Abstract
The cement industry, a foundation of global infrastructure development, significantly contributes to environmental pollution. Key sources of pollution include dust emissions; greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide; and the release of toxic substances such as heavy metals and particulate matter. These pollutants contribute to air, water, and soil degradation and are linked to severe health conditions in nearby populations, including respiratory disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and increased mortality rates. Noise pollution is also a significant issue, inducing auditory diseases that affect most workers in cement plants, and disturbing the population living in the neighborhoods and fauna behavior. This review explores the pollution paths and the multifaceted impacts of cement production on the environment. It also highlights the social challenges faced by communities, underscoring the urgent need for stricter environmental policies and the adoption of greener technologies to mitigate the adverse effects of cement production on both the environment and human health.
1. Introduction
Concrete is the second most utilized material (about 30 billion tons yearly) in terms of consumption after water. Its widespread use is largely due to its high compressive strength, durability, and superior mechanical properties compared to other construction materials [1,2,3,4]. It is also preferred in architecture for its versatility (allowing for the creation of unique, modern, and minimalist designs with clean lines and innovative forms) [5,6] and the possibility of adapting to surroundings. These qualities transform it into an aesthetically appealing material in contemporary and sustainable design projects [7].
Concrete manufacturing relies upon more than 4 billion tons of cement produced annually. Concrete is composed of cement, fine and coarse aggregates, and water. Cement is the primary binding agent of concrete and provides it the strength that enables structures to withstand loads [8,9]. Ordinary Portland cement has gradually become one of the most used construction materials for concrete [10,11], being widely used as a construction material due to its availability and easy application process [12,13,14]. It is a vital element in retrofitting structural reinforced concrete (RC) elements because it binds and strengthens the materials, enhancing their durability and load-bearing capacity [15,16,17,18]. Cement substitutes (slag, ground granulated blast furnace slag, fly ash, limestone powder, calcinated clay, ceramic tiles waste, etc.) have been utilized frequently in recent years to improve the properties of concrete and reduce the environmental impact [19,20].
The cement demand exploded in 1960 due to the necessity of durable construction materials. The concrete industry uses around 50% of the cement produced, the other half being utilized for plasters, mortars, and blocks [21]. During 1995–2024, the total cement production increased from 1.39 billion metric tons to over 4 billion tons, with peaks of 4.4 billion tons in 2021 and 2023 (Figure 1) [22,23].
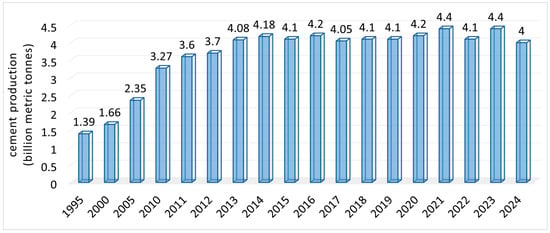
Figure 1.
Worldwide cement manufacturing data from 1995 to 2024 [22,23].
China is the world’s largest cement producer [24], with 1.9 billion metric tons in 2024 (2.1 billion metric tons in 2023 and 2.4 billion metric tons in 2021), i.e., more than half of the world’s production [12,25,26]. The increase in China’s cement production from 1990 was 74% of the worldwide growth [27]. India is the second largest producer in the world, followed by Vietnam, the USA, and Turkey (Figure 2a). In the European Union, Germany is the first-place holder, followed by Spain and Poland (Figure 2b).
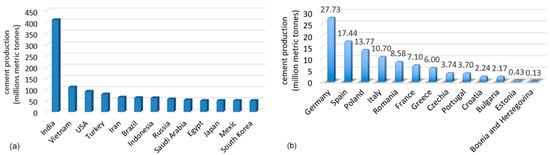
Figure 2.
The biggest cement producers in 2024 (a) worldwide (without China); (b) the biggest manufacturers in European Union. Processed used data available in [22,23,28].
Cement production involves processing raw limestone and other raw materials (e.g., shale, clay, etc.) at high temperatures in a kiln to obtain clinker, which is further mixed with gypsum and ground [29]. Clinker fabrication involves [30] the following:
- Collecting the raw material—calcium carbonate (mainly), shale, sand or clay, and bauxite, in small quantities (depending on the receipt).
- Crushing the raw material into pieces about 10 cm in diameter.
- Obtaining the ‘raw meal’ by grinding the raw material.
- Preheating the ‘raw meal’ using the hot gases evacuated from the kiln, in up to six cyclone stages.
- Precalcining, to decompose the limestone.
- Production of the clinker. After precalcining, the ‘raw meal’ goes to the kiln, where the temperature is about 1000 °C. For heating the ‘raw meal’ to about 1450 °C, necessary for clinker formation, a temperature up to 2000 °C should be reached in the rotating kiln, which is obtained by firing the fuel inside it.
- Cooling and storage: The near-molten mixture is rapidly cooled to 100–200 °C.
Given the complexity of the cement manufacturing process—from raw material extraction and transportation to the final product—numerous sources of pollution emerge, each contributing to potentially harmful environmental impacts. An overview of emissions generated at various stages of cement production is presented in Figure 3.
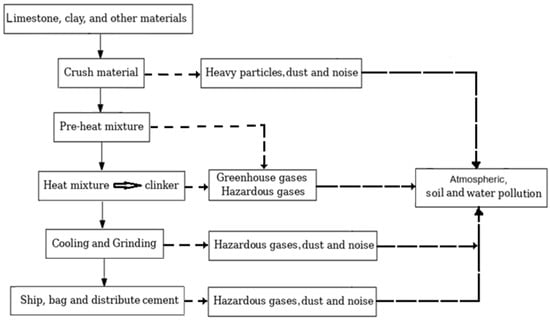
Figure 3.
Environmental impact of cement production (adapted from [31]).
This review explores the main pollution pathways linked to the cement industry and their effects on the environment and public health. This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 addresses atmospheric pollution and its environmental and health impacts. Section 3 presents key findings on noise pollution and its effects on both the population and the environment. Section 4 and Section 5 examine soil and water pollution, respectively, along with their harmful potential. Section 6 provides concluding remarks, summarizes the main findings, discusses the limitations of the review, and suggests directions for future research.
2. Atmospheric Pollution and the Environmental and Health Impacts
2.1. Sources of Atmospheric Pollution and the Environmental Impacts
Cement manufacturing is a significant contributor to environmental pollution and anthropogenic climate change, emitting a broad spectrum of atmospheric contaminants, including particulate matter (PM), chlorine gas, nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), ammonia (NH3), and various greenhouse gases. Among these emissions, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the predominant greenhouse gas driving global warming [32]. Recent studies identified cement production as one of the main industries responsible for CO2 emissions [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], following the energy sector; every ton of cement produced emits about 0.8–0.9 tons of CO2 [35,39]. Furthermore, the industry is estimated to be responsible for approximately 6–8% of total global CO2 emissions [33,40]. For example, only in China, CO2 production increased from 138 to 818 million metric tons during the period 1993–2019 [27].
The production of lime, the main cement component, involves heating limestone in a rotary kiln, which requires the combustion of fossil fuels to obtain the high temperatures necessary for thermally reducing the limestone [41,42]. Therefore, a significant quantity of the CO2 released into the atmosphere originates from this process [43,44]. In the EU, about 60% of emissions result from limestone calcination, about 30% result from reaching high temperatures in the kiln, and about half of the rest result from transportation and electricity consumption [45,46]. Figure 4 compares the emissions resulting from the combustion of coal, oil, and natural gas, alongside emissions from the cement industry in Asia and Europe [33,40], excluding the carbonation sink.
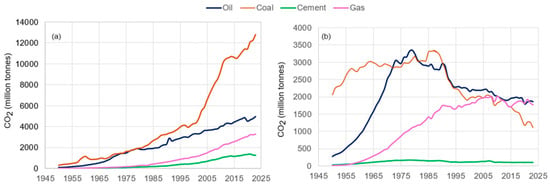
Figure 4.
CO2 resulting from the combustion of oil, coal, natural gas, and cement industry in (a) Asia and (b) Europe—processed using data available in [33,40].
The CO2 emissions from the cement industry increased exponentially, especially after 1978, followed by a slight decrease after 2021, when they reached their peak (Figure 5a) [47,48]. In 2019, cement production emitted 2.4 Gt of CO2, which accounted for 26% of the total emissions from all industrial sectors [49]. In 2023, the emissions decreased to 1.560 million metric tons of CO2, representing approximately 27% of emissions from all industrial sectors [50,51,52]. Within the European Union, the CO2 emissions from cement production represent about 4% of the total CO2 released. From 1960 to 2023, CO2 volume exhibited significant fluctuations, the lowest level being reached in 2022 (Figure 5b) [53].
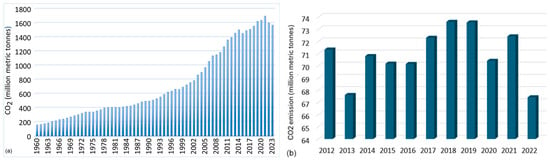
Figure 5.
CO2 emissions from the cement industry (a) worldwide during 1960–2023 [40,47,50,52]; (b) in the European Union from 2013 to 2022 [53].
From the viewpoint of the total CO2 emissions from cement production per country, after 2005, the first position was constantly occupied by China (718 million metric tons in 2023), followed by India (about 4 times lower than China), Vietnam, and the USA, whose emissions were 4, 14, and 18 times lower than those of China, respectively. There was a variation in the ranking of the top ten countries, determined by the age of the manufacturing facilities and the technologies implemented [54,55]. Figure 6 provides a comparison between the CO2 volume emitted in 2021, 2022, and 2023. About 87% of emissions from this industry were issued in China (more than 52%) and developing countries (35%), especially from Asia, in over 2800 production facilities [54].
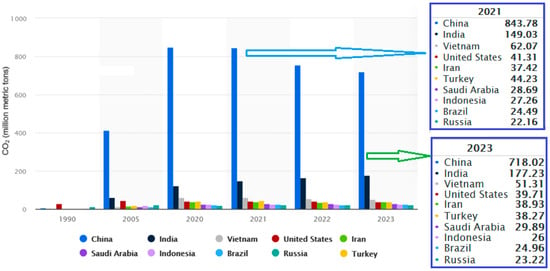
Figure 6.
The highest CO2 producers from the cement industry (processed using data from [55,56]).
The cement industry has historically relied on coal and lignite as primary fuel sources due to their high calorific values and widespread availability. These fuels, however, often contain significant levels of sulfur, which, when combusted, can lead to the formation of sulfur oxides (SO2) and the buildup of sulfur-rich deposits on kiln rings, causing operational inefficiencies and contributing to air pollution [57,58,59].
Cement kilns, which operate under highly alkaline conditions and reach flame temperatures exceeding 2000 °C, are capable of utilizing alternative high-calorific-value waste fuels. These include used tires, solvents, waste oils, plastics, and hazardous organic wastes such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) [60,61]. While this co-processing of waste can reduce fossil fuel consumption and offer waste management solutions, it carries significant environmental and public health concerns. When not properly managed, the combustion of these materials can release a range of toxic substances, including particulate matter, (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs), hydrogen chloride (HCl), hydrogen fluoride (HF), and heavy metals (e.g., lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium) [62,63,64,65,66]. These pollutants can be emitted into the surrounding environment through stack emissions or fugitive releases and pose substantial risks to both ecosystems and human populations.
The concentrations of some gases resulting from cement production typically range as follows: SO2 < 10–3500 mg/Nm3, NOx < 200–3000 mg/Nm3, with NO2 5–10% of NOx emissions [67]. Variation in the levels of NOx and SOx emitted in the European Union from cement production during 1990–2022 is represented in Figure 7 [68]. NOx decreased by more than 60% from 1995 to 2022, while SOx emissions declined by about 50%. However, the reduction in NOx and SOx emissions from cement production in European countries, the USA, and Russia did not significantly impact the total emissions due to their increase in Asian countries, particularly China and India [69]. The decline in SOx and NOx emissions from the cement industry reflects the combined effects of regulations (e.g., EU’s Industrial Emissions Directive, US EPA Clean Air Act standards, India’s National Clean Air Programme), the use of cleaner fuels, better technologies (e.g., Improved Combustion and Process Control), and operational efficiencies (e.g., energy efficiency and decarbonization measures), all part of a broader drive toward sustainability and decarbonization.
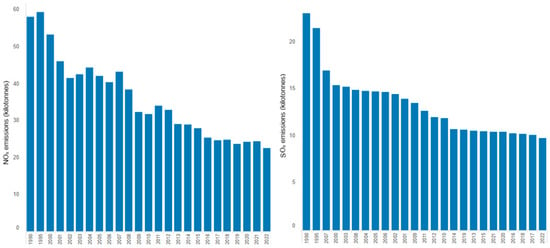
Figure 7.
Variation in NOx and SOx emissions from the cement industry in the European Union (processed from [60,68]).
Figure 8 presents a comparison of NOx and SO2 emissions (in gigatons) in 2019, in various countries, where the ‘rest of the world’ does not include the listed countries.
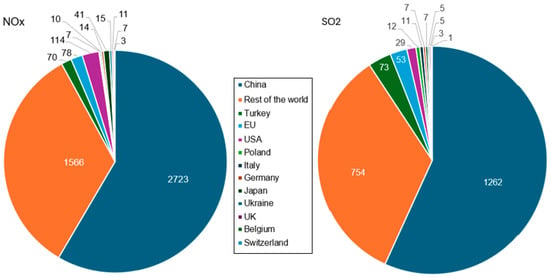
Figure 8.
The volume of NOx and SO2 emissions (gigatons) from the cement industry in 2019. Processed using the data from [66].
China accounts for over 55% of global NOx and SO2 emissions, making it the largest producer of both gases. In comparison, the EU emits about 29 times less NOx and 17 times less SO2. In 2019, the United States emitted 29 gigatons (114 gigatons) of NOx (SO2). Worldwide, the highest NOx emitters are the China National Building Material Group (CNBM), Holcim Group, Anhui Coch (China), Heidelberg Materials, and Cemex (Mexico).
In cement manufacturing, NOx emissions can be categorized into two types, thermal and fuel NOx. The first type results from the oxidation of the nitrogen in air, and the second from the nitrogen compounds from the fuel [70]. Thermal NOx mainly results from the combustion zone of the kiln. In other zones, the NOx thermal formation is negligible because the temperatures are less than 1200 °C. NOx emissions vary in the interval [500, 1500] ppm, the highest proportion (95%) being NO, the smallest (less than 1%) being N2O, and the rest being NO2 [71,72]. NO reacts with oxygen, resulting in NO2. Then, by hydrolyzing, it yields HNO3 [73].
Neuffer and Laney [70] indicated that during kiln combustion, increasing the air excess (which is typically 5–10%) will increase NOx emissions. Additionally, a slight temperature augmentation above 1430 °C can lead to significant augmentations of the NO level. Moreover, it was shown [74,75] that NO significantly contributes to eutrophication.
The United Nations Global Nitrous Oxide Assessment [76] emphasized that, among greenhouse gases, N2O is very stable and is the main gas responsible for destroying the ozone layer and accelerating global warming.
In conclusion, NOx plays a significant role in exacerbating environmental issues such as the formation of ozone in the troposphere, acidification, and eutrophication [77].
SO3 and SO2 emissions are related to burning fuels that contain sulfur or from the decomposition of the calcium sulfate at high temperatures during clinker manufacturing [78]. According to [79,80], the following reactions are produced:
- ▪
- In the raw mills and preheating zone:
Sulfides + O2 → Oxides + SO2; Organic S + O2 → SO2,
- ▪
- In the calcining zone:
Fuel S + O2 → SO2; CaSO4 + C → CaO + SO2 + CO,
- ▪
- In the burning zone:
Fuel S + O2 → SO2; Sulfates → Oxides + SO2 + ½ O2
As SO3 exists as anhydrid, it is easily transformed into SO2 and O2. The reaction of SO3 with alkali and other phases in the kiln tube in the presence of gypsum from raw materials may produce new compounds, such as Ca(Al6O12)(SO3) and Ca5(SiO2)2(SO4), K2SO4, and Na2SO4 [80,81,82]. A total of 90% of SO2 is absorbed in the same zones, based on the following chemical reactions [79]:
- ▪
- In the raw mills and preheating zone:
CaCO3 + SO2 → CaSO3 + CO2
- ▪
- In the calcining zone:
CaSO3 + ½ O2 → CaSO4
- ▪
- In the burning zone:
NaO + SO2 + ½ O2 → NaSO4, K2O + SO2 + ½ O2 → K2SO4
CaO + SO2 + ½ O2 → CaSO4
When water vapor is present in the atmosphere, SO3 reacts to form H2SO4, a major component of acid rain [73,83,84]. This acidic precipitation negatively impacts freshwater ecosystems, harms aquatic life, and impairs plant health and growth by damaging their tissues.
Particulate matter (PM) is among the most common emissions from the cement industry, followed in a lower proportion by Non-Methane Volatile Organic Compounds (NMVOC). Figure 9 presents the extent of these emissions in 2019. The values of ‘0’ in the pie signify recorded values under 0.5 gigatons.
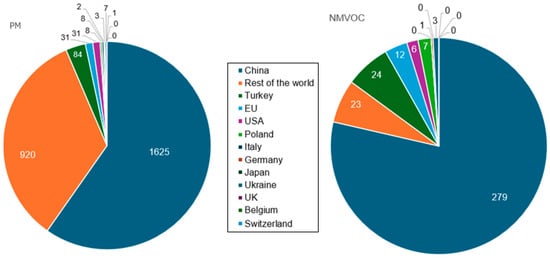
Figure 9.
(left) M emissions (gigatons) and (right) NMVOC from the cement industry in 2019. Processed from the data available in [66].
PM emitted from the cement industry originates from several stages, including quarrying, crushing, grinding, operations in the kiln, packing, landfilled cement kiln dust, etc. [85,86,87]. Although PM generation cannot be avoided, a significant portion can be captured and reused in the production process or recovered and recycled [88]. According to Kalafatoglu et al. [89], studies on dust emissions from various cement plants in Turkey revealed that 44–86% of total emissions were released through the main stacks.
It was also found [90] that the predominant diameters of the PM from the cement industry vary between 0.05 and 5.0 μm. However, the PM’s diameters may vary depending on the technology employed for dust control. For instance, the experiments presented in [86] and cited in [85] have shown that without dust control systems, PM2.5 constituted about 7% in wet process kilns and 18% in dry process kilns, while PM10 made up 24% and 42%, respectively. When implementing dust control technologies, the proportion of PM10 was greater than 80%, and when bag houses were employed, PM2.5 represented around 45% of PM emissions. Li et al. [91] also highlighted that the cement industry was responsible for a significant volume of PM10 emitted in Shanghai.
Kholodov et al. [92] reported that the PM10 emitted from the Spassky factory significantly impacted the air quality in Primorsky Krai and surrounding areas, accounting for 80% of the total particulate matter in the local atmosphere. A study by Smadi et al. [93] in Jordan found that the PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations were higher than the legal limits in a zone situated less than 300 m from a cement plant. Citing some reports of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment from China, Wang et al. [94] indicated that in 2022, the PM (NOX and SO2, respectively) emissions from the cement industry represented 20.9% (17.3% and 5.4%, respectively) of the PM emissions from all industries.
Among the PM emitted during the burning of the fuels to reach the temperatures necessary in the kiln, black carbon can also be released into the atmosphere. This is classified as a short-lived climate pollutant due to its relatively brief atmospheric lifetime, typically spanning only a few weeks before deposition. Despite its transient presence, it exerts a significant influence on the climate system by absorbing solar radiation, thereby contributing to atmospheric warming. Additionally, when deposited on snow and ice surfaces, black carbon reduces their albedo, enhancing solar energy absorption and accelerating cryospheric melt processes [95,96]. Only a few studies considered evaluating its effect, among which was that of Montelongo-Reyes et al. [97], in a study related to the greenhouse and black carbon emissions in Mexico City.
Ammonia (NH3) emissions from the cement industry have become an increasing concern, particularly due to the large-scale use of selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) systems for NOx control. Moreover, ammonia may also be present in raw materials and fuels. While NH3 is partially removed during the cement production process—mainly through absorption onto the alkaline components of the raw meal and oxidation to NOx in the calciner and kiln—these mechanisms may become insufficient when ammonia concentrations are high. Emissions are increased when the raw meal grinding system is inactive, as exhaust gases bypass the mill, which is the primary zone where NH3 is absorbed [98].
A study of 14 cement lines in China reported an average NH3 concentration of 35.29 mg/Nm3, with more than 84% of measurements above the admissible limit [99]. Emission levels were closely linked to the amount of ammonia injected and the operational status of raw mills. The resulting average NH3 emission factor surpassed the U.S.’s recommended guideline of 0.066 kg/t [100].
NH3 utilized for NOx reduction can result in residual amounts being retained in combustion byproducts, particularly fly ash [101,102,103]. Studies by Spanka and Thielen [102] found that the concentrations of NH3 in fly ash varied from 8 to 130 mg/kg. When the proportion of fly ash in concrete was 20%, up to 30% of the ammonia content may be released in less than one week [104].
Similarly, gypsum produced from limestone slurry during flue gas desulfurization may also contain ammonia, posing another potential source. These findings indicate that both amines and ammonium compounds can be released from materials derived from emission control processes [102,104]. Another potential emission source of ammonia is gypsum generated from limestone slurry in flue gas desulfurization [104].
2.2. Health Impact of Atmospheric Pollution from Cement Manufacturing
A considerable number of studies indicate that at a global scale, the CO2, NOx, SO2, and PM emitted in the atmosphere have a greenhouse effect, leading to stratospheric ozone depletion, acid rain formation, biodiversity loss, and reduced agricultural crop productivity. Considering the direct impact on the population, air pollution has been linked to various respiratory problems (e.g., asthma, bronchitis, and tuberculosis) and other health issues, such as eye irritation, heart disease, and premature deaths [105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114]. Here, we emphasize some of them.
CO2 is not a direct pollutant; concentrations up to 1000 ppm are considered safe for human health in indoor environments. However, experimental studies have demonstrated that sustained exposure to elevated levels of CO2 can have detrimental effects on human health [115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123]. Chronic CO2 exposure has been associated with reduced cognitive performance, oxidative stress, bone demineralization, kidney calcification, etc. [118,121]. Beyond human health, elevated CO2 concentrations also exert harmful effects on ecosystems, adversely impacting plant and animal life, as documented in [124,125].
NOx released into the atmosphere poses both direct and indirect risks to human health. Nitrogen dioxide, in particular, is a respiratory irritant capable of penetrating deep into the lungs. Short-term exposure—approximately 15 ppm—can cause throat irritation and coughing, exacerbate asthma symptoms, and disrupt pulmonary function, especially at concentrations exceeding 25 ppm [72,84]. Prolonged exposure has been associated with the development of chronic bronchitis, increased susceptibility to respiratory infections among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and children, and adverse effects on normal childhood development [126]. Indirectly, NOx exposure may exacerbate pre-existing cardiovascular conditions [106,114,127,128,129].
In 2020, about 10.6% of the population was affected by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It represents about 480 million persons all over the world [130]. Many studies indicate an augmentation of COPD at high concentrations of NO2 and O3 [110] and significant dependence on its occurrence on the PM2.5 presence [131,132]. Lang et al. [129] detected correlations between cancer and heart disease cases and exposure to high NOx concentrations for long periods.
As reported in [105], fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone (O3) are considered among the most hazardous air pollutants to human health due to their ability to penetrate deep into the respiratory system and enter the bloodstream. Harrison and Yin [133] emphasized that, in addition to chemical composition, particle size is a critical determinant of particulate matter toxicity. Smaller particles exhibit a greater likelihood of reaching the alveolar regions of the lungs and subsequently entering the circulatory system [134]. The health effects of PM exposure range from respiratory and ocular irritation, infections, and airway inflammation to more severe conditions such as sinusitis, bronchitis, asthma, cardiovascular diseases (including atherosclerosis, hypertension, myocardial infarction, and heart failure), and various forms of cancer. PM has also been linked to cellular-level damage, including oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and lipid peroxidation [108,112,129,131,132,133,135,136,137]. Furthermore, exposure to elevated levels of PM has been associated with reduced infant birth rate and increased mortality [138,139,140].
In a study of Europe, Juginović et al. [141] reported that among 368,006 life losses caused by pollution in 2019, more than 90% were due to long-term exposure to PM2.5. Figure 10 (top) presents people’s estimated exposure to PM-related in 2021, while Figure 10 (bottom) contains a regional map illustrating the life losses due to outdoor PM air pollution for the same year.
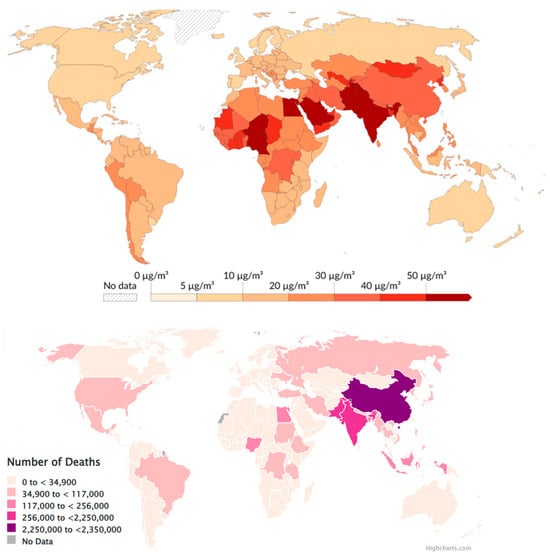
Figure 10.
(top) Exposure to PM in 2019 (from https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/pm25-air-pollution?time=2019) (accessed on 1 June 2025).; (bottom) number of deaths in 2021 due to atmospheric pollution (from https://www.stateofglobalair.org/hap) (accessed on 1 June 2025).
The highest PM pollution from the cement industry was registered in Asia (especially India), Gulf countries, and Western Africa, but the highest mortality associated with PM pollution was found in China and India.
A study conducted in Doroud, Iran [142] found the highest concentrations of PM10 at distances of 1600–1800 m from a local cement factory, downwind. Their values significantly exceeded the World Health Organization (WHO) air quality guidelines, posing serious health risks to factory workers and populations from neighboring settlements. Based on the findings, a distance of at least 7.5 km from the factory was recommended to ensure a safe level of exposure for public health.
Wahas et al. [143] detected high concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 in some cement factories in Haripur (Pakistan). The biggest mean concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 were 1552 and 7867.5 µg/m3, identified in the factory’s main crusher and, respectively, at the cement mill. De Souza Zorzenão al. [144] found that the limits imposed by WHO for PM2.5 were exceeded near a cement factory in Brazil between 2021 and 2022, indicating 3.5% (4.3% and 4.7%, respectively) estimated years of life lost. After analyzing the samples collected in the vicinity of two cement facilities in various seasons, Sánchez-Soberón et al. [145] found the highest concentrations of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 in the cold season, with the biggest risk (non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic) for PM1.
In a study related to a cement plant in Kashmir (in 2011), Mehraj et al. [146] reported that most people living in the facility neighborhood presented allergies and eye irritation, breathing difficulties, asthma, chronic bronchitis, irregular heartbeat, chest pain, etc. Lung cancer affecting 1% of the inhabitants of that area was also documented.
A study conducted in Spain over 10 years [147] reported the highest cancer-related mortality percentage among the population living in zones around cement factories, with the colon–rectum and pleura being the most prominent cancer types. Koh et al. [148] explored the possible correlation between cement dust exposure and cancer risk among male workers in six Korean Portland cement factories. They identify a significantly higher incidence of stomach cancer among workers from the production sector. Although lung cancer mortality was also higher, the association was not statistically significant. The findings suggest a possible link between cement exposure—particularly to hexavalent chromium—and increased cancer risk.
Further evidence comes from a cross-sectional study by Lee et al. [149], which found a higher prevalence of emphysema among individuals more exposed to cement plant emissions, suggesting adverse respiratory effects on nearby residents. Similarly, research on ventilation impairment in a Korean community near a cement facility [150] reported compromised lung function. In a study from the same country, Eom et al. [151] found that the incidence of bronchus and lung cancer was notably higher in the study sample, especially among men, compared to the incidence officially reported. They observed a marginal increase in laryngeal cancer in men and salivary gland cancer in women residing in the vicinity of the cement factory. Etim et al. [109] provided an extensive review of the research on pollution from the cement industry in Nigeria and the impact on the environment and the population’s health, emphasizing the necessity of taking urgent measures to reduce emissions.
3. Noise Pollution and Its Impact on Environment and Population
3.1. Noise Pollution and Its Impact on the Environment
Noise pollution is recognized as a significant environmental concern in areas where cement is produced. The noises in cement plants arise from three principal sources. Mechanical noise is issued when machines (mills, crushers, and collectors) function in the process of grinding the raw material. The electromagnetic noise results from the functioning of the electrical motors [152]. The third kind of noise is the result of the gas dynamics [153].
The noise levels in cement plants, particularly during raw material preparation and processing, generally range from 68.8 to 103.3 dBA. Zhu et al. [154] found higher noise levels in the grinding station (89–105 dBA), exceeding the admissible value of 85 dBA per eight working hours. Mndeme and Mkoma [155] found that in a plant in Tanzania, the noise level varied from 50 dBA to 104.82 dBA in the offices and production sectors. The highest noise was recorded in the power plant, followed by the compressor room (96.67–102.02 dBA), raw mill (92.82–96.48 dBA), and limestone crusher (83.73–93.40 dBA). In a study from China, Zhang et al. [156] reported that in the ball mill and crusher rooms, raw material, and coal mill rooms, the noise was above 100 dBA. In all the other sections, it remained between 85 and 100 dBA. Similar values were determined by Ali et al. [157] and Noorpoor and Orkomi [158] in cement factories in Rabak, Sudan, and Tehran, Iran, respectively.
Generally, cement factories are situated outside cities and villages to avoid a negative impact on the population as much as possible. However, Sordello et al. [159] noted that the noise generated by cement plants negatively impacts local biodiversity. The noise from blasting and other machinery leads to changes in wildlife behavior and reduces the availability of habitats for wildlife. Many species, like birds and mammals, avoid areas of high noise. Furthermore, noise pollution directly impacts wildlife’s communication and reproductive behaviors, contributing to a decline in local ecosystems [160,161]. Pollinators have been shown to decrease their activity in noisy areas, which could hinder agricultural productivity [162].
3.2. Health Impact of Noise Pollution from Cement Manufacturing
Noise pollution originating from cement plants poses serious risks to human health, not only to the environment [156]. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels, particularly those exceeding 80 dB(A), as in the cement factories, can lead to significant health issues, including noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) [153,156,163].
Thai et al. [153] indicated that NIHL was prevalent (in 52% of cases in their study) when sound levels reached around 100–105 dB(A). Hernández-Gaytán et al. [164] reported that the highest noise was recorded in the packer job post, and the largest number of workers with various levels of hearing issues worked in the calcination sector. Moreover, more than half of the study sample suffered from partial hearing loss. Ali et al. [165] showed that more than 12% of people employed in a cement factory experienced moderate hearing loss in the right ear, and two-thirds suffered mild hearing loss in the left ear.
Workers in cement factories for long periods often experience a variety of symptoms, such as irritability, whistling/buzzing, headaches, fatigue, dizziness, insomnia, increased blood pressure, and memory loss [155,166,167,168]. Additionally, continuous exposure to excessive noise may result in neurasthenia, which affects mental and physical well-being [153,156,169]. Even in a mildly noisy environment, workers do not hear clearly and are not able to recognize warning signals that could pose a safety risk [153]. Therefore, they are more exposed to work accidents [169,170,171].
4. Soil Pollution from the Cement Industry and Its Impact on Environment and Population Health
4.1. Soil Pollution from Cement Industry
Numerous studies have confirmed the presence of heavy metal contamination in soils near cement factories [172,173,174,175,176]. For instance, lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) were found at moderately elevated levels in surface soils near cement plants in Nigeria [172]. In Saudi Arabia, concentrations of Pb, Cr, Zn, Ni, and Cu exceeded regulatory limits near a cement factory [173]. Cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and nickel (Ni) were also detected at concerning levels in Nigerian soil samples near cement facilities [174]. Egbe et al. [175] reported increased levels of Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, and Zn close to a cement plant, indicating moderate contamination. Maina et al. [176] observed heavy metal enrichment in soil—2 to 10 times higher than in uncontaminated areas—reaching a maximum at 5–7 km from the Ashaka cement plant in Nigeria. In Pakistan’s Punjab region, Ismail et al. [177] detected contamination with various heavy metals within 500 m of three cement plants, based on the geoaccumulation index and concentration factor. In Spain, Schuhmacher et al. [178] and Rovira et al. [179] found increased levels of heavy metals in both soil and vegetation, especially during the cold season. Olatunde et al. [180] assessed health risks due to heavy metal accumulation in soils around the Ibese cement plant.
Cement production also leads to elevated particulate matter (PM) deposition. Soussia et al. [181] recorded extremely high levels of dust deposition—above regulated limits—especially in the outdoor areas of a cement factory, with peaks in December and January. In Nigeria, increased PM deposition and soil alkalinity were also observed in the vicinity of cement production sites [182].
Several studies report changes in soil physical and chemical properties near cement factories. For example, Anurag et al. [183] found modified soil properties 500 m downwind of a cement plant in Chhattisgarh, India, including elevated organic carbon, silt, and sand content. Lamare and Singh [184] documented increases in soil alkalinity, organic carbon, electrical conductivity, and water retention capacity near the Meghalaya cement plant in India. Uwasu et al. [38] highlighted that waste and slurry disposal during any cement manufacturing process (dry, semi-dry, and wet) contributes to soil degradation and environmental harm. Jadaoon et al. [185] found that the dust and pollutant deposition reduced chlorophyll content in plants, along with decreases in height and stem diameter, indicating impaired plant growth in the vicinity of cement factories.
4.2. Impact of Soil Pollution with Heavy Metals from Cement Industry on Public Health
Soil contamination with heavy metals poses a threat to public health, particularly in regions impacted by industrial activities such as cement manufacturing. Heavy metals are non-biodegradable, tend to accumulate in soils, and can enter the human body through multiple exposure routes: the ingestion of contaminated food or water, inhalation of resuspended dust particles, and dermal contact with polluted soils. Once absorbed, many heavy metals exert toxic effects even at low concentrations, often leading to chronic diseases and systemic dysfunctions.
Lead is among the most toxic environmental pollutants, with well-documented effects on multiple organ systems. Chronic exposure, particularly in children, is associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, reduced intelligence quotient, attention deficits, and behavioral issues. In adults, prolonged exposure may contribute to renal dysfunction, hypertension, reproductive issues, and anemia. Lead interferes with enzymatic functions and calcium-mediated neuronal signaling, making young children and pregnant women especially vulnerable to its neurotoxic effects [186].
Cadmium is primarily absorbed through ingestion or inhalation and accumulates in the kidneys and bones. Long-term exposure is known to cause nephrotoxicity. It also interferes with calcium metabolism, leading to bone demineralization and diseases such as osteoporosis and osteomalacia. Cadmium has been classified as a Group 1 human carcinogen by the IARC due to its role in inducing lung and prostate cancer [187]. The toxicological reference value for this element is 0.21–0.36 µg/(kg body weight per day).
Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] is highly toxic. It penetrates biological membranes and induces oxidative stress, DNA damage, and apoptosis. Inhalation of Cr(VI)-containing dust can cause severe respiratory disorders, including chronic bronchitis, nasal septum perforation, and lung cancer. Ingestion may lead to gastrointestinal irritation and systemic toxicity affecting the liver and kidneys [188,189]. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level for adults is 10 mg/day, but chronic toxicity can occur at 40–50 mg/kg.
Toxicity from nickel can occur through various routes of exposure, including inhalation, ingestion, injection, and dermal absorption. Acute inhalation may cause respiratory inflammation, including pneumonitis and, in extreme cases, acute respiratory distress syndrome. Case reports have shown nickel nanoparticles to deposit in alveolar macrophages, triggering lung injury and systemic inflammation [190,191]. Chronic exposure may lead to allergic contact dermatitis and has been implicated in nasal and lung cancers due to its genotoxic potential [192,193]. The ingestion of nickel salts will acutely manifest toxicity. Gastrointestinal symptoms are prominent, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and hepatic dysfunction [194]. Dermal absorption can lead to type IV skin sensitivity, causing pruritus and erythematous papules [195].
Workplace standards for nickel compounds (measured as nickel) vary. According to OSHA, the limit of Cu exposure is 1 mg/m3 (8 h TWA). NIOSH established 0.015 mg/m3 (10 h TWA) and ACGIH, 0.2 mg/m3 (8 h TWA) [196].
Although zinc and copper are essential micronutrients, excessive environmental concentrations due to industrial contamination may result in toxicity. Elevated zinc intake can disrupt copper metabolism, causing gastrointestinal distress, immune dysfunction, and anemia. Excessive copper exposure may lead to hepatic and neurological damage, especially in individuals with Wilson’s disease, a genetic disorder affecting copper excretion [197,198].
Populations residing near cement factories or other industrial facilities face elevated exposure risks. Children are particularly vulnerable due to their behaviors (e.g., playing outdoors and hand-to-mouth activity) and greater absorption rates. Contaminated soils can also lead to indirect exposure through the food chain, especially in agricultural zones where crops absorb heavy metals from polluted soil.
5. Water Pollution from the Cement Industry and Its Impact on Environment and Population Health
According to van Oss and Padovanni [86], the principal concern about water use in the cement industry is its quality [199] and adequate supply. Water is employed at multiple stages of the cement production process. Directly, water is utilized in washing the raw materials before processing and as a facilitator of raw materials grinding. Various particles (e.g., lime, aluminum oxides, and iron) are washed, leading to water contamination [154]. Indirect use involves cooling kiln bearings, grinding equipment, thermal piping, compressors, etc.
Several studies have investigated the effects of cement wastewater on the water quality of rivers that receive such effluents [200,201,202,203] and provided evidence that water bodies may be contaminated by hazardous substances originating from cement manufacturing facilities. An analysis by Mbaka [204] found that the indicators of water quality of the Athi River (pH, electrical conductivity, turbidity, total suspended and dissolved solids, temperature, and pH) were above the imposed limits, as was the Pb concentration. These results are consistent with [205], indicating that possible surface water contamination may arise from liquid waste and effluent from quarry operations, the press house, and milling processes during cement production.
Additional contamination pathways occur through the leaching of the cement kiln dust (CKD) landfill. Every metric ton of clinker generates approximately 50–150 kg of CKD waste [206], but part is reused in cement manufacturing. Soluble contaminants released during precipitation can increase the heavy metal concentrations in nearby groundwater. Environmental consequences arise from both immediate and long-term effects.
Limited research has been conducted on how aquatic organisms respond to the discharge of cement effluents. A study conducted by Olaleye and Oluyemi [207] in tropical regions found a decline in plankton species richness and diversity in areas surrounding cement factory catchments. Arimoro et al. [208] emphasized the extinction of some macroinvertebrate taxa in the river where the wastewater from a cement plant was permanently evacuated. Oyinlola et al. [209] identified elevated levels of Cd, Cr, and Pb in local rivers downstream of the Ewekoro Cement Factory in Nigeria. They also detected significant abnormalities in the African catfish grown in the river where the wastewater from the Ewekoro Cement Factory was discharged.
Long-term studies of rivers adjacent to cement plants show an average of 40–60% lower macroinvertebrate diversity, with a negligible amount of EPT (Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, Trichoptera) taxa (<1 individual collected) collected within 2 km from discharge [210]. Alkaline pH shocks after discharges may result in 80–100% mortality of organisms sensitive to the change in pH (e.g., Daphnia magna) within 96 h [211].
This water contamination was associated with alterations in fish histopathology, affecting the gills, kidneys, and liver. The consumption of such fish and drinking improperly treated water from these rivers can produce chronic health effects in humans, like kidney and liver damage or digestive issues [109,209]. However, more studies must clarify the impact of the consumption of contaminated water from the cement industry on the population’s health.
6. Conclusions
The cement industry, while vital to infrastructure and economic development, poses significant environmental challenges through its multifaceted pollution outputs. This review has highlighted how atmospheric emissions—particularly CO2, NOx, SO2, and PM—contribute to air quality degradation and climate change. Simultaneously, cement production affects soil health through the deposition of heavy metals and alkaline dust, leading to reduced fertility and ecological imbalances. Water resources are not spared, with cement effluents and slurry runoff introducing suspended solids and toxic elements into nearby water bodies, impairing aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, sonic pollution from quarrying, grinding, and transportation operations generates persistent noise that disrupts both human and wildlife populations.
Researchers have extensively documented the environmental impact of cement production, emphasizing its contribution to atmospheric, soil, water, and sonic pollution. Numerous studies have also proposed a variety of solutions aimed at mitigating these issues. Given the breadth of existing research and the extensive body of literature addressing different aspects of the problem, we believe this review serves as a foundation for further work focused specifically on mitigation strategies and reducing the environmental impact. Accordingly, a follow-up review will be dedicated to discussing the range of solutions that have been proposed or implemented to reduce pollution from the cement industry. In addition, the effectiveness of these measures will be critically assessed in a subsequent article.
Given the scale and complexity of the environmental challenges posed by the cement industry, there is an urgent need for more stringent regulations, the adoption of cleaner technologies, and the implementation of sustainable practices throughout the production lifecycle. Innovations such as carbon capture, waste heat recovery, the use of alternative fuels, and precision environmental monitoring offer promising pathways to reduce the industry’s footprint. Ultimately, addressing this global issue will require coordinated efforts and collaboration among industry stakeholders, policymakers, and the scientific community to ensure a balance between development and ecological sustainability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. and K.H.; methodology, A.B. and K.H.; validation, A.B.; formal analysis, A.B.; investigation, A.B. and K.H.; resources, A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B. and K.H.; writing—review and editing, A.B.; visualization, A.B.; supervision, A.B.; project administration, A.B.; funding acquisition, A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data was created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Aıtcin, P. The durability characteristics of high performance concrete: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, O.S.B.; Al-Kutti, W.A.; Ahmad, S.; Maslehuddin, M. Correlation between compressive strength and certain durability indices of plain and blended cement concretes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, K.; Al Maruf, M.A.; Howlader, R.; Chakma, K.; Mia, M.R. Concrete Strength and Aggregate Properties: In-Depth Analysis of Four Sources. Civ. Eng. J. 2024, 10, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyad, A.M.; Khan, A.H.; Tayeh, B.A. Durability and strength characteristics of high-strength concrete incorporated with volcanic pumice powder and polypropylene fibers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, A.; Nagataki, S.; Saeki, T.; Hisada, M. Freezing and thawing resistance of air-entrained concrete incorporating recycled coarse aggregate: The role of air content in demolished concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.J.; Laws, V. Glass fibre reinforced cement. Mat. Sci. Eng. 1994, 15, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhard, L.; Mata-Falcón, J.; Ammann, R.; Preßmair, N.; Kromoser, B.; Menna, C.; Baghdadi, A.; Kloft, H.; Gabriel, M.; Walch, M.; et al. Enhancing structural efficiency with digital concrete–Principles, opportunities and case studies. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 185, 107645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronin, K.; Permyakov, M.; Davydova, A. Lime slag binding agent for road concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 687, 022042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Kontoleon, K.; Al-Mulali, M.; Shaik, S.; El Ouni, M.; El-Shorbagy, M. Partial substitution of binding material by bentonite clay (BC) in concrete: A review. Buildings 2022, 12, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Lou, L.; Amirkhanian, A.; Amirkhanian, S.N.; Xiao, F. Assessment of effective patching material for concrete bridge deck-A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M. 11—Patching of deteriorated concrete structures. In Failure, Distress and Repair of Concrete Structures; Delatte, N., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 282–295. [Google Scholar]
- Gagg, C.R. Cement and concrete as an engineering material: An historic appraisal and case study analysis. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 40, 114–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilimaa, J. Smart materials and technologies for sustainable concrete construction. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 15, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D. Use of polymers for cement-based structural materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 2973–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechtcherine, V. Novel cement-based composites for the strengthening and repair of concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, K. Seismic vulnerability and rehabilitation strategies for industrial RC structures. Civ. Environ. Eng. Rep. 2024, 34, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazacu, C.E.; Dumitriu, C.Ș.; Bărbulescu, A. Concrete CFRP-Reinforced Beam Performances, Tests and Simulations. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, K. Assessment and Rehabilitation of Seismically Vulnerable Industrial RCC Structures. Computat. Eng. Phys. Model. 2024, 7, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, H.; Huda, N.; Abbasi, R. An overview of eco-friendly alternatives as the replacement of cement in concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1200, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Al Mamun, M.A.; Alyousef, R.; Amran, Y.M.; Aslani, F.; Alabduljabbar, H. Properties and utilizations of waste tire rubber in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaïd, F. How does concrete and cement industry transformation contribute to mitigating climate change challenges? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2022, 15, 200084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Global Cement Report 15th Edition. Available online: https://www.cemnet.com/Publications/global-cement-report (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Statista. Global Cement Production Volume. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1087115/global-cement-production-volume/ (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Du, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, A.; Lv, W. Carbon and air pollutant emissions forecast of China’s cement industry from 2021 to 2035. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 204, 107498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wei, Y.; Cai, W.; Liu, Y.; You, K.; Yu, Y. Tracking cement transportation carbon emissions in China: Historical assessment and future simulation. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2015, 110, 107696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, L.; Sun, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, X.; He, Y.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Hou, L.; Ma, W. Examination of spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of carbon emission and influencing factors in territorial spatial functional areas: A case study of the mountainous city Chongqing. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2025, 21, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourke, I. The Environmental Cost of China’s Addiction to Cement. 2024. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20240419-the-environmental-cost-of-chinas-addiction-to-cement (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- European Production of Cement by Country. Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/dataset/2f9b7c6d05f4b3329b97196c5fc4d3411a0cc1f6 (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Panagoda, L.P.S.S.; Sandeepa, R.A.H.T.; Perera, W.A.V.T.; Sandunika, D.M.I.; Siriwardhana, S.M.G.T.; Alwis, M.K.S.D.; Dilka, S.H.S. Cement Manufacturing Process and Its Environmental Impact. J. Res. Technol. Eng. 2023, 4, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- CEMBUREAU. The Story of Cement Manufacture. Available online: https://cembureau.eu/media/drylkjo0/manufacturing-process-factsheet_update-jan2021.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Mohamad, N.; Muthusamy, K.; Embong, R.; Kusbiantoro, A.; Hashim, M.H. Environmental impact of cement production and Solutions: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Wang, D.; Xia, C.; Tang, J. China’s provincial process CO2 emissions from cement production during 1993–2019. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CarbonBrief. Analysis: CO2 Emissions Will Reach New High in 2024 Despite Slower Growth. Available online: https://www.carbonbrief.org/analysis-global-co2-emissions-will-reach-new-high-in-2024-despite-slower-growth/ (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Fennell, P.; Driver, J.; Bataille, C.; Davis, S.J. Going net zero for cement and steel. Nature 2022, 603, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ige, O.E.; Von Kallon, D.V.; Desai, D. Carbon emissions mitigation methods for cement industry using a systems dynamics model. Clean Technol. Environ. Pol. 2024, 26, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajaste, R.; Hurme, M. Cement industry greenhouse gas emissions—Management options and abatement cost. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4041–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad, K.N.; Yang, H.-M.; Singh, J.K. A path to carbon neutrality in construction: An overview of recent progress in recycled cement usage. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 83, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwasu, M.; Hara, K.; Yabar, H. World cement production and environmental implications. Environ. Dev. 2014, 10, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Vrat, P.; Dahiya, R. Application of a system dynamics approach for assessment and mitigation of CO2 emissions from the cement industry. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 79, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.J.; Andrew, R.M.; Baker, D.C.E.; Hauck, J.; Landschützer, P.; Le Quéré, C.; Luijkx, I.T.; Peters, G.P.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2023. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 5301–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Volaity, S.S.; Kilambi, S.; Kumar, A.; Neithalath, N. A low-carbon approach for lime production using self-propagating high temperature synthesis-driven limestone calcination. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2025, 210, 115192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, M.; Wilkes, M.D.; Brown, S.; Provis, J.L.; Kinoshita, H.; Hanein, T. Decarbonising the lime industry: State-of-the-art. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Srivastava, R.; Koh, J. Utilization of zeolites as CO2 capturing agents: Advances and future perspectives. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 41, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oschatz, M.; Antonietti, M. A search for selectivity to enable CO2 capture with porous adsorbents. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaiyum, M.; Sarker, S.; Kabir, G. Evaluation of carbon emission factors in the cement industry: An emerging economy context. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoey, W.; Ansari, F.S.; Sufian, M.; Deifalla, A.F. Advancements in low-carbon concrete as a construction material for the sustainable built environment. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 16, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figures from the Global Carbon Budget 2024. Available online: https://robbieandrew.github.io/GCB2024/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Marmier, A. Decarbonisation Options for the Cement Industry; European Commission: Joint Research Centre and Publications Office of the European Union: Petten, The Netherlands, 2023; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/174037 (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- IEA. Energy Technology Perspectives 2020. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/7f8aed40-89af-4348-be19-c8a67df0b9ea/Energy_Technology_Perspectives_2020_PDF.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Hanifa, M.; Agarwal, R.; Sharma, U.; Thapliyal, P.; Singh, L. A review on CO2 capture and sequestration in the construction industry: Emerging approaches and commercialised technologies. J. CO2 Util. 2023, 67, 102292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaurova, M.; Soukka, R.; Horttanainen, M. Multi-criteria evaluation of CO2 utilization options for cement plants using the example of Finland. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2021, 112, 103481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Energy Review 2020. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2020 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Eurostat. Greenhouse Emission by Source Sectors. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/env_air_gge__custom_16229276/default/table?lang=en (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Cheng, D.; Reiner, D.M.; Yang, F.; Cu, C.; Meng, J.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tao, S.; Guan, D. Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xu, R.; Tong, D.; Qin, X.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, B.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Q. A striking growth of CO2 emissions from the global cement industry driven by new facilities in emerging countries. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 044007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon Dioxide Emissions from the Manufacture of Cement Worldwide from 1990 to 2023, by Select Country. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1091672/carbon-dioxide-emissions-global-cement-manufacturing/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Schneider, M.; Romer, M.; Tschudin, M.; Bolio, H. Sustainable cement production—Present and future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, C. Sulfur behavior in cement kilns using alternative fuels. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 67, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, A.; Olaru, E.-A.; Dumitru, M.; Iorga, G. Assessment of air pollution by aerosols over a coal open-mine influenced region in southwestern Romania. Rom. J. Phys. 2024, 69, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A.; Font, R. Pollutant emissions from the co-combustion of solid wastes with coal. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Alternative Control Techniques Document—NOx Emissions from Cement Manufacturing; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2007.
- Karstensen, K.H. Formation, release and control of dioxins in cement kilns. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loo, S.; Koppejan, J. The Handbook of Biomass Combustion and Co-Firing; Earthscan: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- European IPPC Bureau. Reference Document on Best Available Techniques in the Cement, Lime and Magnesium Oxide Manufacturing Industries; European Commission: Seville, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Air Pollution Inventories. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Hasanbeigi, A.; Bhadbhade, N.; Ghosh, A. Air Pollution from Global Cement Industry—An International Benchmarking of Criteria Air Pollutants Intensities; Global Efficiency Intelligence: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, August 2022; Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5877e86f9de4bb8bce72105c/t/62ef78a371716a77fcb7790f/1659861171704/Cement+CAP+Study-final.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Ali, M.B.; Saidur, R.; Hossain, M.S. A review on emission analysis in cement industries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMEP Centre on Emission Inventories and Projections. Data Viewer—Reported Emissions Data. Available online: https://www.ceip.at/data-viewer-2/officially-reported-emissions-data (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Edwards, P. Global Cement: Environmental Standards. Available online: https://www.globalcement.com/images/stories/documents/articles/eGC-Mar14-25web.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Neuffer, B.; Laney, M. Alternative Control Techniques Document Update—NOx Emissions from New Cement Kilns. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttncatc1/dir1/cement_updt_1107.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Öztürk, B.; Öztürk, O.; Karademir, A. NOx emission modeling at cement plants with co-processing alternative fuels using ANN. Environ. Eng. Res. 2022, 27, 210277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A. NOx Emissions from the Cement Industry. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/nox-emissions-from-cement-industry-ahmed-younis/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Ibrahim, H.G.; Okasha, A.Y.; Elatrash, M.S.; Al-Meshragi, M.A. Emissions of SO2, NOx and PMs from cement plant in vicinity of Khoms city in Northwestern Libya. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 1, 620–628. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Chae, C.U. Environmental Impact Analysis of Acidification and Eutrophication Due to Emissions from the Production of Concrete. Sustainability 2016, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.; Muthusamy, K. Concrete industry, environment issue, and green concrete: A review. Construction 2022, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Environment Programme. Global Nitrous Oxide Assessment. 2024. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/global-nitrous-oxide-assessment (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Winiwarter, W.; Klimont, Z. The role of N-gases (N2O, NOx, NH3) in cost-effective strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution in Europe. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Sadiq, R.; Hewage, K. An overview of air emission intensities and environmental performance of grey cement manufacturing in Canada. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Siddiqui, N.A. A review on environmental and health impacts of cement manufacturing emissions. Int. J. Geol. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Horkoss, S. 2008 Reducing the SO2 emission from a cement kiln. Int. J. Nat. Soc. Sci 2008, 1, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry; Tomas Telford: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Peng, H.; Wu, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Process compatible desulfurization of NSP cement production: A novel strategy for efficient capture of trace SO2 and the industrial trial. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 411, 137344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaiah, O.O.; Olusegun, O.A.; Blessing, A.G.; Samson, A.O. Environmental and Health Implications of Cement Production Plant Emissions in Nigeria: Ewekoro Cement Plant as a Case Study. Chem. J. 2021, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Najjar, Y.S. Gaseous pollutants formation and their harmful effects on health and environment. Innov. Energy Pol. 2011, 1, E101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Majumdar, D.; Trivedi, J.V.; Bhanarkar, A.D. Particulate matter and elemental emissions from a cement kiln. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 104, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, H.G.; Padovani, A.C. Cement Manufacture and the Environment Part II: Environmental Challenges and Opportunities. J. Ind. Ecol. 2003, 7, 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Al-Dhamri, H.; Ram, G.; Chatterjee, V.P. An overview of alternative raw materials used in cement and clinker manufacturing. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2021, 14, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearing the Air: Dust Collection & Emission Control Technologies for Global Cement Industry. Available online: https://techflow.net/articles/clearing-the-air-dust-collection-emission-control-technologies-for-global-cement-industry (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Kalafatoglu, E.; Ors, N.; Ozdemir, S.S.; Munlafalioglu, I. Trace element emissions from some cement plants in Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 129, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalacic, I. Chronic nonspecific lung disease in cement workers. Arch. Environ. Health 1973, 26, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Guo, P.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Lu, R.; Qiu, H.; Li, M.; Jiang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Preliminary studies on the source of PM10 aerosol particles in the atmosphere of Shanghai City by analyzing single aerosol particles. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2003, 210, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodov, A.; Zakharenko, A.; Drozd, V.; Chernyshev, V.; Kirichenko, K.; Seryodkin, I.; Karabtsov, A.; Olesik, S.; Khvost, E.; Vakhnyuk, I.; et al. Identification of cement in atmospheric particulate matter using the hybrid method of laser diffraction analysis and Raman spectroscopy. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Smadi, B.M.; Al-Zboon, K.K.; Shatnawi, K.M. Assessment of Air Pollutants Emissions from a Cement Plant: A Case Study in Jordan. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 3, 265–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ning, M.; He, J.; He, J.; Lei, W.; Hou, S. The collaborative pollutants and carbon dioxide emission reduction and cost of ultra-low pollutant emission retrofit in China’s cement kiln. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 136939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.-M. Fact Sheet|Short-Lived Climate Pollutants: Why Are They Important? Available online: https://www.eesi.org/papers/view/fact-sheet-short-lived-climate-pollutants (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Schmidt, C.W. Black Carbon: The Dark Horse of Climate Change Drivers. Available online: https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.119-a172 (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Montelongo-Reyes, M.M.; Otazo-Sánchez, E.M.; Romo-Gómez, C.; Gordillo-Martínez, A.J.; Galindo-Castillo, E. GHG and black carbon emission inventories from Mezquital Valley: The main energy provider for Mexico Megacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method for Controlling Ammonia Content in Cement Flue Gas and Cement Plant with Controlled Ammonia Emission. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP3299080A1/en (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Guo, Y.; Mu, B.; Liu, P.; Luo, L.; Hao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T. Ammonia emission estimation for the cement industry in northern China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, S.M.; Spiwey, M.D.; Lindquist, H.C.; Thesing, K.B.; Strait, R.P.; Pechan, E.H.; Assoc. Inc. Estimating Ammonia Emissions from Anthropogenic Nonagricutural Sources-Draft Final Report. 2004. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/eiip_areasourcesnh3.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Koch, H.-J.; Prenzel, H. Versuche uber Geruchsentwicklungen beim Frischestrich mit NH3- befrachteter Flugasche. Betonw. Fert.-Tech. 1989, 11, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Spanka, G.; Thielen, G. Freisetzung fluchtiger Substanzen aus zementgebundenen Bauprodukten (Teil 2). Beton 1999, 3, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chyliński, F.; Goljan, A.; Michalik, A. Fly Ash with Ammonia: Properties and Emission of Ammonia from Cement Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjellström, K. Chemical Emissions from Concrete. Licentiate Thesis, Division of Building Materials, LTH, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2004. Available online: https://lucris.lub.lu.se/ws/files/4892497/1659440.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Huang, Y.-C.T. Outdoor Air Pollution. A Global Perspective. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56, S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- César, A.C.; Carvalho, J.A., Jr.; Nascimento, L.F. Association between NOx exposure and deaths caused by respiratory diseases in a medium-sized Brazilian city. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.S.; Burnett, R.T.; Stieb, D.M.; Brophy, J.M.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; Valois, M.F.; Brook, J.R. Associations between ambient air pollution and daily mortality among elderly persons in Montreal, Quebec. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Multifaceted Health Impacts of Particulate Matter (PM) and Its Management: An Overview. Environ. Skept. Crit. 2015, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Etim, M.-A.; Babaremu, K.; Lazarus, J.; Omole, D. Health risk and environmental assessment of cement production in Nigeria. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, B.; Baek, M.S. The effect of long-term exposure to a mixture of air pollutants on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2025, 292, 117978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiritescu, R.-V.; Luca, E.; Iorga, G. Observational study of major air pollutants over urban Romania in 2020 in comparison with 2019. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2024, 76, 702. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy, T.; Nath, A.; Singh, S.; Mathew, S.; Pant, A.; Sheela, S.; Kaur, G.; Sathishkumar, K.; Mathur, P. Assessing the Global Impact of Ambient Air Pollution on Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2024, 10, e2300427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Impacts of Air Pollution in Canada 2021 Report. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/healthy-living/health-impacts-air-pollution-2021.html (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- US EPA Basic Information About NO2. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/no2-pollution/basic-information-about-no2 (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Hajtar, L.; Herczeg, L. Influence of carbon-dioxide concentration on human well-being and intensity of mental work. Időjárás 2012, 116, 145–169. [Google Scholar]
- Satish, U.; Mendell, M.J.; Shekhar, K.; Hotchi, T.; Sullivan, D.; Strufert, S.; Fisk, W.J. Is CO2 an indoor pollutant? Direct effects of low-to-moderate CO2 concentrations on human decision-making performance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.G.; MacNaughton, P.; Satish, U.; Santanam, S.; Vallarino, J.; Spengler, J.D. Associations of cognitive function scores with carbon dioxide, ventilation, and volatile organic compound exposures in office workers: A controlled exposure study of green and conventional office environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.A.; Kler, J.S.; Hernke, M.T.; Braun, R.K.; Meyer, K.C.; Funk, W.E. Direct human health risks of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, S.; Boyson, A.S.; Paas, K.H.W.; Gough, H.; King, M.-F.; Barlow, J.; Noakes, C.J.; Schraefel, M.C. Exploring the physiological, neurophysiological and cognitive performance effects of elevated carbon dioxide concentrations indoors. Build. Environ. 2019, 156, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiyer, S.; Abbas, S.S. Effect of Greenhouse Gases on Human Health. In Greenhouse Gases: Sources, Sinks and Mitigation; Sonwani, S., Saxena, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D. Is Carbon Dioxide Harmful to People? Available online: https://learn.kaiterra.com/en/air-academy/is-carbon-dioxide-harmful-to-people (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Bărbulescu, A. Modeling Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărbulescu, A. Statistical analysis and modeling of the CO2 series emitted by Thirty European countries. Climate 2024, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Cerling, T.; Dearing, M.D. A History of Atmospheric CO2 and Its Effects on Plants, Animals, and Ecosystems; Ecological Studies 177; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, P. The impact of CO2. The global rise in the levels of CO2 is good for trees, bad for grasses and terrible for corals. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Avol, E.; Gilliland, F. The effect of air pollution on lung development from 10 to 18 years of age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achakulwisut, P.; Brauer, M.; Hystad, P.; Anenberg, S.C. Global, national, and urban burdens of paediatric asthma incidence attributable to ambient NO2 pollution: Estimates from global datasets. Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, E166–E178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowers, A.M.; Walton, H.; Exley, K.S.; Hurley, J.F. Using epidemiology to estimate the impact and burden of exposure to air pollutants. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Requia, W.J.; Sakhvidi, M.J.Z.; Lin, K.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Cao, P.; Yang, L.; et al. Associations of long-term exposure to nitrogen oxides with all-cause and cause-specific mortality. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, E.; Barrett, M.; Su, J.G.; Benjafield, A.V.; Sinha, S.; Kaye, L.; Zar, H.J.; Vuong, V.; Tellez, D.; Gondalia, R.; et al. Global burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2346598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Bai, L.; Hatzopoulou, M.; Van Ryswyk, K.; Kwong, J.C.; Jerrett, M.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Burnett, R.T.; Lu, H.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient ultrafine particles and respiratory disease incidence in in Toronto, Canada: A cohort study. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Lin, C.Q.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chan, J.; Jiang, W.K.; Ta, T.; Yeoh, E.-K.; Chan, T.-C.; et al. Effect of long-term exposure to fine particulate matter on lung function decline and risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Taiwan: A longitudinal, cohort study. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e114–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J. Particulate matter in the atmosphere: Which particle properties are important for its effects on health? Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the air: A review of the effects of particulate matter air pollution on human health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzer, A.; Anenberg, S.C.; Dey, S.; Haines, A.; Lelieveld, J.; Chowdhury, S. Mortality attributable to ambient air pollution: A review of global estimates. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2022GH000711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamra, G.B.; Guha, N.; Cohen, A.J.; Laden, F.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Samet, J.M.; Vineis, P.; Forastiere, F.; Saldiva, P.; Yorfuji, T.; et al. Outdoor particulate matter exposure and lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Tian, D.; He, R.; Cragg, J.J.; Carsten, C.; Giang, A.; Gill, P.K.; Johnson, K.M.; Brigham, E. Ambient air pollution exposure and adult asthma incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2024, 8, e1065–e1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heft-Neal, S.; Burney, J.; Bendavid, E.; Burke, M. Robust relationship between air quality and infant mortality in Africa. Nature 2018, 559, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, K.; Ghosh, S.; Thangavel, G.; Sambandam, S.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Puttaswamy, N.; Sadasivam, A.; Ramaswamy, P.; Johnson, P.; Kuppuswamy, R.; et al. Exposures to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and birthweight in a rural-urban, mother-child cohort in Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stump, Á.; Szabó-Morvai, Á. The effect of air pollution on fertility in 657 European regions. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2025, 130, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juginović, A.; Vuković, M.; Aranza, I.; Biloš, V. Health impacts of air pollution exposure from 1990 to 2019 in 43 European countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Sicard, P.; Taiwo, A.M.; De Marco, A.; Esmaeili, S.; Rashidi, R. Modeling of particulate matter dispersion from a cement plant: Upwind-downwind case study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3104–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahas, A.; Sobia, N.; Nafees, M.; Rahid, H. Assessment of particulate matter (PM10 & PM2.5) and associated health problems in different areas of cement industry, Hattar, Haripur. J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 37, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza Zorzenão, P.C.; dos Santos Silva, J.C.; Bufato Moreira, C.A.; Pinto, V.M.; de Souza Tadano, Y.; Yamamoto, C.I.; Moreton Godoi, R.H. Impacts of PM2.5 exposure near cement facilities on human health and years of life lost: A case study in Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Soberón, F.; Rovira, J.; Mari, M.; Sierra, J.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Schuhmacher, M. Main components and human health risks assessment of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 in two areas influenced by cement plants. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraj, S.S.; Bhat, G.A.; Balkhi, H.M.; Gul, T. Health risks for population living in the neighborhood of a cement factory. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez, J.; López-Abente, G.; Castelló, A.; González-Sánchez, M.; Fernández-Navarro, P. Cancer mortality in towns in the vicinity of installations for the production of cement, lime, plaster, and magnesium oxide. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, D.-H.; Kim, T.-W.; Jang, S.H.; Ryu, H.-W. Cancer mortality and incidence in cement industry workers in Korea. Saf. Health Work 2011, 2, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, C.G.; Kim, D.H.; Song, H.S.; Jung, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, C.H.; Ahn, S.C.; Yu, S.D. Emphysema prevalence related air pollution caused by a cement plant. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 28, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, C.G.; Song, H.S.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, C.H.; Ahn, S.C.; Yu, S.D. Ventilation impairment of residents around a cement plant. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 27, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.-Y.; Cho, E.-B.; Oh, M.-K.; Kweon, S.-S.; Nam, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-D.; Kim, H. Increased incidence of respiratory tract cancers in people living near Portland cement plants in Korea. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2017, 90, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.N.; Straatman, L.V.; Lea, J.; Westerberg, B. Current insights in noise-induced hearing loss: A literature review of the underlying mechanism, pathophysiology, asymmetry, and management options. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2017, 46, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, T.; Kučera, P.; Bernatik, A. Noise pollution and its correlations with occupational noise-induced hearing loss in cement plants in Vietnam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, J.; Quang, Q.; Liu, T. A review on pollution treatment in cement industrial areas: From prevention techniques to python-based monitoring and controlling models. Processes 2022, 10, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mndeme, F.G.; Mkoma, S.L. Assessment of work zone noise levels at a cement factory in Tanga, Tanzania. Ethiop. J. Environ. Stud. Manag. 2012, 5, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, S.; Li, D. Comprehensive control of the noise occupational hazard in cement plant. Procedia Eng. 2012, 43, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.E.A.M.; Elhassan, B.M.; Ali, A.A.H. The noise pollution and heat stress in different parts of Rabak Cement Factory, White Nile State, Sudan. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. Arch. 2022, 2, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Noorpoor, A.; Ahmadi Orkomi, A. Acoustic Analysis of Machineries in the Cement Industry. Open J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordello, R.; Ratel, O.; Flamerie De Lachapelle, F.; Leger, C.; Dambry, A.; Vanpeene, S. Evidence of the impact of noise pollution on biodiversity: A systematic map. Environ. Evid. 2020, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; Dent, M.L.; Gannon, W.L.; McCauley, R.D.; Römer, H.; Southall, B.L.; Stansbury, A.L.; Stoeger, A.S. The effects of noise on animals. In Exploring Animal Behavior Through Sound. Volume 1: Methods; Erbe, C., Thomas, J.A., Eds.; Springer/ASA Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 459–506. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmat, W.; Hesam, A.M.; Atifnigar, H. Exploring noise pollution, causes, effects, and mitigation strategies: A review paper. Eur. J. Theor. Appl. Sci. 2023, 1, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, O.C.; Maggioni, M.; Dani, F.R. Environmental ameliorations and politics in support of pollinators. Experiences from Europe: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 362, 121219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Daud, N.A.; Ismail, Z.; Baharudin, A. Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Among Quarry Workers in a North-Eastern State of Malaysia: A Study on Knowledge, Attitude and Practice. Oman Med. J. 2013, 28, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Gaytán, S.I.; Santos-Burgoa, C.; Becker-Meyer, J.P.; Macías-Carrillo, C.; López-Cervantes, M. Prevalence of hearing loss and correlated factors in a cement plant. Salud Publica Mex. 2000, 42, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Garandawa, H.I.; Nwawolo, C.C.; Somefun, O.O. Noise-Induced Hearing Loss at Cement Company, Nigeria. Online J. Med. Med. Sci. Res. 2012, 1, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, W. Occupational and Environmental Noise Exposure and Extra-Auditory Effects on Humans: A Systematic Literature Review. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2023GH000805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staseva, E.; Kvitkina, M.; Litvinov, A.; Kobzeva, N. The effect of noise on the human body, in particular, on cardiovascular diseases. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 164, 01028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toure, H.; Baïla, D.B.; Amadou, T.C.; Diatta, A.E.R. Risk Assessment of Noise Pollution in a Cement Plant: Perspectives and Recommendations. Glob. J. Med. Commun. Health Arch. 2023, 1, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, N.; Younes, I.; Minallah, M.N. Industrial Noise Pollution and Its Impact on the Hearing Capacity of Workers: A Case Study of Gujranwala City, Pakistan. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2019, 2, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtar, M.; Kamaruddin, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Mallick, Z. A study on the effects of noise on industrial workers in Malaysia. J. Teknol. 2007, 46, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.D.; Quintana, S.; Chavarría, N.; Ballesteros, J.A. Noise exposure of workers of the construction sector. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekola, F.A.; Inyinbo, A.A.; Abdul–Raheem, A.M.O. Heavy metals distribution and speciation in soils around a mega cement factory in north–central Nigeria. Ethiop. J. Environ. Stud. Manag. 2012, 5, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Ismail, A.I.; El-Hefnawy, M.E. A preliminary assessment of potential ecological risk and soil contamination by heavy metals around a cement factory, western Saudi Arabia. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awos, A.; Thompson, S.; Adedeji, O.; Zvomuya, F.; Zhang, Q. Monitoring of Air Quality for Particulate Matter (PM2.5, PM10) and Heavy Metals Proximate to a Cement Factory in Ewekoro, Nigeria. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2024, 12, 152–180. [Google Scholar]
- Egbe, E.R.; Nsonwu-Anyanwu, A.C.; Offor, S.J.; Opara Usoro, C.A.; Etukudo, M.H. Heavy metal content of the soil in the vicinity of united cement factory in Southern Nigeria. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 7, 122–130. [Google Scholar]
- Maina, H.M.; Egila, J.N.; Nkafamiya, I.I.; Shagal, M.H. Impact of cement dust deposition on the elemental composition of soils in the vicinity of Ashaka cement factory, Nigeria. Int. Res. J. Agric. Sci. Soil Sci. 2013, 3, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, Z.; Ali, S.; Zulfiqar, A.; El-Serehy, H.A. Impact of cement industries on potentially toxic elements’ contamination and other characteristics of topsoil: A case study. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2023, 35, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Environmental monitoring of PCDD/Fs and metals in the vicinity of a cement plant after using sewage sludge as a secondary fuel. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, J.; Mari, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Monitoring environmental pollutants in the vicinity of a cement plant: A temporal study. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunde, K.A.; Sosanya, P.A.; Bada, B.S.; Ojekunle, Z.O.; Abdussalaam, S.A. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around a major cement factory, Ibese, Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2020, 9, e00496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussia, T.; Guendon, P.; Lawan, R.; Gbaguidi, C.D.; Edorh, P.A. Assessment of Cement Dust Deposit in a Cement Factory in Cotonou (Benin). J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 6, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ogedengbe, K.; Oke, A. Pollution impact of cement production on air, soil and water in a production location in Nigeria. J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 31, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anurag, K.R.; Sahu, N. Impact of cement industries dust on soil properties in Bhatapara, Chhattisgarh. Ann. Plant Soil Res. 2021, 23, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lamare, R.E.; Singh, O.P. Effect of cement dust on soil physico-chemical properties around cement plants in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadaoon, S.; Amin, A.A.; Malik, A.; Kamal, H. Soil pollution by the cement industry in the Bazian vicinity, Kurdistan region. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 6, 1000413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanphear, B.P.; Hornung, R.; Khoury, J.; Yolton, K.; Baghurst, P.; Bellinger, D.C.; Canfield, R.L.; Dietrich, K.N.; Bornschein, R.; Greene, T.; et al. Low-level environmental lead exposure and children’s intellectual function: An international pooled analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 894–899, Erratum in Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 99001. [Google Scholar]
- Järup, L.; Åkesson, A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Klein, C.B. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of chromium compounds in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemical Agents and Related Occupations. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Volume 100F. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Chemical-Agents-And-Related-Occupations-2012 (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Chang, X.; Zhao, H.; Gao, J.; Chen, L.; Zhu, A.; Wang, C.; Yu, S.; Ren, X.; Ge, P.; Sun, Y. Pulmonary toxicity of exposure to nano nickel oxide. Micro Nano Lett. 2018, 13, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, W.; Rai, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mondal, M.H.; Bhattarai, A.; Saha, B. A comprehensive review on the sources, essentiality and toxicological profile of nickel. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, K.S.; Sunderman, F.W.; Salnikow, K. Nickel carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2003, 533, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaye, R.; Zhao, J. Recent progress in studies of metallic nickel and nickel-based nanoparticles’ genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderman, F.W. Mechanisms of nickel carcinogenesis. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1989, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlström, M.G.; Thyssen, J.P.; Wennervaldt, M.; Menné, T.; Johansen, J.D. Nickel allergy and allergic contact dermatitis: A clinical review of immunology, epidemiology, exposure, and treatment. Contact Dermat. 2019, 81, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Jersey Depatment of Health and Senior Services. Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet. Available online: https://nj.gov/health/eoh/rtkweb/documents/fs/1345.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Brewer, G.J.; Askari, F.K. Wilson’s disease: Clinical management and therapy. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosmire, G.J. Zinc toxicity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmatka, S.H.; Kerkhoff, B.; Panarese, W.C. Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures, EB001, 14th ed.; Portland Cement Association: Skokie, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ani, J.; Asegbeloyin, J.; Melkiti, M. Physicochemical characterization of industrial effluents: Case studies of beverage and fibre cement plants in Enugu, Nigeria. N. Y. Sci. J. 2011, 4, 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ipeaiyeda, A.; Obaje, G. Impact of cement effluent on water quality of rivers: A case study of Onyi river at Obajana, Nigeria. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2017, 3, 1319102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabimana, E.; Hirwa, H. Assessment and Determination of Selected Physical Parameters of Surface Water in Cement Factory, Western Province, Rwanda. Asian J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 9131–9134. [Google Scholar]
- Aga, T.; Anyadike, C.; Mbajiorgu, C.; Ogwo, V. Assessment of the effect of cement industry effluent discharge on water quality of Ngo River in Benue, Nigeria. Niger. J. Technol. 2020, 39, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaka, J. Impact of Cement Industry on Water Quality in the Athi River, Machakos County, Kenya. East Afr. J. Environ. Nat. Resour. 2023, 6, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbede, O.T.; Adeofun, C.O.; Adetunji, M.T.; Taiwo, A.M.; Arowolo, T.A. Environmental impacts of cement production in Ewekoro, Ogun State, southwestern Nigeria from 2005 to 2006 on surface water quality, vegetation, and workers’ health. J. Water Health 2024, 22, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Rajor, A. Use of cement kiln dust in cement concrete and its leachate characteristics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 61, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaleye, V.F.; Oluyemi, E.A. Effects of cement flue dusts from a Nigerian cement plant on air, water and planktonic quality. Environ. Monit. Asses. 2010, 162, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoro, F.O.; Meme, F.K.; Keke, U.N. Effects of effluent discharges from a cement factory on the ecology of macroinvertebrates in an Afrotropical River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53444–53457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyinlola, I.S.; Olagunju, A.S.; Adaramoye, O.A. The Biochemical Effects of Waters from Awba Dam and Rivers Around Ewekoro Cement Factory, Ogun State, Nigeria on Selected Organs of the African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Niger. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2024, 37, 4809–4826. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, N.; Biswas, A.; Qureshi, T.; Borana, K.; Virha, R. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish tissues of a freshwater lake of Bhopal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.H.; Tjørnhøj, R.; Wollenberger, L.; Slothuus, T.; Baun, A. Acute and chronic effects of pulse exposure of Daphnia magna to dimethoate and pirimicarb. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).