Efficient Runtime Firmware Update Mechanism for LoRaWAN Class A Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Developed System
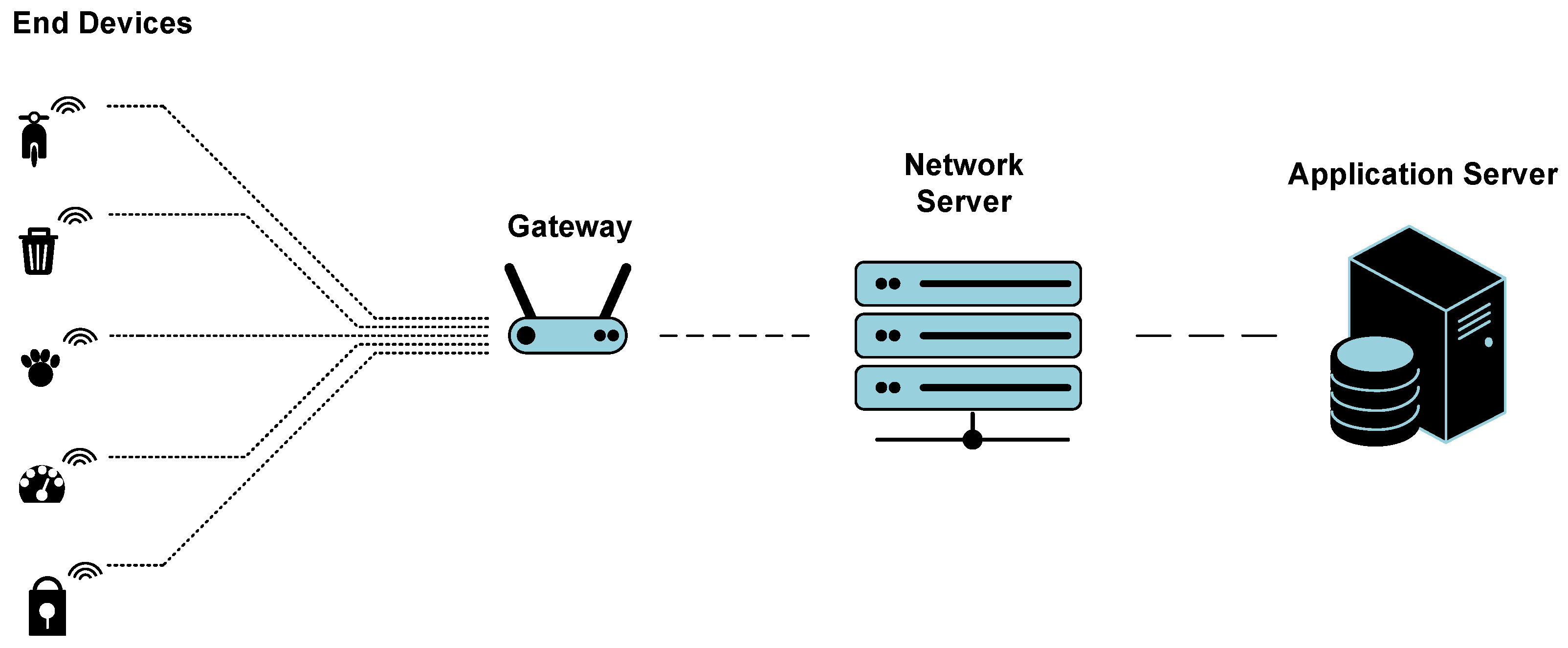
3.1. Background—LoRaWAN Network Specifications
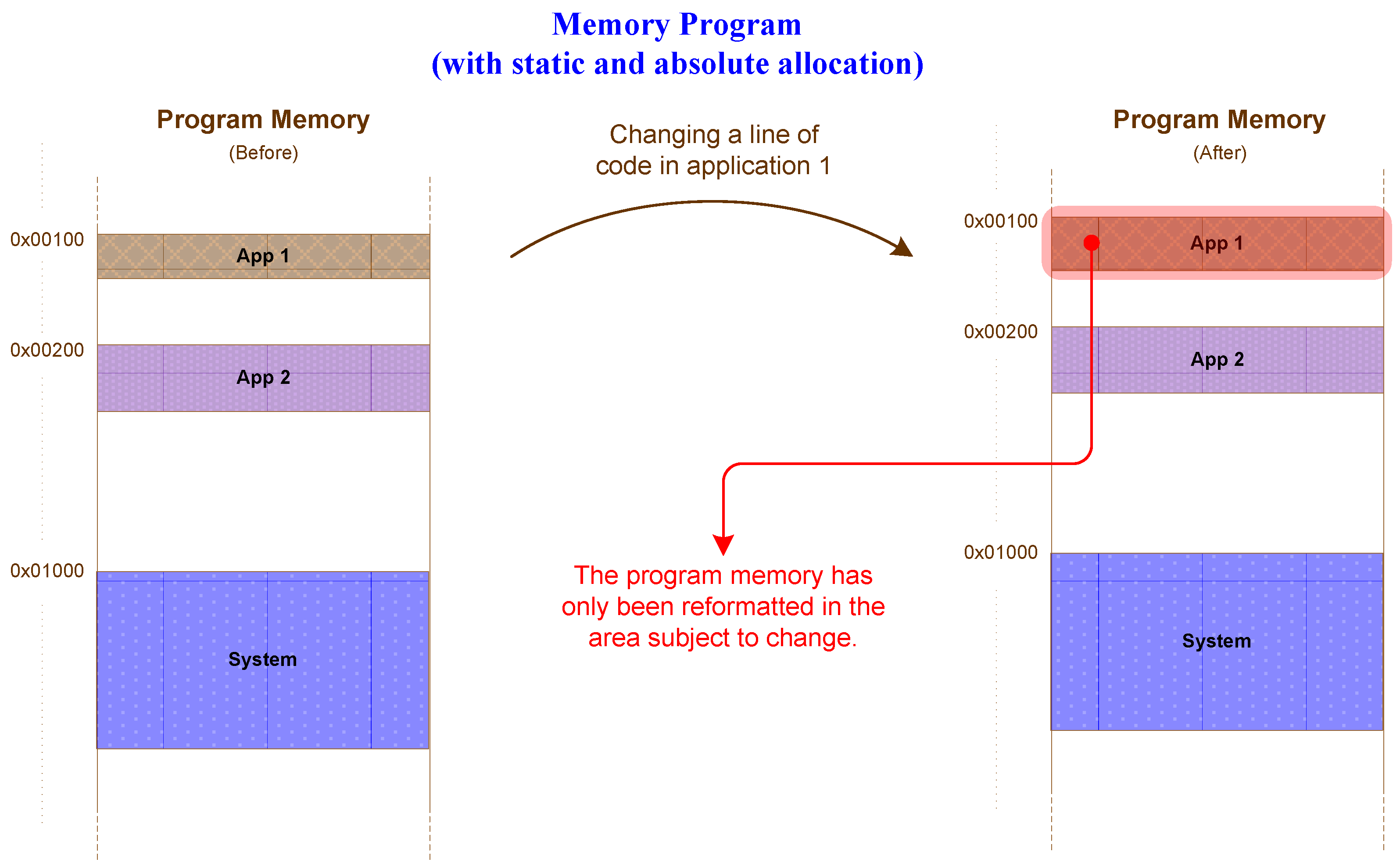
3.2. Background—Firmware Update During Runtime
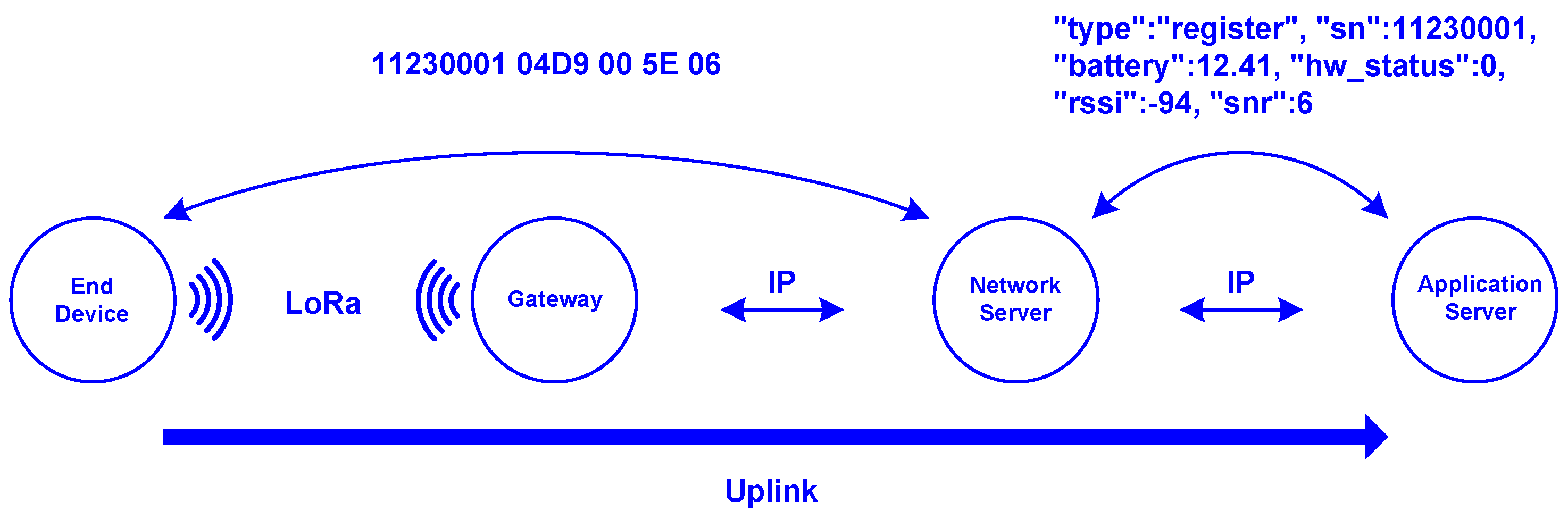
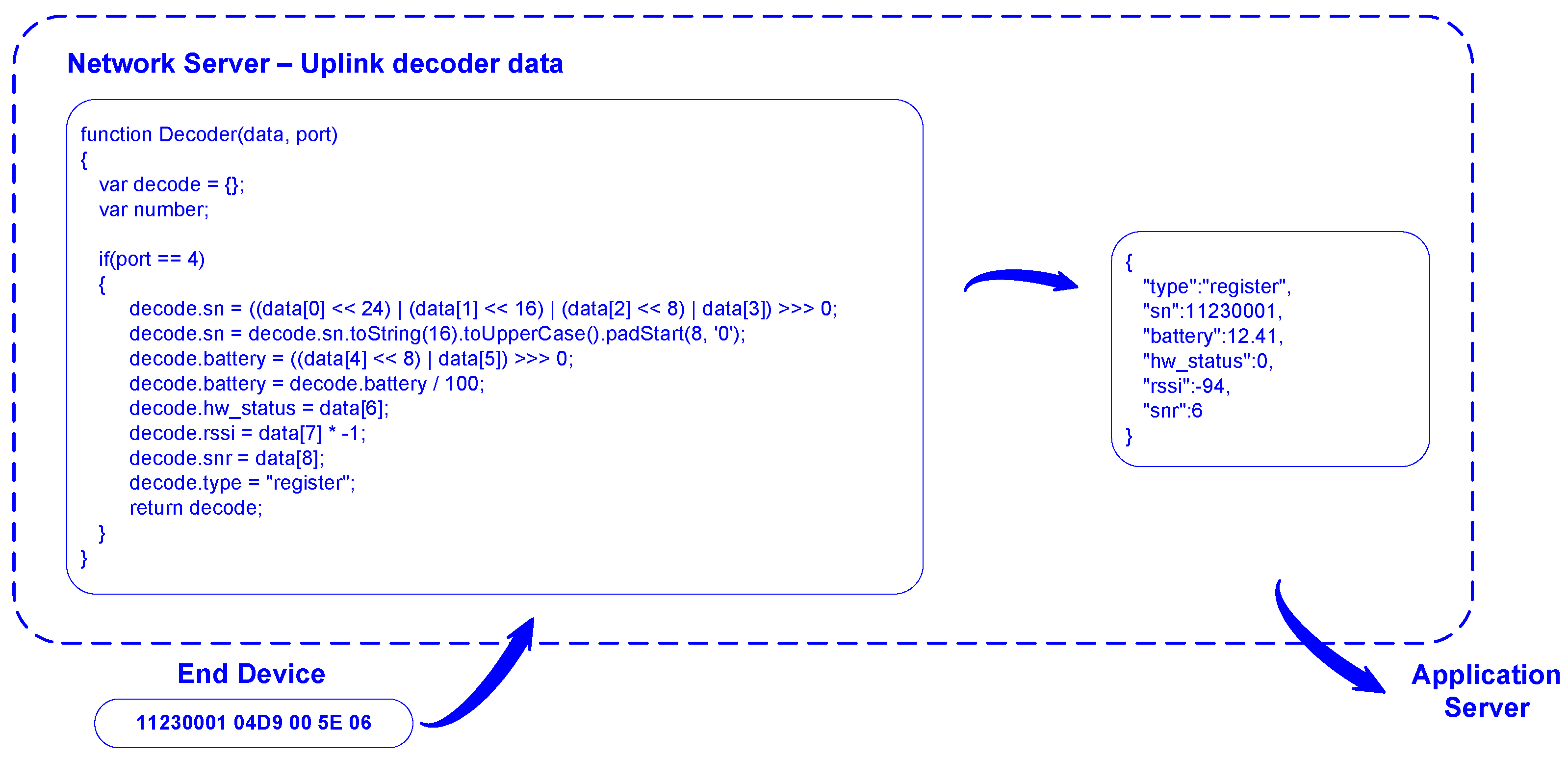
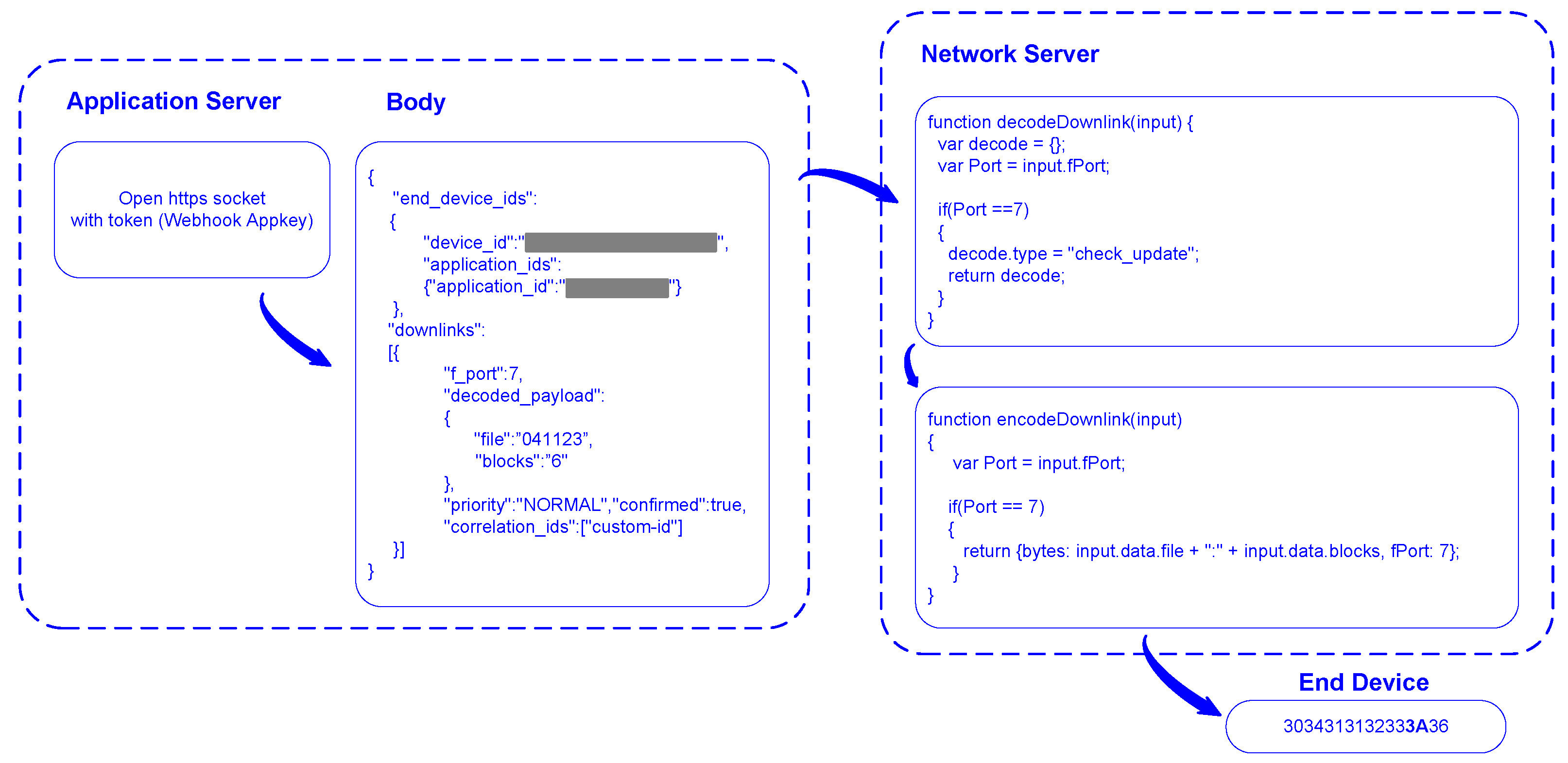
3.3. Uplink and Downlink Configuration
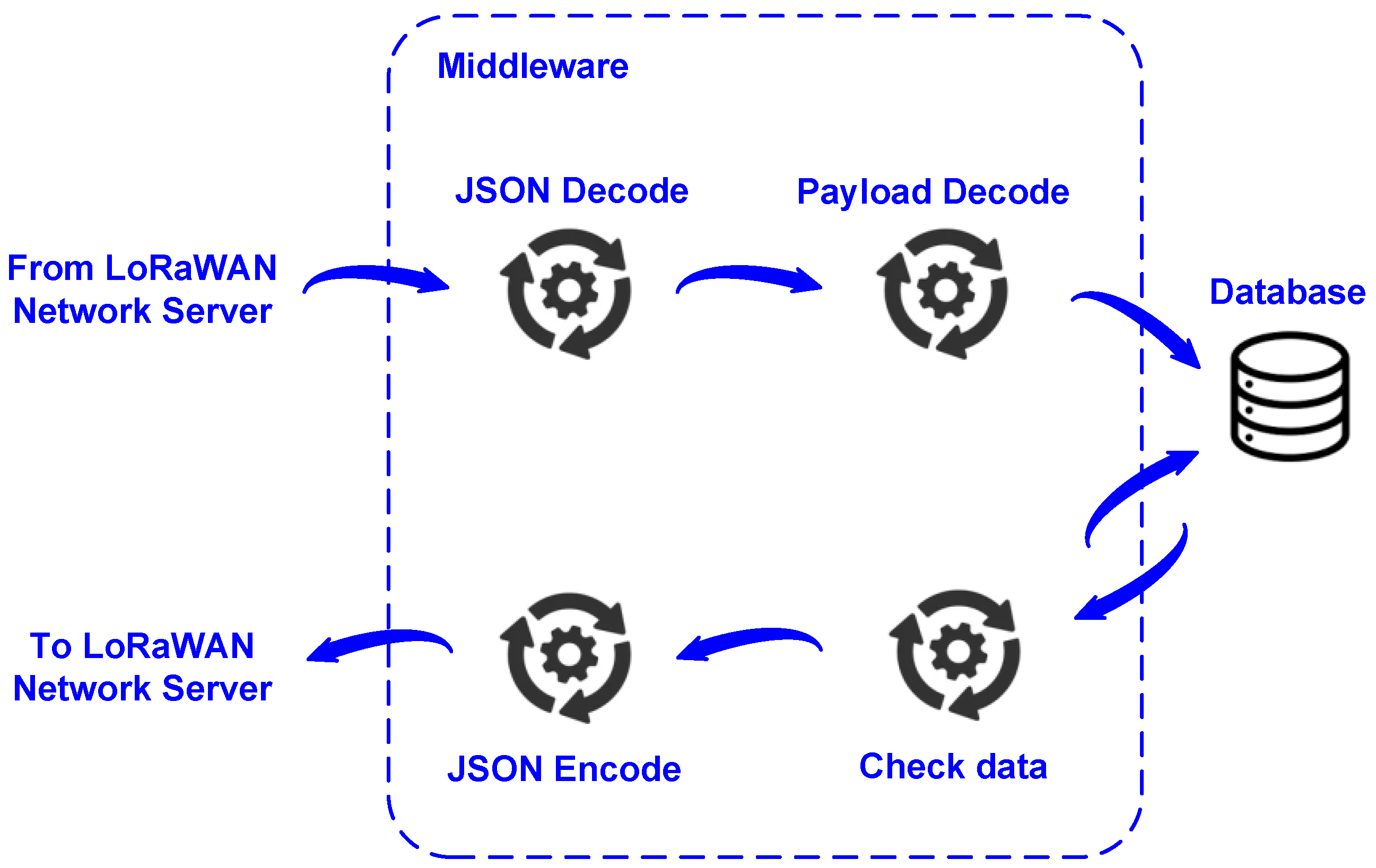
3.4. Application Server
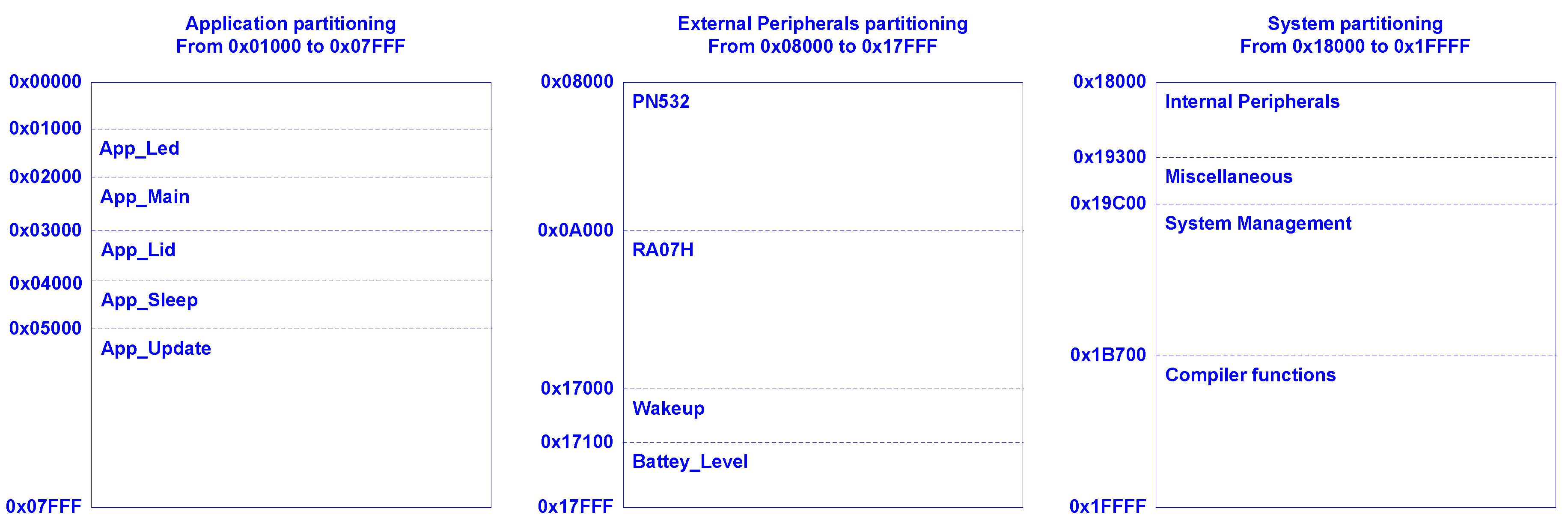
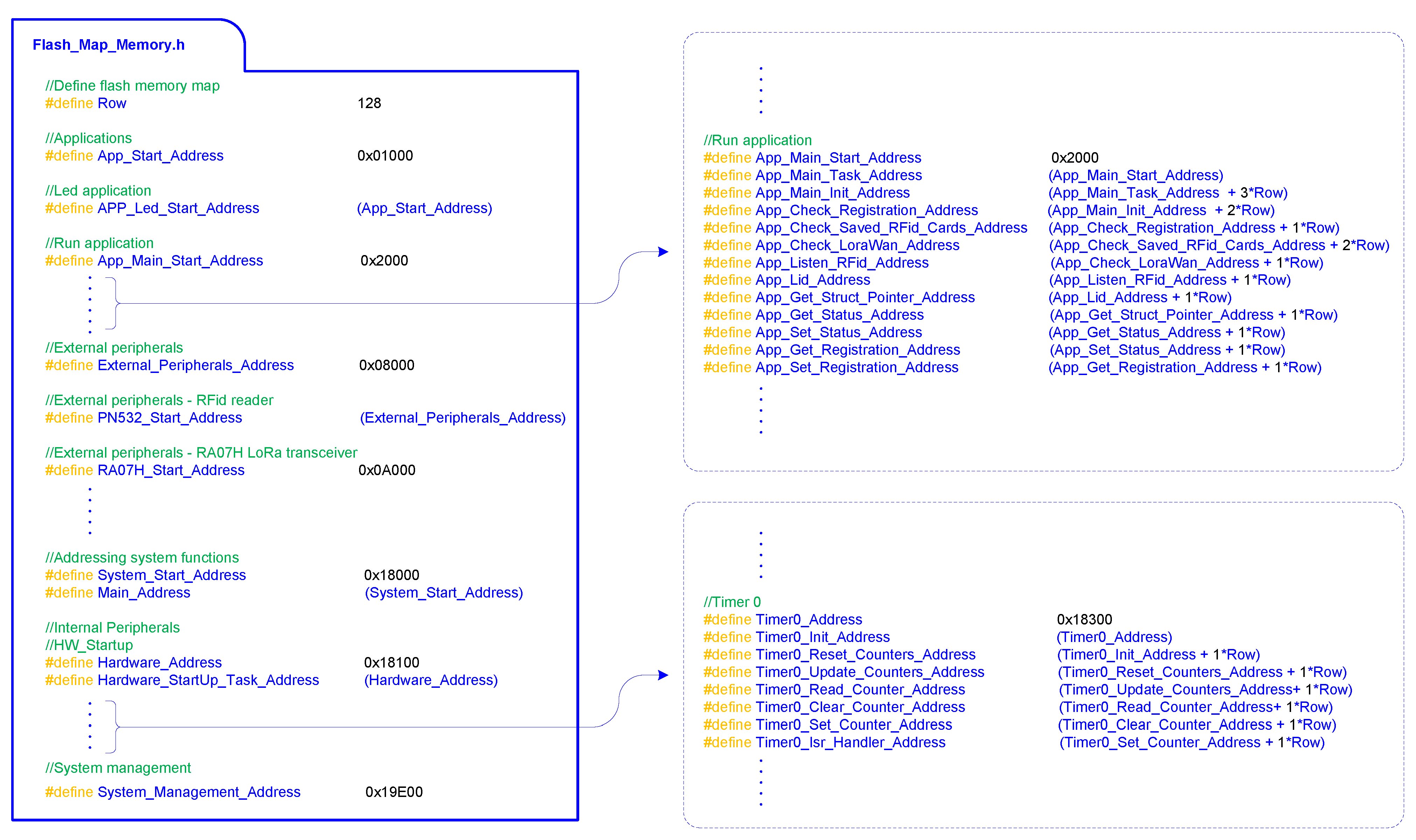
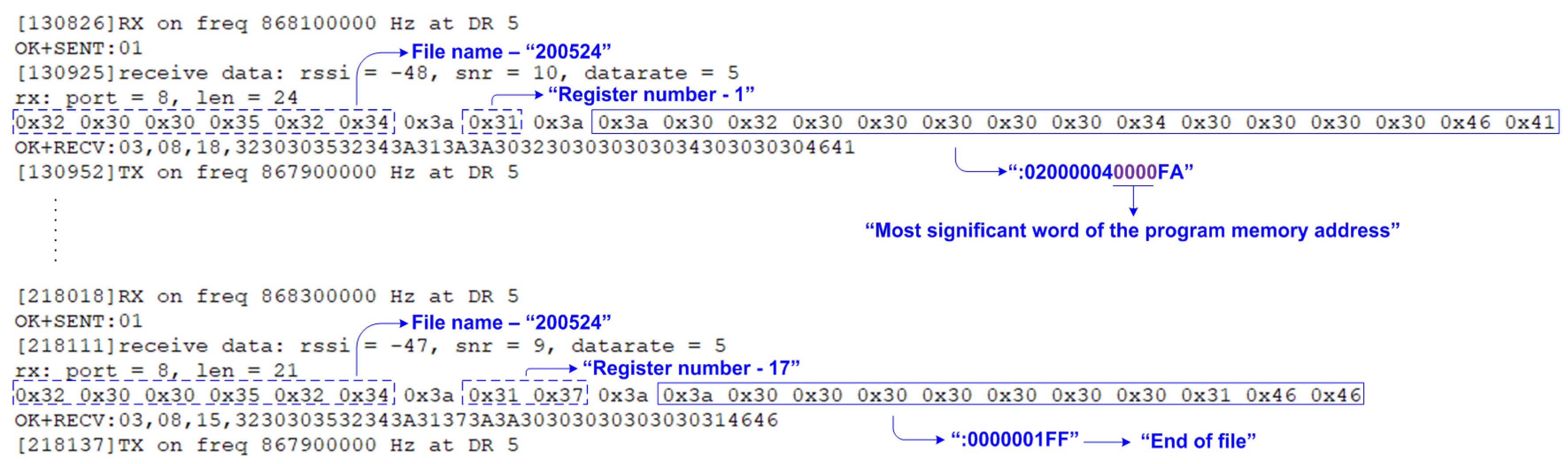
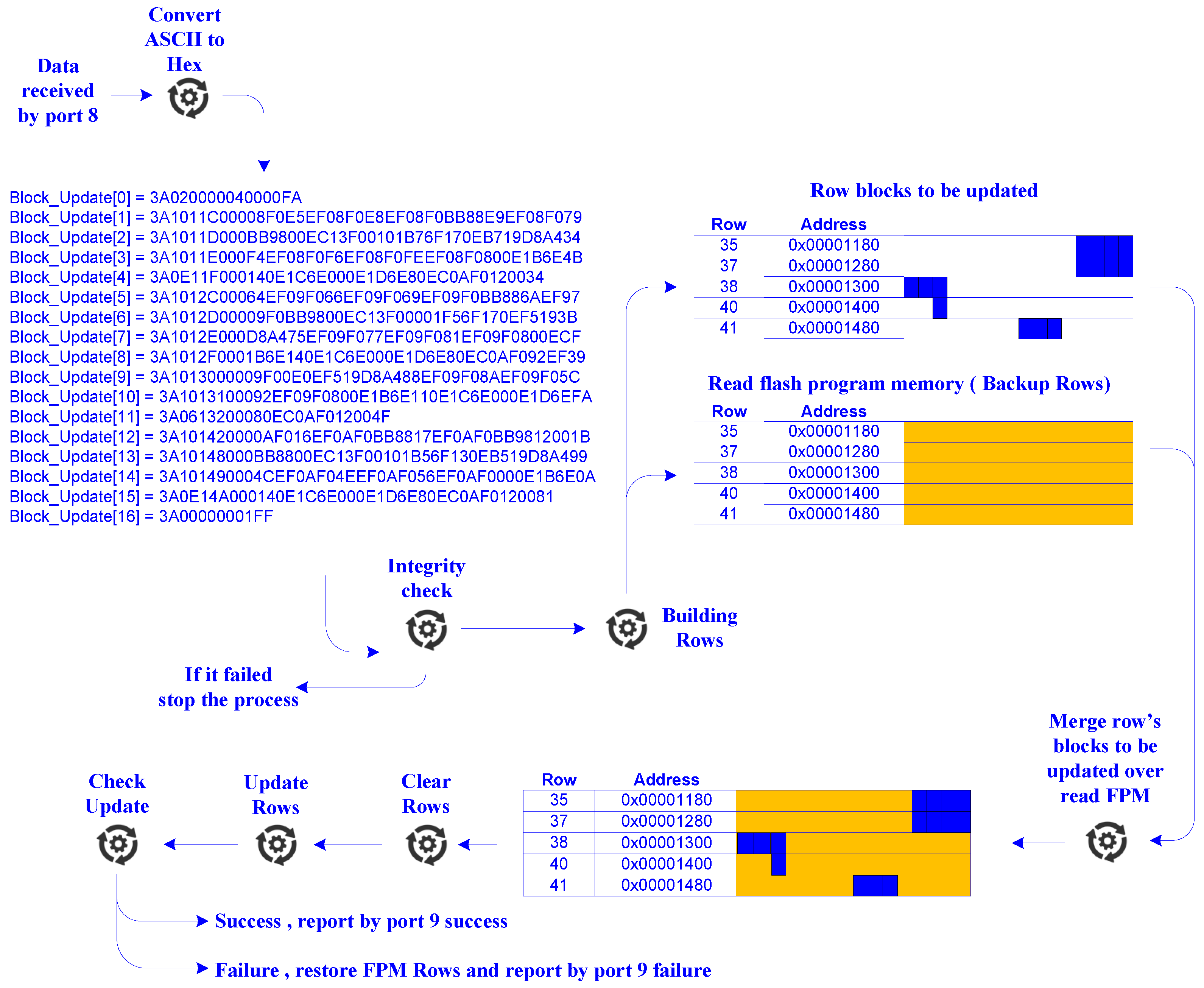
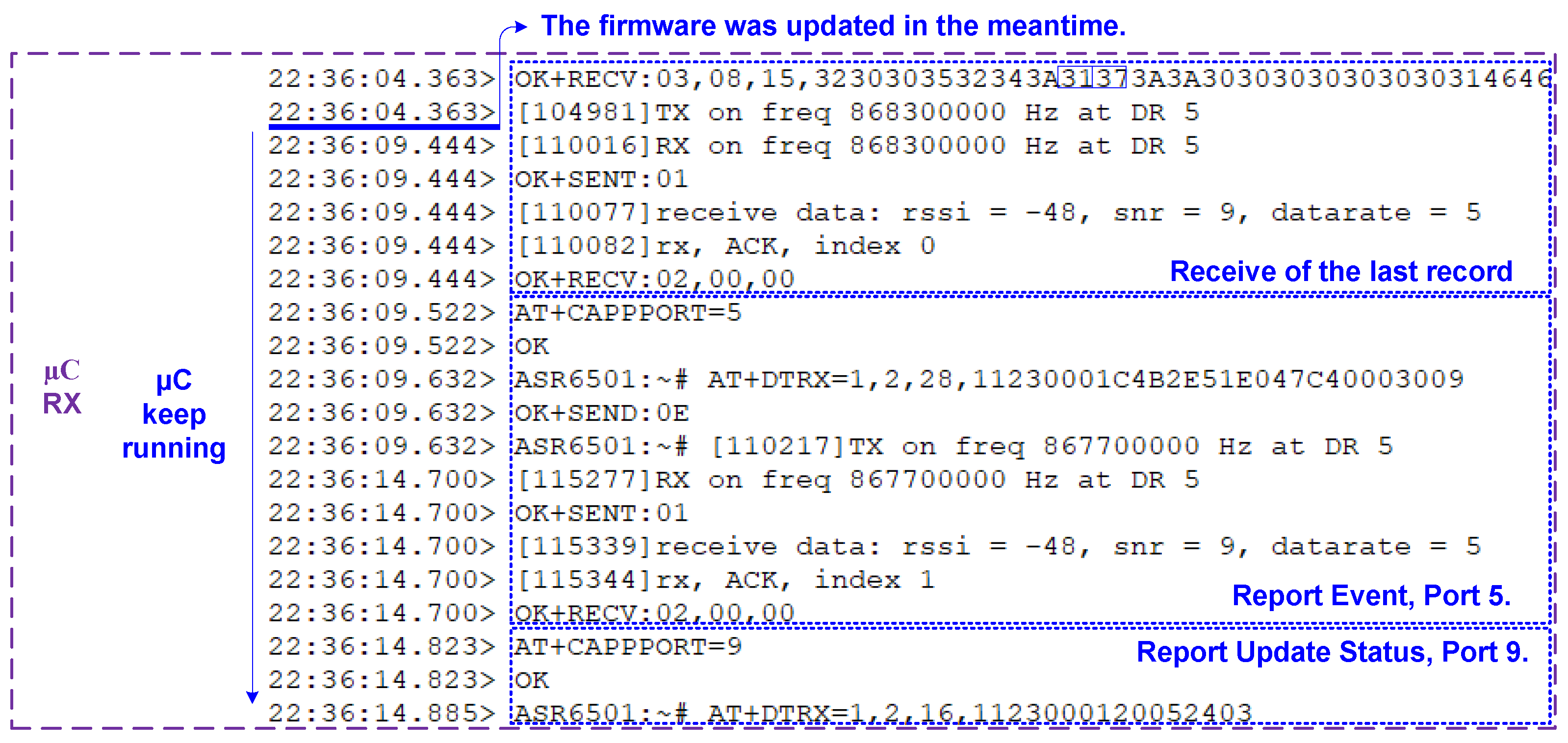
3.5. Implementation of the Proposed System
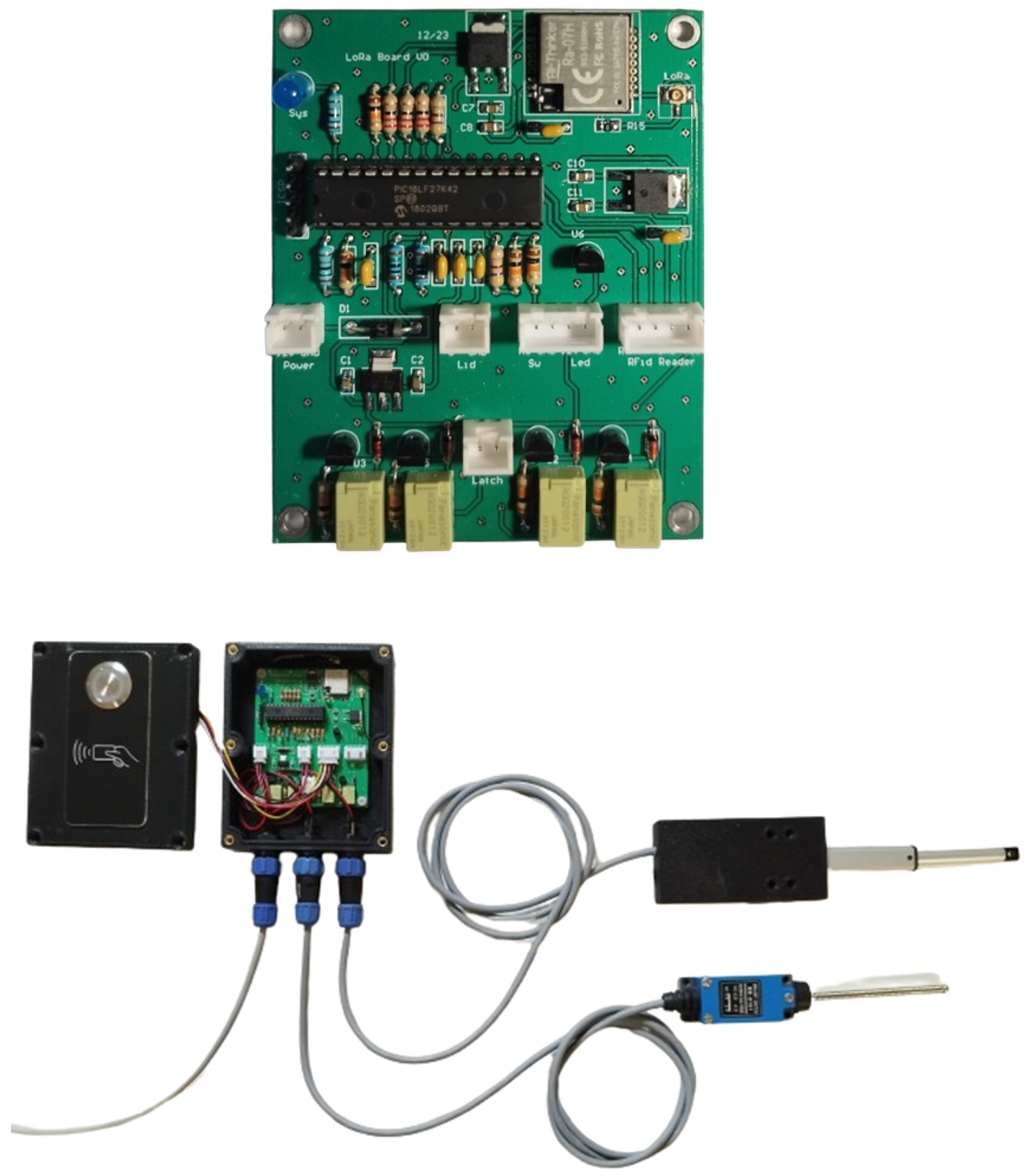
3.5.1. Hardware
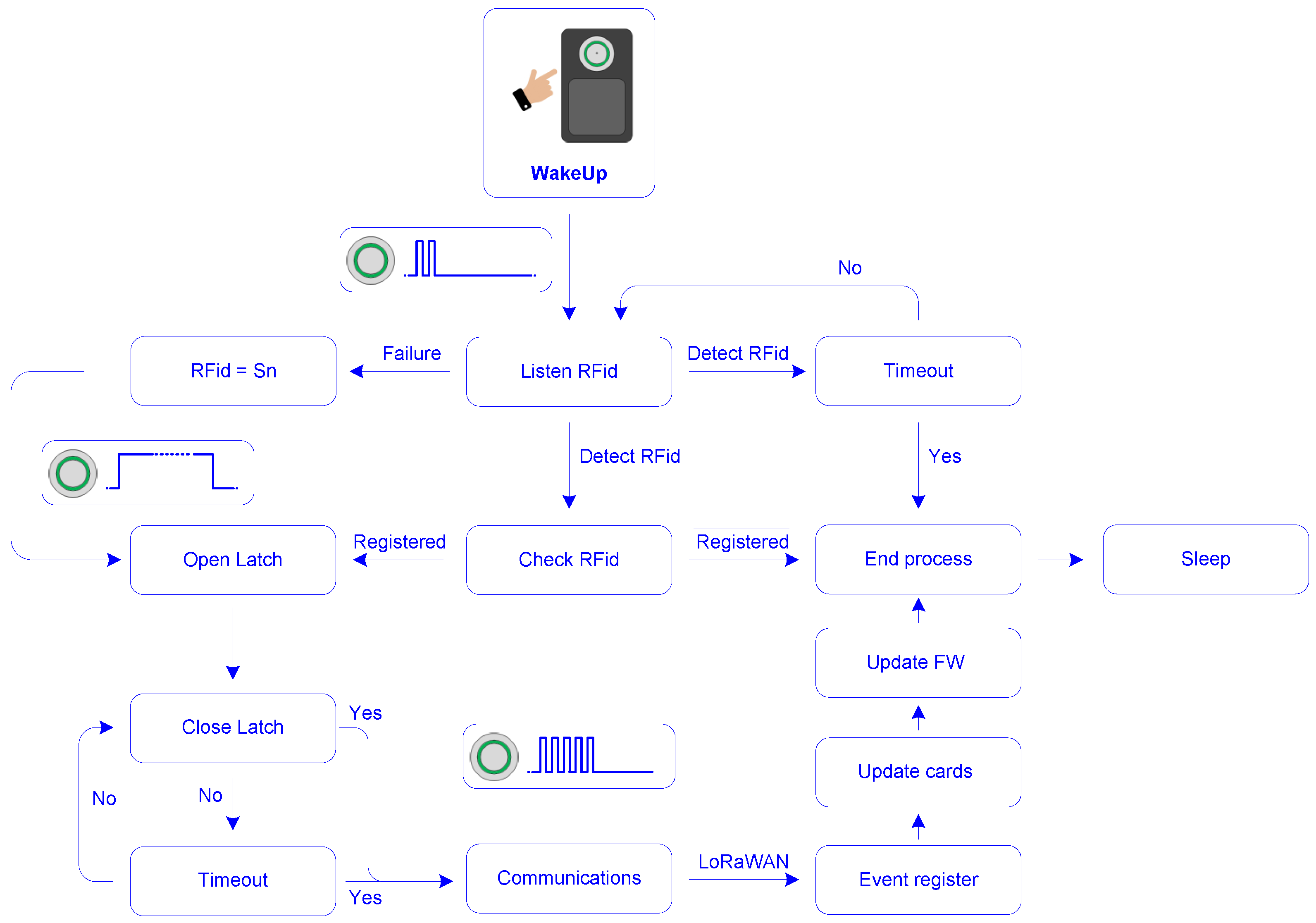
3.5.2. Firmware
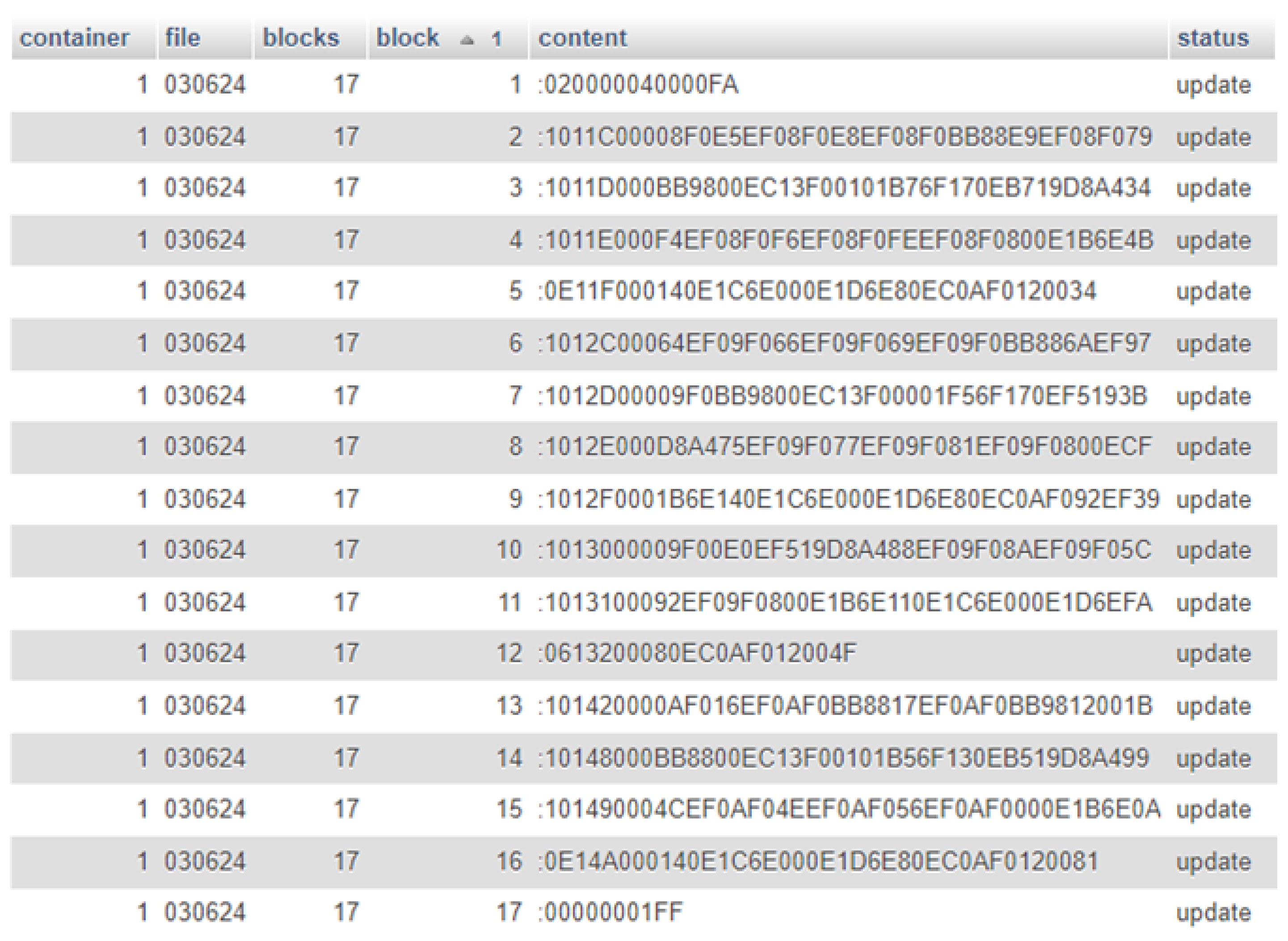
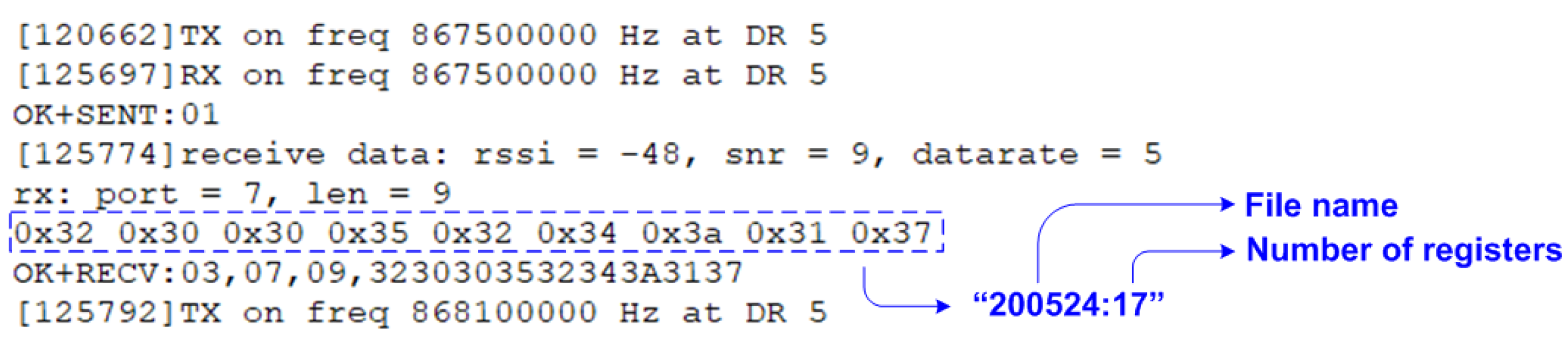
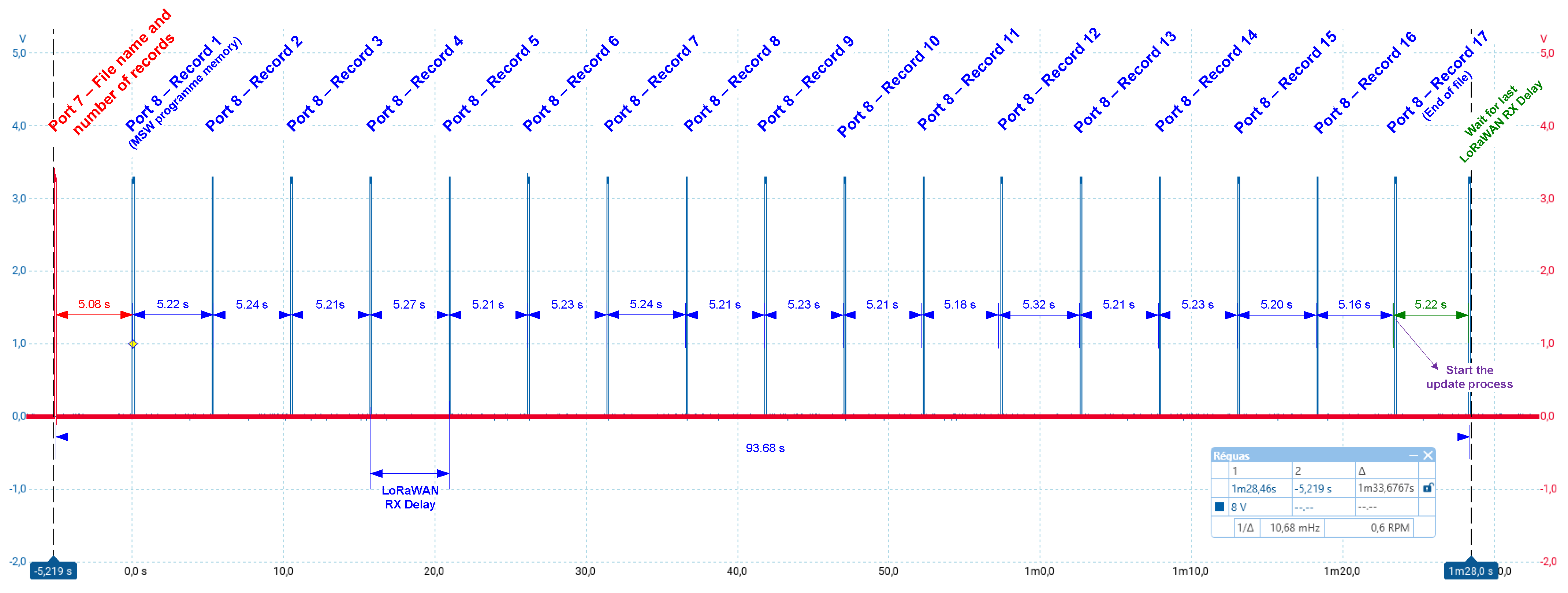
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jongboom, J.; Stokking, J. Enabling firmware updates over LPWANs. In Proceedings of the Embedded World Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 27 February–1 March 2018; Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=Enabling+firmware+updates+over+LPWANs&conference=Proceedings+of+the+Embedded+World+Conference&author=Jongboom,+J.&author=Stokking,+J.&publication_year=2018.
- Schäfer, B. LoRaWAN Firmware Update Over The Air—FUOTA. 2023. Available online: https://stackforce.com/en/about-us/news/LoRaWAN-firmware-update-over-the-air-fuota (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Abdelfadeel, K.; Farrell, T.; McDonald, D.; Pesch, D. How to Make Firmware Updates over LoRaWAN Possible. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 21st International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks” (WoWMoM), Cork, Ireland, 15–18 June 2020; pp. 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatis, I.; Stanoev, A.; Portelli, A.J.; Lockie, C.; Ammann, M.; Jin, Y.; Sooriyabandara, M. Reliable IOT firmware updates: A large-scale mesh network performance investigation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Austin, TX, USA, 10–13 April 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charilaou, C.; Lavdas, S.; Khalifeh, A.; Vassiliou, V.; Zinonos, Z. Firmware Update Using Multiple Gateways in LoRaWAN Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Lee, J.-H. Blockchain-based secure firmware update for embedded devices in an Internet of Things environment. J. Supercomput. 2016, 73, 1152–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AN5554—LoRaWAN® Firmware Update over the Air with STM32CubeWL. 2023. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/application_note/an5554-LoRaWAN-firmware-update-over-the-air-with-stm32cubewl-stmicroelectronics.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Zwart, D. Firmware Updates over the Air for Lora Using Random Linear Network Coding. TU Delft Repositories. 2022. Available online: https://repository.tudelft.nl/islandora/object/uuid%3A60364987-404e-490c-857f-e5958df2c325 (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Hess, T. Ultra-Low-Power Over-the-Air-Update in Secure LoRaWAN Networks. 2020. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2078.1/thesis:25146 (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Mahfoudhi, F.; Sultania, A.K.; Famaey, J. Over-the-Air Firmware Updates for Constrained NB-IoT Devices. Sensors 2022, 22, 7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeger, D.; Garigane, M.; Tsiropoulou, E.E.; Plusquellic, J. Secure LoRa Firmware Update with Adaptive Data Rate Techniques. Sensors 2021, 21, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokking, J. Firmware Updates over Low-Power Wide Area Networks. The Things Network. 2017. Available online: https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/article/firmware-updates-over-low-power-wide-area-networks (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Catalano, J. LoRaWAN Firmware Update Over-The-Air (FUOTA). J. ICT Stand. 2021, 9, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoRa-Alliance. RP002-1.0.4 Regional Parameters. 2022. Available online: https://resources.lora-alliance.org/technical-specifications/rp002-1-0-4-regional-parameters (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- The Things Network. The Things Network. Available online: https://www.thethingsindustries.com/docs/integrations/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- ETSI EN 300 220-2 V3.2.1; Short Range Devices (SRD) Operating in the Frequency Range 25 MHz to 1000 MHz; Part 2: Harmonised Standard for Access to Radio Spectrum for Non Specific Radio Equipment. ETSI: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2018. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_en/300200_300299/30022002/03.02.01_60/en_30022002v030201p.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Neves, B.P.; Santos, V.D.N.; Valente, A. Innovative Firmware Update Method to Microcontrollers during Runtime. Electronics 2024, 13, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microchip Technology Inc. Low-Power High-Performance Microcontrollers with XLP Technology. PIC18(L)F26/27/45/46/47/55/ 56/57K42, Datasheet. 2021. Available online: https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/aemDocuments/documents/MCU08/ProductDocuments/DataSheets/PIC18%28L%29F26-27-45-46-47-55-56-57K42-Data-Sheet-40001919G.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- RA-07H Datasheet. 2019. Available online: https://docs.ai-thinker.com/_media/lora/ra-07h_data_sheet_en.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- ASR650X at Command Introduction. 2024. Available online: https://www.hoperf.com/uploads/ASR650XATCommandIntroduction-20190605_1695629825.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Lora Alliance. Lora Alliance Enhances LoRaWAN Protocol with New Specifications to Support Firmware Updates over the Air. LoRa Alliance®. 2018. Available online: https://lora-alliance.org/lora-alliance-press-release/lora-alliance-enhances-LoRaWAN-protocol-with-new-specifications-to-support-firmware-updates-over-the-air/ (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Guinee, C. Efficient Firmware Update Transmission for LoRa Low Power Wide Area Technology. 2019. Available online: https://publications.scss.tcd.ie/theses/diss/2019/TCD-SCSS-DISSERTATION-2019-013.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Jaouhari, S.E.; Bouvet, E. Toward a generic and secure bootloader for IoT device Firmware Ota Update. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Jeju-si, Republic of Korea, 12–15 January 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| SF | ToA [ms] | Data Rate [bps] | Sensitivity [dBm] | Energy [J] | Max Payload [bytes] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 2430 | 244.14 | −136.5 | 1.389 | 51 |
| 11 | 1310 | 447.59 | −134.0 | 0.738 | 51 |
| 10 | 706 | 813.80 | −131.5 | 0.347 | 51 |
| 9 | 338 | 1464.80 | −129.0 | 0.184 | 115 |
| 8 | 214 | 2604.10 | −126.5 | 0.103 | 212 |
| 7 | 119 | 4557.20 | −124.0 | 0.057 | 212 |
| Port | Data Type |
|---|---|
| 4 | Device registration |
| 5 | Event signaling |
| 6 | Insertion or removal of RFID cards |
| 7 | Firmware update check |
| 8 | Firmware file request |
| 9 | Update status signaling |
| Parameter | Update #1 | Update #2 | Update #3 | Update #4 | Update #5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Hex File records | 6 | 6 | 17 | 57 | 10 |
| Updated rows in the uC flash | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 |
| Intel Hex File size (bytes) | 194 | 198 | 643 | 2373 | 372 |
| Updated bytes in the uC flash | 63 | 64 | 226 | 876 | 128 |
| Average transmission time of the update file using TTN (s) | 37.60 | 37.00 | 96.40 | 317.20 | 65.00 |
| Average transmission time between records (s) | 5.37 | 5.28 | 5.35 | 5.46 | 5.91 |
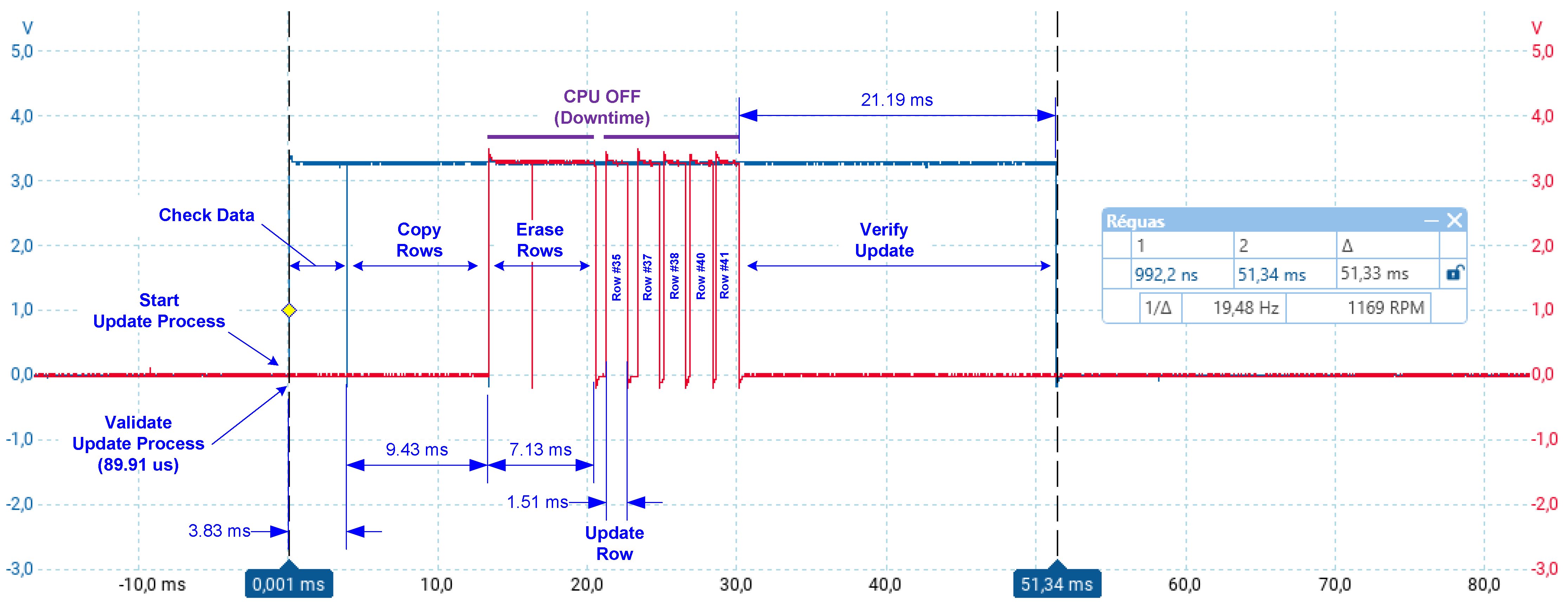
| Overall update process (ms) | 24.12 | 37.4 | 51.33 | 68.12 | 72.75 |
| Check data integrity task (ms) | 1.81 | 1.23 | 3.83 | 14.19 | 2.21 |
| Copy rows task (ms) | 1.75 | 6.71 | 9.43 | 5.91 | 18.45 |
| Erase rows task (ms) | 1.55 | 4.36 | 7.13 | 10.01 | 11.34 |
| Update row task (ms) | 1.37 | 5.61 | 9.75 | 14.91 | 16.77 |
| Verify update task (ms) | 17.64 | 19.49 | 21.19 | 23.10 | 23.98 |
| Downtime (ms) | 2.92 | 9.97 | 16.88 | 24.92 | 28.11 |
| Method | Dirk Pesch et al. [3] | Charilao et al. [5] | Hess, Tim [9] | Heeger, D. [11] | Proposed System |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmission topology | Multicast | Multicast | Multicast | N. A. | Peer to Peer |
| End device class | C | C | C | N. A. | A |
| Memory update type | Full image | Full image | Deltas | Full image | Segments |
| Firmware Update Size (kB) | 100 | 100 | 15.8 | 128 | 0.641 |
| Update firmware image ratio [%] | 100.00 | 100.00 | 11.68 | 100.00 | 0.60 |
| Transmission data records time (min) | 32[DR5] | 1140[DR5] | 5[DR5] | 16[DR6] | 1.61[DR5] |
| Update type | Bootloader | Bootloader | Bootloader | Dual Boot | Self-Programming |
| Downtime (s) | N. A. | N. A. | 42.48 | N. A. | 0.017 |
| Energy consumption (J) | 80.00 | N. A. | 10.68 | 200.00 | 8.04 |
| Efficiency [%] | 45.00 | 100.00 | N. A. | N. A. | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neves, B.P.; Valente, A.; Santos, V.D.N. Efficient Runtime Firmware Update Mechanism for LoRaWAN Class A Devices. Eng 2024, 5, 2610-2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040137
Neves BP, Valente A, Santos VDN. Efficient Runtime Firmware Update Mechanism for LoRaWAN Class A Devices. Eng. 2024; 5(4):2610-2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040137
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeves, Bernardino Pinto, António Valente, and Victor D. N. Santos. 2024. "Efficient Runtime Firmware Update Mechanism for LoRaWAN Class A Devices" Eng 5, no. 4: 2610-2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040137
APA StyleNeves, B. P., Valente, A., & Santos, V. D. N. (2024). Efficient Runtime Firmware Update Mechanism for LoRaWAN Class A Devices. Eng, 5(4), 2610-2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040137









