Synthesis by Sol-Gel and Coprecipitation of Zn1−xFexO Nanoparticles for the Adsorption of Congo Red Dye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Zn1−xFexO Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Assays
3. Results
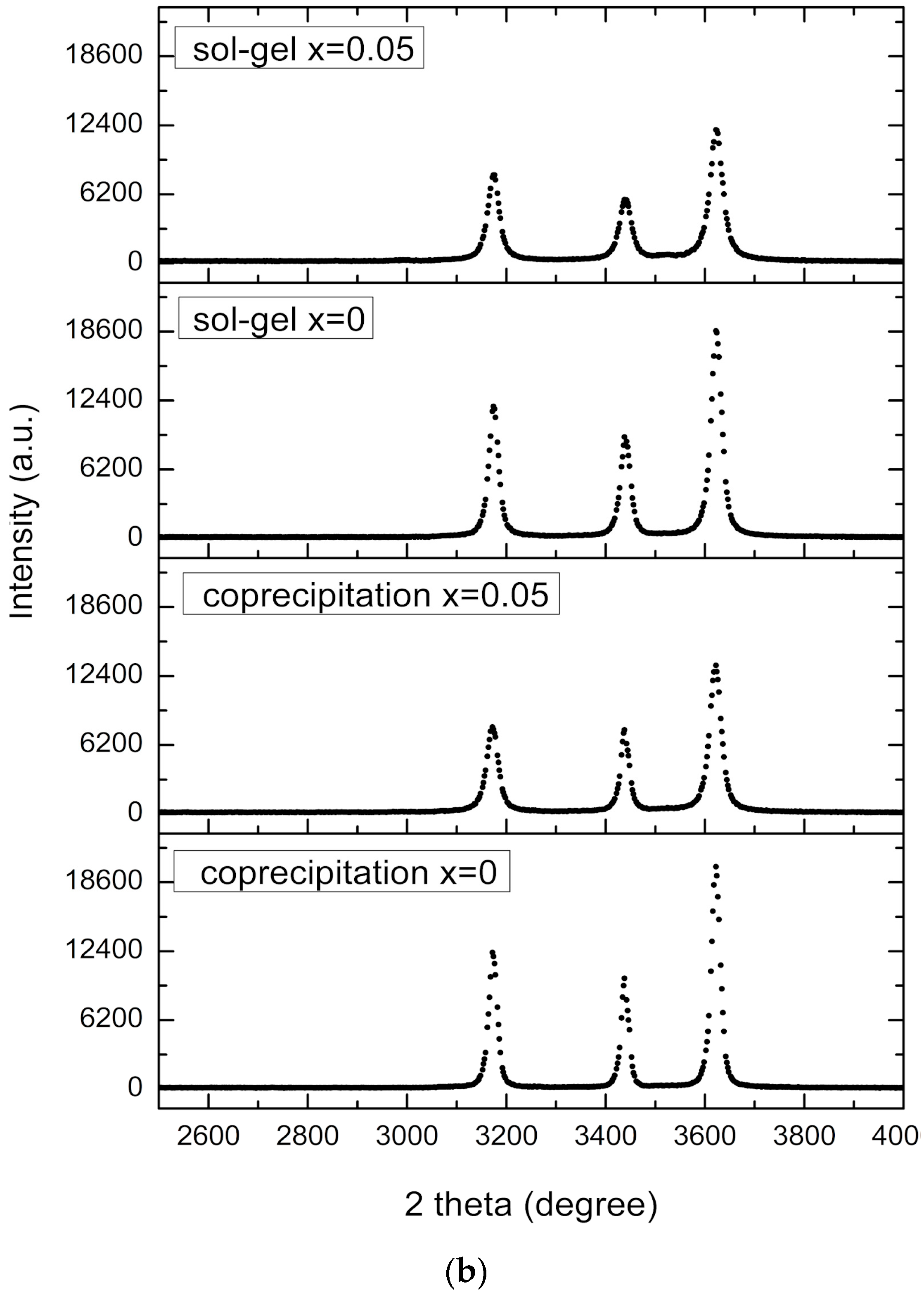
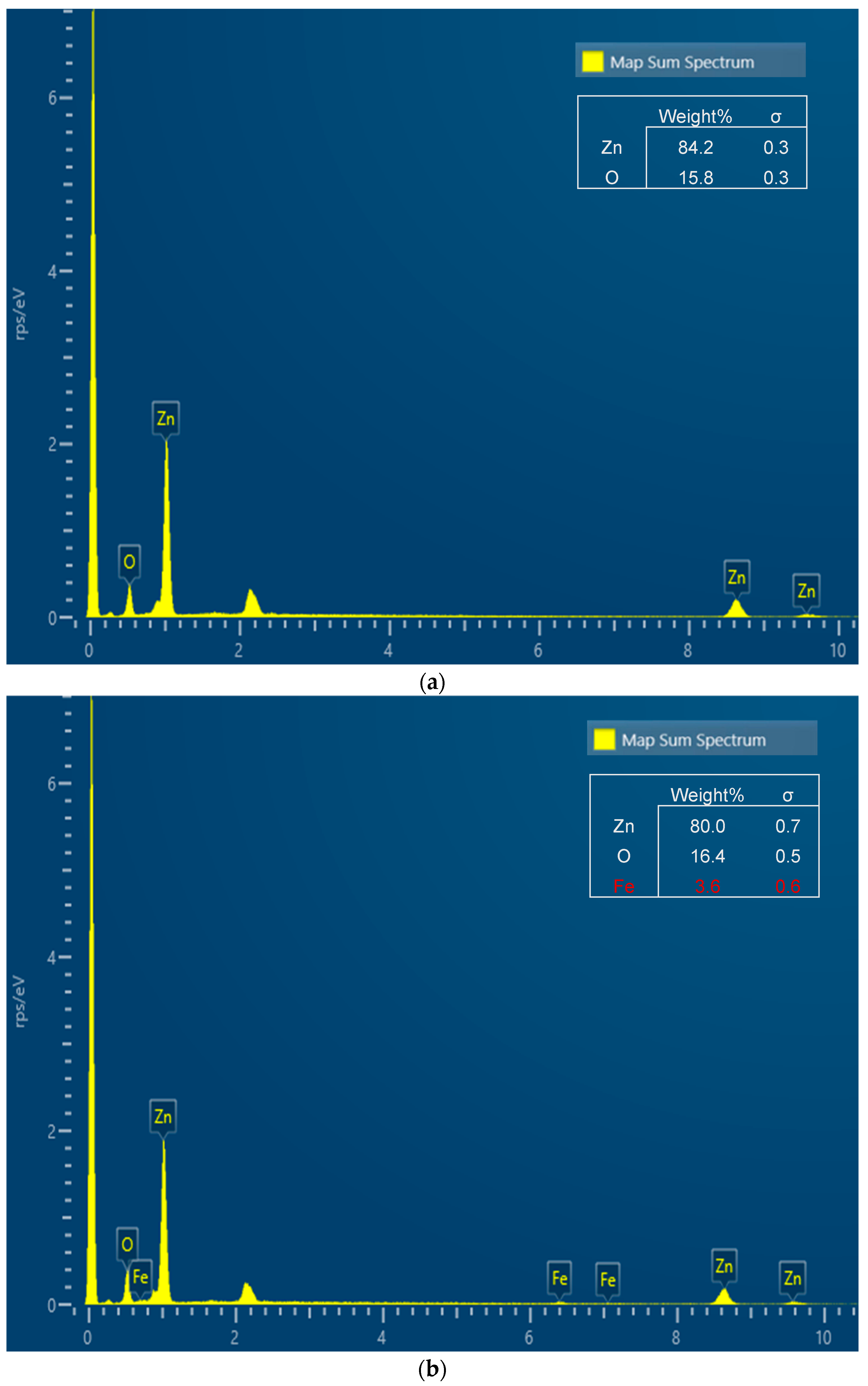
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
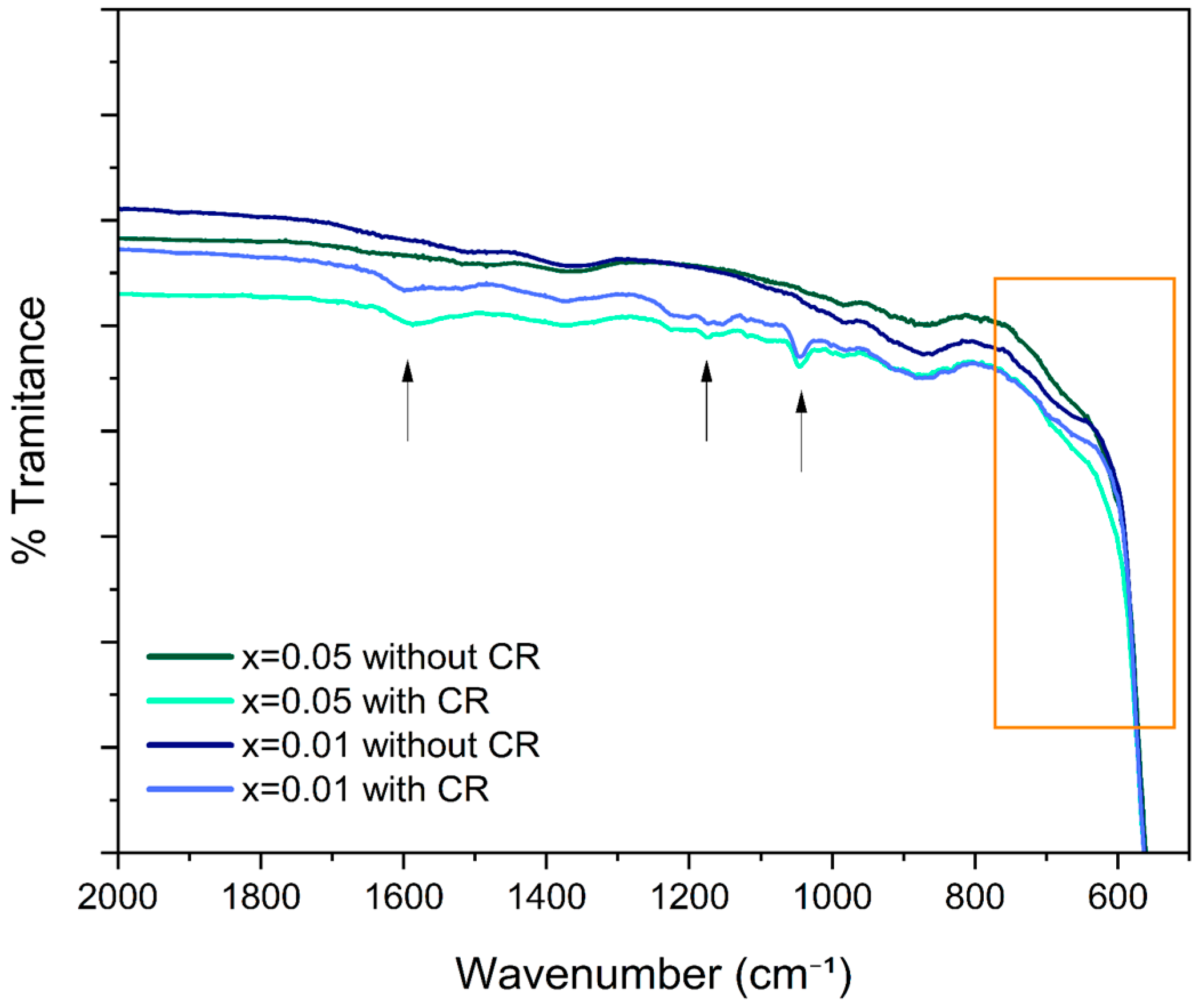
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
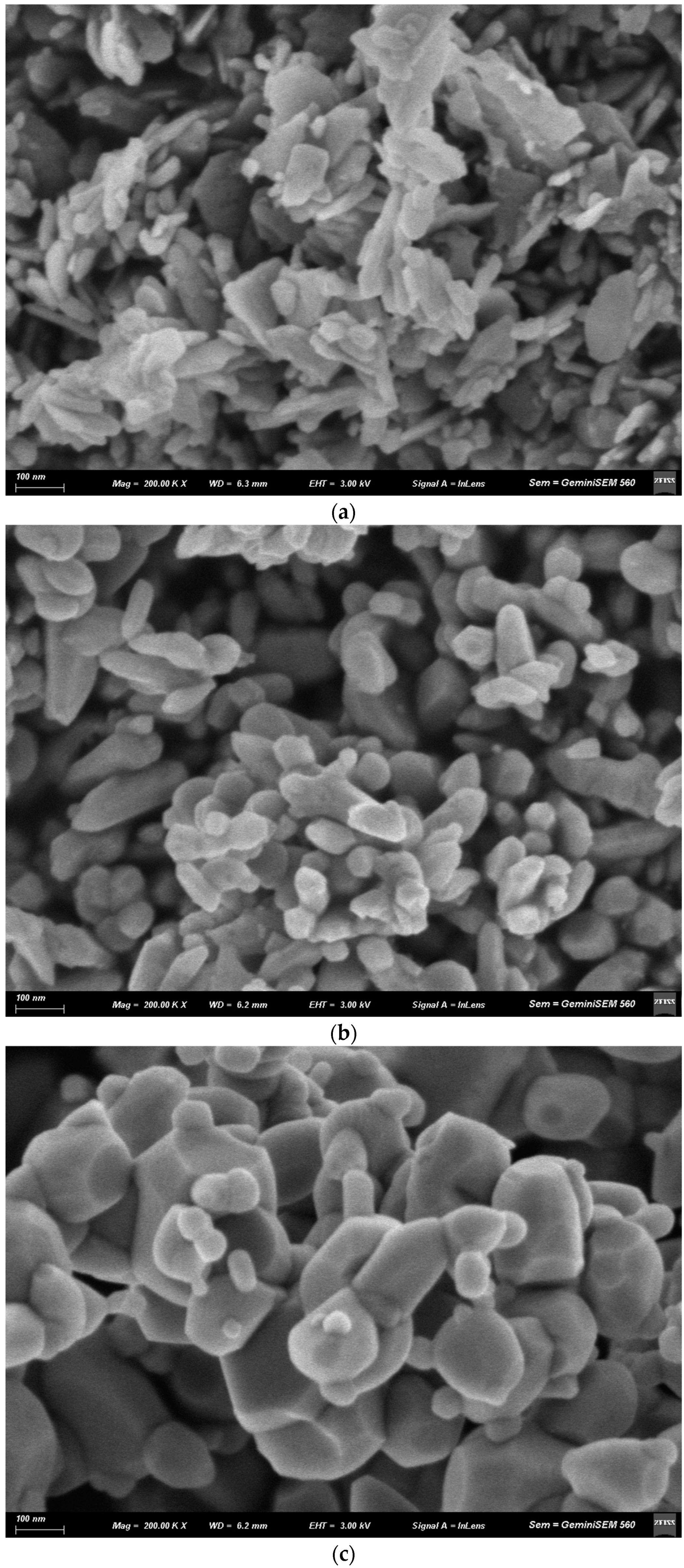
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
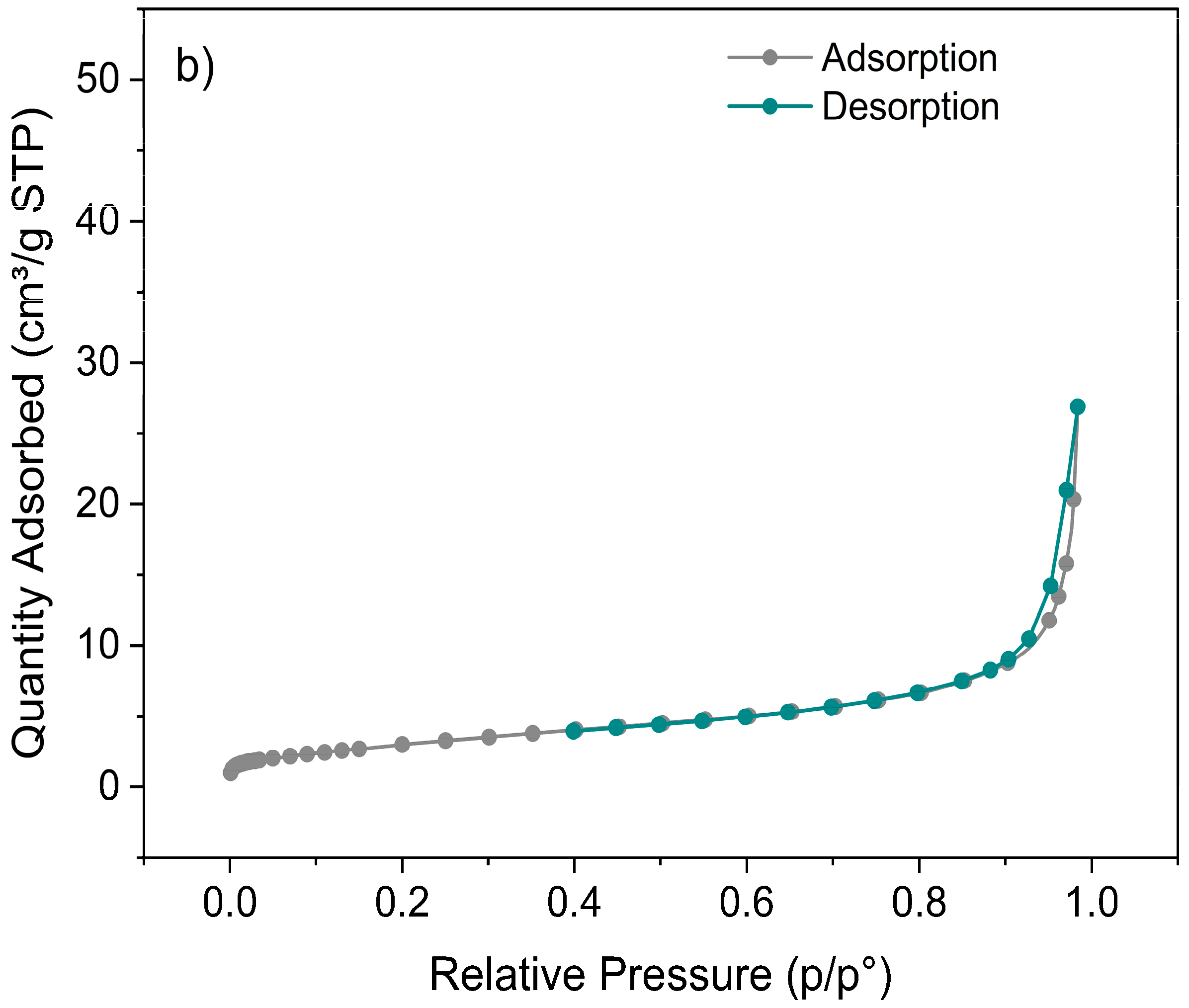
3.4. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller Analysis (BET)
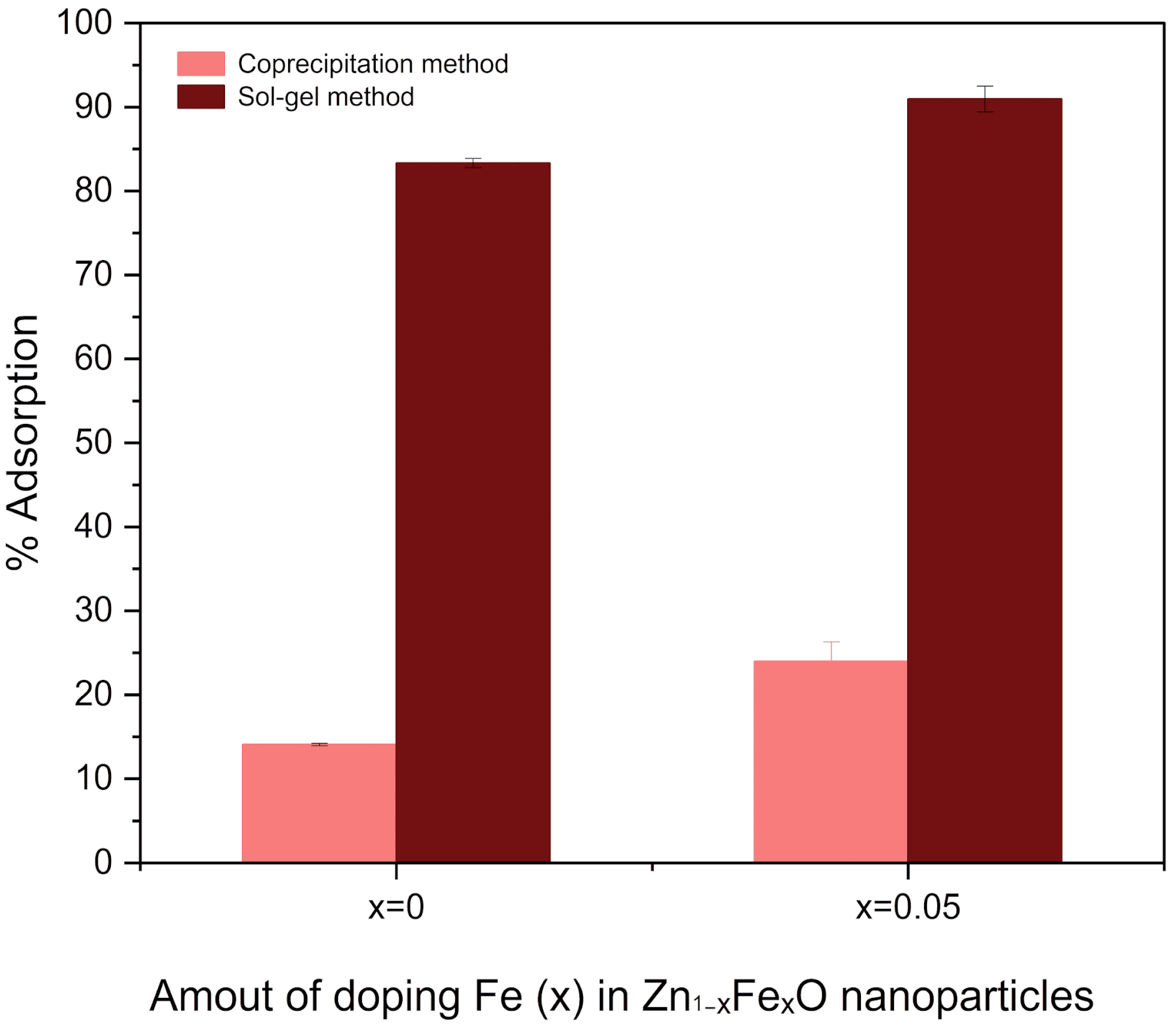
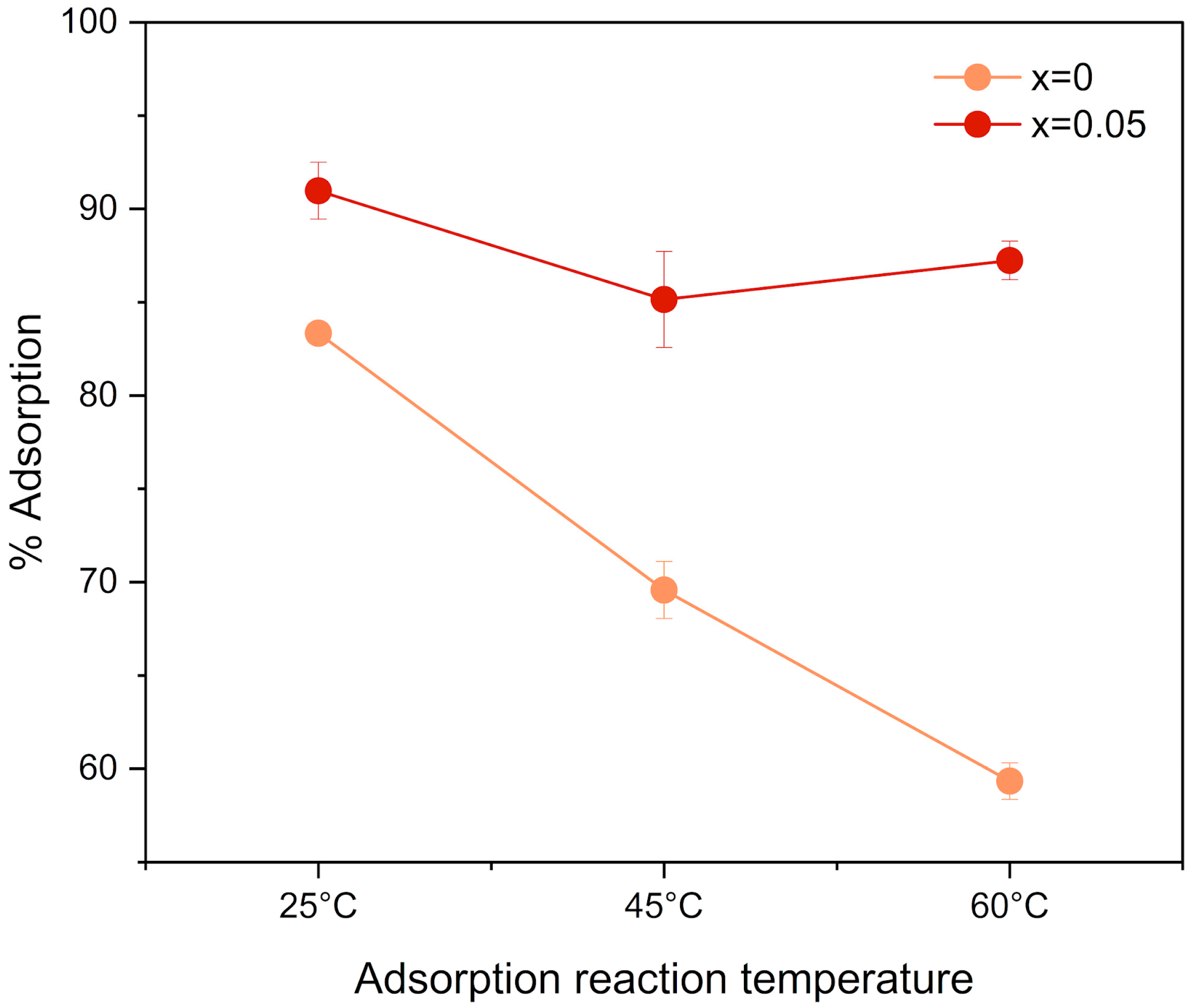
3.5. Adsorption Assays
4. Discussion
4.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller Analysis (BET)
4.5. Adsorption Assays
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lebaka, V.R.; Ravi, P. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Modern Science and Technology: Multifunctional Roles in Healthcare, Environmental Remediation, and Industry. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Gusain, D. Synthesis, characterization and application of zinc oxide nanoparticles (n-ZnO). Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9803–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-C.; Tang, C.-T. Preparation and application of granular ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for the removal of hazardous trichloroethylene. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandolo, B.; Hagfeldt, A. Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Water Treatment: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Crystals 2024, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, N.B.; Saeed, F.R. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles via oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Lett. X 2022, 13, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carofiglio, M.; Barui, S. Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Potential Use in Nanomedicine. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, A.; Khan, Z.M. Formation and characterization of ZnO nanopowder synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 495, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc Oxide—From Synthesis to Application: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, P.; Reisi Nafchi, M. Sol-gel zinc oxide nanoparticles: Advances in synthesis and applications. Synth. Sinter. 2021, 1, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ayon, S.A. Comparative study of structural, optical, and photocatalytic properties of ZnO synthesized by chemical coprecipitation and modified sol–gel methods. Surf. Interface Anal. 2023, 55, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, A.M.S.; Athira, K.K. Textile dyes effluents: A current scenario and the use of aqueous biphasic systems for the recovery of dyes. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 49, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.B.; Blandino, A. Modelling of different enzyme productions by solid-state fermentation on several agro-industrial residues. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9555–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, V.P.; Bhat, S.B.; Kumar, R. Environmental risks of textile dyes and photocatalytic materials for sustainable treatment: Current status and future directions. Discov. Environ. 2025, 3, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbani, P.; Tabatabaii, S.M. Removal of Congo red from textile wastewater by ozonation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, M.F.; Ahmed, I.M. Treatment of industrial wastewater containing Congo Red and Naphthol Green B using low-cost adsorbent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labille, J.; Brant, J. Stability of nanoparticles in water. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Choubey, S. Kinetic and isothermal study of effect of transition-metal doping on adsorptive property of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized via green route using Moringa oleifera leaf extract. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 036306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Hossienzadeh, K. Effects of doping zinc oxide nanoparticles with transition metals (Ag, Cu, Mn) on photocatalytic degradation of Direct Blue 15 dye under UV and visible light irradiation. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachin; Pramanik, B.K.; Singh, N.; Zizhou, R.; Houshyar, S.; Cole, I.; Yin, H. Fast and Effective Removal of Congo Red by Doped ZnO Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, S.; Lo, C.-Y. Defect induced crystal lattice disorder and its effect on the electron-phonon coupling in Fe-doped ZnO thin films. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2024, 190, 111999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-Y.; Wang, S. Modulating nanograin size and oxygen vacancy of porous ZnO nanosheets by highly concentrated Fe-doping effect for durable visible photocatalytic disinfection. Rare Metals 2024, 43, 5905–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, T.H.; Prasad, G.K. Nanocrystalline zinc oxide for the decontamination of sarin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchana, S.; Chithra, M.J. Violet emission from Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by precipitation method. J. Lumin. 2016, 176, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Sarkar, R. Synthesis, characterization and tribological study of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 3606–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathi, G.; Sangari, N.U. Morphology dependent photocatalytic efficiency of nano ZnO towards Azure A dye. Open Ceram. 2023, 16, 100465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, N. Adsorption of Congo red dye on FexCo3−xO4 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şişmanoğlu, T.; Pozan, G.S. Adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solution using various TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13318–13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, B.; Patra, T. An efficient and comparative adsorption of Congo Red and Trypan Blue dyes on MgO nanoparticles: Kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherm studies. J. Magnesium Alloys 2021, 9, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCPDS 36-1451; Zinc Oxide-Powder Diffraction File. International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD): Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2024.
- Wahab, R.; Mishra, A. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles prepared via non-hydrolytic solution route. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapna, P.; Venkatramana Reddy, S. Structural, optical & magnetic properties of (Fe, Al) co-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Rep. 2019, 2, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousslama, W.; Elhouichet, H.; Férid, M. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped ZnO nanocrystals under sunlight irradiation. Optik—Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2017, 134, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramawy, A.M.; Agami, W.R. Tailoring the preparation, microstructure, FTIR, optical properties and photocatalysis of (Fe/Co) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles (Zn0.9FexCo0.1−xO). Ceramics 2025, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, W.; Ullah, N. Optical, morphological and biological analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Papaver somniferum L. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29541–29548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Arjan, W.S. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Application in Adsorption of Toxic Dye from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2022, 14, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janaki, A.C.; Sailatha, E. Synthesis, characteristics and antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 144, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazargan, M.; Ghaderi, E. Effect of temperature on the structure, catalyst and magnetic properties of un-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: Experimental and DFT calculation. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 12345–12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzaia, F.; Djouadi, D. Particularities of pure and Al-doped ZnO nanostructures aerogels elaborated in supercritical isopropanol. Arab J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2020, 27, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.; Mondal, N.K. Effective removal of Congo Red dye from aqueous solution using biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yin, W. Efficient removal of Congo red, methylene blue and Pb(II) by hydrochar–MgAlLDH nanocomposite: Synthesis, performance and mechanism. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Wang, D. Enhanced adsorption of Congo red using chitin suspension after sonoenzymolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 70, 105327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapat, A.; Aslam, M. Computational supported experimental insights in adsorption of Congo Red using ZnO/doped ZnO in aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuli, G.; Eisenmann, T. Structural and Electrochemical Characterization of Zn1−xFexO—Effect of Aliovalent Doping on the Li⁺ Storage Mechanism. Materials 2018, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wei, Z. Optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles obtained by hydrothermal synthesis. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 792102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, C.K.; Nigam, S. Lanthanide Ions-Doped Nanomaterials for Light Emission Applications. In Emerging Trends of Research in Chemical Sciences; Chakraborty, T., Chaudhary, S., Eds.; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 55–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanità, G.; Carrese, B.; Lamberti, A. Nanoparticle Surface Functionalization: How to Improve Biocompatibility and Cellular Internalization. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Pal, U. Photoluminescence and FTIR study of ZnO nanoparticles: The impurity and defect perspective. Phys. Status Solidi C 2006, 3, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, A.; Kumar, Y. Doping concentration driven morphological evolution of Fe-doped ZnO nanostructures. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 164315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, K.B.; Mohite, S.V. Studies on effect of Fe doping on ZnO nanoparticles’ microstructural features using x-ray diffraction technique. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 065904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Nasrallah, M. Biosynthesis, Optical and Magnetic Properties of Fe-Doped ZnO/C Nanoparticles. Surfaces 2023, 6, 410–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.E.; Montero-Muñoz, M. Evidence of a cluster glass-like behavior in Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17E123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesha, H.S.; Mohanty, P. Structure, optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped, Fe + Cr co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.07266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. The pH dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. IX. Update. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 296, 102519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelonka, D.; Tolasz, J. Doping of Zinc Oxide with Selected First Row Transition Metals for Photocatalytic Applications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, Q. Estimation of shale pore-size distribution from N2 adsorption characteristics employing modified BJH algorithm. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2021, 39, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.G.; Salinger, J.L. Determining Surface Areas and Pore Volumes of Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 65716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazon, C.; Fierro, V. Identification of nanomaterials by the volume specific surface area (VSSA) criterion: Application to powder mixes. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 4908–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altammar, K.A. A review on nanoparticles: Characteristics, synthesis, applications, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1155622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolai, J.; Mandal, K. Nanoparticle Size Effects in Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 6471–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.B.S.; Parajuli, D. Effect of Fe-doped and capping agent—Structural, optical, luminescence, and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Impact 2023, 7, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolabella, S.; Borzì, A. Lattice Strain and Defects Analysis in Nanostructured Semiconductor Materials and Devices by High-Resolution X-Ray Diffraction: Theoretical and Practical Aspects. Small Methods 2022, 6, e2100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzì, A.; Dolabella, S. Microstructure analysis of epitaxial BaTiO3 thin films on SrTiO3-buffered Si: Strain and dislocation density quantification using HRXRD methods. Materialia 2020, 14, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, E.A.; Korsa, H.A. Electrolytic synthesis of γ-Al2O3 nanoparticle from aluminum scrap for enhanced methylene blue adsorption: Experimental and RSM modeling. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majani, S.S.; Manoj; Lavanya, M.; Swathi, B.; Anuvarna, N.; Iqbal, M.; Kollur, S.P. Nano-catalytic behavior of CeO2 nanoparticles in dye adsorption: Synthesis through bio-combustion and assessment of UV-light-driven photo-adsorption of indigo carmine dye. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; El-Sayed, G.O. Adsorptive removal of Pb2+ from wastewater using ZnO-biochar nanocomposite: Kinetic, isotherm and morphological studies. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Duan, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, H. Adsorption and sensing performances of transition metal doped ZnO monolayer for CO and NO: A DFT study. SSRN 2024, 26, 4958262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muedi, K.L.; Masindi, V. Effective adsorption of Congo Red from aqueous solution using Fe/Al di-metal nanostructured composite synthesised from Fe(III) and Al(III) recovered from real acid mine drainage. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Characteristic | |
|---|---|
| Generic name | Congo Red |
| Molecular weight | 696.66 g/mol |
| Chemical formula | C32H22N6Na2O6S2 |
| Maximum wavelength (λmax) | 500 nm |
| CAS number | 573-58-0 |
| Molecular structure | 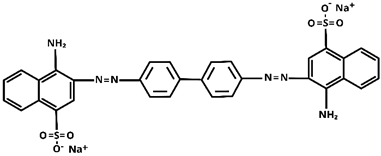 |
| Samples | Ɛ |
|---|---|
| Sol-gel, x = 0 | 0.00013 |
| Sol–gel, x = 0.05 | 0.00017 |
| Coprecipitation, x = 0 | 0.00010 |
| Coprecipitation, x = 0.05 | 0.00012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potiliski, C.Y.; Kramer, G.R.; Bruera, F.A.; Zapata, P.D.; Ares, A.E. Synthesis by Sol-Gel and Coprecipitation of Zn1−xFexO Nanoparticles for the Adsorption of Congo Red Dye. Processes 2025, 13, 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123954
Potiliski CY, Kramer GR, Bruera FA, Zapata PD, Ares AE. Synthesis by Sol-Gel and Coprecipitation of Zn1−xFexO Nanoparticles for the Adsorption of Congo Red Dye. Processes. 2025; 13(12):3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123954
Chicago/Turabian StylePotiliski, Carla Yamila, Gustavo Raúl Kramer, Florencia Alejandra Bruera, Pedro Darío Zapata, and Alicia Esther Ares. 2025. "Synthesis by Sol-Gel and Coprecipitation of Zn1−xFexO Nanoparticles for the Adsorption of Congo Red Dye" Processes 13, no. 12: 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123954
APA StylePotiliski, C. Y., Kramer, G. R., Bruera, F. A., Zapata, P. D., & Ares, A. E. (2025). Synthesis by Sol-Gel and Coprecipitation of Zn1−xFexO Nanoparticles for the Adsorption of Congo Red Dye. Processes, 13(12), 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123954







