From Qualitative to Quantitative Functional Assessment in Stroke Rehabilitation with a Focus on Ultrasound Role
Abstract
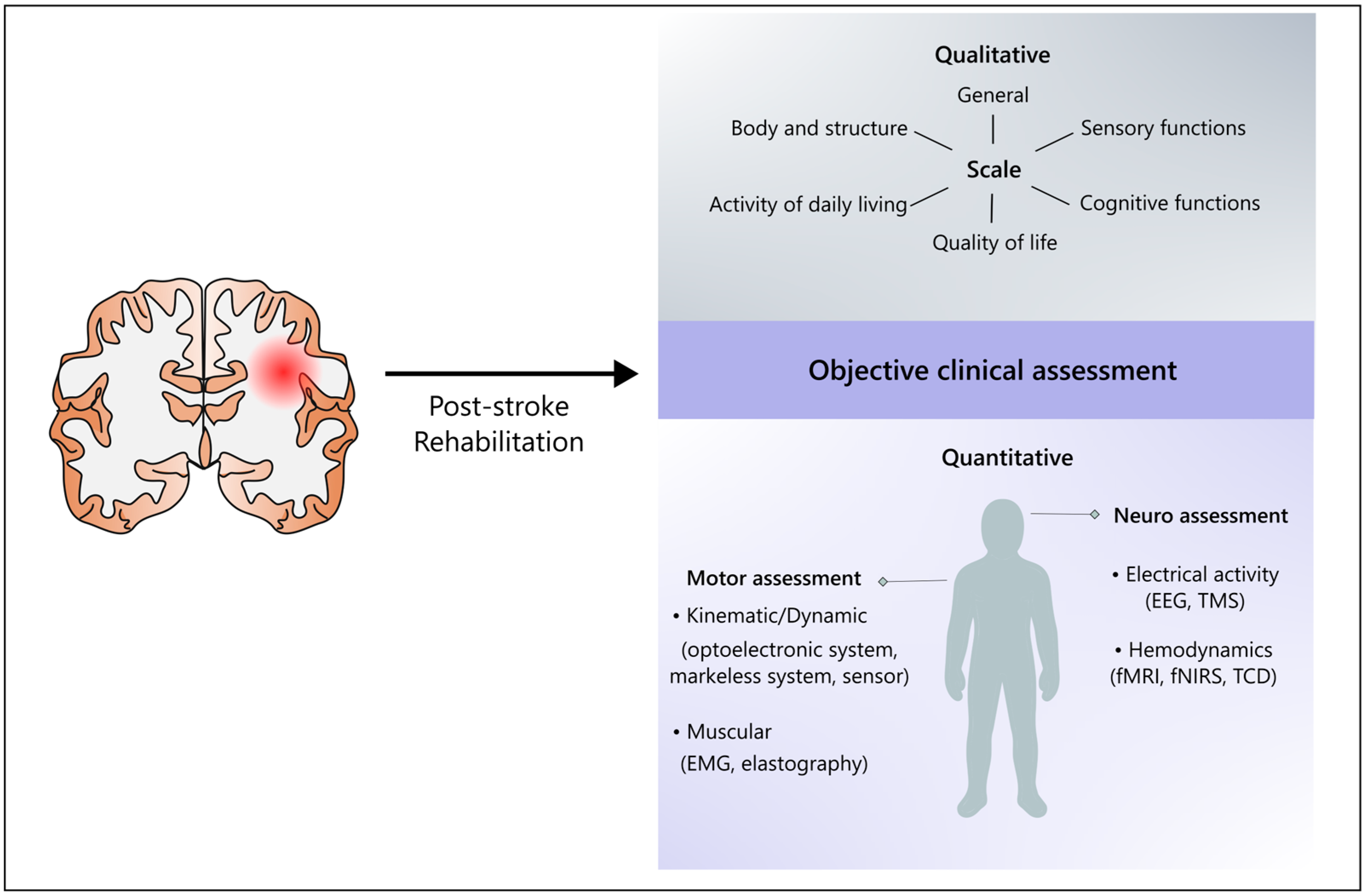
1. Introduction
2. Neurorehabilitation: Principles and Techniques
3. Evaluating Stroke Impact: Insights into Assessment Scales in Neurorehabilitation
3.1. Challenges and the Quest for Objectivity
3.2. Limitations of the Use of Single Scales
3.3. Non-Linear Dynamics and Redundancy
3.4. Reproducibility, External Variables, and Differential Item Functioning
3.5. Inter-Observer Variability
4. Towards Quantitative Assessment of Stroke Impact: Role of Ultrasound Methodologies
4.1. Assessment of Motor Function
4.2. Assessment of Brain Function
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADL | Activities of Daily Living |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AOT | Action Observation Treatment |
| BI | Barthel Index |
| CBF | Cerebral Blood Flow |
| CIMT | Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy |
| DBS | Deep Brain Stimulation |
| DIF | Differential Item Functioning |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| ETC | Cognitive Therapeutic Exercise |
| fMRI | Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| fNIRS | Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy |
| fTCD | Functional Transcranial Doppler |
| FIM | Functional Independence Measure |
| ICF | Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| PNF | Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation |
| QUS | Quantitative Ultrasound |
| rTMS | Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation |
| TCD | Transcranial Doppler |
| tDCS | Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation |
| TMS | Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation |
| TUS | Transcranial Ultrasound Stimulation |
| US | Ultrasound |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Ministero della Salute. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/portale/home.html (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Sacco, R.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Caplan, L.R.; Connors, J.J.; Culebras, A.; Elkind, M.S.; George, M.G.; Hamdan, A.D.; Higashida, R.T.; et al. An Updated Definition of Stroke for the 21st Century: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 2064–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, W.J.; Stanfield, C.L. Principles of Human Physiology, 2nd ed.; Pearson Benjamin Cummings: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-8053-5691-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mtui, E.; Gruener, G.; Dockery, P. Fitzgerald’s Clinical Neuroanatomy and Neuroscience; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 978-0-7020-7909-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kandel, E.; Schwartz, J.; Jessell, T.; Siegelbaum, S.; Hudspeth, A.J. Principles of Neural Science, 5th ed.; Access Neurology: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2013; Available online: https://neurology.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=1049 (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Roots, J.; Trajano, G.S.; Fontanarosa, D. Ultrasound Elastography in the Assessment of Post-Stroke Muscle Stiffness: A Systematic Review. Insights Into Imaging 2022, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.; Gao, J. Quantitative Ultrasound to Assess Skeletal Muscles in Post Stroke Spasticity. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2021, 13, 1179573521996141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteis, M.; Vernieri, F.; Troisi, E.; Pasqualetti, P.; Tibuzzi, F.; Caltagirone, C.; Silvestrini, M. Early Cerebral Hemodynamic Changesduring Passive Movements and Motor Recovery Afterstroke. J. Neurol. 2003, 250, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duschek, S.; Schuepbach, D.; Doll, A.; Werner, N.S.; Reyes del Paso, G.A. Self-Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow by Means of Transcranial Doppler Sonography Biofeedback. Ann. Behav. Med. 2011, 41, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J. Exploration on Neurobiological Mechanisms of the Central–Peripheral–Central Closed-Loop Rehabilitation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 982881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawieh, A.; Zhao, J.; Feng, W. Factors Affecting Post-Stroke Motor Recovery: Implications on Neurotherapy after Brain Injury. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 340, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Chou, L.-W.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation-Based Physical Therapy on the Improvement of Balance and Gait in Patients with Chronic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2022, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Howe, T.-H. Effectiveness of Activity-Based Task-Oriented Training on Upper Extremity Recovery for Adults with Stroke: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2024, 78, 7802180070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.S.; Pollock, A.; Campbell, T.; Durward, B.R.; Hagen, S. Cognitive Rehabilitation for Executive Dysfunction in Adults with Stroke or Other Adult Non-progressive Acquired Brain Damage. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD008391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, C.; Wopfner-Oberleit, S. Der Hemiplegische Patient: Kognitiv Therapeutische Übungen (Pflaum Physiotherapie); Richard Pflaum Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Munchen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bobath, B. Adult Hemiplegia: Evaluation and Treatment, 2nd ed.; Heinemann Medical: Kaltenkirchen, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, P.M. Steps to Follow: A Guide to the Treatment of Adult Hemiplegia; Springer: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-0-387-13436-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hummelsheim, H.; Mauritz, K.H. The neurophysiological basis of exercise physical therapy in patients with central hemiparesis. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 1993, 61, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Gyanpuri, V.; Dev, P.; Dhiman, N.R. The Bobath Concept (NDT) as Rehabilitation in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2021, 10, 3983–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, T.; Maeda, M.; Yokoyama, H.; Kai, S.; Obuchi, K.; Takase, S.; Horimoto, T.; Shimada, R.; Moriya, T.; Ohmae, H.; et al. Therapeutic Effect of Adjuvant Therapy Added to Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy in Patients with Subacute to Chronic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2024, 46, 4098–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, G. Action Observation Treatment: A Novel Tool in Neurorehabilitation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoykov, M.E.; Biller, O.M.; Wax, A.; King, E.; Schauer, J.M.; Fogg, L.F.; Corcos, D.M. Bilateral Upper Extremity Motor Priming (BUMP) plus Task-Specific Training for Severe, Chronic Upper Limb Hemiparesis: Study Protocol for a Randomized Clinical Trial. Trials 2022, 23, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Pendy, J.T.; Li, W.A.; Du, H.; Zhang, T.; Geng, X.; Ding, Y. Motor Imagery-Based Rehabilitation: Potential Neural Correlates and Clinical Application for Functional Recovery of Motor Deficits after Stroke. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, J.; Wolf, S.L.; Kesar, T.M. Biofeedback for Post-Stroke Gait Retraining: A Review of Current Evidence and Future Research Directions in the Context of Emerging Technologies. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 637199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, G.J.B.; Namasivayam, A.A.; Lozano, A.M. Deep Brain Stimulation for Stroke: Current Uses and Future Directions. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, J.S.; Friedl, A.S.; Hansen, K.M.; Harley, M.Y.; Barrett, A.M.; Raghavan, P.; Plow, E.B.; Gunzler, D.D.; Chae, J. Efficacy of Contralaterally Controlled Functional Electrical Stimulation Compared to Cyclic Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation and Task-Oriented Training for Recovery of Hand Function after Stroke: Study Protocol for a Multi-Site Randomized Controlled Trial. Trials 2022, 23, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jin, Y.; Wu, D.; Cun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Y.; Chen, N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ning, R.; et al. Current Evidence, Clinical Applications, and Future Directions of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation as a Treatment for Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1177283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lo, W.L.A.; Hu, H.; Yan, L.; Li, L. Transcranial Ultrasound Stimulation Applied in Ischemic Stroke Rehabilitation: A Review. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 964060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, B.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Luo, N.; Liu, N.; Shen, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Q. The Updated Role of Transcranial Ultrasound Neuromodulation in Ischemic Stroke: From Clinical and Basic Research. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 839023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, L. Short and Long-Term Effects of Robot-Assisted Therapy on Upper Limb Motor Function and Activity of Daily Living in Patients Post-Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, X.; Huang, W.; Yin, J.; Luo, C.; Li, Z.; Dou, Z. Effects of Robot-Assisted Task-Oriented Upper Limb Motor Training on Neuroplasticity in Stroke Patients with Different Degrees of Motor Dysfunction: A Neuroimaging Motor Evaluation Index. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 957972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueye, T.; Dedkova, M.; Rogalewicz, V.; Grunerova-Lippertova, M.; Angerova, Y. Early Post-Stroke Rehabilitation for Upper Limb Motor Function Using Virtual Reality and Exoskeleton: Equally Efficient in Older Patients. Neurol. Neurochir. Polska 2021, 55, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelineau, A.; Perrochon, A.; Robin, L.; Daviet, J.-C.; Mandigout, S. Measured and Perceived Effects of Upper Limb Home-Based Exergaming Interventions on Activity after Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsaki, I.; Dimitriadi, N.; Despoti, A.; Tzoumi, D.; Leventakis, N.; Roussou, G.; Papathanasiou, A.; Nanas, S.; Karatzanos, E. The Effectiveness of Immersive Virtual Reality in Physical Recovery of Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 880447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, D.; Jacoby, A.; Massey, A.; Ford, G. Evaluation of Measures Used to Assess Quality of Life After Stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kongwattanakul, K.; Hiengkaew, V.; Jalayondeja, C.; Sawangdee, Y. A Structural Equation Model of Falls at Home in Individuals with Chronic Stroke, Based on the International Classification of Function, Disability, and Health. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, T.F.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Farias, I.M.A.; Ribeiro, T.S.; Melo, L.P. Comparison of Instruments for Sleep, Cognition and Function Evaluation in Stroke Patients According to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF). Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2012, 16, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria-Fortini, I.; Michaelsen, S.M.; Cassiano, J.G.; Teixeira-Salmela, L.F. Upper Extremity Function in Stroke Subjects: Relationships between the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health Domains. J. Hand Ther. 2011, 24, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional evaluation: The Barthel index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahayu, U.B.; Wibowo, S.; Setyopranoto, I.; Hibatullah Romli, M. Effectiveness of Physiotherapy Interventions in Brain Plasticity, Balance and Functional Ability in Stroke Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2020, 47, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhoun, H.Y.; Tan, B.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yu, L. Task-Based Mirror Therapy Enhances the Upper Limb Motor Function in Subacute Stroke Patients: A Randomized Control Trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.K.; McArthur, K.S.; Quinn, T.J. Assessment Scales in Stroke: Clinimetric and Clinical Considerations. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tsang, R.C.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, M.; Zha, F.; Long, J.; Wang, Y. Relationship of Barthel Index and Its Short Form with the Modified Rankin Scale in Acute Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, A.W.; Michael Linacre, J.; Wright, B.D.; Hamilton, B.B.; Granger, C. Measurement Characteristics of the Functional Independence Measure. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 1994, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Hartzema, A.G.; Duncan, P.W.; Min-Lai, S. Disability Measures in Stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesio, L. Misurare su questionari: Una prospettiva epistemologica. MR G. Ital. Med. Riabil. 2020, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J. Activities of Daily Living Measurement after Ischemic Stroke: Rasch Analysis of the Modified Barthel Index. Medicine 2021, 100, e24926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roorda, L.D.; Houwink, A.; Smits, W.; Molenaar, I.W.; Geurts, A.C. Measuring Upper Limb Capacity in Poststroke Patients: Development, Fit of the Monotone Homogeneity Model, Unidimensionality, Fit of the Double Monotonicity Model, Differential Item Functioning, Internal Consistency, and Feasibility of the Stroke Upper Limb Capacity Scale, SULCS. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopiano, L.; Bergamini, L. Il Bergamini di Neurologia; Libreria Cortina: Milan, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Yin, M.; Cai, Z. Research and Application Advances in Rehabilitation Assessment of Stroke. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2022, 23, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razfar, N.; Kashef, R.; Mohammadi, F. Automatic Post-Stroke Severity Assessment Using Novel Unsupervised Consensus Learning for Wearable and Camera-Based Sensor Datasets. Sensors 2023, 23, 5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Liao, W.-W.; Chen, C.-L.; Wu, C.-Y. Kinematic Descriptions of Upper Limb Function Using Simulated Tasks in Activities of Daily Living after Stroke. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2021, 79, 102834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Szczerbik, E.; Syczewska, M. The Comparison of Two Physiotherapeutic Approaches for Gait Improvement in Sub-Acute Stroke Patients. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2014, 16, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Titus, A.W.; Hillier, S.; Louw, Q.A.; Inglis-Jassiem, G. An Analysis of Trunk Kinematics and Gait Parameters in People with Stroke. Afr. J. Disabil. 2018, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Shin, J.-H.; Kwon, S. Kinematic Assessment to Measure Change in Impairment during Active and Active-Assisted Type of Robotic Rehabilitation for Patients with Stroke. Sensors 2021, 21, 7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswakumar, A.; Rajagopalan, V.; Ray, T.; Gottipati, P.; Parimi, C. Development of a Robust, Simple, and Affordable Human Gait Analysis System Using Bottom-Up Pose Estimation with a Smartphone Camera. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 784865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesevic, J.; Kostic, M.; Kojic, V.; Dordevic, O.; Konstantinovic, L.; Keller, T.; Strbac, M. BEAGLE-A Kinematic Sensory System for Objective Hand Function Assessment in Technology-Mediated Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givon Schaham, N.; Zeilig, G.; Weingarden, H.; Rand, D. Game Analysis and Clinical Use of the Xbox-Kinect for Stroke Rehabilitation. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2018, 41, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeem, R.; Sohn, W.J.; DiCarlo, J.A.; Gochyyev, P.; Lin, D.J.; Sternad, D. Novel Platform for Quantitative Assessment of Functional Object Interactions After Stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Wen, X. Improved Spatial–Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Upper Limb Rehabilitation Assessment Based on Precise Posture Measurement. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1219556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Sudo, T.; Miyashita, M.; Kondo, T. Quantitative Measurement of Finger Usage in Stroke Hemiplegia Using Ring-Shaped Wearable Devices. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Tan, Y.; Klaic, M.; Galea, M.P.; Khan, F.; Oliver, A.; Mareels, I.; Oetomo, D.; Zhao, E. Evaluating Rehabilitation Progress Using Motion Features Identified by Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, B.; Ling, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Xiong, D.; Wang, J. Quantitative Evaluation System of Wrist Motor Function for Stroke Patients Based on Force Feedback. Sensors 2022, 22, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, K.; Kawakami, M.; Tsuchimoto, S.; Ogura, M.; Okada, K.; Mizuno, K.; Ushiba, J.; Liu, M. Depth Sensor–Based Assessment of Reachable Work Space for Visualizing and Quantifying Paretic Upper Extremity Motor Function in People with Stroke. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnini, S.; Arienti, C.; Patrini, M.; Liuzzi, P.; Mannini, A.; Carrozza, M.C. Machine Learning Methods for Functional Recovery Prediction and Prognosis in Post-Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Huang, Z.; Jin, T.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y. Motor Function Assessment of Upper Limb in Stroke Patients. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6621950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Peng, L.; Hou, Z.-G.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J. Quantitative Assessment of Upper-Limb Motor Function for Post-Stroke Rehabilitation Based on Motor Synergy Analysis and Multi-Modality Fusion. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, H. Upper-Limb Functional Assessment after Stroke Using Mirror Contraction: A Pilot Study. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 106, 101877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, X. Motor Function Evaluation of Hemiplegic Upper-Extremities Using Data Fusion from Wearable Inertial and Surface EMG Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Du, L.; Cheng, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Du, K.; He, W.; et al. Quantitative Assessment of Thenar to Evaluate Hand Function after Stroke by Bayes Discriminant. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-H.; Ho, Y.-C.; Hsiao, M.-Y.; Chen, W.-S.; Wang, T.-G. Evaluation of Post-Stroke Spastic Muscle Stiffness Using Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-J.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Wu, J.-Y.; Leong, C.-P. The Sonoelastography and Functional Outcome of Upper Extremity after Kinesiotaping on the Spastic Forearm in Patients with Subacute Stroke. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 1730491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, P.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, M.; Gong, X.; Sun, S. Development of a Wearable Ultrasound–FES Integrated Rehabilitation and Motor-Functional Reconstruction System for Post-Stroke Patients. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 106846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, G.; Antonioni, A.; Baroni, A.; Malerba, P.; Straudi, S. Relation Between EEG Measures and Upper Limb Motor Recovery in Stroke Patients: A Scoping Review. Brain Topogr. 2022, 35, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián-Romagosa, M.; Udina, E.; Ortner, R.; Dinarès-Ferran, J.; Cho, W.; Murovec, N.; Matencio-Peralba, C.; Sieghartsleitner, S.; Allison, B.Z.; Guger, C. EEG Biomarkers Related with the Functional State of Stroke Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartur, G.; Pratt, H.; Soroker, N. Changes in Mu and Beta Amplitude of the EEG during Upper Limb Movement Correlate with Motor Impairment and Structural Damage in Subacute Stroke. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, P.; Mastropietro, A.; Scano, A.; Chiavenna, A.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Caimmi, M.; Molteni, F.; Rizzo, G. Quantitative EEG for Predicting Upper Limb Motor Recovery in Chronic Stroke Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaar, M.P.; Solis-Escalante, T.; Dewald, J.P.A.; van Wegen, E.E.H.; Schouten, A.C.; Kwakkel, G.; van der Helm, F.C.T.; de Munck, J.; Meskers, C.; Saes, M.; et al. Quantification of Task-Dependent Cortical Activation Evoked by Robotic Continuous Wrist Joint Manipulation in Chronic Hemiparetic Stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, A.M.; Croce, P.; Assenza, G.; Merla, A.; Granata, G.; Giannantoni, N.M.; Pizzella, V.; Tecchio, F.; Zappasodi, F. Electroencephalography-Derived Prognosis of Functional Recovery in Acute Stroke Through Machine Learning Approaches. Int. J. Neur. Syst. 2020, 30, 2050067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.Y.; Lee, A.; Kim, M.S.; Park, E.; Chang, W.H.; Shin, Y.-I.; Kim, Y.-H. Prediction of Motor Recovery Using Quantitative Parameters of Motor Evoked Potential in Patients with Stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A.A.; Chan, F.H.; Zheng, M.M.Z.; Krassioukov, A.V.; Ainslie, P.N. Neurovascular Coupling in Humans: Physiology, Methodological Advances and Clinical Implications. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2016, 36, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C. The Neurovascular Unit Coming of Age: A Journey through Neurovascular Coupling in Health and Disease. Neuron 2017, 96, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Mantini, D.; Gillebert, C.R. The Potential of Real-Time fMRI Neurofeedback for Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review. Cortex 2018, 107, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezmaternykh, D.D.; Kalgin, K.V.; Maximova, P.E.; Mel’nikov, M.Y.; Petrovskii, E.D.; Predtechenskaya, E.V.; Savelov, A.A.; Semenikhina, A.A.; Tsaplina, T.N.; Shtark, M.B.; et al. Application of fMRI and Simultaneous fMRI-EEG Neurofeedback in Post-Stroke Motor Rehabilitation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, M.; Rana, M.; Lugato, N.; Terekhin, P.; Gizzi, L.; Brötz, D.; Fallgatter, A.; Birbaumer, N.; Sitaram, R.; Caria, A. Lower Limb Movement Preparation in Chronic Stroke: A Pilot Study Toward an fNIRS-BCI for Gait Rehabilitation. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 2014, 28, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-N.; Han, P.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Bi, X. Applications of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) Neuroimaging During Rehabilitation Following Stroke: A Review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e943785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragoni, M.; Caltagirone, C.; Troisi, E.; Matteis, M.; Vernieri, F.; Silvestrini, M. Correlation of Cerebral Hemodynamic Changes during Mental Activity and Recovery after Stroke. Neurology 2000, 55, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treger, I.; Aidinof, L.; Lehrer, H.; Kalichman, L. Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy Alters Cerebral Blood Flow in Subacute Post-Stroke Patients. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llwyd, O.; Panerai, R.B.; Robinson, T.G. Effects of Dominant and Non-Dominant Passive Arm Manoeuvres on the Neurovascular Coupling Response. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, K.S.; Whitaker, A.A.; Lui, Y.; Witte, E.; Perdomo, S.J.; Ward, J.L.; Eickmeyer, S.; Ledbetter, L.; Abraham, M.; Billinger, S.A. The Effect of Stroke on Middle Cerebral Artery Blood Flow Velocity Dynamics During Exercise. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2019, 43, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbito, R.; Guiot, C.; Roatta, S. Functional Transcranial Doppler (fTCD) Investigation of Brain Lateralization Following Visual Stimuli. In Proceedings of the 2023 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Sydney, Australia, 24–27 July 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbito, R.; Guiot, C.; Roatta, S. Hemispheric Lateralization during Active and Imagined Movements Assessed by Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2026, 112, 108540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Zhu, B.; Xu, Y.; Fan, M.; Tong, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Motor Network Reorganization after Motor Imagery Training in Stroke Patients with Moderate to Severe Upper Limb Impairment. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-Z.; Wu, J.-J.; Cao, Z.; Hua, X.-Y.; Zheng, M.-X.; Xing, X.-X.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.-G. Motor Imagery-Based Brain–Computer Interface Rehabilitation Programs Enhance Upper Extremity Performance and Cortical Activation in Stroke Patients. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2024, 21, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatakrishnan, S.; Khanna, M.; Gupta, A. Transcranial Color Coded Duplex Sonography Findings in Stroke Patients Undergoing Rehabilitation: An Observational Study. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2022, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treger, I.; Streifler, J.Y.; Ring, H. The Relationship between Mean Flow Velocity and Functional and Neurologic Parameters of Ischemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbito, R.; Cinanni, A.; Bussi, L.; Guiot, C.; Roatta, S. A Neuro-Feedback Prototype Based on Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound for Brain Computer Interface Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, G.; Kim, Y.-H. Use of Cortical Hemodynamic Responses in Digital Therapeutics for Upper Limb Rehabilitation in Patients with Stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2024, 21, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, A.Y.; Thorpe, S.G.; Canac, N.; Jalaleddini, K.; Hamilton, R.B. A Review of the Use of Transcranial Doppler Waveform Morphology for Acute Stroke Assessment. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 81, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Feng, W.; Ovbiagele, B. Multimodality Ultrasound Imaging in Stroke: Current Concepts and Future Focus. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2016, 14, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Joo, I.L.; Bazzigaluppi, P.; Koletar, M.M.; Cherin, E.; Stanisz, A.G.; Graham, J.W.; Demore, C.; Stefanovic, B. Micro-Ultrasound Based Characterization of Cerebrovasculature Following Focal Ischemic Stroke and upon Short-Term Rehabilitation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2024, 44, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehoux, M.-C.; Sobczak, S.; Cloutier, F.; Charest, S.; Bertrand-Grenier, A. Shear Wave Elastography Potential to Characterize Spastic Muscles in Stroke Survivors: Literature Review. Clin. Biomech. 2020, 72, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyding, J.; Fung, C.; Niesen, W.-D.; Krogias, C. Twenty Years of Cerebral Ultrasound Perfusion Imaging—Is the Best yet to Come? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.C.; Beishon, L.C.; Castro, P.; Claassen, J.A.H.R.; Minhas, J.S. Transcranial Doppler in the Era of Personalized Medicine: An Important Tool for the Assessment of Cerebrovascular Function. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, N.N.; Podder, K.K.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Rabbani, M.; Wadud, M.S.I.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Mahmud, S.; Khandakar, A.; Zughaier, S.M. A Deep Learning Framework for the Detection of Abnormality in Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaki, J.; Woźniak, M. Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Action (2019–2023): A Review on Brain Stroke Detection, Diagnosis, and Intelligent Post-Stroke Rehabilitation Management. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 52161–52181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, L.B.; Bertels, C.; Davis, J.N. Interrater Reliability of the NIH Stroke Scale. Arch. Neurol. 1989, 46, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brass, L.M.; Kernan, W.N. Canadian Neurological Scale. Neurology 1989, 39, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantson, L.; De Weerdt, W.; De Keyser, J.; Diener, H.C.; Franke, C.; Palm, R.; Van Orshoven, M.; Schoonderwalt, H.; De Klippel, N.; Herroelen, L. The European Stroke Scale. Stroke 1994, 25, 2215–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandinavian Stroke Study Group. Multicenter Trial of Hemodilution in Ischemic Stroke—Background and Study Protocol. Stroke 1985, 16, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, N.; Sonoda, S.; Domen, K.; Saitoh, E.; Kimura, A. Stroke Impairment Assessment Set (SIAS). Jpn. J. Rehabil. Med. 1994, 31, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugl-Meyer, A.R.; Jääskö, L.; Olsson, S.; Steglind, S. The Post-Stroke Hemiplegic Patient. 1. a Method for Evaluation of Physical Performance. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1975, 7, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeurisse, G.; Demol, O.; Robaye, E. Motor Evaluation in Vascular Hemiplegia. Eur. Neurol. 2008, 19, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater Reliability of a Modified Ashworth Scale of Muscle Spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.H.; Shepherd, R.B.; Nordholm, L.; Lynne, D. Investigation of a New Motor Assessment Scale for Stroke Patients. Phys. Ther. 1985, 65, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.J.; Baker, L.L.; Craddock, J.A. Functional Test for the Hemiparetic Upper Extremity. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1984, 38, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K. Measuring Balance in the Elderly: Preliminary Development of an Instrument. Physiother. Can. 1989, 41, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Winckel, A.; Feys, H.; van der Knaap, S.; Messerli, R.; Baronti, F.; Lehmann, R.; Van Hemelrijk, B.; Pante`, F.; Perfetti, C.; De Weerdt, W. Can Quality of Movement Be Measured? Rasch Analysis and Inter-Rater Reliability of the Motor Evaluation Scale for Upper Extremity in Stroke Patients (MESUPES). Clin. Rehabil. 2006, 20, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, K.; Mayo, N.; Wood-Dauphinée, S. Reliability of Scores on the Stroke Rehabilitation Assessment of Movement (STREAM) Measure. Phys. Ther. 1999, 79, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowland, C.; Stratford, P.; Ward, M.; Moreland, J.; Torresin, W.; Van Hullenaar, S.; Sanford, J.; Barreca, S.; Vanspall, B.; Plews, N. Measuring Physical Impairment and Disability with the Chedoke-McMaster Stroke Assessment. Stroke 1993, 24, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enderby, P. Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment. Br. J. Disord. Commun. 1980, 15, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collen, F.M.; Wade, D.T.; Robb, G.F.; Bradshaw, C.M. The Rivermead Mobility Index: A Further Development of the Rivermead Motor Assessment. Int. Disabil. Stud. 1991, 13, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, V.M.; Wade, D.T.; Hewer, R.L. Loss of Arm Function after Stroke: Measurement, Frequency, and Recovery. Int. Rehabil. Med. 1986, 8, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, E.; Miller, N.E.; Novack, T.A.; Cook, E.W.; Fleming, W.C.; Nepomuceno, C.S.; Connell, J.S.; Crago, J.E. Technique to Improve Chronic Motor Deficit after Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1993, 74, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lincoln, N.; Jackson, J.; Adams, S. Reliability and Revision of the Nottingham Sensory Assessment for Stroke Patients. Physiotherapy 1998, 84, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, E. Two-Point Discrimination Test. A Valuable Part of Hand Surgical Rehabilitation, e.g. in Tetraplegia. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1990, 22, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashner, L.M.; Peters, J.F. Dynamic Posturography in the Diagnosis and Management of Dizziness and Balance Disorders. Neurol. Clin. 1990, 8, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, H.M.; Horne, D.J.d.L.; Sheather, S. Clinical Applications of Visual Analogue Scales: A Critical Review. Psychol. Med. 1988, 18, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.W.; Weiner, D.K.; Chandler, J.; Studenski, S. Functional Reach: A New Clinical Measure of Balance. J. Gerontol. 1990, 45, M192–M197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerakkody, N.S.; Blouin, J.S.; Taylor, J.L.; Gandevia, S.C. Local Subcutaneous and Muscle Pain Impairs Detection of Passive Movements at the Human Thumb. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 3183–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R.; Anson, J.; Liu, Y. Assessing Proprioception: A Critical Review of Methods. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddington, G.; Adams, R. Discrimination of active plantarflexion and inversion movements after ankle injury. Aust. J. Physiother. 1999, 45, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-Mental State”: A Practical Method for Grading the Cognitive State of Patients for the Clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2000, 12, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, K.I. Clock-Drawing: Is It the Ideal Cognitive Screening Test? Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2000, 15, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinàs-Reglà, J.; Vilalta-Franch, J.; López-Pousa, S.; Calvó-Perxas, L.; Torrents Rodas, D.; Garre-Olmo, J. The Trail Making Test: Association with Other Neuropsychological Measures and Normative Values for Adults Aged 55 Years and Older from a Spanish-Speaking Population-Based Sample. Assessment 2017, 24, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mioshi, E.; Dawson, K.; Mitchell, J.; Arnold, R.; Hodges, J.R. The Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Revised (ACE-R): A Brief Cognitive Test Battery for Dementia Screening. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajek, V.E.; Rutman, D.L.; Scher, H. Brief Assessment of Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1989, 70, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pekkala, S. Verbal Fluency Tasks and the Neuropsychology of Language. In The Handbook of Neuropsychology of Language; Faust, M., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 619–634. ISBN 978-1-4443-3040-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, E.; Goodglass, H.; Weintraub, S. Boston Naming Test; [Database Record]; APA PsycTests: Washington, DC, USA. [CrossRef]
- De Renzi, A.; Vignolo, L.A. Token Test: A Sensitive Test to Detect Receptive Disturbances in Aphasics. Brain 1962, 85, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.W.; Wallace, D.; Lai, S.M.; Johnson, D.; Embretson, S.; Laster, L.J. The Stroke Impact Scale Version 2.0. Stroke 1999, 30, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrans, C.E.; Powers, M.J. Quality of Life Index: Development and Psychometric Properties. Adv. Nurs. Sci. 1985, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-Ltem Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): I. Conceptual Framework and Item Selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestroni, G.; Bertolotti, G. EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D): An Instrument for Measuring Quality of Life. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2012, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.S.; Weinberger, M.; Harris, L.E.; Clark, D.O.; Biller, J. Development of a Stroke-Specific Quality of Life Scale. Stroke 1999, 30, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M. A rating scale for depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1960, 23, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Vanclay, F.; Cooper, B. Improving the Sensitivity of the Barthel Index for Stroke Rehabilitation. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1989, 42, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelkey, M.; Wallace, M. Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 1999, 25, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.P.; Brody, E.M. Assessment of older people: Self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Nurs. Res. 1969, 19, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass-Haugen, J.; Mathiowetz, V. Optimizing Motor Behavior Using the Occupational Therapy Task-Oriented Approach. In Occupational Therapy for Physical Dysfunction; Radomski, M.V., Latham, C.T., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2008; pp. 598–617. [Google Scholar]
- Law, M.; Baptiste, S.; McColl, M.; Opzoomer, A.; Polatajko, H.; Pollock, N. The Canadian Occupational Performance Measure: An Outcome Measure for Occupational Therapy. Can. J. Occup. Ther. 1990, 57, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, J. Cerebral Vascular Accidents in Patients over the Age of 60: II. Prognosis. Scott. Med. J. 1957, 2, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physical Self-Maintenance Scale (PSMS). Self-Rated Version. Incorporated in the Philadelphia Geriatric Center. Multilevel Assessment Instrument (MAI). Psychopharmacol. Bull. 1988, 24, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Category | Technique | Features | Regulatory Status/ Current Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical treatment protocols | Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT) | CIMT coupled with supplementary therapies yields heightened upper limb function in post-stroke subjects [20]. | Approved/Clinical |
| Action Observation Treatment (AOT) | Approach based on the role of the mirror neuron system in motor learning [21]. | Approved/Clinical | |
| Mirror therapy | Implementation of mirror-symmetric movements as a form of motor priming [22]. | Approved/Clinical | |
| Motor imagery | Mental rehearsal of movements to promote neuroplastic changes [23]. | Approved/Clinical | |
| Biofeedback | Enhances awareness and control over physiological functions [24]. | Approved/Clinical | |
| Instrumental treatment techniques | Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) | Targets specific brain regions for functional improvement [25]. | Experimental |
| Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) | Application of contralaterally controlled functional electrical stimulation [26]. | Experimental | |
| repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) | Targeted transcranial magnetic stimulation on ischemic cortical regions [27]. | Experimental | |
| Transcranial Ultrasound Stimulation (TUS) | Promotes neuroplasticity, thrombus dissolution, and functional recovery through mechanical and neurotrophic effects [28,29] | Early clinical phase/Preclinical | |
| Robotic tools | Robot-assisted therapy | Utilization of robotic tools for training [30,31]; effective for improving strength and increasing patient engagement time. | Approved/Clinical |
| Virtual reality and exoskeleton | Fusion of robotic and virtual reality tools for rehabilitation [32]. | Approved/Clinical | |
| Telemedicine systems | Telerehabilitation: home-based exergaming interventions | Deployment of exergames for training purposes [33]; extends treatment time and supports long-term monitoring. | Approved/Clinical |
| Telerehabilitation: immersive virtual reality | Utilization of augmented or virtual reality for training [34]; supports remote engagement and extended rehabilitation. | Approved/Expanding clinical adoption |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabbito, R.; Ficiarà, E.; Priano, L.; Bigoni, M.; Guiot, C.; Roatta, S. From Qualitative to Quantitative Functional Assessment in Stroke Rehabilitation with a Focus on Ultrasound Role. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112594
Rabbito R, Ficiarà E, Priano L, Bigoni M, Guiot C, Roatta S. From Qualitative to Quantitative Functional Assessment in Stroke Rehabilitation with a Focus on Ultrasound Role. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112594
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabbito, Rosita, Eleonora Ficiarà, Lorenzo Priano, Matteo Bigoni, Caterina Guiot, and Silvestro Roatta. 2025. "From Qualitative to Quantitative Functional Assessment in Stroke Rehabilitation with a Focus on Ultrasound Role" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112594
APA StyleRabbito, R., Ficiarà, E., Priano, L., Bigoni, M., Guiot, C., & Roatta, S. (2025). From Qualitative to Quantitative Functional Assessment in Stroke Rehabilitation with a Focus on Ultrasound Role. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112594








