Abstract
In the Minimum Description Length (MDL) principle, learning from the data is equivalent to an optimal coding problem. We show that the codes that achieve optimal compression in MDL are critical in a very precise sense. First, when they are taken as generative models of samples, they generate samples with broad empirical distributions and with a high value of the relevance, defined as the entropy of the empirical frequencies. These results are derived for different statistical models (Dirichlet model, independent and pairwise dependent spin models, and restricted Boltzmann machines). Second, MDL codes sit precisely at a second order phase transition point where the symmetry between the sampled outcomes is spontaneously broken. The order parameter controlling the phase transition is the coding cost of the samples. The phase transition is a manifestation of the optimality of MDL codes, and it arises because codes that achieve a higher compression do not exist. These results suggest a clear interpretation of the widespread occurrence of statistical criticality as a characterization of samples which are maximally informative on the underlying generative process.
1. Introduction
It is not infrequent to find empirical data which exhibits broad frequency distributions in the most disparate domains. Broad distributions manifest in the fact that if outcomes are ranked in order of decreasing frequency of their occurrence, then the rank frequency plot spans several orders of magnitude on both axes. Figure 1 reports few cases (see caption for details), but many more have been reported in the literature (see e.g., [1,2]). A straight line in the rank plot corresponds to a power law frequency distribution, where the number of outcomes that are observed k times behave as (with being the slope of the rank plot). Yet, as Figure 1 shows, empirical distributions are not always power laws, even though they are broad nonetheless. Countless mechanisms have been advanced to explain this behaviour [1,2,3,4,5,6]. It has recently been suggested that broad distributions arise from efficient representations, i.e., when the data samples relevant variables, which are those carrying the maximal amount of information on the generative process [7,8,9]. Such Maximally Informative Samples (MIS) are those for which the entropy of the frequency with which outcomes occur—called relevance in [8,9]—is maximal at a given resolution, which is measured by the number of bits needed to encode the sample (see Section 1.1). MIS exhibit power law distributions with the exponent governing the tradeoff between resolution and relevance [9]. This argument for the emergence of broad distributions is independent of any mechanism or model. A direct way to confirm this claim is to check that samples generated from models that are known to encode efficient representations are actually maximally informative. In this line, [10] found strong evidence that MIS occur in the representations that deep learning extracts from data. This paper explores the same issue in efficient coding as defined in Minimum Description Length [11].
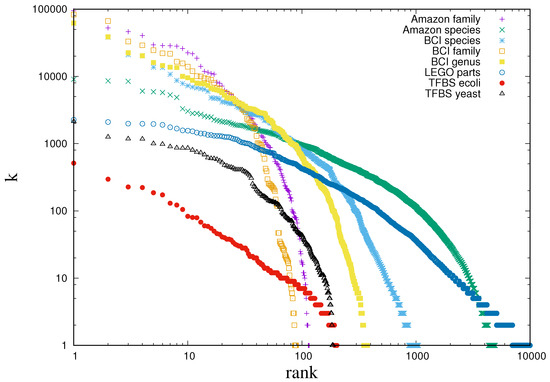
Figure 1.
Rank plot of the frequencies across a broad range of datasets. Log-log plots of rank versus frequency from diverse datasets: survey of 4962 species of trees across 116 families sampled from the Amazonian lowlands [12], survey of 1053 species of trees across 376 genera and 89 families sampled across a 50 hectare plot in the Barro Colorado Island (BCI), Panama [13], counts indicating the inclusion of each 13,001 LEGO parts on 2613 distributed toy sets [14,15] and the number of genes that are regulated by each of the 203 transcription factors (TFs) in E. coli [16] and 188 TFs in S. cerevisiae (yeast) [17] through binding with transcription factor binding sites (TFBS).
Regarding empirical data as a message sent from nature, we expect it to be expressed in an efficient manner if relevant variables are chosen. This requirement can be made quantitative and precise, in information theoretic terms, following Minimum Description Length (MDL) theory [11]. MDL seeks the optimal encoding of data generated by a parametric model with unknown parameters (see Section 1.2). MDL derives a probability distribution over samples that embodies the requirement of optimal encoding. This distribution is the Normalized Maximum Likelihood (NML). This paper studies the NML as a generative process of samples and studies both its typical and atypical properties. In a series of cases, we find that samples generated by NMLs are typically close to being maximally informative, in the sense of [9], and that their frequency distribution is typically broad. In addition, we find that NMLs are critical in a very precise sense, because they sit at a second order phase transition that separates typical from atypical behavior. More precisely, we find that large deviations, for which the resolution attains atypically low values, exhibit a condensation phenomenon whereby all N points in the sample coincide. This is consistent with the fact that NML correspond to efficient coding of random samples generated from a model, so that codes achieving higher compression do not exist. Large deviations enforcing higher compression force parameters to corners of the allowed space where the model becomes deterministic.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: the rest of the introduction lays the background of what follows by recalling the characterization of samples in terms of resolution and relevance, as in [9], and the derivation of NML in MDL, following [11]. Section 2.1 discusses typical properties of NML and Section 2.2 discusses large deviations of the coding cost. We conclude with a series of remarks on the significance of these results.
Setting the Scene
Let be a sample of N observations, , of a system where is a countable finite state space. We define as the number of observations in for which , i.e., the frequency of s. The number of states s that occur k times will be denoted as . Both and depend on the sample .
We assume that is generated in a series of independent experiments or observations, all in the same conditions. This is equivalent to taking as a sequence of N independent draws from an unknown distribution (i.e., the generative process).
1.1. Resolution, Relevance and Maximally Informative Samples
The information content of the sample is measured by the number of bits needed to encode a single data point. This is given by Shannon entropy [18]. Taking the frequency as the probability of point s, this leads to:
where the indicates that the entropy is computed from the empirical frequency. This quantity specifies the level of detail of the description provided by the variable s. At one extreme, all the data points are equal, i.e., , such that for and . With this, one finds that . On the other extreme, all the data points are different, i.e., , , such that and , . Hence, one finds that . This is why we call as the resolution, following [9]. The resolution clearly depends on the cardinality of . Only a part of provides information on the generative process and this is given by the relevance
A simple argument, which is elaborated in detail in [9], is that the empirical frequency is the best estimate of , so conditional on , the sample does not contain any further information on . Note that is a function of s, which implies . Therefore, the difference quantifies the amount of noise the sample contains.
We call a Maximally Informative Sample (MIS) if is such that the relevance is maximal at a given resolution . This implies the maximization of the functional
over , where the Lagrange multipliers and are adjusted to enforce the conditions and , respectively. As shown in [7,8], MIS exhibit a power law frequency distribution
where c is a normalization constant such that . As varies from 0 to , MISs trace a curve in the resolution-relevance plane (see solid lines in Figure 2 and Figure 3 (B, C)) with as the negative slope. As discussed in [9,10], quantifies the trade-off between resolution and relevance: a decrease in resolution of one bit leads to an increase of bits in relevance. The point , which corresponds to Zipf’s law, sets the limit beyond which further reduction in results in lossy compression, because, for , the increase in cannot compensate the loss in resolution.
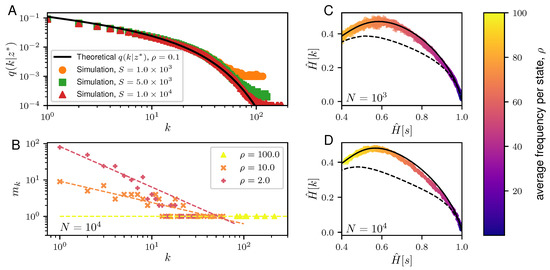
Figure 2.
Properties of the typical samples generated from the NML of the Dirichlet model. (A) A plot showing the frequency distribution of the typical samples of the Dirichlet NML code. Given S, the cardinality of the state space, , with (orange dots), (green squares), and (red triangles), we compute the average frequency distribution across 100 generated samples from the Dirichlet NML of size such that the average frequency per state, , is fixed. This is compared against the theoretical calculations (solid black line) for in Equation (19). (B) Plot showing the degeneracy, , of the frequencies, k, in a representative typical sample of length generated from the Dirichlet NML code with average frequencies per spike: (yellow triangle), (orange x-mark) and (red cross). The corresponding dashed lines depict the best-fit line. (C,D) Plots of versus for the typical samples of the Dirichlet NML code. For a fixed size of the data, N ( in C and in D), we have drawn 100 samples from the Dirichlet NML code varying , ranging from 2 to 100. The results are compared against the and for maximally informative samples (MIS, solid black line) and random samples (dashed black lines). For the MIS, the theoretical lower bound is reported [8]. For the random samples, we compute the averages of and over realizations of random distributions of N balls in L boxes, with L ranging from 2 to . Here, each box corresponds to one state and is the number of balls in box s. Note that all the calculated values for and are normalized by .
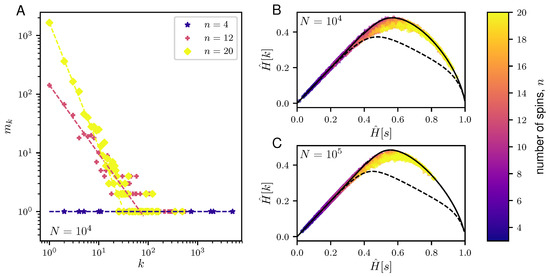
Figure 3.
Properties of typical samples for the NML codes of the paramagnet. (A) Plots showing the degeneracy, , of the frequencies, k, in a representative typical sample of length generated from the NML of a paramagnet with different number of independent spins: (blue star), (red cross) and (yellow diamond). The corresponding dashed lines depict the best-fit line. (B,C) Plots of the versus of the typical samples generated from the paramagnet NML code for varying sizes of the data, (B) and (C), and for varying number of spins, n, ranging from 3 to 20. Given N and n, we compute the and over 100 realizations of the NML code of a paramagnet. The results are compared against the and for maximally informative samples (solid black line) and random samples (dashed black line) as described in Figure 2. Note that all the calculated and are normalized by .
1.2. Minimum Description Length and the Normalized Maximum Likelihood
The main insight of MDL is that learning from data is equivalent to data compression [11]. In turn, data compression is equivalent to assigning a probability distribution over the space of samples.This section provides a brief derivation of this distribution whereas the rest of the paper discuss its typical and atypical properties. We refer the interested reader to [11,19] for a more detailed discussion of MDL.
From an information theoretic perspective, one can think of the sample, , as a message generated by some source (e.g., nature) that we wish to compress as much as possible. This entails translating in a sequence of bits. A code is a rule that achieves this for any and its efficiency depends on whether frequent patterns are assigned short codewords or not. Conversely, any code implies a distribution over the space of samples and the cost of encoding the sample under the code P is given by [18]
bits (assuming logarithm base two). Optimal compression is achieved when the code P coincides with the data generating process [18].
Consider the situation where the data is generated as independent draws from a parametric model . If the value of were known, then the optimal code would be given by . MDL seeks to derive P in the case where is not known (Indeed, MDL aims at deriving efficient coding under f irrespective of whether is the “true” generative model or not. This allows one to compare different models and choose the one providing the most concise description of the data). This applies, for example, to the situation where is a series of experiments or observation aimed at measuring the parameters of a theory.
In hind sight, i.e., upon seeing the sample, the best code is , where is the maximum likelihood estimator for , and it depends on the sample . Therefore, one can define the regret , as the additional encoding cost that one needs to spend to encode the sample , if one uses the code to compress , i.e.,
Notice that . is called regret of P relative to f for sample because it depends both on P and on .
MDL derives the optimal code, , that minimizes the regret, assuming that for any P the source produces the worst possible sample [11]. The solution [20]
is called the Normalized Maximum Likelihood (NML). The optimal regret is given by
which is known in MDL as the parametric complexity (Notice that can be seen as a partition sum. Hence, throughout the paper, we shall refer to the parametric complexity as the UC partition function.). For models in the exponential family, Rissanen showed that the parametric complexity is asymptotically given by [21]
where is the Fisher information matrix with the matrix elements defined by an expectation over the parametric model (see Appendix A for a simple derivation). The NML code is a universal code because it achieves a compression per data point which is as good as the compression that would be achieved with the optimal choice of when one has large enough samples. This is easy to see, because the regret per data point vanishes in the limit , hence the NML code achieves the same compression as .
Notice also that the optimal regret, , in Equation (8) is independent of the sample . It indeed provides a measure of complexity of the model f that can be used in model selection schemes. For exponential families, MDL procedure penalizes models with a cost which equals the one obtained in Bayesian model selection [22] under a Jeffreys prior. Indeed, considering as a generative model for samples, one can show that the induced distribution on is given by Jeffreys prior (see Appendix A).
2. Results
2.1. NML Codes Provide Efficient Representations
In this section we consider as a generative model for samples and we investigate its typical properties for some representative statistical models.
2.1.1. Dirichlet Model
Let us start by considering the Dirichlet model distribution , . The parameters are constrained by the normalization condition . Let denote the cardinality of and define, for convenience, as the average number of points per state. Because each observation is mutually independent, the likelihood of a sample given can be written as
where is the number of times that the state s occurs in the sample . From here, it can be seen that is the maximum likelihood estimator for . Thus, the universal code for the Dirichlet model can now be constructed as
which can be read as saying that for each s, the code needs bits. In terms of the frequencies, , the universal codes can be written as
wherein the multinomial coefficient, , counts the number of samples with a given frequency profile . In order to compute the optimal regret , we have to evaluate the partition function
where
and
The integral in Equation (15) is dominated by the value where the function attains its saddle point value , which is given by the condition
where the average is taken with respect to the distribution
Gaussian integration around the saddle point leads then to
where we used the identity .
The distribution Equation (12) can also be written introducing the Fourier representation of the delta function
For typical sequences , the integral is also dominated by the value that dominates Equation (15), which means that the distribution factorizes as
This means that the NML is, to a good approximation, equivalent to S independent draws from the distribution or, equivalently, that the distribution is the one that characterizes typical samples. This is fully confirmed by Figure 2A, which compares with the empirical distribution of drawn from . For large k, we find , which shows that the distribution of frequencies is broad, with a cutoff at . This underlying broad distribution is confirmed by Figure 2B which shows the dependence of the degeneracy with the frequency k.
In the regime where and k is large, the cutoff extends to large values of k and we find (see Appendix B.1). In addition, the parametric complexity can be computed explicitly via Equation (9) in this regime, with the result
The coding cost of a typical sample is given by
The number of samples with encoding cost E can be computed in the following way. The number of samples that correspond to a given degeneracy of the states that occurs times in , is given by
Therefore, the number of samples with coding cost E is
where is the set of all sequences that are consistent with samples in and satisfy Equation (26). The last expression assumes , which is reasonable for , i.e., when . In this regime we expect the sum over to be dominated by samples with maximal . Indeed, Figure 2C,D show that samples drawn from achieve values of close to the theoretical maximum, especially in the region .
2.1.2. A Model of Independent Spins
In order to corroborate our results for the Dirichlet model, we study the properties of the universal codes for a model of independent spins, i.e., a paramagnet. For a single spin, , in a local field h, the probability distribution is given by
Thus for a sample of size N,
where is the local magnetization. The maximum likelihood estimate for h is , hence the universal code for a single spin can be written as
where (see Appendix B.2). Note that a sample with a magnetization m can be realized by considering the permutation of the up-spins (, where there are of such spins) and the permutation of the down-spins (, where there are of such spins). Consequently, the magnetization for samples drawn from has a broad distribution given by the arcsin law (see Appendix B.2)
It is straightforward to see that the model of a single spin is equivalent to a Dirichlet model with two states . In terms of the number ℓ of up-spins, using , the NML for a single spin can be written as
The NML for a paramagnet with n independent spins reads as
Figure 3 reports the properties of the typical samples of the NML of a paramagnet. We observed that the frequency distribution of typical samples is broad (Figure 3A) and that typical samples attain values of very close to the maximum for a given value of (Figure 3B,C). As the size N of data increases, the NML enters the well-sampled regime where , indicating that the data processing inequality [18] is saturated. In this regime, typical samples are those which maximize the entropy .
2.1.3. Sherrington-Kirkpatrick Model
In the following sections, we extend our findings to systems of interacting variables (graphical models) and discuss the properties of typical samples drawn from the corresponding NML distribution. We shall first consider models in which the observed variables are interacting either directly (Sherrington-Kirkpatrick model) and then restricted Boltzmann machines, where the variables interact indirectly through hidden variables.
In this section, is a configuration of n spins . In the Sherrington-Kirkpatrick (SK) model, the distribution of s, considers all interactions up to two-body
where the partition function
is a normalization constant which depends on the pairwise couplings, with being the coupling strength between and , and external local fields, . Thus, given a sample, of N observations, the likelihood reads as
where and are the magnetization and pairwise correlation respectively. Note that all the needed information about the SK model is encapsulated in the free energy, . Indeed, the maximum likelihood estimators for the couplings, , and local fields, , are the solutions of the self-consistency equations
The universal codes for the SK model then reads as
However, unlike for the Dirichlet model and the paramagnet model, the UC partition function, , for the SK model is analytically intractable (For SK models which possess some particular structures, a calculation of the UC partition function has been done in [23]). To this, we resort to a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) approach to sample the universal codes (See Appendix C.1). Figure 4A,C shows the properties of the typical samples drawn from the universal codes of the SK model in Equation (42).
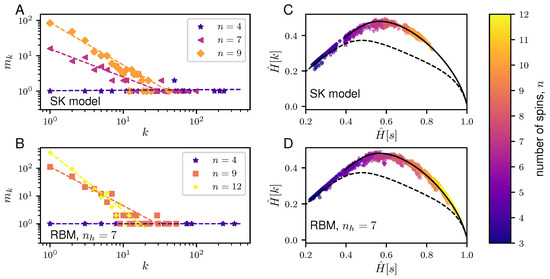
Figure 4.
Properties of typical samples for the NML codes of two graphical models: the Sherrington-Kirkpatrick (SK) model and the restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM). Left panels (A,C) show plots of the degeneracy, , of the frequency, k, for representative typical samples generated from the NML codes for the SK model (A) and the RBM given a number of hidden variables, (B) for different number of (visible) spins, n. The corresponding dashed lines show the best-fit lines. On the other hand, right panels (B,D) show plots of the versus of the typical samples drawn from the NML codes for the SK model (B) and the RBM with (D) for and for varying number of spins, n ranging from 3 to 12. Given N and n of a graphical model, we compute the and for 100 samples drawn from the respective NML codes through a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) approach (see Appendix C.1). Note that for the RBM, varying do not qualitatively affect the observations made in this paper. As before, the and are normalized by and the typical NML samples are compared against maximally informative samples (solid black line) and random samples (dashed black line) as described in Figure 2.
2.1.4. Restricted Boltzmann Machines
We consider a restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) wherein one has a layer composed of independent visible boolean units, , which are interacting with independent hidden boolean units, , in another layer where . The probability distribution can be written down as
where the partition function
is a function of the parameters, , with is the interaction strength between and , and are the local fields acting on the visible and hidden units respectively. Because the hidden units, , are mutually independent, we can factorize and then marginalize the sum over the hidden variables, , to obtain the distribution of a single observation, , as
Then, the probability distribution for a sample, , of N observations is simply
The parameters, , can be estimated by maximizing the likelihood using the Contrastive Divergence (CD) algorithm [24,25] (see Appendix C.2). Once the maximum likelihood parameters, , have been inferred, then the universal codes for the RBM can be built as
In addition, like in the SK model, the UC partition function, , for the RBM cannot be solved analytically. To this, we also resort to a MCMC approach to sample the universal codes (See Appendix C.1). Figure 4B,D shows the properties of the typical samples drawn from the universal codes of the RBM in Equation (47).
Taken together, we see that even for models that incorporate interactions, the typical samples of the NML i) have broad frequency distributions and ii) they achieve values of close to the maximum, given . Due to computational constraints, we only present the results for however, we expect that increasing N will only shift the NML towards the well-sampled regime.
2.2. Large Deviations of the Universal Codes Exhibit Phase Transitions
In this section, we focus on the distribution of the resolution for samples drawn from . We note that
has the form of an empirical average. Hence, we expect it to attain a given value for typical samples drawn from . This also suggests that the probability to draw samples with resolution different from the typical value has the large deviation form , to leading order for . In order to establish this result and to compute the function , as in [26] and [27], we observe that
where we used the integral representation of the function and is the NML distribution in Equation (7). Upon defining
let us assume, as in the Gärtner–Ellis theorem [26], that is finite for for all q in the complex plane. Then Equation (49) can be evaluated by a saddle point integration
where we account only for the leading order. is related to the saddle point value that dominates the integral and it is given by the solution of the saddle point condition
Equation (52) shows that the function is the Legendre transform of , i.e.,
with given by the condition (53), as in the Gärtner–Ellis theorem [26]. Further insight and a direct calculation from the definition in Equation (50) reveals that Equation (53) can also be written as
which is the average of over a “tilted” probability distribution [26]
hence arises as the Lagrange multiplier enforcing the condition . Conversely, when is fixed by the condition Equation (e̊fapp3:saddle2), samples drawn from have . In other words, describes how large deviations with are realized. Therefore, typical samples that realize such large deviations can be obtained by sampling the distribution in Equation (56). Figure 5 show that, for Dirichlet models, samples obtained from exhibit a sharp transition at . The resolution (see green lines in Figure 5) sharply vanishes for negative values of as a consequence of the fact that the distribution localizes to samples where almost all outcomes coincide, i.e., . This is evidenced by the fact that the maximal frequency approaches N very fast (see purple lines in Figure 5). In other words, marks a localization transition where the symmetry between the states in is broken, because one state is sampled an extensive number of times .
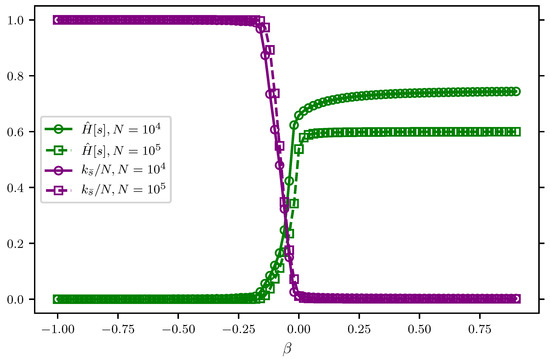
Figure 5.
Typical realizations of large deviations from the NML code of the Dirichlet model. For a fixed parameter, ranging from to , samples are obtained from in Equation (56) for varying length of the dataset, N ( in solid lines with circle markers and in dashed lines with square markers). The resolution normalized by (in green lines) and the maximal frequency normalized by N (in purple lines) are calculated as an average over 100 realizations of given . The point corresponds to the typical samples that are realized from the Dirichlet NML code in Equation (12).
One direct way to see this is to consider the Dirichlet model and use the “tilted” distribution in Equation (56) to compute the distribution
of following the same steps leading to Equation (19), where again z is fixed by the condition . For , we again find, as in Equation (22), that can be considered as independent draws from the same distribution . For , we find that the distribution develops a sharp maximum at indicating that, as mentioned above, the sample concentrates on one state .
This behavior is generic whenever the underlying model itself localizes for certain values of the parameters, i.e., when . In order to see this, notice that, in general, we can write
Thus, by inserting the identity , the NML distribution in Equation (7) can be re-cast as
where is the empirical distribution and
is a Kullback-Leibler divergence.
Now, we observe that
where the inequality in Equation (61) derives from the fact that , the maximum likelihood estimator for sample , is replaced by a generic value and consequently, . The equality in Equation (62), instead, derives from the choice such that . Under this choice, only the term corresponding to “localized” samples where for all points in the sample, survive in the sum on . For such localized samples, , hence Equation (62) follows.
Because of the logarithmic dependence of the regret on N (see Equation (9)), Equation (62) implies that, for all ,
for . Given that in Equation (55), then and therefore, Equation (53) implies that is a non-decreasing function of . In addition, by Equation (50). Taken together, these facts require that for all values . On the other hand, for , the function is analytic with all finite derivatives, which corresponds to higher moments of under . Therefore, , which corresponds to the typical behavior of the NML, coincides with a second order phase transition point because the function exhibits a discontinuity in the second derivative. In terms of , the phase transition separates a region () where all samples have a finite probability from a region () where only one sample, the one with , has non-zero probability and .
The phase transition is a natural consequence of the fact that NML provide efficient coding of samples generated from . It states that codes that achieve a compression different from the one achieved by the NML only exist for higher coding costs. Codes with lower coding cost only describe non-random samples that correspond to deterministic models .
3. Discussion
The aim of this paper is to elucidate the properties of efficient representations of data corresponding to universal codes that arise in MDL. Taking NML as a generative model, we find that typical samples are characterized by broad frequency distributions and that they achieve values of the relevance which are close to the maximal possible .
In addition, we find that samples generated from NML are critical in a very precise sense. If we force NML to use less bits to encode samples, then the code localizes on deterministic samples. This is a consequence of the fact that if there were codes that required fewer bits, then NML would not be optimal.
This contributes to the discussion on the ubiquitous finding of statistical criticality [1,4] by providing a clear understanding of its origin. It suggests that statistical criticality can be related to a precise second order phase transition in terms of large deviations of the coding cost. This phase transition separates random samples that span a large range of possible outcomes (the set in the models discussed above) from deterministic ones, where one outcome occurs most of the time. The phase transition is accompanied by a spontaneous symmetry breaking in the permutation between samples. The frequencies of outcomes in the symmetric phase () are generated as independent draws from the same distribution, that is sharply peaked for as can be checked in the case of the Dirichlet model. Instead, for , only one state is sampled. In the typical case, , the symmetry between outcomes is weakly broken, as there are outcomes that occur more frequently than others. At , the samples maintain the maximal discriminative power over outcomes. This type of phase transitions in large deviations is very generic, and it occurs in large deviations whenever the underlying distribution develops fat tails (see e.g., [27]).
This leads to the conjecture that broad distributions arise as a consequence of efficient coding. More precisely, broad distributions arise when the variables sampled are relevant, i.e., when they provide an optimal representation. This is precisely the point which has been made in [7,8,9]. The results in the present paper add a new perspective whereby maximally informative samples can be seen as universal codes.
Author Contributions
R.J.C., M.M. and Y.R. conceptualized the research, performed the analysis and wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the Kavli Foundation and the Centre of Excellence scheme of the Research Council of Norway—Centre for Neural Computation (grant number 223262).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MDL | minimum description length |
| NML | normalized maximum likelihood |
| MIS | maximally informative sample |
| SK | Sherrington-Kirkpatrick |
| RBM | restricted Boltzmann machine |
| CD | contrastive divergence |
| PCD | persistent contrastive divergence |
| MCMC | Markov chain Monte Carlo |
Appendix A. Derivation for the Parametric Complexity
In order to compute the parametric complexity, given in Equation (8), let us consider the integral for a generic function . For , the integral is dominated by the point that maximizes , and it can be computed by the saddle point method. Performing a Taylor expansion around the maximum likelihood parameters, , one finds (up to leading orders in N)
where
Note that for exponential families, the Hessian of the log-likelihood is independent of the data, and hence it coincides with the Fisher Information matrix [22]
The integral can then be computed by Gaussian integration, as
where k is the number of parameters. If we choose to be
and take a sum over all samples on both sides of Equation (A5), Equation (A6) becomes
Hence, the parametric complexity, , is asymptotically given by Equation (9) when .
Notice also that induces a distribution over the space of parameters . With the choice
the same procedure as above shows that
which is the Jeffreys prior.
Appendix B. Calculating the Parametric Complexity
In this section, we calculate the parametric complexity for the Dirichlet model for where N is the number of observations in the sample and S is the size of the state space and the paramagnetic Ising model.
Appendix B.1. Dirichlet Model
In the regime where and k large such that we can employ Stirling’s approximation, , the normalization can be calculated as
Similarly, we can also calculate
and thus, the saddle point value can now be evaluated as
In the same regime, given the determinant of the Fisher information matrix for the Dirichlet model,
the parametric complexity can be approximated as
which, together with Equation (20) and the fact and the variance , implies that .
Appendix B.2. Paramagnet Model
The parametric complexity for the paramagnetic Ising model, given in Equation (34), is given by
where runs on values. When , the magnetization, , can be treated as a continuous variable and consequently, the sum can be approximated as an integral: . Hence, by using the identities , and , one finds that
Appendix C. Simulation Details
Appendix C.1. Sampling Universal Codes through Markov Chain Monte Carlo
Unlike the Dirichlet model and the independent spin model, analytic calculations for the Sherrington-Kirkpatrick (SK) model and the restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) are generally not possible, because the partition function Z, and consequently, the UC partition function , is computationally intractable. In order to sample the NML for these graphical models, we turn to a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) approach in which the transition probability, , can be built using the following heuristics:
- Starting from the sample, , we calculate the maximum likelihood estimates, , of the parameters of the model, by either solving Equation (41) for the SK model or by Contrastive Divergence (CD) [24,25] for the RBM (see Appendix C.2).
- We generate a new sample, from by flipping a spin in randomly selected r points of the sample. The number of selected spins, r, must be chosen carefully such that r must be large enough to ensure faster mixing but small enough so the new inferred model, , is not too far from the starting model, .
- The maximum likelihood estimators, for the new sample are calculated as in Step 1.
- Computeand accept the move with probability .
Appendix C.2. Estimating RBM Parameters through Contrastive Divergence
Given a sample, , of N observations, the log-likelihood for the restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) is given by
The inference of the parameters, , proceeds by updating such that the log-likelihood, , is maximized. This updating formulation for the parameters is given by
where is the learning rate parameter. The corresponding gradients for the parameters, , and can then be written down respectively as
where the first terms denote averages over the data distribution while the second terms denote averages over the model distribution.
Here, we use the contrastive divergence (CD) approach which is a variation of the steepest gradient descent of . Instead of performing the integration over the model distribution, CD approximates the partition function by averaging over distribution obtained after taking Gibbs sampling steps away from the data distribution.
To do this, we exploit the factorizability of the conditional distributions of the RBM. In particular, the conditional probability for the forward propagation (i.e., sampling the hidden variables given the visible variables) from to reads as
Similarly, the conditional probability for the backward propagation (i.e., sampling the visible variables from the hidden variables) from to reads as
The Gibbs sampling is done by propagating a sample, , forward and backward times: . And thus, the Gibbs sampling approximates the gradient in Equation (A33) as
In the CD approach, each parameter update for a batch is called an epoch. While larger approximates well the partition function, it also induces an additional computational cost. To find the global minimum more efficiently, we randomly divided the samples into groups of mini-batches. This approach introduces stochasticity and consequently reduces the likelihood of the learning algorithm to be confined in a local minima. However, a mini-batch approach can result in data-biased sampling. To circumvent this issue, we adopted the Persistent CD (PCD) algorithm where the Gibbs sampling extends to several epochs, each using different mini-batches. In the PCD approach, the initial visible variable configuration, , was set to random for the first mini-batch, but the final configurations, , of the current batches become the initial configuration for the next mini-batches. In this paper, we performed Gibbs sampling at steps where we update the parameters, , are updated at 2500 epochs at a rate with 200 mini-batches per epochs. For other details regarding inference of parameters of the RBM, we refer the reader to [24,25].
Appendix C.3. Source Codes
All the calculations in this manuscript were done using personalized scripts written in Python 3. The source codes are accessible online (https://github.com/rcubero/UniversalCodes (accessed on 8 May 2012)).
References
- Muñoz, M.A. Colloquium: Criticality and dynamical scaling in living systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2018, 90, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Power laws, Pareto distributions and Zipf’s law. Contemp. Phys. 2005, 46, 323–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, P. How Nature Works: The Science of Self-Organized Criticality; Copernicus: Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, T.; Bialek, W. Are biological systems poised at criticality? J. Stat. Phys. 2011, 144, 268–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simini, F.; González, M.C.; Maritan, A.; Barabási, A.L. A universal model for mobility and migration patterns. Nature 2012, 484, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, D.J.; Nemenman, I.; Mehta, P. Zipf’s law and criticality in multivariate data without fine-tuning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsili, M.; Mastromatteo, I.; Roudi, Y. On sampling and modeling complex systems. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2013, 9, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimovici, A.; Marsili, M. Criticality of mostly informative samples: A bayesian model selection approach. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2015, 10, P10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero, R.J.; Jo, J.; Marsili, M.; Roudi, Y.; Song, J. Minimally sufficient representations, maximally informative samples and Zipf’s law. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1808.00249. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Marsili, M.; Jo, J. Resolution and relevance trade-offs in deep learning. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1710.11324. [Google Scholar]
- Grünwald, P.D. The Minimum Description Length Principle; MIT Press: Massachusetts, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Steege, H.; Pitman, N.C.A.; Sabatier, D.; Baraloto, C.; Salomão, R.P.; Guevara, J.E.; Phillips, O.L.; Castilho, C.V.; Magnusson, W.E.; Molino, J.F.; et al. Hyperdominance in the Amazonian tree flora. Science 2013, 342, 1243092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condit, R.; Lao, S.; Pérez, R.; Dolins, S.B.; Foster, R.; Hubbell, S. Barro Colorado Forest Census Plot Data (Version 2012). Available online: https://repository.si.edu/handle/10088/20925 (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Combine Your Old LEGO® to Build New Creations. Available online: https://rebrickable.com/ (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Mazzolini, A.; Gherardi, M.; Caselle, M.; Lagomarsino, M.C.; Osella, M. Statistics of shared components in complex component systems. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 021023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama-Castro, S.; Salgado, H.; Santos-Zavaleta, A.; Ledezma-Tejeida, D.; Muñiz-Rascado, L.; García-Sotelo, J.S.; Alquicira-Hernández, K.; Martínez-Flores, I.; Pannier, L.; Castro-Mondragón, J.A.; et al. Regulondb version 9.0: High-level integration of gene regulation, coexpression, motif clustering and beyond. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, R.; Park, J.; Karra, K.; Hitz, B.C.; Binkley, G.; Hong, E.L.; Sullivan, J.; Micklem, G.; Cherry, J.M. Yeastmine—An integrated data warehouse for Saccharomyces cerevisiae data as a multipurpose tool-kit. Database 2012, 2012, bar062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Grünwald, P.D. A tutorial introduction to the minimum description length principle. arXiv, 2004; arXiv:math/0406077. [Google Scholar]
- Shtarkov, Y.M. Universal sequential coding of single messages. Transl. Prob. Inf. Transm. 1987, 23, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Rissanen, J.J. Fisher information and stochastic complexity. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1996, 42, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, V. MDL, Bayesian inference, and the geometry of the space of probability distributions. In Advances in Minimum Description Length: Theory and Applications; Grnwald, P.D., Myung, I.J., Pitt, M.A., Eds.; The MIT Press: Massachusetts, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Beretta, A.; Battistin, C.; de Mulatier, C.; Mastromatteo, I.; Marsili, M. The stochastic complexity of spin models: How simple are simple spin models? arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1702.07549. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E. Training products of experts by minimizing contrastive divergence. Neural Comput. 2002, 14, 1771–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezard, M.; Montanari, A. Information, Physics, and Computation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Filiasi, M.; Livan, G.; Marsili, M.; Peressi, M.; Vesselli, E.; Zarinelli, E. On the concentration of large deviations for fat tailed distributions, with application to financial data. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2014, 9, P09030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).