Abstract
The present study is focused on the presentation of a numerical solution for copper-water nanofluid through a stretching channel with spherical and cylindrical shape nanoparticles. The analysis of nanofluid in a channel with stretching walls under slip effects is made by introducing the conservation equation of nanoparticle volume fraction into Hamilton-Crosser’s nanofluid model. Governing partial differential equations are transformed into nonlinear ordinary differential equations by applying similarity transformation and then solved with the help of shooting method. The effects of different physical parameters on the rheology of nanofluids’ particles are presented in tabulation and pictorial representation. The study reveals that the thermal boundary layer thickness increases by increasing the solid volume fraction.
1. Introduction
Progress in nanotechnology has allowed to finding many ways to increase the nominal values of the physical and thermal properties of poor conducting fluids such as water, kerosene oil, glycerol, etc. By including nano-scaled metal particles, properties like conduction can be boosted. These improvements can prompt mechanical and heat systems with more adequate properties. Thus, medical and engineering sciences can take advantage of this innovation. Likewise, it is employed as a part of electrical and mechanical hardware. In the past, several numerical models have been used to investigate the properties and the impacts caused by these nano-scaled particles on different situations. The inclusion of large and small scale measured metal particles into liquids/coolants, which are innately poor heat conductors, was first presented by Maxwell [1]. After him, diverse hypothetical models were displayed, for example the Hamilton-Crosser [2] and Wasp [3] models. Because of certain detriments, the use of full and small scale estimated particles could not hold much consideration. After revelation of nanoparticles, research in the field of nanofluid once again became more interesting. Choi et al. [4,5] presented by first time a nanoparticle suspension as a "nanofluid". After that, Buongiorno [6] proposed a broader model considering the thermophoresis and Brownian movement impacts.
Models of nanofluid flow and heat transfer can be classified into two perceptible models known as single-phase and two-phase models [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. The single-phase model is a single homogeneous fluid that is considered with respect to their effective properties apart from nanoparticles and base fluid. Conversely, the two-phase model considers continuity, momentum and energy equations for nanoparticles and base fluid. The mathematical formulation of nanofluids was simplified by Buongiorno [6], who stated that the basic mechanic contributes to thermal enhancement and Brownian diffusion and thermophoresis. This study was generalized into boundary layer model for free convective flows of nanofluids by Kuznetsov and Nield [15]. Sheikholeslami et al. [16] observed properties of heat transfer and nanofluids in revolving system using binary horizontal plates. They observed that the rate of heat transfer increases during injection and suction of a volume fraction for nanoparticles and Raynolds number. In addition, it was shown that the heat transfer rate is also affected by spin parameter. Raza et al. [17] investigated the different branches of the solution of copper-water nanofluid in a channel with expanding or contracting walls. Domairry et al. [18] examined binary vertical plates, infinite parallel, natural convection of a non-Newtonian copper-water nanofluid. Their study suggests that the size of nanoparticles is directly related to the thickness of boundary layer and inversely related to the thickness of thermal boundary layer. Numerical investigation of copper-water nanofluid in a channel with stretching walls was presented by Raza et al. [19]. This study revealed that the heat transfer rate increased by increasing the values of the solid volume fraction and suction. Additionally, the two-phase model was evaluated by relating the convective heat transfer coefficients and friction factors expected with experimental results extracted from literature. Sheikholeslami et al. [20,21,22] investigated the two-phase model for simulation of nanofluid indifferent fluid flow topologies. Freidoonimehr et al. [23] investigated the problem of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) laminar free convection flow of nanofluid moving through a vertical surface. In addition, the effect of variations in the rheology properties of different kinds of nanoparticles was studied in [24]. A numerical investigation of the problem involving the natural convection heat transfer of nanofluid in a two-dimensional square cavity was carried out by Garoosi et al. [25]. This study revealed that the reduction of the diameter of the nanoparticles increases the heat transfer rate.
It has been identified, at least at a perceptible level, that the occurrences of slip effects at solid boundaries have numerous applications in micro- or nano-channels. In this sense, such effects can appear in the cases where a thin film of light oil is placed on moving walls or when the boundaries are lubricated with a special coating such as thick monolayer of hydrophobic octadecyl-thichorosilane. Due to the several engineering applications, many researchers have shown their interest in slip effects developing several research works. Yu and Ameel [26], Waltannebe et al. [27], Jain and Sharma [28] and Khaled and Vafai [29] are the most prominent among them. MHD flow and heat transfer problem specifically associated to Cu-water nanofluid through a channel with stretching walls under the slip effects can be elucidated by solving a system of nonlinear equations.
2. Mathematical Formulation
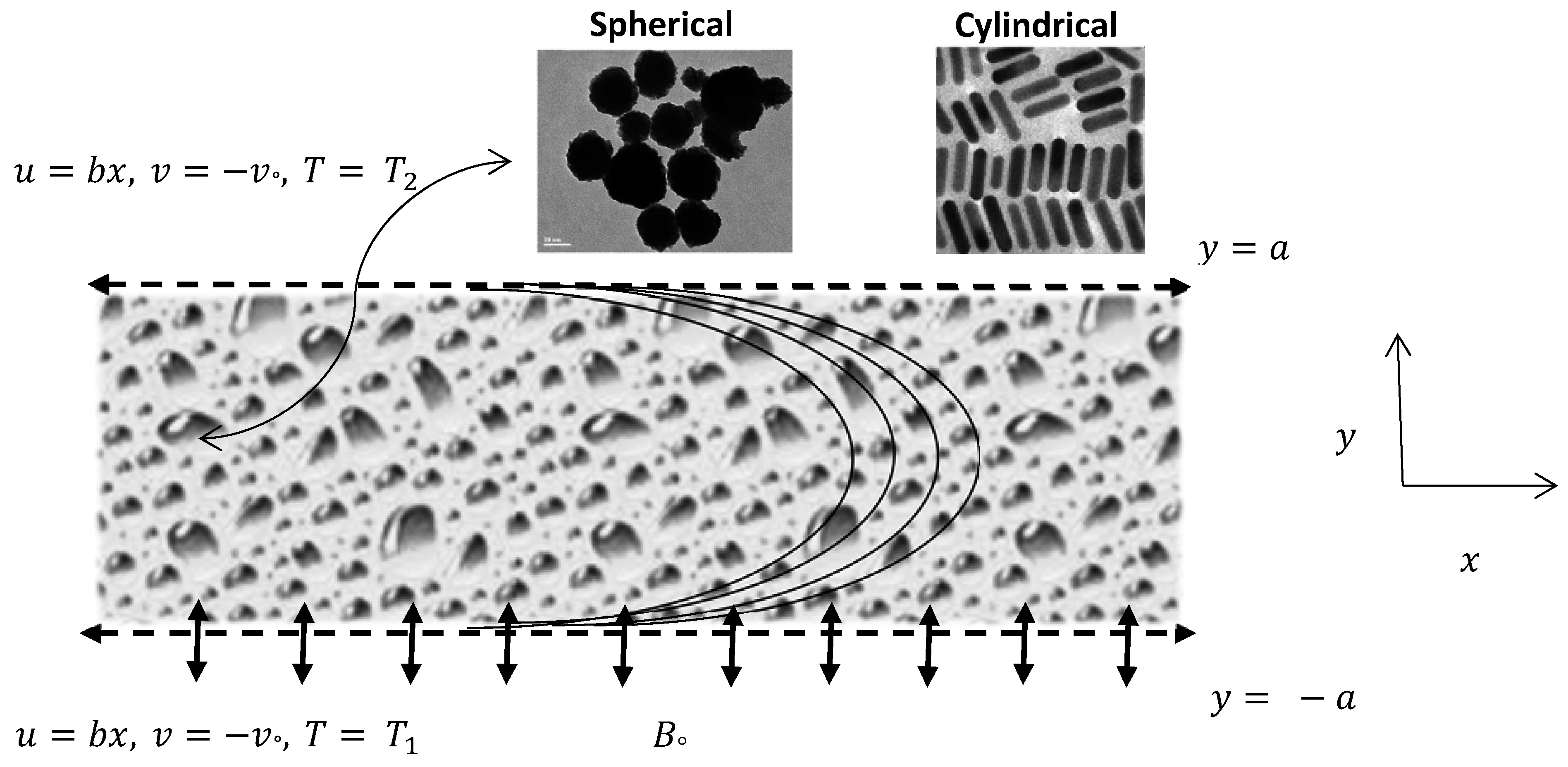
A two-dimensional steady laminar incompressible flow of electrically conductive nanofluid in a porous channel was considered for the mathematical formulation. In addition, we select the Cartesian coordinate system such that the x-axis is taken in the direction of the flow and y-axis is perpendicular to the channel. It has to be considered that the upper wall is located at y = a, which is static and non-permeable, and the lower wall is located at y = −a, which is permeable as well as stretching in the direction of x-axis as shown in Figure 1. Flow is subjected to a magnetic field constantly applied in the y-axis direction. The Hamilton-Crosser’s (H-C) model of thermal conductivity of nanofluid is given by [30].
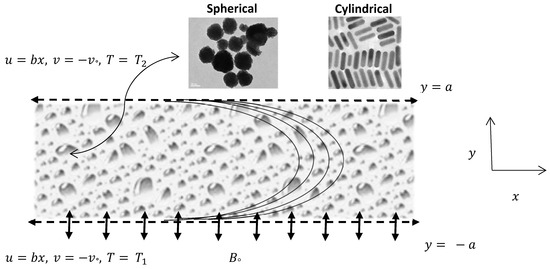
Figure 1.
Physical model of the proposed problem.
Here, represents the effective thermal conductivity of the nanofluid, is the thermal conductivity of the continuous phase (i.e. water in this case), φ is the volume fraction of nanoparticles and n is the shape factor for nanoparticles given by 3ψ where ψ corresponds to the sphericity of the nanoparticles and depends on the shape of the nanoparticles. For spherical nanoparticles ψ = 1 or n = 3 and for cylindrical nanoparticles ψ = 0.5 or n = 6. The main objective of the present analysis will remain to examine the impact of these two models on the heat transfer rate with copper water (Cu-Water) nanoparticles.
Governing equations of the following fluid model are given below.
where and are the velocity component along and axes respectively, is effective electrical conductivity of nanofluid, is effective density, is the effective dynamic viscosity, is heat capacitance and thermal conductivity of the nanofluid. These physical quantities were mathematically described by Raza et al. [19].
Here is the solid volume fraction, is for nanosolid-particles, is for base fluid. Our preference is to solve Equations (2)–(5) through Equations (6)–(9), with boundary conditions
Moreover, b < 0 for shrinking of the channel walls, b > 0 for stretching of the channel wall and represent the slip effects (velocity and thermal) respectively.
By introducing similarity transformation represented by the following expressions:
the governing Equations (2)–(5) can be converted into ordinary differential equations by replacing the similarity transformation into Equations (2)–(5) and using the Equations (6)–(9),
where is the stretching Reynolds number, is the Hartman number, is the Prandtle number, is suction parameter and the values of are:
In addition, the boundary conditions are defined as bellow.
3. Numerical Solution
In order to find the numerical solution, the shooting technique was employed to solve and investigate solutions of Equations (14) and (15), where the boundary conditions described by Equations (19) were applied. Thus, a boundary value problem was converted into an initial value problem by setting.
where the initial conditions are expressed as follows:
Here, are unknown initial conditions. We have to shoot these initial conditions with some arbitrary slope in such a way that the solution of the system (20) of Equations (14–15) satisfies the given conditions at the boundary. A hit-and-trail approach is applied in order to find the unknown initial conditions. Once slope and is assumed, the numerical integration is carried out for the initial value problem and accuracy of missing initial conditions is then checked by comparing calculated value with the given terminal point. The details of the shooting method with Maple 18 implementation shoot has been described by Meade et al. [31].
4. Results and Discussion
The numerical results of this research are presented in this section in the form of tables and graphs. Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 and Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 summarize the effects of different physical parameters on properties such as skin friction, heat transfer and velocity. Based on the work carried out by Raza et al. [20], the range of the nanoparticle volume fraction is considered to be , and the Prandtl number of the water-base fluid is kept constant at 6.2. Table 1 showed the thermophysical properties of the different kind of nanofluids. Table 2 is presented to show the effects of the solid volume fraction on with spherical shape nanoparticles . From this table, it can be stated that heat transfer rate at the lower wall of the channel increases monotonically by increasing the values of solid volume fraction . Furthermore, the heat transfer rate at the lower wall of the channel is increased as the numerical values of solid volume fraction are increased for the case of nanoparticles with cylindrical shape . Compared with base fluid (water), nanofluids exhibit a distinctive property allowing the enhancement of heat transfer, which makes them attractive for many engineering applications such as pharmaceutical processes, thermal management of electronics, heat exchangers, etc. Enhancements of heat transfer of nanofluids depend upon the particle size and its shape. A cylindrical shape and a reduced particle size will be in favor of a better heat transfer. The mentioned results are presented in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 1.
Thermophysical properties of water and nanoparticles [20].

Table 2.
Effect of the solid volume fraction on with spherical shape nanoparticles.

Table 3.
Effect of solid volume fraction on with cylindrical shape nanoparticles.
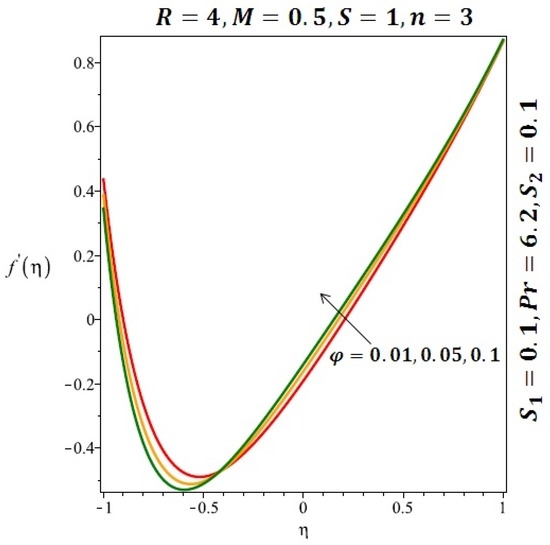
Figure 2.
Effect of the variation of the solid volume fraction (ϕ) on the velocity of spherical nanoparticles
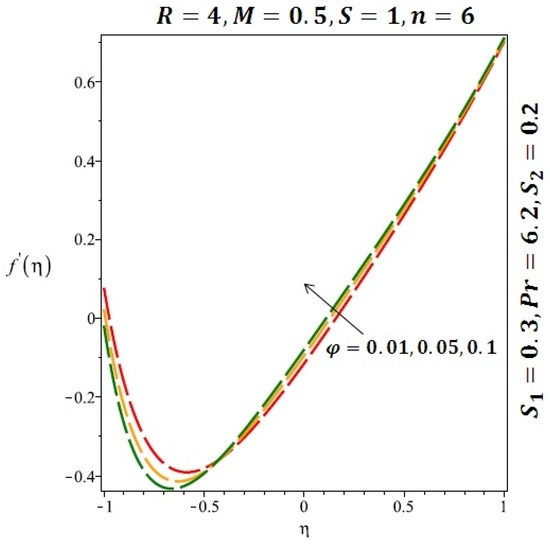
Figure 3.
Effect of the variation of the solid volume fraction on velocity of cylindrical nanoparticles.
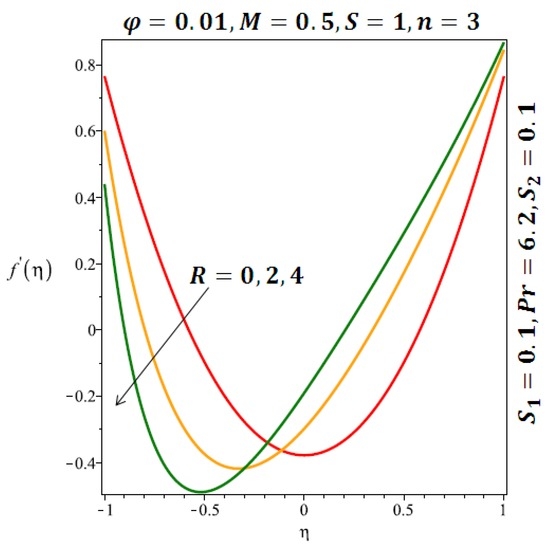
Figure 4.
Effect of the variation of the Reynolds number (R) on the velocity of spherical nanoparticles.
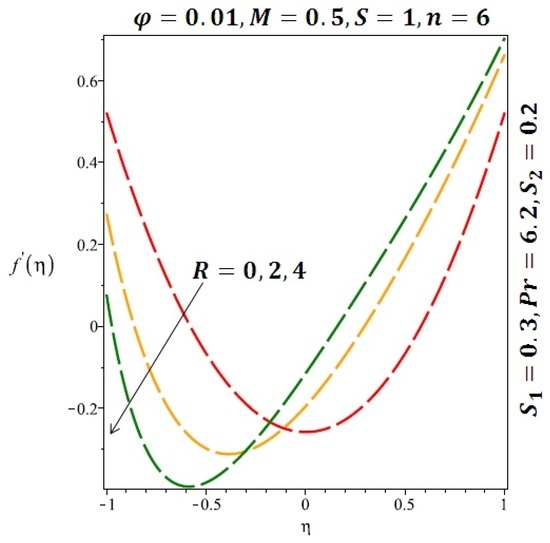
Figure 5.
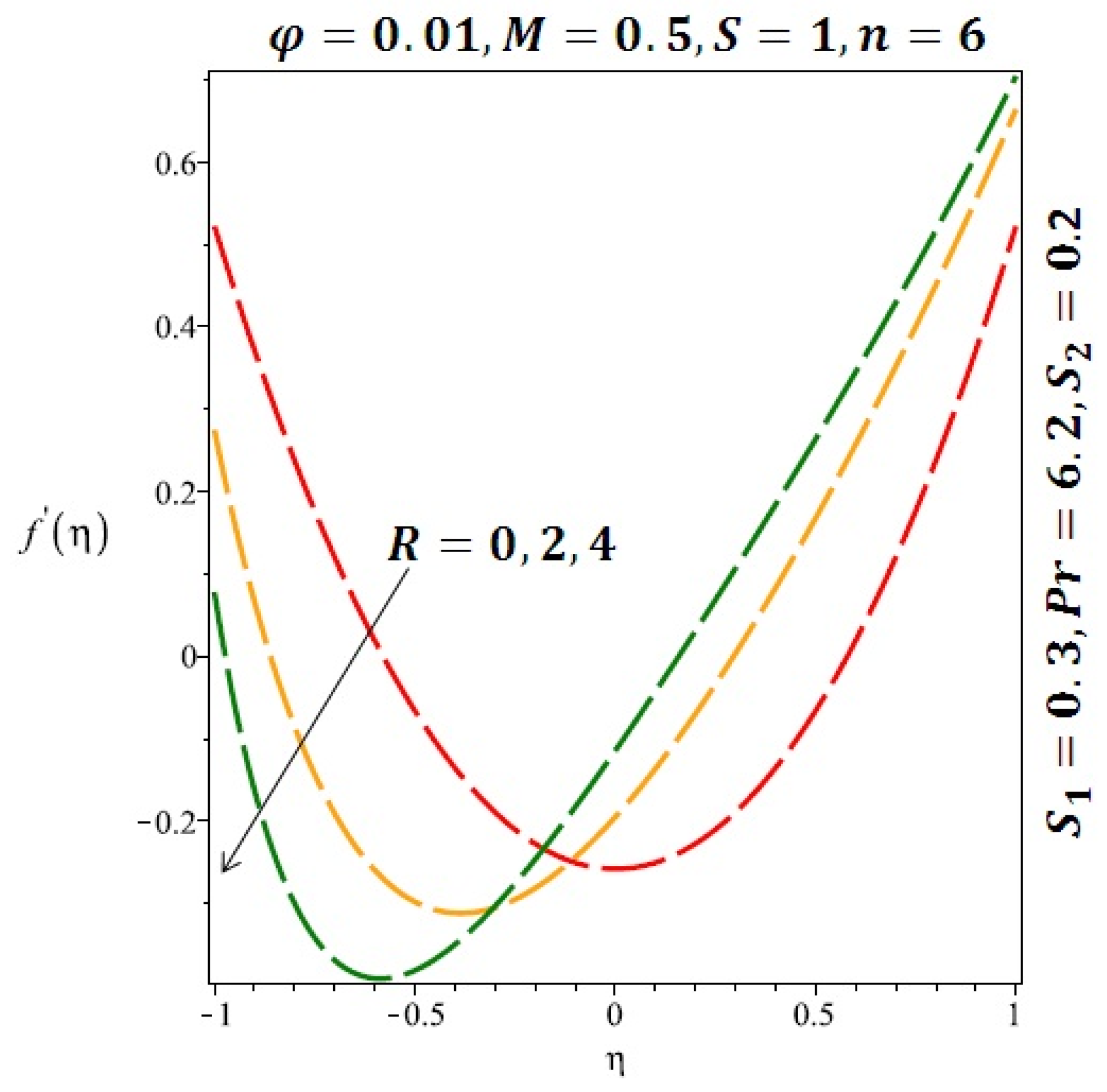
Effect of the variation of the Reynolds number (R) on the velocity for cylindrical nanoparticles.
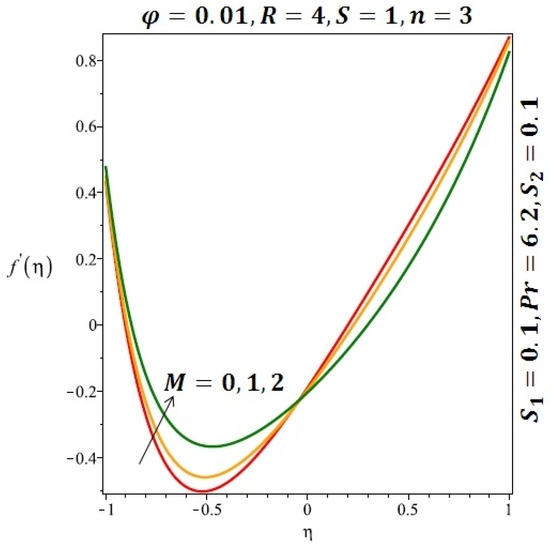
Figure 6.
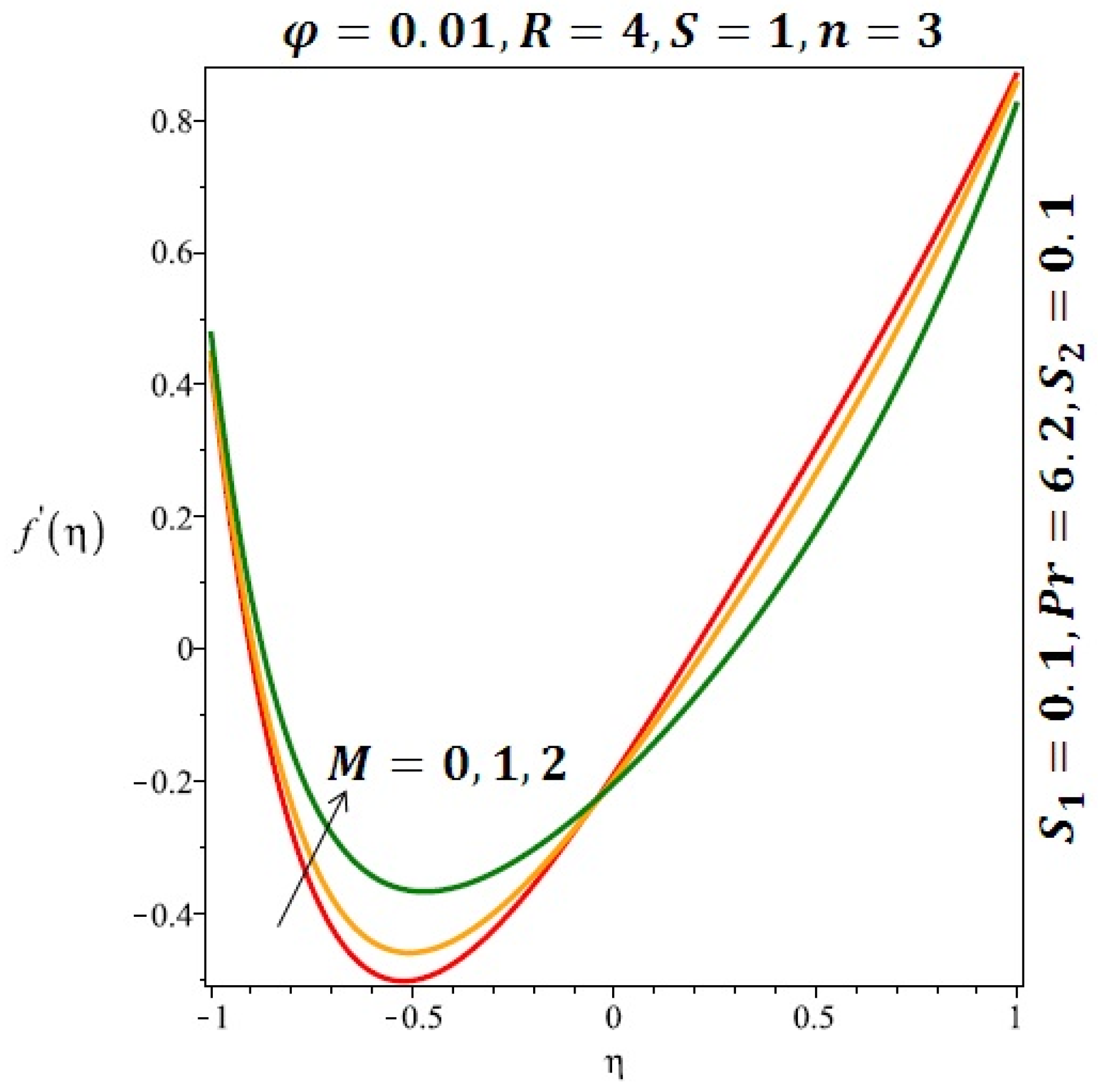
Effect of the variation of the magnetic field (M) on the velocity of spherical nanoparticles.
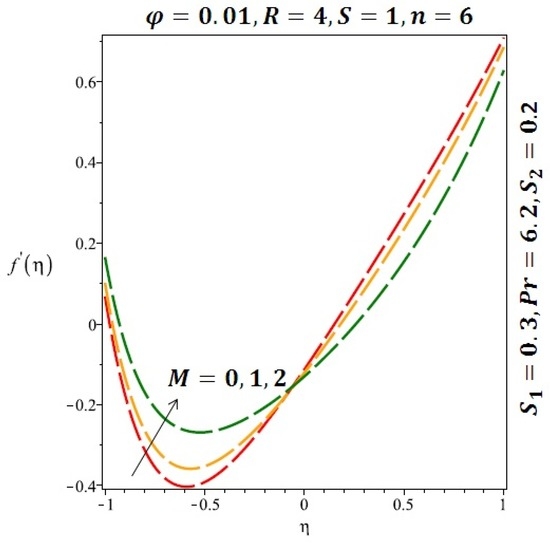
Figure 7.
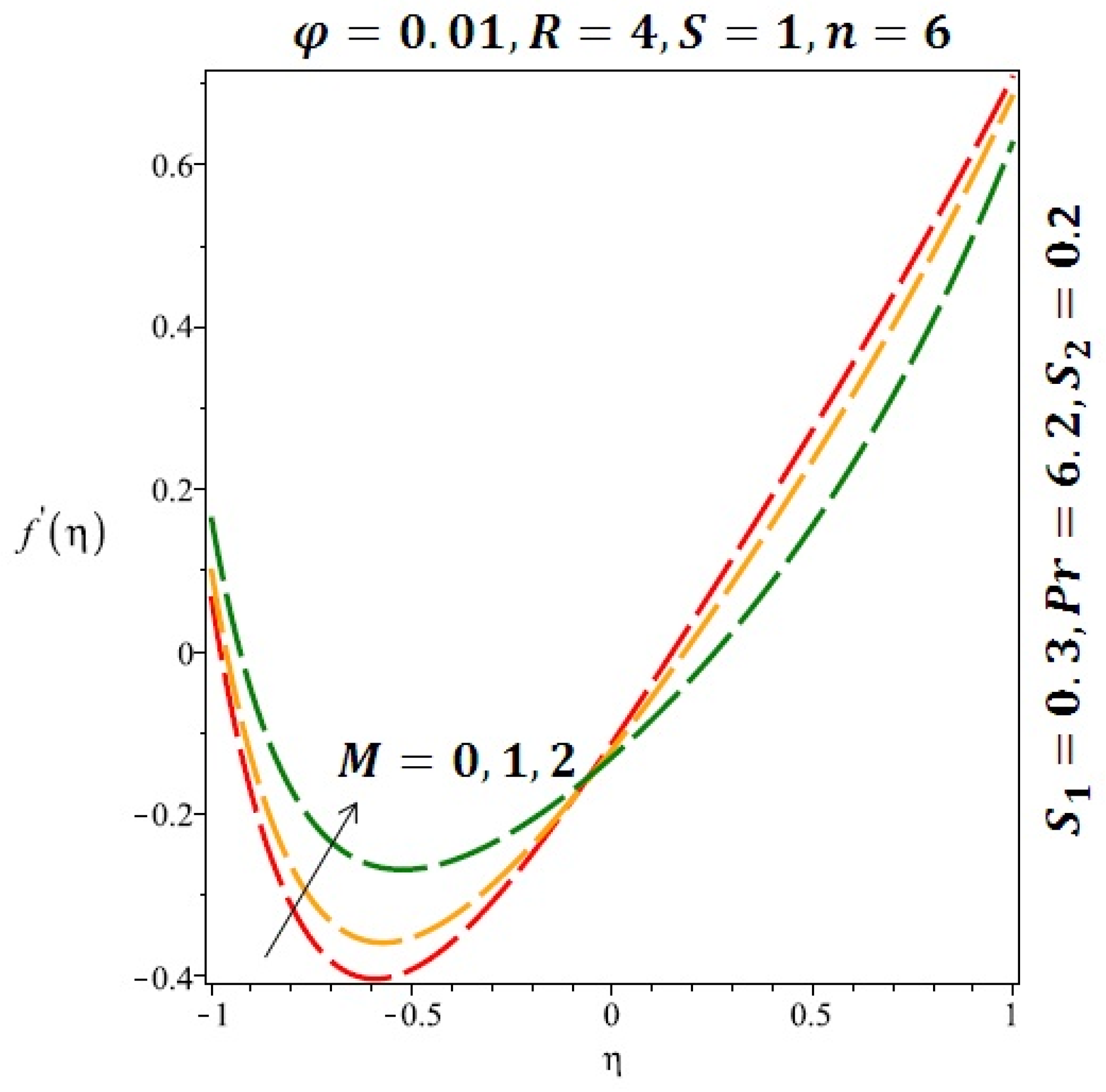
Effect of the variation of the magnetic field (M) on the velocity of cylindrical nanoparticles.
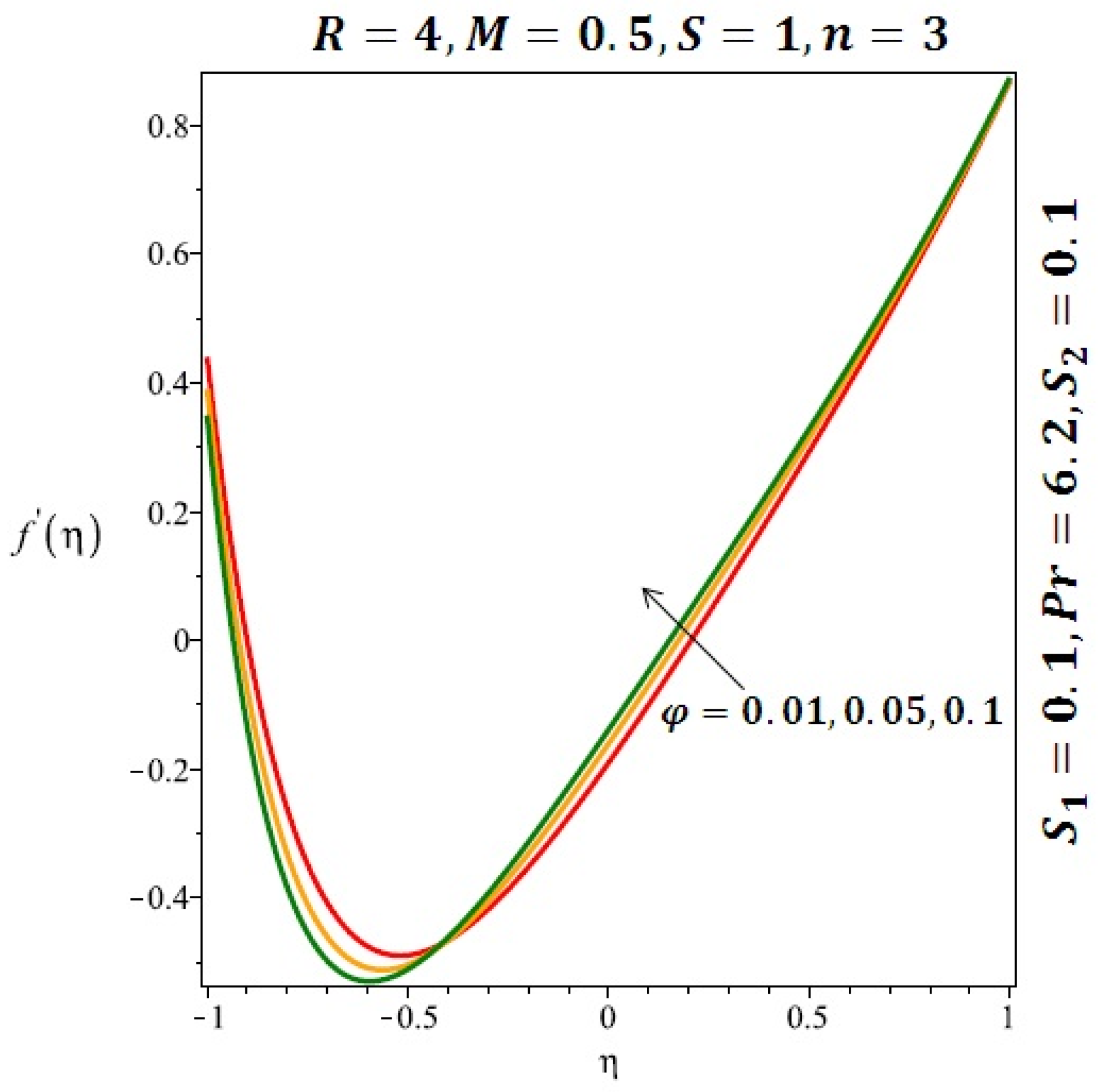
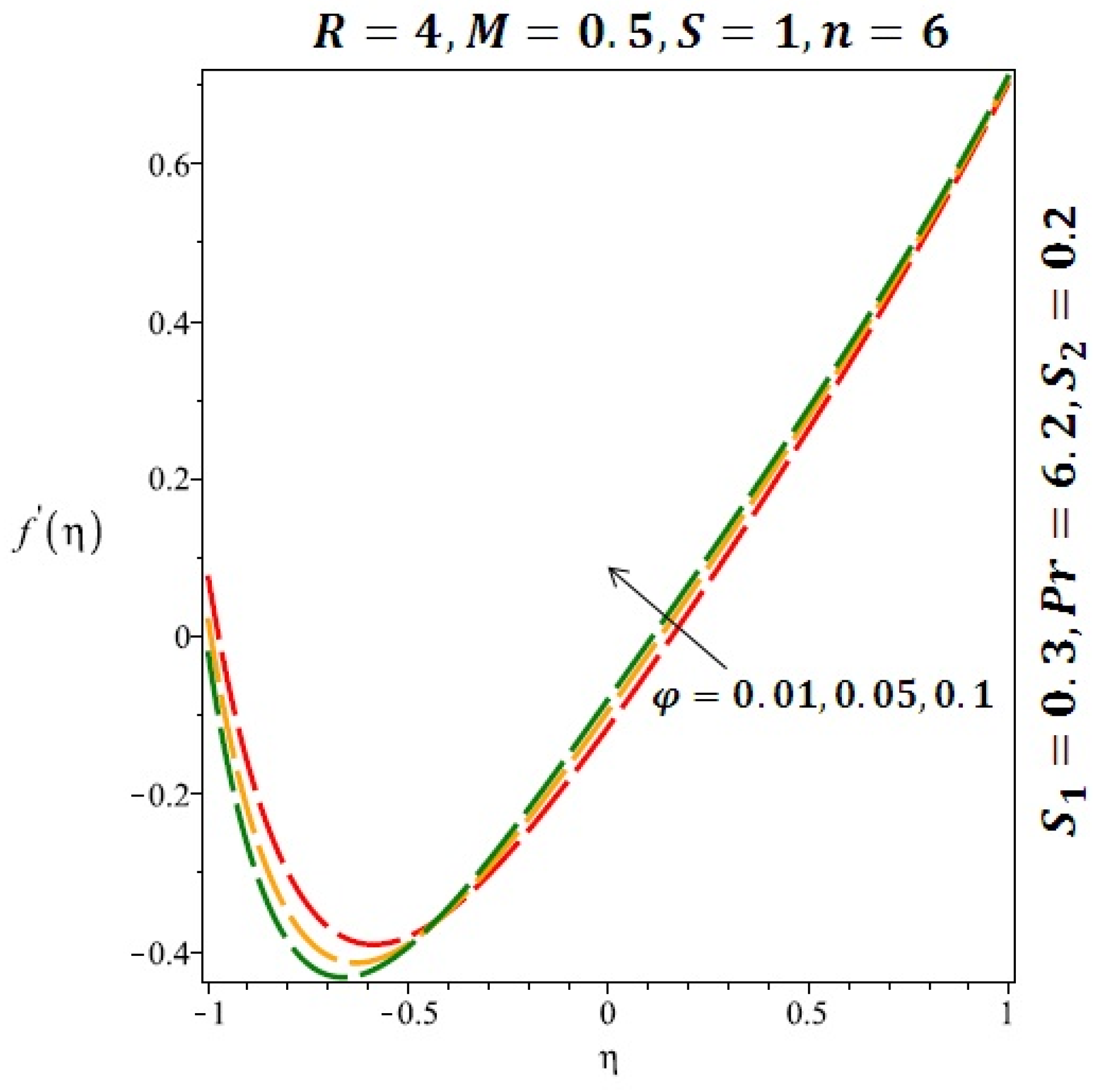
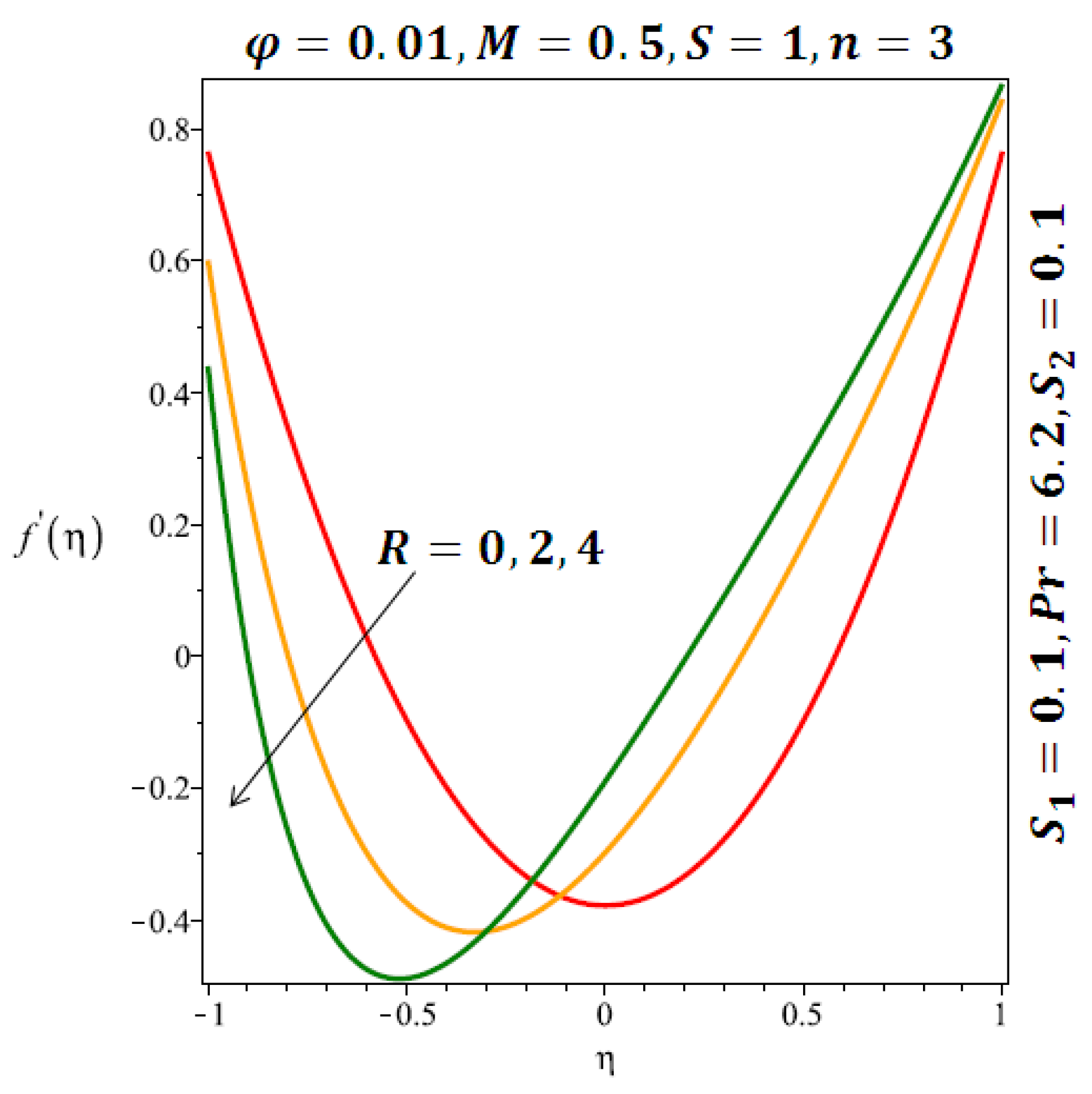
The effects of the solid volume fraction on the velocity profile for spherical and cylindrical shape of nanoparticles are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3 respectively. For spherical shape nanoparticles the other physical parameters were fixed as and such parameters were set as for cylindrical shape of nanoparticles . From these profiles we came to know that velocity profile near the lower wall shiffted towards the lower wall of the channel. In other words, velocity profile decreases near the lower wall of the channel and increases afterwards by increasing the values of solid volume fraction . Figure 4 and Figure 5 elucidate the effect of stretching Reynolds number on velocity profile for spherical and cylindrical shape of nanoparticles. It is observed that decreases near the lower wall of the channel and increases after . Since the lower wall is stretching and the upper wall remains stationary, the effects of stretching Reynolds number are clearly seen near the lower wall of the channel.
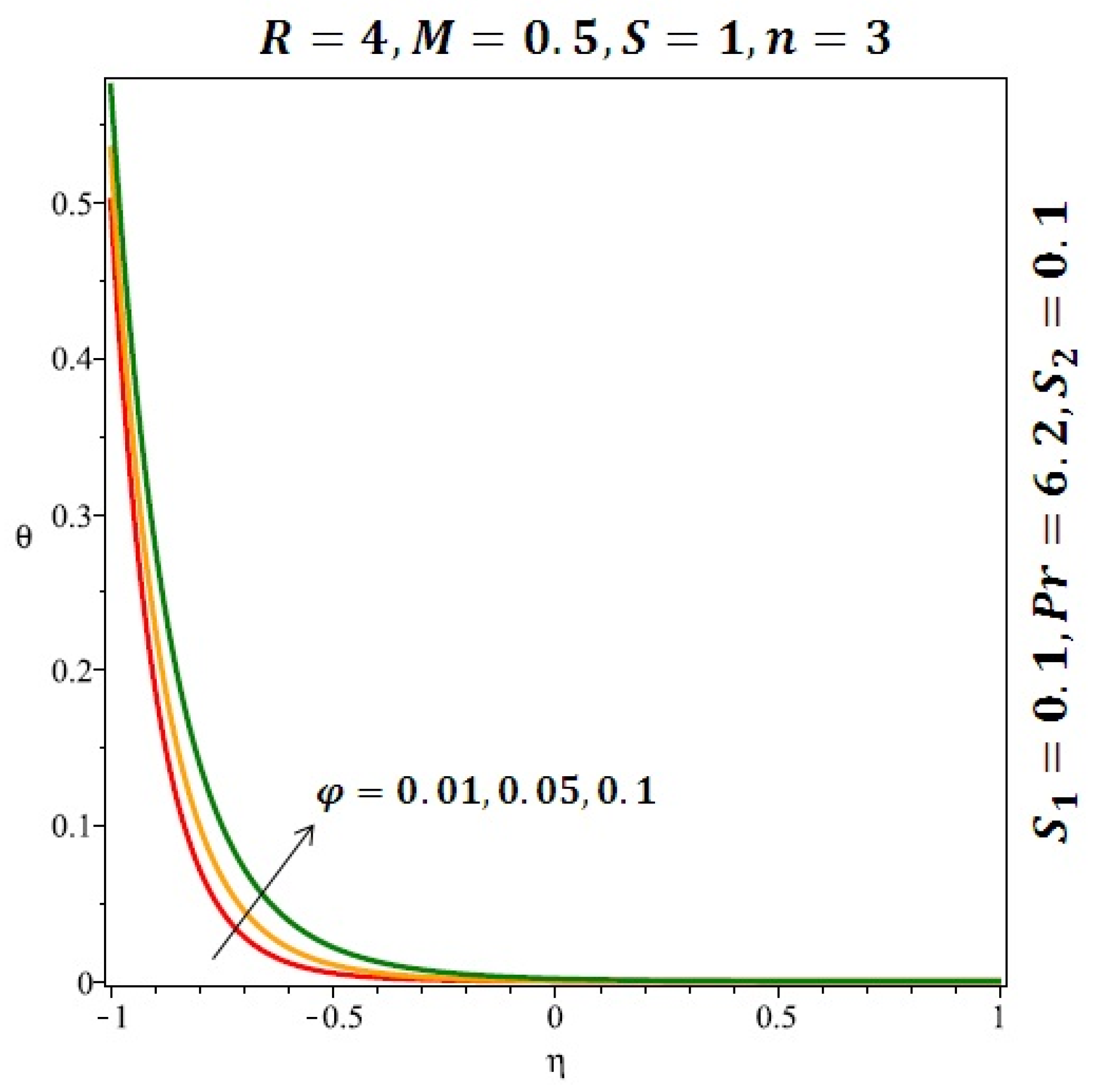
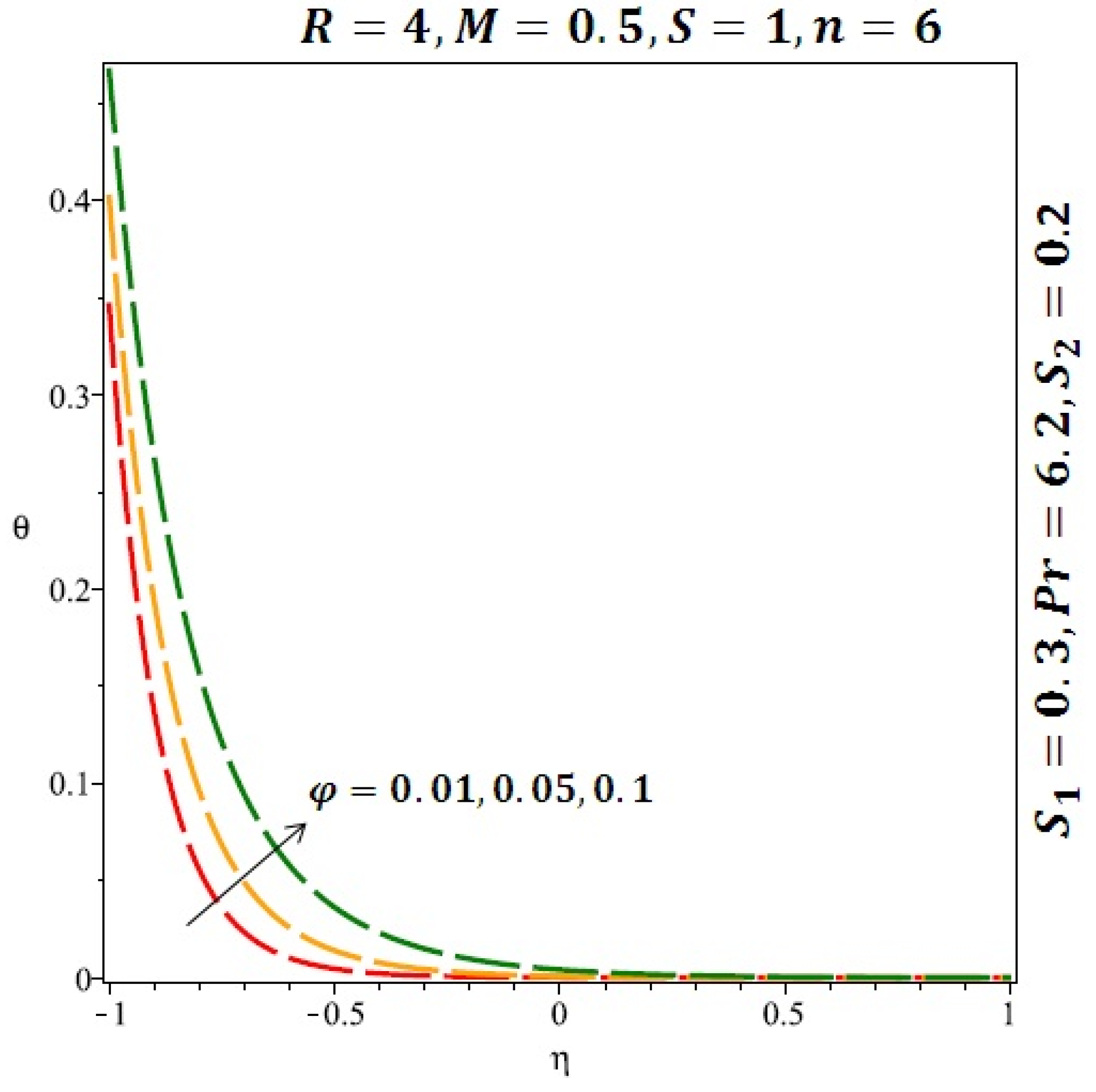
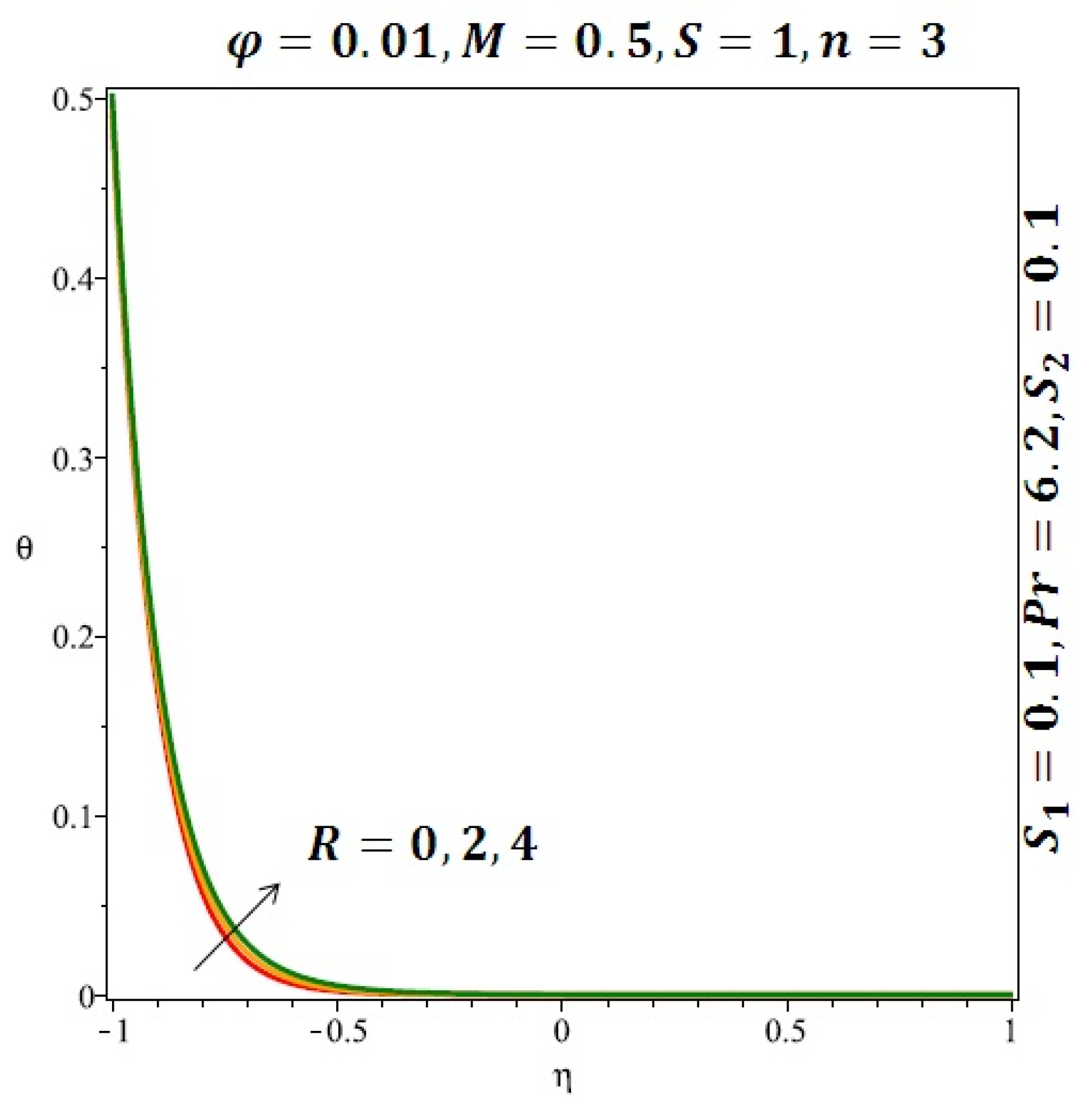
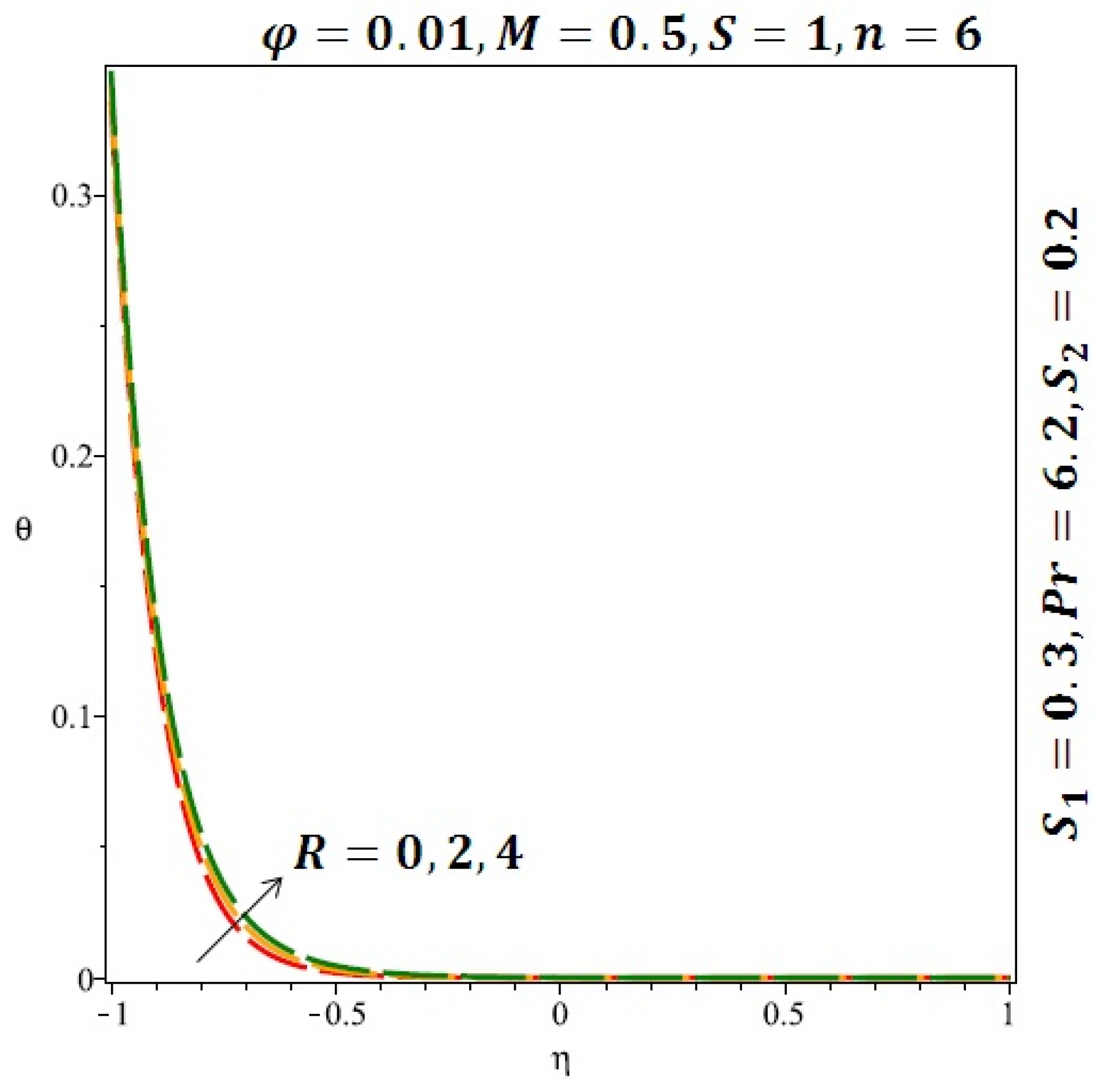
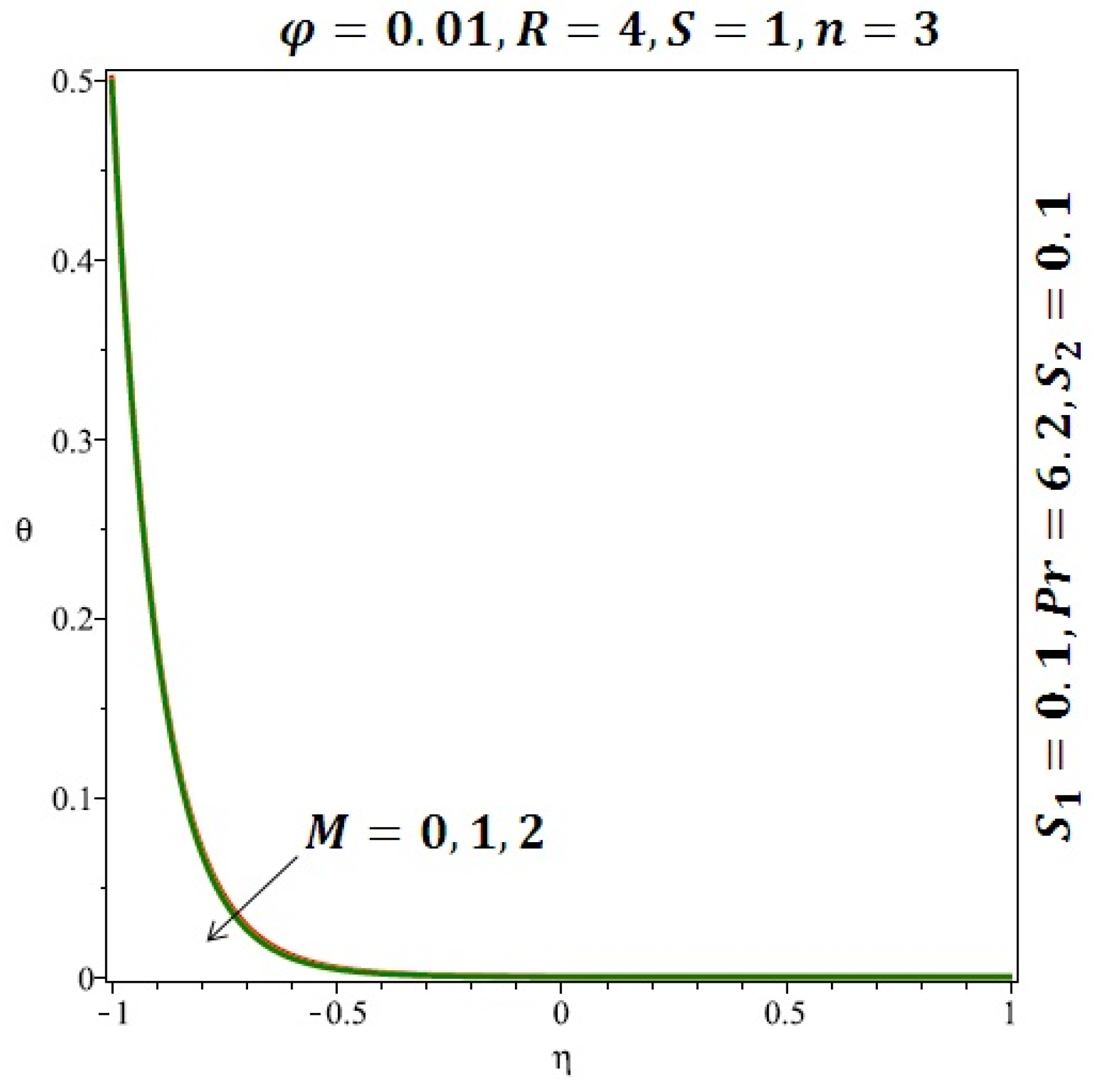
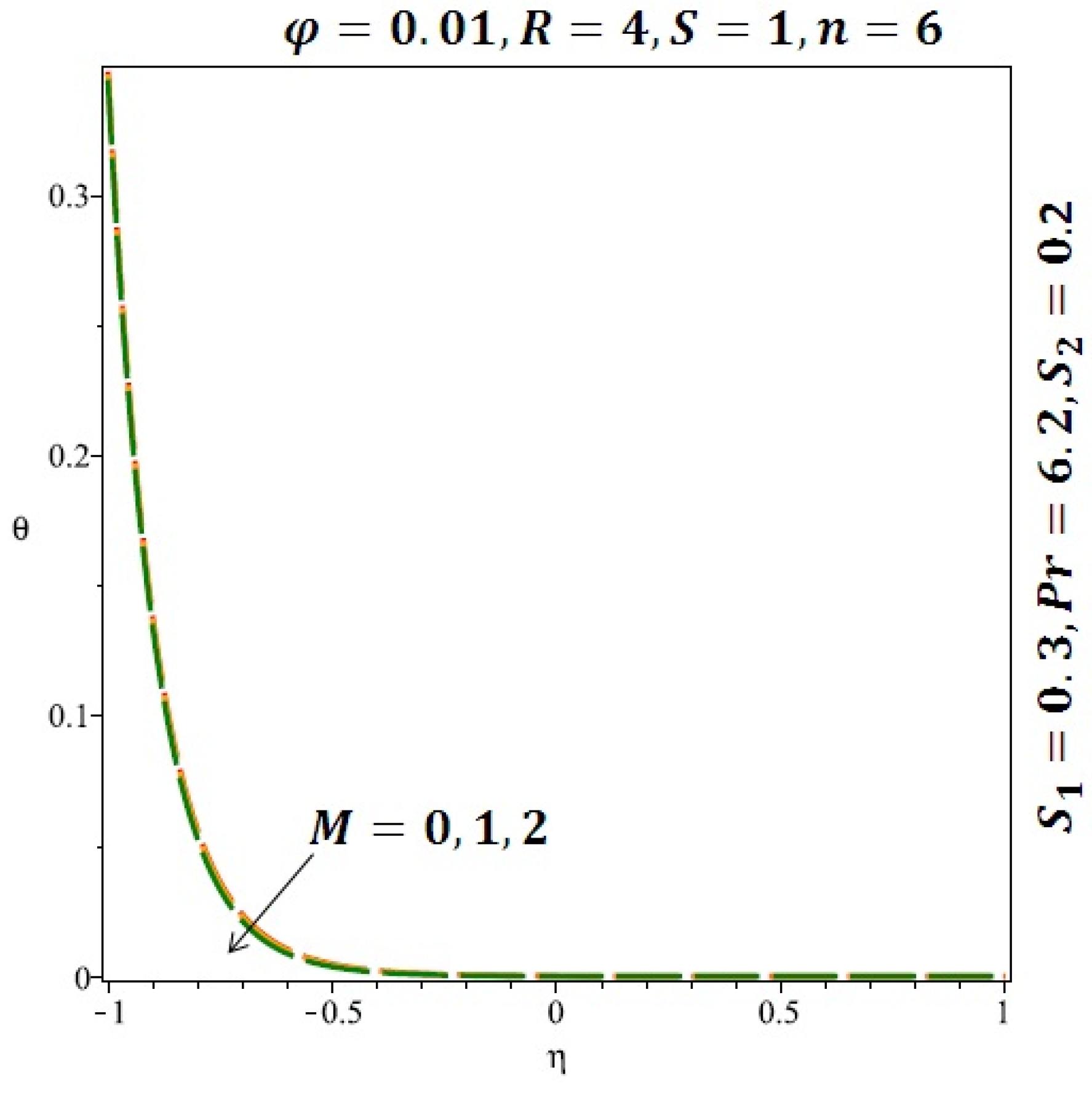
Figure 6 and Figure 7 depicted the effect of a magnetic field on the velocity profile of spherical and cylindrical nanoparticles, respectively. From these results, it can be seen that velocity profile increases from the lower wall to the center of the channel and then decreases monotonically by increasing the strength of the magnetic field . It is shown that the velocity profile has an opposite trend when comparing the lower and the upper side of the channel. It has to be noted that the lower wall of the channel is located at and it is stretching, which induced a flow. Nevertheless, the magnetic field, which is more dominant than the stretching, is applied in the transverse direction of the lower channel causing a decrease in the velocity near the lower wall of the channel. Thus, when the magnetic field is applied to the nanofluid, its apparent viscosity decreases due to the formation of a chain of nanoparticles. The induction of a magnetic field in nanoparticles gives additional kinetic energy to the particles and therefore their velocity increases rapidly. This results in the fact that the flow of nanofluid in a channel can be controlled by applying a magnetic field which can be used in many possible control based applications including MHD power generation, casting of metals, ion propulsion, etc. Figure 8 and Figure 9 depicted the effects of solid volume fraction on the heat transfer profile (HTP) for spherical and cylindrical shapes of nanoparticles, respectively. From these profiles, it can be seen that the thermal boundary layer thickness increases due to the HTP increase by the variation in solid volume fraction to . Effects of stretching Reynolds number on HTP for spherical and cylindrical shape of nanoparticles are shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11. Thermal boundary layer thickness and HTP increase for both cases and due to the increase in the numerical values of stretching Reynolds number . It is an accepted fact that, an increased stretching Reynolds number enhanced the energy in the fluids’ particles. This energy increase is due to the fact that the fluid temperature increases monotonically which can be confirmed in Figure 10 and Figure 11. HTP decreases due to the increase in the strength of magnetic field for spherical and cylindrical shape of nanoparticles (see Figure 12 and Figure 13).
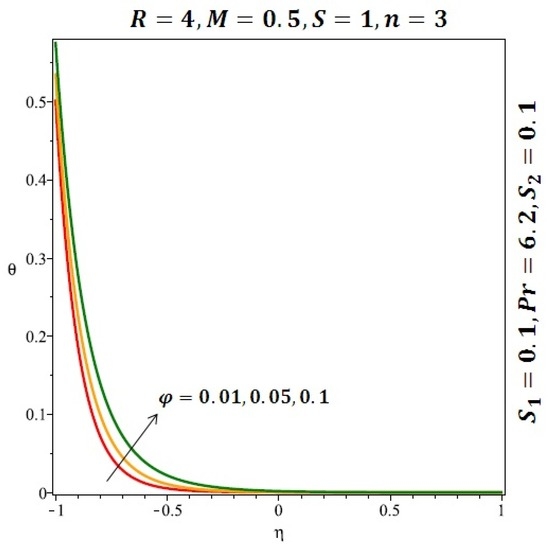
Figure 8.
Effect of the variation of the solid volume fraction (ϕ) on the heat transfer for spherical nanoparticles.
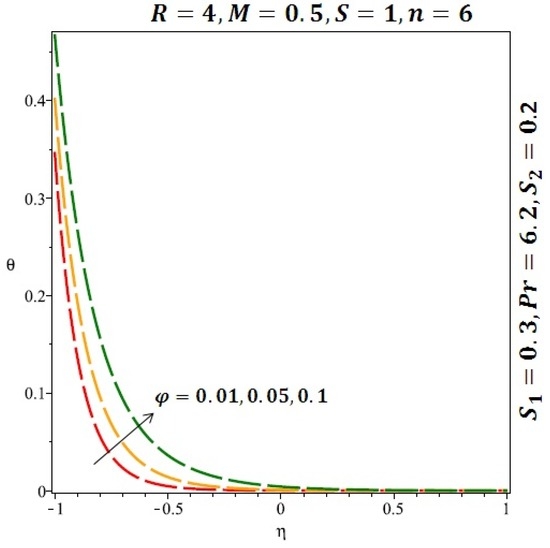
Figure 9.
Effect of the variation of the solid volume fraction (ϕ) on the heat transfer for cylindrical nanoparticles.
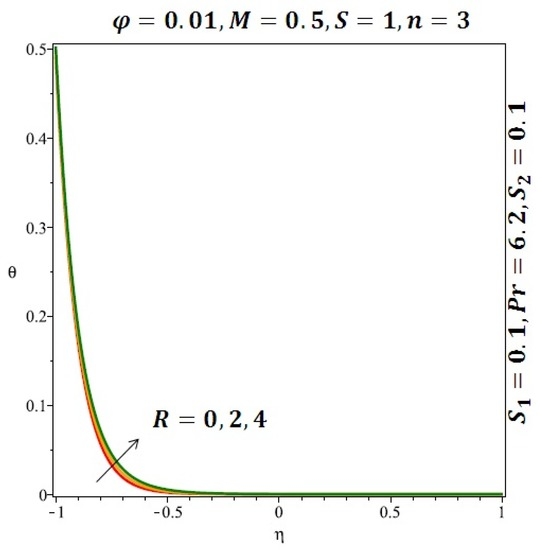
Figure 10.
Effect of the variation of the Reynolds number (R) on the heat transfer for spherical nanoparticles.
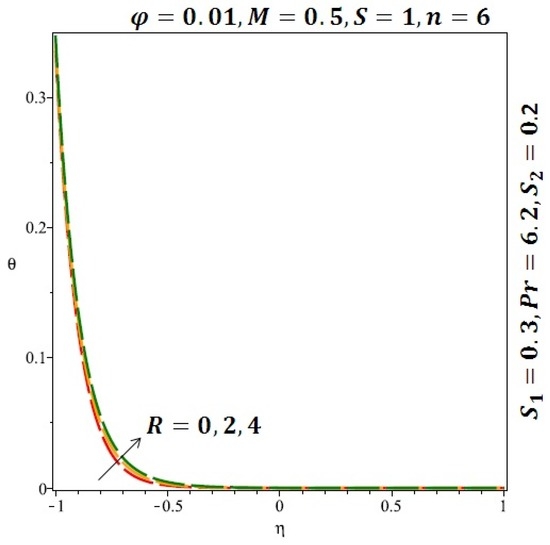
Figure 11.
Effect of the variation of the Reynolds number (R) on the heat transfer for cylindrical nanoparticles.
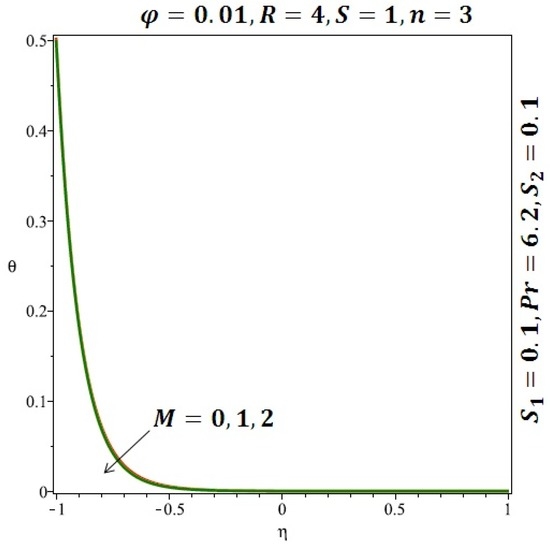
Figure 12.
Effect of the variation of the magnetic field (M) on the heat transfer for spherical nanoparticles.
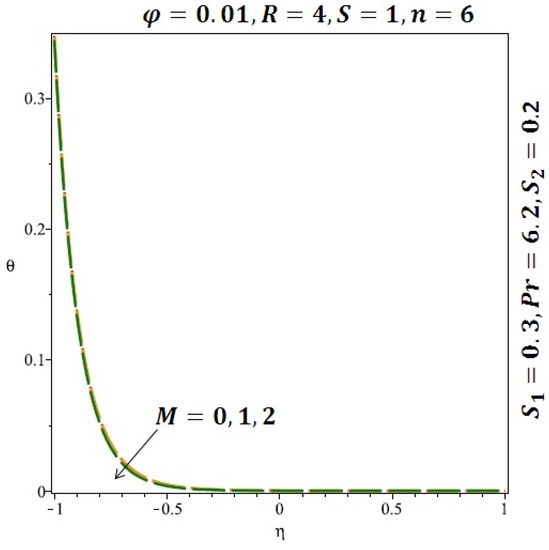
Figure 13.
Effect of the variation of the magnetic (M) field on the heat transfer for cylindrical nanoparticles.
5. Conclusions
The problem of magnetohydrodynamics Copper-water nanofluid flow in a stretchable channel under the influence of an external magnetic field and slip effects was numerically studied in this work. The effects of different physical parameters on the velocity profile and heat transfer profile were graphically presented. On the bases of the numerical results, two relevant aspects must be remarked:
- The heat transfer rate increases by enhancing in the strength of solid volume fraction to
- The stretching Reynolds number decreases the velocity profile near the lower wall of the channel for spherical and cylindrical shape of nanoparticles.
The thermal boundary layer thickness increases by increasing the solid volume fraction to .
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the reviewers and editor for their crucial work in improving this paper. The authors also would like to thank Universiti Utara Malaysia (UUM) and Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia for their financial support.
Author Contributions
All the authors in this paper contributed equally.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript
| External uniform magnetic field | |
| Pressure (Pa) | |
| Thermal conductivity of the solid fraction (W/m·K) | |
| Thermal conductivity of the nanofluid (W/m·K) | |
| Density of the solid fraction (Kg/m3) | |
| Specific heat of nanofluid | |
| Fluid temperature (K or °C) | |
| Injection/suction | |
| Thermal conductivity of the fluid (W/m·K) | |
| Thermal conductivity of the nanofluid (W/m·K) | |
| Shape factor through H-C Model | |
| Specific heat at constant pressure (J/kg·K) | |
| Velocity component in Cartesian coordinate | |
| Greek symbols | |
| Scaled boundary layer coordinate | |
| Effective electrical conductivity of nanofluid (S.m-1) | |
| Dynamic viscosity | |
| Self-similar temperature | |
| Nanoparticle volume fraction parameter | |
| Effective dynamic viscosity of nanofluid | |
| Density (kg/m3) | |
| Dimensionless numbers | |
| Stretching Reynolds number | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Density of the nanofluid | |
| Magnetic parameter | |
| Dynamic viscosity of the nanofluid (Pa·s) | |
| Ratio of effective electrical conductivity of nanofluid to the base fluid | |
| Subscripts | |
| Nanofluid | |
| Solid phase | |
| Upper wall | |
| Fluid phase | |
| Lower wall |
References
- Maxwell, J.C. Electricity and Magnetism, 3rd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, England, UK, 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, R.L.; Crosser, O.K. Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1962, 1, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasp, E.J.; Kenny, J.P.; Gandhi, R.L. Solid-Liquid Flow Slurry Pipeline Transportation; Series on Bulk Materials Handling; Trans. Tech. Publications: Clausthal, Germany, 1977; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle. In Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows, ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–17 November 1995; Siginer, D.A., Wang, H.P., Eds.; pp. 99–105.
- Choi, S.U.S.; Zhang, Z.G.; Yu, W.; Lockwood, F.E.; Grulke, E.A. Anomalously thermal conductivity enhancement in nanotube suspensions. App. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 2252–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transfer 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J. A critical review on convective heat transfer correlations of nano- fluids. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2011, 15, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keblinski, P.; Phillpot, S.R.; Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Mechanisms of heat flow in suspensions of nano-sized particles (nanofluids). Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2002, 45, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heris, S.Z.; Esfahany, M.N.; Etemad, S.G. Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer of Al2O3/water nanofluid in circular tube. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2007, 28, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, B.C.; Cho, Y.I. Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp. Heat Transfer 1998, 11, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, A.D.; Yerkes, K.L. Experimental investigation into the convective heat transfer and system-level effects of Al2O3-propanol nanofluid. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.S.; Ding, Y.L. Experimental investigation into convective heat transfer of nanofluids at the entrance region under laminar flow conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2004, 47, 5181–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.M.; Li, Q. Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. J. Heat Transfer 2003, 125, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, M.H.; Esfahany, M.N.; Talaie, M.R. Numerical study of convective heat transfer of nanofluids in a circular tube two-phase model versus single-phase model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 2010, 37, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.V.; Nield, D.A. Natural convective boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Ashorynejad, H.R.; Domairry, G.; Hashim, I. Flow and heat transfer of Cu-water nanofluid between a stretching sheet and a porous surface in a rotating system. J. Appl. Math 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, J.; Rohni, A.M.; Omar, Z. A Note on Some Solutions of Copper-Water (Cu-Water) Nanofluids in a Channel with Slowly Expanding or Contracting Walls with Heat Transfer. Math. Comput. Appl. 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domairry, D.; Sheikholeslami, M.; Ashorynejad, H.R.; Subba, R.; Gorla, R.; Khani, M. Natural convection flow of a non-Newtonian nanofluid between two vertical flat plates. J. Nanomater. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 2012, 225, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, J.; Rohni, A.M.; Omar, Z. MHD flow and heat transfer of Cu-water nanofluid in a semi porous channel with stretching walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2016, 103, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Rashidi, M.M.; Ganji, D.D. Numerical investigation of magnetic nanofluid forced convective heat transfer in existence of variable magnetic field using two phase model. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Ganji, D.D. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer between parallel plates considering Brownian motion using DTM. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 283, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Ganji, D.D.; Javed, M.Y.; Ellahi, R. Effect of thermal radiation on magnetohydrodynamics nanofluid flow and heat transfer by means of two phase model. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidoonimehr, N.; Rashidi, M.M.; Mahmud, S. Unsteady MHD free convective flow past a permeable stretching vertical surface in a nano-fluid. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 87, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.Z.; Ashraf, M.; Iqbal, M.F.; Ali, K. Heat and mass transfer analysis of unsteady MHD nanofluid flow through a channel with moving porous walls and medium. AIP Advances 2016, 6, 045222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoosi, F.; Jahanshaloo, L.; Rashidi, M.M.; Badakhsh, A.; Ali, M.E. Numerical simulation of natural convection of the nanofluid in heat exchangers using a Buongiorno model. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 254, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ameel, T.A. Slip-flow heat transfer in rectangular microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2001, 44, 4225–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watannebe, K.; Mizunuma, Y.H. Slip of Newtonian Fluids at Solid Boundary. JSME Int. J. Series B Fluids Therm. Eng. 1998, 41, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.R.; Sharma, P.K. Effect of Viscous Heating on Flow past a Vertical Plate in Slip-Flow Regime without Periodic Temperature Variations. J. Rajasthan Acad. Phys. Sci. 2006, 5, 383–398. [Google Scholar]
- Khaled, A.R.A.; Vafai, K. The Effect of the Slip Condition on Stokes and Couette Flows Due to an Oscillating Wall: Exact solutions. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2004, 39, 759–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.L.; Crosser, O.K. Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1962, 1, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, D.B.; Haran, B.S.; White, R.E. The shooting technique for the solution of two-point boundary value problems. Maple Tech. Newsl. 1996, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).