- Article
Theorising an Integrative Framework for Education-Based Interventions as Part of a Whole University Approach to Wellbeing
- Michael Priestley,
- Laura Mazzoli-Smith and
- Sophie Ward
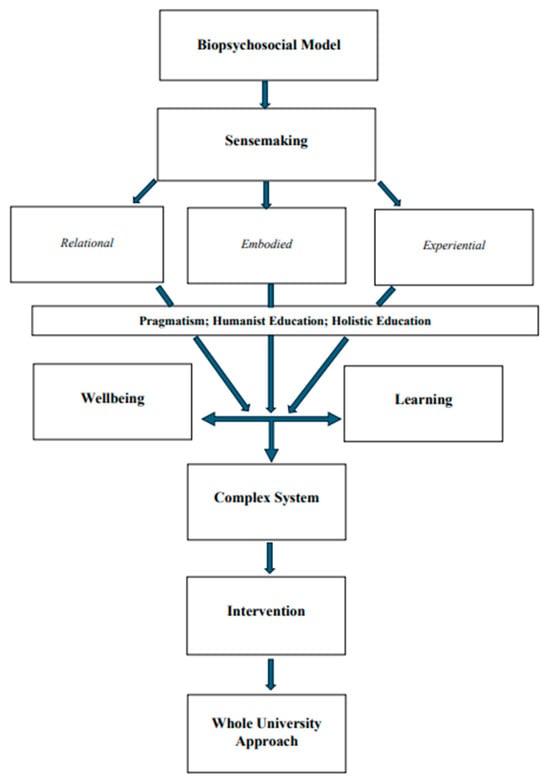
Global interest in student mental health has led to a proliferation of research and practice aimed at operationalising a whole university approach to wellbeing. In education, this has entailed innovation and evaluation of different assessment types and conditions; curricular content and skills interventions; and pedagogical practices. To date however, these studies typically utilise quasi-experimental designs to evaluate isolated, additive, individual-level interventions. The absence of rigorous theoretical framing to conceptualise and operationalise holistic wellbeing-promotive practices and cultures has compromised the translation of this research activity into positive outcomes for students and staff. In response, this paper aims to develop an integrative and enactive framework drawing on the embodied learner and pragmatist philosophy to address the following research question: what value does an integrative framework for conceptualising student wellbeing in education have for policy and practice within a whole university approach? Piloted with narrative data from a case study vignette using a focus group method with five students, the findings demonstrate how this integrative framework can help situate wellbeing-promoting interventions in the wider frame of educational cultures, contexts, and systems, whilst remaining aligned to educational goals and responsive to the diverse experience of multiple learners. The implications for a whole university approach are discussed.
19 December 2025