Memristor-Controlled Reconfigurable N-path Filter Structure Design and Comparison
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Function and Model of Memristor
2.2. Functions of Basic N-path Filter
2.3. One-Memristor-Based N-path Filter
2.4. Multiple-Memristor-Based N-path Filter
3. Results
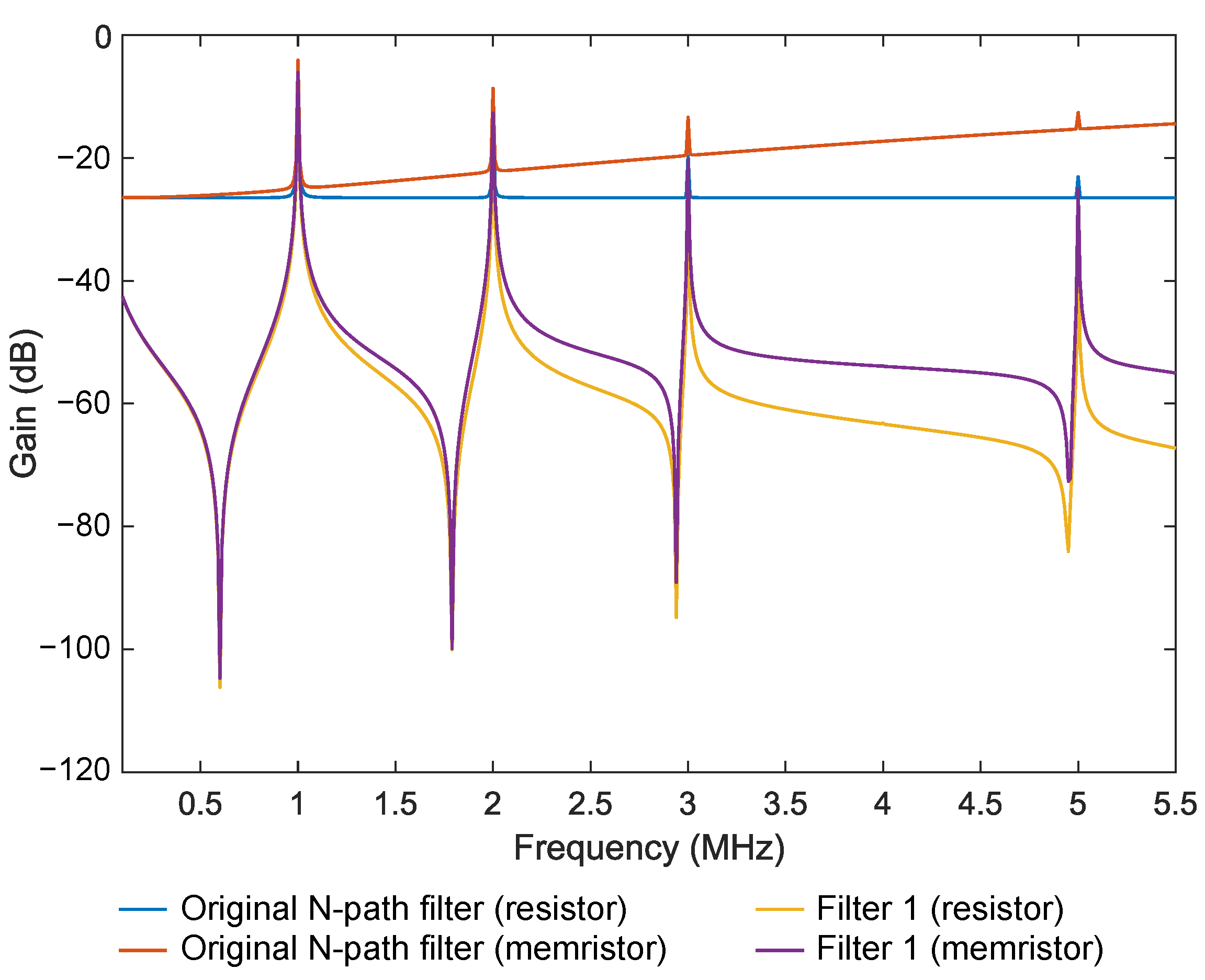
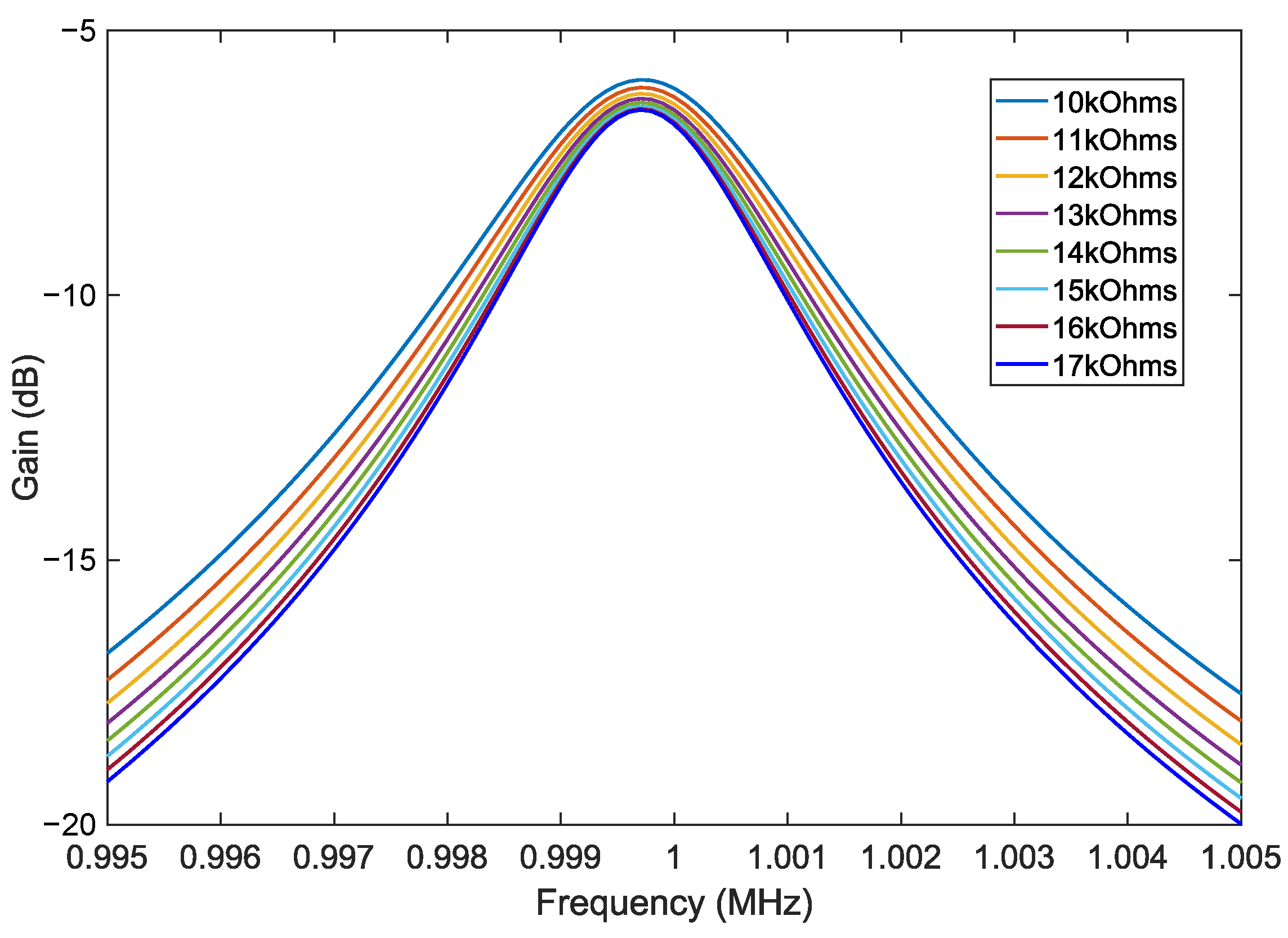
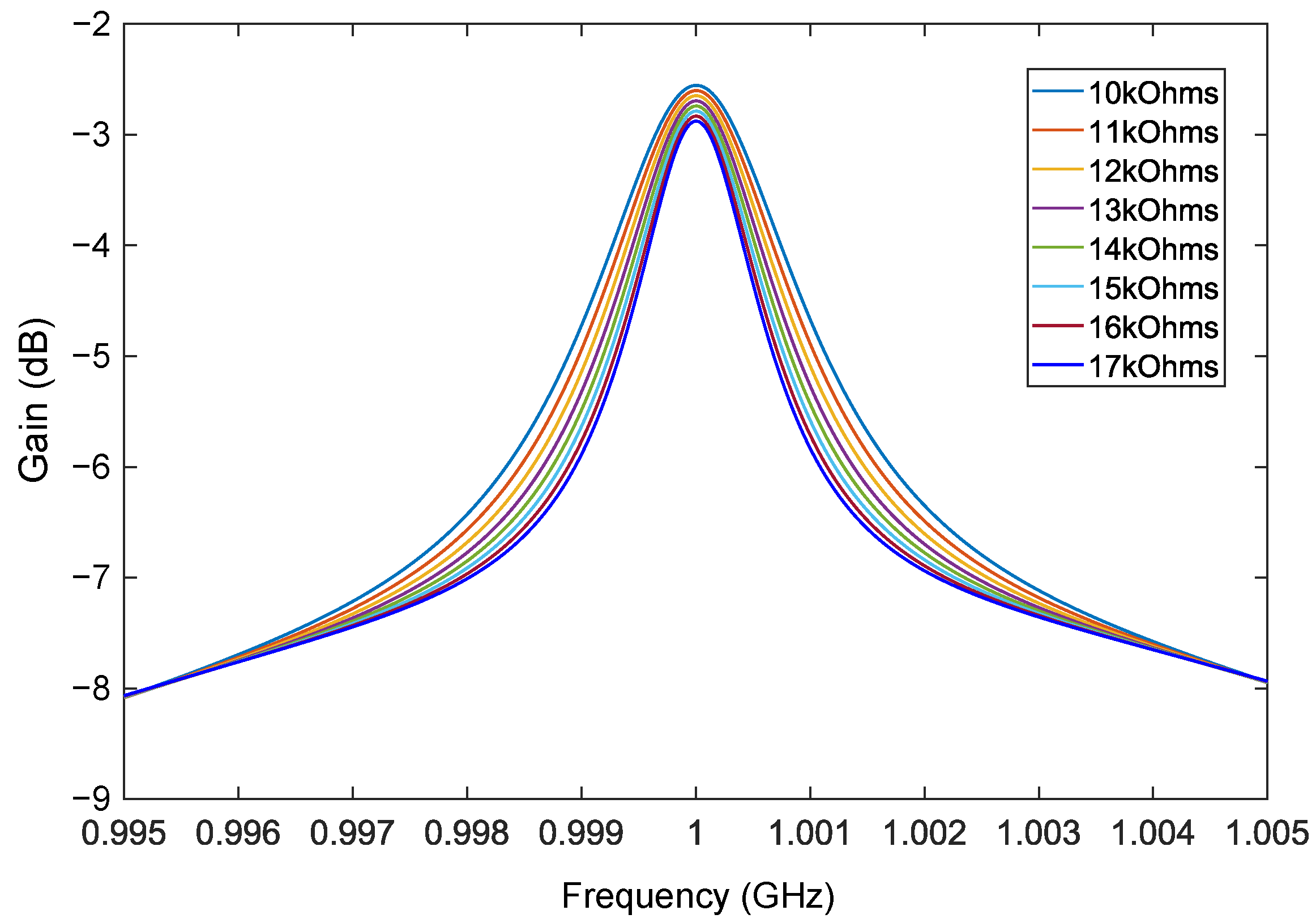
3.1. Simulation Results with 1 MHz Centre Frequency
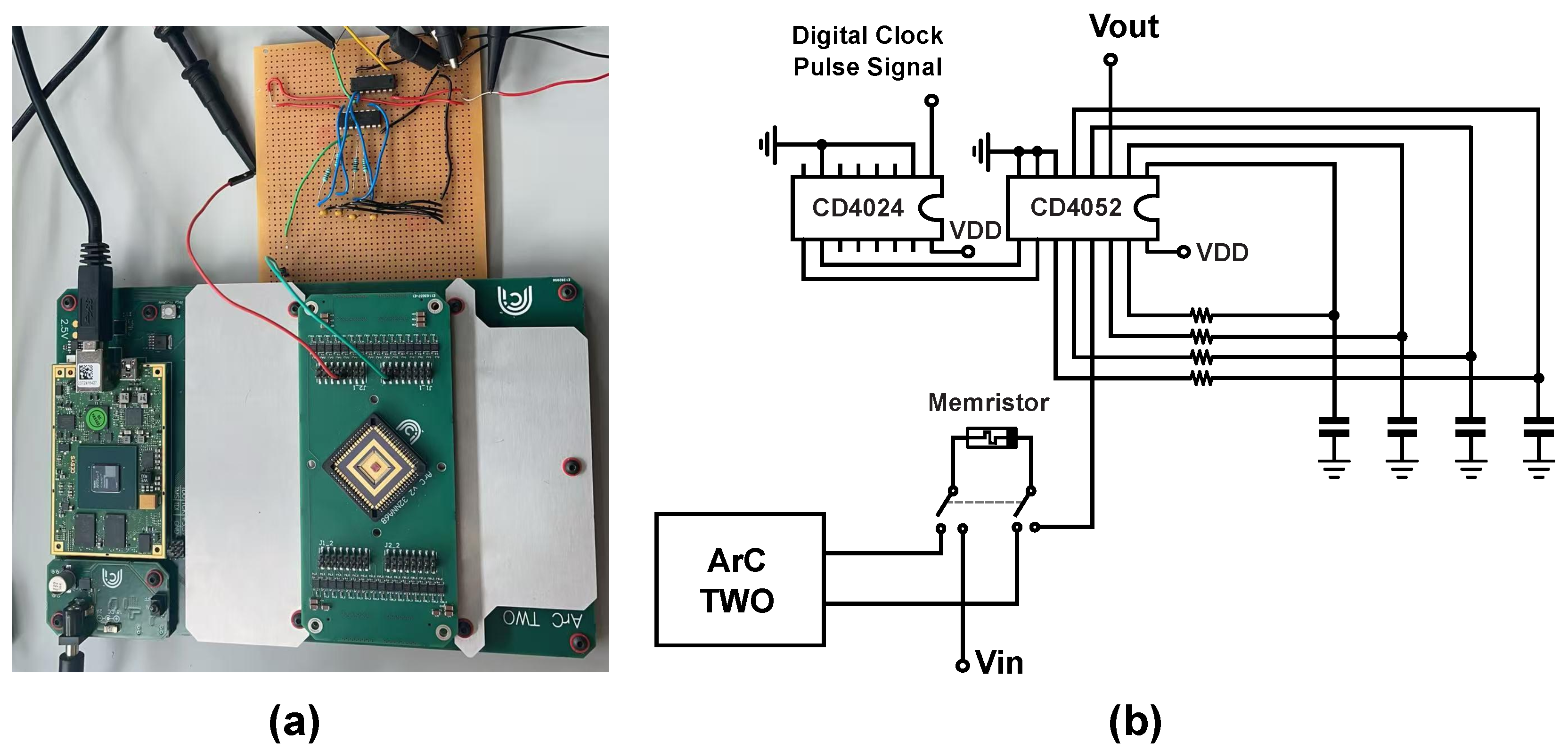
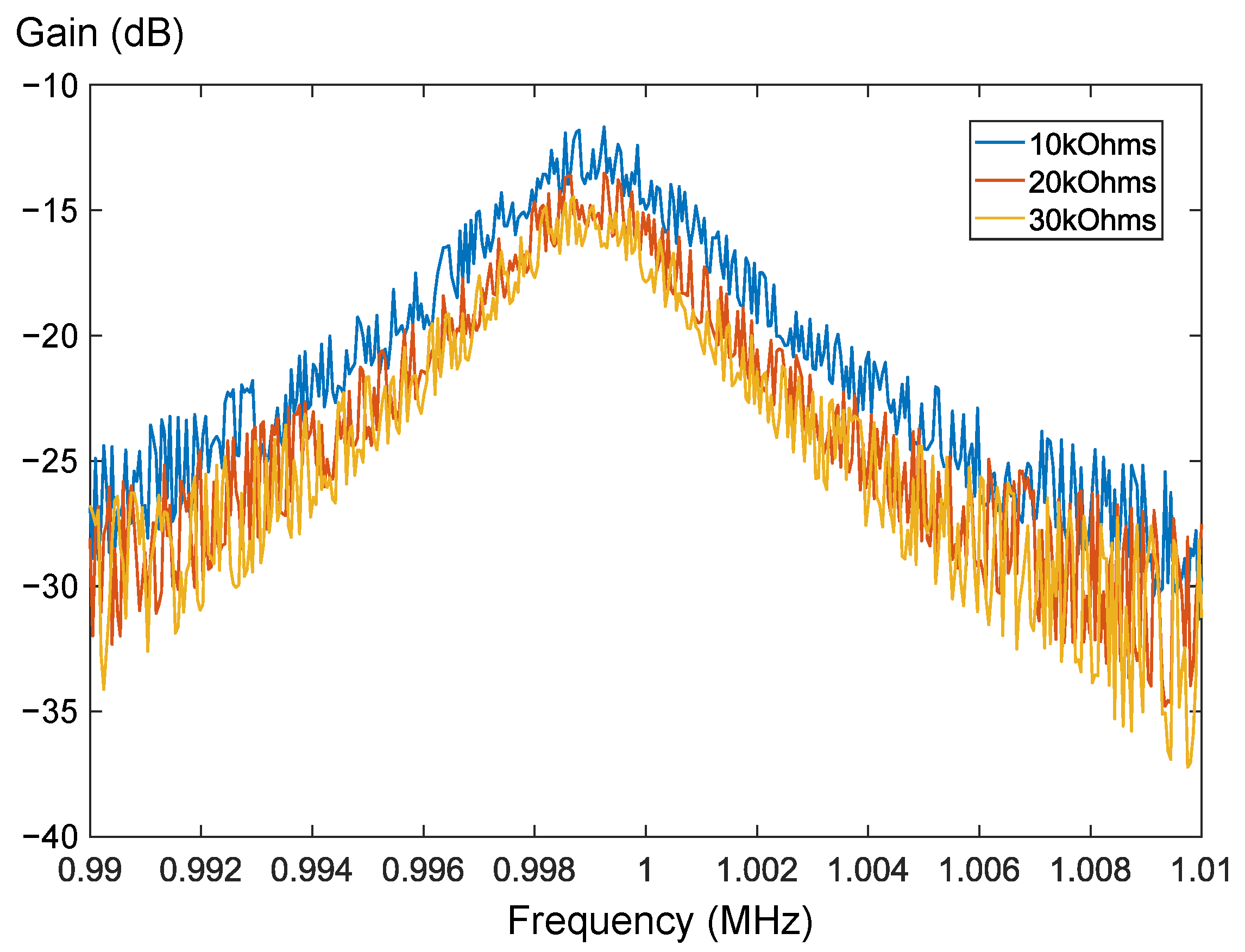
3.2. Measurement Results with Filter 1 Structure and 1 MHz Centre Frequency
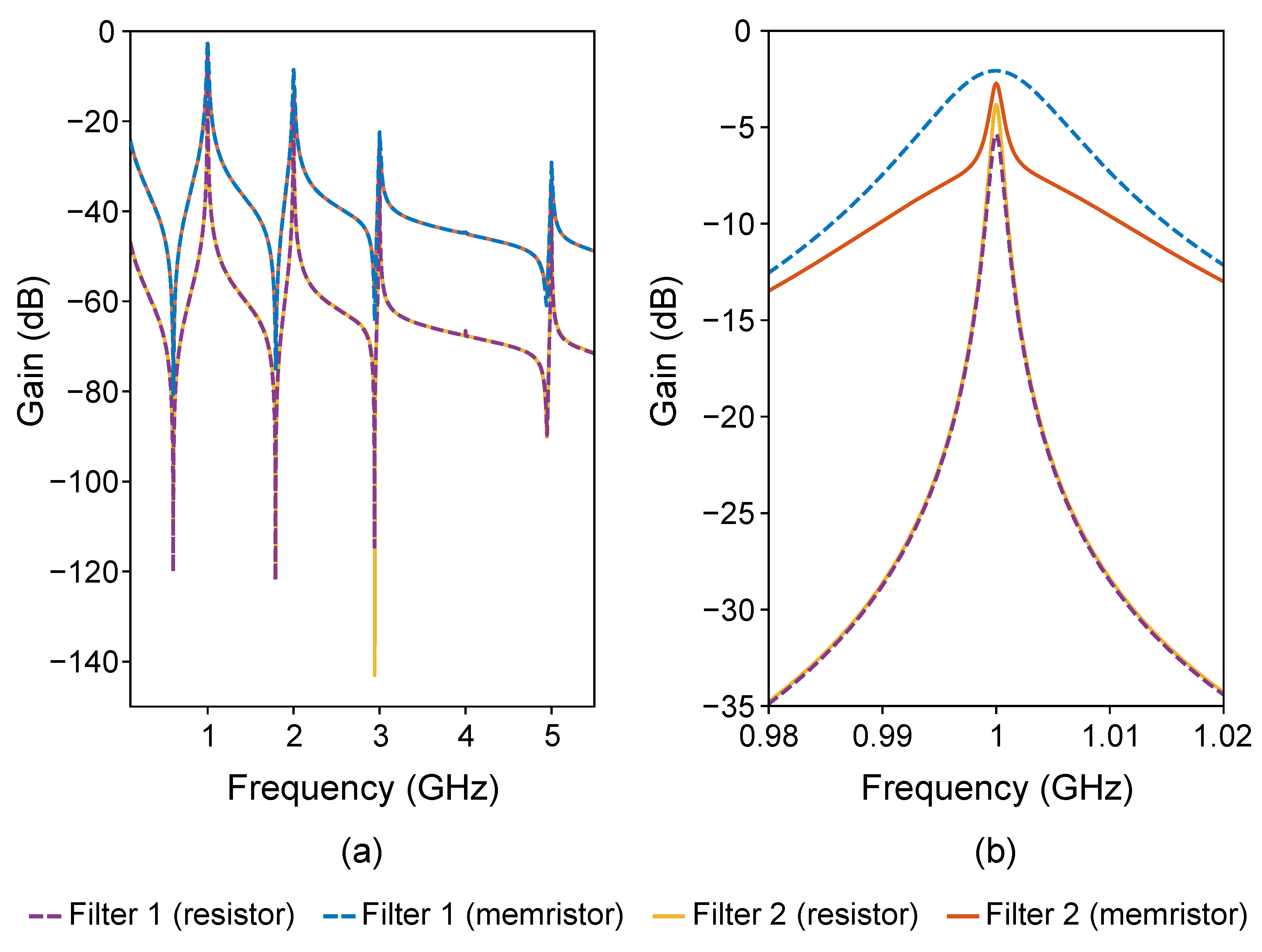
3.3. Simulation Results with Filter 2 Structure and 1 GHz Centre Frequency
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.Y.; Meher, P.K. Efficient FPGA and ASIC realizations of a DA-based reconfigurable FIR digital filter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.K.; Meher, P.K. A high-performance FIR filter architecture for fixed and reconfigurable applications. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2015, 24, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Kohno, K.; Fujita, H.; Hirakawa, K.; Toshiyoshi, H. MEMS reconfigurable metamaterial for terahertz switchable filter and modulator. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 21326–21339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, Y.K. RF-MEMS-based bandpass-to-bandstop switchable single-and dual-band filters with variable FBW and reconfigurable selectivity. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 3824–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, M.; Manekiya, M.; Tagliapietra, G.; Iannacci, J. A reconfigurable pseudohairpin filter based on MEMS switches. Sensors 2022, 22, 9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Ogami, T.; Horita, A.; Obiya, H.; Koshino, M.; Kawashima, M.; Nakajima, N. A new tunable SAW filter circuit for reconfigurable RF. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Galipeau, J.; Mouthaan, K.; Briot, E.H.; Abbott, B. Reconfigurable multiband SAW filters for LTE applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 20–23 January 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Hashemi, H. Passive coupled-switched-capacitor-resonator-based reconfigurable RF front-end filters and duplexers. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–24 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman, A. Filter capacitance reduction in DC/DC step-down reconfigurable switched-capacitor converters by a balanced switching. In Proceedings of the 2012 13th International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Brasov, Romania, 24–26 May 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 776–782. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, L.E.; Sandberg, I.W. An alternative approach to the realization of network transfer functions: The N-path filter. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1960, 39, 1321–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumperink, E.; Nauta, B.N. Path Filters and Mixer-First Receivers—A Review. IC Des. Insights-Sel. Present. CICC 2022, 2017, 221–264. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Gudem, P.S.; Buckwalter, J.F. A 0.2–3.6-GHz 10-dBm B1dB 29-dBm IIP3 tunable filter for transmit leakage suppression in SAW-less 3G/4G FDD receivers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschytz, G.S. Inductorless filters: A survey II. Linear active and digital filters. IEEE Spectr. 1970, 7, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P.; Lin, Z.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P. Analysis and modeling of a gain-boosted N-path switched-capacitor bandpass filter. In Ultra-Low-Power and Ultra-Low-Cost Short-Range Wireless Receivers in Nanoscale CMOS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 57–80. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Kinget, P.R. A switched-capacitor RF front end with embedded programmable high-order filtering. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 1154–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Niknejad, A.M. Design and analysis of enhanced mixer-first receivers achieving 40-dB/decade RF selectivity. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 55, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner-Stewart, J.; Wilson, C.; Floyd, B.A. Tunable 0.7–2.8-GHz reflection-mode N-path filters in 45-nm SOI CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020, 68, 2343–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.C.; Klumperink, E.A.; Tenbroek, B.; Strange, J.; Nauta, B. Enhanced-selectivity high-linearity low-noise mixer-first receiver with complex pole pair due to capacitive positive feedback. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Gudem, P.S.; Buckwalter, J.F. A 0.4–6-GHz 17-dBm B1dB 36-dBm IIP3 channel-selecting low-noise amplifier for SAW-less 3G/4G FDD diversity receivers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, A.; He, C.; Katehi, L.P.; Williams, R.S.; Palermo, S. Design of tunable analog filters using memristive crossbars. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–28 May 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Korkmaz, A.; Palermo, S.; Williams, R.S.; Katehi, L.P. Analog Signal Processing in High Frequency Circuits Using Crossbar Configurations. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Antennas, Communications and Electronic Systems (COMCAS), Tel Aviv, Israel, 1–3 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Waser, R.; Aono, M. Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sah, M.P.; Yang, C.; Chua, L.O. Memristor-based multilevel memory. In Proceedings of the 2010 12th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and their Applications (CNNA 2010), Berkeley, CA, USA, 3–5 February 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Borghetti, J.; Snider, G.S.; Kuekes, P.J.; Yang, J.J.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. ‘Memristive’switches enable ‘stateful’logic operations via material implication. Nature 2010, 464, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Salaoru, I.; Khiat, A.; Xu, H.; Prodromakis, T. Correlated resistive/capacitive state variability in solid TiO2 based memory devices. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapatseli, M.; Cortese, S.; Serb, A.; Khiat, A.; Prodromakis, T. Impact of ultra-thin Al2O3−y layers on TiO2−x ReRAM switching characteristics. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 184505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, S.; Khiat, A.; Trapatseli, M.; Cortese, S.; Serb, A.; Valov, I.; Prodromakis, T. Multibit memory operation of metal-oxide bi-layer memristors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, S.; Li, C.; Jiang, H.; Xia, W.; Xin, H.; Yang, J.J.; Xia, Q. Memristor crossbar arrays with 6-nm half-pitch and 2-nm critical dimension. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, M.D.; Williams, R.S. Sub-100 fJ and sub-nanosecond thermally driven threshold switching in niobium oxide crosspoint nanodevices. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 215202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Si, Z.; Jiang, X.; Malik, A.; Pan, Y.; Stathopoulos, S.; Serb, A.; Wang, S.; Prodromakis, T.; Papavassiliou, C. Multi-state memristors and their applications: An overview. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2022, 12, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, S.; Stathopoulos, S.; Wang, J.; Serb, A.; Pan, Y.; Mifsud, A.; Leene, L.B.; Shen, J.; Papavassiliou, C.; Constandinou, T.G.; et al. Design flow for hybrid CMOS/memristor systems—Part I: Modeling and verification steps. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 4862–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouras, V.; Stathopoulos, S.; Garlapati, S.K.; Serb, A.; Prodromakis, T. Frequency response of metal-oxide memristors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 3636–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Klumperink, E.A.; Soer, M.C.; Nauta, B. Tunable high-Q N-path band-pass filters: Modeling and verification. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.D. Analysis of commutated networks. Trans. IRE Prof. Group Aeronaut. Navig. Electron. 1953, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LePage, W.R.; Cahn, C.R.; Brown, J.S. Analysis of a comb filter using synchronously commutated capacitors. In Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, Part I: Communication and Electronics; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1953; Volume 72, pp. 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Fischl, R. Analysis of a commutated network. In IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Navigational Electronics; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1963; pp. 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Messaris, I.; Serb, A.; Stathopoulos, S.; Khiat, A.; Nikolaidis, S.; Prodromakis, T. A data-driven verilog-a reram model. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdan, R.; Serb, A.; Khiat, A.; Regoutz, A.; Papavassiliou, C.; Prodromakis, T. A μ-controller-based system for interfacing selectorless RRAM crossbar arrays. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serb, A.; Khiat, A.; Prodromakis, T. An RRAM biasing parameter optimizer. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 3685–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, S.; Ghadiri-Sadrabadi, M.; Bardin, J.C.; Xia, Q. Nanoscale memristive radiofrequency switches. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotbi, I.; Behmanesh, B.; Törmänen, M. A reconfigurable RF filter with 1%–40% fractional bandwidth for 5G FR1 receivers. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 2023, 6, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Hameed, S.; Pamarti, S. Periodically time-varying noise cancellation for filtering-by-aliasing receiver front ends. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 56, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Pamarti, S. A dual-channel high-linearity filtering-by-aliasing receiver front-end supporting carrier aggregation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 57, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Ren, M.; Jiang, X. A Tunable Integrated N-Path Bandpass Filter. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2024, 29, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Qian, C. Design of the Reconfigurable N-path Filter. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT), Harbin, China, 12–15 August 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
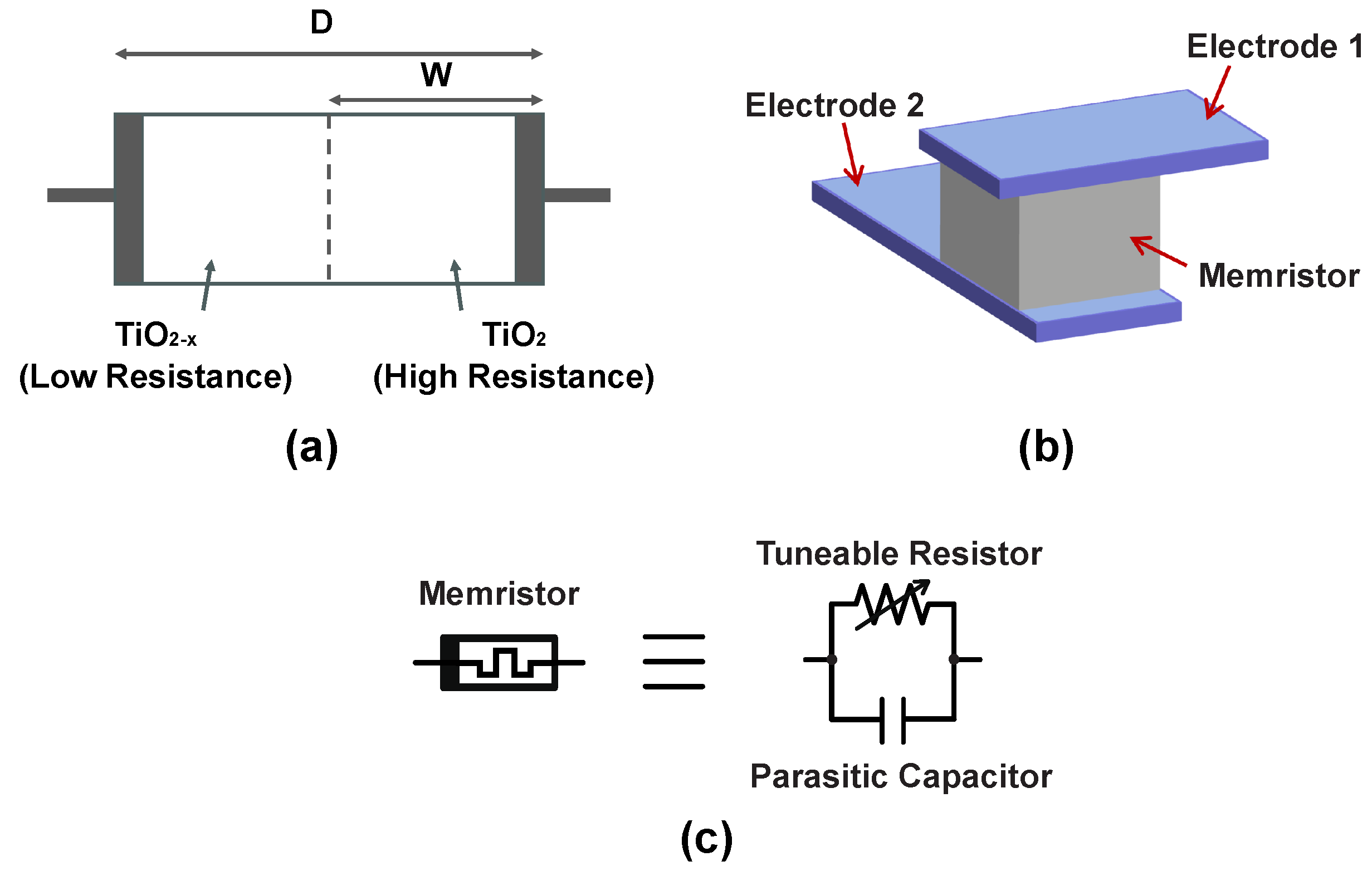
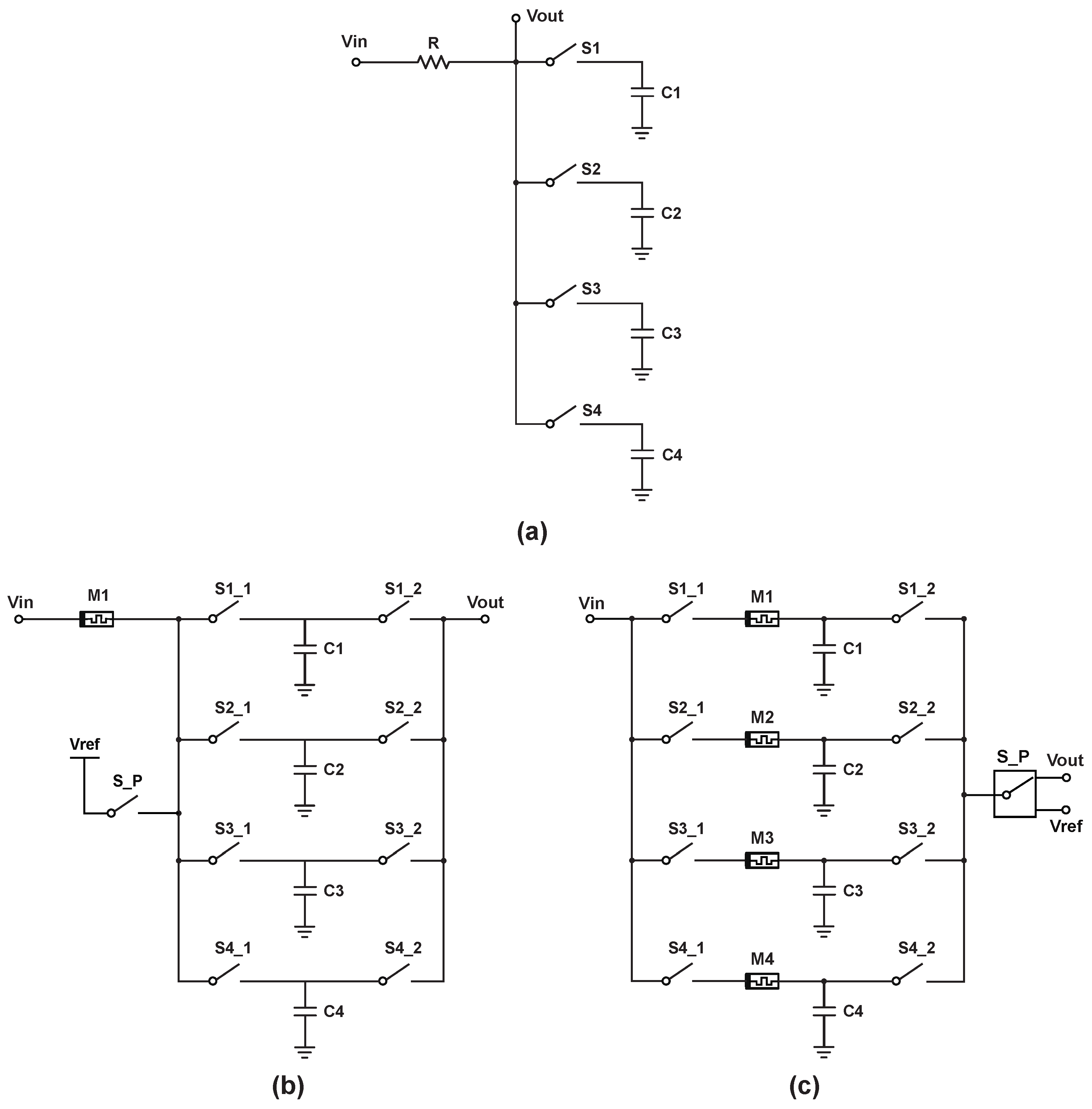

| Normal Operation | Programming Mode 1 | Programming Mode 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5V DC + signal | 2.5V pulse | 0V | |
| 0V | 0V | 2.5V pulse | |
| S_P | OFF | ON | ON |
| S1 to S4 | ON in sequence | OFF | OFF |
| Memristor () | with Resistor (Hz) | Actual (Hz) | Q Factor | with Q = 1 k (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 k | 1105 | 1191 | 839 | 1.19 M |
| 11 k | 1053 | 1140 | 877 | 1.14 M |
| 12 k | 1007 | 1095 | 913 | 1.1 M |
| 13 k | 964 | 1059 | 944 | 1.06 M |
| 14 k | 935 | 1027 | 973 | 1.03 M |
| 15 k | 906 | 1000 | 1000 | 1 M |
| 16 k | 880 | 975 | 1025 | 975 k |
| 17 k | 857 | 954 | 1048 | 954 k |
| Memristor () | 10 k | 11 K | 12 k | 13 k | 14 k | 15 k | 16 k | 17 k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min step (Hz) | 6.7 | 5 | 5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 3.4 | 4 | 3 |
| Memristor () | (Hz) | Q Factor | with Q = 600 (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 k | 2 k | 500 | 1.2 M |
| 15 k | 1.8 k | 556 | 1 M |
| 20 k | 1.6 k | 625 | 0.96 M |
| 30 k | 1.5 k | 667 | 0.9 M |
| Memristor () | with Resistor (Hz) | Actual (Hz) | Q Factor | with Q = 1 k (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 k | 590 k | 1380 k | 725 | 1.38 G |
| 11 k | 543 k | 1310 k | 763 | 1.31 G |
| 12 k | 510 k | 1230 k | 813 | 1.23 G |
| 13 k | 480 k | 1170 k | 855 | 1.17 G |
| 14 k | 456 k | 1120 k | 893 | 1.12 G |
| 15 k | 436 k | 1070 k | 935 | 1.07 G |
| 16 k | 413 k | 1030 k | 971 | 1.03 G |
| 17 k | 395 k | 990 k | 1010 | 0.99 G |
| Memristor () | 10 k | 11 K | 12 k | 13 k | 14 k | 15 k | 16 k | 17 k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min step (Hz) | 7k | 6.5k | 8.4k | 5.6k | 5k | 4k | 3k | 3.7k |
| (F) | Memristor () | Filter 1 (Hz) | Filter 2 (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 f | 10 k | 10.16 M | 3.01 M |
| 17 k | 10.13 M | 1.98 M | |
| 100 f | 10 k | 3.24 M | 2.91 M |
| 17 k | 3.1 M | 1.97 M | |
| 50 f | 10 k | 2.1 M | 2.33 M |
| 17 k | 1.9 M | 1.88 M | |
| 10 f | 10 k | 1.2 M | 1.59 M |
| 17 k | 946 k | 1.22 M | |
| 0 | 10 k | 1.11 M | 1.25 M |
| 17 k | 865 k | 800 k |
| Ref. | Tech. | Frequency [Hz] | Bandwidth [Hz] | Gain [dB] | NF [dB] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [43] | 22 nm | 1.7∼6.4 G | 50∼120 0M | 18∼32 | 4.6∼7.4 |
| [44] | 28 nm | 0.1∼1 G | 2.5∼40 M | 30 | 4.1∼5.8 |
| [45] | 28 nm | 0.1∼1 G | 5∼20 M | 7.8∼10 | 10.5∼14.1 |
| [46] | 65 nm | 50∼100 M | 1.5∼45 M | 15 | / |
| [47] | 55 nm | 0.1∼1 G | 75∼119 M | / | / |
| Filter 1 (simulation) | 180 nm | 1 M | 0.95∼1.2 k | −7∼−6 | 2.1 |
| Filter 2 (simulation) | 180 nm | 1 G | 0.99∼1.4 M | −3∼−2.5 | 3.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Serb, A.; Prodromakis, T. Memristor-Controlled Reconfigurable N-path Filter Structure Design and Comparison. Electronics 2025, 14, 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091858
Yang F, Wang S, Serb A, Prodromakis T. Memristor-Controlled Reconfigurable N-path Filter Structure Design and Comparison. Electronics. 2025; 14(9):1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091858
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fan, Shiwei Wang, Alex Serb, and Themis Prodromakis. 2025. "Memristor-Controlled Reconfigurable N-path Filter Structure Design and Comparison" Electronics 14, no. 9: 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091858
APA StyleYang, F., Wang, S., Serb, A., & Prodromakis, T. (2025). Memristor-Controlled Reconfigurable N-path Filter Structure Design and Comparison. Electronics, 14(9), 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091858









