Abstract
The brain is a complex structure made up of interconnected neurons, and its electrical activities can be evaluated using electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. The characteristics of the brain area affected by partial epilepsy can be studied using focal and non-focal EEG signals. In this work, a method for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals is presented using entropy measures. These entropy measures can be useful in assessing the nonlinear interrelation and complexity of focal and non-focal EEG signals. These EEG signals are first decomposed using the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) method to extract intrinsic mode functions (IMFs). The entropy features, namely, average Shannon entropy (ShEnAvg), average Renyi’s entropy (RenEnAvg), average approximate entropy (ApEnAvg), average sample entropy (SpEnAvg) and average phase entropies (S1Avg and S2Avg), are computed from different IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals. These entropies are used as the input feature set for the least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM) classifier to classify into focal and non-focal EEG signals. Experimental results show that our proposed method is able to differentiate the focal and non-focal EEG signals with an average classification accuracy of 87% correct.
1. Introduction
The electroencephalogram (EEG) is used to measure the electrical activity of the brain characterizing its various pathological states. In the literature, many studies are presented to analyze Alzheimer’s disease [1], attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [2], autism [3], autistic spectrum disorder [4], alcoholism [5], epilepsy [6,7], depth of anesthesia [8,9], etc., using EEG signals. Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder that affects the quality of life of the patient, causing social impairment and a higher risk of death [10]. Epilepsy can be divided into two categories: generalized and focal (partial). About one third of the total patients available for epilepsy treatment become resistant to drug therapy [10]. About 20% of generalized and 60% of partial epilepsy patients developed a drug resistance tendency during the course of epilepsy [10]. Consequently, such patients are left with only the choice of clinical resection of the affected brain area by surgery for the treatment of epilepsy. Hence, the localization of the brain area affected by epilepsy can be useful to treat epilepsy in such patients. The different methods used for presurgical localization of the brain may involve magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [11], positron emission tomography (PET) [12] and ictal single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) [13,14]. The identification of the affected brain area before surgery using EEG signals can help with locating the epileptogenic focus and the assessment of functional properties and activities of the brain.
Several techniques have been developed to delineate the changes in the characteristics of the EEG signals before seizure onset. These techniques involve advanced signal processing methods and can be useful for localization of the epileptogenic focus. In [15], the electrocorticograph (ECoG) signals recorded from the cerebral cortex of the brain of 21 patients were analyzed using wavelet packet and time-frequency waveforms to characterize the spikes in order to localize the epileptic events. The EEG background activities, such as the delta asymmetry of patients with partial epilepsy, were studied and found useful for the lateralization and localization of the epileptic focus [16,17]. It is observed that high frequency oscillations (60–100 Hz) increase before the onset of neocortical epilepsy and help to localize the seizure onset zone [18]. Coherence patterns of EEG signals are studied to establish the relationship between the coherence and cortical anatomy [19]. They show that the alteration in the coherence patterns may help to identify normal and pathological functional relationships between distant cortical areas. In [20], the mean phase coherence algorithm is used to study inter-electrode synchrony and showed that the local hypersynchrony may be an indicator of epileptogenic cortex. Mean phase coherence, which is a statistical measure of phase synchronization, is studied using EEG signals recorded from patients with temporal lobe epilepsy [21]. They have observed a clear difference in the degree of synchronization between EEG recordings from seizure-free intervals and those before an impending seizure. Nonlinear parameters, such as the windowed correlation dimensions and complexity loss measure, are used to characterize the primary epileptogenic area in [22,23], respectively. The EEG recordings from seizure-free intervals can also be used to study the changes in the underlying dynamics of the cortex affected by epilepsy [24–28]. The focal and non-focal EEG signals are recorded from the patients affected by focal epilepsy. Focal epilepsy affects only a limited part of the patient’s brain. The focal EEG signals are acquired from the channels that first detected ictal EEG signal changes by visual inspection [29], and the remaining EEG signals are termed as the non-focal EEG signals. In [29], the authors have shown that the focal EEG signals are less random, more nonlinear-dependent and more stationary, as compared to non-focal EEG signals.
Recently, many empirical mode decomposition (EMD) [30]-based techniques have been developed for analysis and classification of EEG signals [31–38]. The IMFs of EEG signals are symmetric, amplitude and frequency modulated (AM-FM) components. Many features are extracted from the IMFs of EEG signals to study the pathological states of the brain. These features are the mean frequency of IMFs computed from the Fourier–Bessel series expansion [31], the area computed from the analytic signal representation (ASR) of the IMFs [32,33], the 95% confidence ellipse area of the second-order difference plot (SODP) of IMFs [33,34], the 95% confidence ellipse area and interquartile range (IQR) of the Euclidean distances parameters extracted from the 2D and 3D phase space representation (PSR) of IMFs [35], the histogram-based features extracted from time-frequency images obtained using the Hilbert–Huang transform [36], multi-level local patterns [37], the coefficient of variation and the fluctuation index computed from IMFs [38], etc.
In this work, a method for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals based on features extracted from IMFs of EEG signals is presented. The Figure 1 depicts the proposed methodology for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals. The focal and non-focal EEG signals are first decomposed using the EMD method. Then, various entropy measures, namely average Shannon entropy (ShEnAvg), average Renyi’s entropy (RenEnAvg), average approximate entropy (ApEnAvg), average sample entropy (SpEnAvg), average phase entropy 1 (S1Avg) and average phase entropy 2 (S2Avg), are computed from the IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals. The focal and non-focal EEG signals are available in the studied dataset in the pairs of time series. In order to obtain the characteristics of both the time series for classification, the average of entropy measures are computed from the time series. Finally, these computed different entropy measures are used for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG classes using the LS-SVM classifier.
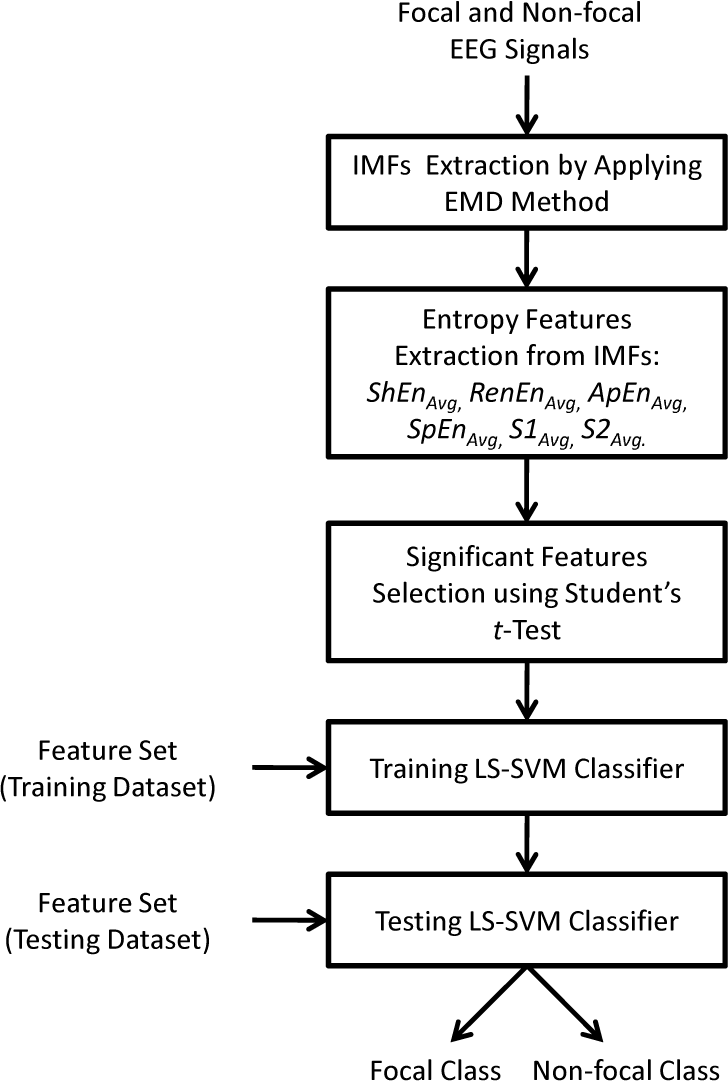
Figure 1.
Proposed system for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals.
The remaining sections of the paper are organized as follows: Section 2 provides the description of the dataset, EMD, entropy measures and LS-SVM classifier. Results are presented in Section 3 and discussed in Section 4. Finally, the paper concludes in Section 5.
2. Methodology
2.1. Dataset
The EEG dataset used in this study was obtained from the Bern-Barcelona EEG database ( www.dtic.upf.edu/~ralph/sc/). A detailed description of the dataset is given in [29]. The dataset consists of recordings of patients who underwent long-term intracranial EEG recordings at the Department of Neurology, University of Bern, Switzerland. The multichannel EEG recordings were acquired from five patients suffering from pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy and were candidates for surgery. The EEG signals were sampled at a 512-Hz sampling frequency. The recordings contain pairs of EEG signals, denoted by “x” and “y”. The dataset consists of 3750 pairs of focal EEG signals and 3750 pairs of non-focal EEG signals, with each EEG signal having 10,240 samples. In this study, we have used the first 50 focal and 50 non-focal pairs of EEG signals. Typical example pairs of the focal and non-focal EEG signals are shown in the Figures 2 and 3, respectively.
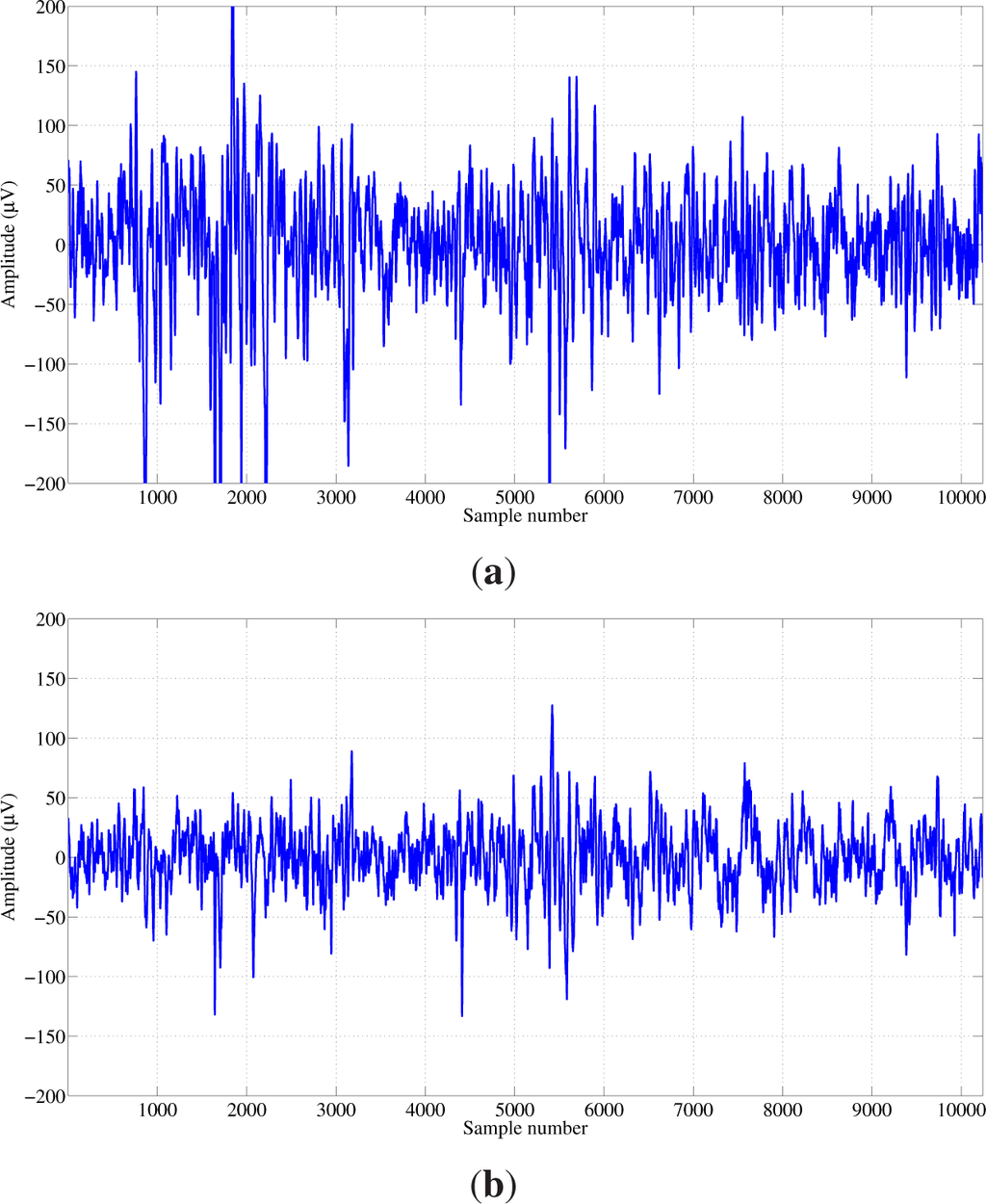
Figure 2.
Typical pair of focal EEG signals: (a) “x” signal; and (b) “y” signal.
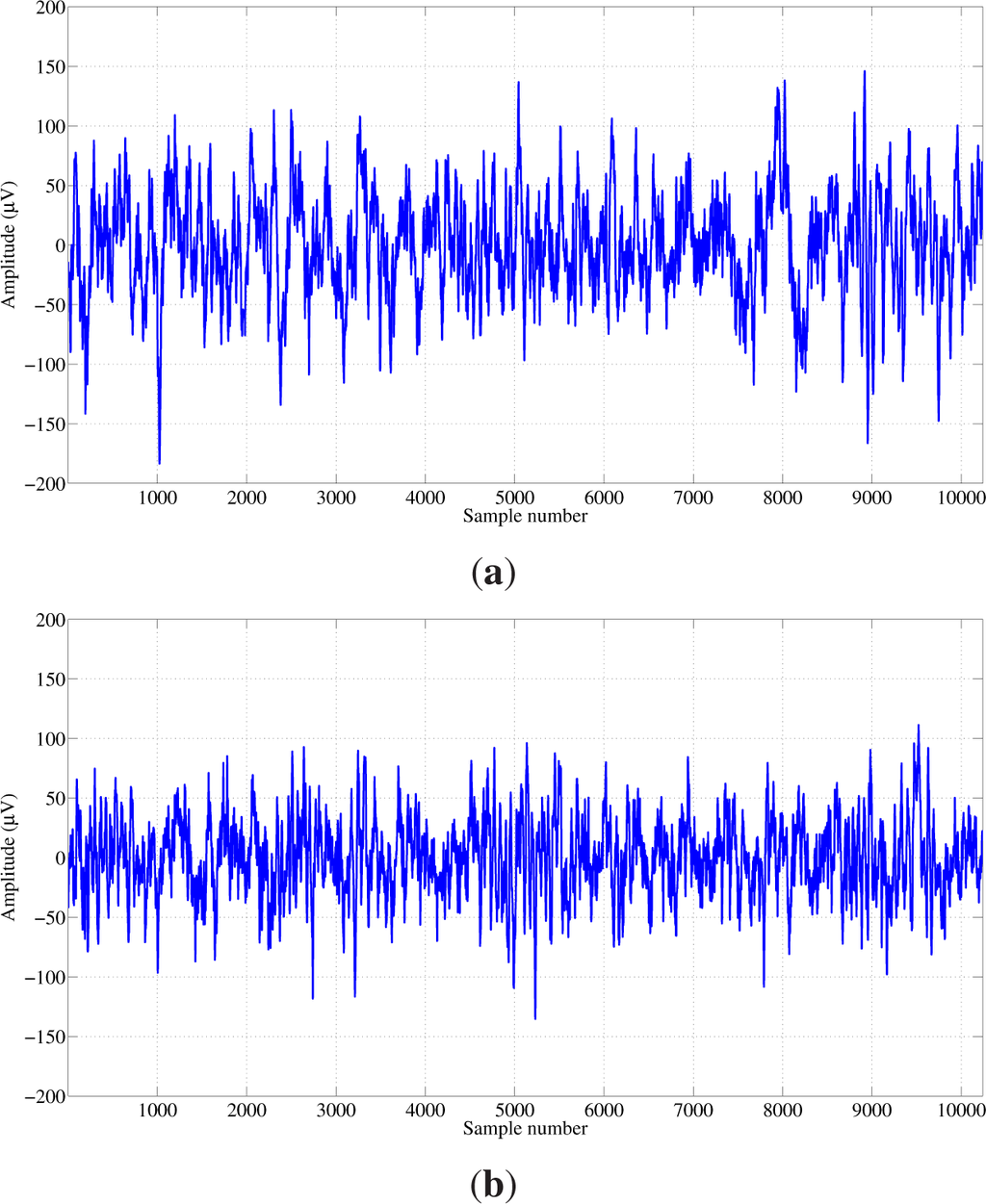
Figure 3.
Typical pair of non-focal EEG signals: (a) “x” signal; and (b) “y” signal.
2.2. Empirical Mode Decomposition
Empirical mode decomposition (EMD), proposed in [30], is an adaptive, data-dependent decomposition method and suitable for the analysis of nonlinear and non-stationary signals. This method decomposes a signal into a finite set of oscillatory components, known as intrinsic mode functions (IMFs). It adaptively represents a non-stationary signal as the sum of IMFs, which can be considered zero-mean, amplitude and frequency modulated (AM-FM) components [39]. Each IMF fulfills the following two conditions [30]:
- In the whole dataset, the number of extrema and the number of zero-crossings should be either equal or differ at most by one.
- The mean value of two envelopes, one defined by connecting local maxima and the other defined by connecting local minima, at any point is zero.
For a given signal x(t), IMFs can be derived using an iterative process, known as the sifting process, which can be summarized in the following steps [30]:
- Extract extrema (maxima and minima) from signal x(t).
- Obtain the envelope εmax(t) by connecting all of the maxima and similarly obtain the envelope εmin(t) by connecting all of the minima using cubic spline interpolation.
- Compute the average of εmax(t) and εmin(t) as:
- Extract D(t) from x(t) as:
- Check whether the D(t) satisfies the two basic conditions of IMF.
- Repeat Steps i–v, for D(t), until it satisfies the conditions of IMF.
Once the IMF is derived, define the IMF1(t) = D(t), which is the first extracted IMF. In order to determine the next remaining IMFs, residual signal r1(t) = x(t) – IMF1(t) can be treated as a new signal. Now, repeat the above-mentioned sifting process until the obtained residual becomes a monotonic function from which, no further IMFs can be derived. Finally, the original signal x(t) can be expressed as the sum of IMFs and the final residual [30]:
where K is the number of extracted IMFs and R(t) is the final residual. The IMFs of the focal and non-focal EEG signals are shown in Figure 4. The first ten IMFs of the focal EEG signal shown in Figure 2a are depicted in Figure 4a. Similarly, Figure 4b depicts the first ten IMFs of the non-focal EEG signal shown in Figure 3a.
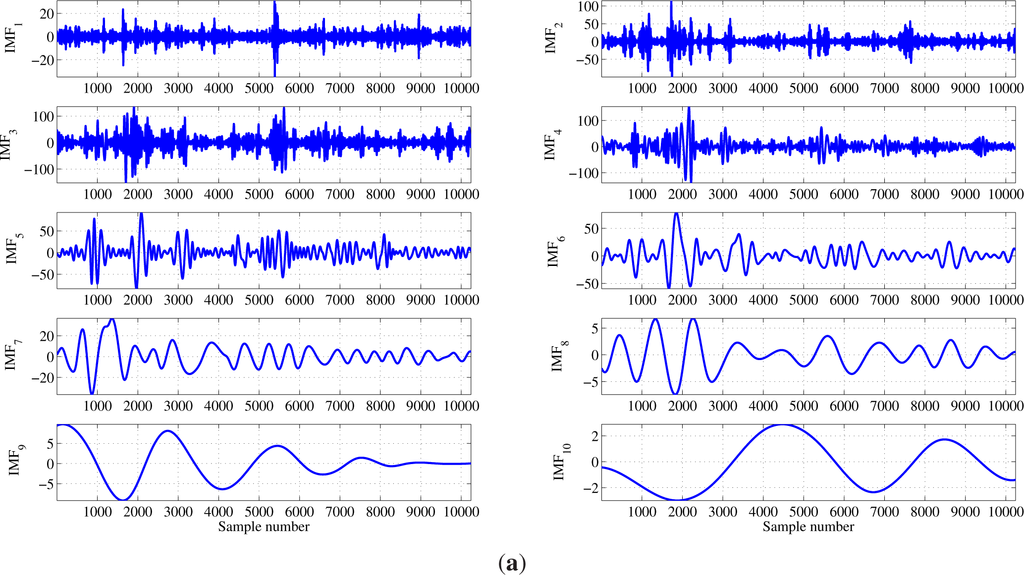
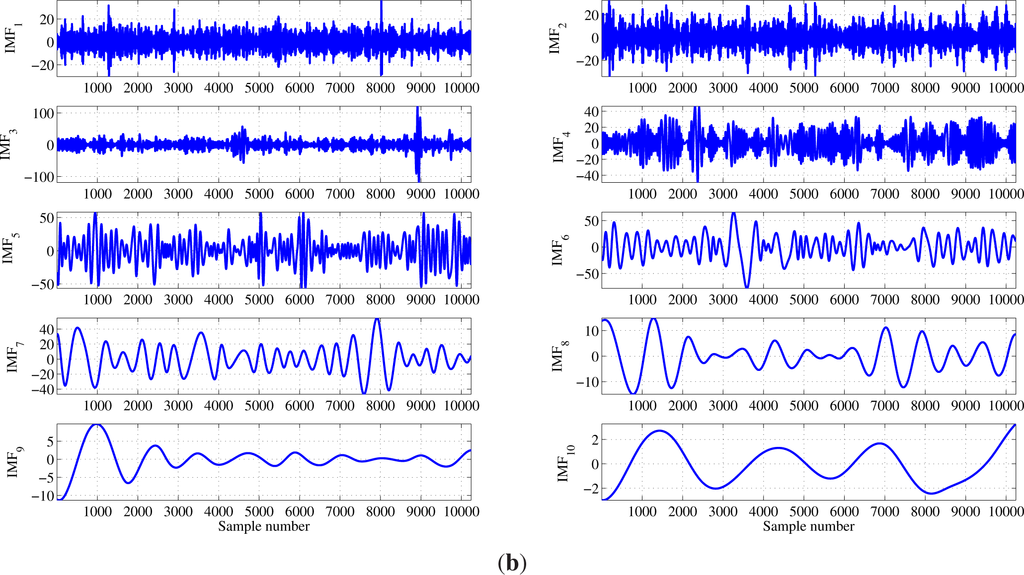
Figure 4.
Empirical mode decomposition of the EEG signal: (a) first ten intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) of the focal EEG signal; and (b) first ten IMFs of the non-focal EEG signal.
2.3. Entropy-Based Features Extraction
In thermodynamics, the entropy is defined as a measure of the degree of disorder [40]. In the context of information theory, the entropy is an indicator of the amount of information stored in a more general probability distribution [40]. Entropy is a measure of the complexity of the time series. The nonlinear parameters can be useful to describe the dynamics of the EEG signals considering the nonlinear and non-stationary nature of EEG signals. A brief description of the entropy-based features extracted from the IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals is given in this section.
2.3.1. Average Spectral Entropies
Spectral entropy uses the power spectrum of the signal to estimate the regularity of time series. The amplitude components of the power spectrum are used to compute the probabilities in entropy computation. Spectral entropy [41,42] is evaluated using the normalized Shannon entropy, which quantifies the spectral complexity of the time series. Fourier transformation is used to obtain the power spectral density (PSD) of the time series. The PSD represents the distribution of power of the signal according to the frequencies present in the signal. In order to obtain the power level for each frequency, the Fourier transform of the signal is computed, and the power level of the frequency component is denoted by Pf. The normalization of the power is performed by computing the total power as ∑ Pf and dividing the power level corresponding to each frequency by the total power as:
The entropy is computed by multiplying the power level in each frequency and the logarithm of the inverse of the same power level. Finally the spectral entropy of the time series is computed using the following formula [40]:
Another entropy measure used for estimating the spectral complexity of the time series is Renyi’s entropy [43,44]. Renyi’s entropy can be defined as [40,44]:
Renyi’s entropy corresponding to α = 2 is known as Renyi’s quadratic entropy, and defined as follows [40,44]:
In this work, we have used (7) to compute the RenEn. These entropy measures can be considered as the measure of uncertainty about the event f. Data with a broad, flat probability distribution have high entropy, and data with a narrow, peaked distribution will have low entropy [40]. These spectral entropy measures are used for the detection of epilepsy using EEG signals in [40]. The focal and non-focal EEG signals are given in a pair of time series, “x” and “y”. The average Shannon entropy is used in this work and defined as:
where ShEnx and ShEny are the Shannon entropies corresponding to “x” and “y” time series of the pair of EEG signals. Similarly, average Renyi’s entropy is defined as:
where RenEnx and RenEny are Renyi’s entropies corresponding to the “x” and “y” time series of the pair of EEG signals.
2.3.2. Average Approximate Entropy
Approximate entropy (ApEn) is a complexity measure of time series [45]. It is widely used in many areas of biomedical signal processing, such as EEG epileptic activity analysis [46], background activity [47], coronary artery disease (CAD) heart rate signal analysis [48], etc. It measures the randomness or the regularity of a time series in multiple dimensions. It expresses the logarithmic likelihood that the signal of length N repeats itself within the tolerance of r for d points and also repeats itself for the next d + 1 points [49]. Considering a time series x(i) of length N, construct N − d + 1 vectors X(1), X(2),…, X(N − d + 1). Any vector X(i) can be expressed as:
where d is the embedding dimension. For a given time series x(i), ApEn is given by [50,51]:
where:
where
is a correlation integral indicating the probability of a vector X(i), which remains similar to X(j) within tolerance limit r.
is given by:
where
counts the distances between two vectors X(i) and X(j), which is smaller than the tolerance r.
Lower values of the ApEn are an indication of more self-similarity or more regularity present in the signal. If the value of the r parameter is small, the conditional probability estimate will be poor and the estimate will also be sensitive to noise [52]. Similarly, for a high value of the r parameter, detail information will be lost [51]. In this work, the value of the r parameter is chosen as r = 0.2 times the standard deviation of the data, and the embedded dimension d is set as two [45]. In this work, the average ApEn is used for the classification of the focal and non-focal EEG signals and is defined as:
where ApEnx and ApEny are the ApEn corresponding to the “x” and “y” time series of the focal and non-focal EEG signals.
2.3.3. Average Sample Entropy
Sample entropy (SpEn) [50] is a modified version of the ApEn and used as a complexity measure of time series. The SpEn averts the bias caused by the use of the self matches in the computation of ApEn and improves performance. Furthermore, SpEn is independent of the long record length and improves the relative consistency [50]. In addition, the SpEn algorithm is simpler than the ApEn algorithm and takes nearly half of the ApEn computation time [50]. Suppose that x(i) is a time series of length N; construct N − d + 1 vectors X(1), X(2),…, X(N − d + 1) as expressed by (10). For a given time series x(i), SpEn can be computed as [50,51]:
where parameters Bd(r) and Ad(r) are defined as:
and
where Ci is the count, such that L [X(i), X(j)] ≤ r, excluding self-matches. The parameter L [X(i), X(j)] is the distance between X(i) and X(j) and can be defined as:
The lower the value of SpEn for a given value of d and r, the more the self-similarity in a given time series will be. In this work, the value of d is chosen as two [50,52], and the value of r is set as 0.2-times the standard deviation of the data [50]. The average SpEn computed from the average of SpEn of the “x” and “y” time series is used as a feature for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals. Average sample entropy can be defined as:
2.3.4. Average Phase Entropies
Phase entropies use higher order spectra (HOS) to compute the entropy. The HOS are defined in terms of higher order statistics, known as cumulants [53]. HOS are spectral representations of higher order moments. For example, a bispectrum is the Fourier spectrum of the third order moments. HOS can be defined for a deterministic signal, as well as random processes [52]. The bispectrum of the signal can be defined as:
where E denotes the expectation operator of a random variable and F(f) is the Fourier transform of the signal x(i).
The bispectrum is a complex valued function of the two frequencies f1 and f2. The computation of the bispectrum depends on the product of the three Fourier coefficients, as shown in (17). The phase entropies S1 and S2 are similar to spectral entropies, but computed from the bispectrum, and can be given by [54]:
where:
where Ω is the principal domain or non-redundant region [52].
where:
.
The two entropies S1 and S2 are computed from the probabilities estimated based on the L1 and L2 norms of the bispectrum of the signal. The pk and qj are similar to the probability distribution functions and computed by normalization using the L1 and L2 norms, respectively, using the sum of the norm over Ω. The spectrum entropies are used for automatic diagnosis of epileptic EEG signals in [52]. In this work, the S1Avg and S2Avg entropies are used for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals and are defined as:
and:
where S1x and S2x are the S1 and S2 corresponding to the “x” time series. Similarly, S1y and S2y are the S1 and S2 corresponding to the “y” time series.
2.3.5. Least Squares Support Vector Machine
The support vector machine (SVM) is based on the idea of maximizing the distance between the separating hyperplanes. It has a good generalization ability [5,55,56]. The least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM) method searches for the optimal hyperplane in the higher dimension input space to create a decision boundary between two different groups of patterns. Originally, this algorithm was developed as a linear classifier. The SVM algorithm has been extended as LS-SVM, which is a least squares version of SVM. For a set of data points
, xk ∈ ℝn is the input data and yk ∈ {+1, −1} is the k-th output class label, the discriminant function can be defined as [57]:
where W is the d-dimensional weight vector, β is a bias and u(x) is a mapping function that maps x into d-dimensional space.
The decision function of the LS-SVM classifier can be expressed as [35,38]:
where
is a kernel function. The following kernels are used in this work:
- The radial basis function (RBF) kernel: It can be defined as [58]:
- The Mexican hat wavelet kernel: It can be derived from the Mexican hat mother wavelet and can be defined as [59,60]:
- The Morlet wavelet kernel: It can be obtained from the Morlet mother wavelet and can be defined as [59,60]:
2.3.6. Performance Evaluation
Ten-fold cross-validation is used for ensuring the reliable classification performance of the LS-SVM classifier. In the k-fold cross-validation procedure, the available data are broken into the k subsets randomly [61]. k – 1 subsets at a time are used for training the classifier, and the one remaining subset is used to test the classification model. In this way, each subset is used to test the classification model exactly once, while the remaining k – 1 subsets are used for training the classifier before testing. All performance parameters are computed for each testing, and finally, the average of the performance parameters for all testing gives the final average performance parameters. In ten-fold cross-validation, the value of k is equal to 10.
The performance of the LS-SVM classifier is evaluated using sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPF), accuracy (ACC), positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC). If TP (true positive) is the number of focal EEG signals identified as focal EEG signals, TN (true negative) is the number of non-focal EEG signals classified as non-focal EEG signals, FP (false positive) is the number of non-focal EEG signals recognized as focal EEG signals and FN (false negative) is the number of focal EEG signals distinguished as non-focal EEG signals, then the mathematical expressions of the performance measure parameters are as follows [62,63]:
where:
and:
A larger value of the MCC parameter indicates better classifier performance [62,63].
3. Results
The EMD decomposes the EEG signals into symmetric, oscillatory and band-limited IMFs. In this work, the focal and non-focal EEG signals decomposed by applying the EMD method, and features are extracted from these obtained IMFs. The IMFs of the signal are arranged from higher frequency components to lower frequency components (IMF1 to IMF10). Six entropies are computed from the IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals and used as features for classification. Due to higher computational complexity, entropy features are computed for a data length of 4, 096 samples. Table 1 presents the results of different features extracted from first ten IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals. Spectral entropies (ShEnAvg and RenEnAvg) quantify the degree of regularity present in the spectral components of the signal. If the number of dominant spectral components present in the signals are more, the spectral entropy will be higher, and vice versa. The ApEnAvg and SpEnAvg entropy measures quantify the self-similarity in the time series. The phase entropies S1Avg and S2Avg are the complexity measures based on the probability density functions of the bispectrum of the signals.

Table 1.
The range (mean ± standard deviation) of the features extracted from different IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals.
Classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals is performed using the LS-SVM classifier with different kernels. The above-mentioned six entropy measures computed for the first ten IMFs of the EEG signals are used to form the input feature set for the LS-SVM classifier. In this work, we have used 100 pairs of EEG signals (50 pairs of focal and 50 pairs of non-focal signals). The size of the input feature set formed using the ten IMFs of the EEG signals is 60×100. In order to reduce the complexity of the classifier, the size of the feature set is reduced using the Student’s t-test (p ≤ 0.05) [55,64]. Finally, the reduced feature set is of a size of 13 × 100. The selected features are statistically significant features (p ≤ 0.05) based on the Student’s t-test and are presented in Table 2. This reduced feature set is given as the input to the LS-SVM classifier, and the obtained results are shown in Table 3. The performance of the LS-SVM classifier is evaluated for three kernels, namely, RBF, Mexican hat wavelet and Morlet wavelet kernels, using a ten-fold cross-validation procedure. The kernel parameters are selected by the trial and error method. In order to ensure the reliable classification of the LS-SVM classifier, ten-fold cross-validation is used, and various performance parameters, namely ACC, SEN, SPF, PPV, NPV and MCC, are evaluated.

Table 2.
Statistically-significant features (p ≤ 0.05) selected for classification based on the Student’s t-test.

Table 3.
Performance of the LS-SVM classifier using different kernels. RBF, radial basis function.
The proposed methodology is carried out in two stages—(i) feature extraction and (ii) classification—using MATLAB programming. Table 3 shows a maximum classification accuracy of 87% using the LS-SVM classifier with the Morlet wavelet kernel. The SEN parameter indicates the ability of the classifier to accurately identify the proportion of true positive samples from the test set [62]. Similarly, SPF indicates the ability of the classifier to accurately identify the proportion of true negative samples from the test set [62]. In this work, we have achieved the highest SEN and SPF of 90% and 84%, respectively, using the LS-SVM classifier with the Morlet wavelet kernel. PPV represents the fraction of positive values identified by the classifier that represents true positives [62]. Similarly, NPV denotes the fraction of the negative values identified by the classifier that are true negative [62]. The values of the PPV and NPV parameters are 87.29% and 90.50%, respectively, when the Morlet wavelet kernel is used with the LS-SVM classifier, which is the highest among all of the kernels used in this study. The maximum classification accuracy obtained using the LS-SVM classifier with the RBF kernel is 86%. Similarly, we obtained an accuracy of 84% using the Mexican hat wavelet kernel. In terms of classification accuracy, the Morlet wavelet kernel shows the best performance and is suitable for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals. MCC evaluates the classification accuracy of imbalanced positive and negative samples in a dataset [62]. The highest value of the MCC parameter for the Morlet wavelet kernel confirms the suitability of the Morlet wavelet kernel for the classification of the focal and non-focal EEG signals. The comparison of our proposed method with previously reported methods [65,66] using the same database is presented in Table 4. Our proposed method shows the highest classification accuracy of 87%.

Table 4.
Summary of studies reporting automated detection of focal and non-focal EEG classes using the same database used in this work. DPE, delay permutation entropy; AVIF, average variance of instantaneous frequencies.
4. Discussion
EMD is suitable for the decomposition of the EEG signals that exhibit a nonlinear and a non-stationary nature [67,68]. It separates the fast oscillations from the slow oscillations present in the signals [69]. These oscillating components can be separated using EMD as the IMFs. The nonlinear signal processing methods are more useful for nonlinear and non-stationary signal analysis. Nonlinear methods efficiently extract the small changes in the nonlinear and non-stationary signals [55]. Hence, we have used entropy measures for extracting features from focal and non-focal EEG signals. Different entropy measures are computed on the IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals. These entropies indicate the complexity measures related to the power spectrum, multiple dimensions and HOS. The spectral entropies ShEnAvg and RenEnAvg reveal the complexity of signals in the frequency domain; ApEnAvg and SpEnAvg measure the self-similarity of time series; and S1Avg and S2Avg represent the complexity in the higher order spectrums of the signals.
The Student’s t-test detects the discrimination ability of the features to separate the two classes. This test estimates the probability, known as the p-value, for each feature using the Student’s t-test. The p-value measures the similarity between the two classes [55]. In other words, the lower p-value indicates the higher discrimination ability of the feature to differentiate the two classes. After running Student’s t-tests, 13 features are found to be significant. Out of these 13 features, one is ApEnAvg, six are SpEnAvg, one is S1Avg, two are S2Avg, one is ShEnAvg and two are RenAvg, computed from different IMFs. The statistically-significant (p ≤ 0.05) features are listed in Table 2 with the resultant p-values.
The ShEnAvg is significant for the discrimination of IMF1; similarly, RenAvg is significant for IMF2 and IMF3. The ApEnAvg is significant for IMF1 only, and SpEnAvg is found to be significant for IMF1, IMF2, IMF3, IMF5, IMF6 and IMF7. The S1Avg is significant for IMF1, and S2Avg is found to be significant for IMF5 and IMF6. Based on the analysis of Table 2, IMF1 and IMF3 are found to be more suitable for the discrimination of focal and non-focal EEG signals. The results show that SpEnAvg is the most sensitive entropy measure for the classification between focal and non-focal EEG signals. It should be noted that the two entropies, namely ApEnAvg and SpEnAvg, among all of the studied entropies, seem to have more computational complexity.
The IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals obtained using the EMD method represent narrow-band frequency components. It would be of interest to develop links between different rhythms and IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals. The physiological understanding of the computed entropies of the IMFs for focal and non-focal EEG signals can be studied. This work also can be extended to determine the affected localized area of the brain with the help of the computation of the entropies in different channels.
LS-SVM is a well-known classifier and is used in the classification of many biomedical signals, like electrocardiograph (ECG) signals [70], heart rate variability signals [71], cardiac sound signals [72], brain MRI classification [73], EEG signals [74,75], etc. In this work, the classification performance of the LS-SVM classifier is evaluated by employing the ten-fold cross-validation procedure. The results obtained from the experiments show that the extracted entropy parameters are able to classify the focal and non-focal EEG signals. The Morlet wavelet is found to be most suitable in creating an accurate decision boundary for the classification of the focal and non-focal EEG signals. The reliability of the proposed method can be further improved using larger and diverse datasets.
The proposed method is also compared with the other existing methods, and the comparison is presented in Table 4. In [65], delay permutation entropy (DPE) is used as the feature for the classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals. The maximum classification accuracy obtained using the SVM classifier for 50 focal and 50 non-focal EEG signals is 84%. In previous work [66], using the average sample entropy (SpEnAvg), the average variance of instantaneous frequencies (AVIF) coupled with the LS-SVM classifier has yielded an accuracy of 85%. The maximum classification accuracy obtained in this work is 87% for the same dataset, which is 2% higher than the previous work [66].
The advantages of our proposed method are as follows:
- We have obtained a higher classification accuracy compared to previously reported works using the same database.
- Our method is rigorous and repetitive, as we have performed a ten-fold cross-validation.
- The developed software can be used for automated identification of focal and non-focal EEG signals.
The limitations of the proposed method are that we have used a small database and that it is computationally intensive.
5. Conclusions
Epilepsy is a mental disorder affecting a large population of the world. Locating the area of brain affected by focal epilepsy can aid in the presurgical diagnosis of seizure. In this work, we have used six entropy measures computed from IMFs of the EEG signals for classification into focal and non-focal EEG signals, which can help to determine the epileptogenic zone of the brain. These entropies are useful in assessing the complexity of the IMFs of focal and non-focal EEG signals. The selected clinically significant features are fed to the LS-SVM classifier, obtaining a classification accuracy of 87%. The classification accuracy can be further improved using a huge database, better features and robust classifiers.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Ralph G. Andrzejak of Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain, for providing permission to use Bern-Barcelona EEG dataset.
Author Contributions
Ram Bilas Pachori and U. Rajendra Acharya designed research problem. Rajeev Sharma performed research and analyzed data. Ram Bilas Pachori and U. Rajendra Acharya interpreted the data, Ram Bilas Pachori wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adeli, H.; Ghosh-Dastidar, S.; Dadmehr, N. A spatio-temporal wavelet-chaos methodology for EEG-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett 2008, 444, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadlou, M.; Adeli, H. Wavelet-synchronization methodology: A new approach for EEG-based diagnosis of ADHD. Clin. EEG Neurosci 2010, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadlou, M.; Adeli, H. Electroencephalograms in diagnosis of autism. In Comprehensive Guide to Autism; Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Martin, C.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 327–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadlou, M.; Adeli, H.; Adeli, A. Fractality and a wavelet-chaos-neural network methodology for EEG-based diagnosis of autistic spectrum disorder. J. Clin. Neurophysiol 2010, 27, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Sree, S.V.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Suri, J.S. Automated diagnosis of normal and alcoholic EEG signals. Int. J. Neural Syst 2012, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, H.; Zhou, Z.; Dadmehr, N. Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 123, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Adeli, H.; Ghosh-Dastidar, S.; Dadmehr, N. A wavelet-chaos methodology for analysis of EEGs and EEG subbands to detect seizure and epilepsy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng 2007, 54, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, Q.; Fan, S.Z.; Lu, C.W.; Lin, T.Y.; Abbod, M.F.; Shieh, J.S. Analysis of EEG via multivariate empirical mode decomposition for depth of anesthesia based on sample entropy. Entropy 2013, 15, 3458–3470. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.R.; Fan, S.Z.; Abbod, M.F.; Jen, K.K.; Wu, J.F.; Shieh, J.S. Application of multivariate empirical mode decomposition and sample entropy in EEG signals via artificial neural networks for interpreting depth of anesthesia. Entropy 2013, 15, 3325–3339. [Google Scholar]
- Pati, S.; Alexopoulos, A.V. Pharmacoresistant epilepsy: From pathogenesis to current and emerging therapies. Clevel. Clin. J. Med 2010, 77, 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzniecky, R.; de la Sayette, V.; Ethier, R.; Melanson, D.; Andermann, F.; Berkovic, S.; Robitaille, Y.; Olivier, A.; Peters, T.; Feindel, W. Magnetic resonance imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy: Pathological correlations. Ann. Neurol 1987, 22, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Savic, I.; Thorell, J.O.; Roland, P. [11C] flumazenil positron emission tomography visualizes frontal epileptogenic regions. Epilepsia 1995, 36, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, M.R.; Berkovic, S.F.; Austin, M.C.; Rowe, C.C.; McKay, W.J.; Bladin, P.F. SPECT in the localisation of extratemporal and temporal seizure foci. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 59, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Spanaki, M.V.; Spencer, S.S.; Corsi, M.; MacMullan, J.; Seibyl, J.; Zubal, I.G. Sensitivity and specificity of quantitative difference SPECT analysis in seizure localization. J. Nucl. Med 1999, 40, 730–736. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Alcántara, R.; Medina, V. Analysis and localization of epileptic events using wavelet packets. Med. Eng. Phys 2001, 23, 623–631. [Google Scholar]
- Panet-Raymond, D.; Gotman, J. Asymmetry in delta activity in patients with focal epilepsy. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol 1990, 75, 474–481. [Google Scholar]
- Marciani, M.G.; Stefanini, F.; Stefani, N.; Maschio, M.C.E.; Gigli, G.L.; Roncacci, S.; Caltagirone, C.; Bernardi, G. Lateralization of the epileptogenic focus by computerized EEG study and neuropsychological evaluation. Int. J. Neurosci 1992, 66, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Worrell, G.A.; Parish, L.; Cranstoun, S.D.; Jonas, R.; Baltuch, G.; Litt, B. High frequency oscillations and seizure generation in neocortical epilepsy. Brain 2004, 127, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Towle, V.L.; Carder, R.K.; Khorasani, L.; Lindberg, D. Electrocorticographic coherence patterns. J. Clin. Neurophysiol 1999, 16, 528–547. [Google Scholar]
- Schevon, C.A.; Cappell, J.; Emerson, R.; Isler, J.; Grieve, P.; Goodman, R.; Mckhann, G., Jr.; Weiner, H.; Doyle, W.; Kuzniecky, R.; Devinsky, O.; Gilliam, F. Cortical abnormalities in epilepsy revealed by local EEG synchrony. NeuroImage 2007, 35, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mormann, F.; Lehnertz, K.; David, P.; Elger, C.E. Mean phase coherence as a measure for phase synchronization and its application to the EEG of epilepsy patients. Physica D 2000, 144, 358–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lehnertz, K.; Elger, C.E. Spatio-temporal dynamics of the primary epileptogenic area in temporal lobe epilepsy characterized by neuronal complexity loss. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol 1995, 95, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Widman, G.; Lehnertz, K.; Urbach, H.; Elger, C.E. Spatial distribution of neuronal complexity loss in neocortical lesional epilepsies. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Casdagli, M.C.; Iasemidis, L.D.; Savit, R.S.; Gilmore, R.L.; Roper, S.N.; Sackellares, J.C. Non-linearity in invasive EEG recordings from patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol 1997, 102, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejak, R.G.; Chicharro, D.; Lehnertz, K.; Mormann, F. Using bivariate signal analysis to characterize the epileptic focus: The benefit of surrogates. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83. 046203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejak, R.G.; Mormann, F.; Widman, G.; Kreuz, T.; Elger, C.E.; Lehnertz, K. Improved spatial characterization of the epileptic brain by focusing on nonlinearity. Epilepsy Res 2006, 69, 30–44. [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejak, R.G.; Widman, G.; Lehnertz, K.; Rieke, C.; David, P.; Elger, C.E. The epileptic process as nonlinear deterministic dynamics in a stochastic environment: An evaluation on mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 2001, 44, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Varotto, G.; Tassi, L.; Franceschetti, S.; Spreafico, R.; Panzica, F. Epileptogenic networks of type II focal cortical dysplasia: A stereo-EEG study. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejak, R.G.; Schindler, K.; Rummel, C. Nonrandomness, nonlinear dependence, and nonstationarity of electroencephalographic recordings from epilepsy patients. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86. 046206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.; Wu, M.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar]
- Pachori, R.B. Discrimination between ictal and seizure-free EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. Res. Lett. Signal Process 2008, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachori, R.B.; Bajaj, V. Analysis of normal and epileptic seizure EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed 2011, 104, 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Pachori, R.B.; Sharma, R.; Patidar, S. Classification of normal and epileptic seizure EEG signals based on empirical mode decomposition. In Complex System Modelling and Control through Intelligent Soft Computations; Zhu, Q., Azar, A.T., Eds.; Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing; Volume 319, Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 367–388. [Google Scholar]
- Pachori, R.B.; Patidar, S. Epileptic seizure classification in EEG signals using second-order difference plot of intrinsic mode functions. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed 2014, 113, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Pachori, R.B. Classification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals based on phase space representation of intrinsic mode functions. Expert Syst. Appl 2015, 42, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.; Qu, J.; Chai, Y.; Dong, Y. Classification of seizure based on the time-frequency image of EEG signals using HHT and SVM. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 13, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Kanhangad, V.; Pachori, R.B. Classification of seizure and seizure-free EEG signals using multi-level local patterns. Proceedings of the IEEE 19th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Hong Kong, China, 20–23 August 2014; pp. 646–650.
- Li, S.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, Q.; Geng, S.; Cai, D. Feature extraction and recognition of ictal EEG using EMD and SVM. Comput. Biol. Med 2013, 43, 807–816. [Google Scholar]
- Flandrin, P.; Rilling, G.; Goncalves, P. Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank. IEEE Signal Process. Lett 2004, 11, 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kannathal, N.; Choo, M.L.; Acharya, U.R.; Sadasivan, P. Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed 2005, 80, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar]
- Fell, J.; Röschke, J.; Mann, K.; Schäffner, C. Discrimination of sleep stages: A comparison between spectral and nonlinear EEG measures. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol 1996, 98, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Grassberger, P.; Schreiber, T.; Schaffrath, C. Nonlinear time sequence analysis. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1991, 1, 521–547. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, K.; Salam, F. A data-derived quadratic independence measure for adaptive blind source recovery in practical applications. Proceedings of the 45th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Tulsa, OK, USA, 4–7 August 2002; 3, pp. III-473–III-476.
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Rivero, D.; Pazos, A. Epileptic seizure detection using multiwavelet transform based approximate entropy and artificial neural networks. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 193, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Abásolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Espino, P.; Poza, J.; Sánchez, C.I.; de la Rosa, R. Analysis of regularity in the EEG background activity of Alzheimer’s disease patients with approximate entropy. Clin. Neurophysiol 2005, 116, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Faust, O.; Sree, V.; Swapna, G.; Martis, R.J.; Kadri, N.A.; Suri, J.S. Linear and nonlinear analysis of normal and CAD-affected heart rate signals. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed 2014, 113, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, D.E.; Richman, J.S.; Griffin, M.P.; Moorman, J.R. Sample entropy analysis of neonatal heart rate variability. Am. J. Physiol.–Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol 2002, 283, R789–R797. [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, D.; Wang, J.; Bian, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Analysis of entropies based on empirical mode decomposition in amnesic mild cognitive impairment of diabetes mellitus. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci 2015, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Molinari, F.; Sree, S.V.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Ng, K.H.; Suri, J.S. Automated diagnosis of epileptic EEG using entropies. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2012, 7, 401–408. [Google Scholar]
- Nikias, C.L.; Mendel, J.M. Signal processing with higher-order spectra. IEEE Signal Process. Mag 1993, 10, 10–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, K.C.; Chandran, V.; Rajendra Acharya, U.; Lim, C.M. Analysis of epileptic EEG signals using higher order spectra. J. Med. Eng. Technol 2009, 33, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Faust, O.; Kadri, N.A.; Suri, J.S.; Yu, W. Automated identification of normal and diabetes heart rate signals using nonlinear measures. Comput. Biol. Med 2013, 43, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory, 2nd ed.; Statistics for Engineers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Suykens, J.A.; Vandewalle, J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett 1999, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Khandoker, A.H.; Lai, D.T.; Begg, R.K.; Palaniswami, M. Wavelet-based feature extraction for support vector machines for screening balance impairments in the elderly. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng 2007, 15, 587–597. [Google Scholar]
- Zavar, M.; Rahati, S.; Akbarzadeh-T, M.R.; Ghasemifard, H. Evolutionary model selection in a wavelet-based support vector machine for automated seizure detection. Expert Syst. Appl 2011, 38, 10751–10758. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, V.; Pachori, R.B. Classification of seizure and nonseizure EEG signals using empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed 2012, 16, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Kohavi, R. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 1137–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Azar, A.T.; El-Said, S.A. Performance analysis of support vector machines classifiers in breast cancer mammography recognition. Neural Comput. Appl 2014, 24, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Cai, C.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Wen, Y. Diagnosis of breast tumours and evaluation of prognostic risk by using machine learning approaches. In Advanced Intelligent Computing Theories and Applications. With Aspects of Contemporary Intelligent Computing Techniques, Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Qingdao, China, 21–24 August 2007; Huang, D.S., Heutte, L., Loog, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; 2, pp. 1250–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Boneau, C.A. The effects of violations of assumptions underlying the t test. Psychol. Bull 1960, 57, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Wen, P.P.; Wang, S.; Xi, M. Epileptogenic focus detection in intracranial EEG based on delay permutation entropy. AIP Conf. Proc 2013, 1559, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Pachori, R.B.; Gautam, S. Empirical mode decomposition based classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals. Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Biometrics, Shenzhen, China, 30 May–1 June 2014; pp. 135–140.
- Boashash, B.; Colitz, P.; Mesbah, M. Time-frequency detection of EEG abnormalities. In Time-Frequency Signal Analysis and Processing: A Comprehensive Reference; Boashash, B., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Pachori, R.B.; Sircar, P. EEG signal analysis using FB expansion and second-order linear TVAR process. Signal Process 2008, 88, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Rilling, G.; Flandrin, P.; Goncalves, P.; Lilly, J. Bivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett 2007, 14, 936–939. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy, R.K.; Acharya, A.; Choudhary, S.K. Gender classification from ECG signal analysis using least square support vector machine. Am. J. Signal Process 2012, 2, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Asl, B.M.; Setarehdan, S.K.; Mohebbi, M. Support vector machine-based arrhythmia classification using reduced features of heart rate variability signal. Artif. Intell. Med 2008, 44, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Patidar, S.; Pachori, R.B. Classification of cardiac sound signals using constrained tunable-Q wavelet transform. Expert Syst. Appl 2014, 41, 7161–7170. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj, H.; Selvi, S.T.; Selvathi, D.; Gewali, L. Brain MRI slices classification using least squares support vector machine. Int. J. Intell. Comput. Med. Sci. Image Process 2007, 1, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, P.; Li, Y.; Polkowski, L.; Yao, Y.; Tsumoto, S.; Wang, G. Classification of EEG signals using sampling techniques and least square support vector machines. In Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference, Gold Coast, Australia, 14–16 July 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; 5589, pp. 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Siuly; Li, Y.; Wen, P. Clustering technique-based least square support vector machine for EEG signal classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed 2011, 104, 358–372. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).