Food-Grade Polar Extracts from Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) By-Products: Unlocking Potential for the Food Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
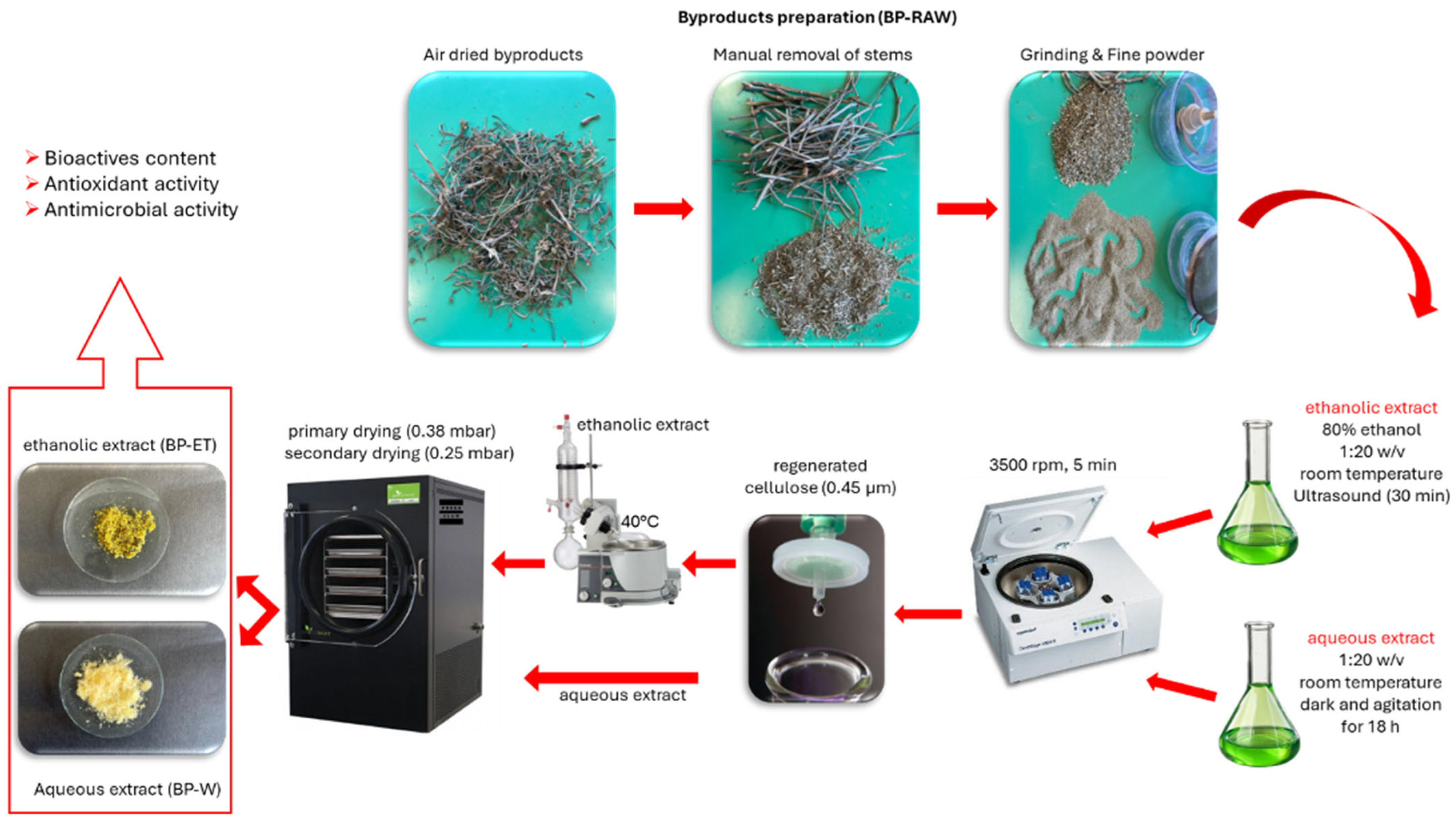
2.2. Sea Fennel By-Product Supply
2.3. Preparation of Aqueous and Hydroethanolic Extract from Sea Fennel By-Product
2.4. Total Phenols and Flavonoids Contents
2.5. Polyphenol Profile
2.6. Carotenoids and Tocopherols
2.7. Antioxidant Activity
2.8. Bacterial Strains and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.8.1. Agar Well Diffusion Method
2.8.2. Broth Microdilution Method
2.8.3. Agar Dilution Method
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polyphenols Profile and Bioactive Compounds Content
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renna, M. Reviewing the Prospects of Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) as Emerging Vegetable Crop. Plants 2018, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radman, S.; Brzović, P.; Radunić, M.; Rako, A.; Šarolić, M.; Ninčević Runjić, T.; Urlić, B.; Generalić Mekinić, I. Vinegar-Preserved Sea Fennel: Chemistry, Color, Texture, Aroma, and Taste. Foods 2023, 12, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraouia, M.; Nartea, A.; Maoloni, A.; Osimani, A.; Garofalo, C.; Fanesi, B.; Ismaiel, L.; Aquilanti, L.; Pacetti, D. Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) as an Emerging Crop for the Manufacturing of Innovative Foods and Nutraceuticals. Molecules 2023, 28, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoloni, A.; Cardinali, F.; Milanović, V.; Osimani, A.; Garofalo, C.; Ferrocino, I.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Cocolin, L.; Aquilanti, L. Microbial Dynamics and Key Sensory Traits of Laboratory-Scale Co-Fermented Green Olives (Olea europaea L. Cv. Ascolana Tenera) and Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.). Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowska, A.; Jeswani, H.K.; Azapagic, A. Environmental Impacts of Vegetables Consumption in the UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duca, D.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.A.; Ilari, A.; Aquilanti, L.; Foppa Pedretti, E. Life Cycle Assessment of Open Field Sea Fennel Production in Central Italy. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2024, 13, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Noguerol, R.; Matías, L.; Pérez-Ramos, I.M.; Moreira, X.; Francisco, M.; Pedroche, J.; DeAndrés-Gil, C.; Gutiérrez, E.; Salas, J.J.; Moreno-Pérez, A.J.; et al. Soil Physicochemical Properties Associated with the Yield and Phytochemical Composition of the Edible Halophyte Crithmum maritimum. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhotohwo, O.L.; Nartea, A.; Lucci, P.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S.; Pacetti, D. Application of Sea Fennel’s Bioactive Compounds in the Development of Edible Films and Coatings: A Review. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalić Mekinić, I.; Politeo, O.; Ljubenkov, I.; Mastelić, L.; Popović, M.; Veršić Bratinčević, M.; Šimat, V.; Radman, S.; Skroza, D.; Ninčević Runjić, T.; et al. The Alphabet of Sea Fennel: Comprehensive Phytochemical Characterisation of Croatian Populations of Crithmum maritimum L. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politeo, O.; Popović, M.; Veršić Bratinčević, M.; Koceić, P.; Ninčević Runjić, T.; Mekinić, I.G. Conventional vs. Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation: Influence on the Chemistry of Sea Fennel Essential Oil and Its By-Products. Plants 2023, 12, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartea, A.; Orhotohwo, O.L.; Fanesi, B.; Lucci, P.; Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Aquilanti, L.; Casavecchia, S.; Quattrini, G.; Pacetti, D. Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) Leaves and Flowers: Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant Activity and Hypoglycaemic Potential. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politeo, O.; Ćurlin, P.; Brzović, P.; Auzende, K.; Magné, C.; Generalić Mekinić, I. Volatiles from French and Croatian Sea Fennel Ecotypes: Chemical Profiles and the Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antiageing Activity of Essential Oils and Hydrolates. Foods 2024, 13, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, I.; Antunes, M.; Tecelão, C.; Neves, M.; Pires, C.L.; Cruz, P.F.; Rodrigues, M.; Peralta, C.C.; Pereira, C.D.; Reboredo, F.; et al. Nutritive Value and Bioactivities of a Halophyte Edible Plant: Crithmum maritimum L. (Sea Fennel). Plants 2024, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meot-Duros, L.; Magné, C. Antioxidant Activity and Phenol Content of Crithmum maritimum L. Leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souid, A.; Della Croce, C.M.; Frassinetti, S.; Gabriele, M.; Pozzo, L.; Ciardi, M.; Abdelly, C.; Hamed, K.B.; Magné, C.; Longo, V. Nutraceutical Potential of Leaf Hydro-Ethanolic Extract of the Edible Halophyte Crithmum maritimum L. Molecules 2021, 26, 5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houta, O.; Akrout, A.; Neffati, M.; Amri, H. Phenolic Contents, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Potentials of Crithmum maritimum Cultivated in Tunisia Arid Zones. J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat. 2011, 1, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidi, I.; Kollaros, D.; Manios, T.; Daliakopoulos, I.N. Drought- and Salt-Tolerant Plants of the Mediterranean and Their Diverse Applications: The Case of Crete. Land 2022, 11, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Sanches-Silva, A.; Castilho, M.; Cavaleiro, C.; Ramos, F. Halophytes as Source of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Their Potential Applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1078–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksouri, R.; Ksouri, W.M.; Jallali, I.; Debez, A.; Magné, C.; Hiroko, I.; Abdelly, C. Medicinal Halophytes: Potent Source of Health Promoting Biomolecules with Medical, Nutraceutical and Food Applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierascu, R.C.; Ortan, A.; Fierascu, I.C.; Fierascu, I. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Antioxidant Properties of Wild-Growing Plants. A Short Review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Pateiro, M.; Domínguez, R.; Nieto, G.; Kumar, M.; Dhama, K.; Lorenzo, J.M. Bioactive Compounds from Fruits as Preservatives. Foods 2023, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Akacha, B.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Elhadef, K.; Ben Saad, R.; Brini, F.; Mnif, W.; Smaoui, S.; Ben Hsouna, A. The Essential Oil of Tunisian Halophyte Lobularia Maritima: A Natural Food Preservative Agent of Ground Beef Meat. Life 2022, 12, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kibar, E.A.A.; Gniewosz, M.; Kraśniewska, K. Novel Materials in the Preparation of Edible Films and Coatings—A Review. Coatings 2020, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asioli, D.; Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Caputo, V.; Vecchio, R.; Annunziata, A.; Næs, T.; Varela, P. Making Sense of the “Clean Label” Trends: A Review of Consumer Food Choice Behavior and Discussion of Industry Implications. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, A.; Marín, D.; Taladrid, D.; Montero, P.; Carmen Gómez-Guillén, M. Encapsulation of Antioxidant Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum) Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts in Freeze-Dried Soy Phosphatidylcholine Liposomes. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanesi, B.; Ismaiel, L.; Nartea, A.; Orhotohwo, O.L.; Kuhalskaya, A.; Pacetti, D.; Lucci, P.; Falcone, P.M. Bioactives and Technological Quality of Functional Biscuits Containing Flour and Liquid Extracts from Broccoli By-Products. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, A.; Abdeshahi, A.; Alizadeh Behbahani, B.; Falah, F. Exploring the Impact of Plantago lanceolata Mucilage Edible Coating Enhanced with Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CWKu-12 Postbiotics on the Shelf Life of Lamb Meat Slices. Appl. Food Res. 2025, 5, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinco, C.M.; Benítez-González, A.M.; Hernanz, D.; Vicario, I.M.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J. Development and Validation of a Rapid Resolution Liquid Chromatography Method for the Screening of Dietary Plant Isoprenoids: Carotenoids, Tocopherols and Chlorophylls. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1370, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicari, V.; Tundis, R.; Romeo, R.; Reitano, A.; Belsito, E.L.; Leggio, A.; Loizzo, M.R. Evaluation of the Shelf Life of Ready-to-Eat Fresh Bamboo Sprouts (Phyllostachys edulis) Packaged in a Modified Atmosphere or Vacuum: A Comparative Study. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATCC: The Global Bioresource Center|ATCC. Available online: https://www.atcc.org/ (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Leibniz Institute DSMZ: Welcome to the Leibniz Institute DSMZ. Available online: https://www.dsmz.de/ (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in Vitro Evaluating Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST Reading Guide for Broth Microdilution. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Disk_test_documents/2022_manuals/Reading_guide_BMD_v_4.0_2022.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- EUCAST Breakpoint Tables. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_13.1_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID). Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) of Antibacterial Agents by Agar Dilution. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatti, D.; Angeloni, S.; Maggi, F.; Caprioli, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Arnoldi, L.; Bosisio, S.; Mombelli, G.; Drenaggi, E.; Sagratini, G. Comprehensive Characterization of Phytochemicals in Edible Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L., Apiaceae) Grown in Central Italy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalić Mekinić, I.; Blažević, I.; Mudnić, I.; Burčul, F.; Grga, M.; Skroza, D.; Jerčić, I.; Ljubenkov, I.; Boban, M.; Miloš, M.; et al. Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.): Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidative, Cholinesterase Inhibitory and Vasodilatory Activity. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.G.; Hu, Q.P.; Liu, Y. Antioxidant and DNA-Protective Activities of Chlorogenic Acid Isomers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11625–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.M.; Elvira López-Caballero, M.; Martínez-Alvarez, O. Identification of Polyphenols in Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum) and Seaside Arrowgrass (Triglochin maritima) Extracts with Antioxidant, ACE-I, DPP-IV and PEP-Inhibitory Capacity. Foods 2023, 12, 3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souid, A.; Della Croce, C.M.; Pozzo, L.; Ciardi, M.; Giorgetti, L.; Gervasi, P.G.; Abdelly, C.; Magné, C.; Hamed, K.B.; Longo, V. Antioxidant Properties and Hepatoprotective Effect of the Edible Halophyte Crithmum maritimum L. against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury in Rats. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglidou, K.; Irakli, M.; Boutsika, A.; Mellidou, I.; Maninis, N.; Sarrou, E.; Georgiadou, V.; Tourvas, N.; Krigas, N.; Moysiadis, T.; et al. Metabolomic Fingerprinting and Molecular Characterization of the Rock Samphire Germplasm Collection from the Balkan Botanic Garden of Kroussia, Northern Greece. Plants 2022, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radman, S.; Mastelić, L.; Ljubenkov, I.; Lazarevski, S.; Politeo, O.; Podrug, R.; Prga, I.; Čorić, I.; Popović, M.; Bratinčević, M.V.; et al. Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) Flowers as an Emerging Source of Bioactive Compounds. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2024, 2024, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, M.; Radman, S.; Generalić Mekinić, I.; Ninčević Runjić, T.; Urlić, B.; Veršić Bratinčević, M. A Year in the Life of Sea Fennel: Annual Phytochemical Variations of Major Bioactive Secondary Metabolites. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallali, I.; Megdiche, W.; M’Hamdi, B.; Oueslati, S.; Smaoui, A.; Abdelly, C.; Ksouri, R. Changes in Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activities of the Edible Halophyte Crithmum maritimum L. With Physiological Stage and Extraction Method. Acta Physiol. Plant 2012, 34, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, C.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Dauvergne, X.; Cérantola, S.; Custódio, L.; Magné, C. A Characterization of Biological Activities and Bioactive Phenolics from the Non-Volatile Fraction of the Edible and Medicinal Halophyte Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.). Foods 2024, 13, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive—2009/32/EC. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2009/32/oj (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Veršić Bratinčević, M.; Kovačić, R.; Popović, M.; Radman, S.; Generalić Mekinić, I. Comparison of Conventional and Green Extraction Techniques for the Isolation of Phenolic Antioxidants from Sea Fennel. Processes 2023, 11, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunea, A.; Cenariu, M.C.; Andrei, S.; De Rossi, L.; Rocchetti, G.; Lucini, L.; Rebecchi, A. Antimicrobial Potential of Polyphenols: Mechanisms of Action and Microbial Responses—A Narrative Review. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugaie, O.A.; Mohammed, H.A.; Alsamani, S.; Messaoudi, S.; Aroua, L.M.; Khan, R.A.; Almahmoud, S.A.; Altaleb, A.D.; Alsharidah, M.; Aldubaib, M.; et al. Antimicrobial, Antibiofilm, and Antioxidant Potentials of Four Halophytic Plants, Euphorbia Chamaesyce, Bassia Arabica, Fagonia Mollis, and Haloxylon Salicornicum, Growing in Qassim Region of Saudi Arabia: Phytochemical Profile and In Vitro and In Silico Bioactivity Investigations. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

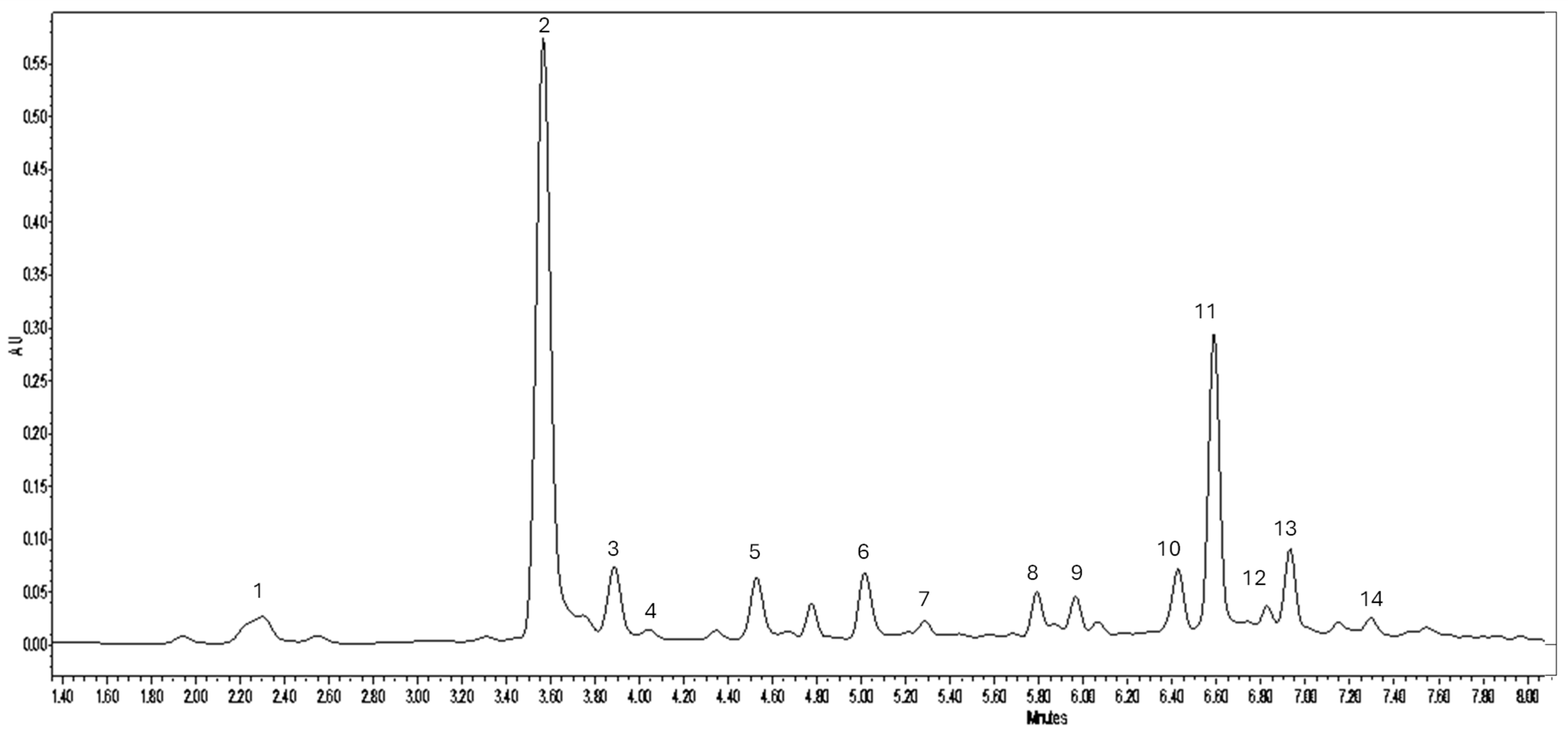
| BP-RAW | BP-W | BP-ET | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [M-H]-(m/z) | Polyphenol Profile (mg CGA eq/g dw) | |||
| Hydroxycinnamic acids and derivatives | 4.31 ± 0.14 | 22.40 ± 2.22 | 22.99 ± 2.89 | |
| Caffeoylquinic acid isomers (peaks 1–3) | 353 | 2.77 ± 0.10 a | 14.16 ± 1.92 b | 13.55 ± 2.58 b |
| Caffeic acid (peak 4) | 179 | 0.09 ± 0.00 a | 0.30 ± 0.01 b | 0.31 ± 0.00 b |
| Coumaroylquinic acids (peaks 5, 7) | 337 | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 1.63 ± 0.04 b | 1.52 ± 0.08 b |
| Feruloylquinic acid (peak 6) | 367 | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | 1.18 ± 0.07 b | 1.21 ± 0.02 b |
| Dicaffeoylquinic acids (peaks 10, 11, 13) | 515 | 0.70 ± 0.06 a | 5.13 ± 0.21 b | 6.40 ± 0.21 c |
| * Flavones and flavonols | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 1.69 ± 0.03 | |
| Quercetin-glucoside isomer (peak 8) | 475 | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.04 a | 0.57 ± 0.01 b |
| Isoquercetin (peak 9) | 463 | 0.18 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.55 ± 0.02 c |
| Diosmin (peak 12) | 607 | 0.24 ± 0.02 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 b |
| Apigenin hexoside (peak 14) | 431 | 0.09 ± 0.00 a | 0.30 ± 0.01 b | 0.30 ± 0.02 b |
| TPC (mg GAE/g dw) | 27.93 ± 1.4 a | 49.27 ± 1.4 b | 55.10 ± 0.24 b | |
| TFC (mg QE/g dw) | 2.31 ± 0.52 a | 5.27 ± 0.71 b | 8.62 ± 1.12 c | |
| Carotenoids and Tocopherols (mg/kg dw) | ||||
| Lutein | 29.62 ± 0.46 a | n.d. | 56.41 ± 1.72 b | |
| α-tocopherol | 18.98 ± 0.76 a | n.d. | 30.89 ± 1.45 b | |
| γ-tocopherol | 19.23 ± 0.81 b | n.d. | 16.74 ± 0.38 a | |
| Sample | ABTS Test | DPPH Test | β-Carotene Bleaching Test | FRAP Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min Incubation | 60 min Incubation | ||||
| IC50 (μg/mL) | IC50 (μg/mL) | IC50 (μg/mL) | IC50 (μg/mL) | μM Fe (II)/g | |
| BHT | - | - | - | - | 63.19 ± 2.22 |
| BP-W | 120.75 ± 8.83 a | 119.91 ± 6.54 a | 6.31 ± 0.94 b | 4.39 ± 0.67 a | 44.78 ± 2.35 b |
| BP-ET | 121.82 ± 9.04 a | 354.55 ± 10.31 b | 3.38 ± 0.35 a | 3.27 ± 0.29 a | 60.20 ± 3.98 a |
| Sign. | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** |
| Positive Controls | |||||
| Ascorbic acid | 1.85 ± 0.15 | 5.11 ± 0.78 | - | - | - |
| Propyl gallate | - | - | 1.1 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | - |
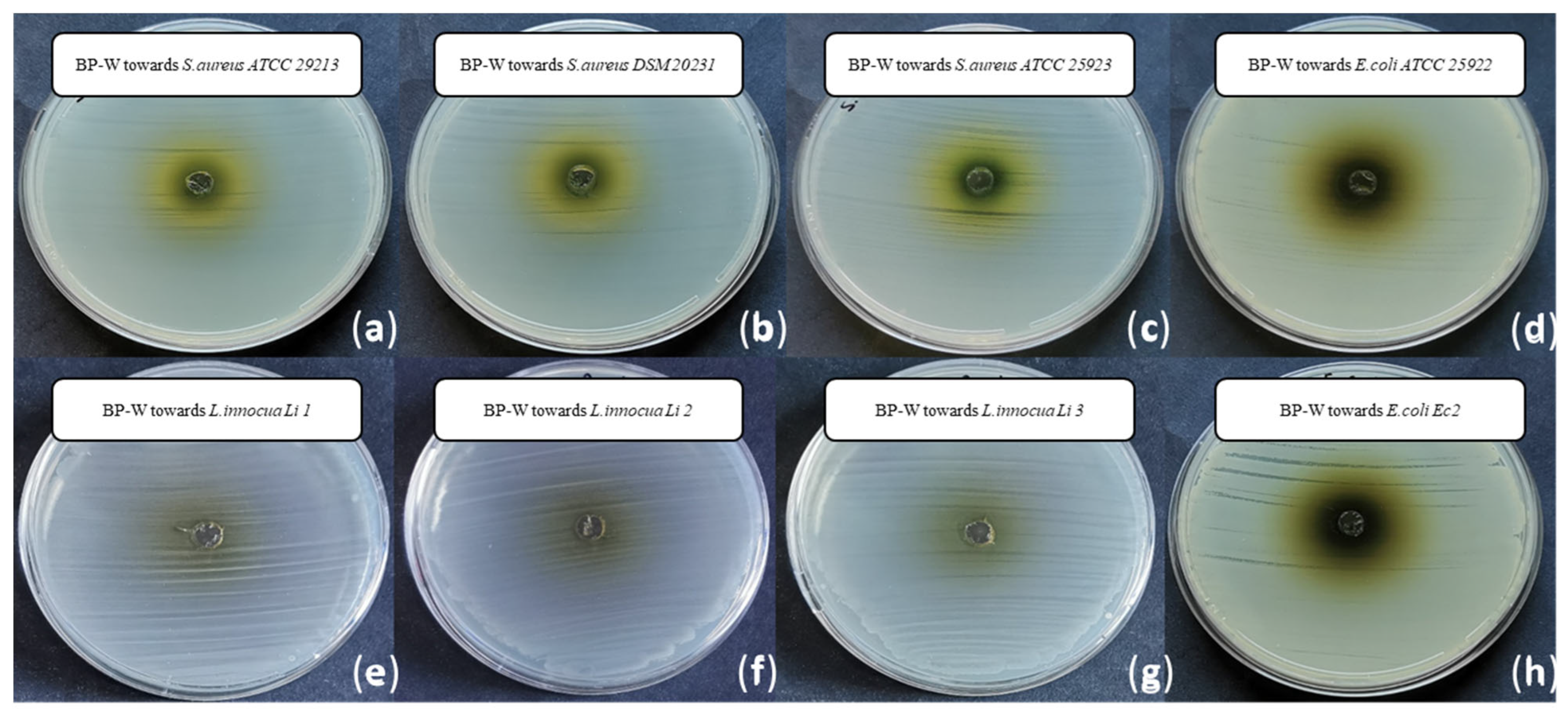
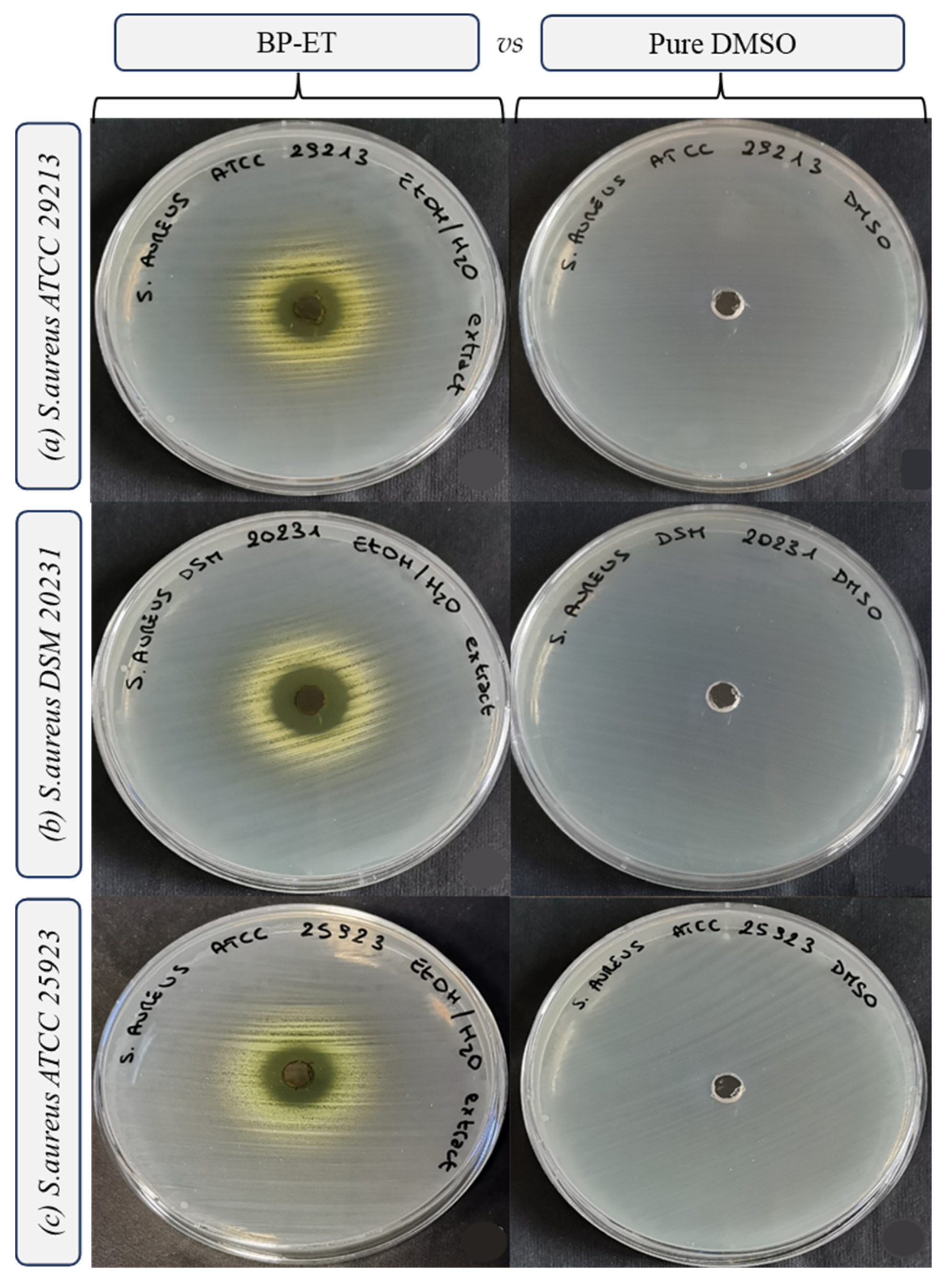
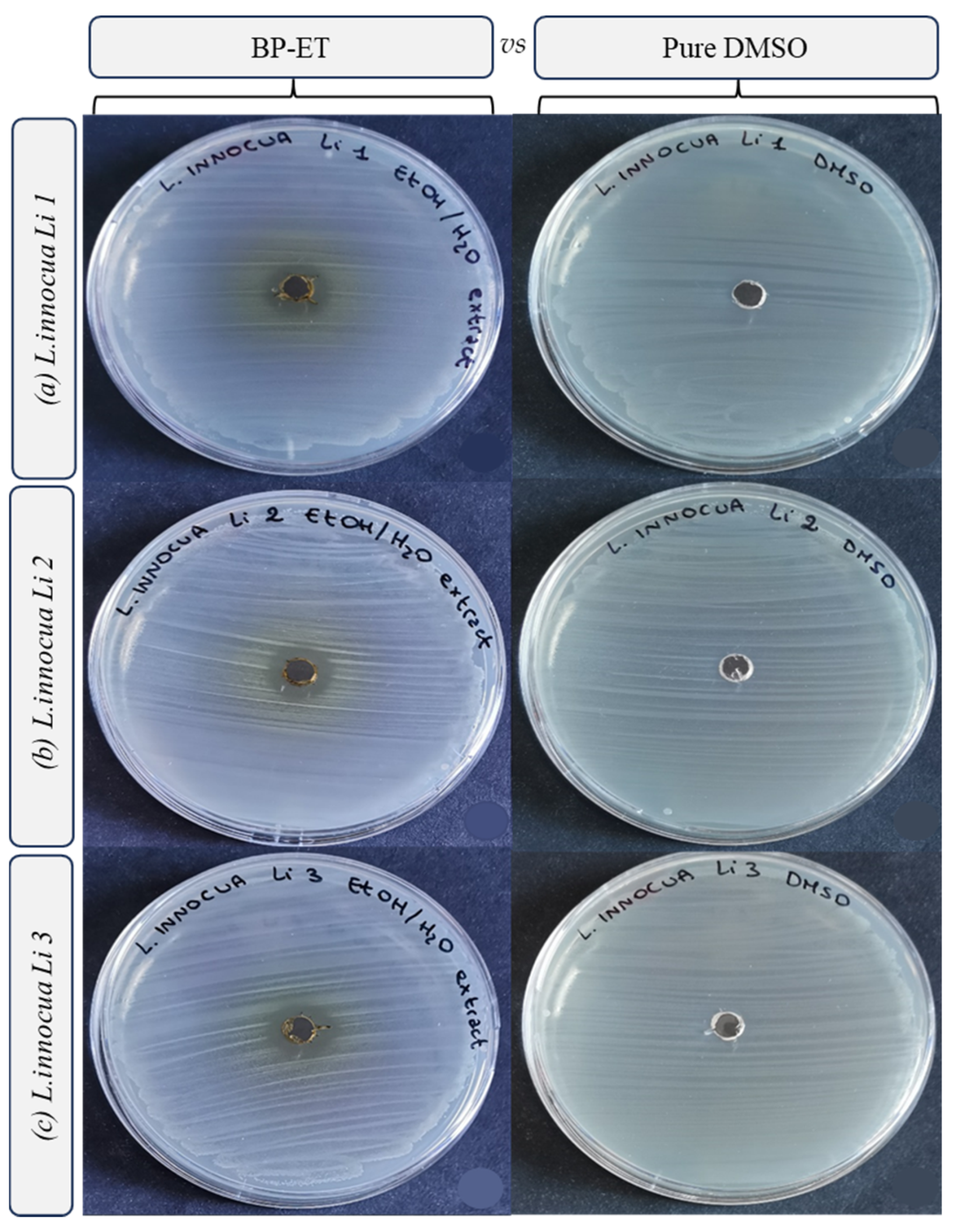
| Species | Strain | Inhibition Growth Zones (mm) | MIC (mg mL−1) | MBC (mg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC 29213 | 3.31 ± 0.09 b | 2.5 ± 0.0 c | 10.0 b |
| Staphylococcus aureus | DSM 20231 | 4.50 ± 0.00 a | 2.5 ± 0.0 c | 10.0 b |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC 25923 | 3.13 ± 0.00 b | 5.0 ± 0.0 b | >10.0 a |
| Listeria innocua | Li 1 | 3.00 ± 0.18 b | 5.0 ± 0.0 b | >10.0 a |
| Listeria innocua | Li 2 | 3.13 ± 0.00 b | 5.0 ± 0.0 b | >10.0 a |
| Listeria innocua | Li 3 | 3.19 ± 0.27 b | 5.0 ± 0.0 b | >10.0 a |
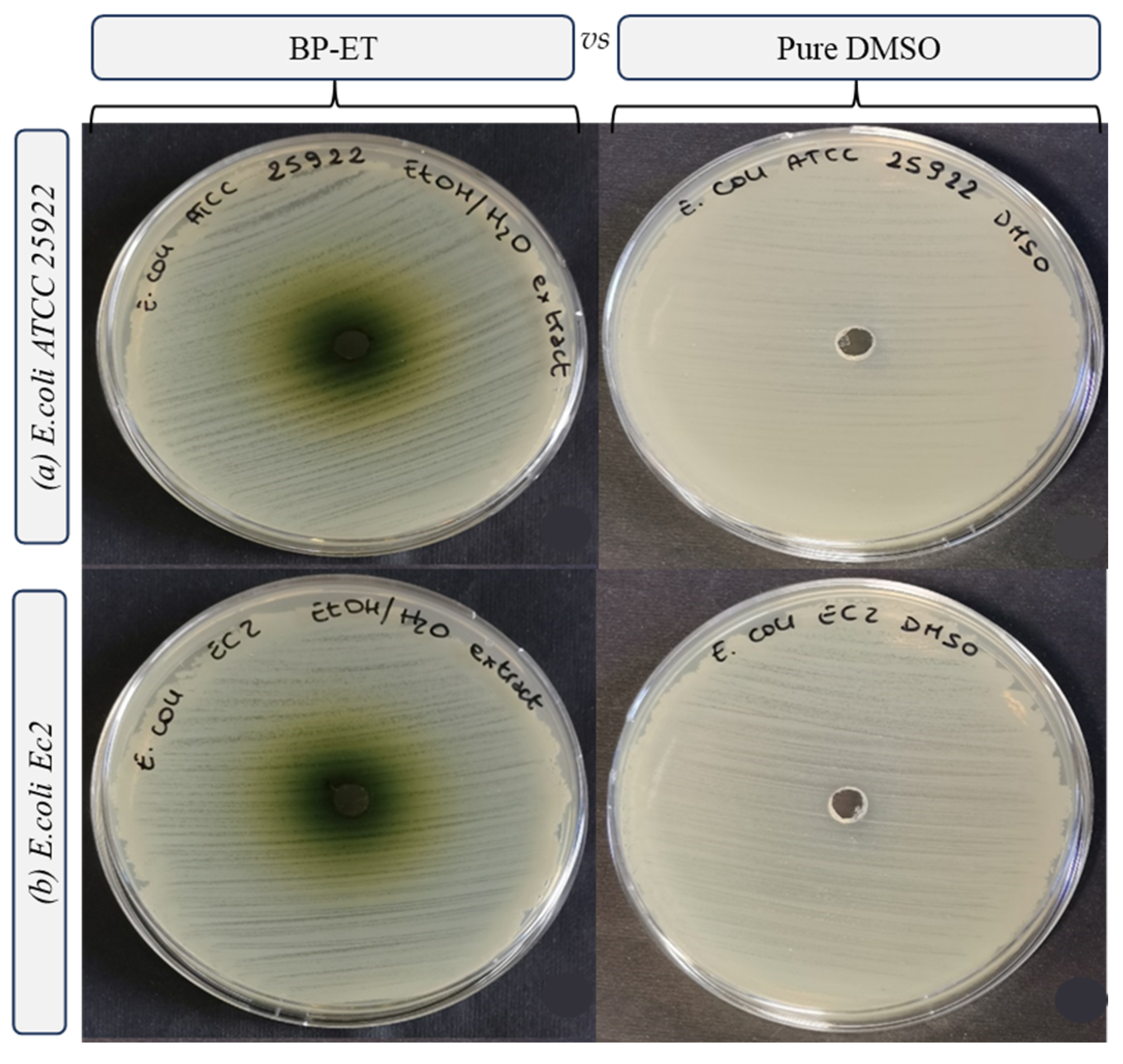
| Escherichia coli | ATCC 25922 | n.d. c | >10.0 a | >10.0 a |
| Escherichia coli | Ec 2 | n.d. c | >10.0 a | >10.0 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashim, A.; Ismaiel, L.; Fanesi, B.; Nartea, A.; Maoloni, A.; Orhotohwo, O.L.; Darko, H.S.O.; Lucci, P.; Aquilanti, L.; Pacetti, D.; et al. Food-Grade Polar Extracts from Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) By-Products: Unlocking Potential for the Food Industry. Foods 2025, 14, 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132304
Ashim A, Ismaiel L, Fanesi B, Nartea A, Maoloni A, Orhotohwo OL, Darko HSO, Lucci P, Aquilanti L, Pacetti D, et al. Food-Grade Polar Extracts from Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) By-Products: Unlocking Potential for the Food Industry. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132304
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshim, Aizhan, Lama Ismaiel, Benedetta Fanesi, Ancuta Nartea, Antonietta Maoloni, Oghenetega Lois Orhotohwo, Helen Stephanie Ofei Darko, Paolo Lucci, Lucia Aquilanti, Deborah Pacetti, and et al. 2025. "Food-Grade Polar Extracts from Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) By-Products: Unlocking Potential for the Food Industry" Foods 14, no. 13: 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132304
APA StyleAshim, A., Ismaiel, L., Fanesi, B., Nartea, A., Maoloni, A., Orhotohwo, O. L., Darko, H. S. O., Lucci, P., Aquilanti, L., Pacetti, D., Pino, R., Tundis, R., & Loizzo, M. R. (2025). Food-Grade Polar Extracts from Sea Fennel (Crithmum maritimum L.) By-Products: Unlocking Potential for the Food Industry. Foods, 14(13), 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132304













