The Bacterial Microbiota of Artisanal Cheeses from the Northern Caucasus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. Organic Acids Analysis
2.3. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Metagenome Assembly and Dominant Genomes Reconstruction
2.6. Gene Prediction and Functional Annotation
2.7. Data Availability
3. Results
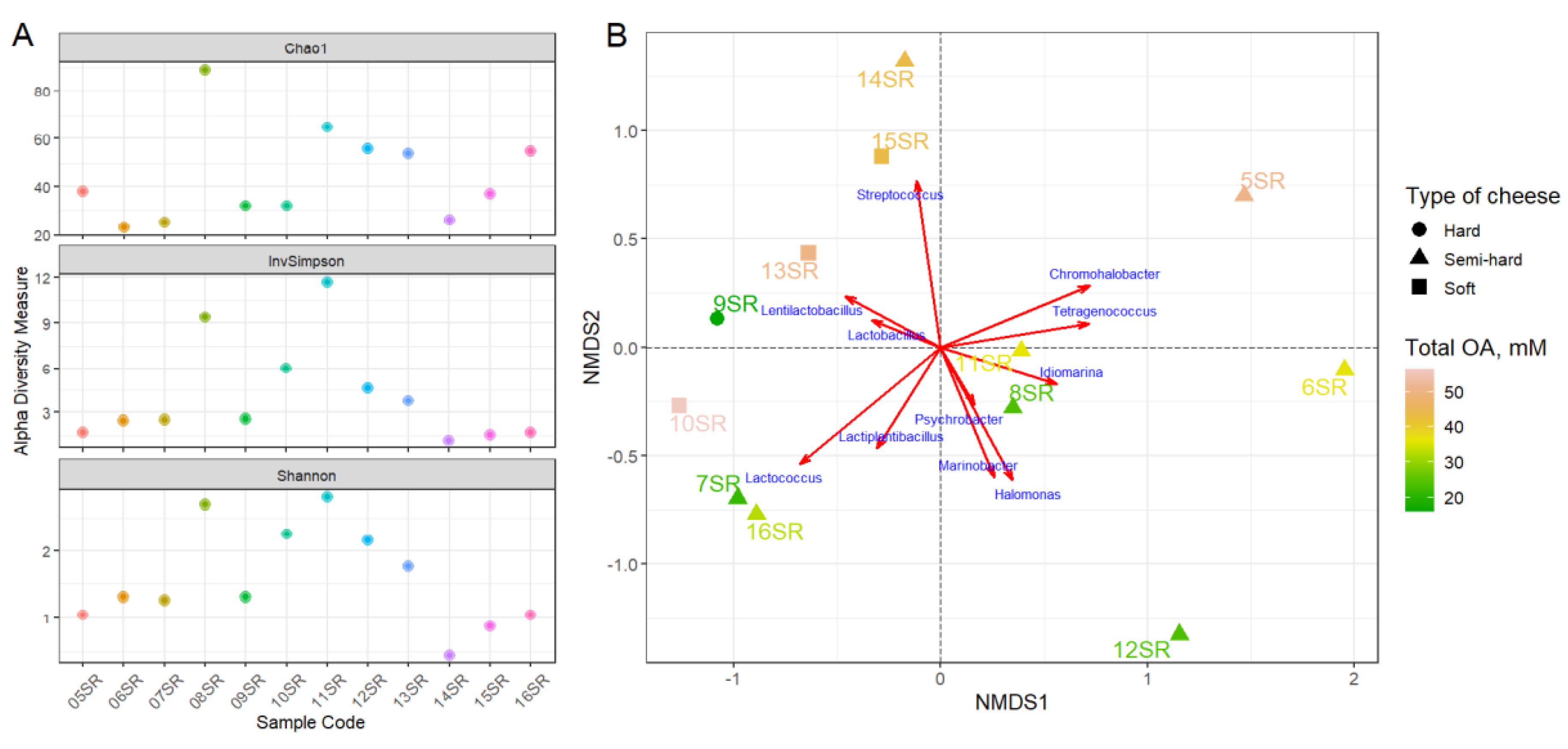
3.1. Organic Acids Content
3.2. Sequencing, Taxonomic Annotation and Genome Reconstruction
3.2.1. Taxonomic Analysis by Amplicons of V4 Region of the 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
3.2.2. Metagenomic Assembly, Gene Prediction and Functional Annotation
Search for Bacteriocin Gene Clusters
Search for Genes of Antibiotic Resistance
Synthesis of Biogenic Amines and Some Non-Proteinogenic Amino Acids
CAZymes, Esterases and Proteases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marco, M.L.; Heeney, D.; Binda, S.; Cifelli, C.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Foligné, B.; Gänzle, M.; Kort, R.; Pasin, G.; Pihlanto, A.; et al. Health benefits of fermented foods: Microbiota and beyond. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, L.; Guàrdia, M.D.; Xicola, J.; Verbeke, W.; Vanhonacker, F.; Zakowska-Biemans, S.; Sajdakowska, M.; Sulmont-Rossé, C.; Issanchou, S.; Contel, M.; et al. Consumer-driven definition of traditional food products and innovation in traditional foods. A qualitative cross-cultural study. Appetite 2009, 52, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Beniwal, A.; Semwal, A.; Navani, N.K. Mechanistic Insights Into Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Associated With Ethnic Fermented Dairy Products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldfeldt, L.U.; Sørensen, K.I.; Strøman, P.; Behrndt, H.; Williams, D.; Johansen, E. Effect of starter cultures with a genetically modified peptidolytic or lytic system on Cheddar cheese ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siragusa, S.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Coda, R.; Gobbetti, M. Synthesis of γ-Aminobutyric Acid by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Variety of Italian Cheeses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7283–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; Algaron, F.; Rizzello, C.G.; Fox, P.F.; Monnet, V.; Gobbetti, M. Angiotensin I-Converting-Enzyme-Inhibitory and Antibacterial Peptides from Lactobacillus helveticus PR4 Proteinase-Hydrolyzed Caseins of Milk from Six Species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5297–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moreno de LeBlanc, A.; Matar, C.; LeBlanc, N.; Perdigón, G. Effects of milk fermented by Lactobacillus helveticusR389 on a murine breast cancer model. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, R477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghshenas, B.; Nami, Y.; Abdullah, N.; Radiah, D.; Rosli, R.; Khosroushahi, A.Y. Anticancer impacts of potentially probiotic acetic acid bacteria isolated from traditional dairy microbiota. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.; Alipour, B.; Faghfoori, Z.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. Cellular and molecular effects of yeast probiotics on cancer. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, I.; Rodríguez, A.; Alía, A.; Martínez-Blanco, M.; Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Córdoba, J.J. Control of Listeria monocytogenes growth and virulence in a traditional soft cheese model system based on lactic acid bacteria and a whey protein hydrolysate with antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 361, 109444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulumoğlu, Ş.; Kaya, H.İ.; Şimşek, Ö. Probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus fermentum strains isolated from tulum cheese. Anaerobe 2014, 30, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaidoutis, E.; Keramydas, D.; Papalexis, P.; Migdanis, A.; Migdanis, I.; Lazaris, A.; Kavantzas, N. Foodborne botulism: A brief review of cases transmitted by cheese products (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2022, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.C.; Mercogliano, R. Focus on histamine production during cheese manufacture and processing: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 419, 136046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilari, E.; Tomazou, M.; Antoniades, A.; Tsaltas, D. High Throughput Sequencing Technologies as a New Toolbox for Deep Analysis, Characterization and Potentially Authentication of Protection Designation of Origin Cheeses? Int. J. Food Sci. 2019, 2019, 5837301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Rackerby, B.; Goddik, L.; Park, S.H. Shifts of microbiota during cheese production: Impact on production and quality. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, H.M.; Zha, M.S.; Qing, Y.T.; Bai, N.; Ren, Y.; Xi, X.X.; Liu, W.J.; Menghe, B.L.G.; Zhang, H.P. Molecular identification and quantification of lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented dairy foods of Russia. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5143–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Mo, L.; Pan, L.; Hou, Q.; Li, C.; Darima, I.; Yu, J. Using PacBio sequencing to investigate the bacterial microbiota of traditional Buryatian cottage cheese and comparison with Italian and Kazakhstan artisanal cheeses. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6885–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, J.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Walsh, A.M.; Macori, G.; Walsh, C.J.; Barton, W.; Finnegan, L.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Claesson, M.J.; et al. Fermented-Food Metagenomics Reveals Substrate-Associated Differences in Taxonomy and Health-Associated and Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. mSystems 2020, 5, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, T.V.; Grabarnik, I.P.; Klyukina, A.A.; Zayulina, K.S.; Elizarov, I.M.; Shestakova, O.O.; Gavirova, L.A.; Malysheva, A.D.; Shcherbakova, P.A.; Barkhutova, D.D.; et al. Microbial Communities of Artisanal Fermented Milk Products from Russia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugerth, L.W.; Wefer, H.A.; Lundin, S.; Jakobsson, H.E.; Lindberg, M.; Rodin, S.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. DegePrime, a Program for Degenerate Primer Design for Broad-Taxonomic-Range PCR in Microbial Ecology Studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5116–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, A.Y.; Tarnovetskii, I.Y.; Podosokorskaya, O.A.; Toshchakov, S.V. Analysis of 16S rRNA Primer Systems for Profiling of Thermophilic Microbial Communities. Microbiology 2019, 88, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohl, D.M.; Vangay, P.; Garbe, J.; MacLean, A.; Hauge, A.; Becker, A.; Gould, T.J.; Clayton, J.B.; Johnson, T.J.; Hunter, R.; et al. Systematic improvement of amplicon marker gene methods for increased accuracy in microbiome studies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vortsepneva, E.; Chevaldonné, P.; Klyukina, A.; Naduvaeva, E.; Todt, C.; Zhadan, A.; Tzetlin, A.; Kublanov, I. Microbial associations of shallow-water Mediterranean marine cave Solenogastres (Mollusca). PeerJ 2021, 9, e12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. metaSPAdes: A new versatile metagenomic assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uritskiy, G.V.; DiRuggiero, J.; Taylor, J. MetaWRAP—A flexible pipeline for genome-resolved metagenomic data analysis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-W.; Simmons, B.A.; Singer, S.W. MaxBin 2.0: An automated binning algorithm to recover genomes from multiple metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alneberg, J.; Bjarnason, B.S.; de Bruijn, I.; Schirmer, M.; Quick, J.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Lahti, L.; Loman, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Quince, C. Binning metagenomic contigs by coverage and composition. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 1144–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.-A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk v2: Memory friendly classification with the genome taxonomy database. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 5315–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.-L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yohe, T.; Huang, L.; Entwistle, S.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Busk, P.K.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y. dbCAN2: A meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W95–W101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, J.; Finn, R.D.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A.; Punta, M. Challenges in homology search: HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Finn, R. Twenty years of the MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D343–D350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitch, T.C.A.; Clavel, T. A proposed update for the classification and description of bacterial lipolytic enzymes. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; Sharma, A.N.; et al. CARD 2017: Expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Fetter, A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Metcalf, W.W.; Helfrich, E.J.N.; et al. antiSMASH 7.0: New and improved predictions for detection, regulation, chemical structures and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, gkad344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutet, E.; Lieberherr, D.; Tognolli, M.; Schneider, M.; Bansal, P.; Bridge, A.J.; Poux, S.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I. UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, the Manually Annotated Section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: How to Use the Entry View. In Plant Bioinformatics: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 23–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bogaardt, C.; van Tonder, A.J.; Brueggemann, A.B. Genomic analyses of pneumococci reveal a wide diversity of bacteriocins–including pneumocyclicin, a novel circular bacteriocin. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhart, B.J.; Schwalen, C.J.; Mann, G.; Naismith, J.H.; Mitchell, D.A. YcaO-Dependent Posttranslational Amide Activation: Biosynthesis, Structure, and Function. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 5389–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Huys, G.; Daube, G. Probiotics: An update. J. De Pediatr. 2015, 91, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciata, M.; Sannino, C.; Ercolini, D.; Scatassa, M.L.; De Filippis, F.; Mancuso, I.; La Storia, A.; Moschetti, G.; Settanni, L. Animal Rennets as Sources of Dairy Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2050–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Aubert, J.; Maillard, M.-B.; Boissel, F.; Leduc, A.; Thomas, J.-L.; Deutsch, S.-M.; Camier, B.; Kerjouh, A.; Parayre, S.; et al. Fine-Tuning of Process Parameters Modulates Specific Metabolic Bacterial Activities and Aroma Compound Production in Semi-Hard Cheese. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8511–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peaker, M.; Linzell, J.L. Citrate in milk: A harbinger of lactogenesis. Nature 1975, 253, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, E.G.; Steele, J.L. Succinate production and citrate catabolism by Cheddar cheese nonstarter lactobacilli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablé, S.; Cottenceau, G. Current Knowledge of Soft Cheeses Flavor and Related Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4825–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, M.; Bittante, G. From milk to cheese: Evolution of flavor fingerprint of milk, cream, curd, whey, ricotta, scotta, and ripened cheese obtained during summer Alpine pasture. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3918–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; La Storia, A.; Stellato, G.; Gatti, M.; Ercolini, D. A Selected Core Microbiome Drives the Early Stages of Three Popular Italian Cheese Manufactures. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzić-Vidojević, A.; Veljović, K.; Tolinački, M.; Živković, M.; Lukić, J.; Lozo, J.; Fira, Đ.; Jovčić, B.; Strahinić, I.; Begović, J.; et al. Diversity of non-starter lactic acid bacteria in autochthonous dairy products from Western Balkan Countries-Technological and probiotic properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhao, F.; Hou, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Sun, Z. PacBio sequencing reveals bacterial community diversity in cheeses collected from different regions. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, F.; Ferrocino, I.; Milanović, V.; Belleggia, L.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Garofalo, C.; Foligni, R.; Mannozzi, C.; Mozzon, M.; Cocolin, L.; et al. Microbial communities and volatile profile of Queijo de Azeitão PDO cheese, a traditional Mediterranean thistle-curdled cheese from Portugal. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Peng, C.; Kwok, L.; Zhang, H. The Bacterial Diversity of Spontaneously Fermented Dairy Products Collected in Northeast Asia. Foods 2021, 10, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; Gatto, V.; Sabattini, G.; Torriani, S. An assessment of factors characterizing the microbiology of Grana Trentino cheese, a Grana-type cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2012, 65, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Zepeda, A.; Sanchez-Flores, A.; Quirasco Baruch, M. Metagenomic analysis of a Mexican ripened cheese reveals a unique complex microbiota. Food Microbiol. 2016, 57, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surber, G.; Schäper, C.; Wefers, D.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Exopolysaccharides from Lactococcus lactis affect manufacture, texture and sensory properties of concentrated acid milk gel suspensions (fresh cheese). Int. Dairy J. 2021, 112, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.I.; Neto, D.M.; Capucho, J.C.; Gião, M.S.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Malcata, F.X. How three adventitious lactic acid bacteria affect proteolysis and organic acid production in model Portuguese cheeses manufactured from several milk sources and two alternative coagulants. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, J.; Shimizu, H.; Hisa, K.; Matsuzaki, C.; Inuki, S.; Ando, Y.; Nishida, A.; Izumi, A.; Yamano, M.; Ushiroda, C.; et al. Host metabolic benefits of prebiotic exopolysaccharides produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2161271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrete-Tapia, A.; Escobar-Ramírez, M.C.; Tamplin, M.L.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M. High-throughput sequencing of microbial communities in Poro cheese, an artisanal Mexican cheese. Food Microbiol. 2014, 44, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, R.; Tomar, S.K.; Singh, A.K. Response surface optimization of the cultivation conditions and medium components for the production of folate by Streptococcus thermophilus. J. Dairy Res. 2010, 77, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazhar, S.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Hill, C.; McAuliffe, O. A Systems-Wide Analysis of Proteolytic and Lipolytic Pathways Uncovers The Flavor-Forming Potential of The Gram-Positive Bacterium Macrococcus caseolyticus subsp. caseolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carasi, P.; Malamud, M.; Serradell, M.A. Potentiality of Food-Isolated Lentilactobacillus kefiri Strains as Probiotics: State-of-Art and Perspectives. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.R. Metabolic Engineering for Improved Fermentation of L-Arabinose. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharof, M.P.; Lovitt, R.W. Bacteriocins Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria a Review Article. APCBEE Procedia 2012, 2, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Stauber, N.; Scherer, S. Isolation and characterization of Linocin M18, a bacteriocin produced by Brevibacterium linens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3809–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Shi, C.; Bothwell, I.R.; van der Donk, W.A.; Zhao, H. Discovery and Characterization of a Class IV Lanthipeptide with a Nonoverlapping Ring Pattern. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessione, E.; Cirrincione, S. Bioactive Molecules Released in Food by Lactic Acid Bacteria: Encrypted Peptides and Biogenic Amines. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessione, E.; Pessione, A.; Lamberti, C.; Coïsson, D.J.; Riedel, K.; Mazzoli, R.; Bonetta, S.; Eberl, L.; Giunta, C. First evidence of a membrane-bound, tyramine and β-phenylethylamine producing, tyrosine decarboxylase in Enterococcus faecalis: A two-dimensional electrophoresis proteomic study. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2695–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Opinion on risk based control of biogenic amine formation in fermented foods. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2393. [CrossRef]
- Eller, K.; Henkes, E.; Rossbacher, R.; Höke, H. Amines, Aliphatic. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J.; Zhao, S. Isolation and pan-genome analysis of Enterobacter hormaechei Z129, a ureolytic bacterium, from the rumen of dairy cow. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1169973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mehra, S. A Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) Efflux Pump, SCO4121, from Streptomyces coelicolor with Roles in Multidrug Resistance and Oxidative Stress Tolerance and Its Regulation by a MarR Regulator. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaa, M.; Seo, Y.-S.; Park, I. Addition of Coriander during Fermentation of Korean Soy Sauce (Gangjang) Causes Significant Shift in Microbial Composition and Reduction in Biogenic Amine Levels. Foods 2020, 9, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lülf, R.H.; Vogel, R.F.; Ehrmann, M.A. Microbiota dynamics and volatile compounds in lupine based Moromi fermented at different salt concentrations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 354, 109316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Porro, C.; Tokunaga, H.; Tokunaga, M.; Ventosa, A. Chromohalobacter japonicus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a Japanese salty food. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2262–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haastrup, M.K.; Johansen, P.; Malskær, A.H.; Castro-Mejía, J.L.; Kot, W.; Krych, L.; Arneborg, N.; Jespersen, L. Cheese brines from Danish dairies reveal a complex microbiota comprising several halotolerant bacteria and yeasts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 285, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, L.; Verce, M.; De Vuyst, L.; Weckx, S. Amplicon and shotgun metagenomic sequencing indicates that microbial ecosystems present in cheese brines reflect environmental inoculation during the cheese production process. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 87, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Kang, K.H.; Park, Y.-H. Psychrobacter jeotgali sp. nov., isolated from jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitdhipol, J.; Visessanguan, W.; Benjakul, S.; Yukphan, P.; Tanasupawat, S. Idiomarina piscisalsi sp. nov., from fermented fish (pla-ra) in Thailand. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xing, P.; Zhai, L.; Phurbu, D.; Tang, Q.; Wu, Q. Halomonas tibetensis sp. nov., isolated from saline lakes on Tibetan Plateau. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegría, Á.; Szczesny, P.; Mayo, B.; Bardowski, J.; Kowalczyk, M. Biodiversity in Oscypek, a Traditional Polish Cheese, Determined by Culture-Dependent and -Independent Approaches. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcenserie, V.; Taminiau, B.; Delhalle, L.; Nezer, C.; Doyen, P.; Crevecoeur, S.; Roussey, D.; Korsak, N.; Daube, G. Microbiota characterization of a Belgian protected designation of origin cheese, Herve cheese, using metagenomic analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6046–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montel, M.-C.; Buchin, S.; Mallet, A.; Delbes-Paus, C.; Vuitton, D.A.; Desmasures, N.; Berthier, F. Traditional cheeses: Rich and diverse microbiota with associated benefits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kodama, K.; Yasuda, H.; Okamoto-Kainuma, A.; Koizumi, K.; Yamasato, K. Presence of halophilic and alkaliphilic lactic acid bacteria in various cheeses. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 44, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: Environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivistö, A.T.; Karp, M.T. Halophilic anaerobic fermentative bacteria. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 152, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakinaka, T.; Iwata, S.; Takeishi, Y.; Watanabe, J.; Mogi, Y.; Tsukioka, Y.; Shibata, Y. Isolation of halophilic lactic acid bacteria possessing aspartate decarboxylase and application to fish sauce fermentation starter. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, J.K.; Carstens, C.K.; Ramachandran, P.; Shazer, A.G.; Narula, S.S.; Reed, E.; Ottesen, A.S.K. Metagenomics of pasteurized and unpasteurized gouda cheese using targeted 16S rDNA sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, F.; Maxwell, A. The Microbial Toxin Microcin B17: Prospects for the Development of New Antibacterial Agents. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3400–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Chun, B.H.; Jeong, S.E.; Jeon, C.O. Tetragenococcus halophilus MJ4 as a starter culture for repressing biogenic amine (cadaverine) formation during saeu-jeot (salted shrimp) fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.-A.; Jo, Y.M.; Seo, H.; Kim, G.Y.; Cheon, S.W.; Yang, S.H.; Jeon, C.O.; Han, N.S. Probiotic potential of Tetragenococcus halophilus EFEL7002 isolated from Korean soy Meju. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
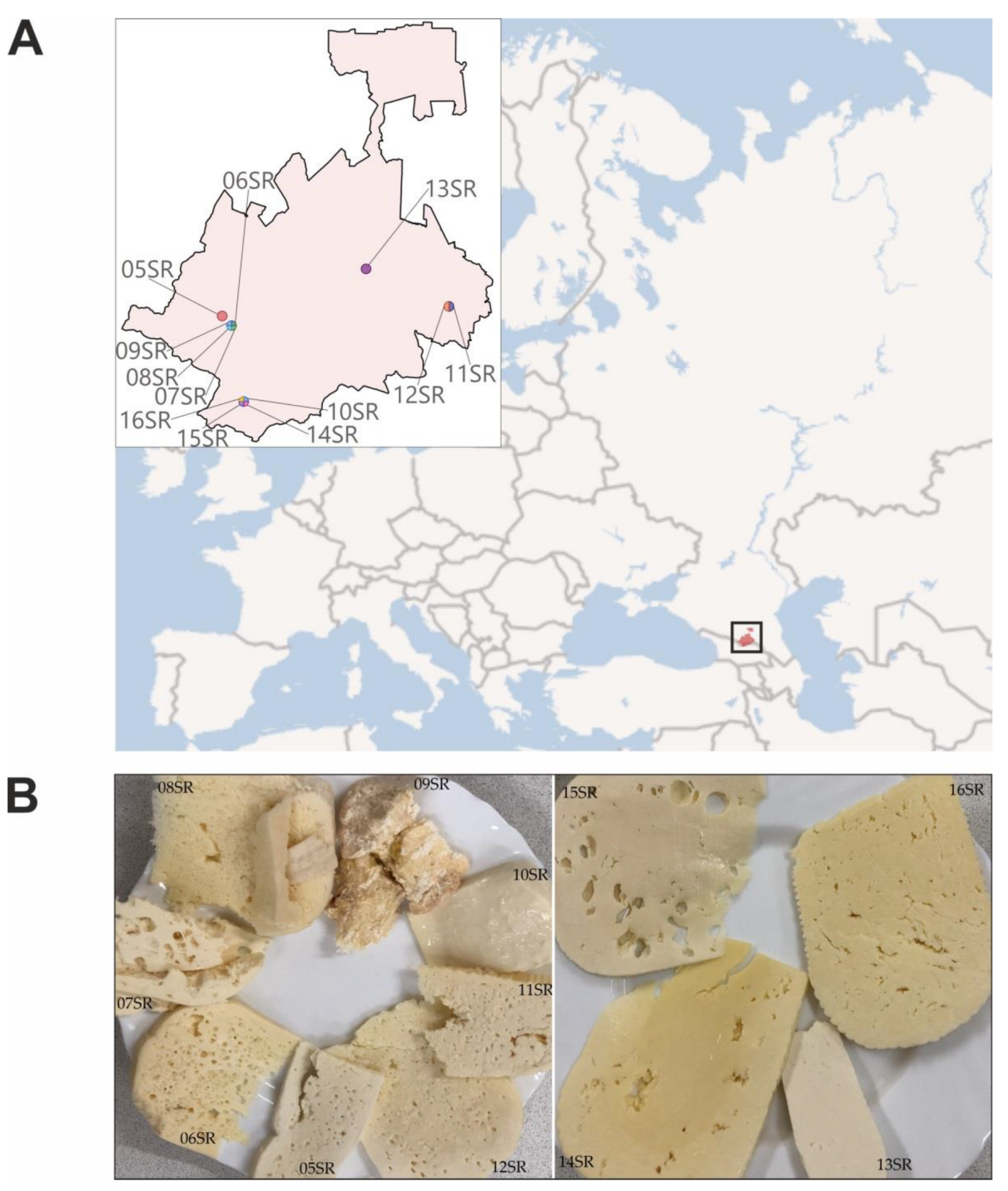




| Sample Designation | Type of Cheese | Time of Ripening in Salt Brine | District | GPS | pH | DNA, ng/μL | DNA Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05SR | SH | 6 months | Irafsky | 42.936421, 43.818312 | 5.0 | 38.6 | V4 16S |
| 06SR | SH | 12 months | Irafsky | 42.906694, 43.857689 | 5.3 | 104.3 | V4 16S Metagenomics |
| 07SR | SH | 6 months | Irafsky | 42.906694, 43.857689 | 5.0 | 92.1 | V4 16S Metagenomics |
| 08SR | SH | ND | Irafsky | 42.906694, 43.857689 | 5.0 | 9.9 | V4 16S |
| 09SR | H | ND, but long dried on a shelf | Irafsky | 42.906694, 43.857689 | 4.5 | 62.0 | V4 16S |
| 10SR | S | Without ripening | Alagirsky | 42.674195 43.909169 | 5.5 | 56 | V4 16S |
| 11SR | SH | 12 months | Prigorodny | 42.965969, 44.773623 | 5.3 | 62 | V4 16S |
| 12SR | SH | 12 months | Prigorodny | 42.965969, 44.773623 | 5.3 | 97.6 | V4 16S |
| 13SR | S | Without ripening | Ardonsky | 43.081601, 44.424295 | 5.0 | 38 | V4 16S Metagenomics |
| 14SR | SH | 8 months | Alagirsky | 42.674195 43.909169 | 5.5 | 21.6 | V4 16S |
| 15SR | S | Without ripening | Alagirsky | 42.674195 43.909169 | 5.0 | 3.4 | V4 16S |
| 16SR | SH | 1 month | Alagirsky | 42.674195 43.909169 | 5.3 | 6.8 | V4 16S |
| Sample | Size (Mb) | Scaffolds | N50 | Mapped Reads | Average Mean Coverage | Assembly ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13SR | 45.75 | 25125 | 4958 | 98.72% | 423 | GCA_029266255.1 |
| 06SR | 26.53 | 12922 | 7578 | 96.83% | 300 | GCA_029255955.1 |
| 07SR | 26.16 | 7794 | 15908 | 68.15% | 114 | GCA_029255935.1 |
| Sample | Bin # | Compl., % | Contamin., % | GC, % | Size, Mb | Scaffolds | N50 | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 06SR | bin.5 | 100 | 0.336 | 47 | 2.73 | 32 | 169731 | Idiomarina sp. |
| bin.3 | 99.93 | 0 | 60.4 | 2.77 | 52 | 83372 | Halomonas sp. | |
| bin.2 | 98.99 | 0.862 | 60.9 | 3.37 | 83 | 85018 | Chromohalobacter japonicus | |
| bin.4 | 93.77 | 0.883 | 35.6 | 2.25 | 182 | 17110 | Tetragenococcus halophilus | |
| bin.1 | 92.73 | 2.55 | 32.9 | 2.65 | 272 | 14553 | Staphylococcus equorum | |
| 07SR | bin.2 | 100 | 0.793 | 37.6 | 2.17 | 92 | 77980 | Leuconostoc mesenteroides |
| bin.3 | 99.62 | 0.377 | 34.9 | 2.32 | 73 | 45232 | Lactococcus lactis | |
| bin.4 | 99.06 | 0 | 45.5 | 2.61 | 154 | 62186 | Levilactobacillus brevis | |
| bin.5 | 98.57 | 1.075 | 58.2 | 6.06 | 565 | 17370 | Pseudomonas_E helleri | |
| bin.6 | 96.29 | 2.777 | 44.6 | 3.08 | 97 | 55608 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | |
| bin.1 | 86.92 | 2.064 | 55.8 | 4.04 | 720 | 6846 | Enterobacter hormaechei_A | |
| 13SR | bin.2 | 99.25 | 0 | 41.8 | 2.28 | 80 | 36800 | Lentilactobacillus kefiri |
| bin.5 | 99.11 | 0.034 | 34.8 | 2.26 | 217 | 19019 | Lactococcus lactis | |
| bin.3 | 98.76 | 2.777 | 45 | 2.85 | 168 | 25798 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | |
| bin.10 | 98.16 | 0.478 | 38.9 | 1.97 | 93 | 35113 | Streptococcus thermophilus | |
| bin.6 | 96.17 | 0.187 | 39.8 | 1.85 | 78 | 38196 | Streptococcus parasuis | |
| bin.7 | 94.8 | 3.37 | 37.6 | 2.8 | 200 | 19197 | Enterococcus faecalis | |
| bin.4 | 94.27 | 0.552 | 37.2 | 1.83 | 145 | 18105 | Macrococcus caseolyticus | |
| bin.8 | 93.26 | 0.084 | 37.5 | 1.6 | 79 | 32698 | Streptococcus macedonicus | |
| bin.1 | 91.48 | 0.754 | 39.4 | 1.78 | 186 | 12108 | Streptococcus dysgalactiae | |
| bin.9 | 84.43 | 1.131 | 38.7 | 1.52 | 131 | 14625 | Pediococcus parvulus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kochetkova, T.V.; Grabarnik, I.P.; Klyukina, A.A.; Zayulina, K.S.; Gavirova, L.A.; Shcherbakova, P.A.; Kachmazov, G.S.; Shestakov, A.I.; Kublanov, I.V.; Elcheninov, A.G. The Bacterial Microbiota of Artisanal Cheeses from the Northern Caucasus. Fermentation 2023, 9, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080719
Kochetkova TV, Grabarnik IP, Klyukina AA, Zayulina KS, Gavirova LA, Shcherbakova PA, Kachmazov GS, Shestakov AI, Kublanov IV, Elcheninov AG. The Bacterial Microbiota of Artisanal Cheeses from the Northern Caucasus. Fermentation. 2023; 9(8):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080719
Chicago/Turabian StyleKochetkova, Tatiana V., Ilya P. Grabarnik, Alexandra A. Klyukina, Kseniya S. Zayulina, Liliya A. Gavirova, Polina A. Shcherbakova, Gennady S. Kachmazov, Andrey I. Shestakov, Ilya V. Kublanov, and Alexander G. Elcheninov. 2023. "The Bacterial Microbiota of Artisanal Cheeses from the Northern Caucasus" Fermentation 9, no. 8: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080719
APA StyleKochetkova, T. V., Grabarnik, I. P., Klyukina, A. A., Zayulina, K. S., Gavirova, L. A., Shcherbakova, P. A., Kachmazov, G. S., Shestakov, A. I., Kublanov, I. V., & Elcheninov, A. G. (2023). The Bacterial Microbiota of Artisanal Cheeses from the Northern Caucasus. Fermentation, 9(8), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080719






