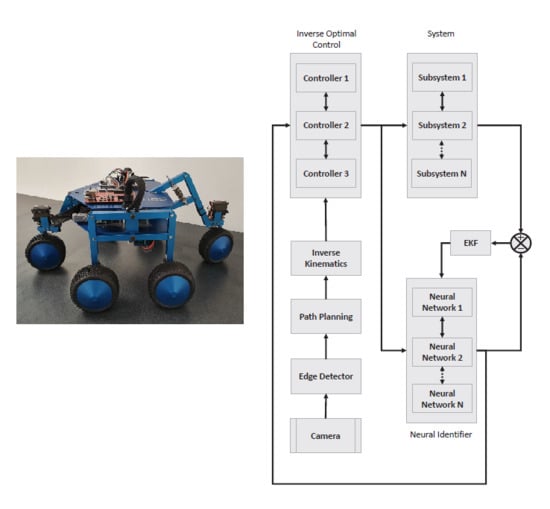
An Autonomous Path Controller in a System on Chip for Shrimp Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
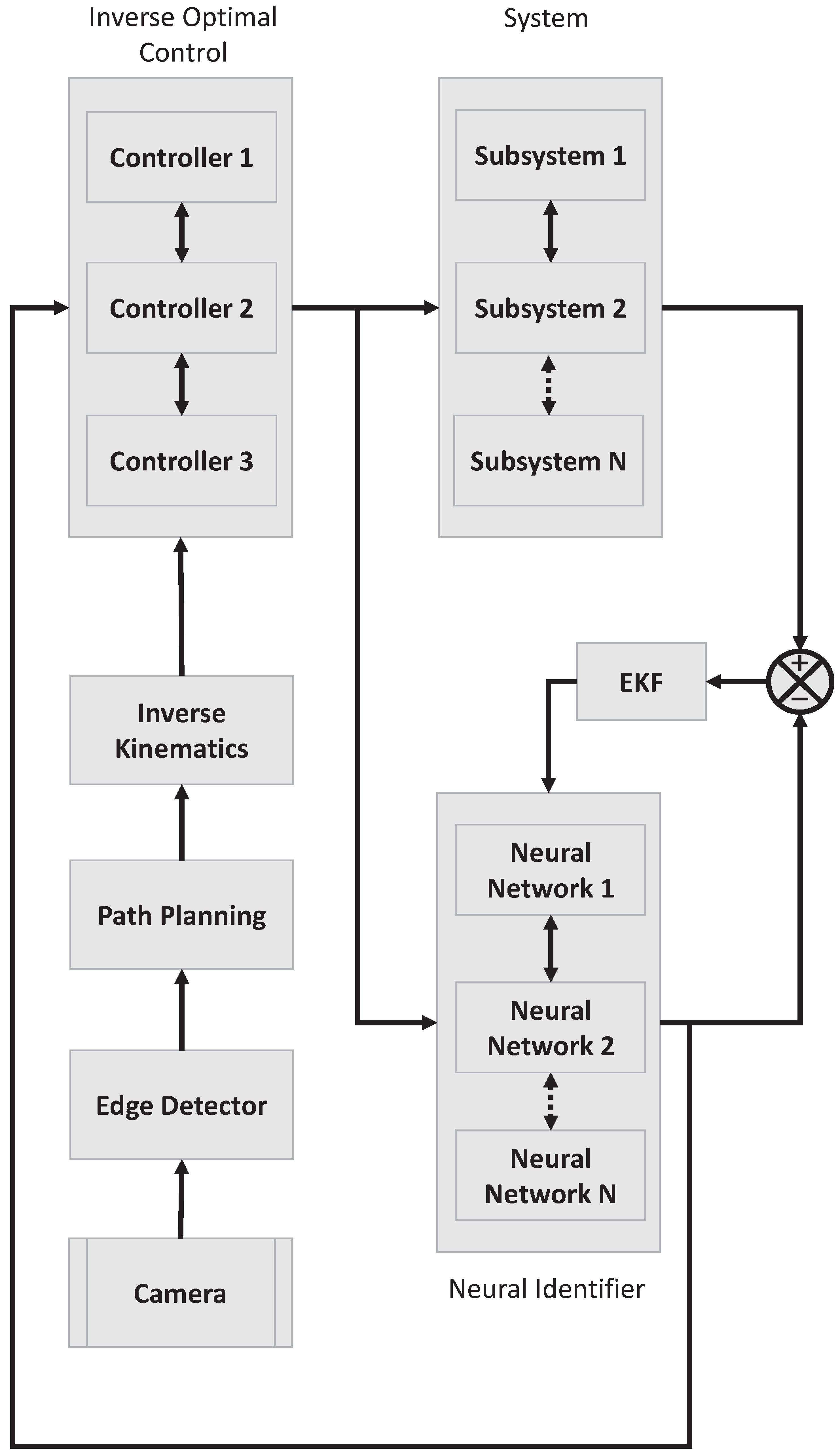
2. Inverse Optimal Controller
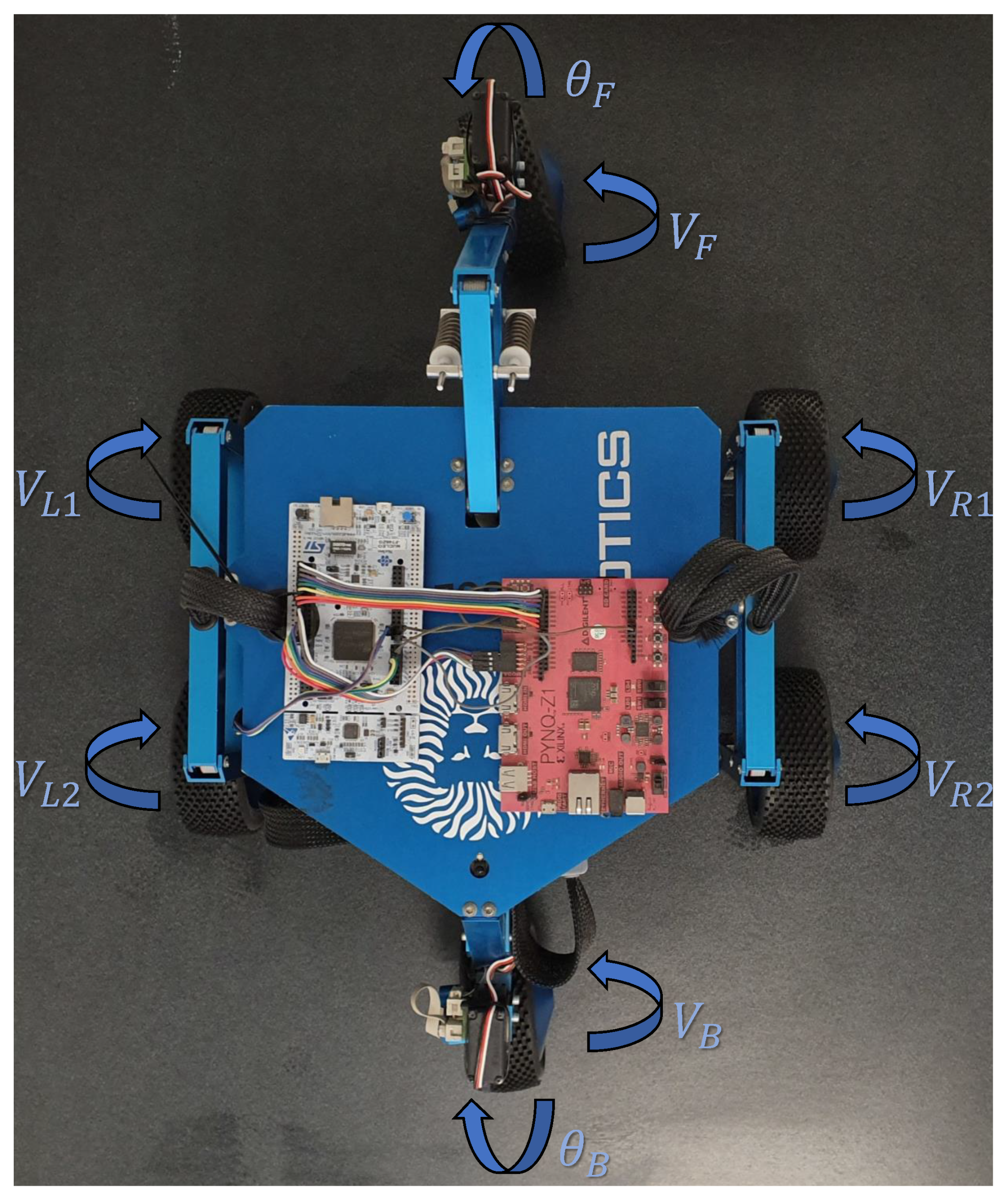
3. Shrimp’s Kinematic Model
4. Neural Identifier
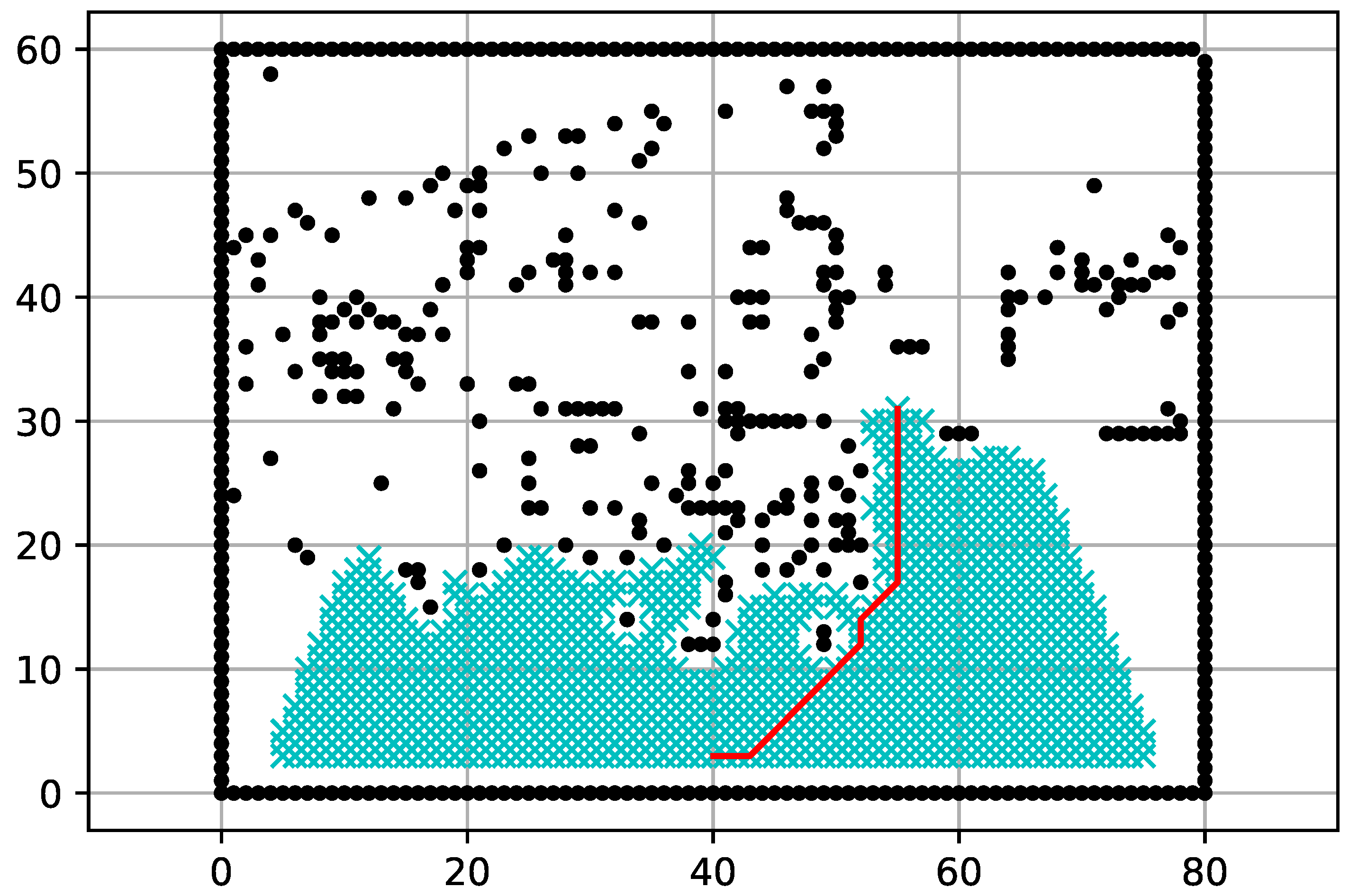
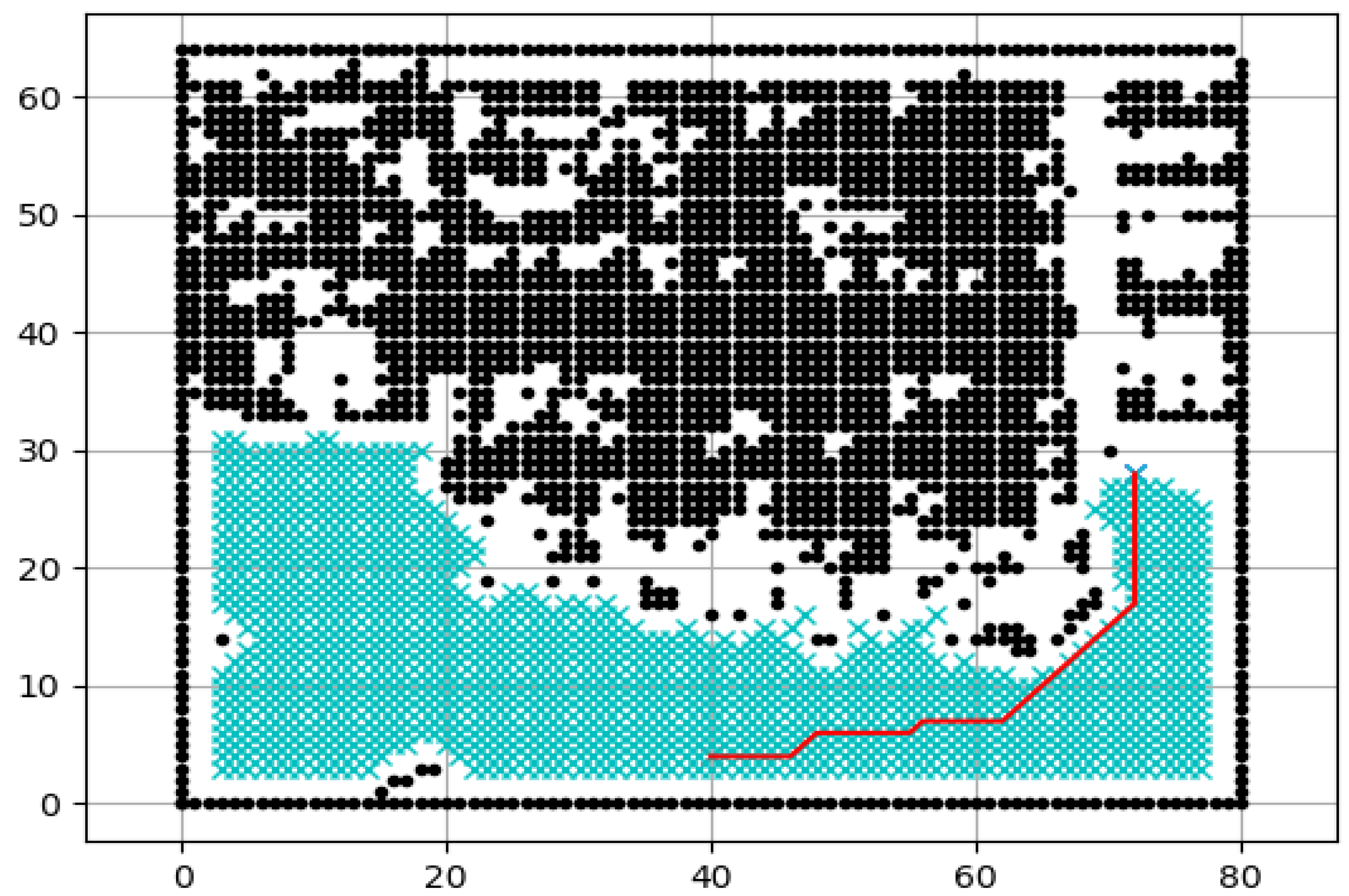
5. Path Planning
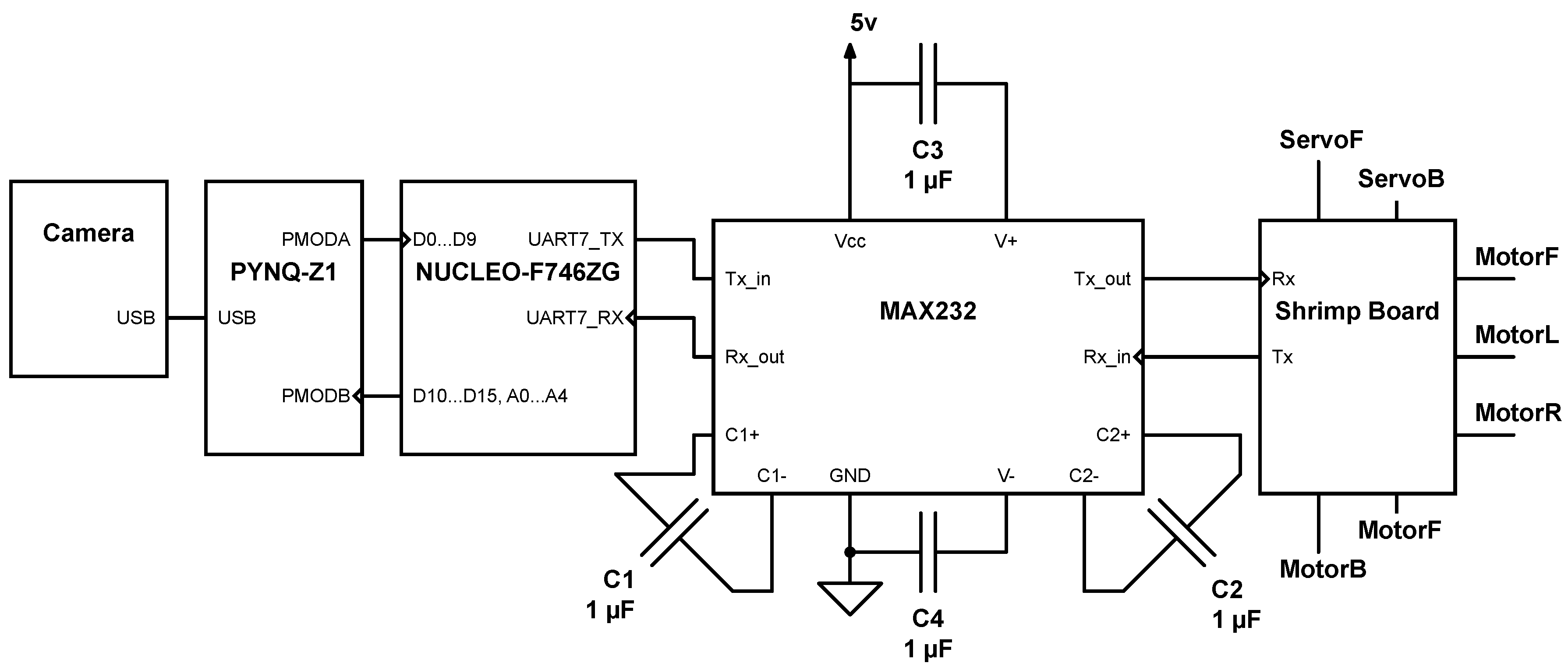
6. Hardware Implementation
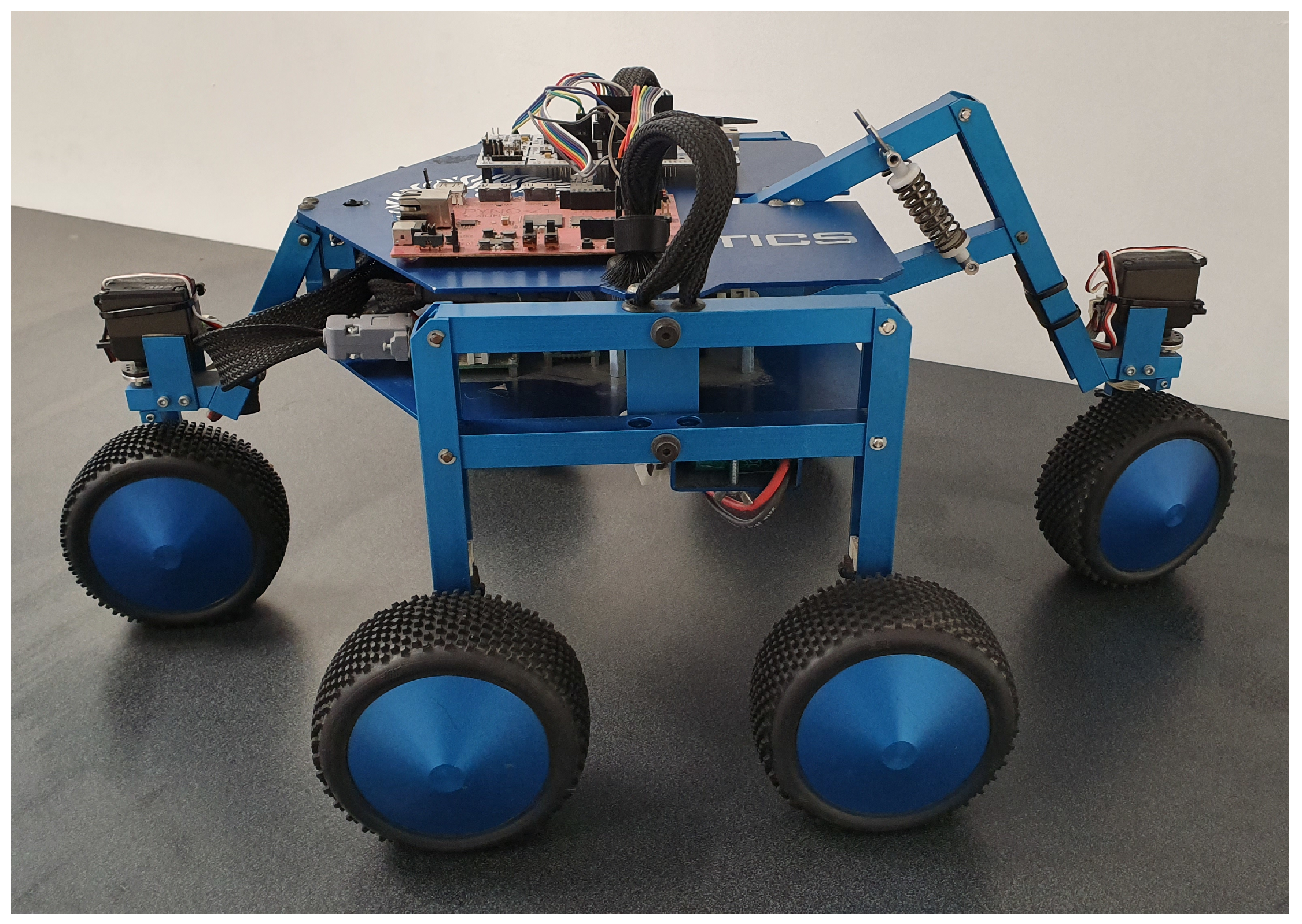
6.1. BlueBotics Shrimp III
6.2. Xilinx PYNQ-Z1
6.3. STMicroelectronics NUCLEO-F746ZG
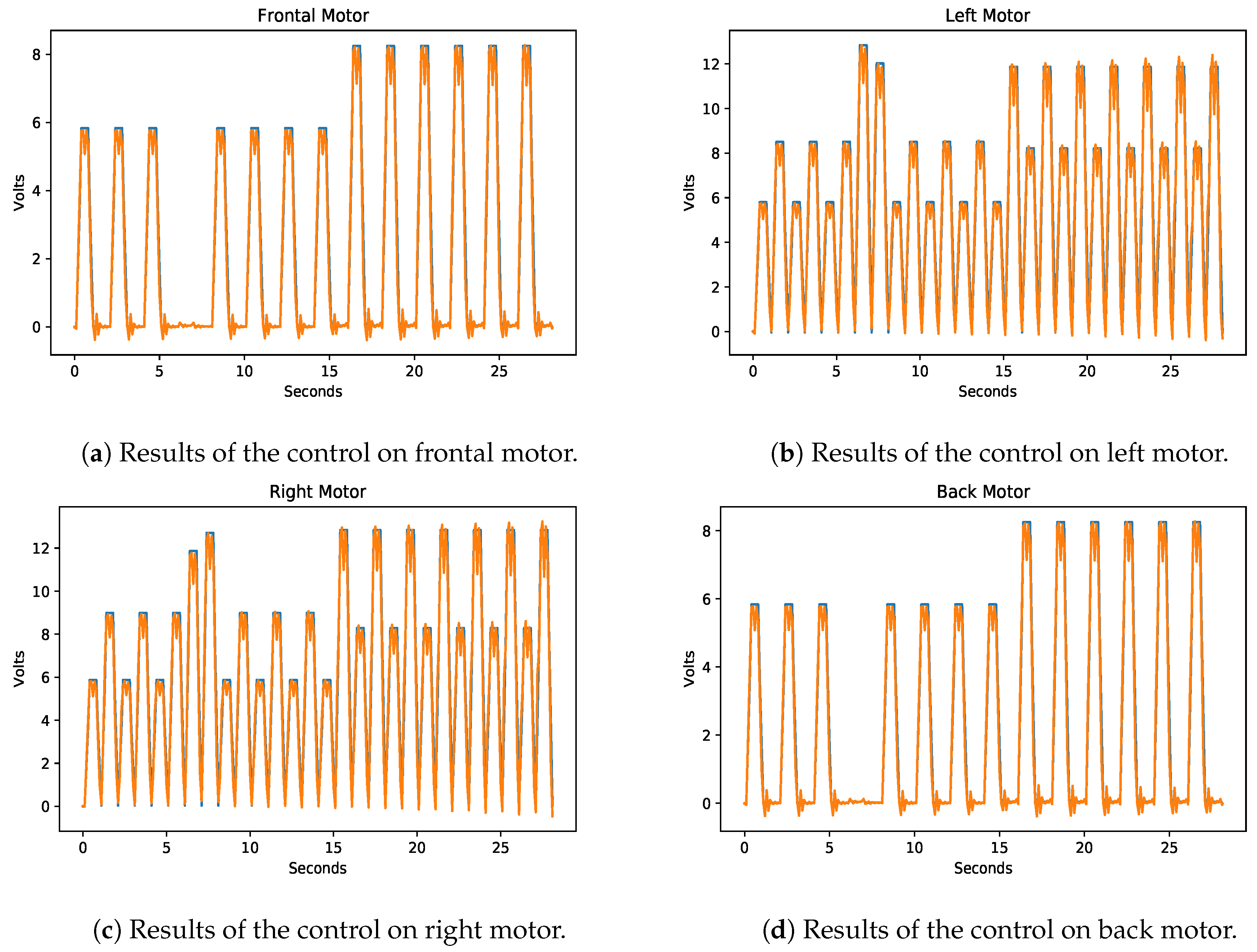
7. Results
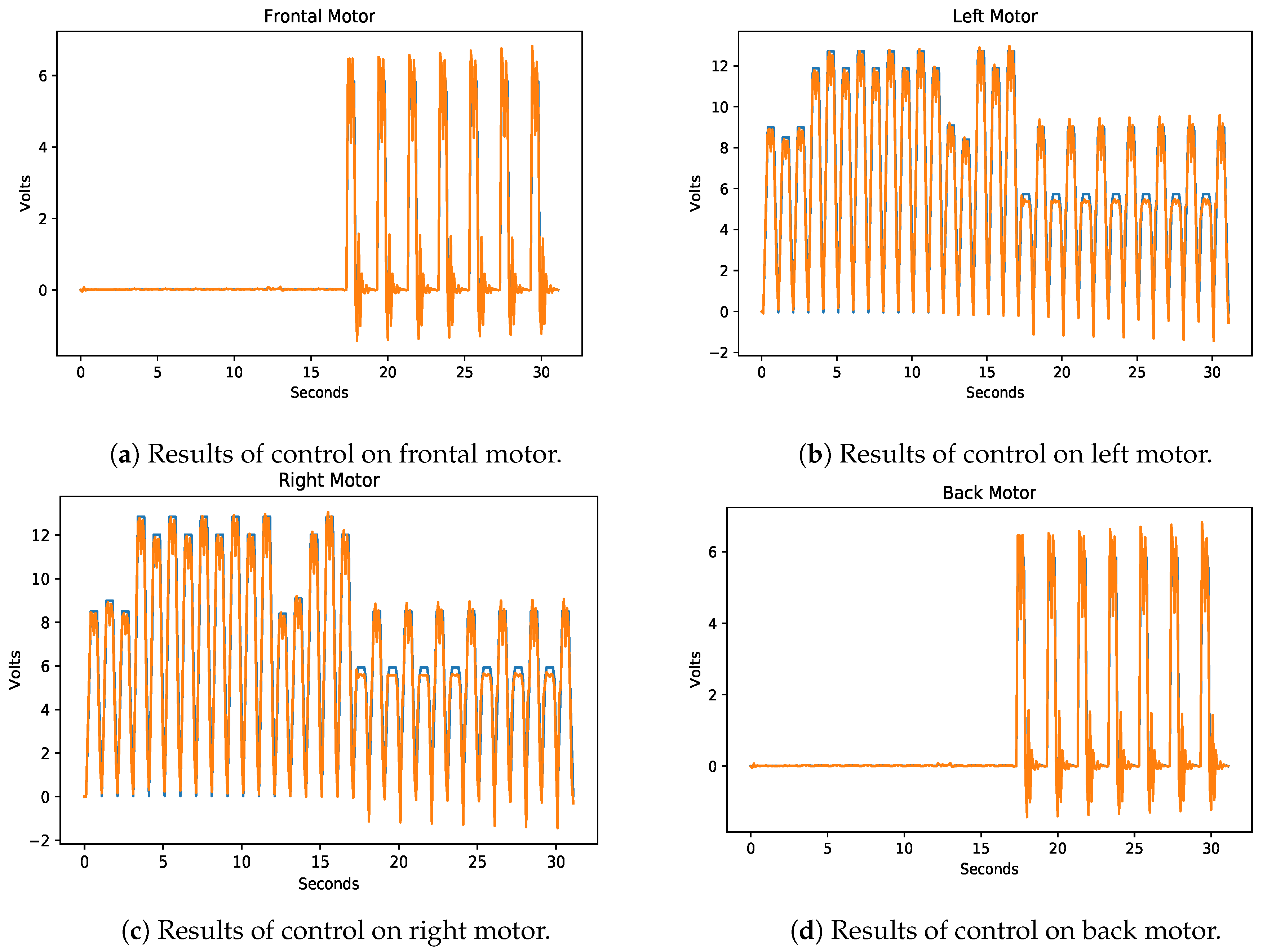
7.1. Experimental Results
7.2. Comparative Analysis
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RHONN | Recurrent High Order Neural Network |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| HJB | Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CED | Canny Edge Detector |
References
- Bravo-Muñoz, I.; Lázaro-Galilea, J.L.; Gardel-Vicente, A. FPGA and SoC Devices Applied to New Trends in Image/Video and Signal Processing Fields. Electronics 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Wu, N.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F. Compact Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for IoT Endpoint SoC. Electronics 2019, 8, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Yi, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, L. An All-Region State-of-Charge Estimator Based on Global Particle Swarm Optimization and Improved Extended Kalman Filter for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electronics 2018, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renteria-Cedano, J.; Rivera, J.; Sandoval-Ibarra, F.; Ortega-Cisneros, S.; Loo-Yau, R. SoC Design Based on a FPGA for a Configurable Neural Network Trained by Means of an EKF. Electronics 2019, 8, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, M.; Mathe, L.; Hammami, M.; Franco, F.L.; Rossi, C.; Teodorescu, R. AA Capacitor Voltage Balancing Approach Based on Mapping Strategy for MMC Applications. Electronics 2019, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.N.; Alanis, A.Y.; Loukianov, A.G. Discrete Time High Order Neural Control; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Roka, R. Advanced Path Planning for Mobile Entities, 1st ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Franco, C.; Hernandez-Barragan, J.; Alanis, A.Y.; Arana-Daniel, N. A soft computing approach for inverse kinematics of robot manipulators. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 74, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastire, E.A.; Sanchez, E.N.; Alanis, A.Y.; Ornelas-Tellez, F. Passivity analysis of discrete-time inverse optimal control for trajectory tracking. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 3192–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.D.; Alanis, A.Y.; Lopez-Franco, M.; Lopez-Franco, C.; Arana-Daniel, N. Real-time neural identification and inverse optimal control for a tracked robot. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.D.; Alanis, A.Y.; Arana-Daniel, N.; Lopez-Franco, C. Neural Identifier-Control Scheme for Nonlinear Discrete Systems with Input Delay. In Fuzzy Logic in Intelligent System Design; Melin, P., Castillo, O., Kacprzyk, J., Reformat, M., Melek, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, L.A.; Jurado, F.; Castañeda, C.E.; Alanis, A.Y. Real-Time Implementation of a Neural Integrator Backstepping Control via Recurrent Wavelet First Order Neural Network. Neural Process. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis, A.Y.; Sanchez, E.N. Discrete-Time Neural Observers: Analysis and Applications, 1st ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, J.D.; Alanis, A.Y.; Lopez-Franco, C.; Arana-Daniel, N. RHONN identifier-control scheme for nonlinear discrete-time systems with unknown time-delays. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 355, 218–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.N.; Ornelas-Tellez, F. Discrete-Time Inverse Optimal Control for Nonlinear Systems; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, D.E. Optimal Control Theory. An Introduction; Dover Publications, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tamimi, A.; Lewis, F.L.; Abu-Khalaf, M. Discrete-time nonlinear HJB solution using approximate dynamic programming: Convergence proof. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2008, 38, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Krstic, M.; Bekiaris-Liberis, N. Robust adaptive control: Legacies and horizons. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2012, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, O.; Fridman, L.; Chairez, I. Discrete time super-twisting observer for 2n dimensional systems. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Electrical Engineering Computing Science and Automatic Control 2011 (CCE), Merida City, Mexico, 26–28 October 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, E.N.; Ornelas-Tellez, F.; Loukianov, A.G. Discrete-time neural inverse optimal control for nonlinear systems via passivation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Franco, M.; Sanchez, E.N.; Alanis, A.Y.; Arana-Daniel, N. Real-time decentralized inverse optimal neural control for a Shrimp robot. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Dallas, TX, USA, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diriba, B.; Zhongmin, W. Design and Control for Differential Drive Mobile Robot. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. (IJERT) 2017, 6, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Kutz, M. Mechanical Engineers’ Handbook, Volume 2: Design, Instrumentation, and Controls; Wiley: Bethlehem, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Norgaard, M. Neural Networks for Modelling and Control of Dynamic Systems: A Practitioner’s Handbook; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, F.L.; Vrabie, D.L.; Syrmos, V.L. Optimal Control; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, R.; Hwang, P.Y.C. Introduction to Random Signals and Applied Kalman Filtering with Matlab Exercises; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alanis, A.Y.; Sanchez, E.N.; Loukianov, A.G. Discrete-time adaptive backstepping nonlinear control via high-order nerual networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2007, 18, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrau, A.; Bonnabel, S. The Invariant Extended Kalman Filter as a Stable Observer. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Tang, H.; Park, J. Energy Efficient Canny Edge Detector for Advanced Mobile Vision Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, S. Computer Vision with Python 3; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ertam, F.; Aydın, G. Data classification with deep learning using Tensorflow. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), Antalya, Turkey, 5–8 October 2017; pp. 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariff, N.; Buniyamin, N. An Overview of Autonomous Mobile Robot Path Planning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 4th Student Conference on Research and Development (2006), Selangor, Malaysia, 27–28 June 2006; pp. 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Cormen, T.H.; Leiserson, C.E.; Rivest, R.L.; Stein, C. Introduction to Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 595–601. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, A.; Ingram, D.; Dinius, J.; Chawla, K.; Raffin, A.; Paques, A. PythonRobotics: A Python Code Collection of Robotics Algorithms. 2018. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/1808.10703 (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Quintal, G.; Sanchez, E.N.; Alanis, A.Y.; Arana-Daniel, N.G. Real-time FPGA Decentralized Inverse Optimal Neural Control for a Shrimp Robot. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th System of Systems Engineering Conference (SoSE), San Antonio, TX, USA, 17–20 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arana-Daniel, N.; Alanis, A.Y.; Lopez-Franco, C. Artificial Neural Networks for Robotics an Engineering Perspective; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]

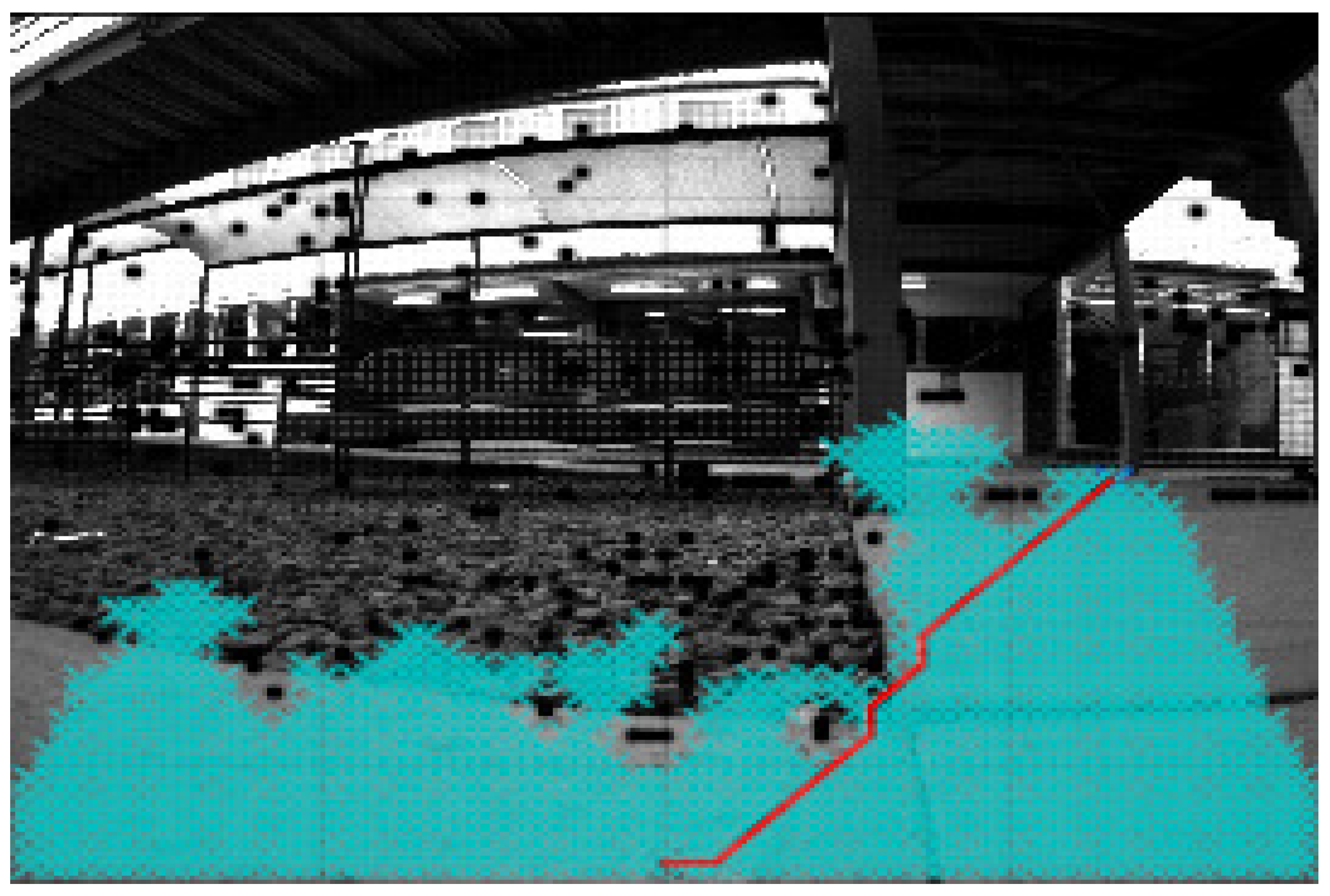
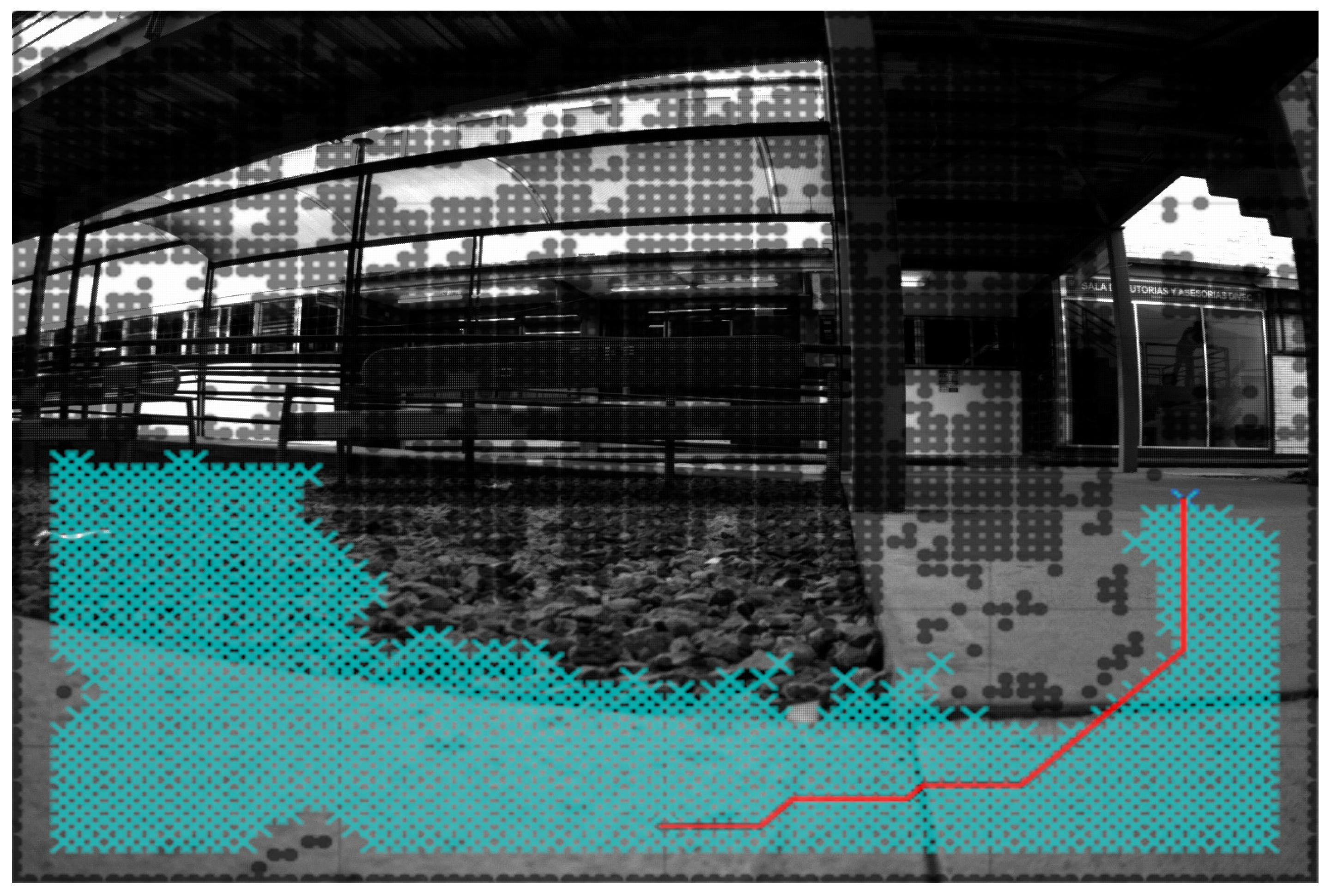

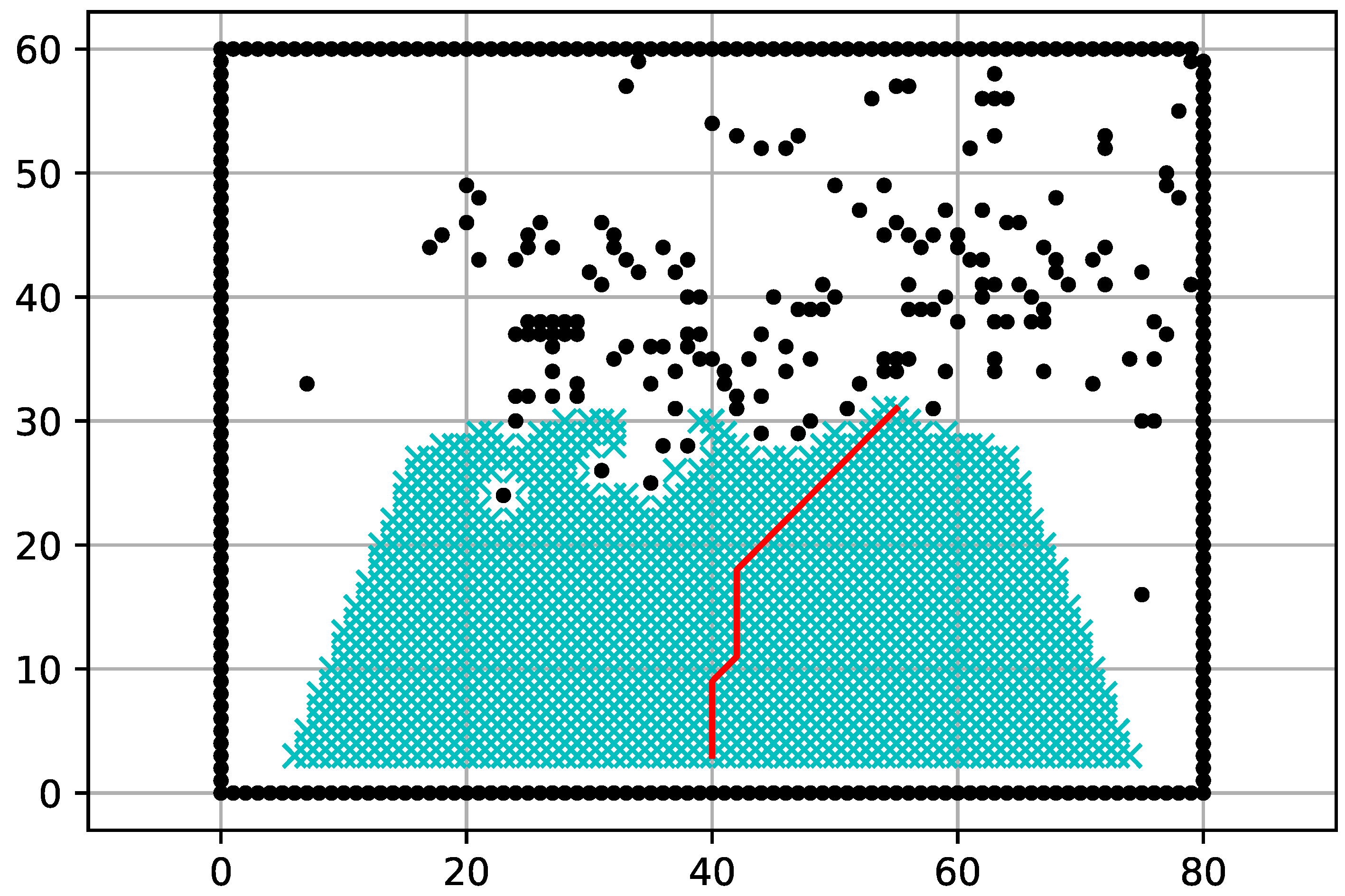
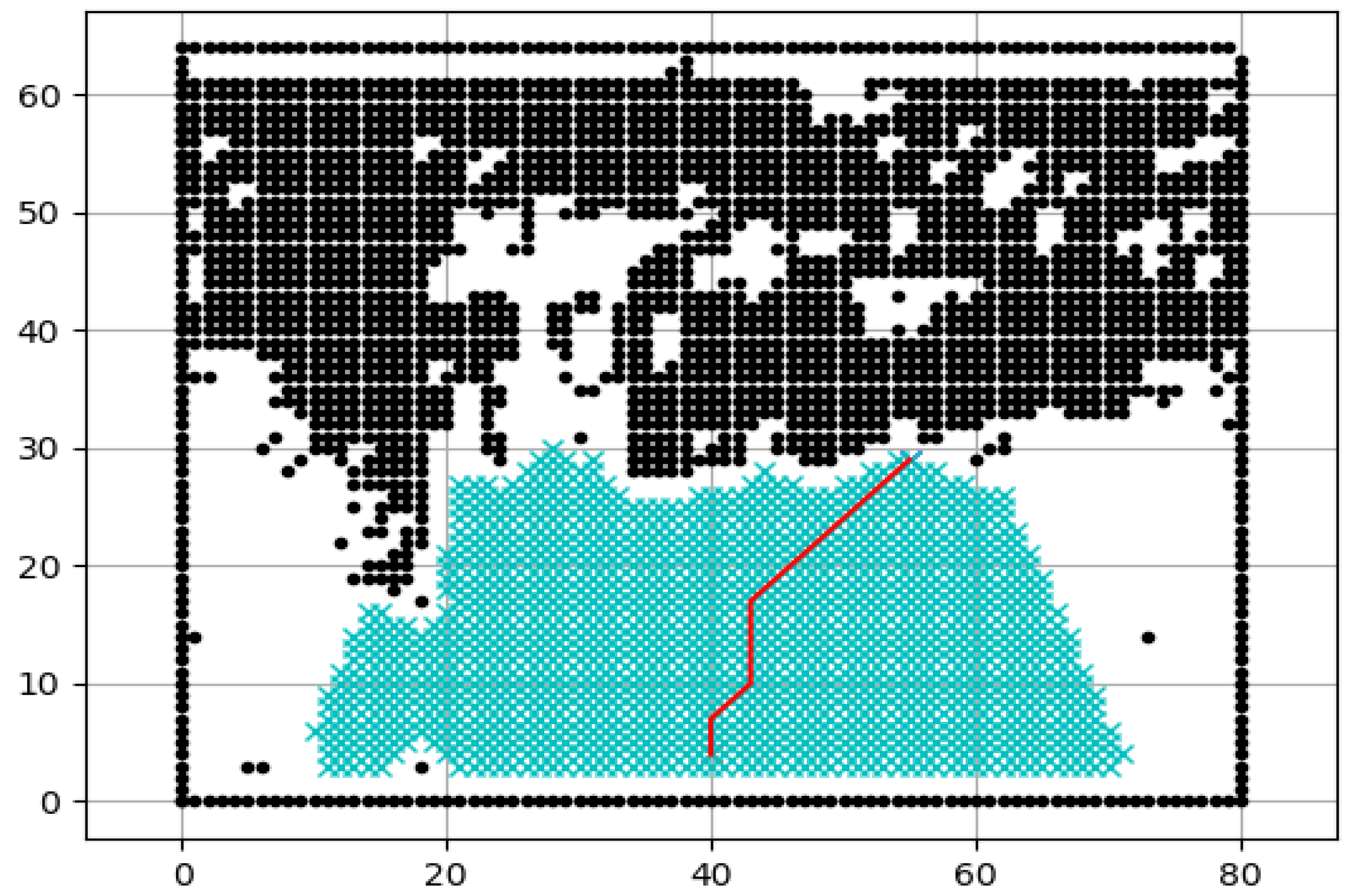
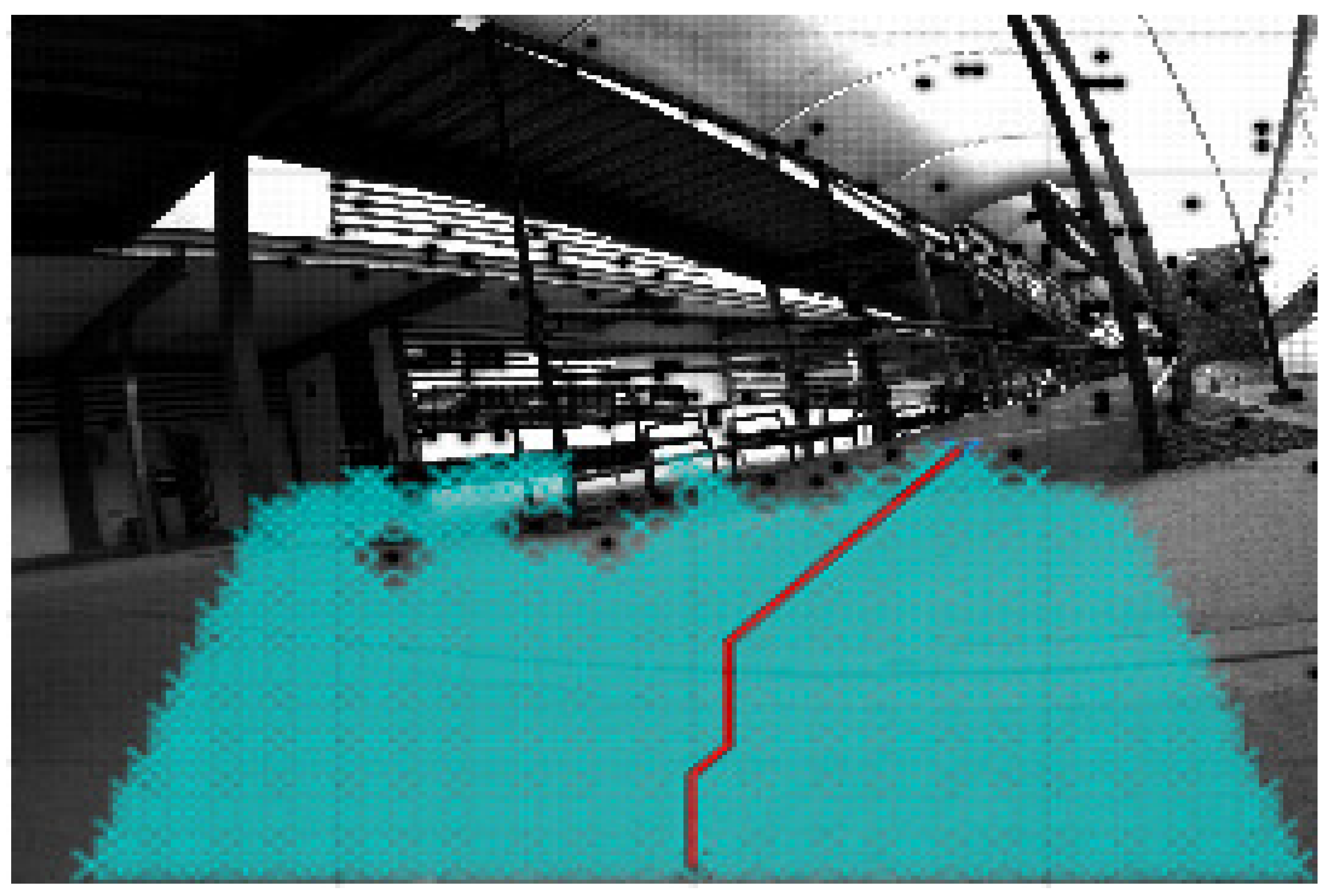
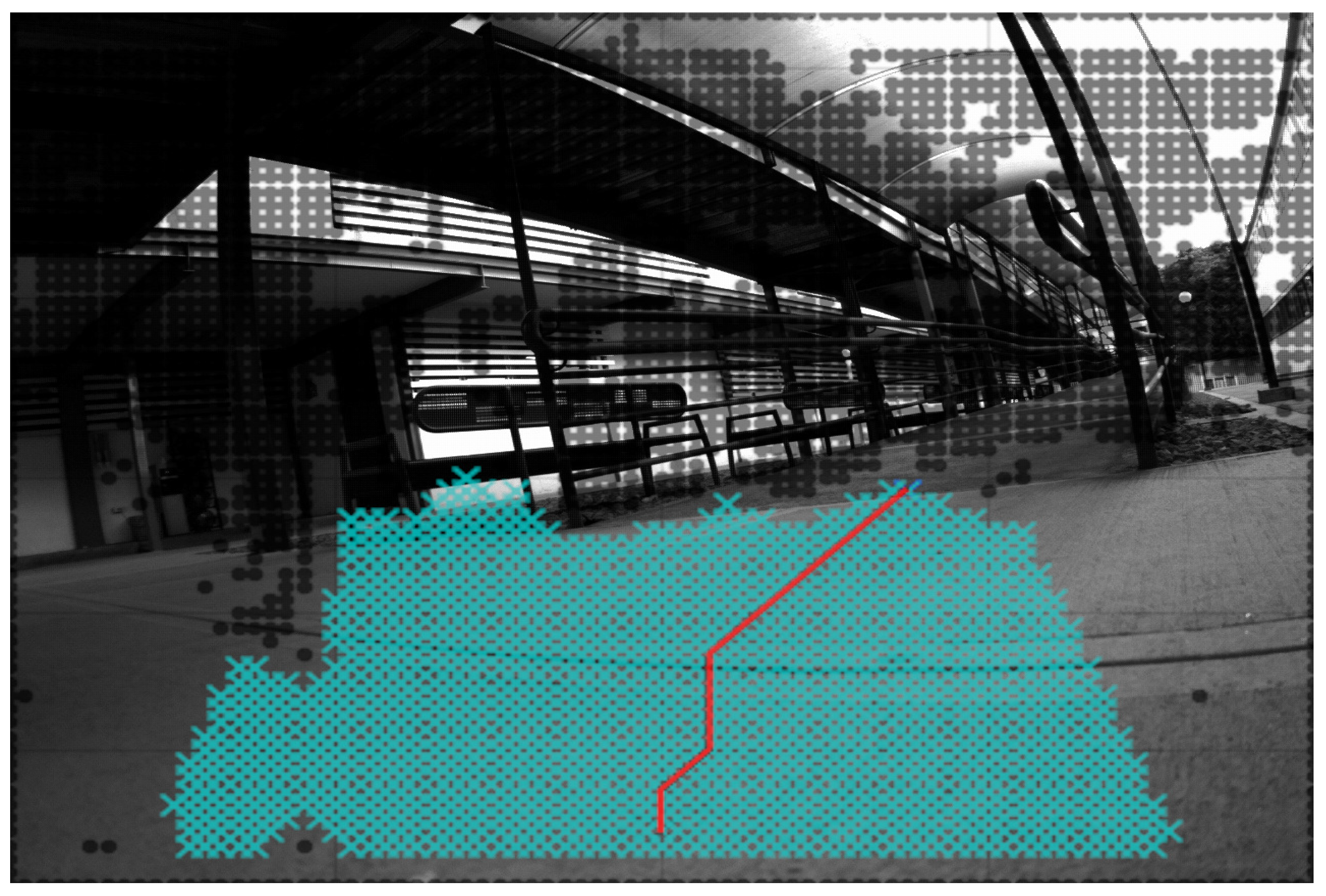
| Process Time | Dijkstra in PC | A* in PC | Dijkstra in SoC | A* in SoC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total time | 51.5293 s | 39.0263 s | 192.3780 s | 161.4557 s |
| Edge detector time | 0.6654 s | 0.5661 s | 7.2546 s | 7.3049 s |
| Map time | 0.0846 s | 0.0859 s | 1.0832 s | 1.0992 s |
| Route time | 15.5700 s | 3.9897 s | 60.1439 s | 28.9141 s |
| Control time | 0.0430 s | 0.0152 s | 0.3516 s | 0.3335 s |
| Time to start motion | 16.3631 s | 4.6571 s | 68.8334 s | 37.6519 s |
| Movement in route | 35.1661 s | 34.3692 s | 123.5445 s | 123.8038 s |
| Process Time | Dijkstra in PC | A* in PC | Dijkstra in SoC | A* in SoC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total time | 53.9585 s | 37.6130 s | 197.6433 s | 150.2245 s |
| Edge detector time | 0.6343 s | 0.6338 s | 6.8708 s | 7.2072 s |
| Map time | 0.0922 s | 0.1002 s | 1.0592 s | 1.0576 s |
| Route time | 21.3259 s | 5.0940 s | 76.0095 s | 29.4022 s |
| Control time | 0.0178 s | 0.0134 s | 0.3348 s | 0.3397 s |
| Time to start motion | 22.0704 s | 5.8416 s | 84.2744 s | 38.0069 s |
| Movement in route | 31.8881 s | 31.7714 s | 113.3688 s | 112.2176 s |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrios-dV, S.; Lopez-Franco, M.; Rios, J.D.; Arana-Daniel, N.; Lopez-Franco, C.; Alanis, A.Y. An Autonomous Path Controller in a System on Chip for Shrimp Robot. Electronics 2020, 9, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030441
Barrios-dV S, Lopez-Franco M, Rios JD, Arana-Daniel N, Lopez-Franco C, Alanis AY. An Autonomous Path Controller in a System on Chip for Shrimp Robot. Electronics. 2020; 9(3):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030441
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrios-dV, Sergio, Michel Lopez-Franco, Jorge D. Rios, Nancy Arana-Daniel, Carlos Lopez-Franco, and Alma Y. Alanis. 2020. "An Autonomous Path Controller in a System on Chip for Shrimp Robot" Electronics 9, no. 3: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030441
APA StyleBarrios-dV, S., Lopez-Franco, M., Rios, J. D., Arana-Daniel, N., Lopez-Franco, C., & Alanis, A. Y. (2020). An Autonomous Path Controller in a System on Chip for Shrimp Robot. Electronics, 9(3), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030441