Abstract
This study aims to investigate the performance of a two-stage anaerobic digestion system using a hybrid methane reactor to deal with biodegradable municipal solid waste. The reactor allowed both suspended sludge and granular sludge to work together. The feedstock was fermented in one continuous stirred tank at different pH conditions for 5 d. Furthermore, the liquid hydrolysate was diluted and pumped into a methane reactor with different organic loading rates. In the fermentative reactor, raising the pH condition from 4.5 to 6.5 caused a sharp increase in volatile fatty acids concentration, mainly due to the increase in acetate and propionate. The efficiency of the methane reactor was proven by the results of hydrodynamic analysis and biogas production. The relationship between biogas production and operating parameters in this reactor was modeled using a quadratic multivariate regression model. Overall, by maintaining the fermentative reactor at a pH of 6.0–6.5, the methane reactor was able to achieve an organic loading rate of 7.6 g-TS.L−1·d−1 with outstanding biogas quality and yield. In terms of microbiology, the most dominant phyla in the reactor included Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Euryarchaeota, Synergistetes, and Chloroflexi. Among them, the species with the highest relative abundance in granular sludge was Firmicutes, while that in suspended sludge was Bacteroidetes.
1. Introduction
The generation of biodegradable municipal solid waste (BMSW) and its satisfactory treatment have become great hardships that researchers around the world have to deal with. BMSW is considered to account for the largest percentage of municipal solid waste (44%), generates more than one billion tons of waste annually, and constantly increases each year [1]. Lack of control over this type of waste is the main reason that humans have to confront a series of ecological issues, including odor pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and the spreading of dangerous diseases [1,2]. To deal with the matters mentioned above, some different approaches, including incineration, composting, and anaerobic digestion (AD), have been applied [1]. However, among those methods, only the AD process can create a source of residual energy, and residual products from the AD process can be used as fertilizer or compost. Therefore, AD technology is gaining more and more attention from the research community and is gradually becoming a crucial part of a sustainable solid waste management system.
Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes, including hydrolysis/acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis [3,4]. Many reports have shown that separating hydrolysis and methanogenesis in two distinct reactors (two-stage anaerobic digestion-TAD) would bring benefits to its performance and flexibility to the operation [3,5,6]. Recently, the application of TAD at the large-scale level has also begun to be commercialized. GICON is a two-stage dry-wet anaerobic digestion process. The technology was developed, tested, and commercialized in Germany by the GICON group. The first industrial-scale plant using this system is the Harvest Energy Garden located in Richmond (Canada), which is also one of the largest high-solid digestion plants in North America. The plant processes approximately 30,000 tons of combined food and yard waste per year and produces approximately 770 kW of electrical energy [7]. Another example is the Eisenmann system, which is based on a two-stage process using continuous plug-flow reactors to deal with high solid waste. The proven Eisenmann systems are expandable with add-on modules, allowing for a wide range of process capacities, from 3000 to over 100,000 tons per year [8]. The main concern in the TAD is the methane reactor (MR), because methane-forming microorganisms have a much slower growth rate and are much more sensitive compared with other groups of microorganisms [3,4]. There are two growth mechanisms in the MR, which are suspended sludge (SS) and attached sludge processes [4,9,10]. In the SS reactor, the microorganisms are maintained in suspension within the liquid. In the other mechanism, they attach and grow on supporting media with the most effective technique called granular sludge (GS). As a result, the second mechanism has a much higher density of microorganisms than the first one [9]. This makes the GS technique have more advantages than the SS, such as the fact that it is not washed away by water flow, is resistant to toxins, and has high concentrations of microorganisms [11]. Nevertheless, the current application of the GS technique requires a high-speed flow (through a circulating flow) to maintain good contact between the GS and the substrate [9,11,12]. As a result, the operation might consume much more energy than the suspended growth one does. These technologies have been widely used in wastewater treatment. However, the GS technique to process BMSW has been limited in the literature.
The performance of the AD systems is first shaped by operational conditions such as organic loading rate (OLR), hydraulic retention time (HRT), and pH [3]. Thus, many studies have been performed to investigate how these elements affect the systems and to point out suitable operating states [3,13]. Nonetheless, the requirement of high quantity and quality experiments is a matter when studying multivariate impacts. As a result, the majority of the papers examine the influence of only one or two elements. A recent research paper by Boonsawang et al. [14] is one of the few studies that shows the effects of more elements on the TAD system operated in the batch process. However, the simultaneous impact of the same elements on the continuous process system, especially the AD using GS, is still limited in the literature.
Hence, this research attempts to apply a new technique using both GS and SS for the methane reactor without circulating flow. The simultaneous effects of pH, OLR, and HRT on the reactor in dealing with BMSW were also scrutinized. In addition, to the extent of the authors’ knowledge, this is also the first time that microbial analysis for both GS and SS in one methane reactor has been performed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics
The characteristics of samples including carbon (C), nitrogen (N), total solid (TS), volatile solid (VS), total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD), and soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) were analyzed by the approaches presented by Dinh et al. [15] and Dinh et al. [2].
Compositions of VFAs, including acetate/alcohol (C2), propionate (C3), butyrate (C4), and valerate (C5), were measured by a GC-14A (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with an FID detector and a capillary column. One ml of samples was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 15 min. The supernatant was collected and then mixed with TCA 10% in a ratio of 1:1. The mixture was kept on ice for one hour to complete protein precipitation reactions. Then it continued to be centrifuged at 4 °C and 8000 rpm for 10 min to remove suspended matters. Finally, one µL of the supernatant was collected to determine VFA components by GC-14A.
Biogas compositions were detected by gas chromatography (GC-2014, Shimadzu, Japan): Injection temperature: 250 °C; carrier gas: He, 40 mL/min; detector temperature: 200 °C; column temperature: program rate 40 °C~200 °C (10 °C/min).
2.2. Substrate and Inoculum
BMSW was collected from municipal solid waste at a solid waste treatment plant. BMSW was passed through pretreatment processing, including being chopped and ground into fine particles. It was then mixed with horse dung in a ratio of 9:1 (VS/VS) for the inoculation of hydrolysis. The characteristics of substrate and feedstock were analyzed as described in Section 2.1 and shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the substrates (n = 3).
2.3. Experimental Setups
Hybrid methane reactor: This study manipulated a novel way of employing an up-flow reactor in methanogenesis. Figure 1 illustrates the operating principle of the reactor. In this process, the substrate was slowly pumped into the reactor to allow the GS (diameter in the range of 1.5–2.0 mm) to settle at the bottom, forming a filter bed. The multilayer structure of the GS would allow the reactor to contact substrates with a high VFA concentration. In addition, a SS layer was kept at the upper of the filter bed, where anaerobic microorganisms would degrade the substrate’s remainder. In particular, biogas being produced and ejected at a high speed would push the SS up and down within the liquid phase, which would form a fluidized zone with sufficiently high loads, leading to good contact between the SS and substrate. As a result, the performance of MR would be significantly improved.
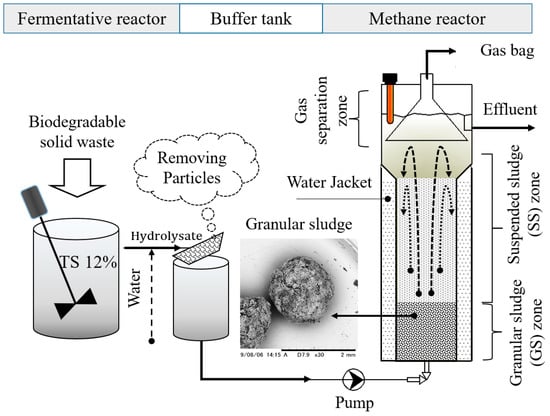
Figure 1.
Scheme of the two-stage anaerobic digestion system.
The experimental model of the TAD system contained one hydrolysis/acidogenesis reactor (FR, 5 L), one methanogenic reactor (MR, 6 L), and one buffer tank (BT, 2 L) between these reactors. The substrate flow of the experimental model is shown in Figure 1. At first, water was added to the substrate to adjust its initial TS to 12%. The FR was a complete mixed reactor operating in batch mode. The pH of the FR was controlled by a 10M NaOH solution at 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, and 6.5. After a five-day retention time, the substrate was diluted with water at different dilution rates (n = 3, 2, and 1). The solid fraction was removed by filtering (1mm), while the liquid fraction continued to be pumped into the MR. Both FR and MR were controlled at a mesophilic temperature (37 °C). Sixteen different experimental stages were conducted at different pH, n, and OLR conditions, with an observation period of 12 days for each stage. The details of the tests are presented in Table 2. Observation time is often set longer than HRT, whereby experiments T1, T2, T3, T4, and T5 appear to be the limitations of the current study. However, the time only needs to be long enough for the observed signals to reach a steady state. In this study, the results of methane yield and methane concentration obtained at all experimental stages were stable after only a few days. Therefore, the observation duration of 12 days was long enough for data collection on biogas production. For other purposes, an appropriate observation period should be chosen carefully. The difference compared with other TAD systems is the requirement for solid-liquid phase separation after the fermentation process. This process is made easy by the screw press that is available on the market.

Table 2.
Experimental stages.
2.4. Hydrodynamic Analysis
The degree of disturbance in the fluidized zone of the methane reactor was evaluated by the Reynolds number (Re) of the bubble as calculated by Equation (1) below:
where Q: gas flow (m3/s); ρ: density of gas phase (0.9578 kg/m3); d: diameter of bubble (2 × 10−3 m); µ: kinematic viscosity (1.1984 × 10−5 kg·m−1·S−1, at 35 °C) [12,16].
2.5. Microbiological Analysis
Microbiological analysis was performed for both GS and SS. It is useful not only for comparing the microbiological characteristics between attached and suspended organisms but also for the distribution assessment of the functional microbial groups in the methane tank used in this study.
The details of bacterial DNA extraction procedures were described by Yu and Morrison [17]. The bacterial DNA of samples was extracted from 0.2 g of wet samples by beating with sterile zirconia beads in the presence of 1 mL lysis buffer [500 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM EDTA, and 4% sodium dodecyl sulfate]. Most of the impurities and the sodium dodecyl sulfate were then removed by precipitation with 10 M Ammonium Acetate. The nucleic acids were recovered by precipitation with isopropanol and dissolved in a Tris-EDTA buffer. The bacterial DNA was then purified via sequential digestions with RNase and proteinase K before using the QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit columns.
The DNA amplification was performed following the method described by Nguyen et al. [18]. The method used a quantitative real-time PCR targeting the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene (forward: 5′-ACACTC TTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′; reverse: 5′-TGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTGGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). The details of the protocol were attached to the report of Nguyen et al. [18]. After the purification process, the purified DNA was pair-end sequenced (2 × 250 bp) on an Illumina MiSeq platform at FASMAC Co., Ltd (Kanagawa, Japan).
The archived raw sequences were processed using Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology (QIIME, version 1.9.1) software. All data were statistically analyzed using JMP software (version 11; SAS Institute). The statistical significance of the differences was determined by the non-parametric Wilcoxon test.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fermentation Reactor (FR)
The sodium hydroxide consumption depended on the controlled pH levels. To keep the pH condition at 4.5, the sodium hydroxide consumption was 8.6 mg/g-VS. This amount was lifted to 79.1 mg/g-VS and 113.5 mg/g-VS to attain pH values of 5.5 and 6.5, respectively. This result could be explained by the fact that higher pH levels could cause a significant increase in hydrolytic kinetic rate constant (more hydrolytic enzyme activities) [19], hence a rising concentration of acidified product required a higher amount of NaOH for neutralization. In fact, the acid (VFA) concentration analysis results in Figure 2a also clearly showed this. For kitchen waste, Zhang et al. [20] indicated that a dosage of 156.5 mg-Na+/g-TS (equivalent to 272.1 mg-NaOH/g-TS) helped maintain FR at pH 5. Sambusiti et al. [21] had to add a dosage of 10 mg-NaOH/g-TS to keep fermentation at pH 6.7 for wheat straw substrate and at pH 6.3 for ensiled sorghum forage substrate, respectively. Therefore, alkaline consumption during fermentation depended not only on the pH levels but also on the type of raw materials.
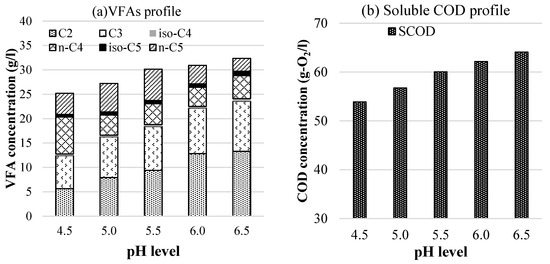
Figure 2.
Effects of pH levels on the fermentative products.
The effects of pH levels on hydrolysis are shown in Figure 2b. The average effectiveness of hydrolysis was 62% (measured by the ratio of SCOD to TCOD). Obviously, that was an uncompleted hydrolytic process, and a large amount of the initial matter was still in the solid state. This trouble has been reported in the literature [22,23,24]. The reason could be that BMSW contained a high content of raw fiber (13.6–39.5%), which is difficult to hydrolyze [25].
The current study showed a strong positive linear correlation between the concentrations of hydrolyzed matter (SCOD) and pH levels. The SCOD concentration obtained at pH 4.5 was 54 g/L (equivalent to 0.66 g-SCOD/g-VS). This value was 19% lower than that obtained in the pH 6.5 condition. However, the difference between the SCOD levels obtained at pH 6.5 and 6.0 was only 3%. Thus, this study agrees with the results concluded by Yu and Fang [26], Sanders [19], and Van et al. [3] that pH in the range of 6.0–6.5 is the best condition for fermentation. This could be explained by the fact that in a low acidic condition, the VFAs produced exist mainly in the form of undissociated molecules that can pass through the cell membrane, causing an imbalance in energy production in the cell and inhibiting the fermentative activity of microorganisms [27,28].
Performing hydrolysis at the same conditions of pH and solid-state compared with the current study, Jiang et al. [29] obtained a yield of 0.76 g-SCOD/g-VS, which could be compared with those reported in the current study. At a much higher solid condition (TS = 20–29%), Sans et al. [22] only obtained a yield of 0.07–0.16 g-SCOD/g-VS, and Bolzonella et al. [23] obtained 0.27 g-SCOD/g-VS. Meanwhile, at a lower solid state (6.8–7.8%), Cheah et al. [30] collected a concentration of 1.5–1.6 g-SCOD/g-VS in the hydrolysis. This could be explained by the solid state, which is closely related to the saturation concentrations of fermentative products. Therefore, the effectiveness of the hydrolysis is affected by not only the type of waste but also operation conditions such as pH and solid state.
The efficiency of acidogenesis is measured by the ratio of CODVFA to SCOD. The rate in the current investigation was in the range of 0.73 to 0.79, which is comparable to the results of the acidogenesis of kitchen waste conducted by Jiang et al. [29]. In fact, the yield of VFA gradually increased along with fermentation time, but for organic solid matters, the yield did not increase significantly after 5–6 days [22,30,31]. For long enough fermentation as in the present study (RT= 5 d), the acidogenic efficiency showed a strong correlation with pH conditions (see Figure 2). At pH 6.5, the total VFA obtained in the liquid hydrolysate was 32.4 g/L, equivalent to a yield of 326.1 mg-VFA/g-VS. This concentration decreased by 4.4%, 6.9%, 15.9%, and 22.2% at 6.0, pH 5.5, pH 5.0, and pH 4.5, respectively. Sans et al. [22] performed experiments at much higher solid conditions (TS = 20–30%) compared with the current study and only obtained 74–160 mg-VFA/g-VS. Thus, VFA formation depends on not only digestion time and pH conditions but also on the solid state. As shown in Figure 2a, the ratio of VFA composition also varies with pH conditions. The C2, C3, n-C4, and n-C5 were dominant. Only the C2 and C3 acids accounted for 49% of the total VFAs at pH 4.5 and increased linearly with the pH levels. This amount was up to 72% at pH 6.0 and reached 73% at pH 6.5. Yu and Fang [26] and Grzelak et al. [28] figured out a similar trend when acidifying dairy wastewater (pH = 4.0–6.5) and kitchen waste (pH = 6–8). The cause is thought to be because microbial fermentation is inhibited at low pH as mentioned above.
3.2. Methane Reactor
After fermentation, changing the dilution rate (n) and HRT led to a variation in substrate concentration (CODin) and OLR. In addition, fermentation was carried out at different pH levels. Thus, these brought a complex matrix of parameters to a methane reactor operation. The changes caused significant variations in the methanogenesis process. In the end, the results revealed a biogas yield ranging from 193.3 to 327.0 Nml/g-TS (containing 54–72% CH4). The evolution of the influence of operating parameters on the quality and quantity of biogas over time is illustrated in Figure 3.
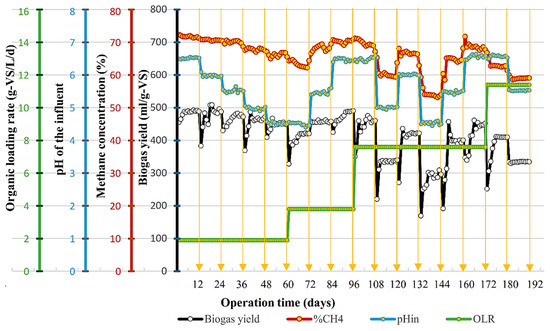
Figure 3.
The influence of operating parameters on the quality and quantity of biogas over time.
As shown in Figure 3, the design in the current study was able to work well with the influent pH as low as 4.5, while most previous studies had shown that MRs had been sensitive to pH < 6.0 [3,10], which can be explained by the following reasons. Firstly, the reactor used GS, which has a microbiological multi-layer structure with an outer layer consisting of acetogens and hydrogen-consuming organisms [11,32]. While acidogenic and acetogenic bacteria could thrive in an acidic environment, hydrogen-consuming organisms helped to avoid diffusion-free hydrogen into methane-forming bacteria inside. Secondly, most VFA components were converted by the GS layer. Therefore, the suspended methanogens (in the fluidized zone) contacted the converted products, which could not harm their growth. Thirdly, proteins in the BMSW were broken into amino acids in the FR, then they continued to be converted into ammonia (NH3), which created an alkali buffer solution in the methane reactor due to: NH3 + H2O ↔ NH4+ + OH− [10]. Thus, the methanogens were actually still active under favorable conditions.
The relationship between biogas production and the pH of the influent at different OLRs is described closely in Figure 4. They had strong positive linear correlations. The slope of these lines rising with the increase in OLR indicated that the influence of pH on biogas production was getting stronger at higher OLRs. At the stage having the lowest OLR (1.9 g-TS·L−1·d−1), the biogas yield increased linearly from 302 Nml/g-TS (66%) CH4) to 327 Nml/g-TS (72%), following pH conditions from 4.5 to 6.5. At an OLR of 3.8 g-TS·L−1·d−1, there seemed to be a breakpoint at the pH 5.5 position (the slope in the range of pH 4.5–5.5 was higher than that in pH 5.5–6.5). This phenomenon was clearer at higher OLR. As we can see, pH 5.5 seemed to be a critical point where the efficiency of MR was significantly inhibited when working with the influent pH below this value.
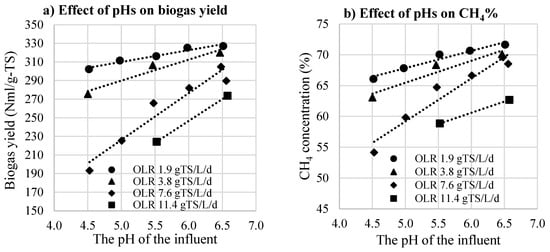
Figure 4.
Effects of the pH on biogas production.
The results shown in Figure 4 revealed that at low OLR, the relationship between the outcomes (biogas quality and quantity) and pH levels was a linear correlation. However, it seemed to be a curve line at high OLR. Therefore, quadratic multivariate regression models were applied to determine the law of the effect of these variables on the outcomes. The variables included pHs, OLRs, HRTs, and CODin, and the relationship between OLR, HRT, and CODin was calculated by the equation: CODin = OLR/HRT. The predicted equations for biogas production that were considered a response of the model were given in Table 3 only with significant coefficients (p < 0.05). The modeling analysis showed that pHs, OLRs, and HRTs had major effects on biogas production. The outcome values can be predicted from these operating parameters.

Table 3.
Multivariate regression analysis of biogas production models.
3.3. Hydrodynamics in the Methane Reactor
The GS particles have a much higher density (d = 1.5–2.0 mm, 1010–1050 g/L) than water (998 g/L), so they could easily settle to the bottom under operating conditions with a very low velocity (RT of 3–5 d). Meanwhile, very fine sludge created a suspended state in the fluidized zone due to the drag force of the biogas bubbles. The calculation results of the Reynolds number at different OLRs in the fluidized zone of MR are shown in Figure 5. The higher the OLRs the reactor operated at, the greater the Reynolds number was, which indicated a higher activity level in the fluidized zone. Many studies have agreed that flow was laminar at Re < 2300, transitional at Re between 2100 and 4000, and turbulent at Re > 4000 [12,33]. Accordingly, the flow mode in the reactor was laminar flow at an OLR of 1.9 kg-TS.m−3·d−1 and transition flow at an OLR of 3.8 kg-TS.m−3·d−1. The reactor started to show turbulent mode at OLR above 3.8 kg-TS.m−3·d−1. Thus, through the Re values, the fluidized zone formation hypothesis in Section 2.3 was completely proven at high OLRs. However, excessive turbulence in the reactor could lead to the washing-out of SS in the fluidized zone of the reactor [12]. That might cause a reduction in treatment efficiency, as occurred at an OLR of 11.4 kg-TS·m−3·d−1 in this study.
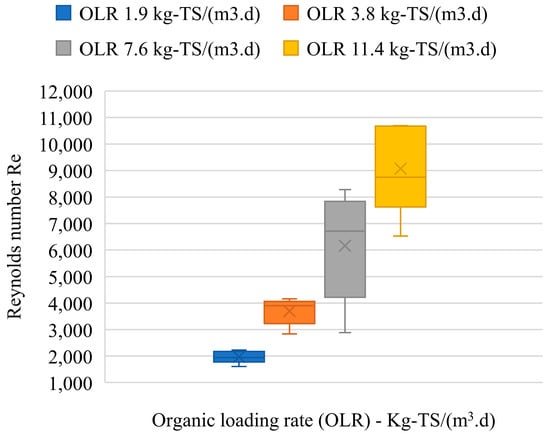
Figure 5.
Reynolds number at different OLRs in the methane reactor.
3.4. Microorganisms in the Methane Reactor
The results of microbiological composition analysis (phylum level) in the GS at the filter bed and the SS at the fluidized zone are presented in Figure 6. The six most dominant phyla in the GS included Firmicutes (30.8%), Bacteroidetes (21.5%), Proteobacteria (14.6%), Euryarchaeota (12.6%), Synergistetes (6%), and Chloroflexi (5.7%). In the SS, they were 12.2%, 37.2%, 15.9%, 3.0%, 6.4%, and 8.4%, respectively. Their presence was also indicated to be the most abundant phyla in anaerobic digestion processes, as reported by Liu et al. [34], Guo et al. [35], Chen et al. [36], and Shin et al. [37].
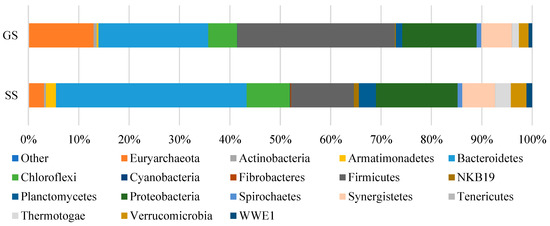
Figure 6.
Distribution of microorganisms (Phylum level) in GS and SS.
Among those, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes have been detected with a relative abundance of more than 50%. They play the roles of hydrolysis, acidogenesis, and acetogenesis. These phyla are especially related to the production of extracellular enzymes with cellulases, lipases, or proteases, which are responsible for hydrolysis [38,39]. They also directly perform the conversion of soluble monomers into VFAs [34,38,39]. In this study, the ratio between Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes was significantly higher in the GS than in the SS. The GS was in direct contact with the influent, which had abundant VFAs, while the SS worked in a zone with much less harsh conditions. This result revealed that Firmicutes could thrive better than Bacteroidetes in a high VFA concentration. Having the same opinion, Fernandes et al. [40] found significant negative correlations between Bacteroidetes and the ratio of acetate, propionate, butyrate, and total short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) concentrations, whereas the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes was positively correlated with VFA concentrations. Besides these phyla, Chloroflexi also greatly contributed to the fermentation, which was often thought to be related to glucose sources [39]. The total relative abundance of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Chloroflexi was the same in both GS and SS (58%). Therefore, the general function of hydrolytic/acidogenic activity seemed independent of the form of the microorganism.
Proteobacteria are also a large phylum that can perform hydrolysis and acidogenesis, but their most important role is the conversion of SCFAs in acetogenesis [35,38]. There are many groups of Proteobacteria which are well-known glucose, propionate, butyrate, and acetate-utilizing microbial communities such as Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, and Delta-proteobacteria [41]. They formed a close spatial association with different methanogenic populations [35]. Some bacteria belonging to the order Syntrophobacterales of the Proteobacteria phylum are known for their syntrophic acetogenesis activity, especially due to their propionate-oxidizing capacity. This function is very important to maintain a stable state of anaerobic digestion because high concentrations of propionate inhibit methanogenesis [38]. Similar to Proteobacteria, Synergistetes are considered to take on the role of acetogens; they can degrade monocarboxylic, amino acid, and long-chain fatty acids (butyrate, iso-heptanoate, oleate, etc.) and produce hydrogen, acetate, and CO2 [36,39,42]. The total relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Synergistetes in the GS could be compared with those detected in the SS. Therefore, it could be stated that the acidogenic/acetogenic activities in both cases were similar.
Methanogenesis is the main metabolic process in autotrophs of Euryarchaeota [37,43]. Most of the Euryarchaeota are strictly anaerobic, although some of them can grow at low oxygen concentrations. They lack defense mechanisms against oxidative stress [43]. Therefore, they are very sensitive to the presence of oxygen. The result in Figure 5 showed that the relative abundance of Euryarchaeota in GS was much higher than those determined in SS. This indicated that the multilayer structure of GS helped methanogens thrive, as shown in Section 2.3. And biogas production also mainly occurred in the GS zone, while SS in the fluidized zone played the role of performance enhancement.
4. Conclusions
There was a strong positive linear correlation between concentrations of fermentative matter obtained and pH levels (4.5–6.5). In the best pH condition (6.0–6.5), the fermentative reactor obtained a yield of 0.77–0.79 g-SCOD/g-VS and 311–326 mg-VFA/g-VS.
The operation of the hybrid methane reactor with the GS at the bottom and SS at the fluidized zone as proposed was completely verified by hydrodynamic assessments and biogas production. The best performance was obtained at OLR 7.6 g-TS/(L.d) and the influent having pH 6.5. The impacts of the operating conditions on biogas production were clarified in a quadratic multivariate equation with statistical significance.
The most dominant phyla in the MR comprised Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Euryarchaeota, Synergistetes, and Chloroflexi. Among them, the species with the highest relative abundance in GS was Firmicutes, whereas Bacteroidetes were found in SS. Methanogenic archaea in GS were more abundant than in SS.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study. P.V.D. performing experiments and writing original draft; T.F.: supervision, writing, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the Vietnamese Ministry of Education and Training under grant number B2021-XDA-03.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Hanoi University of Civil Engineering for helping us get the fund. We also would like to thank Naoki Nishino and Nguyen Dang Qui from Okayama University for supporting us analyze microorganisms.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, P.V.; Takeshi, F.; Minh, G.H.; Phu, S.T.P. Comparison Between Single and Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Vegetable Waste: Kinetics of Methanogenesis and Carbon Flow. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6095–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, D.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Tho, B.L.; Toan, P.P.S.; Minh, G.H. A review of anaerobic digestion systems for biodegradable waste: Configurations, operating parameters, and current trends. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lier, J.B.; Mahmoud, N.; Zeeman, G. Anaerobic wastewater treatment. In Biological Wastewater Treatment: Principles, Modelling and Design; Henze, M., van Loosdrecht, M.C.M., Ekama, G.A., Brdjanovic, D., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008; pp. 415–456. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr, N.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Hafez, H.; Nakhla, G.; El Naggar, M.H. Comparative assessment of single-stage and two-stage anaerobic digestion for the treatment of thin stillage. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, P.; Fujiwara, T.; Giang, H.; Phu, S.P. The fate of carbon in two-stage anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 25–28 February 2019; p. 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The-Eco-Ambassaor. Solid Anaerobic Digestion Technology. Available online: https://www.theecoambassador.com/SolidAnaerobicDigestion.html (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Eisenmann. Anaerobic Digestion Technology. Available online: https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/133998/file-608889867-pdf/docs/eisenmann_biogas_brochure.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D.; Tchobanoglous, G. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gerardi, M.H. The Microbiology of Anaerobic Digesters; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Pol, L.H.; de Castro Lopes, S.; Lettinga, G.; Lens, P. Anaerobic sludge granulation. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1376–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz Arita, C.E. Anaerobic Digestion Comparison of Manure Leachate by High-Rate Anaerobic Reactors; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, T.; Tauseef, S.; Abbasi, S.A. Biogas Energy; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 2, p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Boonsawang, P.; Rerngnarong, A.; Tongurai, C.; Chaiprapat, S. Effect of pH, OLR, and HRT on performance of acidogenic and methanogenic reactors for treatment of biodiesel wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 3317–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, P.V.; Takeshi, F.; Minh, G.H.; Phu, S.T.P. A new kinetic model for biogas production from co-digestion by batch mode. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2018, 4, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Bastiani, C.; Alba, J.L.; Mazzarotto, G.T.; de Farias Neto, S.R.; Reynolds, A.; Kennedy, D.; Beal, L.L. Three-phase hydrodynamic simulation and experimental validation of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 83, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Morrison, M. Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques 2004, 36, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Tsuruta, T.; Nishino, N. Examination of milk microbiota, fecal microbiota, and blood metabolites of Jersey cows in cool and hot seasons. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 91, e13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, W.T.M. Anaerobic Hydrolysis during Digestion of Complex Substrates; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Shi, H.; Cai, W. The influence of pH on hydrolysis and acidogenesis of kitchen wastes in two-phase anaerobic digestion. Environ. Technol. 2005, 26, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambusiti, C.; Monlau, F.; Ficara, E.; Carrère, H.; Malpei, F. A comparison of different pre-treatments to increase methane production from two agricultural substrates. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, C.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Cecchi, F.; Pavan, P.; Bassetti, A. Volatile fatty acids production by mesophilic fermentation of mechanically-sorted urban organic wastes in a plug-flow reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 1995, 51, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzonella, D.; Fatone, F.; Pavan, P.; Cecchi, F. Anaerobic fermentation of organic municipal solid wastes for the production of soluble organic compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 3412–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavinato, C.; Bolzonella, D.; Fatone, F.; Cecchi, F.; Pavan, P. Optimization of two-phase thermophilic anaerobic digestion of biowaste for hydrogen and methane production through reject water recirculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8605–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, R.; González-Martínez, S. Characteristics of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste and methane production: A review. Waste Manag. 2016, 54, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.G.; Fang, H.H.P. Acidogenesis of dairy wastewater at various pH levels. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Fukushi, K.; Sitanrassamee, B. Effect of acid speciation on solid waste liquefaction in an anaerobic acid digester. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelak, J.; Ślęzak, R.; Krzystek, L.; Ledakowicz, S. Effect of pH on the production of volatile fatty acids in dark fermentation process of organic waste. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2018, 25, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Gong, C.; Li, M. Volatile fatty acids production from food waste: Effects of pH, temperature, and organic loading rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, Y.-K.; Vidal-Antich, C.; Dosta, J.; Mata-Álvarez, J. Volatile fatty acid production from mesophilic acidogenic fermentation of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and food waste under acidic and alkaline pH. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35509–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, P.; Pavan, P.; Bolzonella, D.; Innocenti, L.; Cecchi, F.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Acidogenic fermentation of source separated mixtures of vegetables and fruits wasted from supermarkets. Biodegradation 2000, 11, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, S.; O’reilly, C.; Mahony, T.; Colleran, E.; O’flaherty, V. Anaerobic granular sludge bioreactor technology. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2003, 2, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle-Gotla, A. Membrane fouling in industrial anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Si, D.; Chen, Q. Evolution of microbial community along with increasing solid concentration during high-solids anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Ni, B.-J.; Han, X.; Fan, L.; Yuan, Z. Dissecting microbial community structure and methane-producing pathways of a full-scale anaerobic reactor digesting activated sludge from wastewater treatment by metagenomic sequencing. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, H.; Wyckoff, K.N.; He, Q. Linkages of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes populations to methanogenic process performance. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Cho, S.-K.; Lee, J.; Hwang, K.; Chung, J.W.; Jang, H.-N.; Shin, S.G. Performance and microbial community dynamics in anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: Impact of immigration. Energies 2019, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.I.; Oulego, P.; Collado, S.; Laca, A.; González, J.M.; Díaz, M. Impact of anaerobic digestion and centrifugation/decanting processes in bacterial communities fractions. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Chen, Y.; Ndegwa, P. Association between methane yield and microbiota abundance in the anaerobic digestion process: A meta-regression. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Su, W.; Rahat-Rozenbloom, S.; Wolever, T.; Comelli, E. Adiposity, gut microbiota and faecal short chain fatty acids are linked in adult humans. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariesyady, H.D.; Ito, T.; Okabe, S. Functional bacterial and archaeal community structures of major trophic groups in a full-scale anaerobic sludge digester. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1554–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumas-Bilak, E.; Marchandin, H. The Phylum Synergistetes. In The Prokaryotes: Other Major Lineages of Bacteria and The Archaea, 1st ed.; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 931–954. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Fernandez, V.; Zamora, R.; Herrera-Morande, A.; Vallejos, G.; Gonzalez-Ordenes, F.; Guixé, V. Evolution, metabolism and molecular mechanisms underlying extreme adaptation of Euryarchaeota and its biotechnological potential. In Archaea-New Biocatalysts, Novel Pharmaceuticals and Various Biotechnological Applications; Sghaier, H., Najjari, A., Ghedira, K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).