Abstract
Radix Rehmanniae, Fructus Schisandrae, Radix Bupleuri, and Fructus Gardeniae are often used alongside with clozapine (CLZ) for schizophrenia patients in order to reduce side effects and enhance therapeutic efficacy. However, worse outcomes were observed raising concern about a critical issue, herb-drug interactions, which were rarely reported when antipsychotics were included. This study aims to determine whether the concomitant use of these herbal medicines affects the pharmacokinetic characteristics of CLZ in rat models. Rats were given a single or multiple intraperitoneal injections of 10 mg/kg CLZ, either alone or with individual herbal water extracts administered orally. CLZ and its two inactive metabolites, norclozapine and clozapine N-oxide, were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. In the acute treatment, the formation of both metabolites was reduced, while no significant change was observed in the CLZ pharmacokinetics for any of the herbal extracts. In the chronic treatment, none of the four herbal extracts significantly influenced the pharmacokinetic parameters of CLZ and its metabolites. Renal and liver functions stayed normal after the 11-day combined use of herbal medicines. Overall, the four herbs had limited interaction effect on CLZ pharmacokinetics in the acute and chronic treatment. Herb-drug interaction includes both pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic mechanisms. This result gives us a hint that pharmacodynamic herb-drug interaction, instead of pharmacokinetic types, may exist and need further confirmation.
1. Introduction
Clozapine (CLZ), a tricyclic dibenzodiazepine antipsychotic drug, is commonly prescribed for the long-term maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. CLZ is therapeutically effective for treating patients with schizophrenia that is refractory to other neuroleptics, without producing significant extrapyramidal symptoms. However, the associated adverse effects, such as hypersalivation, idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity, agranulocytosis, and cardiactoxicity, restrict its clinical use [1,2]. Herbal medicines are increasingly used in the treatment of schizophrenia to improve the therapeutic efficacy and reduce adverse side effects. Our previous epidemiological survey showed that approximately 37% of schizophrenia patients received antipsychotics in combination with herbal medicines, including Radix Rehmanniae, Fructus Gardeniae, Radix Bupleuri, and Fructus Schisandrae, etc. [3]. Radix Rehmanniae (RR, Di-Huang), derived from the roots of Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC., is a traditional Chinese medicine frequently used for the treatment of anemia, diabetes, dizziness, tinnitus, nocturnal emission, and palpitation. According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, this herb can “nourish yin and replenish blood, reinforcing essence and marrow” [4]. In other words, it has a hemostatic effect, removing heat and enriching the blood [5]. Fructus Schisandrae (FS, Wu-Wei-Zi), the dried fruit from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., is known to possess hepatoprotective and general detoxifying functions which is commonly used for the treatment of chronic cough and dyspnea, enuresis, frequent urination, and night sweating [6]. Radix Bupleuri (RB, Chai-Hu), the root of Bupleurum chinense DC., is traditionally used for metabolic regulation and beneficial in treating fever, influenza, inflammation, malaria, and menstrual disorders [4,7]. Fructus Gardeniae (FG, Zhi-Zi), the dried fruit of Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis, can suppress the evil fire, relieve internal heat, and cool the blood in the body according to Chinese medical theory. It is used to treat inflammation, jaundice, hepatitis, diabetes, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, and depression [4,8]. Because of these effects, the four herbs are commonly used in combination with CLZ by patients with schizophrenia. However, our previous study indicated that the concomitant use is, contrary to expectation, strongly associated with worse clinical outcomes [3]. The underlying mechanism is still unclear. Unfortunately, few reports focus on the interaction of herbal medicines and antipsychotics. Therefore, in this research, we evaluated the pharmacokinetic influence of herbs on clozapine metabolism.
Previous studies have found that CLZ is metabolized to norclozapine (norCLZ) and clozapine N-oxide (CLZ N-oxide) via cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, mainly CYP1A2, CYP3A4, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 [9,10]. The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of CLZ may change if the activities of CYP enzymes are altered by disease or CYP modulators [11,12]. The concomitant use of rifampicin and St John’s wort, both of which induce CYP1A2 and CYP3A4, is known to decrease CLZ plasma levels in patients [13,14]. Oral contraceptives have been reported to cause elevated CLZ plasma levels due to CYP inhibition [15]. Therefore, the conjecture that metabolic inhibition or induction of CLZ takes place as a consequence of herbal addition seemed plausible. This would provide an explanation for the unfavorable therapeutic effects observed in clinic.
The current study examined the influence of acute or chronic co-administration of the aforementioned four herbal preparations on CLZ pharmacokinetics in rats. Safety evaluation of 11-day combined use of herbal medicines on liver and kidney function were conducted by determination of the biochemical parameters, including aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), creatinine (CR), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels.
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Herbal Medicine on CLZ Pharmacokinetics in Rats
All calibration curves in biological samples exhibited good linearity. The accuracy calculated of bias% for CLZ, norCLZ and CLZ N-oxide were 16.8%, 14.7% and 15.1%, respectively. The precision calculated of RSD% were 9.1%, 9.1%, and 9.4% for CLZ, norCLZ, and CLZ N-oxide, respectively. The method sensitivity in plasma was determined by the LLOQ, which were 9.8, 13.6, and 17.1 nM for CLZ, norCLZ, and CLZ N-oxide, respectively.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the mean plasma concentrations of CLZ, norCLZ and CLZ N-oxide over time, following acute or chronic administration of CLZ in rats. The plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of the three compounds are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2.
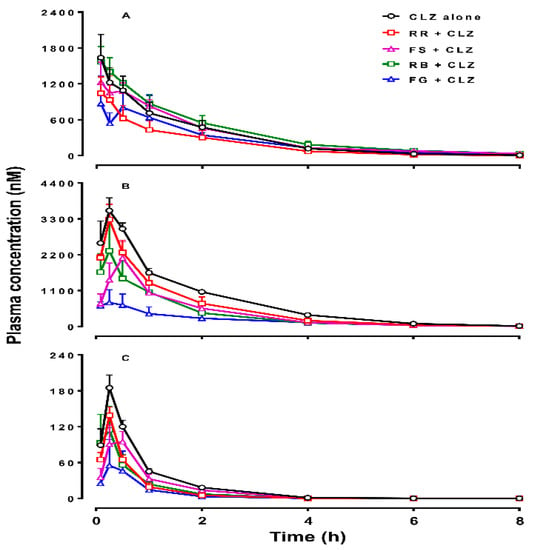
Figure 1.
Plasma concentrations of clozapine (CLZ, A), norclozapine (norCLZ, B), and clozapine N-oxide (CLZ N-oxide, C) over time in rats treated with an intraperitoneal dose of 10 mg/kg of CLZ alone (n = 5), or pretreated orally with Radix Rehmanniae (RR; n = 4), Fructus Schisandrae (FS; n = 6), Radix Bupleuri (RB; n = 6), and Fructus Gardeniae (FG; n = 4), respectively. The data are presented as mean ± SEM.
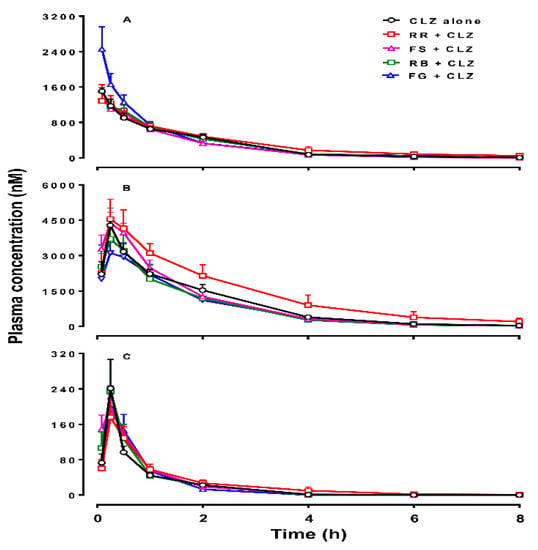
Figure 2.
Plasma concentrations of clozapine (CLZ, A), norclozapine (norCLZ, B), and clozapine N-oxide (CLZ N-oxide, C) over time in rats treated with an intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg of CLZ for 11 days alone (n = 5), or pretreated orally with Radix Rehmanniae (RR; n = 6), Fructus Schisandrae (FS; n = 4), Radix Bupleuri (RB; n = 4), and Fructus Gardeniae (FG; n = 4), respectively, every day. The data are presented as mean ± SEM.

Table 1.
Effects of acute cotreatment with Radix Rehmanniae (RR), Fructus Schisandrae (FS), Radix Bupleuri (RB), and Fructus Gardeniae (FG) on the pharmacokinetics of plasma clozapine, norclozapine (norCLZ), and clozapine N-oxide (CLZ N-oxide) in rats after an intraperitoneal dose of 10 mg/kg clozapine a,b.

Table 2.
Effects of chronic co-treatment with Radix Rehmanniae (RR), Fructus Schisandrae (FS), Radix Bupleuri (RB), and Fructus Gardeniae (FG) on the pharmacokinetics of plasma clozapine, norclozapine (norCLZ), and clozapine N-oxide (CLZ N-oxide) in rats after intraperitoneal administration of 10 mg/kg clozapine for 11 days a,b.
In the acute CLZ treatment, RR cotreatment reduced the AUC0-∞ of CLZ N-oxide by approximately 50% (F = 3.596, p = 0.023), but did not significantly affect the AUC0-∞ of CLZ, norCLZ, or the Cmax of CLZ (Table 1 and Figure 1). FS cotreatment reduced the AUC0-∞ and Cmax values of norCLZ by 50% compared with CLZ alone (F = 3.902, p = 0.013), but did not significantly alter the systemic exposure of CLZ and CLZ N-oxide. The addition of RB extract reduced the AUC0-∞ of norCLZ by 51% (F = 3.902, p = 0.014) and the AUC0-∞ of CLZ N-oxide by 49% (F = 3.596, p = 0.012). A single-dose administration of FG extract decreased the AUC0-∞ of norCLZ by 75% (F = 3.902, p = 0.002), CLZ N-oxide by 73% (F = 3.596, p = 0.007), and CLZ by 21%. The Cmax value of CLZ N-oxide was reduced by 31% (F = 2.638, p = 0.008) after adding FG.
The values of concentration ratios of norCLZ to CLZ (norCLZ/CLZ) at 0.25 h post-dose in the presence of FS and RB and the values of CLZ N-oxide/CLZ at 1 h post-dose in the presence of RB and 2 h post-dose in the presence of RB and FG were significantly different from that in the control group. The other metabolism ratios (plasma concentration of either metabolite to CLZ) between the herbal addition groups and CLZ alone group were comparable (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials). In the chronic treatment, the combination of individual herbal extracts did not significantly change the kinetic parameters of CLZ, norCLZ, or CLZ N-oxide (Table 2). Despite that, co-administration of RR with CLZ for 11 days increased the mean AUC0-∞ value of CLZ, norCLZ, and CLZ N-oxide by 33%, 60%, and 37%, respectively. Figure 2 shows that the plasma concentrations of CLZ in the FG group were higher than those in the control group at 5, 15, and 30 min. However, there was no difference in metabolism ratios of either metabolite to CLZ between the groups treated with and without herbal medicines (Table S2). Comparison of the pharmacokinetic parameters of CLZ, norCLZ, and CLZ N-oxide between the groups of acute and chronic administration of CLZ alone showed no self-induction/inhibition and there was no accumulation of the three compounds in the rats, consistent with a previous report [16].
2.2. Biodistribution of CLZ in Various Organs
The LLOQ in all the tissues was 3.28 nM for CLZ, 5.45 nM for norCLZ and 29.8 nM for CLZ N-oxide, respectively. Rat organs were collected 24 h after the last dose in the long-term treatment group. CLZ and its metabolites were almost undetectable in the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and whole brain, which were in parallel with the plasma levels.
2.3. Safety Evaluation of Chronic Administration of Herbs on Rat Liver and Renal Functions
Comparison of the serum AST, ALT, CR, and BUN levels between the herbal additive groups and the CLZ alone group indicated that rat liver and renal functions were not affected by the four herbs in the chronic study (Figure 3).
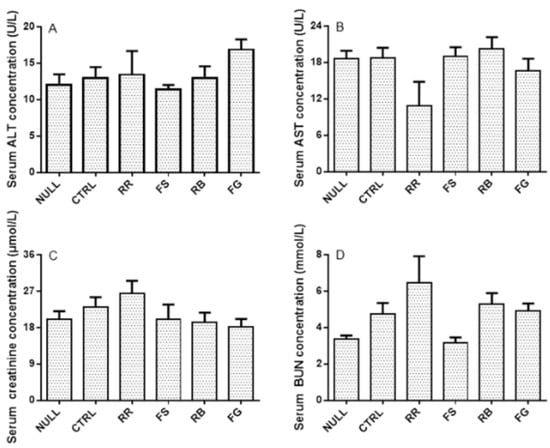
Figure 3.
Serum concentrations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT; A), aspartate aminotransferase (AST; B), creatinine (CR; C), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN; D) after 11-day treatment of vehicle (CTRL) and clozapine (CLZ) with or without Radix Rehmanniae (RR), Fructus Schisandrae (FS), Radix Bupleuri (RB), and Fructus Gardeniae (FG), respectively. The data are presented as mean ± SEM.
3. Discussion
Previous studies have demonstrated that schizophrenia patients have a higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome than the general population, while antipsychotic drugs can aggravate glucose and lipid metabolism disorders [17,18]. Combined administration of herbs and drug has enjoyed increasing popularity in recent decades. RR, FS, RB, and FG are widely used in psychiatric patients for relieving adverse effects and improving efficacy. It has been reported that the administration of FS and RR in combination with other herbs has the potential to treat various cardiovascular diseases [19] and improve serum lipid and glucose levels [20]. An animal study with vinegar-baked RB indicated its effect on the regulation of lipid disorders by increasing fatty acid oxidation [21]. Geniposide from FG was confirmed to alleviate insulin resistance and abnormal lipid metabolism [22]. Crocetin and crocin from a water extract of FG showed anti-hypertensive effects [8]. However, the concomitant use of certain herbs and antipsychotics did not reach the intended outcome. On the contrary, worse clinical outcomes were observed [3]. Therefore, disclosure of the underlying mechanisms is urgently required. The altered efficacy of drugs can be due to herb-drug interaction which includes both pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions. This study investigated the effect of co-administration of individual water extracts of four herbs on the pharmacokinetics of an effective atypical antipsychotic agent, CLZ, in rats.
It has been reported that the four herbs investigated in this study, RR, FS, RB, and FG, have the potential to inhibit CYP activitities. RR was reported to inhibit the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 using probe substrates in vitro [23]. Vinegar-baked RB was shown to significantly inhibit the activity of CYP2C9 but not that of CYP1A2 or CYP3A4 [24]. Genipin, an aglycone of geniposide from FG, is a main component exhibiting pharmacological activity that can significantly induce CYP2D6 enzyme, and inhibit CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 activity [25]. A single dose of FS in rats was reported to have an inhibitory effect on CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 and an inducible effect on CYP2E1, using theophylline, midazolam, and dapsone as probe substrates [26,27]. As CLZ is mainly metabolized by CYPs, the four herbs may affect CLZ pharmacokinetics via CYP enzyme modulation.
In the acute study, the formation of norCLZ and CLZ N-oxide dropped to various extents when CLZ was used in combination with individual herbs. The greatest reduction in the AUC0-∞ of norCLZ was observed in the FG group (75%), followed by the RB (51%) and FS groups (50%). The decreased systemic exposure of CLZ metabolites suggested CYP enzyme inhibition by FS, RB, and FG in CLZ metabolism, which is consistent with the reported inhibitory effect of these four herbs. However, the decreased extent of CLZ metabolism is due to the cooperative contribution of each isozyme, the intrinsic inhibitory potential of and in vivo concentrations of active components from herbs. The systemic exposure of CLZ showed no significant difference among different groups. ClZ was metabolized via oxidation, sulfation, and glucuronidation to hydroxylated metabolites, CLZ-glucuronides, norCLZ-glucuronides as well as the two major metabolites norCLZ and CLZ N-oxide [28]. Compensatory metabolism of other metabolic pathways with the addition of herb extract may lead to the same CLZ level in the acute study. NorCLZ is a metabolite with limited pharmacological activity and CLZ N-oxide had little activity. Clinical outcomes are reported to be related to the concentration ratios of norCLZ to CLZ [29]. However, the norCLZ/CLZ ratio remained unchanged except at 0.25 h after dosing with CLZ and FS or RB in the acute study. It could be concluded that the four herbs tested played very limited role in causing pharmacokinetic herb-CLZ interaction.
Studies of herb-drug interactions are commonly performed with a single bolus dose, whereas the clinical use of herbs and drugs often lasts for longer periods. Therefore, in the chronic study, the herbal medicines were repeatedly administered at their human equivalent doses over an 11-day period to mimic clinical usage. No statistically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of CLZ were observed in the presence and absence of the herbal medicines, although there was a trend of increased systemic exposure of CLZ with RR and FG addition, of norCLZ with RR addition, and of CLZ N-oxide with each herbal addition. It has been reported that multiple doses of FS can induce CYP3A4 activity but decrease CYP1A2 and CYP2E1 activity in rats using probe substrates [26,27]. One-week administration of ethanol/water extraction of RB robustly induced CYP2E1, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 when chlorzoxazone, dextromethorphan, and midazolam were chosen as substrates, respectively. However, RB had no significant effect on CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 when caffeine, tolbutamide, and omeprazole were selected as probe substrates, respectively [30]. Collectively, multiple components contained in each herb may have different effects on CYP isozymes. Moreover, the low systemic exposure of bioactive components in herbs may lead to a lack of modulation of CYP enzymes in vivo. In summary, it seems impossible that the four herbs would cause an interaction with CLZ pharmacokinetics.
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
CLZ and its two metabolites, norCLZ and CLZ N-oxide, were obtained from Selleck Chemicals (Houston, TX, USA), Tocris (Bristol, UK), and Enzo (New York, NY, USA), respectively. Olanzapine was purchased from Meryer Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Bioactive compounds contained in the four herbs including saikosaponin A, saikosaponin D, geniposide, gardein A, catalpol, acteoside, schisandrin, and schisandrol B were purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). ALT and AST Elisa kits were bought from Yuan Ye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). CR and BUN assay kits were purchased from Jian Cheng Chemical Industrial Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Heparin sodium salt was obtained from Sigma Aldrich. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-grade actonitrile was supplied by Duksan Pure Chemical Co., Ltd. (Ansan, South Korea) and other analytical reagents by Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
4.2. Herbal Extraction Preparation
Raw materials of Radix Rehmanniae (RR, Di-Huang), Fructus Schisandrae (FS, Bei Wu-Wei-Zi), Radix Bupleuri (RB, Chai-Hu), and Fructus Gardeniae (FG, Zhi-Zi) were supplied and deposited by the pharmacy of the School of Chinese Medicine at the University of Hong Kong (Hong Kong, China). The specimens were identified before use by Dr. Yan-Bo Zhang at the University of Hong Kong. The extraction was conducted as recommended in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia to preserve the bioactive constituents. Briefly, the raw material of each herb (1.8 kg) was sliced, broiled, immersed, and boiled in a 10-fold volume of distilled water for 2 h. The residue was then extracted by repeating the same process, as previously reported [31]. The extracted solution was pooled and concentrated using a vacuum rotary evaporator. The four herbs used in the present work are well known plants with fully known active compounds [4]: catalpol and acteoside from RR, schisandrin and chisandrol B from FS, saikosaponin A and saikosaponin D from RB, geniposide and gardenin A from FG. Therefore, the eight compounds were selected as marker components and measured using HPLC. The contents of catalpol, acteoside, schisandrin, schisandrol B, saikosaponin A, geniposide, and gardenin A were 5.60 ± 0.28, 1.59 ± 0.24, 0.65 ± 0.05, 1.84 ± 0.37, 0.39 ± 0.05, 48.3 ± 12.0, 0.32 ± 0.02 (mean ± SD, n = 3) mg/g raw material [32]. The content of saikosaponin D in the water extraction was too low to quantitate. A stock solution of 1 g raw material/mL was prepared for each herb.
4.3. Rat Pharmacokinetic Studies
All rat studies were approved by the Committee on the Use of Live Animals in Teaching and Research of the LKS Faculty of Medicine at the University of Hong Kong. Male Sprague-Dawley rats with a body weight of 250 ± 20 g were housed in an animal room at 23 ± 1 °C with a 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on 06:00–18:00 h). Water and food were available ad libitum. In the acute treatment, the rats were randomly assigned to five groups (at least four rats per group) and administered with CLZ alone or in combination with RR (15 g/kg), FS (5 g/kg), RB (5 g/kg), or FG (8 g/kg). Following an overnight fast, the rats were injected intraperitoneally with CLZ at 10 mg/kg alone or 15 min after oral administration of each herbal preparation. CLZ was intraperitoneally injected to avoid the influence on its intestinal absorption by herbal addition and to investigate the underlying mechanism with respect of metabolism. The 15-min interval was set to produce high concentrations of herbal constituents when CLZ was injected to rats. Individual herbal preparations were administered at 5 to 8 times the clinical dose. Serial blood samples (0.3 mL each) were collected from the jugular vein at 0, 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 h post-treatment. In the chronic study, the rats were randomly assigned to five groups (at least four rats per group) and administered with CLZ alone, or in combination with RR (3 g/kg), FS (1 g/kg), RB (1 g/kg), or FG (1 g/kg). The dosages of these herbal preparations were equivalent to the dosages used in clinical practice. Rats were injected intraperitoneally with CLZ at 10 mg/kg alone or in combination with orally administered individual herbal preparations once daily for 11 consecutive days. Serial blood samples (0.3 mL each) were collected from the jugular vein at 0, 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 h after the last dose. After centrifugation, the obtained plasma samples were stored at −80 °C until further analysis. During sample collection period, 0.3 mL sterile isotonic saline containing 20 IU/L heparin was injected through jugular vein after sampling at each time point to compensate for the blood loss.
After blood samples were taken from the rats receiving long-term treatment, the rats were sacrificed and trunk blood, heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and brain were obtained. Blood was also collected from the rats receiving no drug treatment and served as control. Tissues were homogenized with addition of 4 volumes of iced water. Serum samples were stored at −80 °C until determination of AST, ALT, CR, and BUN levels and tissue homogenate were stored at −80 °C for analysis of CLZ and its metabolites.
4.4. Biochemical Assay of AST, ALT, CR, and BUN Levels in Chronic Treated Rats
All of the procedures for determining AST, ALT, CR, and BUN levels were exactly the same as the protocols provided by the manufacturers.
4.5. The Measurement of CLZ, norCLZ, and CLZ N-oxide
Plasma and tissue homogenates were deproteinized and the mixed solution was vortexed and centrifuged [33]. The supernatants were obtained and an aliquot of 10 μL of each sample was injected to the LC-MS/MS system. CLZ and its metabolites were measured using an API 3200 Qtrap mass spectrometer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) connected with an Agilent 1200 HPLC system (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA). An ACE 5 AQ column (5 μm, 4.6 × 250 mm) maintained at room temperature was applied for chromatographic separation. The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile (A) and water containing 0.1% formic acid (B) and was delivered at 0.7 mL/min following a gradient program: 40% to 95% A (0–7.0 min), 95% (7.0–8.0 min), 95% to 40% A (8.0–8.1 min), and 40% A (8.1–11 min). The precursor-to-product ion pairs used for monitoring the multiple reactions of CLZ, CLZ N-oxide, and norCLZ were m/z 327.2→270.1, 343.2→192.1, and 313.2→192.1, respectively. Olanzapine was selected as the internal standard. Analyst software version 1.5.2 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) was used for the HPLC-MS/MS system operation, data acquisition, and processing. Validation of the method was conducted. Only intra-day precision and accuracy were provided because biological samples were analyzed within one day every time.
4.6. Data Analysis
Pharmacokinetic parameters were determined using the Kinetica program ((InnaPhase Corp., Philadelphia, PA, USA). The peak concentration (Cmax), time to reach Cmax (tmax), area under the concentration-time curve between time 0 and infinity (AUC0-∞), elimination half-life (t1/2), total body clearance (CL/F), mean residence time (MRT), and volume of distribution (Vd) were obtained. All data are expressed as the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM). Biochemical data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by post hoc multiple comparisons. Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test was performed for multiple comparisons if equal variance was assumed; otherwise, the Dunnet T3 method was applied. p < 0.05 was considered to be the minimum level of statistical significance.
5. Conclusions
The present study demonstrated that an acute dose of individual water preparation of RR, FS, RB, and FG inhibited CLZ metabolism in rats but both acute and chronic combination use of the herbal medicines did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of CLZ. Our study indicates that CLZ efficacy was little influenced by pharmacokinetic interaction between the abovementioned herbal medicines and CLZ in rats. These results provide valuable information for our understanding of why combined use of RR, FS, RB, or FG and CLZ gives worse results. Other mechanisms, like pharmacodynamic interaction between herbs and CLZ, should be evaluated in the future. Further studies with human subjects are also needed to confirm the results in rats.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/21/6/696/s1.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Health and Medical Research Fund (HMRF) of Hong Kong (project reference no.: 1011138). We are grateful to A-H editing company and Sanja Särman of the University of Hong Kong for their kind help in English editing.
Author Contributions
All authors involved in experimental design. Dan-Dan Tian and Wei Wang carried out the experiments and drafted the manuscript. Dan-Dan Tian, Wei Wang and Zhang-Jin Zhang performed data analysis. Hua-Ning Wang, Stephen Cho Wing Sze, and Zhang-Jin Zhang gave critical comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
CLZ, clozapine; norCLZ, norclozapine; CLZ N-oxide, clozapine N-oxide; CYPs, cytochrome P450s; RR, Radix Rehmanniae (Di-Huang); FS, Fructus Schisandrae (Wu-Wei-Zi); RB, Radix Bupleuri (Chai-Hu); FG, Fructus Gardeniae (Zhi-Zi); HPLC/MS/MS, high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry; Cmax, peak concentration; Tmax, time to reach Cmax; AUC0-∞, area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity; t1/2, elimination half-life; CL/F, total body clearance; MRT, mean residence time; Vd, volume of distribution.
References
- Asenjo Lobos, C.; Komossa, K.; Rummel-Kluge, C.; Hunger, H.; Schmid, F.; Schwarz, S.; Leucht, S. Clozapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 11, CD006633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hert, M.; Detraux, J.; van Winkel, R.; Yu, W.; Correll, C.U. Metabolic and cardiovascular adverse effects associated with antipsychotic drugs. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Tan, Q.R.; Tong, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Ho, L.M.; Wong, H.K.; Feng, Y.B.; Wang, D.; Ng, R.; et al. An epidemiological study of concomitant use of Chinese medicine and antipsychotics in schizophrenic patients: Implication for herb-drug interaction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 2010 ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.X.; Li, M.X.; Jia, Z.P. Rehmannia glutinosa: Review of botany, chemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.H.; Toma, D.; Ren, S.; Huang, L.; Yaramus, M.; Baum, A.; Venkataramanan, R.; et al. Traditional Chinese medicines Wu Wei Zi (Schisandra chinensis Baill) and Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch) activate pregnane X receptor and increase warfarin clearance in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, M.L.; Wink, M. Genus Bupleurum: A review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology and modes of action. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.F.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.Y. Fructus Gardenia (Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis) phytochemistry, pharmacology of cardiovascular, and safety with the perspective of new drugs development. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Tian, D.D.; Zheng, B.; Wang, D.; Tan, Q.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.J. Peony-Glycyrrhiza Decoction, an Herbal Preparation, Inhibits Clozapine Metabolism via Cytochrome P450s, but Not Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase in in Vitro Models. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetty, M.; Murray, M. CYP-mediated clozapine interactions: How predictable are they? Curr. Drug Metab. 2007, 8, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfuhlmann, B.; Hiemke, C.; Unterecker, S.; Burger, R.; Schmidtke, A.; Riederer, P.; Deckert, J.; Jabs, B. Toxic clozapine serum levels during inflammatory reactions. J. Clin. Psychopharm. 2009, 29, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.G.; Nelson, S.; Takala, C.R.; Goren, J.L. Infection and inflammation leading to clozapine toxicity and intensive care: A case series. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, S.; Dixon, T.; Docherty, M.; Shergill, S.S. Optimising plasma levels of clozapine during metabolic interactions: A review and case report with adjunct rifampicin treatment. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Strater, A.C.; Bogers, J.P. Interaction of St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) with clozapine. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 27, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbay, V.; O’Dowd, M.A.; Mamamtavrishvili, M.; Asnis, G.M. Clozapine and oral contraceptives: A possible drug interaction. J. Clin. Psychopharm. 2002, 22, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, G.; Wiatr, G.; Wachsmuth, H.; Dachtler, M.; Albert, K.; Gaertner, I.; Breyer-Pfaff, U. Isolation and identification of clozapine metabolites in patient urine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casey, D.E. Metabolic issues and cardiovascular disease in patients with psychiatric disorders. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118 (Suppl. 2), 15S–22S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhong, Z.; Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; Diao, F.; Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, J.; et al. The comparison of glycometabolism parameters and lipid profiles between drug-naive, first-episode schizophrenia patients and healthy controls. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 150, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.N.; Cho, M.; So, I.; Jeon, J.H. The protective effects of Schisandra chinensis fruit extract and its lignans against cardiovascular disease: A review of the molecular mechanisms. Fitoterapia 2014, 97, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Pan, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, P.L.; Chu, Z.S.; Yu, Z.L.; Zhou, S.F.; Ko, K.M. Dietary pulp from Fructus Schisandra Chinensis supplementation reduces serum/hepatic lipid and hepatic glucose levels in mice fed a normal or high cholesterol/bile salt diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, T.F.; Lu, H.J.; Liou, S.S.; Chang, C.J.; Liu, I.M. Vinegar-Baked Radix Bupleuri Regulates Lipid Disorders via a Pathway Dependent on Peroxisome-Proliferator-Activated Receptor-alpha in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, K.; Shimada, T.; Nagareda, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Ishizaki, J.; Sai, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Aburada, M. Preventive effect of geniposide on metabolic disease status in spontaneously obese type 2 diabetic mice and free fatty acid-treated HepG2 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Or, P.M.; Lam, F.F.; Kwan, Y.W.; Cho, C.H.; Lau, C.P.; Yu, H.; Lin, G.; Lau, C.B.; Fung, K.P.; Leung, P.C.; et al. Effects of Radix Astragali and Radix Rehmanniae, the components of an anti-diabetic foot ulcer herbal formula, on metabolism of model CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4 probe substrates in pooled human liver microsomes and specific CYP isoforms. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Mao, S. Modulatory effects of extracts of vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri and saikosaponins on the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes in vitro. Xenobiotica 2014, 44, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.N.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.L.; Yan, K. Evaluation of genipin on human cytochrome P450 isoenzymes and P-glycoprotein in vitro. Fitoterapia 2014, 98, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Mao, C.; Yin, F.; Yu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Song, Y.; Lu, T. Effects of unprocessed versus vinegar-processed Schisandra chinensis on the activity and mRNA expression of CYP1A2, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4 enzymes in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.; Hao, H.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G.; Kang, A.; Peng, Y.; et al. Effects of short-term and long-term pretreatment of Schisandra lignans on regulating hepatic and intestinal CYP3A in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson-Ridout, K.K.; Sun, D.; Lazarus, P. Glucuronidation of the second-generation antipsychotic clozapine and its active metabolite N-desmethylclozapine. Potential importance of the UGT1A1 A(TA)7TAA and UGT1A4 L48V polymorphisms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 22, 561–576. [Google Scholar]
- Lameh, J.; Burstein, E.S.; Taylor, E.; Weiner, D.M.; Vanover, K.E.; Bonhaus, D.W. Pharmacology of N-desmethylclozapine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.Q.; Zahng, Z.J. Assessment of the effects of Radix bupleuri and vinegar-baked Radix bupleuri on cytochrome 450 activity by a six-drug cocktail approach. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.N.; Wang, C.Y.; Sze, C.W.; Tong, Y.; Tan, Q.R.; Feng, X.J.; Liu, R.M.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.J. A randomized, crossover comparison of herbal medicine and bromocriptine against risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia in patients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharm. 2008, 28, 264–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Tian, D.D.; Zhang, Z.J. In-vitro effects of concomitant use of herbal preparations on cytochrome P450s involved in clozapine metabolism. Molecules 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravagiri, M.; Marder, S.R. Simultaneous determination of clozapine and its N-desmethyl and N-oxide metabolites in plasma by liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem mass spectrometry and its application to plasma level monitoring in schizophrenicpatients. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 26, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).