Dietary Habits, TCM Constitutions, and Obesity: Investigating the Protective Effects of Vegetarian Dietary Patterns in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. Taiwan Biobank Database
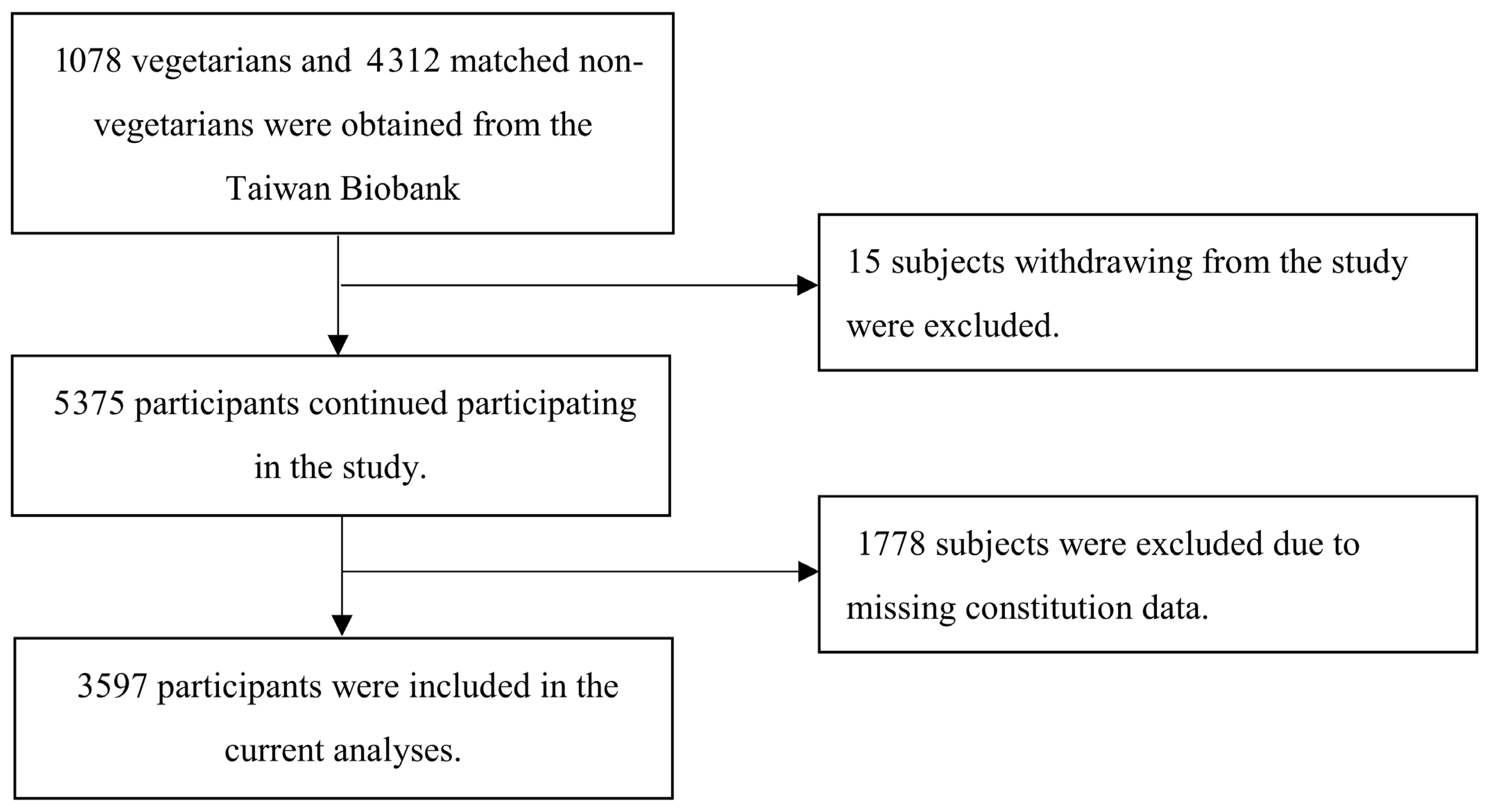
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Dietary Score Calculation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- (1)
- Model 1 included basic demographic covariates (age and sex) and lifestyle factors (e.g., current alcohol use, smoking, and exercise habits) to estimate their associations with the odds of being overweight or obese. This baseline model provided an initial assessment of conventional risk factors without consideration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) body constitution types.
- (2)
- Model 2 added Phlegm stasis constitution to the covariate set to assess its independent contribution to BMI status, thereby evaluating whether individuals with this constitution type were more likely to be overweight or obese, independent of other lifestyle and demographic factors.
- (3)
- Model 3 further incorporated dietary habits, specifically vegetarian dietary patterns, to investigate their association with BMI status and their potential role in modulating the relationship between constitution type and obesity-related outcomes.
- (4)
- Model 4 introduced an interaction term between vegetarian dietary patterns and Phlegm stasis constitution to evaluate whether the relationship between dietary habits and BMI differed by constitutional type. This model enabled the assessment of potential effect modification, shedding light on whether dietary interventions may yield different outcomes depending on one’s TCM body constitution.
- (5)
- Together, these models provide a stepwise framework to disentangle the complex interplay between demographic factors, constitution type, lifestyle behaviors, and dietary patterns in relation to obesity and overweight. This layered approach supports the development of constitution-informed, individualized prevention strategies targeting metabolic health.
3. Results
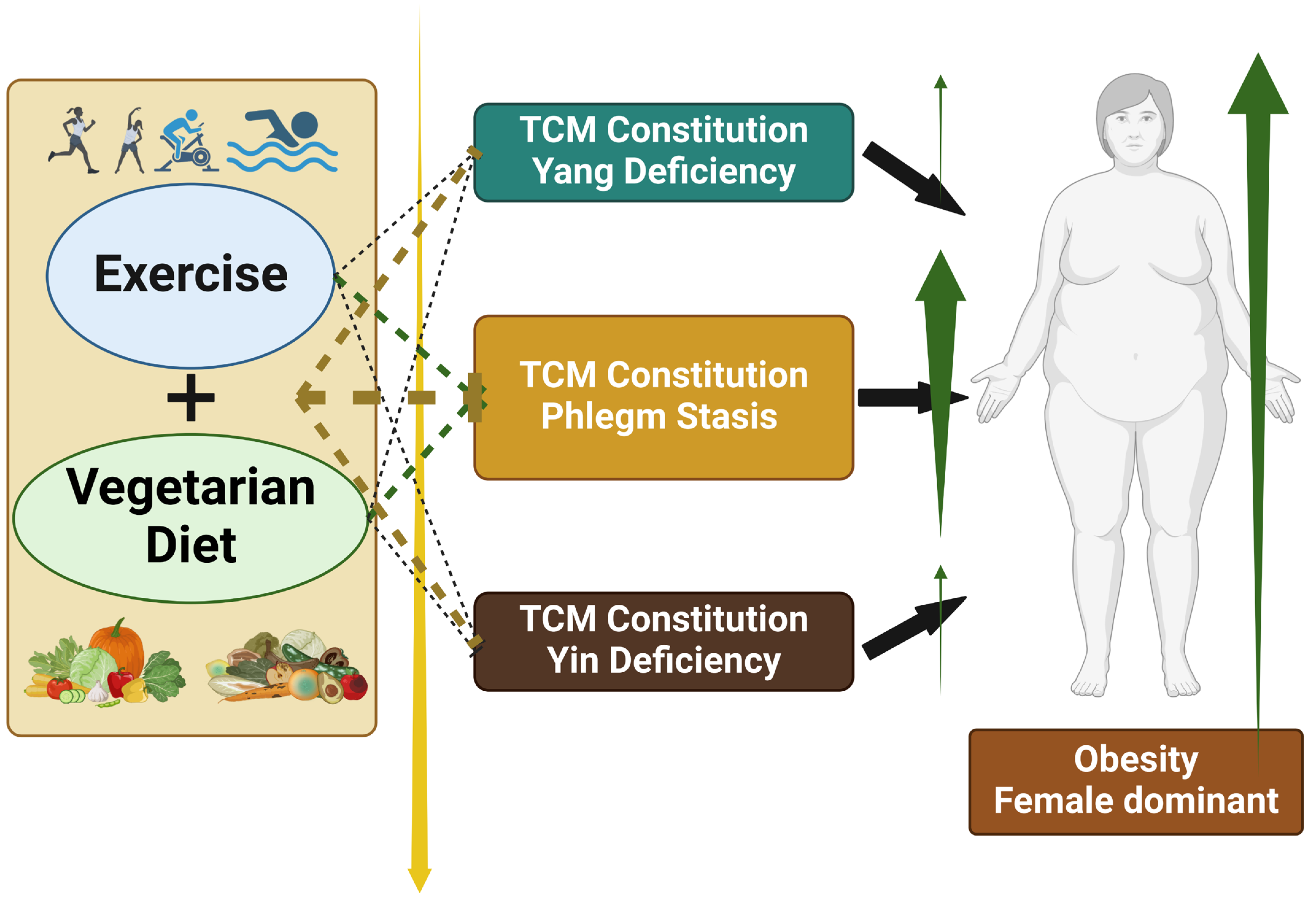
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Muniesa, P.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Hu, F.B.; Despres, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.A.; Martinez, J.A. Obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; McPherson, K.; Marsh, T.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Brown, M. Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet 2011, 378, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.O.; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stival, C.; Lugo, A.; Odone, A.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Fernandez, E.; Tigova, O.; Soriano, J.B.; Jose Lopez, M.; Scaglioni, S.; Gallus, S.; et al. Prevalence and Correlates of Overweight and Obesity in 12 European Countries in 2017–2018. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.F. Prevalence of obesity in Taiwan. Obes. Rev. 2005, 6, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.C. Obesity and its related diseases in Taiwan. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9 (Suppl. S1), 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Wen, T.; Yeh, P.; Chang, H. Costs of metabolic syndrome-related diseases induced by obesity in Taiwan. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9 (Suppl. S1), 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U.; Hu, F.B.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolically healthy obesity: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnqvist, F.; Arner, P.; Nordfors, L.; Schalling, M. Overexpression of the obese (ob) gene in adipose tissue of human obese subjects. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.J.; West, N.P.; Cripps, A.W. Obesity, inflammation, and the gut microbiota. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.; Lam, C.L.; Wong, V.T.; Yang, Z.M.; Ziea, E.T.; Kwan, A.K. Validation of the constitution in chinese medicine questionnaire: Does the traditional chinese medicine concept of body constitution exist? Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 481491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Clinical research linking Traditional Chinese Medicine constitution types with diseases: A literature review of 1639 observational studies. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 40, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. The Role of Chinese Medicine in Health Maintenance and Disease Prevention: Application of Constitution Theory. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Cai, J.; Huang, Z. The Interaction Effect between Blood Stasis Constitution and Atherosclerotic Factors on Cognitive Impairment in Elderly People. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8914090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Mohammadtursun, N.; Lv, Y.; Tang, Z.; Dong, J. The Analysis of Constitutions of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Relation to Cerebral Infarction in a Chinese Sample. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2018, 24, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Huang, N.; Lin, W.; Luo, Z.; Ling, C. Identification of Traditional Chinese Medicine Constitutions and Physiological Indexes Risk Factors in Metabolic Syndrome: A Data Mining Approach. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1686205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Chen, K.H.; Hwang, J.S. Association of Menopausal Symptoms with Different Constitutions in Climacteric Women. Complement. Med. Res. 2018, 25, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. Effect of health nursing intervention on quality of life and complications of peptic ulcer patients on the basis of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) constitution identification. Minerva Med. 2020, 113, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Yao, H.; Yang, W.J.; Ren, X.X.; Teng, L.; Yang, M.C. Correlation between Traditional Chinese Medicine Constitution and Dyslipidemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1896746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Zhang, T.; Feng, W.; Gai, Y. Association of TCM body constitution with insulin resistance and risk of diabetes in impaired glucose regulation patients. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.I.; Su, Y.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Lee, I.T.; Lee, C.H.; Li, T.C. Reduced health-related quality of life in body constitutions of yin-xu, and yang-xu, stasis in patients with type 2 diabetes: Taichung diabetic body constitution study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 309403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Di, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Yan, H. Association between Nine Types of TCM Constitution and Five Chronic Diseases: A Correspondence Analysis Based on a Sample of 2660 Participants. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 9439682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzker, S.; Hui, K.K. Building an Evidence-Base for TCM and Integrative East-West Medicine: A Review of Recent Developments in Innovative Research Design. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2012, 2, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannotta, R.; Malik, S.; Chan, A.Y.; Urgun, K.; Hsu, F.; Vadera, S. Integrative Medicine as a Vital Component of Patient Care. Cureus 2018, 10, e3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.C.; Fei, Y.T.; Lai, X.Z.; Lan, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.W.; Fang, H.; Liu, J.P.; Rong, H.G. Progress and challenges in integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine in China from 2002 to 2021. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1425940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, V.C.; Ho, F.F.; Lao, L.; Liu, J.; Lee, M.S.; Chan, K.W.; Nilsen, P. Implementation science in traditional, complementary and integrative medicine: An overview of experiences from China and the United States. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Enlightenment about using TCM constitutions for individualized medicine and construction of Chinese-style precision medicine: Research progress with TCM constitutions. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 2092–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Xu, X.; Liu, P.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zuo, D.; Lai, Z.; Cheng, J. Integrative analysis of microbiota and metabolomics in individuals exhibiting different TCM constitutions utilizing 16S rDNA sequencing and LC/MS metabolomics. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 205, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Li, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Li, L.; Li, Y. Obese Individuals with and Without Phlegm-Dampness Constitution Show Different Gut Microbial Composition Associated with Risk of Metabolic Disorders. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 859708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chang, D.; Shang, X. Constitutions in Traditional Chinese Medicine and Factors Influencing Them in Jilin Province of China. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2023, 29, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, J. Constitution of traditional chinese medicine and related factors in women of childbearing age. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Q.; Li, X.; Fang, J.; Yu, X.; Wu, Z.E.; Yang, C.; Jian, H.; Li, F. Comprehensive biomarker analysis of metabolomics in different syndromes in traditional Chinese medical for prediabetes mellitus. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, P.L.; Liu, C.F.; Huang, H.T.; Jou, H.J.; Chen, S.M.; Young, T.G.; Wang, Y.F.; Liao, P.H. Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Establishment of an Association Model between Metabolic Syndrome, TCM Constitution, and the Guidance of Medicated Diet Care. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5530717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tan, X.; Shi, H.; Xia, D. Nutrition and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): A system’s theoretical perspective. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jia, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Chen, Q. Association between the traditional Chinese medicine constitution and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in older people: A cross-sectional study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Miao, J.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, J.; Tang, X.; Lee, H.C.; et al. A Scoping Review of Cross-Sectional Studies on Traditional Chinese Medicine. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 1275–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jang, B.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.C.; Kuon, W.J.; Kim, C.K. Prevalence of and associations between metabolic syndrome and the constitutions defined by Korean Eight Constitution Medicine. Medicine 2020, 99, e19074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Sohn, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Hwang, M.W.; Kwon, Y.K.; Bae, N.Y.; Chae, H. Digestive system-related pathophysiological symptoms of Sasang typology: Systematic review. Integr. Med. Res. 2013, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mo, S.; Lv, Y.; Tang, Z.; Dong, J. A Study of Traditional Chinese Medicine Body Constitution Associated with Overweight, Obesity, and Underweight. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 7361896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.I.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, J.J.; Chang, S.C.; Li, H.Y.; Jiang, K.H.; Chen, J.L. The Relationships between Leptin, Genotype, and Chinese Medicine Body Constitution for Obesity. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5510552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.C.; Fan, C.T.; Liao, C.C.; Chen, Y.S. Taiwan Biobank: Making cross-database convergence possible in the Big Data era. Gigascience 2018, 7, gix110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.D.; Lin, J.S.; Chen, L.L.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Su, Y.C. BCQs: A Body Constitution Questionnaire to assess Stasis in traditional Chinese medicine. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2012, 4, e379–e391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.C.; Chen, L.L.; Lin, J.D.; Lin, J.S.; Huang, Y.C.; Lai, J.S. BCQ+: A body constitution questionnaire to assess Yang-Xu. Part I: Establishment of a first final version through a Delphi process. Forsch. Komplementärmed. 2008, 15, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Lin, J.S.; Lin, J.D.; Chang, C.H.; Kuo, H.W.; Liang, W.M.; Su, Y.C. BCQ+: A body constitution questionnaire to assess Yang-Xu. Part II: Evaluation of reliability and validity. Forsch. Komplementärmed. 2009, 16, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.D.; Chen, L.L.; Lin, J.S.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Su, Y.C. BCQ-: A body constitution questionnaire to assess Yin-Xu. Part I: Establishment of a provisional version through a Delphi process. Forsch. Komplementärmed. 2012, 19, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guan, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, C.L.; Lin, X.M.; Zheng, G.Q. History and mechanism for treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage with scalp acupuncture. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 895032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.H.; Lee, M.S.; Chuang, S.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Fu, M.L. Obesity pandemic, correlated factors and guidelines to define, screen and manage obesity in Taiwan. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9 (Suppl. S1), 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.; Chen, L.L.; Lin, J.D.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, C.H.; Mayer, P.K.; Su, Y.C. BCQ-: A Body Constitution Questionnaire to assess Yin-Xu. Part II: Evaluation of reliability and validity. Forsch. Komplementärmed. 2012, 19, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, F.; Osaili, T.; Naqeeb, H.; Faris, M.E.; Ismail, L.C.; Obaid, R.S.; Naja, F.; Radwan, H.; Hasan, H.; Hashim, M.; et al. Scientific basis of dietary inflammatory index (DII): A dietary tool to metabolic syndrome risk. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2025, 61, 138–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Li, S.X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, G.; Gong, T.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z. A comprehensive study of psychological well-being and traditional Chinese medicine constitutions among model workers in Beijing. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1425757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Jin, H.; Jin, L. Physical and mental health conditions of young college students with different Traditional Chinese Medicine constitutions in Zhejiang Province of China. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 35, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, L.; He, Y.; Xue, S.A.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, N.; Chen, J. Characteristics of TCM constitutions of adult Chinese women in Hong Kong and identification of related influencing factors: A cross-sectional survey. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Su, Y.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Lee, I.T.; Tsai, C.I.; Li, T.C. Associations of traditional Chinese medicine body constitution and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study of a Taiwanese medical center. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1320861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, T.; Arsenis, N.C.; Disanzo, B.L.; Lamonte, M.J. Effects of exercise training on chronic inflammation in obesity : Current evidence and potential mechanisms. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.; Fang, S.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Lin, W.L.; Tsai, S.F.; Huang, S.M. The Effect of Physical Activity on Body Constitution and Psychological Health in Older Adults: Evidence from an Analysis of a Biobank Research Database. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2023, 31, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.K.; Rai, M.; Rehkopf, D.H.; Abrams, B. Educational attainment and obesity: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Roesler, N.M.; von dem Knesebeck, O. Causation or selection—Examining the relation between education and overweight/obesity in prospective observational studies: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.C.K.; Sichieri, R.; Verly, E., Jr.; Boccolini, C.S.; de Moura Souza, A.; Cunha, D.B. Trends in obesity prevalence among Brazilian adults from 2002 to 2013 by educational level. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiolero, A.; Faeh, D.; Paccaud, F.; Cornuz, J. Consequences of smoking for body weight, body fat distribution, and insulin resistance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. High salt intake: Independent risk factor for obesity? Hypertension 2015, 66, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | All | Non-Vegetarian | Vegetarian |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 3597 | 2910 (80.9) | 687 (19.1) |
| Age | 50.1 ± 9.4 | 50.3 ± 9.4 | 49.6 ± 9.2 |
| Female | 2568 (71.4) | 2082 (71.5) | 486 (70.7) |
| Education * | |||
| Middle school or less | 549 (15.3) | 422 (14.5) | 127 (18.5) |
| High school | 1298 (36.1) | 1074 (36.9) | 224 (32.6) |
| College or higher | 1750 (48.7) | 1414 (48.6) | 336 (48.9) |
| Employment | 2257 (63.2) | 1805 (62.5) | 452 (66.1) |
| BMI ** | 23.9 ± 3.5 | 24.0 ± 3.6 | 23.5 ± 3.5 |
| BMI status * | |||
| Normal | 2001 (55.6) | 1576 (54.2) | 425 (61.9) |
| Overweight | 981 (27.3) | 824 (28.3) | 157 (22.9) |
| Obesity | 615 (17.1) | 510 (17.5) | 105 (15.3) |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 82.6 ± 9.6 | 82.7 ± 9.6 | 81.9 ± 9.4 |
| Phlegm stasis | 570 (15.8) | 476 (16.4) | 94 (13.7) |
| Yang deficiency | 819 (22.8) | 678 (23.3) | 141 (20.5) |
| Yin deficiency * | 838 (23.3) | 706 (24.3) | 132 (19.2) |
| Current drinking ** | 155 (4.3) | 150 (5.2) | 5 (0.7) |
| Current smoking ** | 230 (6.4) | 214 (7.4) | 16 (2.3) |
| Exercise habits * | 1659 (46.1) | 1377 (47.3) | 282 (41.0) |
| Dietary score ** | 15.1 ± 5.2 | 14.9 ± 5.6 | 16.0 ± 3.1 |
| Variable | Phlegm Stasis | Yang Deficiency | Yin Deficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.96 (0.95, 0.97) ** | 0.96 (0.96, 0.97) ** | 0.97 (0.96, 0.98) ** |
| Female | 2.44 (1.88, 3.16) ** | 2.27 (1.83, 2.82) ** | 1.77 (1.44, 2.17) ** |
| Employment | 1.04 (0.84, 1.29) | 0.95 (0.79, 1.15) | 0.89 (0.74, 1.07) |
| Drinking | 0.80 (0.45, 1.41) | 1.10 (0.71, 1.71) | 1.13 (0.75, 1.71) |
| Smoking | 1.09 (0.71, 1.68) | 1.12 (0.78, 1.62) | 1.16 (0.82, 1.65) |
| Exercise | 0.70 (0.57, 0.85) ** | 0.76 (0.64, 0.90) * | 0.79 (0.67, 0.93) * |
| Vegetarian | 0.77 (0.60, 0.98) * | 0.83 (0.67, 1.02) | 0.72 (0.58, 0.89) * |
| Predictor | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight vs. Normal | Obesity vs. Normal | Overweight vs. Normal | Obesity vs. Normal | Overweight vs. Normal | Obesity vs. Normal | Overweight vs. Normal | Obesity vs. Normal | |
| Age | 1.03 (1.02, 1.04) ** | 1.00 (0.99, 1.02) | 1.03 (1.02, 1.04) ** | 1.01 (0.99, 1.02) | 1.03 (1.02, 1.04) ** | 1.01 (0.99, 1.02) | 1.03 (1.02, 1.04) ** | 1.01 (0.99, 1.02) |
| Female | 0.35 (0.29, 0.43) ** | 0.39 (0.31, 0.48) ** | 0.36 (0.29, 0.43) ** | 0.37 (0.30, 0.47) ** | 0.35 (0.29, 0.42) ** | 0.37 (0.29, 0.46) ** | 0.35 (0.29, 0.42) ** | 0.37 (0.29, 0.46) ** |
| Education | ||||||||
| Middle school or less | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| High school | 0.77 (0.60, 0.98) * | 0.59 (0.45, 0.78) ** | 0.78 (0.62, 1.00) * | 0.60 (0.45, 0.78) ** | 0.76 (0.60, 0.97) * | 0.58 (0.44, 0.77) ** | 0.76 (0.60, 0.97) * | 0.58 (0.44, 0.77) ** |
| College or higher | 0.58 (0.45, 0.74) ** | 0.39 (0.29, 0.51) ** | 0.59 (0.46, 0.76) ** | 0.39 (0.29, 0.52) ** | 0.58 (0.45, 0.74) ** | 0.38 (0.29, 0.51) ** | 0.58 (0.45, 0.74) ** | 0.38 (0.29, 0.50) ** |
| Employment | 1.17 (0.97, 1.41) | 1.21 (0.97, 1.51) | 1.17 (0.97, 1.40) | 1.20 (0.96, 1.50) | 1.17 (0.97, 1.41) | 1.21 (0.97, 1.51) | 1.17 (0.97, 1.41) | 1.21 (0.97, 1.51) |
| Drinking | 0.97 (0.65, 1.44) | 1.07 (0.69, 1.67) | 1.03 (0.68, 1.54) | 1.14 (0.73, 1.78) | 0.97 (0.65, 1.45) | 1.08 (0.69, 1.69) | 0.97 (0.65, 1.44) | 1.07 (0.69, 1.67) |
| Smoking | 1.00 (0.71, 1.41) | 1.30 (0.90, 1.88) | 1.06 (0.75, 1.49) | 1.36 (0.94, 1.96) | 1.00 (0.71, 1.41) | 1.30 (0.90, 1.87) | 1.00 (0.71, 1.41) | 1.30 (0.90, 1.87) |
| Exercise | 0.90 (0.76, 1.06) | 0.76 (0.62, 0.93) * | 0.92 (0.78, 1.08) | 0.79 (0.64, 0.96) * | 0.90 (0.76, 1.07) | 0.78 (0.64, 0.95) * | 0.90 (0.76, 1.07) | 0.78 (0.64, 0.95) * |
| Vegetarian | 0.67 (0.55, 0.83) ** | 0.72 (0.56, 0.92) * | 0.68 (0.55, 0.84) ** | 0.73 (0.57, 0.93) * | 0.67 (0.54, 0.84) ** | 0.67 (0.51, 0.88) * | ||
| Phlegm stasis constitution | 1.21 (0.96, 1.52) | 1.58 (1.23, 2.02) ** | 1.19 (0.95, 1.50) | 1.56 (1.22, 2.00) ** | 1.18 (0.92, 1.51) | 1.44 (1.10, 1.89) * | ||
| Vegetarian * Phlegm stasis constitution | 1.07 (0.57, 1.99) | 1.58 (0.85, 2.96) | ||||||
| Predictor | All | Non-Vegetarian | Vegetarian | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight vs. Normal | Obesity vs. Normal | Overweight vs. Normal | Obesity vs. Normal | Overweight vs. Normal | Obesity vs. Normal | |
| Age | 1.03 (1.02, 1.04) ** | 1.01 (0.999, 1.02) | 1.04 (1.02, 1.05) ** | 1.02 (1.01, 1.03) * | 1.02 (0.99, 1.04) | 0.97 (0.94, 0.998) * |
| Female | 0.37 (0.31, 0.45) ** | 0.40 (0.32, 0.50) ** | 0.33 (0.27, 0.41) ** | 0.40 (0.31, 0.52) ** | 0.55 (0.36, 0.85) * | 0.35 (0.21, 0.58) ** |
| Education | ||||||
| Middle school or less | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| High school | 0.79 (0.62, 1.00) | 0.60 (0.45, 0.78) ** | 0.75 (0.57, 0.99) * | 0.58 (0.42, 0.78) ** | 0.78 (0.46, 1.34) | 0.53 (0.28, 0.998) * |
| College or higher | 0.60 (0.47, 0.77) ** | 0.40 (0.30, 0.52) ** | 0.58 (0.44, 0.77) ** | 0.40 (0.29, 0.55) ** | 0.57 (0.33, 0.99) * | 0.27 (0.14, 0.54) ** |
| Employment | 1.16 (0.96, 1.40) | 1.20 (0.96, 1.49) | 1.15 (0.93, 1.41) | 1.34 (1.05, 1.72) * | 1.35 (0.86, 2.13) | 0.73 (0.43, 1.24) |
| Drinking | 1.02 (0.68, 1.52) | 1.12 (0.72, 1.75) | 1.01 (0.67, 1.52) | 1.09 (0.69, 1.73) | - | 0.37 (0.035, 3.90) |
| Smoking | 1.02 (0.72, 1.43) | 1.28 (0.89, 1.85) | 0.85 (0.59, 1.22) | 1.32 (0.90, 1.94) | 2.75 (0.95, 7.98) | - |
| Exercise | 0.94 (0.80, 1.11) | 0.81 (0.67, 0.99) * | 0.95 (0.79, 1.15) | 0.79 (0.63, 0.99) * | 0.79 (0.52, 1.18) | 0.94 (0.58, 1.53) |
| Dietary score | 0.97 (0.96, 0.99) ** | 0.96 (0.94, 0.98) ** | 0.97 (0.96, 0.99) * | 0.96 (0.94, 0.98) ** | 0.99 (0.93, 1.06) | 0.99 (0.92, 1.06) |
| Phlegm stasis constitution | 1.17 (0.93, 1.46) | 1.50 (1.17, 1.92) ** | 1.17 (0.92, 1.50) | 1.40 (1.06, 1.84) * | 1.09 (0.61, 1.96) | 2.22 (1.23, 4.02) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, P.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Lin, H.-C.; Chang, C.-M. Dietary Habits, TCM Constitutions, and Obesity: Investigating the Protective Effects of Vegetarian Dietary Patterns in Taiwan. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141641
Huang P-Y, Chen C-H, Chiu Y-F, Lin H-C, Chang C-M. Dietary Habits, TCM Constitutions, and Obesity: Investigating the Protective Effects of Vegetarian Dietary Patterns in Taiwan. Healthcare. 2025; 13(14):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141641
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Po-Yu, Chien-Hsiun Chen, Yen-Feng Chiu, Hong-Chun Lin, and Ching-Mao Chang. 2025. "Dietary Habits, TCM Constitutions, and Obesity: Investigating the Protective Effects of Vegetarian Dietary Patterns in Taiwan" Healthcare 13, no. 14: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141641
APA StyleHuang, P.-Y., Chen, C.-H., Chiu, Y.-F., Lin, H.-C., & Chang, C.-M. (2025). Dietary Habits, TCM Constitutions, and Obesity: Investigating the Protective Effects of Vegetarian Dietary Patterns in Taiwan. Healthcare, 13(14), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141641







