Thromboembolism and Bleeding in COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Prevalence
2.1. Hospitalized Patients
2.2. Hospitalized Patients Admitted to the ICU
2.3. Hospitalized Patients Receiving ECLS
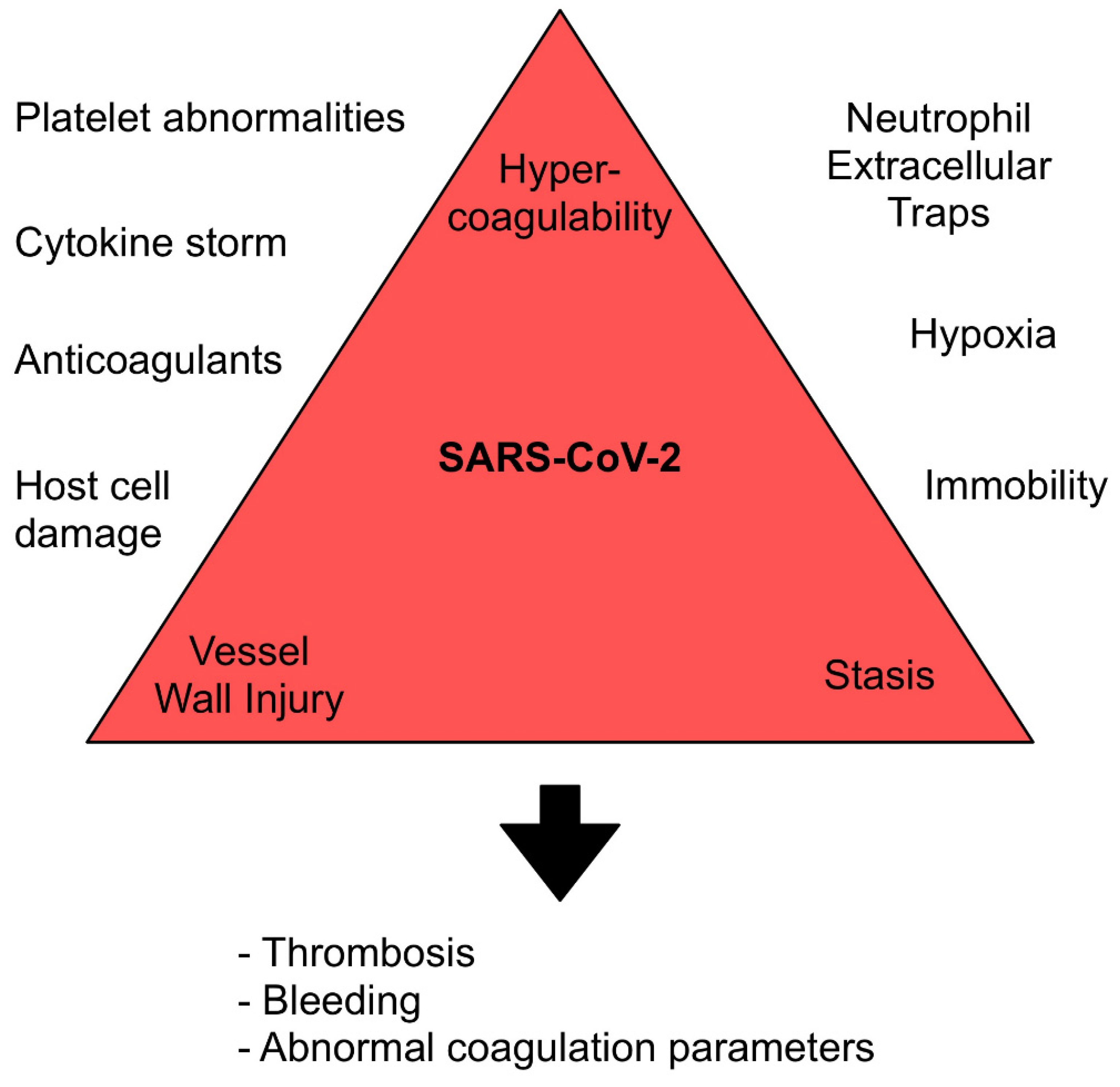
3. Mechanisms
3.1. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Receptor Binding
3.2. Regulated Cell Death
3.3. Cytokine Storm
3.4. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
3.5. Platelet Abnormalities
3.6. Hypoxia and Immobility
3.7. Anticoagulants
4. Screening
5. Laboratory Testing
6. Thromboprophylaxis
6.1. Indication
6.2. Type and Dosing
6.3. Extended Prophylaxis
6.4. Pregnancy
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, F.; Wu, K.L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.H.; Zhu, C.L. Prominent changes in blood coagulation of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, S.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2020, 18, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Paz, L.; Capodanno, D.; Montalescot, G.; Angiolillo, D.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019–Associated Thrombosis and Coagulopathy: Review of the Pathophysiological Characteristics and Implications for Antithrombotic Management. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malas, M.B.; Naazie, I.N.; Elsayed, N.; Mathlouthi, A.; Marmor, R.; Clary, B. Thromboembolism risk of COVID-19 is high and associated with a higher risk of mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 29, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thachil, J.; Tang, N.; Gando, S.; Falanga, A.; Cattaneo, M.; Levi, M.; Clark, C.; Iba, T. ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Bai, H.; Chen, X.; Gong, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsu, S.; Gunay, E.; Konstantinides, S.V. A review of venous thromboembolism in COVID-19: A clinical perspective. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 15, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talasaz, A.H.; Sadeghipour, P.; Kakavand, H.; Aghakouchakzadeh, M.; Kordzadeh-Kermani, E.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Gheymati, A.; Ariannejad, H.; Hosseini, S.H.; Jamalkhani, S.; et al. Recent Randomized Trials of Antithrombotic Therapy for Patients with COVID-19: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1903–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, R.P.; MacLaren, G.; Boonstra, P.S.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Slutsky, A.S.; Fan, E.; Bartlett, R.H.; Tonna, J.E.; Hyslop, R.; Fanning, J.J.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support in COVID-19: An international cohort study of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization registry. Lancet 2020, 396, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, M.C.; Sy, E.; Lequier, L.; Fan, E.; Kanji, H.D. Anticoagulation Practices during Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Respiratory Failure. A Systematic Review. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granja, T.; Hohenstein, K.; Schüssel, P.; Fischer, C.; Prüfer, T.; Schibilsky, D.; Wendel, H.P.; Jaschonek, K.; Serna-Higuita, L.; Schlensak, C.; et al. Multi-Modal Characterization of the Coagulopathy Associated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e400–e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Mainbourg, S.; Friggeri, A.; Bertoletti, L.; Douplat, M.; Dargaud, Y.; Grange, C.; Lobbes, H.; Provencher, S.; Lega, J.-C. Arterial and venous thromboembolism in COVID-19: A study-level meta-analysis. Thorax 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, D.; García-Sanchez, A.; Rali, P.; Muriel, A.; Bikdeli, B.; Ruiz-Artacho, P.; Le Mao, R.; Rodríguez, C.; Hunt, B.J.; Monreal, M. Incidence of VTE and Bleeding Among Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chest 2021, 159, 1182–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, W.J.; Kanji, R.; Mirsadraee, S.; Gue, Y.X.; Price, S.; Prasad, S.; Gorog, D.A. Thrombotic complications in 2928 patients with COVID-19 treated in intensive care: A systematic review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonyawat, K.; Chantrathammachart, P.; Numthavaj, P.; Nanthatanti, N.; Phusanti, S.; Phuphuakrat, A.; Niparuck, P.; Angchaisuksiri, P. Incidence of thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb. J. 2020, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannoni, S.; de Groot, R.; Bell, S.; Markus, H.S. Stroke in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2021, 16, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, K.; Kersten, A.; Grottke, O.; Zayat, R.; Dreher, M.; Autschbach, R.; Marx, G.; Marx, N.; Spillner, J.; Kalverkamp, S. Thromboembolic and Bleeding Events in COVID-19 Patients receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raasveld, S.J.; Delnoij, T.S.R.; Broman, L.M.; Lansink-Hartgring, A.O.; Hermans, G.; De Troy, E.; Taccone, F.S.; Quintana Diaz, M.; van der Velde, F.; Miranda, D.D.R.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Patients With COVID-19: An International Multicenter Cohort Study. J. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 36, 8850666211007063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalager-Pedersen, M.; Lund, L.C.; Mariager, T.; Winther, R.; Hellfritzsch, M.; Larsen, T.B.; Thomsen, R.W.; Johansen, N.B.; Søgaard, O.S.; Nielsen, S.L.; et al. Venous thromboembolism and major bleeding in patients with COVID-19: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, ciab003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaatz, S.; Ahmad, D.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Schulman, S. Definition of clinically relevant non-major bleeding in studies of anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolic disease in non-surgical patients: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, C.; Mohammed, A.R.; Ravuri, S.; Luthra, V.; Rajagopal, N.; Karre, S. COVID-2019—A comprehensive pathology insight. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Peerschke, E.I. Complement and coagulation: Key triggers of COVID-19–induced multiorgan pathology. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5674–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avolio, E.; Madeddu, P. Discovering cardiac pericyte biology: From physiopathological mechanisms to potential therapeutic applications in ischemic heart disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 86, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, W.; Yang, X.; Yang, D.; Bao, J.; Li, R.; Xiao, Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; et al. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-Y.; Ma, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Xie, X. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, C.-M.; Ma, C.-W.; Chan, W.-Y.; Chan, H.Y.E. The SARS-Coronavirus Membrane protein induces apoptosis through modulating the Akt survival pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 459, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.-S.; Nabar, N.R.; Huang, N.-N.; Kehrl, J.H. SARS-Coronavirus Open Reading Frame-8b triggers intracellular stress pathways and activates NLRP3 inflammasomes. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, N.C.; Weitz, J.I. COVID-19 coagulopathy, thrombosis, and bleeding. Blood 2020, 136, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.-H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricchio, R.; Gallucci, M.; Dass, C.; Zhang, X.; Gallucci, S.; Fleece, D.; Bromberg, M.; Criner, G.J. Preliminary predictive criteria for COVID-19 cytokine storm. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzi, B.; Bencini, S.; Capone, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Maggi, L.; Salvati, L.; Vanni, A.; Orazzini, C.; Nozzoli, C.; Morettini, A.; et al. Quantitative and qualitative alterations of circulating myeloid cells and plasmacytoid DC in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Immunology 2020, 161, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.J.; Adrover, J.M.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Borczuk, A.; Cools-Lartigue, J.; Crawford, J.M.; Daßler-Plenker, J.; Guerci, P.; Huynh, C.; Knight, J.S.; et al. Targeting potential drivers of COVID-19: Neutrophil extracellular trapsNeutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Wagner, D.D. Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) Impact on Deep Vein Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1777–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolai, L.; Leunig, A.; Brambs, S.; Kaiser, R.; Weinberger, T.; Weigand, M.; Muenchhoff, M.; Hellmuth, J.C.; Ledderose, S.; Schulz, H.; et al. Immunothrombotic Dysregulation in COVID-19 Pneumonia Is Associated with Respiratory Failure and Coagulopathy. Circulation 2020, 142, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Zuo, M.; Yalavarthi, S.; Gockman, K.; Madison, J.A.; Shi, H.; Woodard, W.; Lezak, S.P.; Lugogo, N.L.; Knight, J.S.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps and thrombosis in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 51, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigada, M.; Bottino, N.; Tagliabue, P.; Grasselli, G.; Novembrino, C.; Chantarangkul, V.; Pesenti, A.; Peyvandi, F.; Tripodi, A. Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit: A report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsure, M.; Sarangi, B.; Shankar, G.H.; Reddy, V.S.; Walimbe, A.; Sharma, V.; Prayag, S. Mechanisms of Hypoxia in COVID-19 Patients: A Pathophysiologic Reflection. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Evans, C.E. The stimulation of thrombosis by hypoxia. Thromb. Res. 2019, 181, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatt, M.E.; Paltiel, O.; Bursztyn, M. Is prolonged immobilization a risk factor for symptomatic venous thromboembolism in elderly bedridden patients? Results of a historical-cohort study. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, P.; Hardouin, J.B.; Lejeune, S.; Jolliet, P.; Gillet, B.; Planchon, B. Immobilization and the risk of venous thromboembolism. A Meta-Anal. Epidemiol. Stud. Thromb. Res. 2009, 124, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapébie, F.-X.; Minville, V.; Ribes, A.; Combis, B.; Thery, A.; Geeraerts, T.; Silva, S.; Bura-Rivière, A.; Vardon-Bounes, F. Systematic Screening for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Critically Ill Inpatients With COVID-19: Impact on the Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 624808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Xiong, J. Risk factors for systemic and venous thromboembolism, mortality and bleeding risks in 1125 patients with COVID-19: Relationship with anticoagulation status. Aging 2021, 13, 9225–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demelo-Rodríguez, P.; Cervilla-Muñoz, E.; Ordieres-Ortega, L.; Parra-Virto, A.; Toledano-Macías, M.; Toledo-Samaniego, N.; García-García, A.; García-Fernández-Bravo, I.; Ji, Z.; de-Miguel-Diez, J.; et al. Incidence of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and elevated D-dimer levels. Thromb. Res. 2020, 192, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Cheng, L.; Yan, S.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Diagnostic Value of D-Dimer in COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 27, 10760296211010976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonla, C.; Sosothikul, D.; Chiasakul, T.; Rojnuckarin, P.; Uaprasert, N. Anticoagulation and In-Hospital Mortality from Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 27, 10760296211008999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.M.; Tan, J.A. Stratified meta-analysis of intermittent pneumatic compression of the lower limbs to prevent venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients. Circulation 2013, 128, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO). Guidelines for Adult Respiratory Failure. Version 1.4. 2017. Available online: https://www.elso.org/Portals/0/ELSO%20Guidelines%20For%20Adult%20Respiratory%20Failure%201_4.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Bikdeli, B.; Madhavan, M.V.; Gupta, A.; Jimenez, D.; Burton, J.R.; Der Nigoghossian, C.; Chuich, T.; Nouri, S.N.; Dreyfus, I.; Driggin, E.; et al. Pharmacological Agents Targeting Thromboinflammation in COVID-19: Review and Implications for Future Research. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1004–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, B.L.; Lawler, P.R.; Goligher, E.C.; Farkouh, M.E.; Bradbury, C.; Carrier, M.; Dzavik, V.; Fergusson, D.A.; Fowler, R.A.; Galanaud, J.P.; et al. Anti-Thrombotic Therapy to Ameliorate Complications of COVID-19 (ATTACC): Study design and methodology for an international, adaptive Bayesian randomized controlled trial. Clin. Trials 2020, 17, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Noncritically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Investigators, I. Effect of Intermediate-Dose vs Standard-Dose Prophylactic Anticoagulation on Thrombotic Events, Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Treatment, or Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: The INSPIRATION Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Zeng, Y.; Qu, H.-Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, N.; Huang, H.; Zheng, P.; Hu, H.; Zhou, L.; Duan, Z.; et al. Heparin-binding protein levels correlate with aggravation and multiorgan damage in severe COVID-19. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00741–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Lipardi, C.; Xu, J.; Peluso, C.; Spiro, T.E.; De Sanctis, Y.; Barnathan, E.S.; Raskob, G.E. Modified IMPROVE VTE Risk Score and Elevated D-Dimer Identify a High Venous Thromboembolism Risk in Acutely Ill Medical Population for Extended Thromboprophylaxis. TH Open 2020, 4, e59–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durak, K. Thromboembolism and Bleeding in COVID-19. J 2021, 4, 476-485. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030036
Durak K. Thromboembolism and Bleeding in COVID-19. J. 2021; 4(3):476-485. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurak, Koray. 2021. "Thromboembolism and Bleeding in COVID-19" J 4, no. 3: 476-485. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030036
APA StyleDurak, K. (2021). Thromboembolism and Bleeding in COVID-19. J, 4(3), 476-485. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030036





