The aim of this study was to establish the influence of ferns extracts (Asplenium scolopendrium and Dryopteris filix-mas) on spore germination and gametophyte development in two Dryopteris species.
The extracts were obtained from Asplenium scolopendrium (EA) and Dryopteris filix-mas (ED) leaves. Some variants contained, beside the extracts, Ag nanoparticles (EAN, EDN) [1,2]. Variants with alcohol were also tested (HA). For each variant, dilutions were made (1:10, 1:100).
The percentage of germinated spores decreased after extracts exposure (Figure 1 and Figure 2). In variants with AgNPs, no germination was observed regardless of extract, dilution or species. In the variants with alcohol, the germination of spores was significantly inhibited compared with the control (C, Figure 3) at the smallest dilution, in both species (Figure 4). The lack of the spore’s rhizoid affected the gametophyte development (Figure 5).
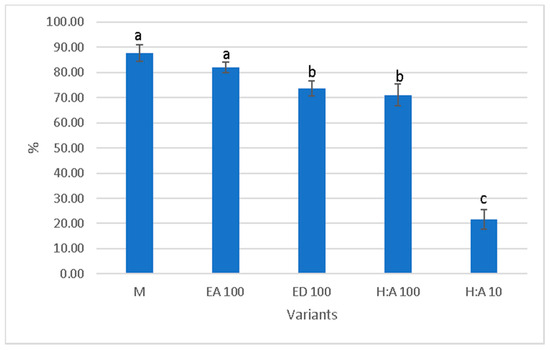
Figure 1.
The influence of extracts on spore germination in Dryopteris affinis.
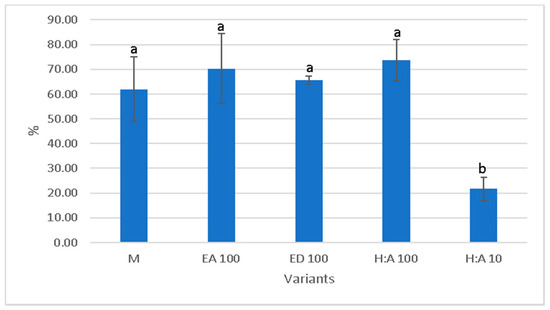
Figure 2.
The influence of extracts on spore germination in Dryopteris filix-mas.
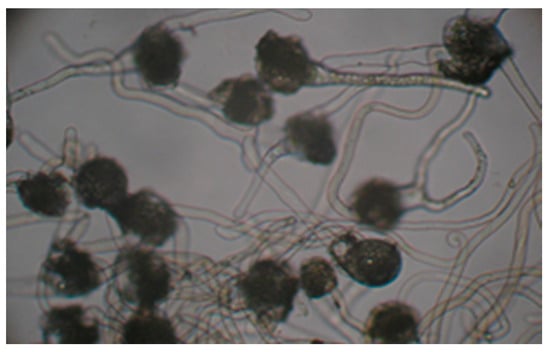
Figure 3.
Dryopteris affinis—germinated spores: Control, ×100.
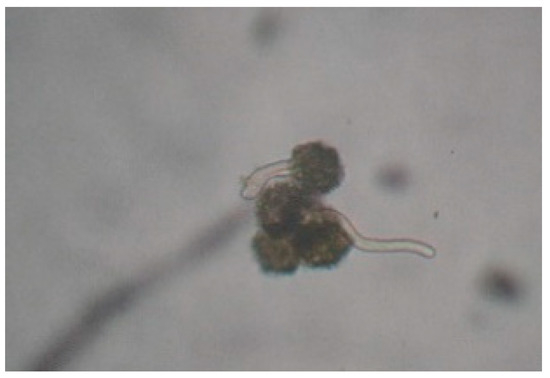
Figure 4.
Dryopteris filix-mas—germinated spores: HA 1:10 variant, ×100.
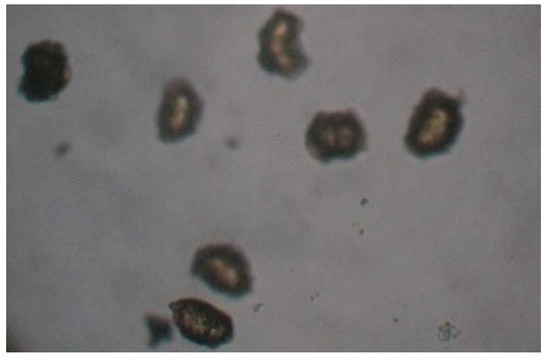
Figure 5.
Dryopteris affinis—ungerminated spores EAN variant (100), ×100.
Overall, the ferns extracts had a negative influence on ferns spores by reducing the germination percentage and by inhibiting gametophyte development in both species.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant of the Romanian Ministery of Research and Innovation, CCCDI-UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-P1-1.2-PCCDI-2017-0332/Project 3, contract 6PCCDI/2018, within PNCDI II.
References
- Șutan, A.N.; Fierăscu, I.; Fierăscu, R.C.; Manolescu, D.Ș.; Soare, L.C. Comparative analytical characterization and in vitro cytogenotoxic activity evaluation of Asplenium scolopendrium L. leaves and rhizome extracts prior to and after Ag nanoparticles phytosynthesis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, L.C.; Şuţan, N.A. Current Trends in Pteridophyte Extracts: From Plant to Nanoparticles. In Current Advances in Fern Research; Fernández, H., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).