Error in Figure
Figure 5 in the original publication [1] was selected by mistake instead of the right one. The subfigures of panel A (a–c′; f′) and panel B (d–f′; g–i′) have now been replaced with the correct version, as the one originally submitted with the manuscript was uploaded by mistake. The corrected Figure 5 now appears below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
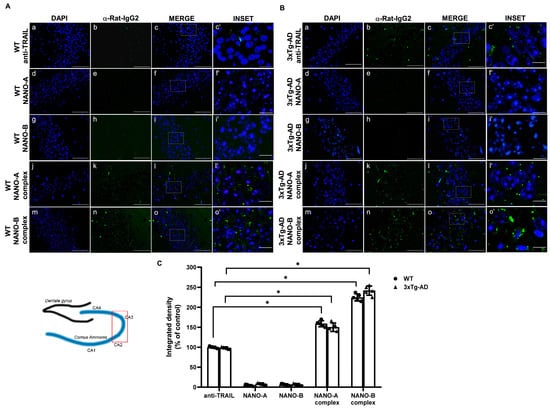
Figure 5.
Comparison of polymeric or lipidic nanoparticles complexed with anti-TRAIL in the hippocampus of 3xTg-AD mice after intranasal administration. Representative immunofluorescence microscopy images showing the localization of the anti-TRAIL monoclonal antibody in the hippocampal sections from WT (A) or 3×Tg-AD (B) mice intranasally administered for 24 h with the anti-TRAIL monoclonal antibody, empty, or anti-TRAIL-loaded NANO-A, NANO-B nanoparticles. The fluorescence signal was detected by using a fluorescent secondary anti-rat IgG. The insets represent the respective areas magnified. (C) The densitometric count of fluorescence was performed with the aid of ImageJ software (available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 12 January 2022)) and represented as integrated density (% of control). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test was used for statistical analysis. * p < 0.05. (a–o scale bar = 50 µm; c’, f’, i’, l’, o’ scale bar = 10 µm).
Reference
- Musumeci, T.; Di Benedetto, G.; Carbone, C.; Bonaccorso, A.; Amato, G.; Lo Faro, M.J.; Burgaletto, C.; Puglisi, G.; Bernardini, R.; Cantarella, G. Intranasal Administration of a TRAIL Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Adsorbed in PLGA Nanoparticles and NLC Nanosystems: An In Vivo Study on a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).