hexahydroxyflavone).
Reference
- Kang, K.A.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, R.; Piao, M.J.; Kim, K.C.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Hyun, J.W. Myricetin protects cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via regulation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4348–4360. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).