Abstract
NMR studies of bioactive semicarbazones are described.
Introduction
Within our work on the development of bioactive compounds, we have employed the semicarba-zone moiety as a joining function between different pharmacophores.
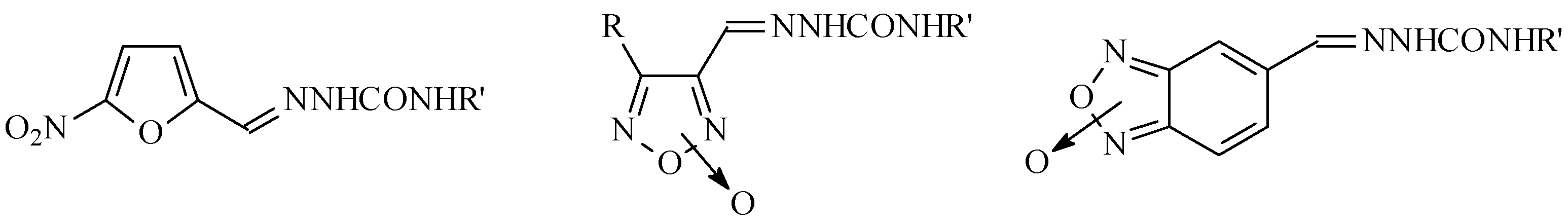
Knowing the geometric isomer at the iminic union of the semicarbazone group, as well as the N-oxide positional isomer that was obtained in the synthetic procedure, were very important for deter-mining the structure of the biologically active compound. The lack of crystals to determine unequivo-cally the exact structure of the product obtained led us to use NMR spectroscopy for this purpose.
Experimental
All the experiments were carried out on a DPX-Bruker 400 (400 y 100 MHz) instrument. We car-ried out NOE difference (1D y 2D) experiments at different mixing times in order to determine the geometric isomer of the iminic junction.
We also carried out 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR experiments at variable temperatures and EXSY ex-periments in order to determine the N-oxide position.
Results and Discussion
All the semicarbazones studied were in the E isomeric form. The N-oxide moiety in the derivatives of the heterocycle 1,2,5-oxadiazoles was found fixed at the 2 position. The derivatives of the heterocy-cle benzo[1,2-c]1,2,5-oxadiazoles were presented as a mixture of the different positional isomers of the N-oxide function, at room temperature.
Acknowledgements
C.H.L.C.C., PEDECIBA.
References and Notes
- Perrin, C.; Dwyer, T. Chem. Rev. 1990, 90, 935.