Action Recognition with 3D Residual Attention and Cross Entropy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Human Action Recognition
2.2. 3D ResNets
2.3. Attention Mechanism
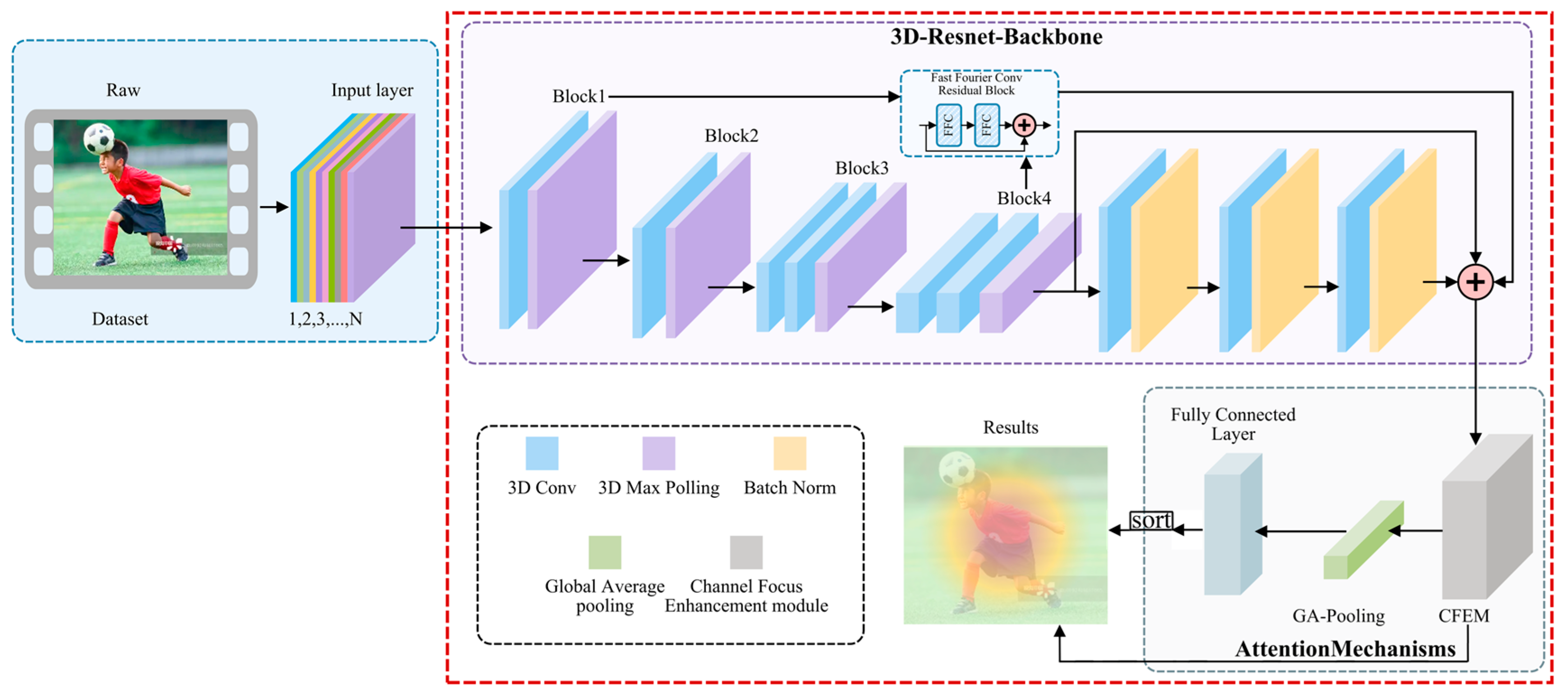
3. Methodology
3.1. Overall Structure of 3DRFNet
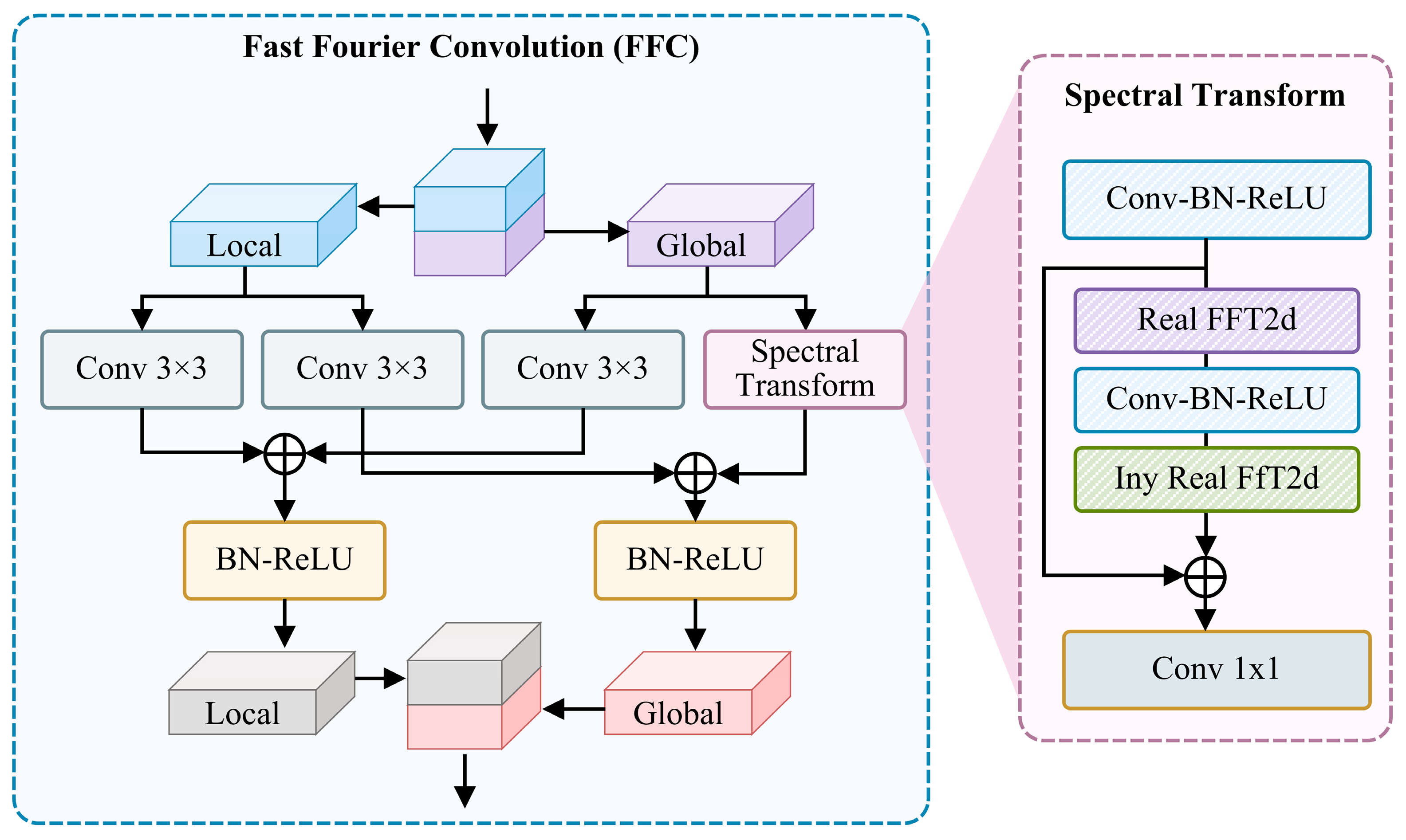
3.2. FFC: Fast Fourier Conv Residual Block
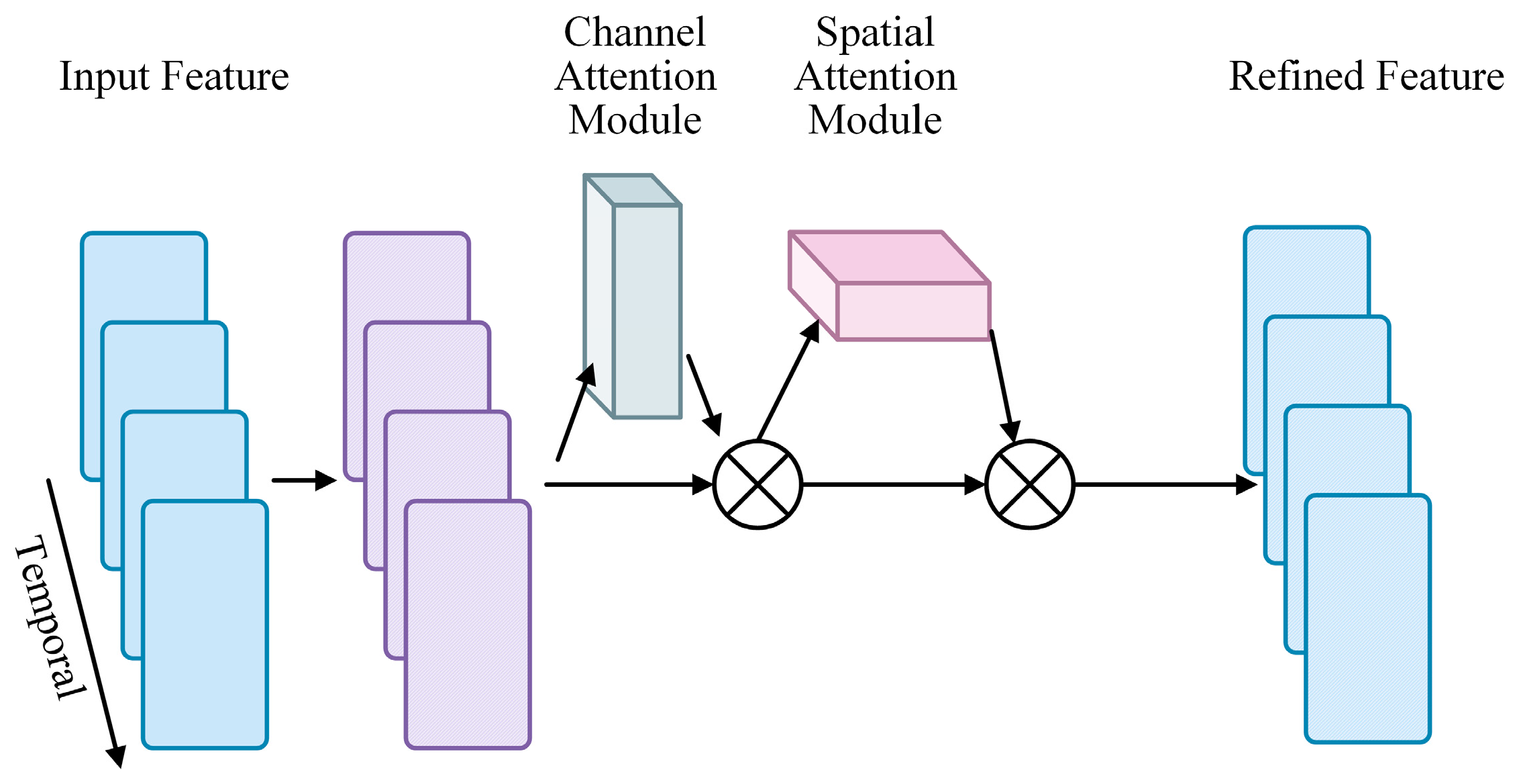
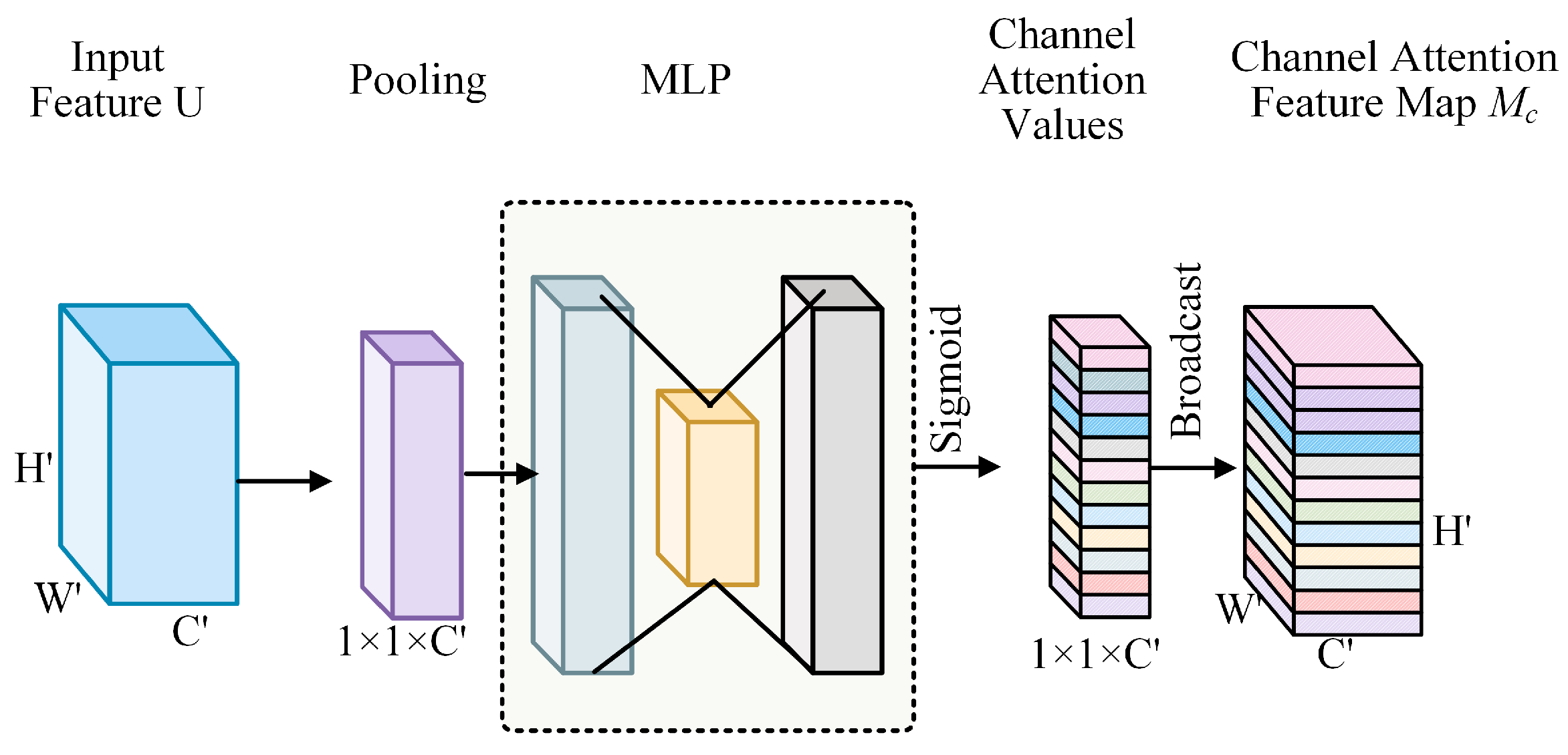
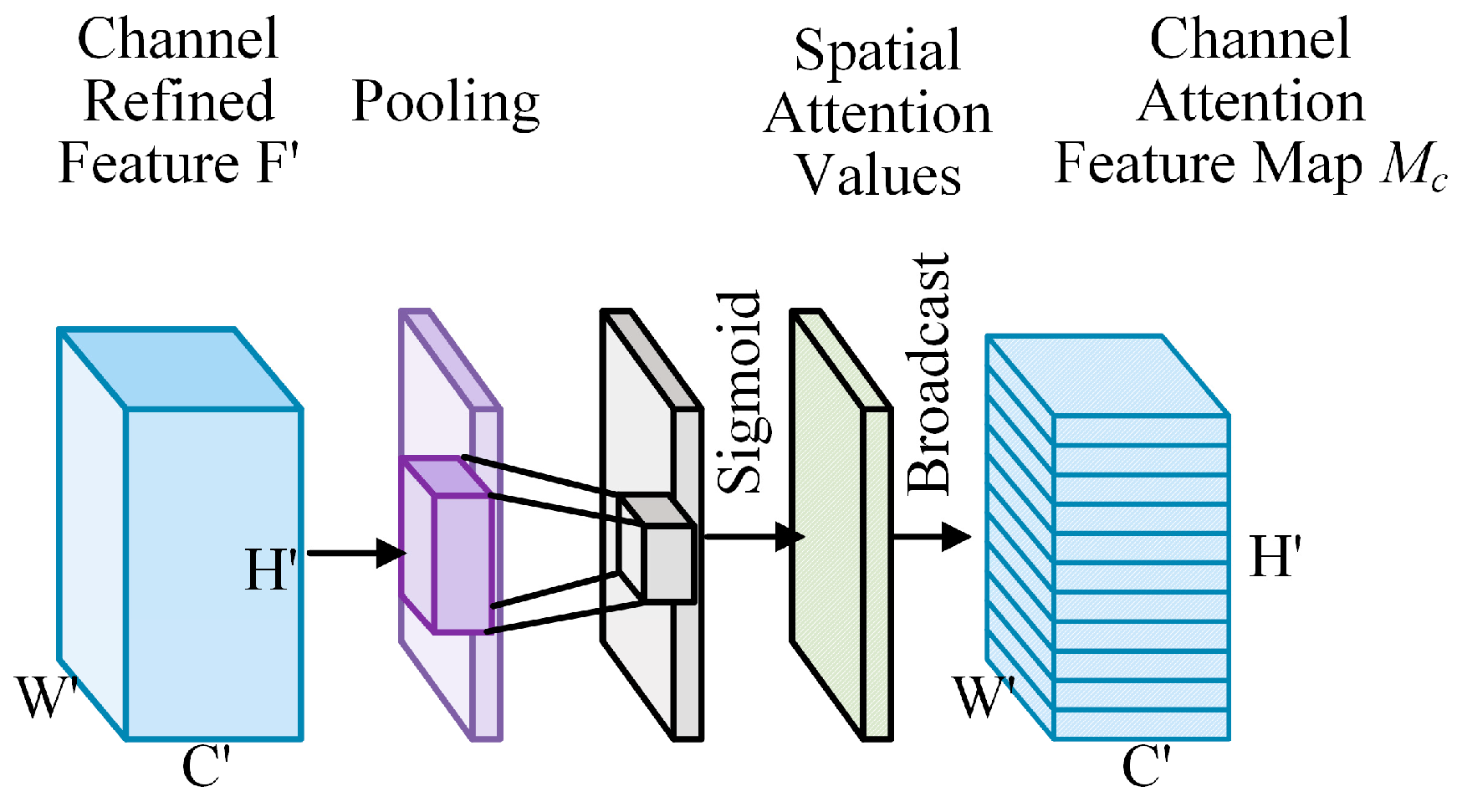
3.3. CFEM: Channel Focus Enhancement Module
3.4. Cross-Entropy Loss
4. Experiment
4.1. Datases and Setup
4.2. Ablation Studies
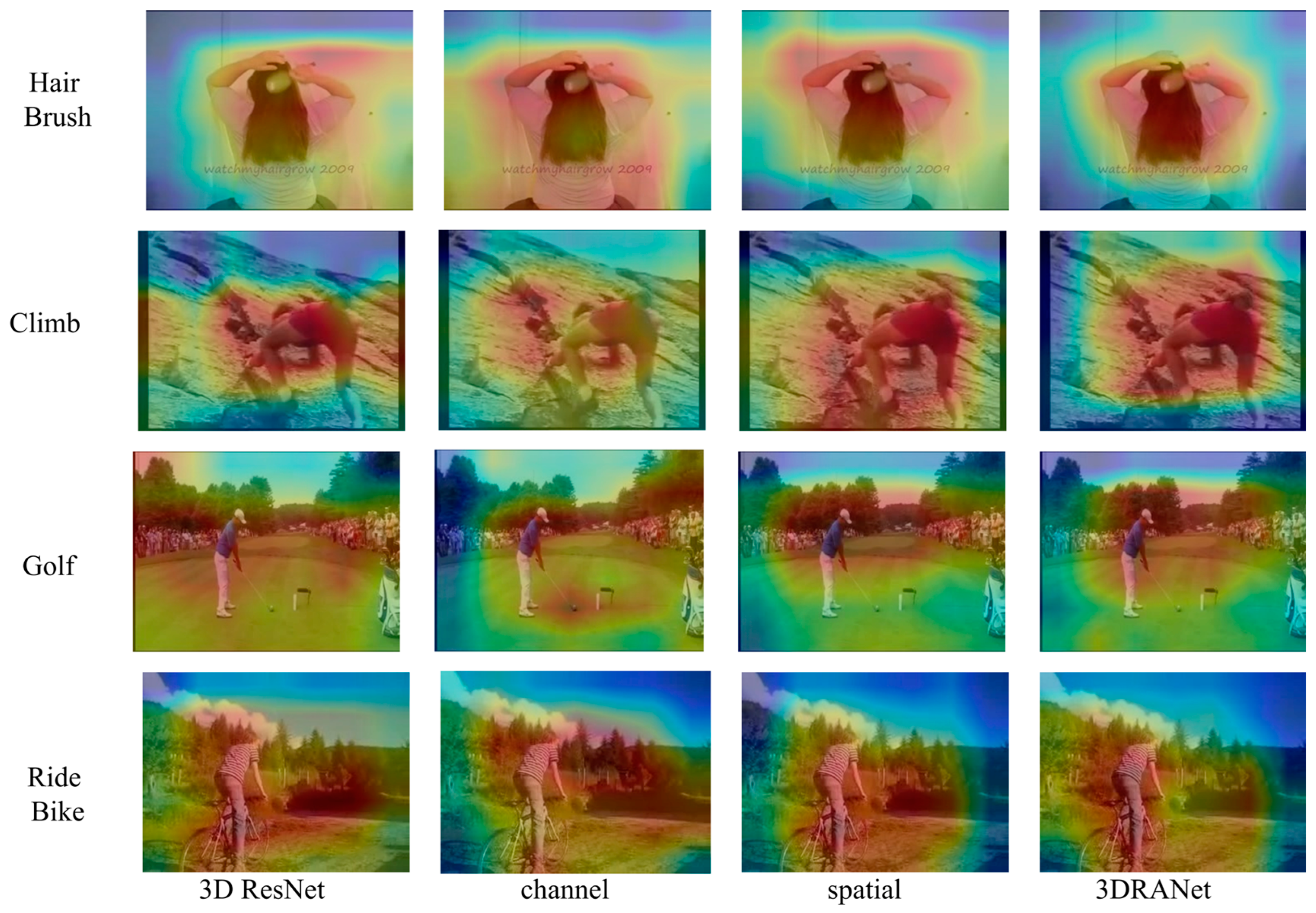
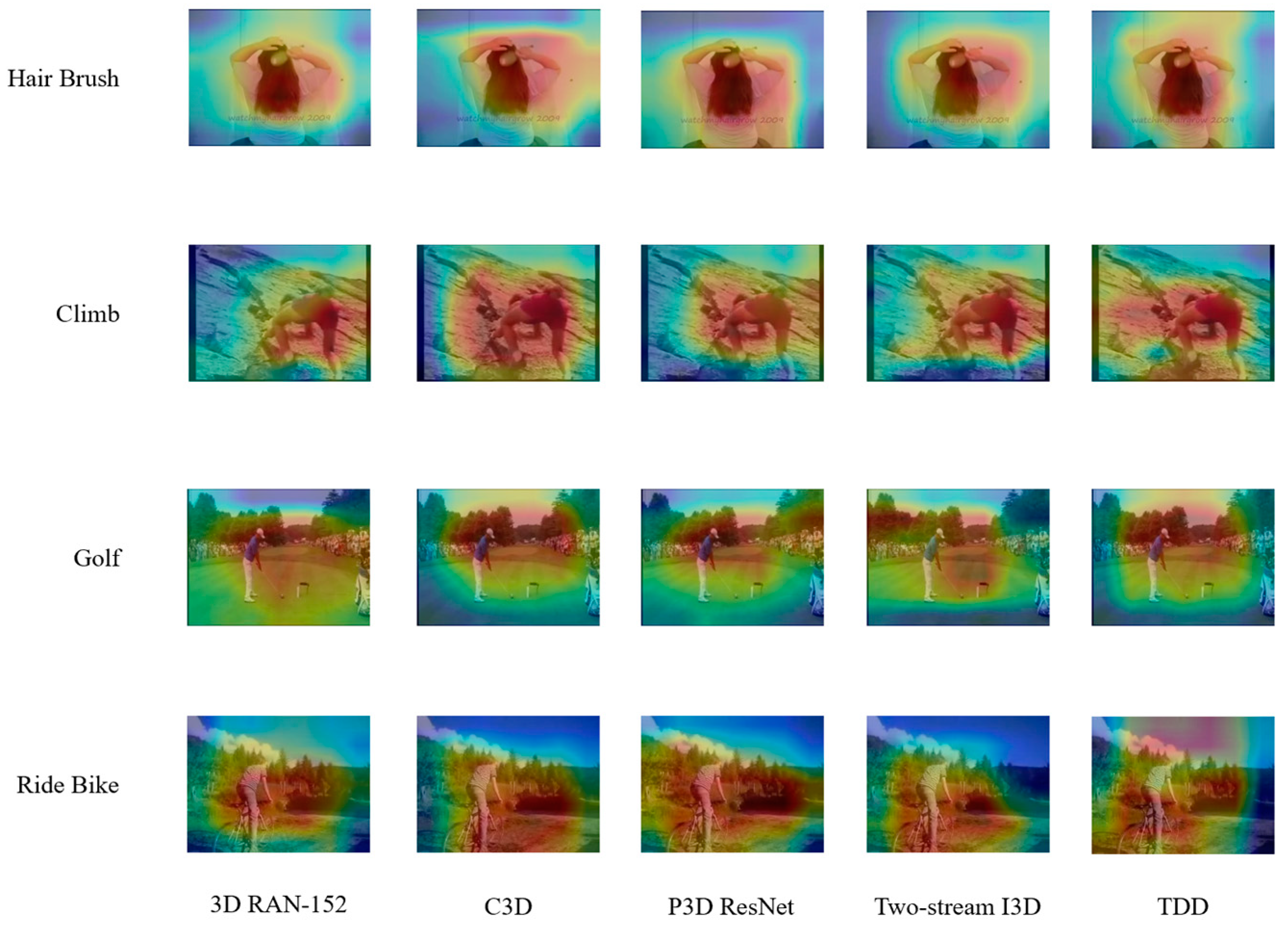
4.3. Performance Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Yi, Y.; Gan, C.; Tang, Z.; Kong, D. Scene Chinese Recognition with Local and Global Attention. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 158, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Fu, Y. Human action recognition and prediction: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1366–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Kataoka, H.; Satoh, Y. Learning spatio-temporal features with 3d residual networks for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Bi, S.; Chen, J. AR3D: Attention residual 3D network for human action recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, H.; Kundu, R.; Singh, P.K.; Ijaz, M.F.; Woźniak, M.; Sarkar, R. A union of deep learning and swarm-based optimization for 3D human action recognition. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yu, H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.-H.; Xu, T.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Liu, Z.-N.; Jiang, P.-T.; Mu, T.-J.; Zhang, S.-H.; Martin, R.R.; Cheng, M.-M.; Hu, S.-M. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Yan, Z.; Yu, W.; Sun, L. An attention mechanism based convolutional LSTM network for video action recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 20533–20556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, T.; Näppi, J.J.; Hironaka, T.; Kim, H.; Yoshida, H. Comparative performance of 3D-DenseNet, 3D-ResNet, and 3D-VGG models in polyp detection for CT colonography. In Medical Imaging 2020: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; SPIE: St Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11314. [Google Scholar]
- Archana, N.; Hareesh, K. Real-time human activity recognition using ResNet and 3D convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication, Embedded and Secure Systems (ACCESS), Ernakulam, India, 2–4 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Weng, L.; Wang, L.; Min, X.; Pan, C. Two-stream designed 2d/3d residual networks with lstms for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Recurrent spatial-temporal attention network for action recognition in videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizler-Cinbis, N.; Sclaroff, S. Object, scene and actions: Combining multiple features for human action recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2010: 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Proceedings, Part I 11. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Lu, M.; Jiang, H. An improved scheme of visual words description and action recognition using local enhanced distribution information. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2016, 38, 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Arnab, A.; Dehghani, M.; Heigold, G.; Sun, C.; Lucic, M.; Schmid, C. ViViT: A Video Vision Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6816–6826. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Feichtenhofer, C. Video Transformers: A Survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.11869. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Liang, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Deep convolutional BiLSTM fusion network for facial expression recognition. Vis. Comput. 2020, 36, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lan, Z.; Newsam, S.; Hauptmann, A. Hidden two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ACCV 2018: 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; Revised Selected Papers, Part III 14. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hung, K.-W.; Lui, S. Real-time video super-resolution using lightweight depthwise separable group convolutions with channel shuffling. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 75, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tong, Z.; Ji, B.; Wu, G. TDN: Temporal Difference Networks for Efficient Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Hu, J. 3D RAN: 3D residual attention networks for action recognition. Vis. Comput. 2019, 36, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Pinz, A.; Zisserman, A. Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Pei, M. Spatio-Temporal Contrastive Learning for Compositional Action Recognition. In Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision; PRCV 2024; Lin, Z., Cheng, M.-M., He, R., Ubul, K., Silamu, W., Zha, H., Zhou, J., Liu, C.-L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 15037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X. Residual attention network for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Muhammad, K.; Ding, W.; Palade, V.; Haq, I.U.; Baik, S.W. Efficient activity recognition using lightweight CNN and DS-GRU network for surveillance applications. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 103, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Qian, R.; Li, J.; Bello, I. Revisiting 3d resnets for video recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.01696. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, X.; Zong, M.; Ma, Y.; Ji, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, R. Multi-cue based four-stream 3D ResNets for video-based action recognition. Inf. Sci. 2021, 575, 654–665. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Su, R.; Ben, X.; Chen, L. EST transformer: Enhanced spatiotemporal representation learning for time series anomaly detection. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2025, 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhang, C. An Enhanced Vision-Language Pre-Training Approach for Scene Text Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Symposium on Computer Engineering and Intelligent Communications (ISCEIC), Wuhan, China, 8–10 November 2024; pp. 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volodymyr, M.; Heess, N.; Graves, A. Recurrent models of visual attention. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2204–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Brauwers, G.; Frasincar, F. A General Survey on Attention Mechanisms in Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021, 35, 3279–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.H.; Min, Z. A Review of Attention Mechanisms in Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Dalian, China, 27–29 July 2023; pp. 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soydaner, D. Attention mechanism in neural networks: Where it comes and where it goes. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 13371–13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kiros, R.; Salakhutdinov, R. Action recognition using visual attention. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.04119. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Quebec, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, C.; Wu, F.; Wang, M.; Gao, Q. Cattle behavior recognition based on feature fusion under a dual attention mechanism. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2022, 85, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, H. Driving behavior recognition algorithm combining attention mechanism and lightweight network. Entropy 2022, 24, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Guan, Y.; Hong, J. Dynamic graph convolutional network for assembly behavior recognition based on attention mechanism and multiscale feature fusion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7394. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, L.; Li, S. Human behavior recognition based on attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (ICAIE), Tianjin, China, 26–28 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.D.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. C3D: Generic Features for Video Analysis. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.0767. [Google Scholar]
- Midya, M.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Mitra, M. A Compact Circularly Polarized Open Slot Antenna for WLAN applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Indian Conference on Antennas and Propogation (InCAP), Ahmedabad, India, 19–22 December 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4724–4733. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Andonian, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Temporal Relational Reasoning in Videosa. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bertasius, G.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L. Is Space-Time Attention All You Need for Video Understanding? arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.05095. [Google Scholar]
- Neimark, D.; Bar, O.; Zohar, M.; Asselmann, D. Video Transformer Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3156–3165. [Google Scholar]
- Fannjiang, C.; Listgarten, J. Autofocused oracles for model-based design. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.08052. [Google Scholar]
- Klotins, E.; Gorschek, T. Continuous Software Engineering in the Wild. In International Conference on Software Quality. Process Automation in Software Development; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
| Dataset Name | Release Year | Number of Videos | Number of Action Classes | Average Video Length | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCF101 | 2012 | 13,320 | 101 | 6.98 s | 320 × 240 |
| HMDB51 | 2011 | 6849 | 51 | 5.06 s | 320 × 240 |
| Kinetics | 2017 | 650,000 | 400/600/700 | 0.86 s | Various |
| Combination | Channel | Spatial | FFC | UCF101 Accuracy (%) | HMDB51 Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 83.2 | 52.8 | |||
| channel | ✓ | 84.6 | 57.4 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 90.1 | 70.89 | ||
| spatial | ✓ | ✓ | 92.6 | 78.8 | |
| ✓ | 85.2 | 59.6 | |||
| 3DRFNet | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 98.7 | 91.7 |
| Loss Function | UCF-101 Acc (%) | HMDB-51 Acc (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Focal Loss | 85.8 | 63.5 |
| Dice Loss | 85.5 | 63.2 |
| Triplet Loss | 85.7 | 63.4 |
| Label Smoothing Loss | 86.1 | 64 |
| Softmax Cross-Entropy | 98.7 | 91.7 |
| Method | Dim | Pre-Trained | UCF-101 Acc (%) | HMDB-51 Acc (%) | Inference Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3D [45] | 3D | Kinetics | 85.4 | 63.3 | 120 |
| P3D ResNet [46] | 3D | Kinetics | 85.3 | 63.5 | 110 |
| Two-stream I3D [47] | 3D | Kinetics | 84.6 | 64.3 | 130 |
| TDD [48] | 2D | ImageNet | 84.9 | 63.1 | 90 |
| TimeSformer [49] | 3D | Kinetics | 87.2 | 65.1 | 150 |
| Vision Vision Transformer [50] | 3D | Kinetics | 86.8 | 64.7 | 140 |
| Audio-Visual SlowFast [51] | 3D | Kinetics | 87.0 | 65.0 | 160 |
| Cross-Attention [52] | 3D | Kinetics | 86.6 | 64.5 | 135 |
| MobileNetV3 + 3D CNN [53] | 3D | Kinetics | 85.8 | 63.6 | 105 |
| 3DRFNet | 3D | Kinetics | 98.7 | 91.7 | 91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, Y.; Li, X. Action Recognition with 3D Residual Attention and Cross Entropy. Entropy 2025, 27, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040368
Ouyang Y, Li X. Action Recognition with 3D Residual Attention and Cross Entropy. Entropy. 2025; 27(4):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040368
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Yuhao, and Xiangqian Li. 2025. "Action Recognition with 3D Residual Attention and Cross Entropy" Entropy 27, no. 4: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040368
APA StyleOuyang, Y., & Li, X. (2025). Action Recognition with 3D Residual Attention and Cross Entropy. Entropy, 27(4), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040368








