Deep Q-Learning for Gastrointestinal Disease Detection and Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Proposed a two-phase system integrating Q-learning-enhanced CNN for classification and attention-based U-Net for segmentation of gastrointestinal ulcer images.
- Developed a custom CNN model with seven layers (convolutional, ReLU, max pooling, flatten, and fully connected layer) integrated with Q-learning for stable and accurate classification, where a Q-table maps image features to actions based on reward signals.
- Designed an attention-based U-Net with encoder, decoder, and attention blocks to accurately segment lesion regions by emphasizing spatially important features extracted from the encoder.
- The proposed model was evaluated on both publicly available datasets and real patient data to ensure a comprehensive performance assessment.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Methodology
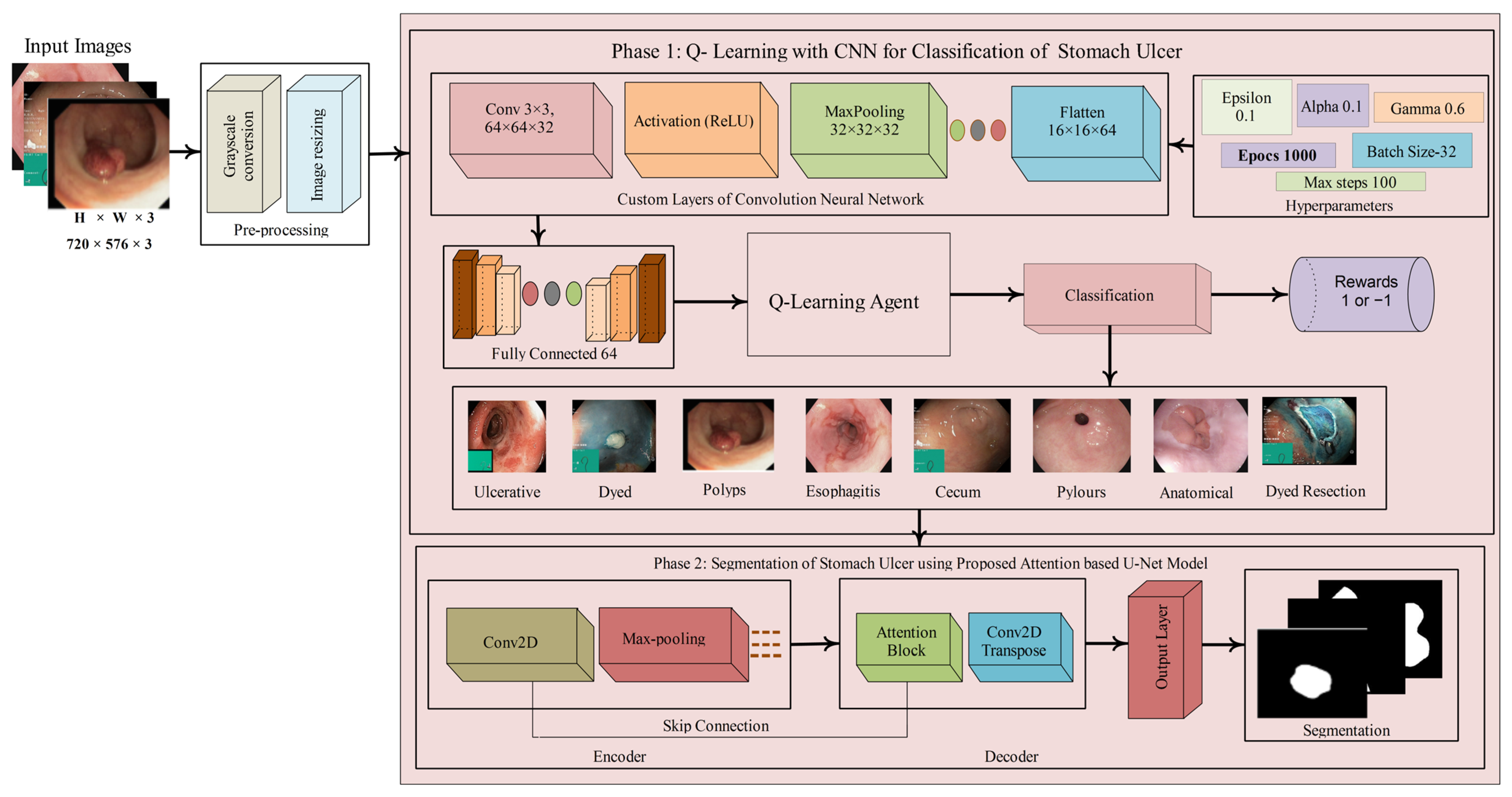
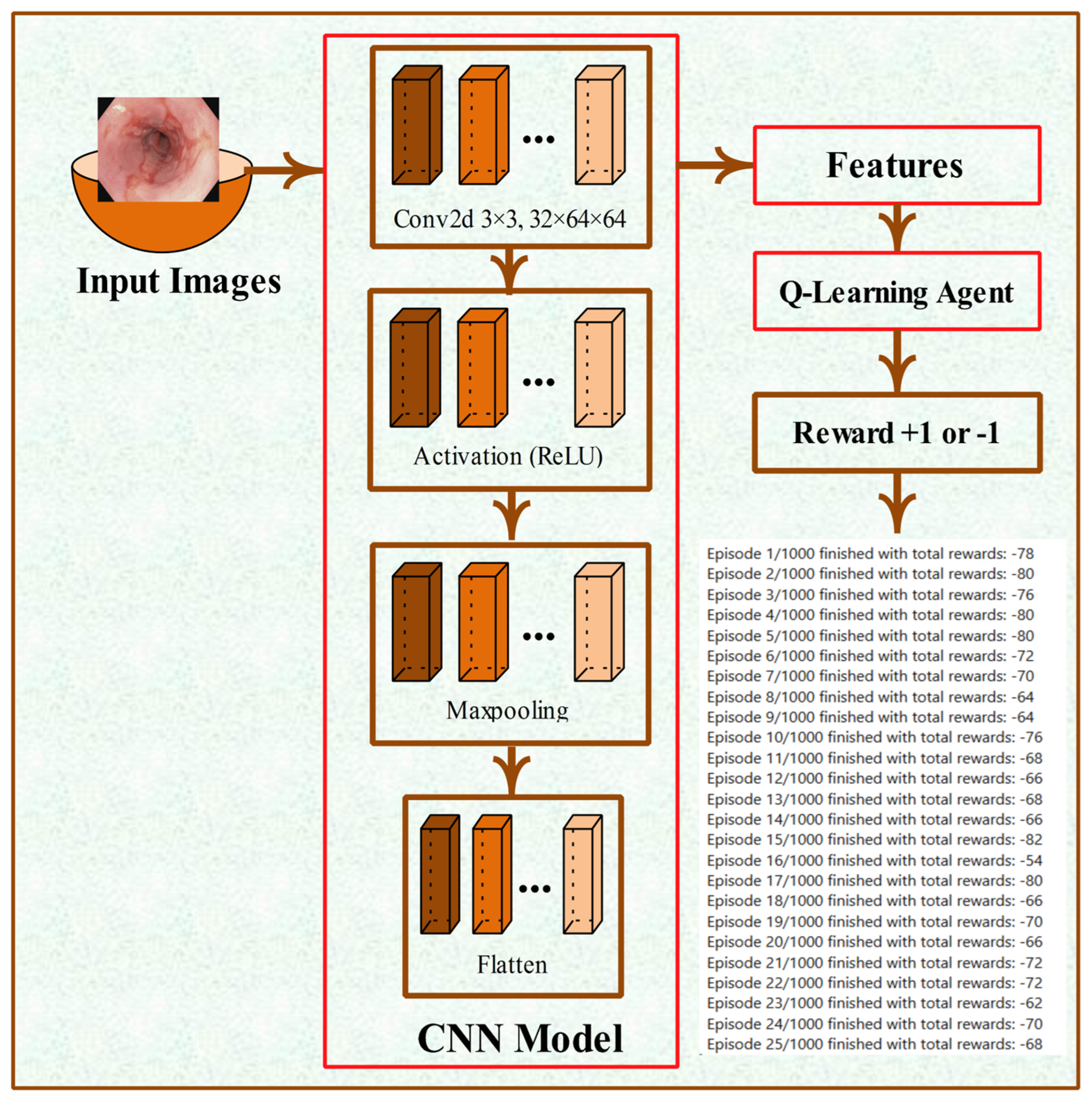
3.1. Stomach Ulcer Classification Using the Proposed Q-Learning with CNN Model
3.2. CNN Architecture and Feature Extraction
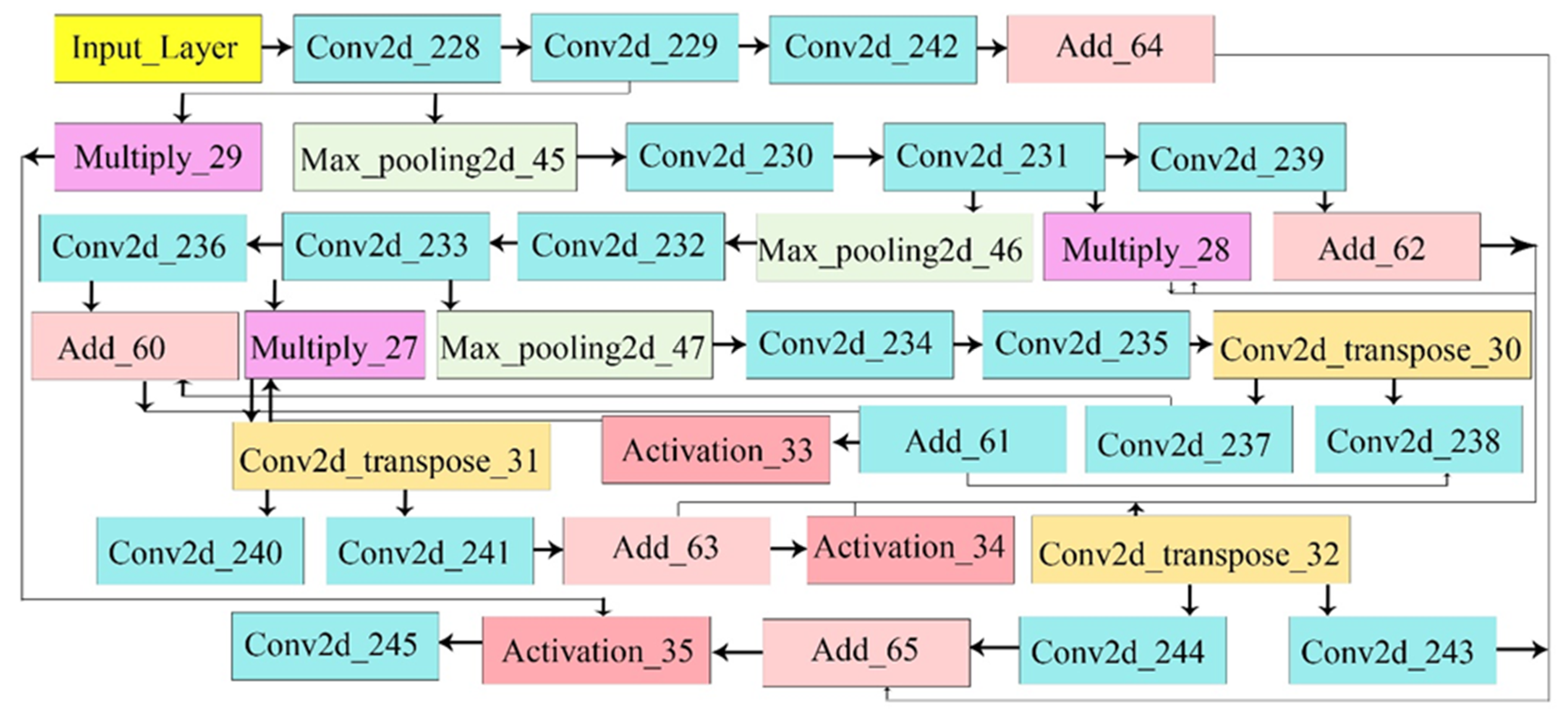
3.3. Proposed U-Net Model
3.3.1. Attention Block
3.3.2. Attention U-Net Architecture
3.3.3. Model Compilation and Training
4. Experimentation and Discussion
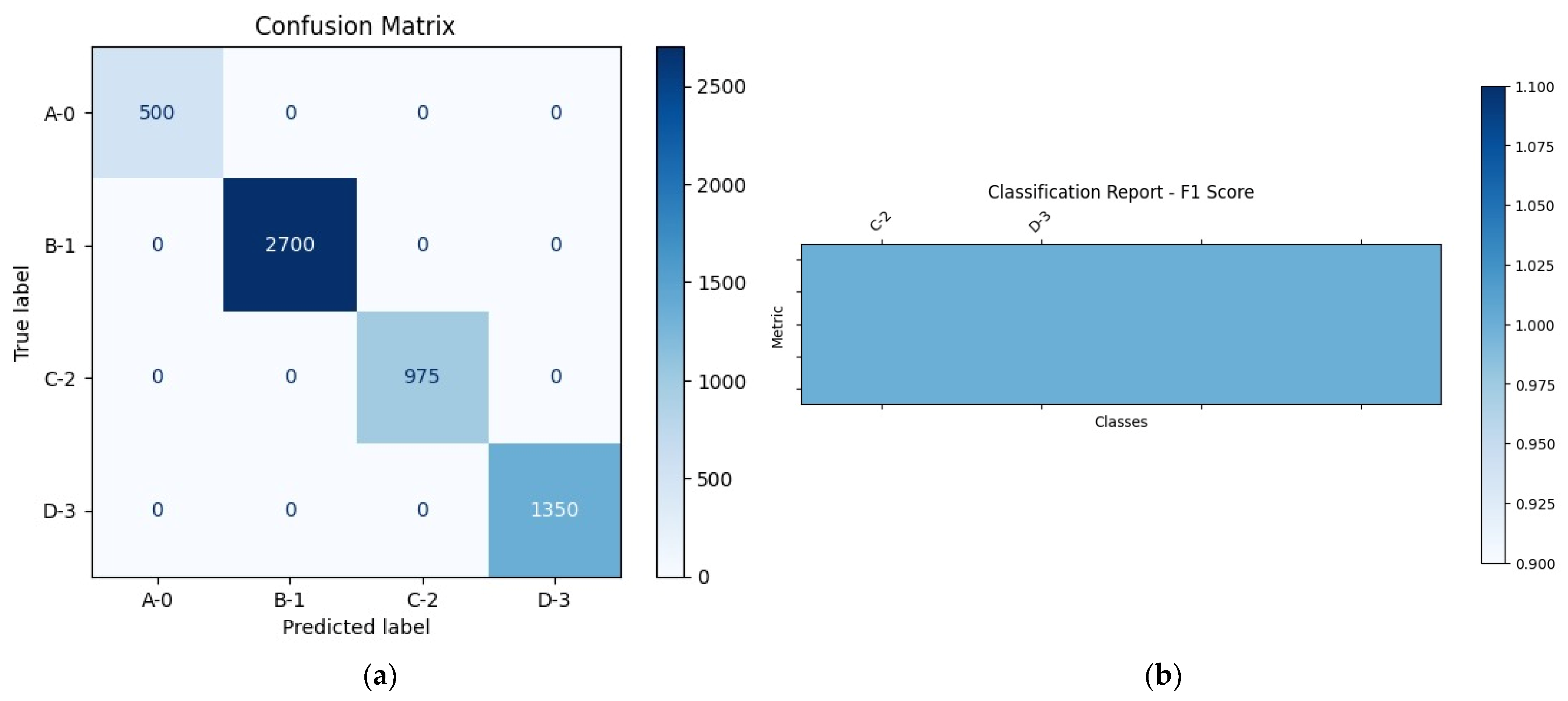
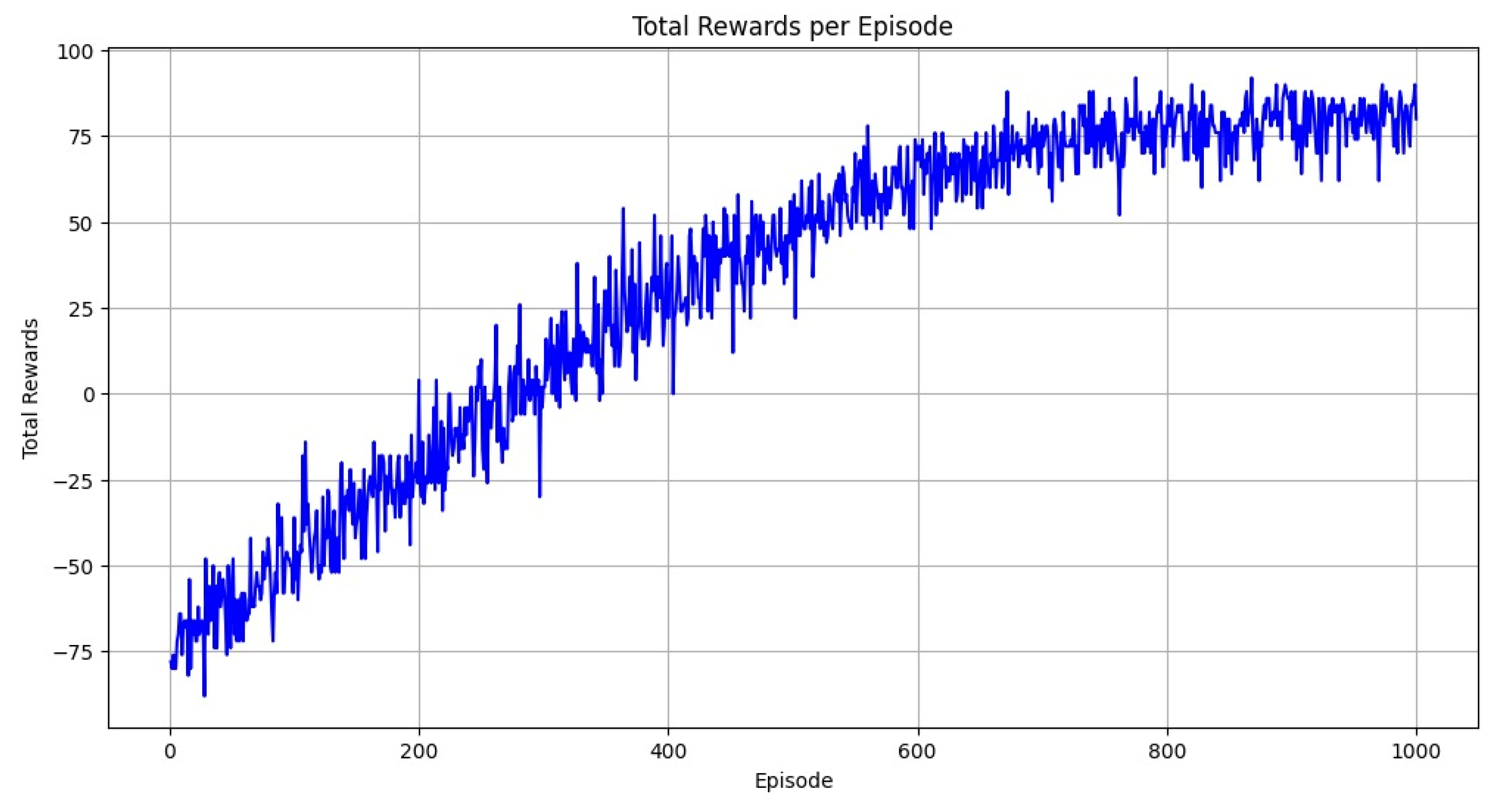
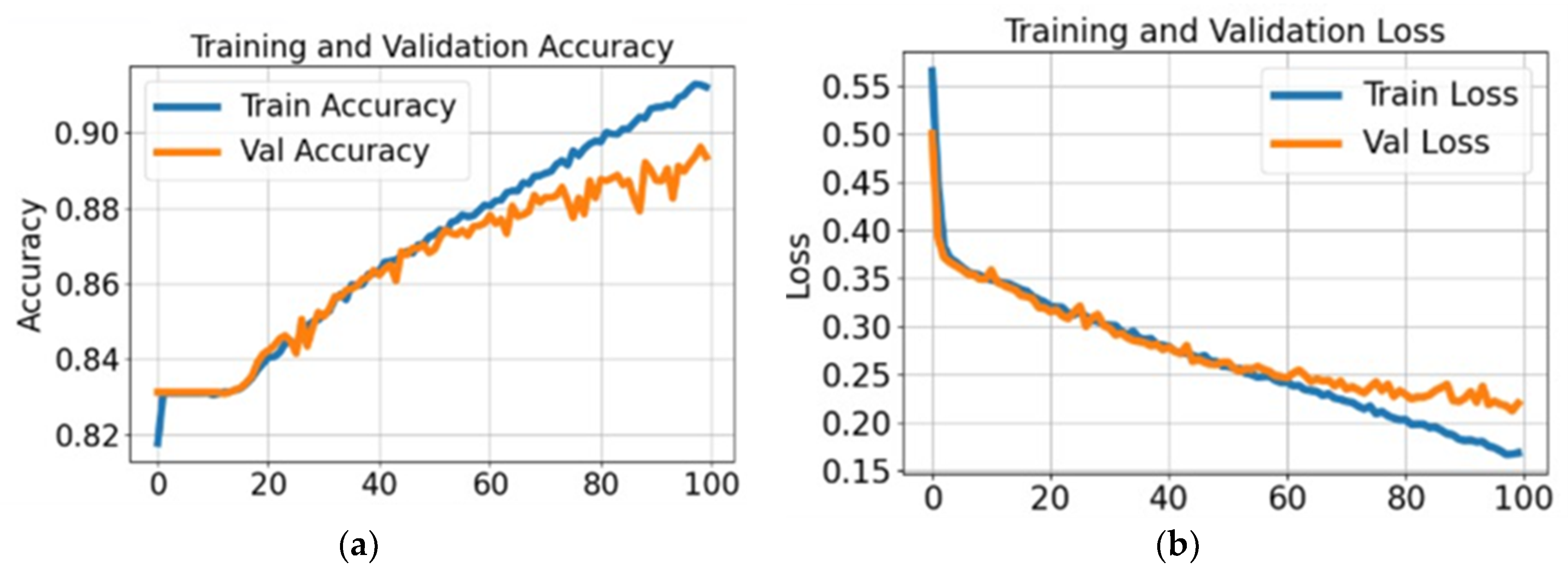
4.1. Experiment #1: Classification of Stomach Disease
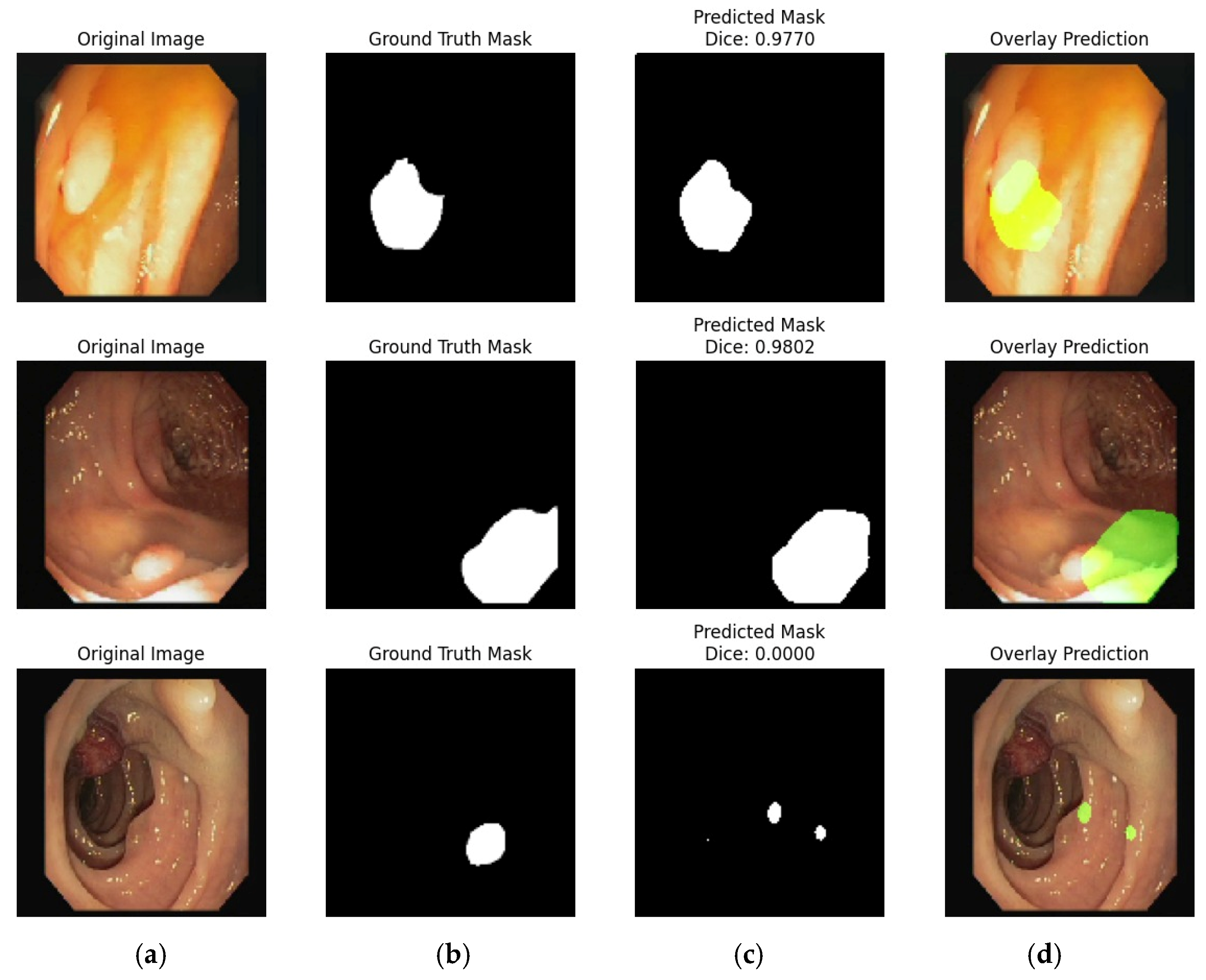
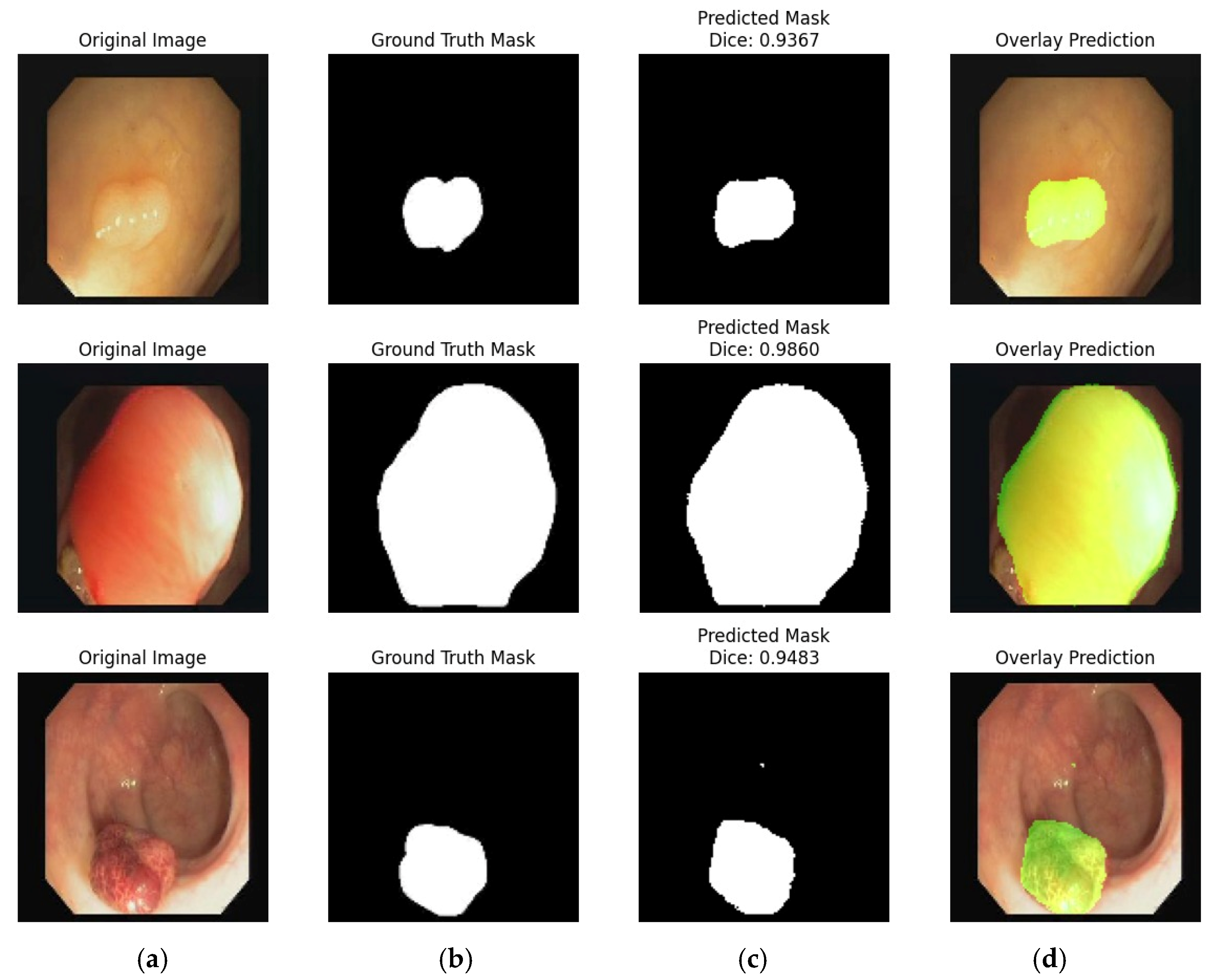
4.2. Experiment #2: Segmentation of the Stomach Ulcer
4.3. Visual Representation of Segmentation Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chase, R.C.; Li, T.; Ramai, D.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Antwi, S.O.; Keaveny, A.P.; Pang, M. Global burden of digestive diseases: A systematic analysis of the global burden of diseases study, 1990 to 2019. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danpanichkul, P.; Suparan, K.; Tothanarungroj, P.; Dejvajara, D.; Rakwong, K.; Pang, Y.; Barba, R.; Thongpiya, J.; Fallon, M.B.; Harnois, D.; et al. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancers: A systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021. Gut 2025, 74, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D. Global, regional, and national burden of 10 digestive diseases in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1061453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okagawa, Y.; Abe, S.; Yamada, M.; Oda, I.; Saito, Y. Artificial intelligence in endoscopy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 1553–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaki, C.; Uche-Anya, E.N.; Berzin, T.M. Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastroenterol. Clin. 2024, 53, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; DeSantis, C.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Du, M.; Schoen, R.E.; Hoffmeister, M.; Newcomb, P.A.; Berndt, S.I.; Caan, B.; Campbell, P.T.; Chan, A.T.; Chang-Claude, J.; et al. Determining risk of colorectal cancer and starting age of screening based on lifestyle, environmental, and genetic factors. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedizadeh, R.; Majidi, F.; Khorasani, H.R.; Abedi, H.; Sabour, D. Colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review of carcinogenesis, diagnosis, and novel strategies for classified treatments. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 729–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, V.; Sakulsaengprapha, V.; Mathews, S.C. The benefit of artificial intelligence-based diagnosis in gastroenterology and hepatology is highly variable: A diagnostic need and burden analysis. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkash, O.; Siddiqui, A.T.S.; Jiwani, U.; Rind, F.; Padhani, Z.A.; Rizvi, A.; Hoodbhoy, Z.; Das, J.K. Diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence for detecting gastrointestinal luminal pathologies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1018937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosain, A.S.; Islam, M.; Mehedi, H.K.; Kabir, I.E.; Khan, Z.T. Gastrointestinal disorder detection with a transformer based approach. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–15 October 2022; pp. 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Lonseko, Z.M.; Adjei, P.E.; Du, W.; Luo, C.; Hu, D.; Zhu, L.; Gan, T.; Rao, N. Gastrointestinal disease classification in endoscopic images using attention-guided convolutional neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.; Sanchez, K.; Hinojosa, C.; Arguello, H.; Castillo, S. Accurate deep learning-based gastrointestinal disease classification via transfer learning strategy. In Proceedings of the 2021 XXIII Symposium on Image, Signal Processing and Artificial Vision (STSIVA), Popayan, Colombia, 15–17 September 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, S.; He, X. A review of deep learning methods for gastrointestinal diseases classification applied in computer-aided diagnosis system. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2025, 63, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.F.; Ramzan, M.; Raza, M.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, K.; Kim, T.; Cha, J.-H. Deep convolutional neural networks for accurate classification of gastrointestinal tract syndromes. CMC-Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 78, 1207–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambay, V.Y.; Barua, P.D.; Baig, A.H.; Dogan, S.; Baygin, M.; Tuncer, T.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of gastrointestinal diseases using resnet50*-based explainable deep feature engineering model with endoscopy images. Sensors 2024, 24, 7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbaş, A.A.; Üzen, H.; Fırat, H. Spatial-attention convmixer archi- tecture for classification and detection of gastrointestinal diseases using the kvasir dataset. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2024, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, I.; Soygazi, F. Gastrointestinal image classification using deep learning architectures via transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), Mugla, Turkey, 10–12 October 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Regmi, S.; Subedi, A.; Tomar, N.K.; Bagci, U.; Jha, D. Vision transformer for efficient chest x-ray and gastrointestinal image classification. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2025: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–20 February 2025; Volume 13407, pp. 912–923. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Goel, P.; Kapoor, N. Stomach Cancer Prediction and Detection using Deep Learning: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Machine Learning and Autonomous Systems (ICMLAS), Prawet, Thailand, 10–12 March 2025; pp. 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Bamini, A. MNETGIDD: A heuristic-oriented segmentation and deep learning multi-disease detection model for gastrointestinal tracts. Int. J. Syst. Innov. 2025, 9, 129–149. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, P.L.; Jana, S. Gastrointestinal tract disease detection via deep learning based Duo-Feature Optimized Hexa-Classification model. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2025, 100, 106994. [Google Scholar]
- Bajhaiya, D.; Unni, S.N. Deep learning-enabled detection and localization of gastrointestinal diseases using wireless-capsule endoscopic images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2024, 93, 106125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, A.S.N.; Jayavel, K.; Rajalakshmi, T.; Rajababu, M. Crcfusion- aicadx: Integrative cnn-lstm approach for accurate colorectal cancer diagnosis in colonoscopy images. Cogn. Comput. 2025, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Q.; He, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, R.; Qu, R.; Qiu, G. Cfformer: Cross cnn-transformer channel attention and spatial feature fusion for improved segmentation of low quality medical images. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.03629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Fan, K.; Ma, H. Federal learning-based a dual-branch deep learning model for colon polyp segmentation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 84, 10425–10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikha, R.; Jamal, D.N.; Rafiammal, S.S. An approach of polyp segmentation from colonoscopy images using dilated-u-net-seg–a deep learning network, Biomedical Signal Processing and Control. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2024, 93, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, M.; E Mobeen, N.; Imran, A.S.; Daudpota, S.M.; Kastrati, Z.; Cheikh, F.A.; Ullah, M. Deep insights into gastrointestinal health: A compre- hensive analysis of gastrovision dataset using convolutional neural networks and explainable ai. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2025, 102, 107260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oukdach, Y.; Garbaz, A.; Kerkaou, Z.; El Ansari, M.; Koutti, L.; Papachrysos, N.; El Ouafdi, A.F.; de Lange, T.; Distante, C. Vision transformer distillation for enhanced gastrointestinal abnormality recognition in wireless capsule endoscopy images. J. Med. Imaging 2025, 12, 014505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, A.S.N.; Venkatesh, K.; Padmaja, B.; Reddy, G.S. GiensemformerCADx: A hybrid ensemble learning approach for enhanced gastrointestinal cancer recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 46283–46323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Anand, V.; Gupta, S.; Almogren, A.; Bharany, S.; Altameem, A.; Rehman, A.U. Enhanced detection of colon diseases via a fused deep learning model with an auxiliary fusion layer and residual blocks on endoscopic images. Curr. Med. Imaging Former. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2025, 21, e15734056353246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Shafiq, U.; Hamza, A.; Mirza, A.M.; Baili, J.; AlHammadi, D.A.; Cho, H.-C.; Chang, B. A novel network-level fused deep learning architecture with shallow neural network classifier for gastrointestinal cancer classification from wireless capsule endoscopy images, BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2025, 25, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, D.; Omura, H.; Minamoto, T.; Minamoto, M. Detection and classification method for early-stage colorectal cancer using dyadic wavelet packet transform. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 9276–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Fan, K.; Xu, C.; Ma, H.; Jiao, K. Cmnet: Deep learning model for colon polyp segmentation based on dual-branch structure. J. Med. Imaging 2024, 11, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Mu, Y.; Ma, C.; He, Q. Tfcnet: A texture-aware and fine-grained feature compensated polyp detection network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 171, 108144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiziloluk, S.; Yildirim, M.; Bingol, H.; Alatas, B. Multi-feature fusion and dandelion optimizer based model for automatically diagnosing the gastrointestinal diseases. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelov, K.; Randel, K.R.; Griwodz, C.; Eskeland, S.L.; de Lange, T.; Johansen, D.; Spampinato, C.; Dang-Nguyen, D.-T.; Lux, M.; Schmidt, P.T.; et al. Kvasir: A multi-class image dataset for computer aided gastrointestinal disease detection. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM on Multimedia Systems Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–23 June 2017; pp. 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Pogorelov, K.; Randel, K.R.; de Lange, T.; Eskeland, S.L.; Griwodz, C.; Johansen, D.; Spampinato, C.; Taschwer, M.; Lux, M.; Schmidt, P.T.; et al. Nerthus: A bowel preparation quality video dataset. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM on Multimedia Systems Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–23 June 2017; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, J.; Sánchez, F.J.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.; Gil, D.; Rodríguez, C.; Vilariño, F. Wm-dova maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: Validation vs. saliency maps from physicians, Computerized medical imaging and graphics. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2015, 43, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Raza, M.; Sharif, M.; Khan, M.A.; Nam, Y. Gastrointestinal tract infections classification using deep learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 69, 3239–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Raza, M.; Sharif, M.I.; Azam, F.; Kim, J.; Kadry, S. Gastrointestinal tract disorders classification using ensemble of InceptionNet and proposed GITNet based deep feature with ant colony optimization. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, X.; Raj, A.P.W.; Evangeline, C.S.; Neebha, T.M.; Kumaravelu, V.B.; Manimegalai, P. Multi-class Classification of Gastrointestinal Diseases using Deep Learning Techniques. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, D.; Theja, G.; Prusty, M.R.; Chinara, S. Efficient colorectal polyp segmentation using wavelet transformation and adaptunet: A hybrid u-net. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.; Tapu, S.; Sarkar, N.K.; Ali, F.B.; Sabrin, L. Med-2d segnet: A light weight deep neural network for medical 2d image segmentation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.14715. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, W.; Zhu, X.; Cheikh, F.A.; Ullah, M.; Imaizumi, M.; Murono, S.; Kubota, S. A simple framework for depth-augmented contrastive learning for endoscopic image classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinimoxon, L. Polyp Detection Using U-Net Deep Learning Method. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2024, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, O.; Yilmaz, B. Tree-net: Enhancing medical image segmentation through efficient low-level feature training. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.02140. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Ali, S.; Emanuelsen, K.; Hicks, S.A.; Thambawita, V.; Garcia-Ceja, E.; Riegler, M.A.; de Lange, T.; Schmidt, P.T.; Johansen, H.D.; et al. Kvasir-instrument: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tool Segmentation Dataset in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. In MultiMedia Modeling, Proceedings of the 27th International Conference, MMM 2021, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–24 June 2021; Proceedings, Part II 27; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 218–229. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitru, R.G.; Peteleaza, D.; Craciun, C. Using DUCK-Net for polyp image segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gautam, A.; Maji, P.; Pachori, R.B.; Balabantaray, B.K. Li-segpnet: Encoder-decoder mode lightweight segmentation network for colorectal polyps analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 70, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, J.; Sharif, M.; Gul, E.; Nayak, R.S. 3D-semantic segmentation and classification of stomach infections using uncertainty aware deep neural networks. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 3041–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, V.; Wittenberg, T.; Raithel, M.; Bruns, V.; Lehmann, E.; Eixelberger, T.; Hackner, R. Automatic detection of foreign objects and contaminants in colonoscopic video data using deep learning. In Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2022; Volume 8, pp. 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Huang, B.; Chen, L.; Xu, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T. Colorectal polyp segmentation using a fully convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), Shanghai, China, 14–16 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. Doubleu-net: A deep convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rochester, MN, USA, 28–30 July 2020; pp. 558–564. [Google Scholar]


| Hyperparmeter | Value |
|---|---|
| α | 0.1 |
| γ | 0.6 |
| ε | 0.1 |
| Episodes | 1000 |
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Img Size | (64, 64) |
| Num Classes | 8 |
| Loss | BinaryCrossentropy |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 8 |
| Segmenter | Attention-Based U-Net |
| Epochs | 50 |
| Ref. # | Year | Datasets | Classes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | 2017 | Kvasir | 8 | 8000 |
| [38] | 2017 | Nerthus | 4 | 5525 |
| [39] | 2015 | CVC-ClinicDB | 1 | 1224 |
| [37] | 2017 | Kvasir Segmentation | 1 | 1800 |
| [38] | 2017 | Nerthus Segmentation | 1 | 826 |
| 2022 | POF Private Dataset | 2 | 600 |
| Episodes | Rewards | Episodes | Rewards |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 94 | 21 | 94 |
| 2 | 84 | 22 | 84 |
| 3 | 92 | 23 | 88 |
| 4 | 90 | 24 | 84 |
| 5 | 86 | 25 | 88 |
| 6 | 82 | 26 | 92 |
| 7 | 92 | 27 | 78 |
| 8 | 88 | 28 | 96 |
| 9 | 86 | 29 | 78 |
| 10 | 74 | 30 | 92 |
| 11 | 82 | 31 | 92 |
| 12 | 88 | 32 | 84 |
| 13 | 84 | 33 | 80 |
| 14 | 84 | 34 | 86 |
| 15 | 82 | 35 | 78 |
| 16 | 74 | 36 | 86 |
| 17 | 90 | 37 | 84 |
| 18 | 82 | 38 | 84 |
| 19 | 76 | 39 | 90 |
| 20 | 76 | 40 | 90 |
| Classes | Accuracy | F1 Score | Recall | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-0 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| B-1 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| C-2 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| D-3 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Classes | Accuracy | F1 Score | Recall | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyed-lifted-polyps (DLP) | 99% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Dyed-resection-margins (DRM) | 99% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Esophagitis (E) | 99% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Normal-cecum (NC) | 99% | 99% | 100% | 99% |
| Normal-pylorus (NP) | 99% | 99% | 100% | 99% |
| Normal-z-line (NZL) | 99% | 99% | 99% | 98% |
| Polyps (P) | 99% | 98% | 99% | 97% |
| Ulcerative-colitis (UC) | 99% | 97% | 95% | 100% |
| Ref. # | Year | Datasets | Accuracy% |
|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | 2021 | Nerthus | 95.0 |
| [41] | 2023 | Kvasir | 99.0 |
| [15] | 2024 | Kvasir | 98.2 |
| [42] | 2023 | Kvasir | 96.8 |
| [16] | 2024 | Kvasir | 92.0 |
| [17] | 2024 | Kvasir | 93.3 |
| [18] | 2024 | Kvasir | 88.6 |
| [19] | 2025 | Kvasir | 94.3 F-score |
| Proposed Method | Nerthus | 100 | |
| Kvasir | 99.08 | ||
| Datasets | Accuracy | Dice Score | IOU | Epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kvasir | 0.9809 | 0.9359 | 0.8795 | 50 |
| Nerthus | 0.9977 | 0.9871 | 0.9746 | 50 |
| CVC-ClinicDB | 0.9849 | 0.9189 | 0.8500 | 50 |
| POF Private dataset | 0.9913 | 0.8845 | 0.7929 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saba, A.; Amin, J.; Ali, M.U. Deep Q-Learning for Gastrointestinal Disease Detection and Classification. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111184
Saba A, Amin J, Ali MU. Deep Q-Learning for Gastrointestinal Disease Detection and Classification. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111184
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaba, Aini, Javaria Amin, and Muhammad Umair Ali. 2025. "Deep Q-Learning for Gastrointestinal Disease Detection and Classification" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111184
APA StyleSaba, A., Amin, J., & Ali, M. U. (2025). Deep Q-Learning for Gastrointestinal Disease Detection and Classification. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111184






