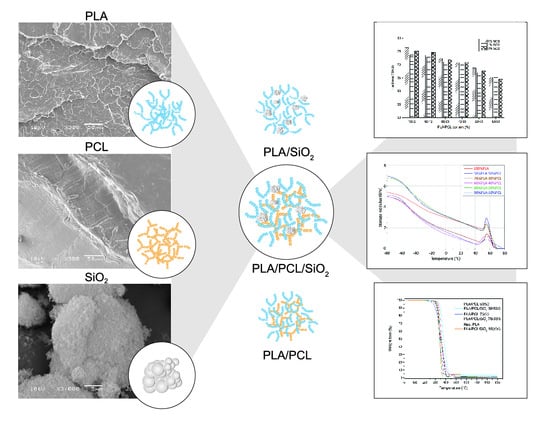
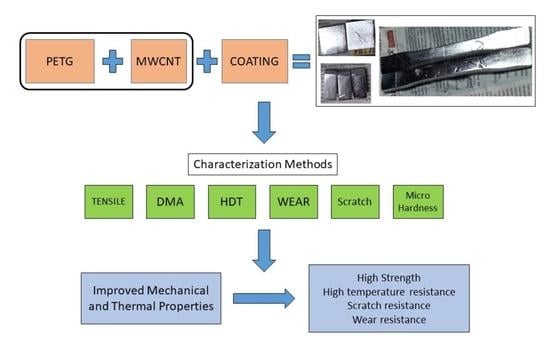
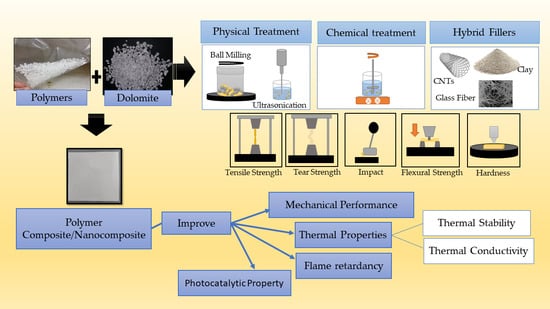
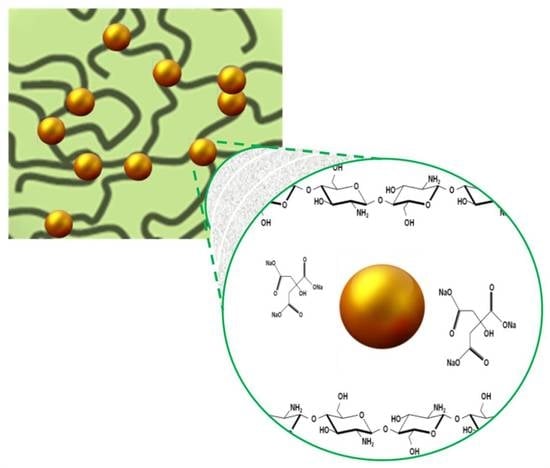
Progress in Polymer Composites and Nanocomposites
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Composites and Nanocomposites".
Submission Status: Closed (1 September 2025) | Viewed by 85949Editor
Interests: processing and characterization of composite materials and nanocomposites; evaluation of structure-properties relationships in composite materials; study of elastomer compounds
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Polymer composites with both discrete fillers or continuous fibres have long been shown to provide a set of properties that cannot be achieved by their constitutive components alone, while the advent of nanofillers with a large surface area provided new multifunctional properties to polymer nanocomposites. Such features have demonstrated the potential of these systems, consolidating their use in countless applications. Thus, the aim of this topical collection is to offer a focal point for the community with critical discussions of the past, present and future of these materials. We invite reviews in polymer composites and nanocomposites and encourage both young and established researchers to share their views on the subject. Be part of this seminal collection and submit your contribution before January 2022.
Topics include, but are not limited to:
- Fiber reinforced polymers;
- Green polymer composites;
- Foam composites;
- Composites for biomedical applications;
- Additive manufacturing of polymer composites;
- Organic thermoelectric polymer composites;
- Graphene polymer composites;
- Sensor and energy harvesting;
- Liquid crystal polymer composites;
- Polymer composites membranes;
- Electrospinning nanofibers;
- Natural fiber composites;
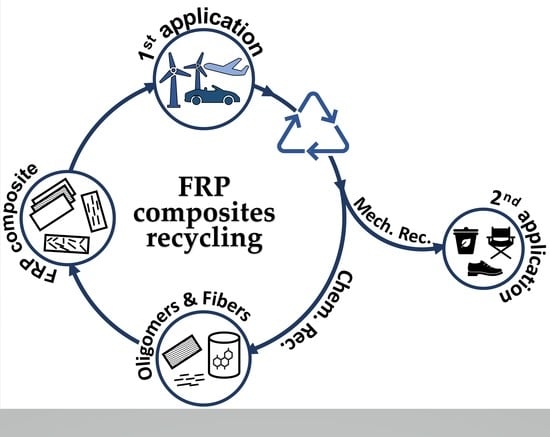
- Recycling of polymer composites;
- Electrical and magnetic properties;
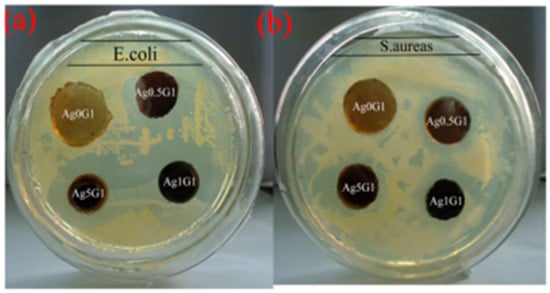
- Antibacterial activity of polymer composites;
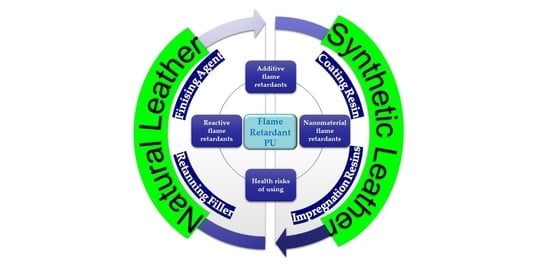
- Flame retardancy of polymer composite;
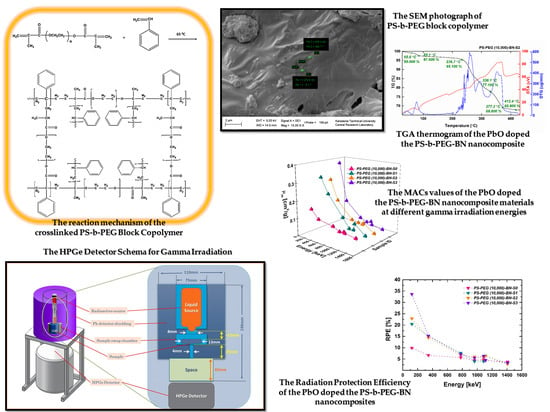
- Molecular dynamic in polymer composites;
- Mechanical properties of polymer composites;
- Modelling of fracture in polymer composites;
- Polymers for smart textile applications.
Prof. Dr. Miguel Ángel López Manchado
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.