Epidemiology of Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens in Animals: A One Health Perspective
A special issue of Antibiotics (ISSN 2079-6382). This special issue belongs to the section "Antibiotics in Animal Health".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 31 January 2026 | Viewed by 154
Special Issue Editors
Interests: antimicrobial compounds; veterinary infectious diseases; zoonoses; molecular epidemiology of AMR
Interests: antimicrobial resistance; veterinary epidemiology; public health; surveillance systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: bacterial pathogenesis; mechanisms of antibiotic resistance; veterinary microbiology; diagnostics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
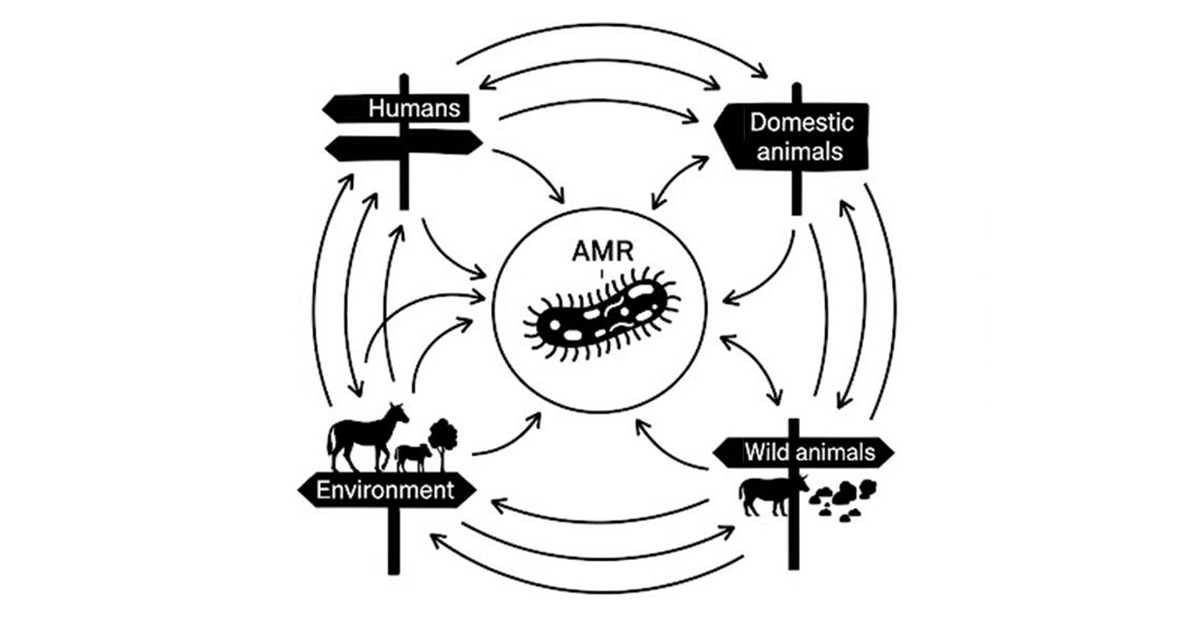
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global threat that profoundly impacts human, animal, and environmental health. The emergence, selection, and dissemination of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens within livestock, companion animals, and wildlife populations present critical challenges to veterinary medicine and public health. A comprehensive understanding of the complex epidemiology of AMR, including the genetic determinants of resistance and transmission dynamics across different ecosystems, is pivotal for the development and implementation of effective evidence-based strategies to combat this problem. The World Health Organization (WHO) have noted that AMR is associated with almost 2 million of deaths annually and poses a significant economic burden worldwide (WHO, 2024; Centre for Disease Control and prevention, 2024). Specifically, the use of antimicrobials in animal agriculture and veterinary practice is recognized as an area that could significantly increase the AMR burden.
This Special Issue, entitled "Epidemiology of Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens in Animals: A One Health Perspective," aims to publish high-impact research, novel approaches, and comprehensive reviews to further advance our understanding of AMR in various animal populations. Our broad scope encourages submissions that address the multifaceted nature of AMR from a One Health standpoint.
Key topics will include the following:
- Molecular epidemiology and evolution of resistance: genetic mechanisms involved in AMR in animal pathogens, including the characterization of novel resistance genes, mobile genetic elements easing horizontal gene transfer, and the evolutionary trajectories of resistant strains under selective pressure.
- Transmission dynamics and ecological drivers: Investigating the complex pathways through which resistant microorganisms and resistance determinants spread:
- Within and between different animal populations.
- Between animals and humans (zoonotic and reverse zoonotic transmission).
- Through environmental matrices.
- Surveillance, monitoring, and risk assessment: advancements in surveillance methodologies and risk assessment models that quantify the threat posed by AMR in animal populations to public health.
- Impact of Antimicrobial Use (AMU): Evaluating the quantitative and qualitative impact of antimicrobial consumption patterns in veterinary medicine on the selection, emergence, and persistence of AMR.
- Next-Generation Sequencing applied to AMR: use of novel NGS technologies to discover, diagnose, and investigate AMR patterns in clinical and environmental studies.
- One Health approaches to AMR: We will highlight studies that adopt an integrated One Health approach, using multidisciplinary collaboration to address AMR at the human–animal–environment interface.
By focusing on these critical areas, this collection aims to make a substantial contribution to the global understanding of AMR in animals, informing policy decisions and guiding future research directions to safeguard animal and public health.
We invite the submission of original research articles and systematic reviews, which will offer significant insights into the epidemiology of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens in animals.
Dr. Francesco Pellegrini
Dr. Paolo Capozza
Dr. Marialaura Corrente
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Antibiotics is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
- veterinary epidemiology
- one health
- zoonotic pathogens
- surveillance systems
- molecular epidemiology
- resistance mechanisms
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.







