Research on the Dynamics of Phytoplankton in Eutrophic Water
A special issue of Water (ISSN 2073-4441). This special issue belongs to the section "Biodiversity and Functionality of Aquatic Ecosystems".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (10 August 2025) | Viewed by 2613
Special Issue Editors
Interests: diatom; river; community assembly; dispersal; environmental filters
Interests: phytoplankton ecology; marine ecology; harmful algal bloom; eutrophication; transcriptomics; biodiversity; phylogeography; transcriptional regulation; CRISPR-Cas9riptional regulation; CRISPR-Cas9
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: cyanobacteria; genomic evolution; biodiversity; ecosystem functioning
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
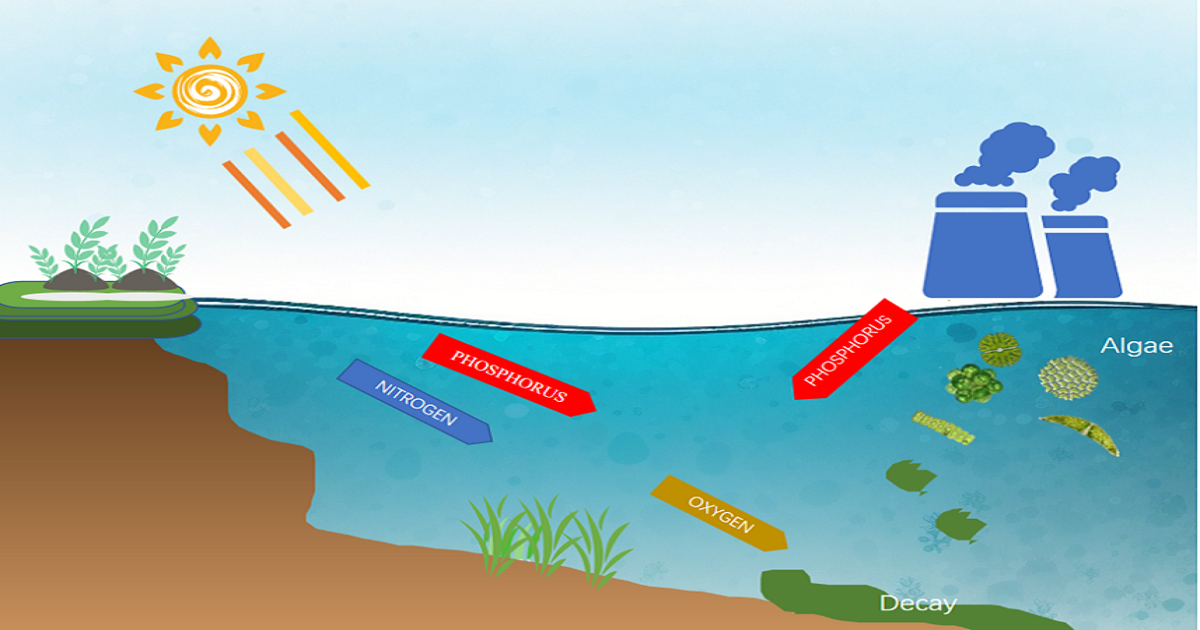
This Special Issue focuses on advancing our understanding of the dynamics of phytoplankton in eutrophic water systems. Eutrophication, driven by excessive nutrient inputs, has become a pressing global environmental issue, resulting in harmful algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and biodiversity loss. Phytoplankton, as primary producers and key indicators of water quality, play a pivotal role in the ecological processes of eutrophic environments.
This Special Issue invites contributions exploring the drivers, mechanisms, and impacts of phytoplankton dynamics in eutrophic waters. Topics of interest include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Factors influencing phytoplankton growth and community composition (e.g., nutrients, light, temperature, and hydrodynamics).
- Modeling and predicting phytoplankton blooms.
- Interactions between phytoplankton and other aquatic organisms in eutrophic systems.
- The effects of eutrophication on ecosystem functions and services.
- Innovative monitoring and mitigation strategies for controlling phytoplankton blooms.
We welcome original research articles, reviews, and case studies addressing these critical challenges. This Special Issue aims to provide a platform for interdisciplinary research that advances the sustainable management and restoration of eutrophic water ecosystems.
Dr. Xinxin Lu
Dr. Lei Cui
Dr. Da Huo
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Water is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- eutrophic
- rivers
- lakes
- phytoplankton
- harmful algal bloom
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.







