Overview of Hydrogels and the Use of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels in Pharmaceutical Transdermal Delivery Systems and Topical Cosmetic Skin Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Skin Physiology
1.1.1. Dermatological Conditions and Skin Diseases
1.1.2. Role of Skin Hydration and Cosmetic Formulations Used for Skin Hydration
2. Overview of Hydrogels
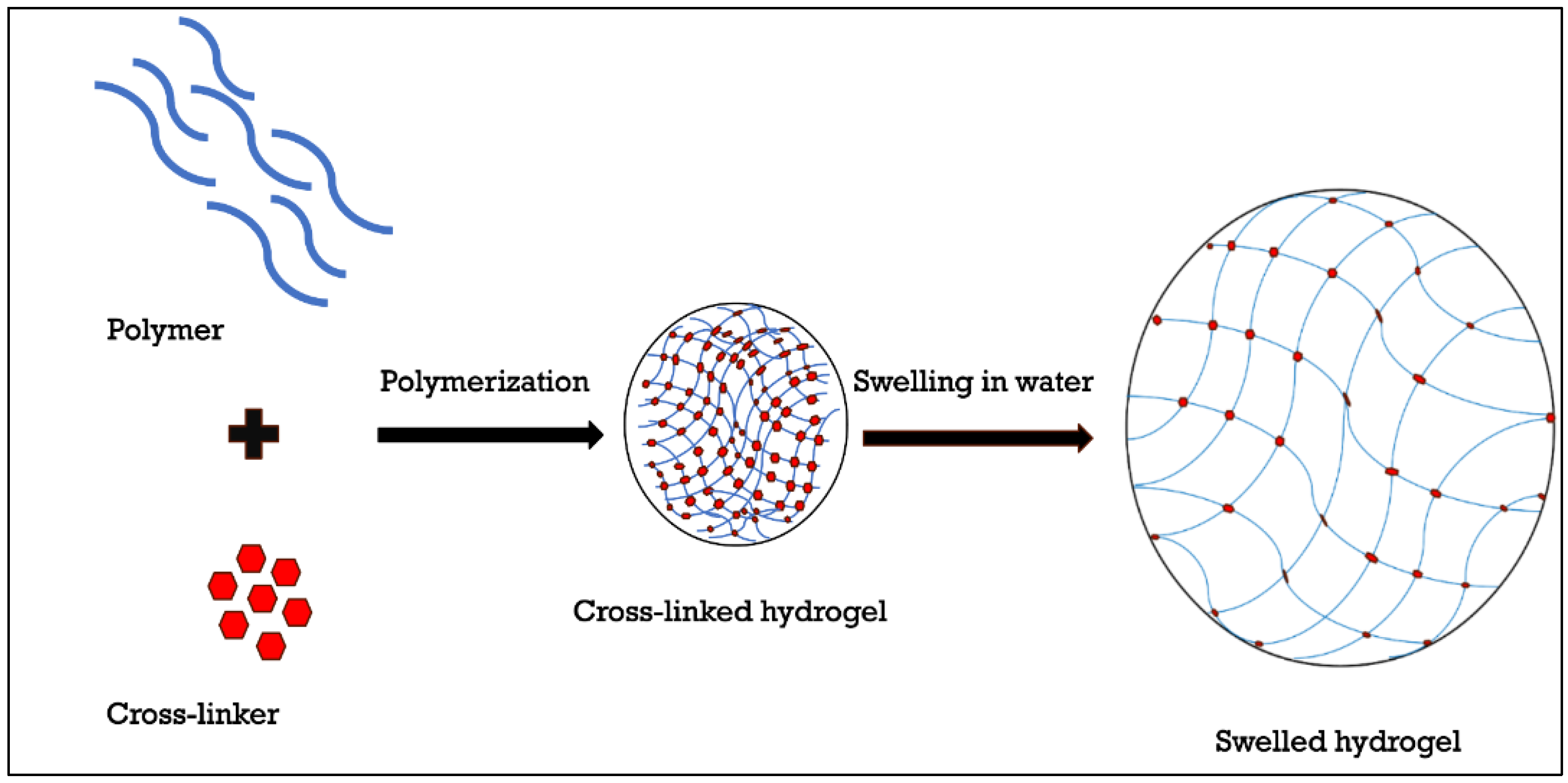
2.1. Introduction to Hydrogels
2.2. Classifications of Hydrogels
2.3. Rheological Properties of Hydrogels
2.4. Characterisation of the Physical and Chemical Properties of the Hydrogels
3. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels: Properties and Preparation
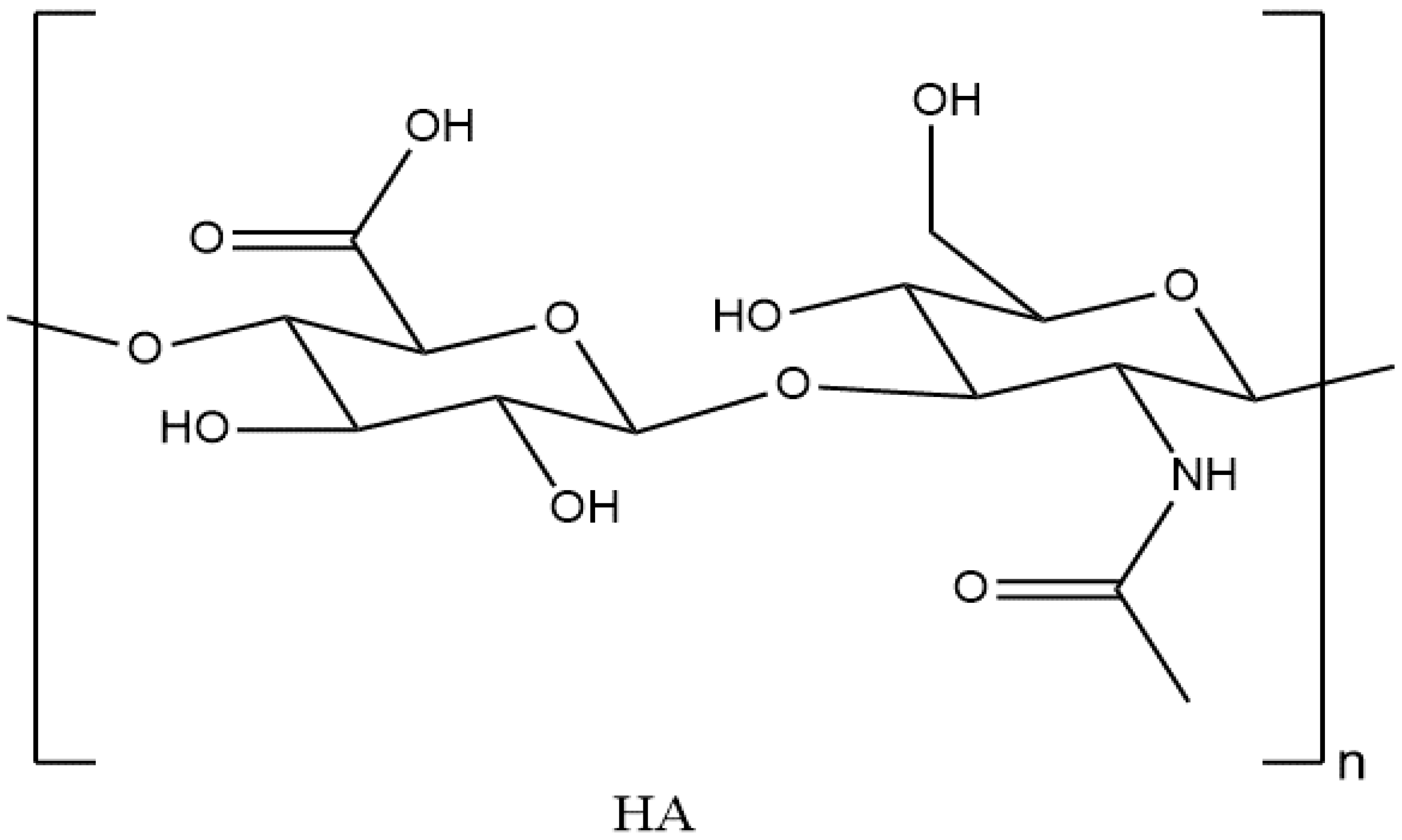
3.1. Introduction to Hyaluronic Acid
3.2. Classification of HA
3.3. Physical and Chemical Properties of HA
3.4. Preparation of HA-Based Hydrogels
3.4.1. Effect of Temperature on Preparation and Gelation Mechanism of HA-Based Hydrogel
3.4.2. Effect of pH on Preparation and Gelation Mechanism of HA-Based Hydrogel
3.4.3. Effect of HA Molecular Weight on Preparation and Gelation Mechanism of HA-Based Hydrogel
3.5. Preparation of HA-Based Hydrogels Using Cross-Linking Agents
4. Hydrogels Applications in Pharmaceutical Transdermal Delivery Systems
4.1. Uses of HA in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications
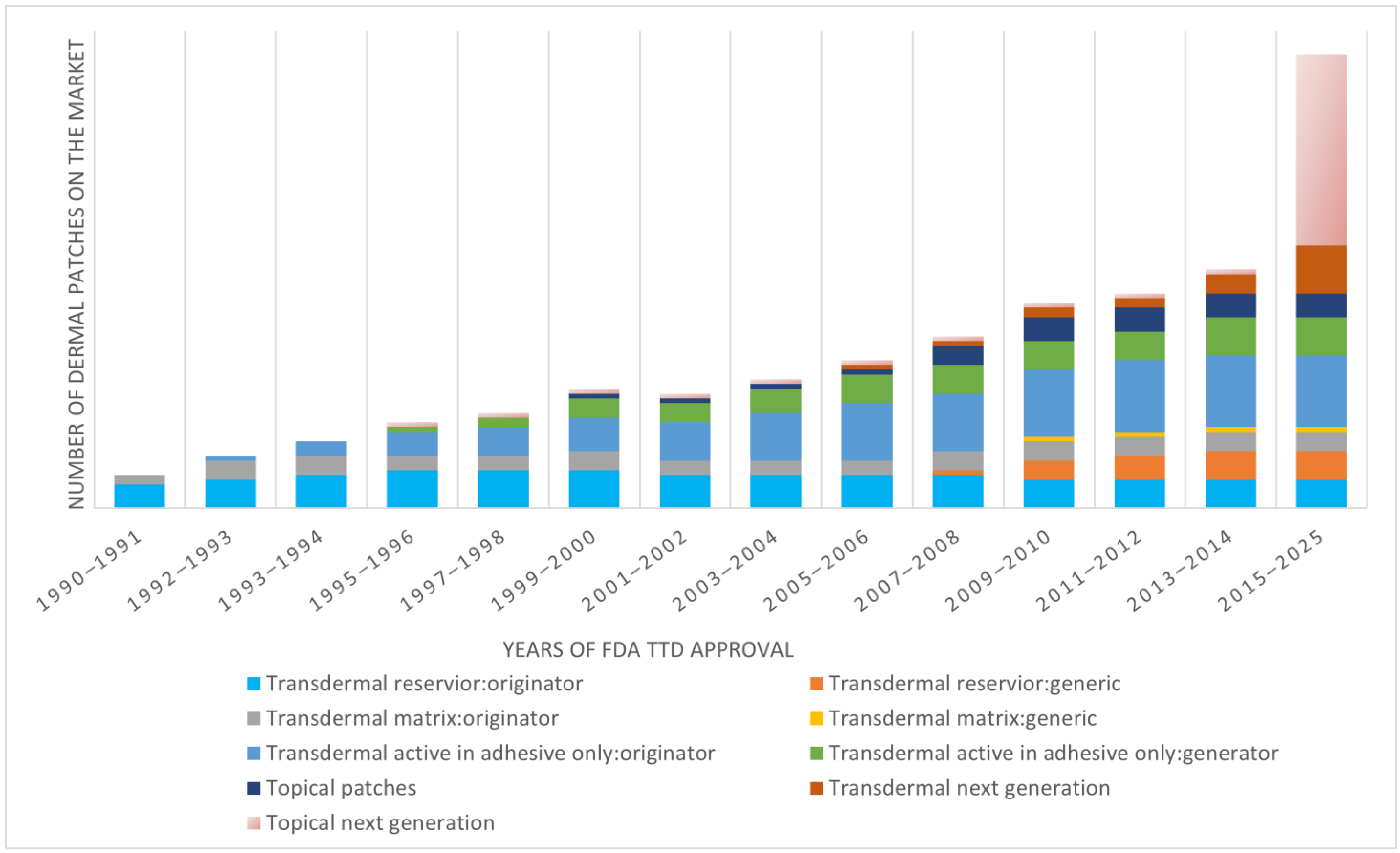
4.2. Overview of Transdermal Delivery Systems
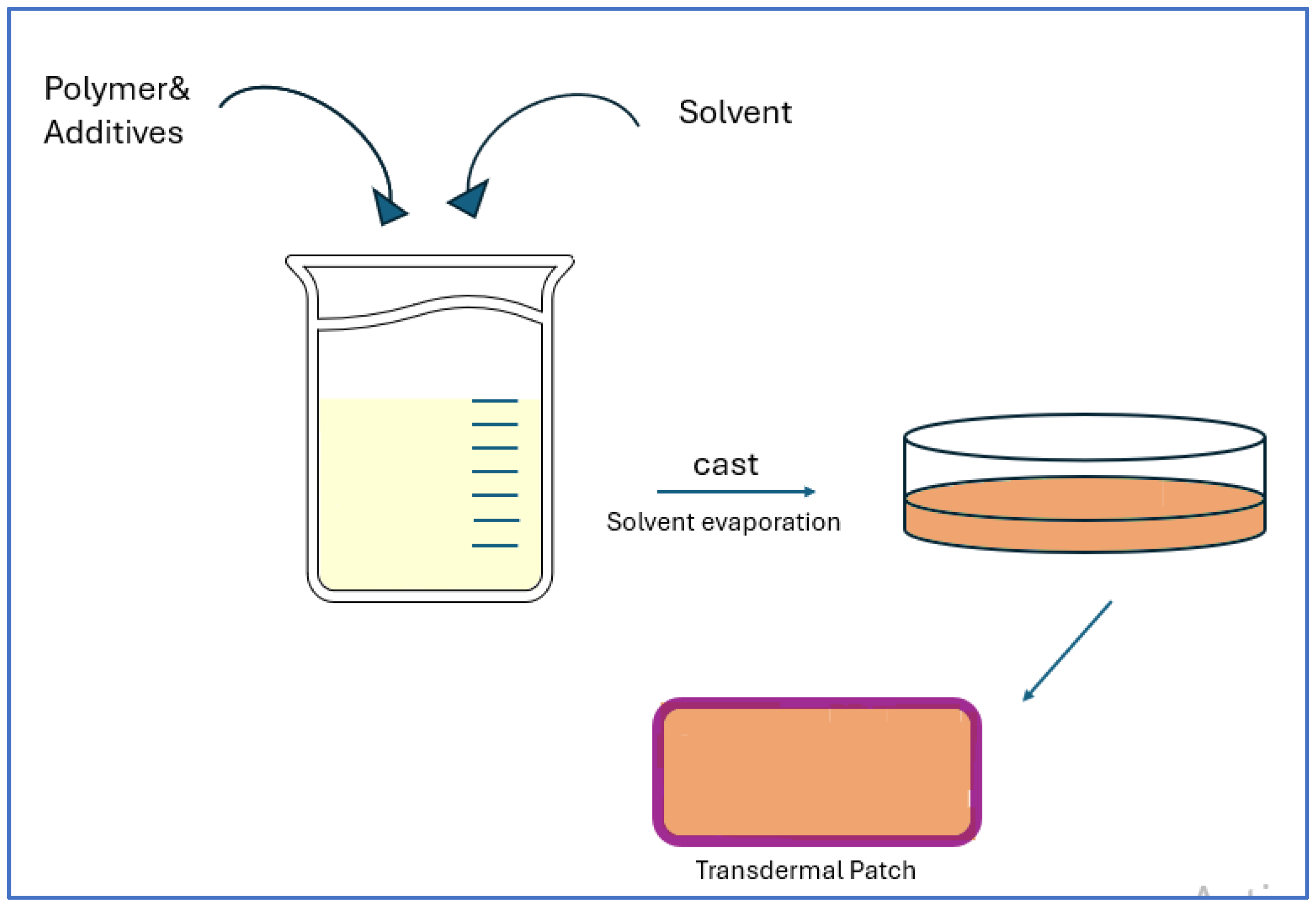
4.2.1. API Delivery via Transdermal Patches
4.2.2. API Loading in Hydrogel Patches as TDD System
4.2.3. Post-Loading (Osmosis Dependent Loading) Method in the Hydrogel Patches
4.2.4. In Situ Loading Method in the Hydrogel Patches
4.2.5. API Release from the Hydrogel Patch
4.3. Recent Advances in Transdermal Delivery Systems
4.4. HA-Based Hydrogels in Transdermal Delivery
4.5. HA-Based Hydrogel Phase Transition by Changing the pH for Full Absorption via the Skin
5. Hydrogels Applications in Cosmetic Skin Topical Applications
5.1. Uses of HA in the Cosmetic Field
5.2. HA-Based Hydrogels in Cosmetic Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gholamali, I.; Vu, T.T.; Jo, S.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Lim, K.T. Exploring the Progress of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels: Synthesis, Characteristics, and Wide-Ranging Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfollahi, Z. The Anatomy, Physiology and Function of All Skin Layers and the Impact of Ageing on the Skin. Wound Pract. Res. 2024, 32, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, I. Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Studied by X-ray Diffraction. Dermato 2022, 2, 79–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharakan, M.; Lonczak, L. Supporting Skin Structure and Its Barrier Functions with Evidence-Based Skin Care Ingredients. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2024, 14, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparr, E.; Wennerström, H.; Engblom, J.; Norlén, L. The Stratum Corneum Barrier—From Molecular Scale to Macroscopic Properties. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 67, 101725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylińska, N.; Maciejczyk, M. Hyaluronic Acid and Skin: Its Role in Aging and Wound-Healing Processes. Gels 2025, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostkowska, E.; Gromadzka, M.; Sławińska, M.; Górska, A.; Górska, R. Dermatological Management of Aged Skin. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, J.M.; Sopko, N.A.; Milner, S.M. The Applied Anatomy of Human Skin: A Model for Regeneration. Wound Med. 2020, 28, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargnoli, M.C.; De Simone, C.; Gisondi, P.; Pellacani, G.; Calzavara-Pinton, P. Topical Treatment for the Management of Mild-to-Moderate Psoriasis: A Critical Appraisal of the Current Literature. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 1249–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-W.; Jee, S.-H. Strategies to Develop a Suitable Formulation for Inflammatory Skin Disease Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, M.; Ding, J.; Lin, Y. Hydrogels: A Promising Therapeutic Platform for Inflammatory Skin Diseases Treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 8007–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Qiu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Injectable Hyaluronate/Collagen Hydrogel with Enhanced Safety and Efficacy for Facial Rejuvenation. Collagen Leather 2024, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggett, S.; Lyles, E.; Schlesinger, T. Update on Low-Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid in Dermatology: A Scoping Review. EMJ Dermatol. 2024, 12, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Jain, S.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Mehta, P.; Kesharwani, P. An Insight on Topically Applied Formulations for Management of Various Skin Disorders. J. Drug Target. 2022, 30, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Sobczak, M. Hydrogel-Based Active Substance Release Systems for Cosmetology and Dermatology Application: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Albayati, M.; Dodou, K. Novel Crosslinked HA Hydrogel Films for the Immediate Release of Active Ingredients. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications—A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Albayati, M.; Dodou, K. Studies on Novel Methods for Formulating Novel Cross-Linked Hydrogel Films of Hyaluronic Acid. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.F.; Hanif, M.; Ranjha, N.M. Methods of Synthesis of Hydrogels: A Review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Salman, S.; Khan, S.A.; Amin, A.; Rahman, Z.U.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; Akhtar, K.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Versatility of Hydrogels: From Synthetic Strategies, Classification, and Properties to Biomedical Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuri, A.; Gupta, D.; Pawar, R.; Tanwar, S.S. A Comprehensive Review of Hydrogel Classification, Fabrication, and Utility. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev. 2025, 6, 521–530. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Choi, Y. The Role of Rheology in Cosmetics Research: A Review. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2024, 36, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Du, B.; Stadler, F.J. A Novel Approach to Analyze the Rheological Properties of Hydrogels with Network Structure Simulation. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, E.; Billi, A.; Spagnuolo, E.; Scuderi, M.M.; Collettini, C. Characterization of Carbopol® Hydrogel Rheology for Experimental Tectonics and Geodynamics. Tectonophysics 2015, 642, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic acid: The influence of molecular weight on structural, physical, physico-chemical, and degradable properties of biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protsak, I.S.; Morozov, Y.M. Fundamentals and Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels and Their Applications: A Review. Gels 2025, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, H.; Faheem, S.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Sarwar, H.S.; Jamshaid, M. A Comprehensive Review of Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Classification, Properties, Recent Trends, and Applications. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labie, H.; Blanzat, M. Hydrogels for Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 4073–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, G.; Gonçalves, L.M.D.; Marto, J.; Carvalho, F.A.; Simões, S.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Almeida, A.J. Increased Therapeutic Efficacy of SLN Containing Etofenamate and Ibuprofen in Topical Treatment of Inflammation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M. Optimization of Chlorphenesin Emulgel Formulation. AAPS J. 2004, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, U.; Dhote, V.; Dhote, K.; Jain, S. Formulation and Evaluation of Topical Hydrogel of Terbinafine HCL for Effective Management of Dermatophyte. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2023, 10, 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Rajalakshmi, P.; Rani, S.; Kumar, S. Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Sodium Gel Using Carbopol 934 and 940. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2020, 9, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Nanoparticle-Hydrogel Systems Containing Platensimycin for Local Treatment of MRSA. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3456–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoshari, Y. Novel Hydrogels for Topical Applications: An Updated Comprehensive Review Based on Source. Gels 2022, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Chávez, S.A.; Alcalá-Alcalá, S.; Cerecedo, D.; Ganem-Rondero, A. Platelet Lysate-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles in a Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Intended for the Treatment of Wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 146, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Xie, J.; Luo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tang, S.; Yue, P.; Yang, M. Hyaluronic Acid Based Nanocrystals Hydrogels for Enhanced Topical Delivery of Drug: A Case Study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, M.A.; Hong, B.M.; Park, W.H. Hyaluronic Acid/Tannic Acid Hydrogel Sunscreen with Excellent Anti-UV, Antioxidant, and Cooling Effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazidi, R.; Hammami, M.; Ghadhoumi, H.; Ben Abdennebi, A.; Selmi, S.; Zayani, K.; Horchani-Naifer, K.; Bettaieb Rebey, I.; Saidani Tounsi, M. Development and Optimization of a Quercetin-Loaded Chitosan Lactate Nanoparticle Hydrogel with Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties for Topical Skin Applications. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marafon, P.; Fachel, F.N.S.; Dal Prá, M.; Bassani, V.L.; Koester, L.S.; Henriques, A.T.; Braganhol, E.; Teixeira, H.F. Development, Physico-Chemical Characterization and In-Vitro Studies of Hydrogels Containing Rosmarinic Acid-Loaded Nanoemulsion for Topical Application. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska, M.; Sala, K.; Bańkosz, M.; Grzela, K.; Potemski, P.; Miernik, K.; Tyliszczak, B. Enhanced Hydrogel Materials: Incorporating Vitamin C and Plant Extracts for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Childs, S.; Dodou, K. Comparison of Analytical Methods for the Detection of Residual Crosslinker in Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Films. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Carter, P.; Childs, S. Novel Injectable Hydrogel Formulations and Gas Chromatography Analysis of the Residual Crosslinker in Formulations Intended for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, G.D.; Bonanno, A.; Giacomazza, D.; Cavalieri, L.; Sammarco, M.; Ingrassia, E.; Gagliardo, R.; Riccobono, L.; Moscato, M.; Anzalone, G.; et al. A 3D “In Vitro” Model to Study Hyaluronan Effect in Nasal Epithelial Cell Line Exposed to Double-Stranded RNA Poly(I:C). Biomol. Ther. 2020, 28, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowman, M.K.; Lee, H.G.; Schwertfeger, K.L.; McCarthy, J.B.; Turley, E.A. The Content and Size of Hyaluronan in Biological Fluids and Tissues. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, F.; Babaeipour, V.; Saharkhiz, S. Comprehensive Review on Biosynthesis of Hyaluronic Acid with Different Molecular Weights and Its Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, L.A.; Hernández, R.; Alonso, J.M.; Pérez-González, R.; Sáez-Martínez, V. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Crosslinked in Physiological Conditions: Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y. Modification and Crosslinking Strategies for Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Biomaterials. Smart Med. 2023, 2, e20230029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, J.; Takahashi, M.; Hatakeyama, T.; Hatakeyama, H. Gelation of hyaluronic acid through annealing. Polym. Int. 2000, 49, 1604–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Shi, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Su, L.; Zhang, K.; Nishinari, K.; Yang, G. Ultrafast Gelation of Hyaluronan Hydrogels via Alternate Compression–Decompression. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, J.; Park, H.; Park, T.G. Thermo-Sensitive, Injectable, and Tissue Adhesive Sol–Gel Transition Hyaluronic Acid/Pluronic Composite Hydrogels Prepared from Bio-Inspired Catechol-Thiol Reaction. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Kjøniksen, A.-L.; Nyström, B. Effect of pH on the Behavior of Hyaluronic Acid in Dilute and Semidilute Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 274, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.M.; Andrade Del Olmo, J.; Domínguez-Arca, V.; Pérez-González, R.; Pérez-González, R.; Pérez-González, R. Injectable Hydrogels: From Laboratory to Industrialization. Polymers 2021, 13, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade Del Olmo, J.; Alonso, J.M.; Pérez-González, R.; Domínguez-Arca, V. Drug Delivery from Hyaluronic Acid-BDDE Injectable Hydrogels for Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Henry, M.; Irwin, N.J.; Trotter, J.; Perminova, A.A.; Donnelly, R.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Crosslinked Using a Solvent-Free Process for Potential Biomedical Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, C.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Park, Y.; Kim, M. Effect of Molecular Weight of Hyaluronic Acid (HA) on Viscoelasticity and Particle Texturing Feel of HA Dermal Biphasic Fillers. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wei, X.; Ji, Y.; Yin, L.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhong, M.; Shen, J.; Liu, Z.; Chang, L. Adjustable and ultrafast light-cured hyaluronic acid hydrogel: Promoting biocompatibility and cell growth. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3437–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, H. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: From Polymer to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapuła, P.; Bialik-Wąs, K.; Malarz, K. Are Natural Compounds a Promising Alternative to Synthetic Cross-Linking Agents in the Preparation of Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengyuan, H.; Changlin, W.; Tong, X.; Ping, D.; Xiaojun, Y.; Huaying, S.; Congying, L.; Peng, G.; Zhufeng, C. Modification and Preparation of Four Natural Hydrogels and Their Application in Biopharmaceutical Delivery. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 7101–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasvani, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Rawtani, D. Hyaluronic acid: A review on its biology, aspects of drug delivery, route of administrations and a special emphasis on its approved marketed products and recent clinical studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashkina, E.; Bykova, M.; Berishvili, M.; Lazarev, Y.; Kozlov, V. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2025, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, M.S.; Kazi, M.; Alsenaidy, M.A.; Ahmad, M.Z. Advances in Oral Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 618411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, K.C.; Choi, K.Y. Barriers and Strategies for Oral Peptide and Protein Therapeutics Delivery: Update on Clinical Advances. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giram, R.; Bhagwat, D.; Kakad, A.; Nimse, A. A Comprehensive Review on Parenterals. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 2, 2318–2336. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Deng, T.; Cheng, H.; Lu, J.; Wu, J. Advances in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems and Clinical Applications in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, R.; Palei, N.N. Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: Different Generations and Dermatokinetic Assessment of Drug Concentration in Skin. Pharm. Med. 2024, 38, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kwon, M.; Choi, H.E.; Kim, K.S. Recent Advances in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hanbali, O.A.; Khan, H.M.S.; Sarfraz, M.; Arafat, M.; Ijaz, S.; Hameed, A. Transdermal Patches: Design and Current Approaches to Painless Drug Delivery. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2019, 76, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.N.; Kalia, Y.N.; Horstmann, M.; Roberts, M.S. Transdermal Patches: History, Development and Pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2179–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transdermal Skin Patches Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Type (Matrix, Reservoir, Drug-in-Adhesive), by Application (Pain Relief, Smoking Cessation, Hormone Replacement Therapy), by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2024–2030; Grand View Research: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/transdermal-skin-patches-market-report (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- Penn, M.; Hennessy, M. Optimal Loading of Hydrogel-Based Drug-Delivery Systems. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 112, 649–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumon, M.M.H.; Rahman, M.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, M.S. Advances in Cellulose-Based Hydrogels: Tunable Swelling Dynamics and Their Versatile Real-Time Applications. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 11688–11712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, A.; Farjadian, F. Commercial Hydrogel Products for Drug Delivery Based on Route of Administration. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1336717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshikur, R.M.; Carrier, R.L.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Goto, M. Recent Advances in Biocompatible Ionic Liquids in Drug Formulation and Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, S.; Sun, C.; Xu, W. A Review of Recent Advances in Drug Loading, Mathematical Modeling, and Applications of Hydrogel Drug Delivery Systems. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 15077–15116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam El-Din, H.M.; El-Naggar, A.W.M.; Abu-El Fadle, F.I. Characterization and Drug Release Kinetics of Polyacrylamide/Sodium Alginate Blend Hydrogels Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 6149–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, P.; Jain, H.; Jain, S.; Rajput, S.; Tiwari, R.; Choudhury, H.; Tekade, R.K. Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels in Drug Delivery System: An Update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghnani, P.N.; Nelson, A.Z.; Wong, K.; Lee, Y.W.; Khan, S.A.; Doyle, P.S. From Burst to Controlled Release: Using Hydrogel Crosslinking Chemistry to Tune Release of Micro-Crystalline Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. RSC Pharm. 2025, 2, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrotek, K.; Zarzycki, R.; Modrzejewska, Z. Drug Release from Hydrogel Matrices: Mathematical Modeling and Structural Influence. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2024, 26, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, O.S.; Rao, K.M.; Subha, M.C.; Reddy, C.S.; Reddy, B.S. Fabrication and Characterization of Smart Karaya Gum/Sodium Alginate Semi-IPN Microbeads for Controlled Release of D-Penicillamine Drug. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Yamagishi, R.; Ando, M.; Hachikubo, Y.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Md Fadilah, N.I.; Maarof, M.; Oshima, M.; Goo, S.L.; Hayashi, H.; et al. Fabrication and Evaluation of Dissolving Hyaluronic Acid Microneedle Patches for Minimally Invasive Transdermal Drug Delivery by Nanoimprinting. Gels 2025, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Park, J.-H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Drug and Vaccine Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Ma, Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Jung, H. Clinical Evaluation of a Low-Pain Long Microneedle for Subcutaneous Insulin Injection. BioChip J. 2018, 12, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Oliveira, N.; Ferreira, S.; Botelho, C.M. Microneedles’ Device: Design, Fabrication, and Applications. Macromol 2024, 4, 320–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettis, R.J.; Harvey, A.J.; Ham, A.S.; Buckheit, R.W.; Singla, S.K.; Sachdeva, V.; Shin, C.I.; Jeong, S.D.; Rejinold, N.S.; Kim, Y.-C.; et al. Microneedle Delivery: Clinical Studies and Emerging Medical Applications. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, J.; Lan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Tao, J. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Dissolving Microneedle Patch Loaded with Methotrexate for Improved Treatment of Psoriasis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43588–43598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, J.; Park, S. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Kim, D.-D. Recent Studies on Modulating Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Investig. 2022, 52, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, E.; Scialla, S. Nanogels Based on Hyaluronic Acid as Potential Active Carriers for Dermatological and Cosmetic Applications. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.-P.; Cai, X.-Y.; Chen, S.-L.; Yu, H.-W.; Fang, Y.; Feng, X.-C.; Zhang, L.-M.; Li, C.-Y. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanocarriers for Anticancer Drug Delivery. Polymers 2023, 15, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, K.S.; Jain, M. Nanocarriers Revolutionizing Transdermal Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 14, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Servidio, C.; Curcio, F.; Cassano, R. Strategies for Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Design in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.; Hafiz, A.; Amin, H.; Karn, P.R.; Meghani, N.; Nagendran, S. Hyaluronic Acid: Comprehensive Review of a Multifunctional Biopolymer. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondiah, P.J.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Marimuthu, P.; Kumar, P.; Du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. A Review of Injectable Polymeric Hydrogel Systems for Application in Bone Tissue Engineering. Molecules 2016, 21, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.I.; Lee, S.B.; Chong, M.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, Y.H. Preparation of thermo-responsive and injectable hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and their drug release behaviors. Macromol. Res. 2006, 14, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, J.; Shukla, V. Cross-Linking in Hydrogels—A Review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 4, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, H.; Badshah, S.F.; Minhas, M.U.; Barkat, K.; Khan, S.A.; Hussain, M.D.; Kazi, M. pH-Sensitive Hydrogels Fabricated with Hyaluronic Acid as a Polymer for Site-Specific Delivery of Mesalamine. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 28827–28840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.-W.; Wan, J.; Park, Y.; Yoo, J.; Cartier, H.; Garson, S.; Haykal, D.; Yi, K.-H. Manufacturing Process of Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers. Polymers 2024, 16, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Xue, J.F.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Shuhaidi, M.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic Acid, an Efficient Biomacromolecule for Treatment of Inflammatory Skin and Joint Diseases: A Review of Recent Developments and Critical Appraisal of Preclinical and Clinical Investigations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez-Martin, P.; García-Martínez, O.; Ruiz, C.; De Luna-Bertos, E.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J. A Novel Hyaluronic Acid Matrix Ingredient with Regenerative, Anti-Aging and Antioxidant Capacity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosiya, M.; Hafiz, A.; Karn, P.R.; Meghani, N.; Nagendran, S. Hyaluronic Acid in Modern Cosmeceuticals: A Review of Skin Health and Anti-Aging Innovations. J. Dermatol. Cosmetol. 2025, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncan, A.M.; Moisă, D.G.; Santini, A.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.L.; Vonica-Țincu, A.L.; Loghin, F. Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid and Its Combination with Other Bioactive Ingredients in Cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrone, A.; Czajka, A.; Sibilla, S. Thermosensitive Hydrogel Mask Significantly Improves Skin Moisture and Skin Tone; Bilateral Clinical Trial. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, V.; Roveda, G.; Spartà, E.; Tursi, F. Oral Intake and Topical Application of Hyaluronic Acid Ameliorates Skin Aging Signs: Efficacy Results of a Placebo-Controlled In&Out Trial. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hydrogel Polymer | Drug/Active Ingredient | Therapeutic Application (Pharmaceutical or Cosmetic Use) | Main Outcome/Benefit | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPMC | Etofenamate, Ibuprofen | Anti-inflammatory-Analgesic | Provided controlled drug release with improved skin permeation; reduced systemic adverse reaction and enhanced local anti-inflammatory action. | Labie et al., Mancini et al. [28,29] |
| Chlorphenesin | Antifungal | Enhanced local drug delivery with minimised the irritation; enabled drug retention at infection site and improved antifungal efficacy. | Mohammed et al. [30] | |
| Carbopol 940 | Terbinafine | Antifungal | Improved drug stability and skin adherence; facilitated prolonged antifungal activity with reduced dosing frequency. | Sheikh et al. [31] |
| Diclofenac, Mefenamic acid | Anti-inflammatory-Analgesic | Enhanced transdermal penetration and controlled drug release; reduced gastrointestinal side effects that associate oral NSAIDs. | Rajalakshm et al. [32] | |
| Betamethasone, salicylic acid | Psoriasis | Enabled dual-action delivery—anti-inflammatory and keratolytic; enhanced lesion clearance and reduced recurrence. | Zagorska et al. [15] | |
| Polyacrylamide | Platensimycin | Antibacterial | Provided targeted antibacterial action with reduced cytotoxicity; hydrogel matrix enhanced drug stability and skin compatibility. | Wang et al. [33] |
| Chitosan | Silver sulfadiazine | Burns | Accelerated wound healing and antimicrobial effect | Almoshari et al. [34] |
| Pluronic F-127 | Platelet lysate | Wound healing | Accelerated wound healing and tissue regeneration; offered antimicrobial protection and moisture retention at burn sites. | Bernal et al. [35] |
| HA | Vitamin B3 | Antioxidant, brightening, skin hydrating, reduce fine wrinkles (Cosmetic applications) | Enhanced skin hydration and barrier repair; reduced fine lines and improved skin tone through deep dermal delivery. | Rashid et al. [16] |
| Baicalin | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory | Enhanced transdermal absorption and bioavailability; reduced inflammation and oxidative stress in skin tissues. | Wei et al. [36] | |
| Tannic acid | Antioxidant, anti UV, suncream (Cosmetic applications) | Enhanced delivery and supported multifunctional performance-—UV protection, antioxidant activity, cooling effect, and skin hydration—all in a stable, biocompatible formulation. | Gawak et al. [37] | |
| Xanthan gum | Quercetin | Antioxidant, antibacterial | Enhanced delivery of quercetin and stabilised it; improved the solubility and functional performance. | Yazidi et al. [38] |
| Salicylic acid | Skin exfoliating agent (Cosmetic application) | Provided controlled skin exfoliation with reduced irritation; improved skin clarity and reduced pore congestion. | Rashid et al. [16] | |
| Hydroxyethyl cellulose | Rosmarinic acid | Anti-ageing skin products (Cosmetic application) | Delivered antioxidant with high skin compatibility; reduced oxidative damage and improved elasticity and hydration. | Marafon et al. [39] |
| PVP (polyvinylpyrrolidone) and chitosan | Vitamin C | Antioxidant, whitening agent, reduce dark spots (Cosmetic applications) | Improved skin brightening and collagen synthesis; stabilised vitamin C and enhanced its penetration and efficacy. | Kedzierska at al. [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, F.; Carter, P.; Childs, S. Overview of Hydrogels and the Use of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels in Pharmaceutical Transdermal Delivery Systems and Topical Cosmetic Skin Applications. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060265
Rashid F, Carter P, Childs S. Overview of Hydrogels and the Use of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels in Pharmaceutical Transdermal Delivery Systems and Topical Cosmetic Skin Applications. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(6):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060265
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Fatimah, Paul Carter, and Stephen Childs. 2025. "Overview of Hydrogels and the Use of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels in Pharmaceutical Transdermal Delivery Systems and Topical Cosmetic Skin Applications" Cosmetics 12, no. 6: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060265
APA StyleRashid, F., Carter, P., & Childs, S. (2025). Overview of Hydrogels and the Use of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels in Pharmaceutical Transdermal Delivery Systems and Topical Cosmetic Skin Applications. Cosmetics, 12(6), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060265






