Presence and Dermal Exposure to Benzene and Acetaldehyde in Hand Sanitizers Available in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Instrumentation
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Dermal Exposure Assessment
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Analysis with GC-MS
3.2. Sample Analysis
3.3. Estimations of Exposures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Hand Sanitizer Use out and About. 2021. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/106061 (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Costa, B.; Haddad, L.P.E.; Caleffo Piva Bigão, V.L.; Martinis, B.S. Quantifying Ethanol in Ethanol-Based Hand Sanitizers by Headspace Gas Chromatography with Flame Ionization Detector (HS-GC/FID). J. AOAC Int. 2022, 105, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, T.J.; Nelson, F.B.; Reaney, M.J.T. Analyses of Commercially Available Alcohol-Based Hand Rubs Formulated with Compliant and Non-Compliant Ethanol. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuga, K.; Nyamweya, N. Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizers in COVID-19 Prevention: A Multidimensional Perspective. Pharmacy 2021, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.L.J.; Pei Yi, T.; Bose, R.J.C.; McCarthy, J.R.; Tharmalingam, N.; Madheswaran, T. Hand Sanitizers: A Review on Formulation Aspects, Adverse Effects, and Regulations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Shahin Ahmed, K.; Karim, R.; Nath, B.D.; Prosad Moulick, S.; Islam, R.; Mahmudul Hassan, S.M.; Hossain, H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Jahan, M.S.; et al. Alcohol-based Hand Sanitizers amid COVID-19: Chemical Formulation, Analysis, Safety. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202203290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.; Khadka, P.; Das, S.C. Alcohol-based hand sanitizer—Composition, proper use and precautions. Germs 2021, 11, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US FDA. FDA Advises Consumers Not to Use Hand Sanitizer Products Manufactured by Eskbiochem. US FDA. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-advises-consumers-not-use-hand-sanitizer-products-manufactured-eskbiochem (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Govender, K.; Mdanda, S.; Baijnath, S.; Kruger, H.G.; Govender, T.; Naicker, T. The analysis of alcohol content in hand sanitisers (in the Durban region) using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry during the COVID-19 pandemic. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2022, 76, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, H.; Choi, J.W.; Yoon, S.Y. Analysis of Consumer Exposure Cases for Alcohol-Based Disinfectant and Hand Sanitizer Use against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, I.S.; Maibach, H.I. Irritant contact dermatitis. Rev. Environ. Health 2014, 29, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.L.; Hughes, C.A.; Pyrek, J.D.; Sparks, S.M.; Cagatay, E.U.; Bartkus, J.M. Changes in bacterial flora associated with skin damage on hands of health care personnel. Am. J. Infect. Control 1998, 26, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misteli, H.; Weber, W.P.; Reck, S.; Rosenthal, R.; Zwahlen, M.; Fueglistaler, P.; Bolli, M.K.; Oertli, D.; Widmer, A.F.; Marti, W.R. Surgical glove perforation and the risk of surgical site infection. Arch. Surg. 2009, 144, 553–558; discussion 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, K.P. Prevention of surfactant-induced irritant contact dermatitis. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 1996, 25, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.C. Contact allergy to cosmetics: Causative ingredients. Contact Dermat. 1987, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erasmus, V.; Daha, T.J.; Brug, H.; Richardus, J.H.; Behrendt, M.D.; Vos, M.C.; van Beeck, E.F. Systematic review of studies on compliance with hand hygiene guidelines in hospital care. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guin, J.D.; Goodman, J. Contact urticaria from benzyl alcohol presenting as intolerance to saline soaks. Contact Dermat. 2001, 45, 182–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patty, F.A.; Clayton, G.D.; Clayton, F.E. Patty’s Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Part E Edition, Toxicology; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, J.M.; Kelliher, S.; Vallande, N. Skin irritation and dryness associated with two hand-hygiene regimens: Soap-and-water hand washing versus hand antisepsis with an alcoholic hand gel. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2000, 21, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.L.; Aiello, A.E.; Bastyr, J.; Lyle, C.; Stahl, J.; Cronquist, A.; Lai, L.; Della-Latta, P. Assessment of two hand hygiene regimens for intensive care unit personnel. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. Policies and Procedures on Infection Control, 2nd ed.; Quality Medical Care Section, Medical Development Division, Ministry of Health Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bedner, M.; Murray, J.; Urbas, A.A.; MacCrehan, W.A.; Wilson, W.B. A Comparison of Measurement Methods for Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizers; NIST Interagency/Internal Report No. 8342; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition (Final Report) (EPA/600/R-09/052F). 2011. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/efp/recordisplay.cfm?deid=236252 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pal, V.K.; Lee, S.; Naidu, M.; Lee, C.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of and dermal exposure to benzene, toluene and styrene found in hand sanitizers from the United States. Environ. Int. 2022, 167, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. List of Classifications, Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Risk to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2019; Volumes 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hornung, R.W.; Reed, L.D. Estimation of Average Concentration in the Presence of Nondetectable Values. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 1990, 5, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. <467> Residual solvents. In United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP 43–NF 38). 2020. Available online: https://www.uspnf.com/sites/default/files/usp_pdf/EN/USPNF/generalChapter467Current.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Kresge, A.J.; Weeks, D.P. Hydrolysis of acetaldehyde diethyl acetal and ethyl vinyl ether: Secondary kinetic isotope effects in water and aqueous dioxane and the stability of the ethoxyethyl cation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 7140–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Thayumanavan, S. Substituent Effects on the pH Sensitivity of Acetals and Ketals and Their Correlation with Encapsulation Stability in Polymeric Nanogels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2306–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrigo, N.; Ruzicka, C.; Faustino, P.; Stiber, N.; NguyenPho, A.; O’Connor, T.; Shakleya, D. Development and validation of a headspace GC-MS method to evaluate the interconversion of impurities and the product quality of liquid hand sanitizers. AAPS Open 2022, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valisure LLC. Citizen Petition on Hand-Sanitizer Products Containing Benzene Contamination and Other Significant Issues (Docket No. FDA-2021-P-0338). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 24 March 2021. Available online: https://downloads.regulations.gov/FDA-2021-P-0338-0001/attachment_1.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Saab, Y.; Zgheib, R.; Nakad, Z.; Khnayzer, R.S. Determination of volatile impurities and ethanol content in ethanol-based hand sanitizers: Compliance and toxicity. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 13, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, T.; Jones, K.; Roseberry-Lincoln, A.; Zidek, A.; MacKinnon, L.; Marro, L. Adult and children’s use of hand sanitizer during a pandemic—An observational study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Exposure Dose Guidance for Body Weight (Version 1). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service. 2023. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/pha-guidance/resources/ATSDR-EDG-Body-Weight-508.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Choi, K.; Sim, S.; Choi, J.; Park, C.; Uhm, Y.; Lim, E.; Kim, A.Y.; Yoo, S.J.; Lee, Y. Changes in handwashing and hygiene product usage patterns in Korea before and after the outbreak of COVID-19. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
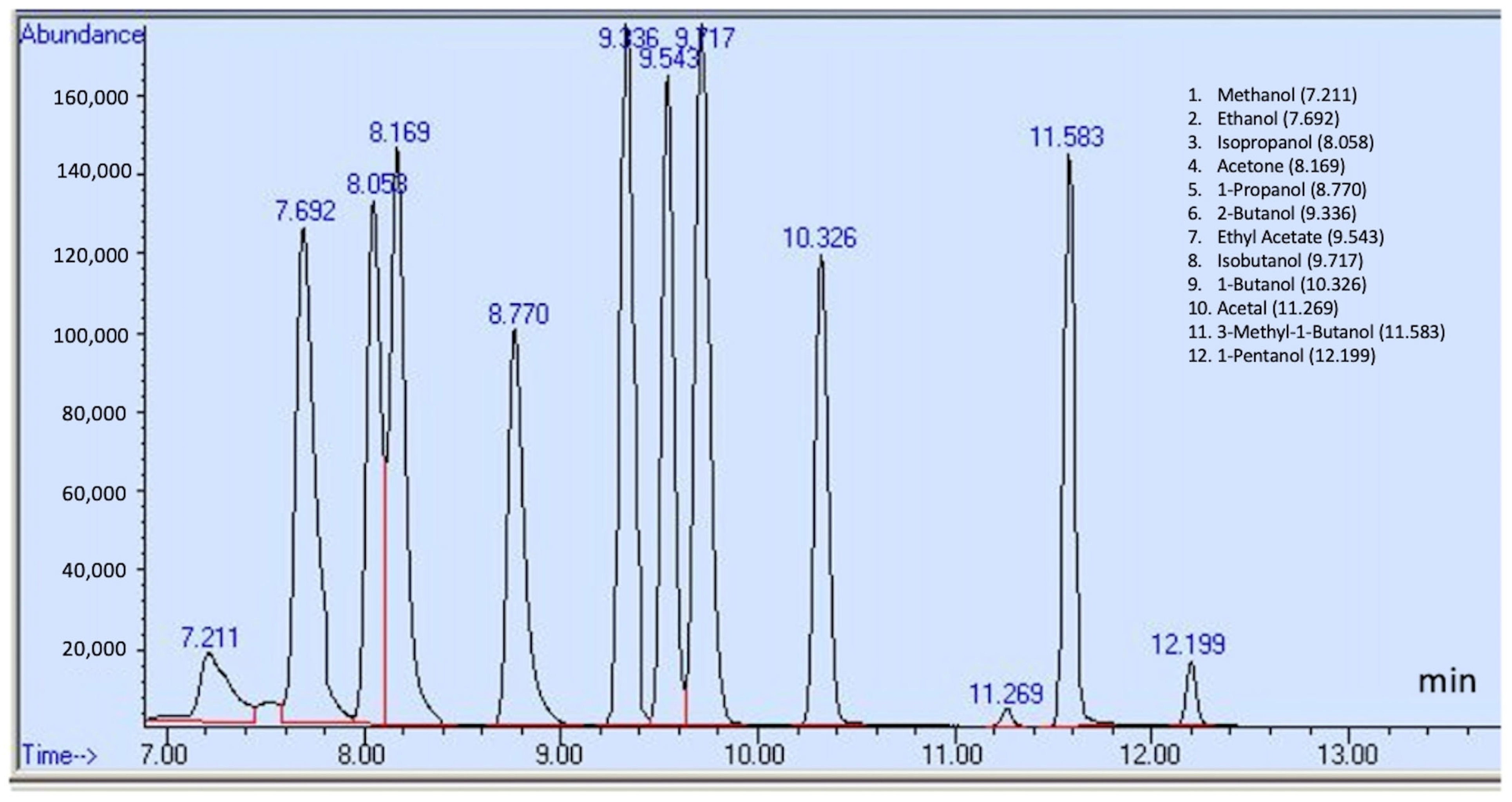
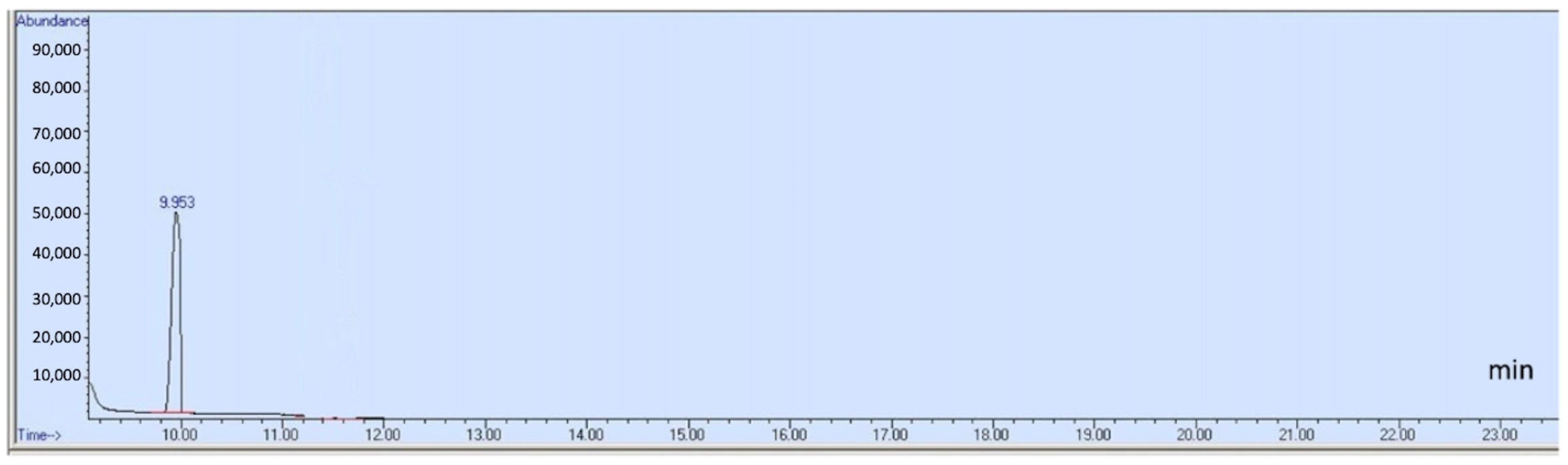

| Compounds | Retention Time (min) | Quantification Ion (m/z) | Identification Ions (m/z) | Calibration Range (μg/mL) | MDLs (μg/mL) | RSD (%) Low Conc | RSD (%) High Conc | Interim Limit Listed in FDA Guidance (ppm) a, b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol | 7.211 | 31 | 32, 29 | 20–200 | 3.74 | 8.41 | 2.56 | NMT 630 |
| Ethanol | 7.692 | 31 | 45, 29 | 20–200 | 2.41 | 1.24 | 2.20 | |
| Isopropanol | 8.058 | 45 | 43, 27 | 20–200 | 2.57 | 7.27 | 2.89 | |
| Acetaldehyde | 9.953 | 29 | 44, 43 | 0.5–5 | 0.0017 | 3.48 | 0.93 | NMT 50 |
| Benzene | 11.338 | 78 | 77, 51 | 0.5–1 | 0.0077 | 9.85 | 1.31 | NMT 2 |
| Acetone | 8.169 | 43 | 58, 15 | 0.5–5 | 0.0231 | 10.79 | 7.93 | NMT 4400 |
| Ethyl acetate | 9.543 | 43 | 61, 45 | 0.5–5 | 0.0334 | 1.25 | 1.75 | NMT 2200 |
| Isobutanol | 9.717 | 43 | 41, 42 | 0.5–5 | 0.0346 | 2.04 | 3.20 | NMT 21,700 |
| Acetal | 11.269 | 45 | 73, 29 | 0.5–5 | 0.0151 | 4.05 | 8.82 | NMT 50 |
| 1-propanol | 8.770 | 31 | 29, 59 | 0.5–5 | 0.0221 | 1.73 | 2.77 | NMT 1000 |
| 1-butanol | 10.326 | 56 | 31, 41 | 0.5–5 | 0.028 | 4.51 | 4.49 | NMT 1000 |
| 2-butanol | 9.336 | 45 | 27, 59 | 0.5–5 | 0.0389 | 9.96 | 2.74 | NMT 6200 |
| 3-methyl-1-butanol | 11.583 | 55 | 42, 43 | 0.5–5 | 0.0152 | 9.7 | 12.68 | NMT 4100 |
| 1-pentanol | 12.199 | 42 | 55, 41 | 0.5–5 | 0.0283 | 2.90 | 3.68 | NMT 4100 |
| Chemical | Methanol | Acetone | 1-Propanol | 2-Butanol | Ethyl Acetate | Isobutanol | 1-Butanol | Acetal | 3-Methyl-1-butanol | 1-Pentanol | Benzene | Acetaldehyde |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| detection rates * (%) | 11 of 85 (12.9) | 11 of 85 (12.9) | 13 of 85 (15.3) | 14 of 85 (16.5) | 16 of 85 (18.8) | 7 of 85 (8.2) | 10 of 85 (11.8) | 2 of 85 (2.4) | 12 of 85 (14.1) | 2 of 85 (2.3) | 5 of 85 (5.9) | 19 of 85 (22.4) |
| Mean ** | 14.61 | 4.53 | 6.73 | 13.83 | 26.34 | 7.24 | 10.23 | 28.24 | 4.65 | 1.32 | 0.84 | 22.39 |
| GM *** | 3.91 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Max | 318.99 | 61.32 | 105.68 | 365.07 | 433.25 | 167.56 | 217.54 | 387.57 | 73.12 | 72.82 | 33.99 | 429.03 |
| Min | 7.15 | 7.92 | 2.85 | 0.13 | 21.18 | 31.78 | 12.71 | 23.21 | 13.96 | 37.69 | 1.57 | 30.09 |
| Median | 50.74 | 25.96 | 39.57 | 29.64 | 99.45 | 86.96 | 53.11 | 114.66 | 28.95 | 55.26 | 4.19 | 54.67 |
| The non-carcinogenic risks | |||||||||
| Application amount (3 g/day) Body weight (24.6 kg) 2~11 years old | Application amount (3 g/day) Body weight (64.2 kg) 11~21 years old | Application amount (3 g/day) Body weight (80 kg) >21 years old | Application amount (9 g/day) Body weight (24.6 kg) 2~11 years old | Application amount (9 g/day) Body weight (64.2 kg) 11~21 years old | Application amount (9 g/day) Body weight (80 kg) >21 years old | Application amount (13.5 g/day) Body weight (24.6 kg) 2~11 years old | Application amount (13.5 g/day) Body weight (64.2 kg) 11~21 years old | Application amount (13.5 g/day) Body weight (80 kg) >21 years old | |
| Mean | 2.57 × 10−2 | 9.86 × 10−3 | 7.92 × 10−3 | 7.72 × 10−2 | 2.96 × 10−2 | 2.37 × 10−2 | 1.16 × 10−1 | 4.44 × 10−2 | 3.56 × 10−2 |
| GM | 2.34 × 10−4 | 8.98 × 10−5 | 7.21 × 10−5 | 7.03 × 10−4 | 2.69 × 10−4 | 2.16 × 10−4 | 1.05 × 10−3 | 4.04 × 10−4 | 3.24 × 10−4 |
| Max | 1.04 × 100 | 3.97 × 10−1 | 3.19 × 10−1 | 3.11 × 100 | 1.19 × 100 | 9.56 × 10−1 | 4.66 × 100 | 1.79 × 100 | 1.43 × 100 |
| min | 1.52 × 10−4 | 5.84 × 10−5 | 4.69 × 10−5 | 4.57 × 10−4 | 1.75 × 10−4 | 1.41 × 10−4 | 6.86 × 10−4 | 2.63 × 10−4 | 2.11 × 10−4 |
| Median | 1.52 × 10−4 | 5.84 × 10−5 | 4.69 × 10−5 | 4.57 × 10−4 | 1.75 × 10−4 | 1.41 × 10−4 | 6.86 × 10−4 | 2.63 × 10−4 | 2.11 × 10−4 |
| The cancer risks | |||||||||
| Application amount (3 g/day) Body weight (24.6 kg) 2~11 years old | Application amount (3 g/day) Body weight (64.2 kg) 11~21 years old | Application amount (3 g/day) Body weight (80 kg) >21 years old | Application amount (9 g/day) Body weight (24.6 kg) 2~11 years old | Application amount (9 g/day) Body weight (64.2 kg) 11~21 years old | Application amount (9 g/day) Body weight (80 kg) >21 years old | Application amount (13.5 g/day) Body weight (24.6 kg) 2~11 years old | Application amount (13.5 g/day) Body weight (64.2 kg) 11~21 years old | Application amount (13.5 g/day) Body weight (80 kg) >21 years old | |
| Mean | 5.15 × 10−6 | 1.97 × 10−6 | 1.58 × 10−6 | 1.54 × 10−5 | 5.92 × 10−6 | 4.75 × 10−6 | 2.32 × 10−5 | 8.88 × 10−6 | 7.12 × 10−6 |
| GM | 4.69 × 10−8 | 1.80 × 10−8 | 1.44 × 10−8 | 1.41 × 10−7 | 5.39 × 10−8 | 4.32 × 10−8 | 2.11 × 10−7 | 8.08 × 10−8 | 6.49 × 10−8 |
| Max | 2.07 × 10−4 | 7.94 × 10−5 | 6.37 × 10−5 | 6.22 × 10−4 | 2.38 × 10−4 | 1.91 × 10−4 | 9.33 × 10−4 | 3.57 × 10−4 | 2.87 × 10−4 |
| min | 3.05 × 10−8 | 1.17 × 10−8 | 9.38 × 10−9 | 9.15 × 10−8 | 3.50 × 10−8 | 2.81 × 10−8 | 1.37 × 10−7 | 5.26 × 10−8 | 4.22 × 10−8 |
| Median | 3.05 × 10−8 | 1.17 × 10−8 | 9.38 × 10−9 | 9.15 × 10−8 | 3.50 × 10−8 | 2.81 × 10−8 | 1.37 × 10−7 | 5.26 × 10−8 | 4.22 × 10−8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.-A.; Tsai, S.-W. Presence and Dermal Exposure to Benzene and Acetaldehyde in Hand Sanitizers Available in Taiwan. Toxics 2025, 13, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070537
Cheng C-A, Tsai S-W. Presence and Dermal Exposure to Benzene and Acetaldehyde in Hand Sanitizers Available in Taiwan. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070537
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chieh-An, and Shih-Wei Tsai. 2025. "Presence and Dermal Exposure to Benzene and Acetaldehyde in Hand Sanitizers Available in Taiwan" Toxics 13, no. 7: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070537
APA StyleCheng, C.-A., & Tsai, S.-W. (2025). Presence and Dermal Exposure to Benzene and Acetaldehyde in Hand Sanitizers Available in Taiwan. Toxics, 13(7), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070537