Coagulated Mineral Adsorbents for Dye Removal, and Their Process Intensification Using an Agitated Tubular Reactor (ATR)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
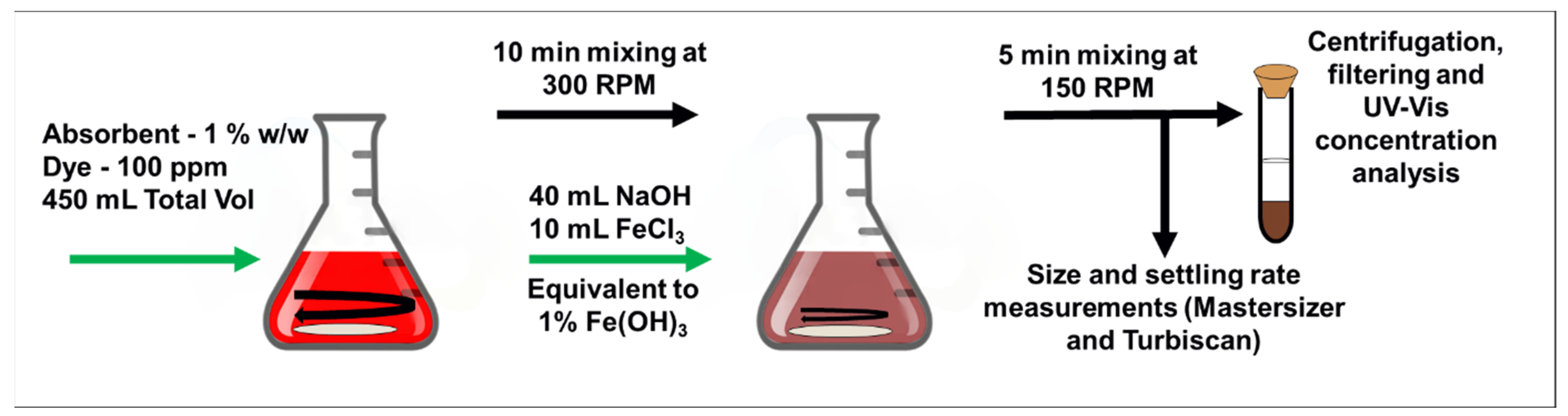
2.2. Batch Adsorption and Coagulation Studies
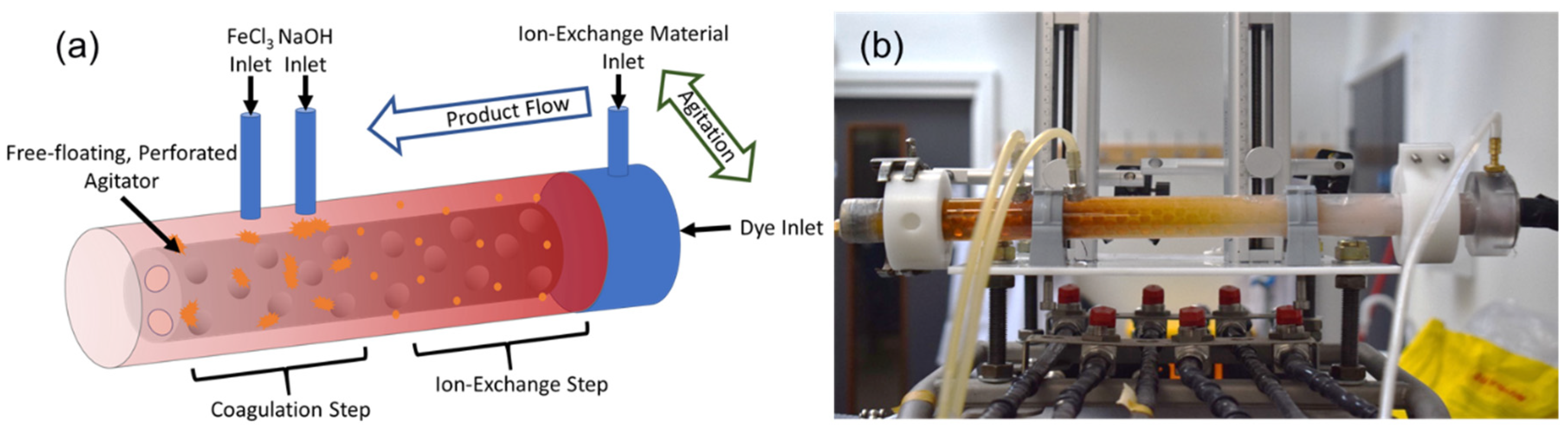
2.3. Process Intensification in an ATR
3. Results and Discussion
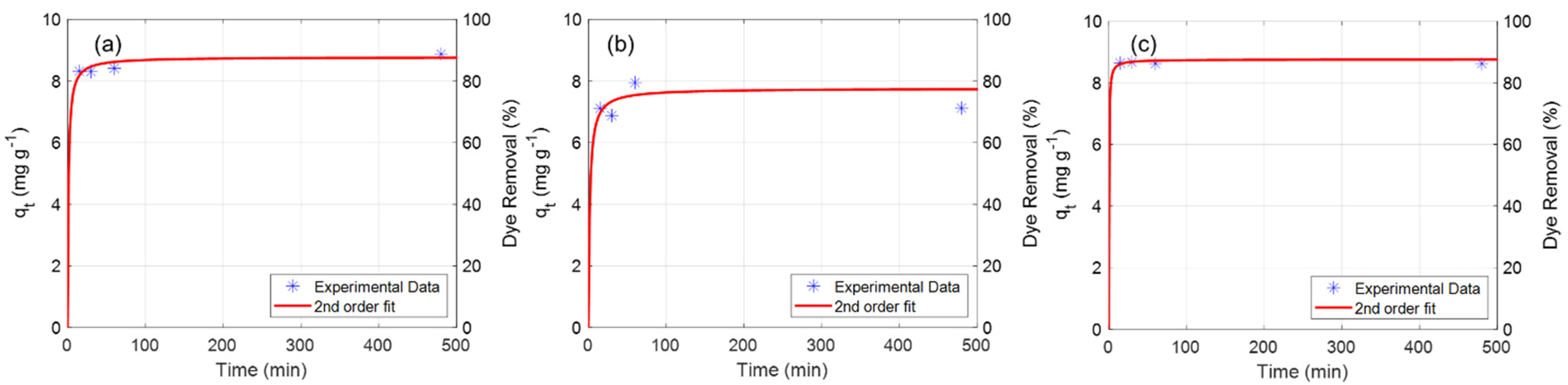
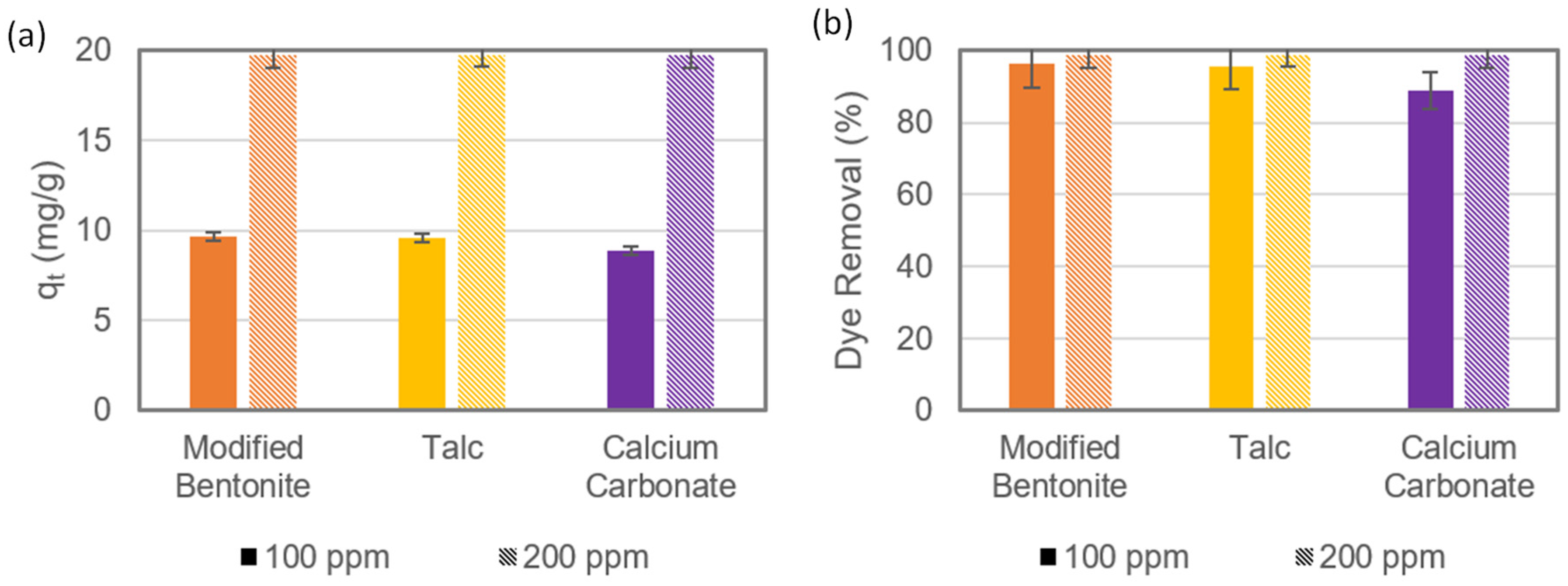
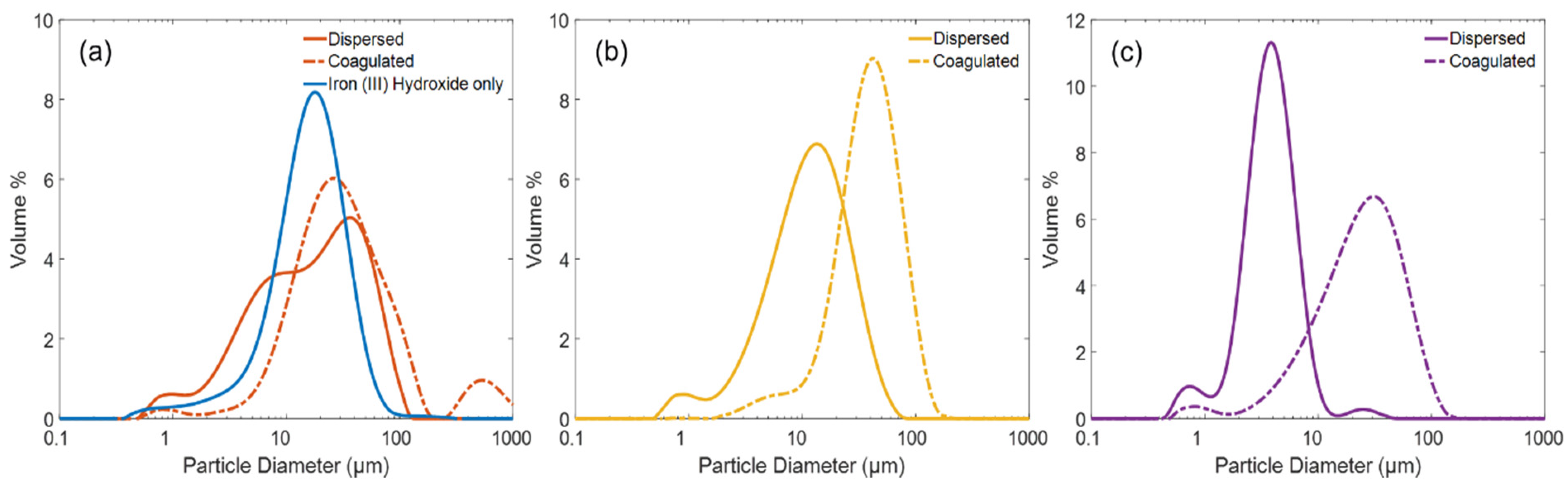
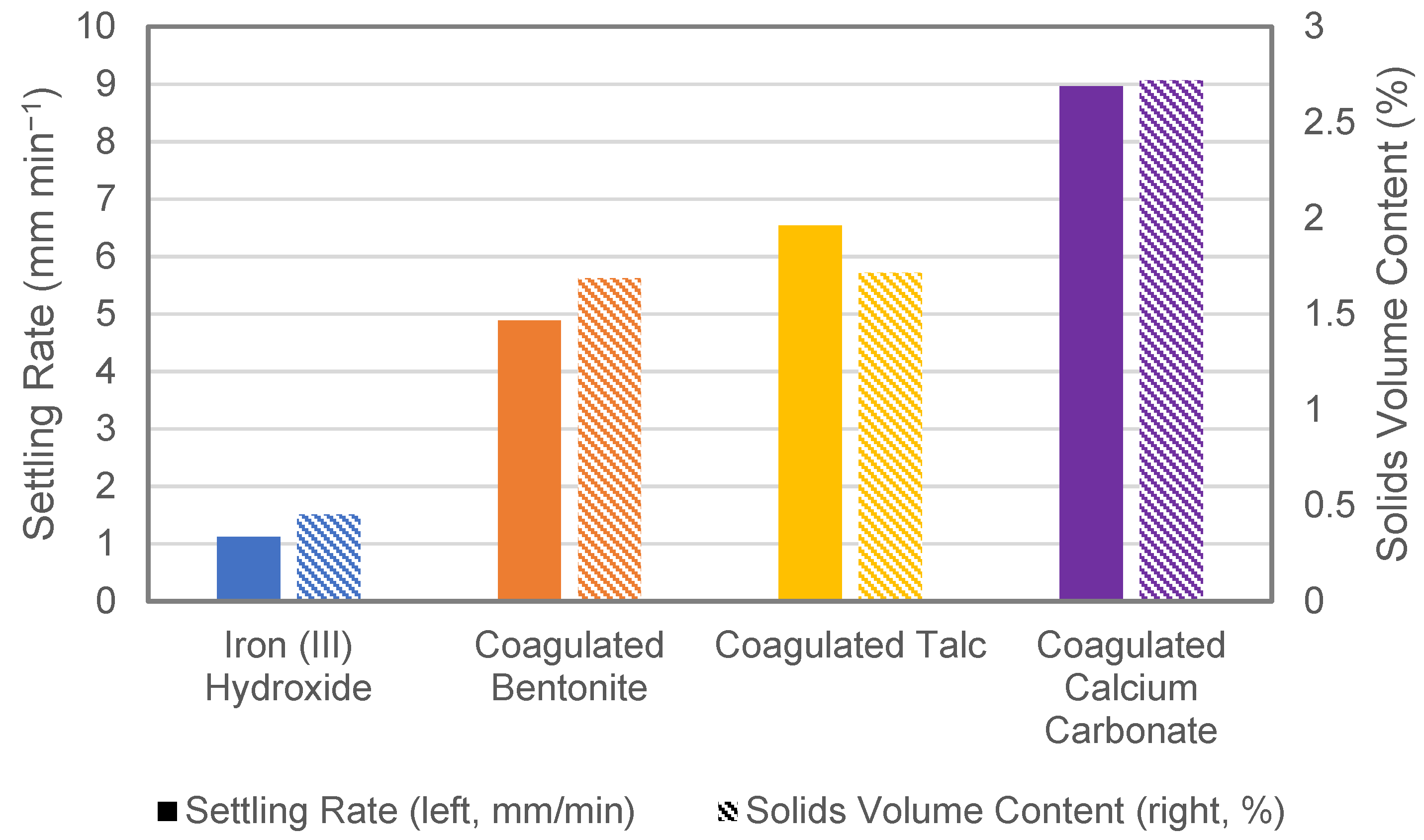
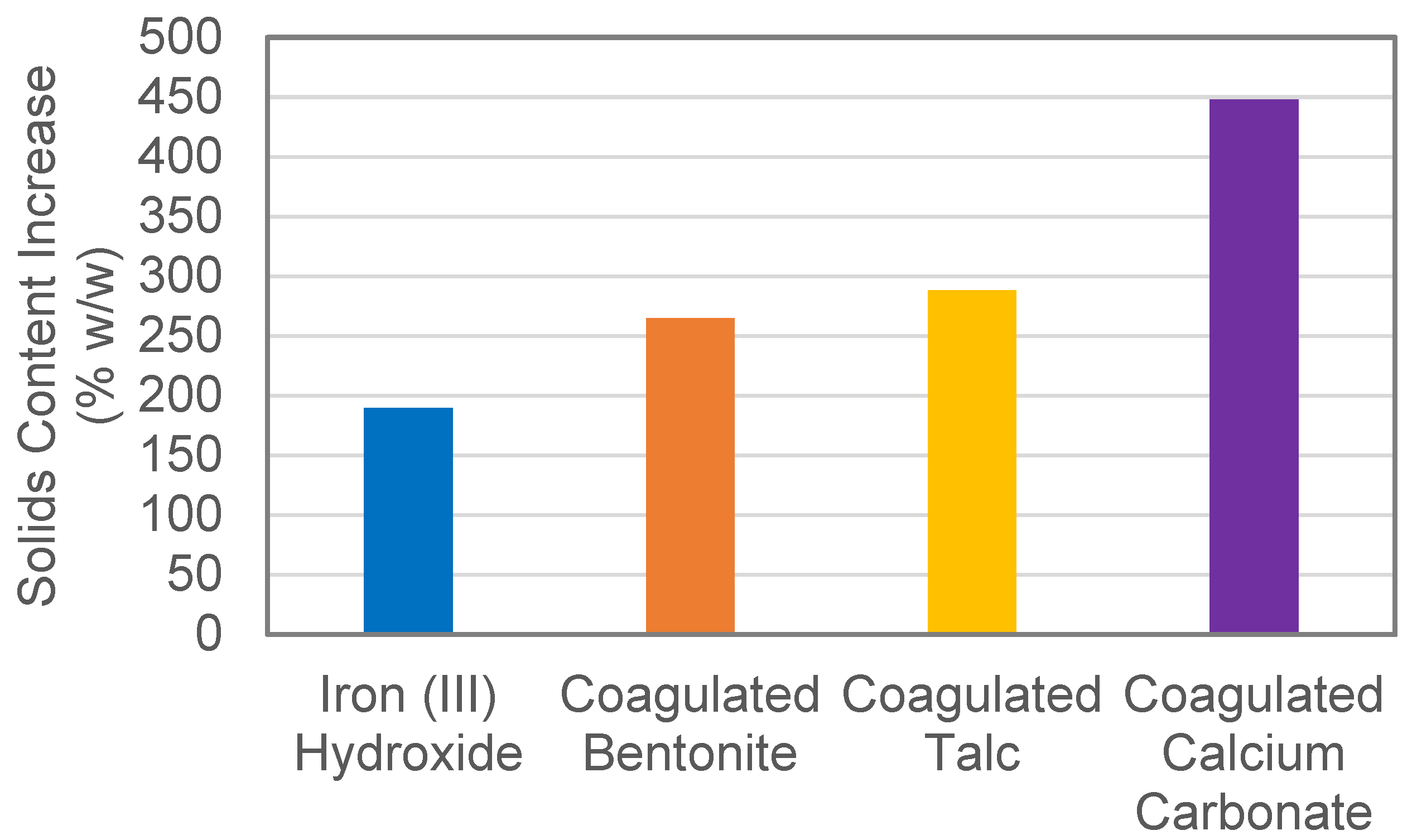
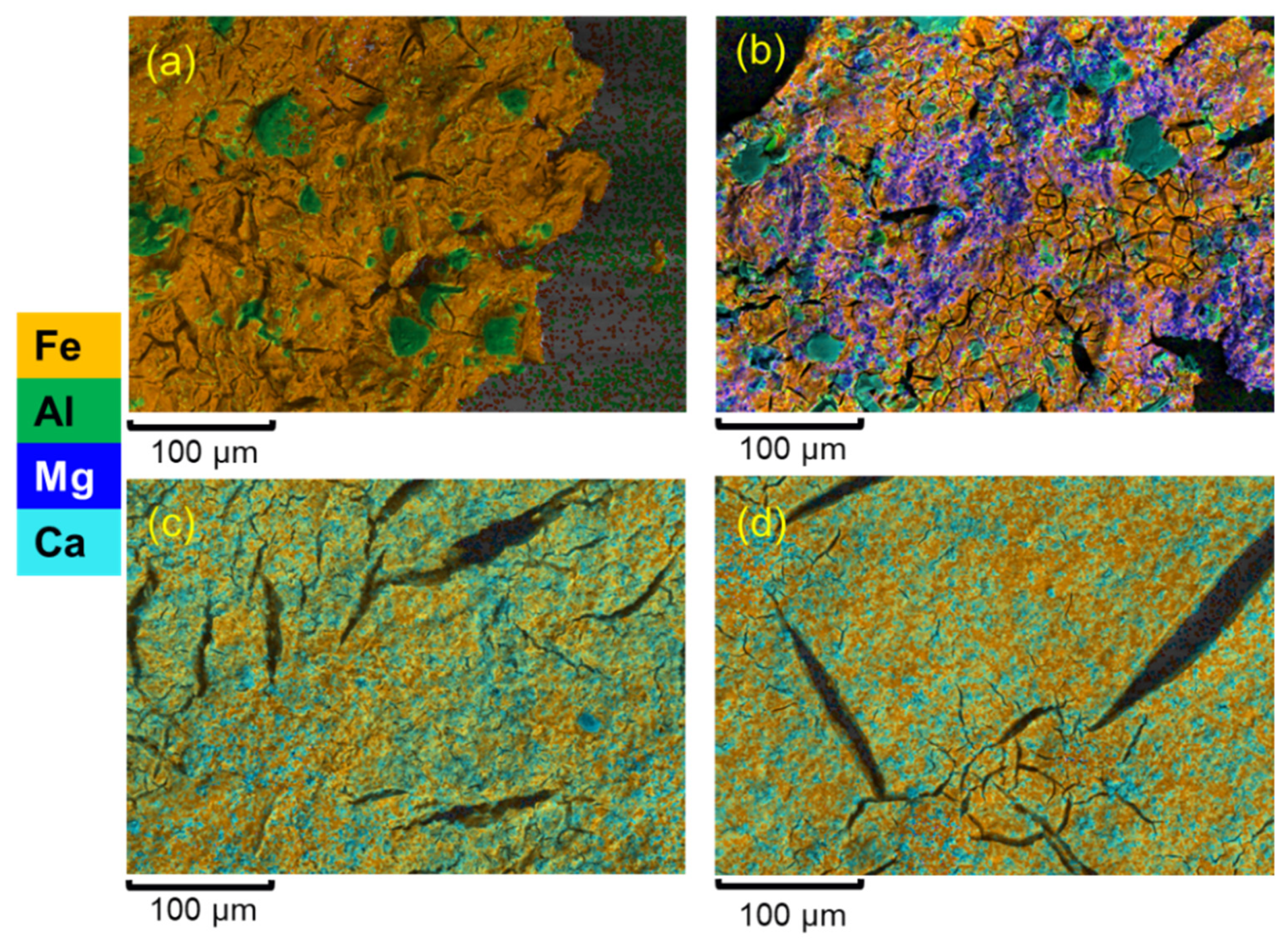
3.1. Performance of Adsorbents and Physical Characterisation of Composite Coagulate Flocs
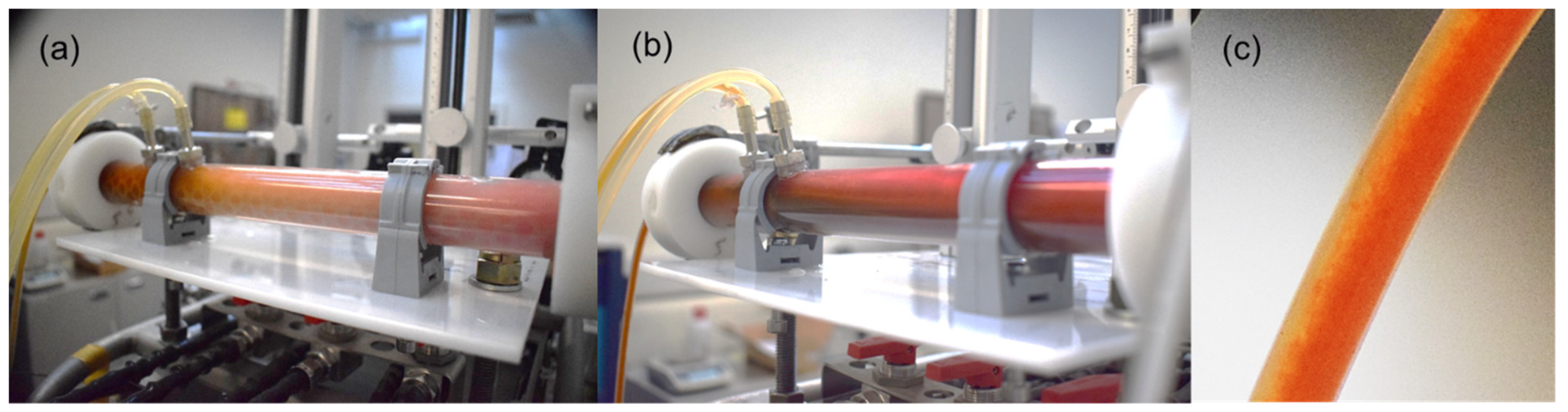
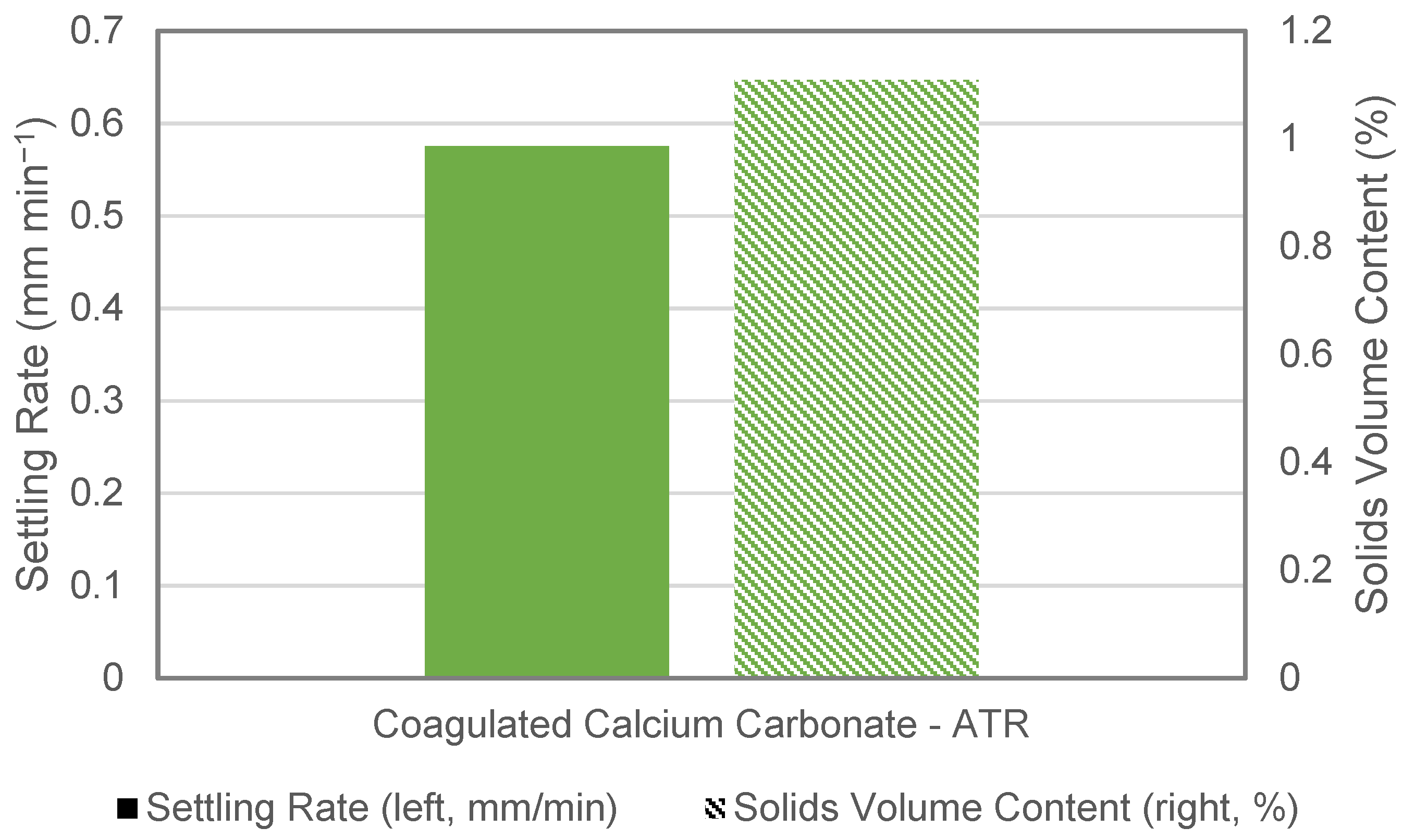
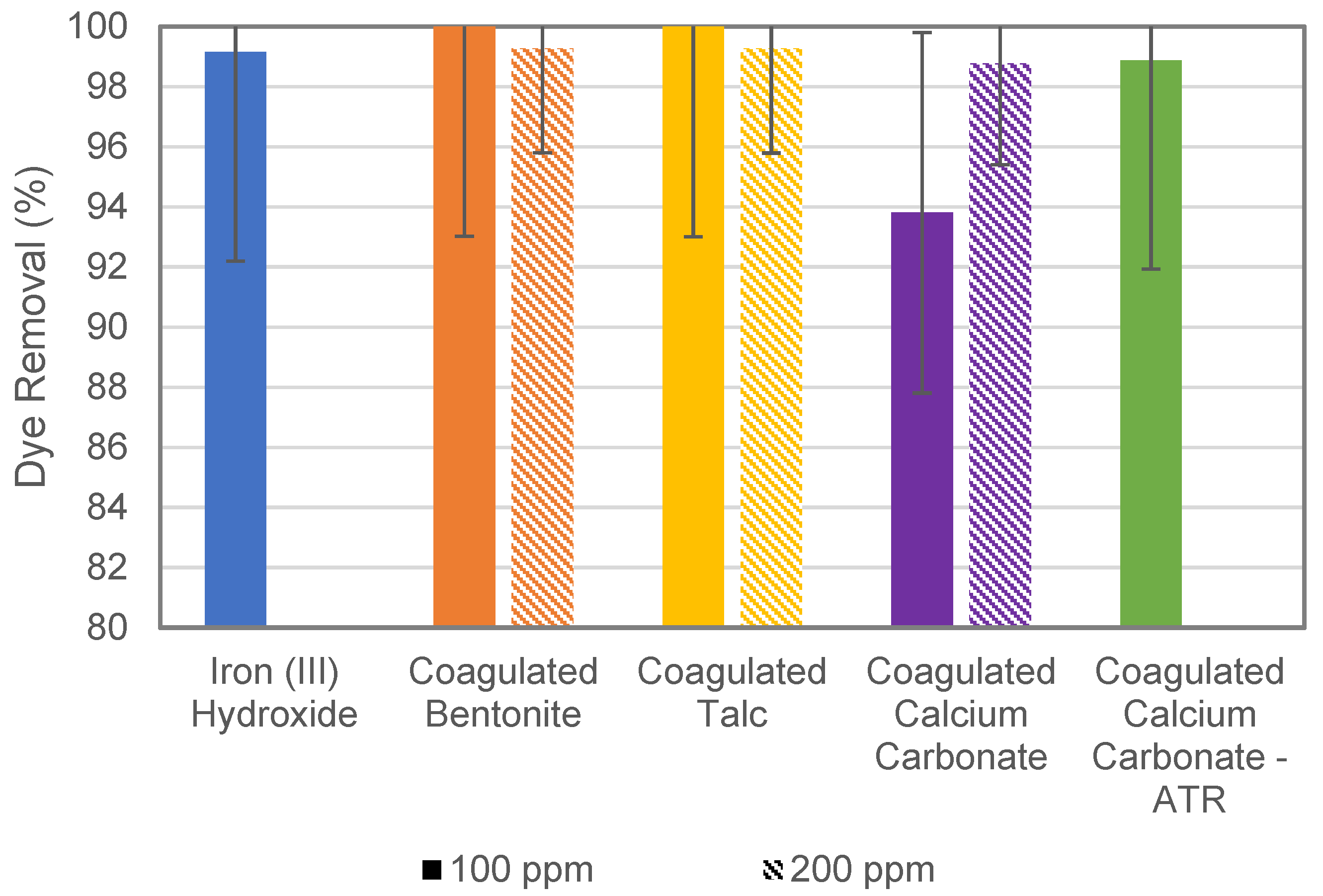
3.2. ATR Assessment and Overall Dye Removal Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furlan, F.R.; de Melo da Silva, L.G.; Morgado, A.F.; de Souza, A.A.U.; Guelli Ulson de Souza, S.M.A. Removal of reactive dyes from aqueous solutions using combined coagulation/flocculation and adsorption on activated carbon. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-T.; Li, M.; Li, J.-H.; Sun, H.-W. Decolorization of azo dye direct scarlet 4BS solution using exfoliated graphite under ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y. Biosorption of Direct Fast Scarlet 4BS from aqueous solution using the green-tide-causing marine algae Enteromorpha prolifera. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 223, 117347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, M.; Dinari, M. Synthesis of new imine-linked covalent organic framework as high efficient absorbent and monitoring the removal of direct fast scarlet 4BS textile dye based on mobile phone colorimetric platform. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchana-Rosero, M.; Lima, E.; Mella, B.; Costa, D.; Poll, E.; Gutterres, M. A coagulation-flocculation process combined with adsorption using activated carbon obtained from sludge for dye removal from tannery wastewater. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2018, 63, 3867–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.H.; Chen, M.L. Purification of textile wastewater effluents by a combined Fenton process and ion exchange. Desalination 1997, 109, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri Moghaddam, S.; Alavi Moghaddam, M.R.; Arami, M. Coagulation/flocculation process for dye removal using sludge from water treatment plant: Optimization through response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wong, L.M.; Wong, L.H.; Chiam, S.Y.; Li, S.F.Y.; Ren, Y. Immobilization of dye pollutants on iron hydroxide coated substrates: Kinetics, efficiency and the adsorption mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13280–13288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papić, S.; Koprivanac, N.; Lončarić Božić, A.; Meteš, A. Removal of some reactive dyes from synthetic wastewater by combined Al(III) coagulation/carbon adsorption process. Dyes Pigment. 2004, 62, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Choi, S.-P.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Shim, W.-G.; Moon, H. Evaluation of the performance of adsorption and coagulation processes for the maximum removal of reactive dyes. Dyes Pigment. 2006, 69, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez, J.M.; Allen, S.J.; Walker, G.M. Reactive dye adsorption onto a novel mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc-Grabowska, E.; Gryglewicz, G.; Gryglewicz, S. Development of mesoporosity in activated carbons via coal modification using Ca- and Fe-exchange. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 76, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derylo-Marczewska, A.; Marczewski, A.W.; Winter, S.; Sternik, D. Studies of adsorption equilibria and kinetics in the systems: Aqueous solution of dyes–mesoporous carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5164–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wu, Z.; Cravotto, G.; Manzoli, M.; Cintas, P.; Wu, Z. Cork wastewater purification in a cooperative flocculation/adsorption process with microwave-regenerated activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.G.; Wells, J.D.; Johnson, B.B. Selective adsorption of dyes and other organic molecules to kaolinite and oxide surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 180, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armağan, B.; Turan, M.; ęlik, M.S. Equilibrium studies on the adsorption of reactive azo dyes into zeolite. Desalination 2004, 170, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.M.; Hansen, L.; Hanna, J.-A.; Allen, S.J. Kinetics of a reactive dye adsorption onto dolomitic sorbents. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, S.K.A.; Üstün, G.E.; Birgül, A.; Taşdemir, Y. Treatability studies with chemical precipitation and ion exchange for an organized industrial district (OID) effluent in Bursa, Turkey. Desalination 2007, 217, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younker, J.M.; Walsh, M.E. Bench-scale investigation of an integrated adsorption–coagulation–dissolved air flotation process for produced water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajitno, M.Y.; Tangparitkul, S.; Zhang, H.; Harbottle, D.; Hunter, T.N. The effect of cationic surfactants on improving natural clinoptilolite for the flotation of cesium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Zhou, W.; Yue, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Shen, X. The Combination of Coagulation and Adsorption for Controlling Ultra-Filtration Membrane Fouling in Water Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ismail, S.; Bhatia, S. Optimization of coagulation-flocculation process for palm oil mill effluent using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2828–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, S. Treatment of wastewater from dye manufacturing industry by coagulation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2006, 7, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfang, B.C.; Klein, A.; Grützner, T. Extraction Centrifuges—Intensified Equipment Facilitating Modular and Flexible Plant Concepts. ChemEngineering 2019, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, T.N.; Peakall, J.; Egarr, D.; Cowell, D.M.J.; Freear, S.; Tonge, A.S.; Horton, L.; Rice, H.P.; Smith, I.; Malone, K.; et al. Concentration profiling of a horizontal sedimentation tank utilising a bespoke acoustic backscatter array and CFD simulations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 218, 115560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, S.P.; Spehar, R.; Scales, P.J. Theoretical analysis of aggregate densification: Impact on thickener performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scales, P.J.; Kumar, A.; van Deventer, B.B.G.; Stickland, A.D.; Usher, S.P. Compressional dewatering of flocculated mineral suspensions. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 93, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Gao, B.; Ren, J.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: A review. Water Res. 2018, 143, 608–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chiang, P.-C.; Shah, K.J. Evaluation and optimization of enhanced coagulation process: Water and energy nexus. Water-Energy Nexus 2019, 2, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D.; Boucherit, A. Review of Coagulation’s Rapid Mixing for NOM Removal. J. Res. Dev. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coward, T.; Tribe, H.; Harvey, A.P. Opportunities for process intensification in the UK water industry: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 21, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Mustaffar, A.; Phan, A.N.; Zivkovic, V.; Reay, D.; Law, R.; Boodhoo, K. A review of process intensification applied to solids handling. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 118, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.S. Treatment Plant Operations: Optimize Initial Mixing with Plug-Flow Reactors. Opflow 2002, 28, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.C.; Amirtharajah, A.; Sotiropoulos, F.; Skeens, B.M. Using Static Mixers to Mix Coagulants: CFD Modeling and Pilot-Plant Experiments BT-Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment VI.; Hahn, H.H., Hoffmann, E., Ødegaard, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Derksen, J.J. Mixing in an agitated tubular reactor. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Bayly, A.E.; Hassanpour, A.; Fairweather, M.; Muller, F. Flow behaviour of an agitated tubular reactor using a novel dynamic mesh based CFD model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 212, 115333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kim, Y.K.; Hunter, T.N.; Brown, A.P.; Lee, J.W.; Harbottle, D. Organically modified clay with potassium copper hexacyanoferrate for enhanced Cs+ adsorption capacity and selective recovery by flotation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15130–15143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prajitno, M.Y.; Harbottle, D.; Hondow, N.; Zhang, H.; Hunter, T.N. The effect of pre-activation and milling on improving natural clinoptilolite for ion exchange of cesium and strontium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 102991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, I.G. The impact of effluent regulations on the dyeing industry. Rev. Prog. Color. Relat. Top. 1991, 21, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, T.R. Dye pollution clean-up by synthetic mineral. Int. Dye. 1994, 79, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, J. Colour in textile effluents—The origins of the problem. J. Soc. Dye. Colour. 1994, 110, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildred, K.; Townson, P.; Hutson, G.; Williams, R. Characterisation of particulates in the BNFL Enhanced Actinide Removal Plant. Powder Technol. 2000, 108, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajitno, M.Y.; Taufiqurrakhman, M.; Harbottle, D.; Hunter, T.N. Kinetic studies of Cs+ and Sr2+ ion exchange using clinoptilolite in static columns and an agitated tubular reactor (ATR). ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.-P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyer, T.H. Removal of Dissolved Organic Matter by Magnetic Ion Exchange Resin. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elliott, L.N.; Bourne, R.A.; Hassanpour, A.; Edwards, J.L.; Sutcliffe, S.; Hunter, T.N. Salt enhanced solvent relaxation and particle surface area determination via rapid spin-lattice NMR. Powder Technol. 2018, 333, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Qin, W.; Jiao, F. Depression mechanism of the zinc sulfate and sodium carbonate combined inhibitor on talc. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 501, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremmell, K.E.; Addai-Mensah, J. Interfacial-chemistry mediated behavior of colloidal talc dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q.; Ou, L.; Ouyang, K. Effect of calcium ionic concentrations on the adsorption of carboxymethyl cellulose onto talc surface: Flotation, adsorption and AFM imaging study. Powder Technol. 2018, 331, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tangparitkul, S.; Hendry, B.; Harper, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Hunter, T.N.; Lee, J.W.; Harbottle, D. Selective separation of cesium contaminated clays from pristine clays by flotation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzkiewicz, M. Anion Exchange Resins as Effective Sorbents for Removal of Acid, Reactive, and Direct Dyes from Textile Wastewaters. In Ion Exchange: Studies and Applications; Kilislioglu, Z.H.E.-A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzkiewicz, M. Anion Exchange Resins as Effective Sorbents for Acidic Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions and Wastewaters. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2012, 30, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.; Chandran, B.; Nigam, P. Removal of dyes from a synthetic textile dye effluent by biosorption on apple pomace and wheat straw. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2824–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherill, J.S.; Morris, K.; Bots, P.; Stawski, T.M.; Janssen, A.; Abrahamsen, L.; Blackham, R.; Shaw, S. Ferrihydrite Formation: The Role of Fe13 Keggin Clusters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9333–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehin, S.; kumar Kulandaivelu, J.; Rebosura, M.; van der Kolk, O.; Keller, J.; Doederer, K.; Gernjak, W.; Donose, B.C.; Yuan, Z.; Pikaar, I. Effects of aging of ferric-based drinking water sludge on its reactivity for sulfide and phosphate removal. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Miyafuji, A.; Kandori, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakayama, T. Effect of Cu(II) on the formation, morphology and molecular adsorption properties of α-FeOOH rust particles prepared from acidic Fe(III) solutions. Corros. Sci. 2013, 66, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristić, M.; Opačak, I.; Štajdohar, J.; Musić, S. The influence of CTAB and gum arabic on the precipitation of α-FeOOH in a highly alkaline medium. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1090, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, W.H.; Nutaitis, C.F.; Anderton, C.A. Iron(III) Chloride as a Lewis Acid in the Friedel-Crafts Acylation Reaction. J. Chem. Educ. 1996, 73, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, S. Precipitation of Hematite and Recovery of Hydrochloric Acid from Aqueous Iron(II, III) Chloride Solutions by Hydrothermal Processing; Department of Mining and Materials Engineering, McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rouchon, V.; Belhadj, O. Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate (Bicarbonate) Deacidification. J. Pap. Conserv. 2016, 17, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.B.; Gidley, J.L.; Guin, J.A.; Schechter, R.S. Characterization of Liquid-Solid Reactions. Hydrochloric Acid-Calcium Carbonate Reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1970, 9, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, M.-L.; Wu, H.-M.; Huang, C.-H. Study of the zeta potential of Fe(O)OH colloids. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 5473–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.-A.; Liang, J.-Y.; Li, R.-J.; Hong, Z.; Wang, Y.-J.; Chang, K.-L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Yang, Z.-Y. Aromatic amine contents, component distributions and risk assessment in sludge from 10 textile-dyeing plants. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotonimaro, T.V.; Neculita, C.M.; Bussière, B.; Benzaazoua, M.; Zagury, G.J. Recovery and reuse of sludge from active and passive treatment of mine drainage-impacted waters: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Ning, X.-A.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F. The agricultural use potential of the detoxified textile dyeing sludge by integrated Ultrasound/Fenton-like process: A comparative study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, R.G.; Andersen, L.F.; Maia, L.K.K.; José, H.J.; Moreira, R.d.F.P.M. Recovery of iron oxides from acid mine drainage and their application as adsorbent or catalyst. J. Environ. Man. 2012, 111, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, F.M.; Hunter, T.N.; Holdich, R.G. A study of cake filtration parameters using the constant rate process. Processes 2019, 7, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tonge, A.S.; Harbottle, D.; Casarin, S.; Zervaki, M.; Careme, C.; Hunter, T.N. Coagulated Mineral Adsorbents for Dye Removal, and Their Process Intensification Using an Agitated Tubular Reactor (ATR). ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030035
Tonge AS, Harbottle D, Casarin S, Zervaki M, Careme C, Hunter TN. Coagulated Mineral Adsorbents for Dye Removal, and Their Process Intensification Using an Agitated Tubular Reactor (ATR). ChemEngineering. 2021; 5(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleTonge, Alastair S., David Harbottle, Simon Casarin, Monika Zervaki, Christel Careme, and Timothy N. Hunter. 2021. "Coagulated Mineral Adsorbents for Dye Removal, and Their Process Intensification Using an Agitated Tubular Reactor (ATR)" ChemEngineering 5, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030035
APA StyleTonge, A. S., Harbottle, D., Casarin, S., Zervaki, M., Careme, C., & Hunter, T. N. (2021). Coagulated Mineral Adsorbents for Dye Removal, and Their Process Intensification Using an Agitated Tubular Reactor (ATR). ChemEngineering, 5(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030035






